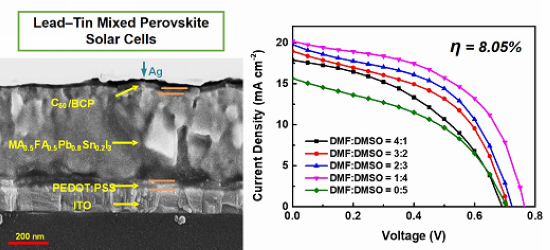
Co-Solvent Controllable Engineering of MA0.5FA0.5Pb0.8Sn0.2I3 Lead–Tin Mixed Perovskites for Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells with Improved Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of MA0.5FA0.5Pb0.8Sn0.2I3 Lead–Tin Mixed Perovskite Films
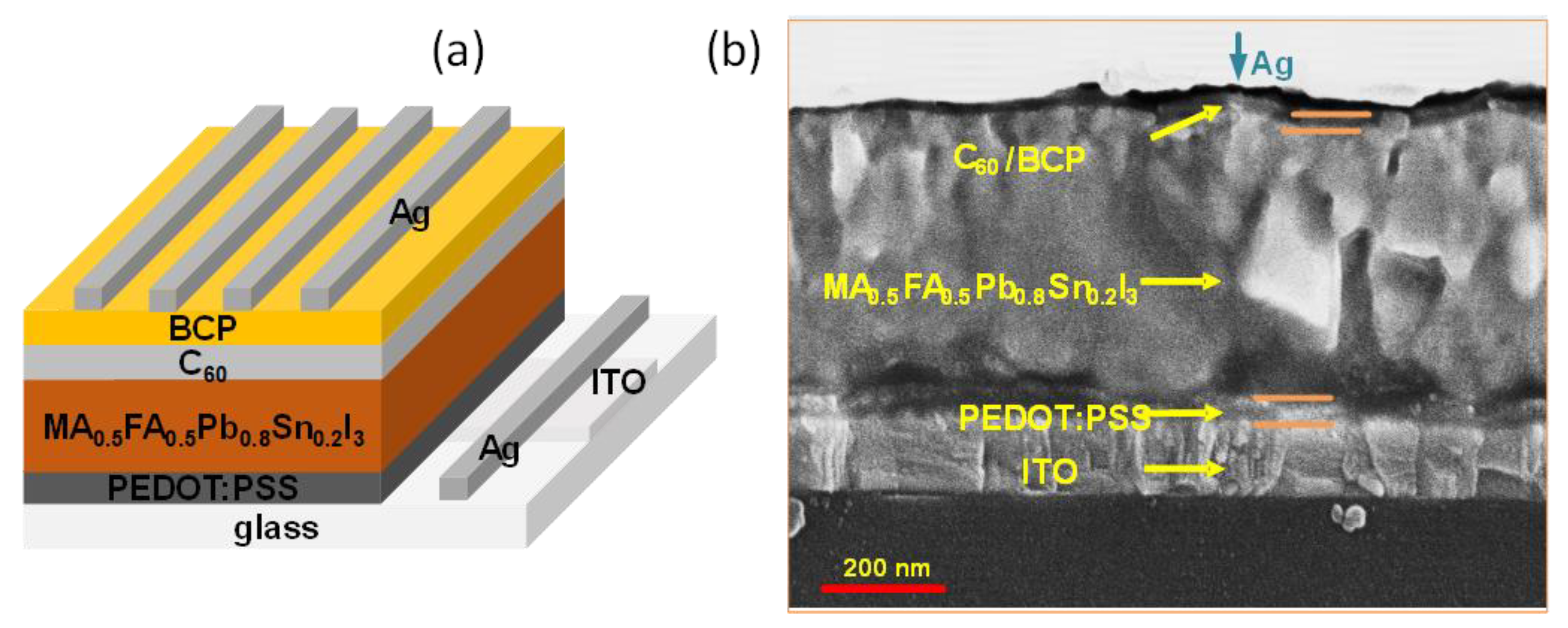
2.3. Fabrication of Perovskite Solar Cells
2.4. Characterization
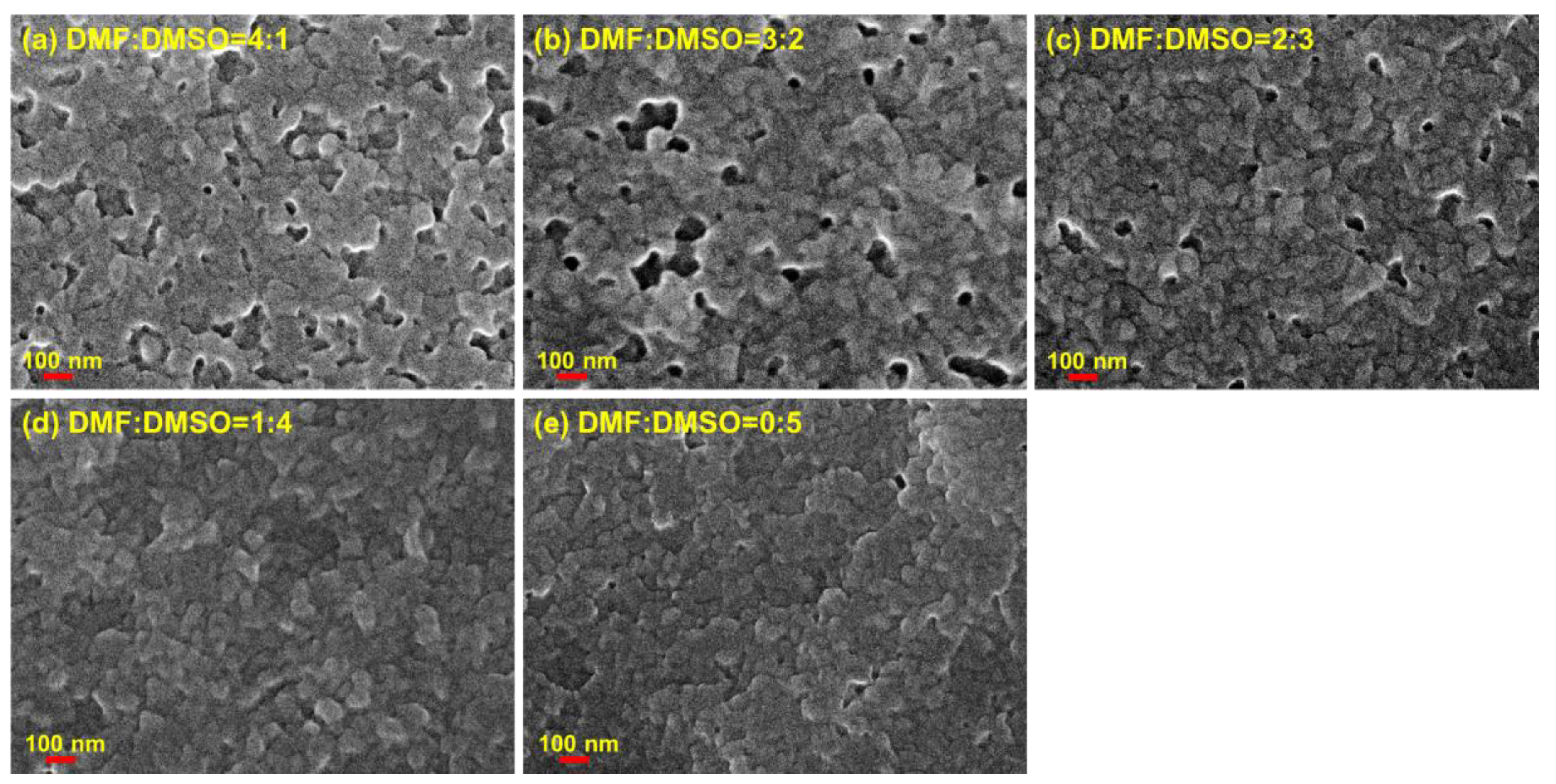
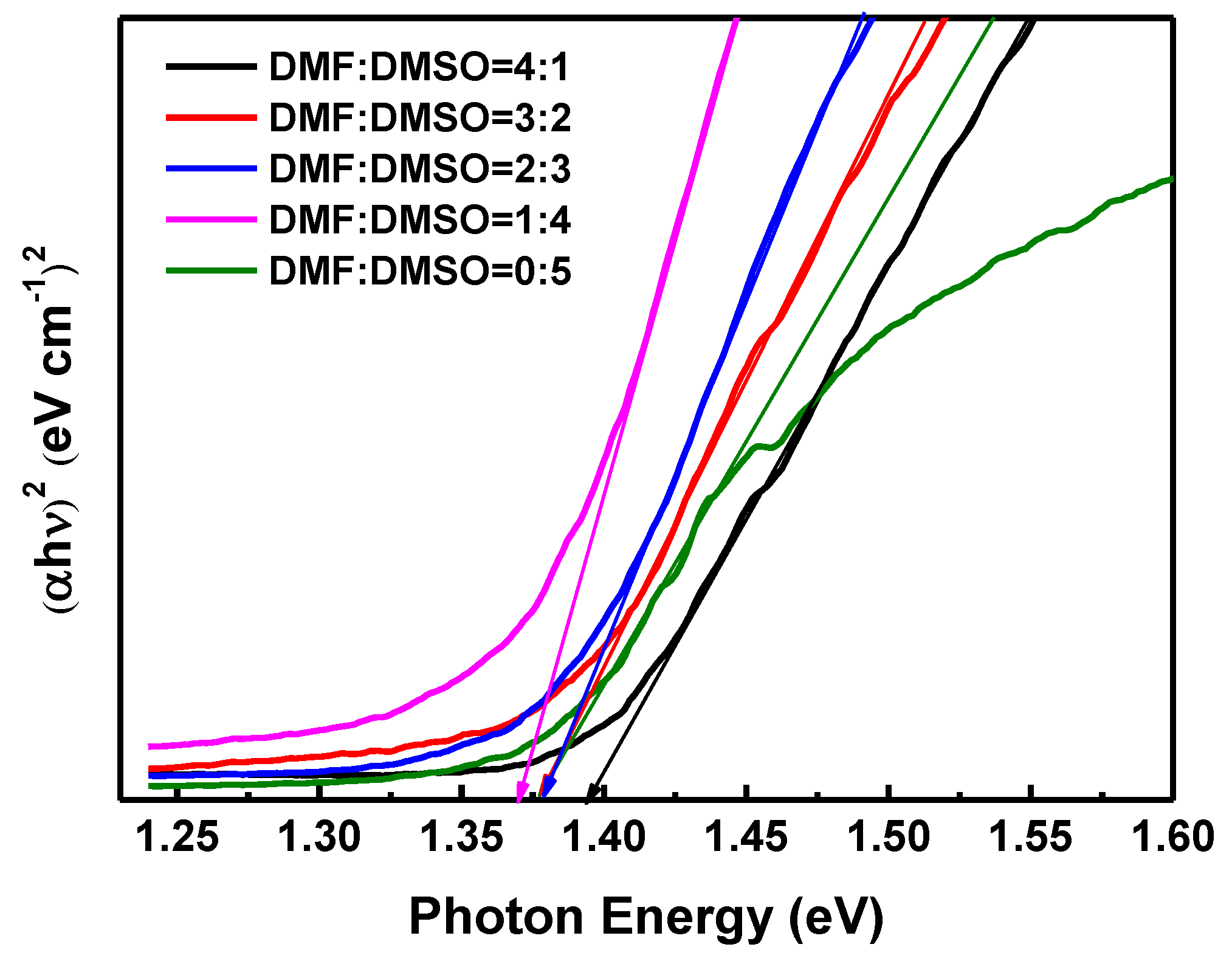
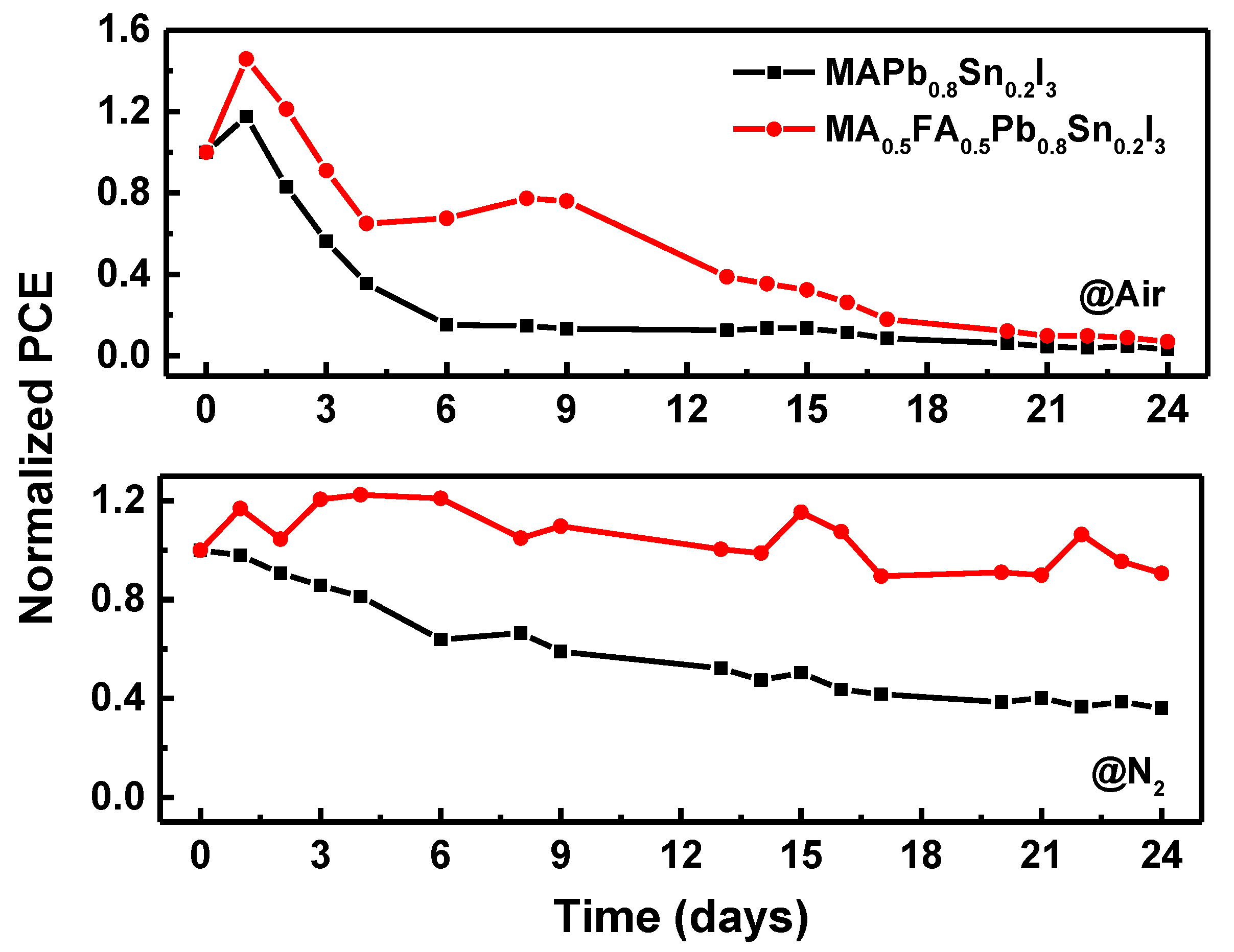
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Y.; Du, X.; Scheiner, S.; McMeekin, D.P.; Wang, Z.; Li, N.; Killian, M.S.; Chen, H.; Richter, M.; Levchuk, I.; et