Modular Isolated DC-DC Converters for Ultra-Fast EV Chargers: A Generalized Modeling and Control Approach †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A generalized model for the multimodule ISIP-OSOP DC-DC converter is provided. It is worth mentioning that the work presented in [40] is extended to include the SSM as well as the control schemes for the three other multimodule configurations, which are ISOS, IPOP, and IPOS. In addition to a generalized SSM applicable for all the basic architectures for multimodule DC-DC converters.
- Detailed SSM for the four architectures of the multimodule converter, which are ISOS, ISOP, IPOP, and IPOS, is provided in detail.
- The control strategy to guarantee uniform power distribution among the modules is studied. The strategies are based on current control Reflex Charging (RC) considering high-power-level UFC stations.
2. Input-Series Output-Series (ISOS) DC-DC Converter
2.1. ISOS Circuit Diagram
2.2. ISOS Small-Signal Analysis
2.2.1. Control-to-Output Voltage Transfer Function
2.2.2. Control-To-Filter Inductor Current Transfer Function
2.2.3. Control-To-Module Input Voltage Transfer Function
2.2.4. Converter Output Impedance
2.2.5. Converter Gain
3. Input-Series Output-Parallel (ISOP) DC-DC Converter
4. Input-Parallel Output-Parallel (IPOP) DC-DC Converter
4.1. IPOP Circuit Diagram
4.2. IPOP Small-Signal Analysis
4.2.1. Control-To-Output Voltage Transfer Function
4.2.2. Control-To-Filter Inductor Current Transfer Function
4.2.3. Control-To-Module Filter Inductor Current Transfer Function
4.2.4. Converter Output Impedance
4.2.5. Converter Gain
5. Input-Parallel Output-Series (IPOS) DC-DC Converter
5.1. IPOS Circuit Diagram
5.2. IPOS Small-Signal Analysis
5.2.1. Control-To-Output Voltage Transfer Function
5.2.2. Control-To-Filter Inductor Current Transfer Function
5.2.3. Control-To-Module Filter Inductor Current Transfer Function
5.2.4. Converter Output Impedance
5.2.5. Converter Gain
6. Generalized Small-Signal Analysis for Dual Series/Parallel Input-Output (ISIP-OSOP) DC-DC Converter
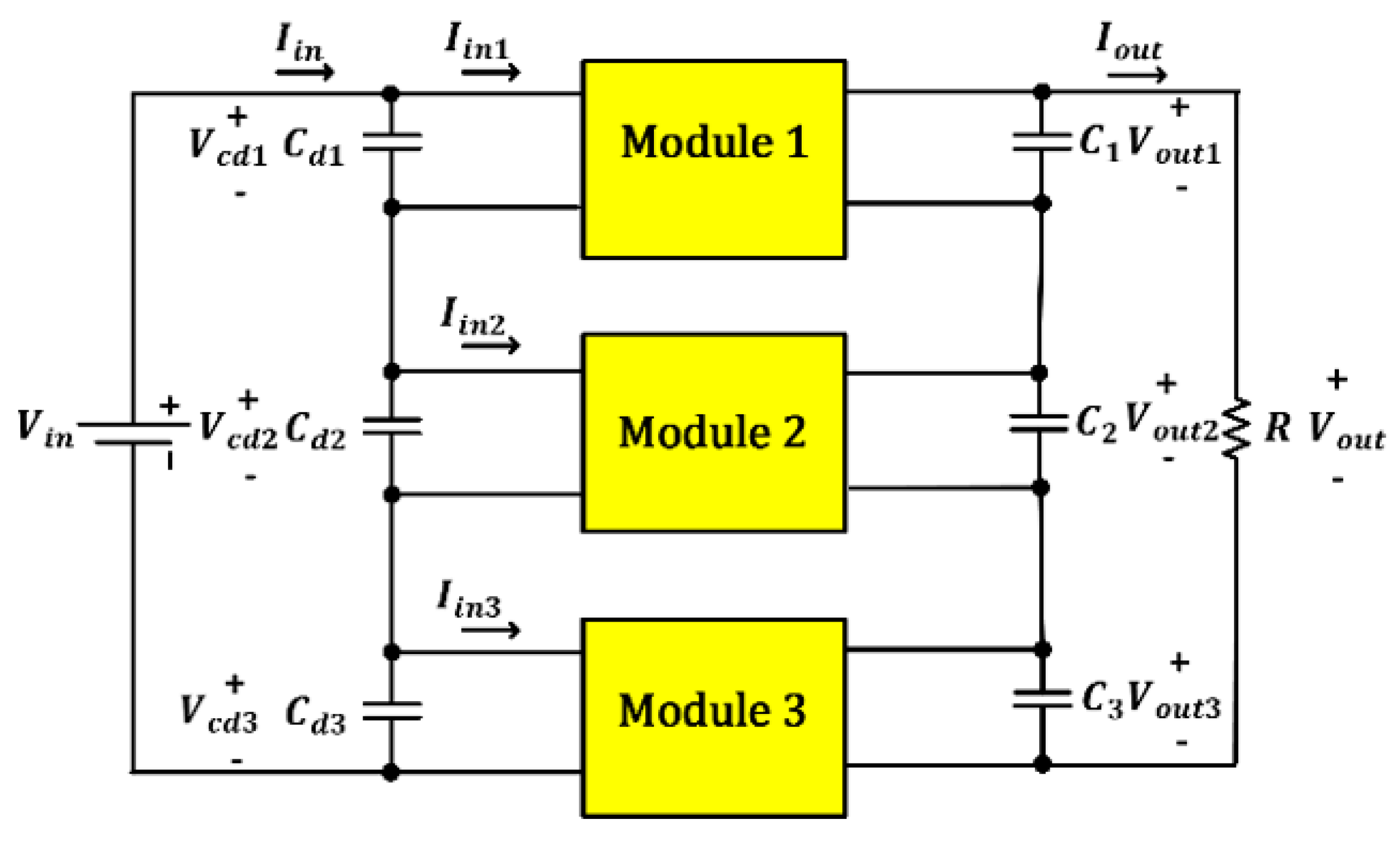