al. A generic interface to reduce the efficiency-stability-cost gap of perovskite solar cells. Science 2017, 358, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Tien, C.H.; Tseng, Z.L.; Ruan, J.H. Enhance efficiency of MAPbI3 perovskite solar cells with FAPbX3 perovskite quantum dots. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xie, F.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Su, H.; Cai, M.; Zhou, Z.; Noda, T.; Han, L. Thermally stable MAPbI3 perovskite solar cells with efficiency of 19.19% and area over 1 cm2 achieved by additive engineering. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Chen, C.C.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Cai, M.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Han, L. Vertical recrystallization for highly efficient and stable formamidinium-based inverted-structure perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.H.; Wu, C.G. Bulk heterojunction perovskite–PCBM solar cells with high fill factor. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Yang, W.; Luo, D.; Zhu, R.; Gong, Q. Applications of cesium in the perovskite solar cells. J. Semicond. 2017, 38, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Pisoni, S.; Weiss, T.P.; Feurer, T.; Wackerlin, A.; Fuchs, P.; Nishiwaki, S.; Zortea, L.; Tiwari, A.N.; Buecheler, S. Compositionally graded absorber for efficient and stable near-infrared-transparent perovskite solar cells. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Li, D.; Lin, F.; Mao, J.; Liang, C.; Jen, A.K.; Grätzel, M.; Choy, W.C. Toward all room-temperature, solution-processed, high-performance planar perovskite solar cells: A new scheme of pyridine-promoted perovskite formation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Q.; You, J. Recent progress in stability of perovskite solar cells. J. Semicond. 2017, 38, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best Research-Cell Efficiencies, National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/pv/assets/pdfs/best-research-cell-efficiencies.20200128.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2020).
- Wang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W. Stability of perovskite solar cells: A prospective on the substitution of the A cation and X anion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1190–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Y.; Zheng, C.; Gao, D.; Huang, W. Advancements in the stability of perovskite solar cells: Degradation mechanisms and improvement approaches. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 38079–38091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavney, A.H.; Smaha, R.W.; Smith, I.C.; Jaffe, A.; Umeyama, D.; Karunadasa, H.I. Chemical approaches to addressing the instability and toxicity of lead–halide perovskite absorbers. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Liu, J.; Portale, G.; Fang, H.; Blake, G.R.; Brink, G.H.; Koster, L.J.; Loi, M.A. Highly reproducible Sn-based hybrid perovskite solar cells with 9% efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.L.; Xiao, J.; Mao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Choy, W.C.H. Controllable crystallization of CH3NH3Sn0.25Pb0.75I3 perovskites for hysteresis-free solar cells with efficiency reaching 15.2%. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, R.; Leijtens, T.; Dunfield, S.P.; Raiford, J.A.; Wolf, E.J.; Swifter, S.A.; Werner, J.; Eperon, G.E.; de Paula, C.; Palmstrom, A.F.; et al. Design of low bandgap tin–lead halide perovskite solar cells to achieve thermal, atmospheric and operational stability. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.X.; Xiao, K.; Qin, Z.Y.; Han, Q.L.; Zhang, C.F.; Wei, M.Y.; Saidaminov, M.I.; Gao, Y.; Xu, J.; Xiao, M.; et al. Monolithic all-perovskite tandem solar cells with 24.8% efficiency exploiting comproportionation to suppress Sn(II) oxidation in precursor ink. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoumpos, C.C.; Malliakas, C.D.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Semiconducting tin and lead iodide perovskites with organic cations: Phase transitions, high mobilities, and near-infrared photoluminescent properties. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, T.; Duan, J.; Ahmadi, M.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, B. Exploring spin-orbital coupling effects on photovoltaic actions in Sn and Pb based perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, G.; Fujisawa, J.I.; Segawa, H.; Yamashita, K. Cation role in structural and electronic properties of 3D organic–inorganic halide perovskites: A DFT analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 12176–12183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Xiao, B. Effective masses and electronic and optical properties of nontoxic MASnX3 (X = Cl, Br, and I) perovskite structures as solar cell absorber: A theoretical study using HSE06. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 19655–19660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Chueh, C.C.; Rajagopal, A.; Williams, S.T.; Sun, Y.; Jen, A.K.Y. Improved efficiency and stability of Pb–Sn binary perovskite solar cells by Cs substitution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 17939–17945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Stoumpos, C.C.; Cao, D.H.; Chang, R.P.H.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Lead-free solid-state organic–inorganic halide perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Noh, J.H.; Jeon, N.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Ryu, S.; Seo, J.; Seok, S.I. High-performance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange. Science 2015, 348, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y.; Huang, W. Lead-free organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites for photovoltaic applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Cahen, D.; Hodes, G. How SnF2 impacts the material properties of lead-free tin perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 13926–13936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zhao, D.; Yu, Y.; Grice, C.R.; Wang, C.; Cimaroli, A.J.; Schulz, P.; Meng, W.; Zhu, K.; Xiong, R.G.; et al. Lead-free inverted planar formamidinium tin triiodide perovskite solar cells achieving power conversion efficiencies up to 6.22%. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9333–9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fan, J.; Li, J.; Mai, Y.; Wang, L. Controllable grain morphology of perovskite absorber film by molecular self-assembly toward efficient solar cell exceeding 17%. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10399–10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Islam, A.; Yang, X.; Qin, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, K.; Peng, W.; Han, L. Retarding the crystallization of PbI2 for highly reproducible planar-structured perovskite solar cells via sequential deposition. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2934–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, N.J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Yang, W.S.; Ryu, S.; Seok, S.I. Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic-organic hybrid perovskite solar cells. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.M.; Teuscher, J.; Miyasaka, T.; Murakami, T.N.; Snaith, H.J. Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 2012, 338, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, A.; Teshima, K.; Shirai, Y. Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6050–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Rajagopal, A.; Chueh, C.C.; Jo, S.B.; Liu, B.; Zhao, T.; Jen, A.K.Y. Stable low-bandgap Pb–Sn binary perovskites for tandem solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8990–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, J.C.; Wu, C.G. Annealing effects on high-performance CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cells prepared by solution-process. Sol. Energy 2015, 122, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eperon, G.E.; Stranks, S.D.; Menelaou, C.; Johnston, M.B.; Herz, L.M.; Snaith, H.J. Formamidinium lead trihalide: A broadly tunable perovskite for efficient planar heterojunction solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, G.; Ripolles, T.S.; Hamada, K.; Ogomi, Y.; Bessho, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Chantana, J.; Yoshino, K.; Shen, Q.; Toyoda, T.; et al. Highly efficient 17.6% tin–lead mixed perovskite solar cells realized through spike structure. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3600–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, W.; Yan, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, W.; Chen, H. Low-bandgap mixed tin–lead iodide perovskite with large grains for high performance solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13090–13095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Bi, P.; Wang, S.; Xue, R.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Integrating ultrathin bulk-heterojunction organic semiconductor intermediary for high-performance low-bandgap perovskite solar cells with low energy loss. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Shang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Peng, Z.; Ning, Z. Energy level tuning of PEDOT:PSS for high performance tin-lead mixed perovskite solar cells. Sol. RRL 2019, 3, 1800256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chi, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, F.; Huang, S. Improved performance of lead-tin mixed perovskite solar cells with PEDOT:PSS treated by hydroquinone. Sol. Energy 2020, 201, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Voc (V) | Jsc (mA cm−2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMF:DMSO = 4:1 | 0.69 | 17.89 | 44.1 | 5.45 |
| DMF:DMSO = 3:2 | 0.71 | 18.96 | 49.0 | 6.59 |
| DMF:DMSO = 2:3 | 0.72 | 19.80 | 50.3 | 7.21 |
| DMF:DMSO = 1:4 | 0.76 | 20.18 | 52.5 | 8.05 |
| DMF:DMSO = 0:5 | 0.71 | 15.65 | 43.9 | 4.85 |
| Perovskite | Bandgap | Voc (V) | Jsc (mA cm−2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) | Ref. | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA0.5MA0.5Pb0.5Sn0.5I3 | 1.25 | 0.75 | 30.56 | 76 | 17.07 | [36] | Spike structure ETL |
| FA0.7MA0.3Pb0.7Sn0.3I3 | 1.26 | 0.78 | 23.8 | 72.8 | 13.4 | [37] | PTAA HTL |
| FA0.6MA0.4Pb0.4Sn0.6I3 | 1.25 | 0.85 | 27.9 | 74.0 | 17.55 | [38] | Ultrathin BHJ structure HTL |
| FA0.6MA0.4Sn0.6Pb0.4I3 | 1.25 | 0.78 | 27.22 | 74.4 | 15.85 | [39] | PFI-PEDOT:PSS HTL |
| FA0.3MA0.7Pb0.7Sn0.3I3 | 1.33 | 0.74 | 27.07 | 73.4 | 14.65 | [40] | HQ-PEDOT:PSS HTL |
| FA0.5MA0.5Pb0.8Sn0.2I3 | 1.37 | 0.76 | 20.2 | 52.5 | 8.05 | This work | Active layer |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.-C.; Tien, C.-H.; Jhou, Y.-C.; Lin, W.-C. Co-Solvent Controllable Engineering of MA0.5FA0.5Pb0.8Sn0.2I3 Lead–Tin Mixed Perovskites for Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells with Improved Stability. Energies 2020, 13, 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102438
Chen L-C, Tien C-H, Jhou Y-C, Lin W-C. Co-Solvent Controllable Engineering of MA0.5FA0.5Pb0.8Sn0.2I3 Lead–Tin Mixed Perovskites for Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells with Improved Stability. Energies. 2020; 13(10):2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102438
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lung-Chien, Ching-Ho Tien, Yang-Cheng Jhou, and Wei-Cheng Lin. 2020. "Co-Solvent Controllable Engineering of MA0.5FA0.5Pb0.8Sn0.2I3 Lead–Tin Mixed Perovskites for Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells with Improved Stability" Energies 13, no. 10: 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102438
APA StyleChen, L.-C., Tien, C.-H., Jhou, Y.-C., & Lin, W.-C. (2020). Co-Solvent Controllable Engineering of MA0.5FA0.5Pb0.8Sn0.2I3 Lead–Tin Mixed Perovskites for Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells with Improved Stability. Energies, 13(10), 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102438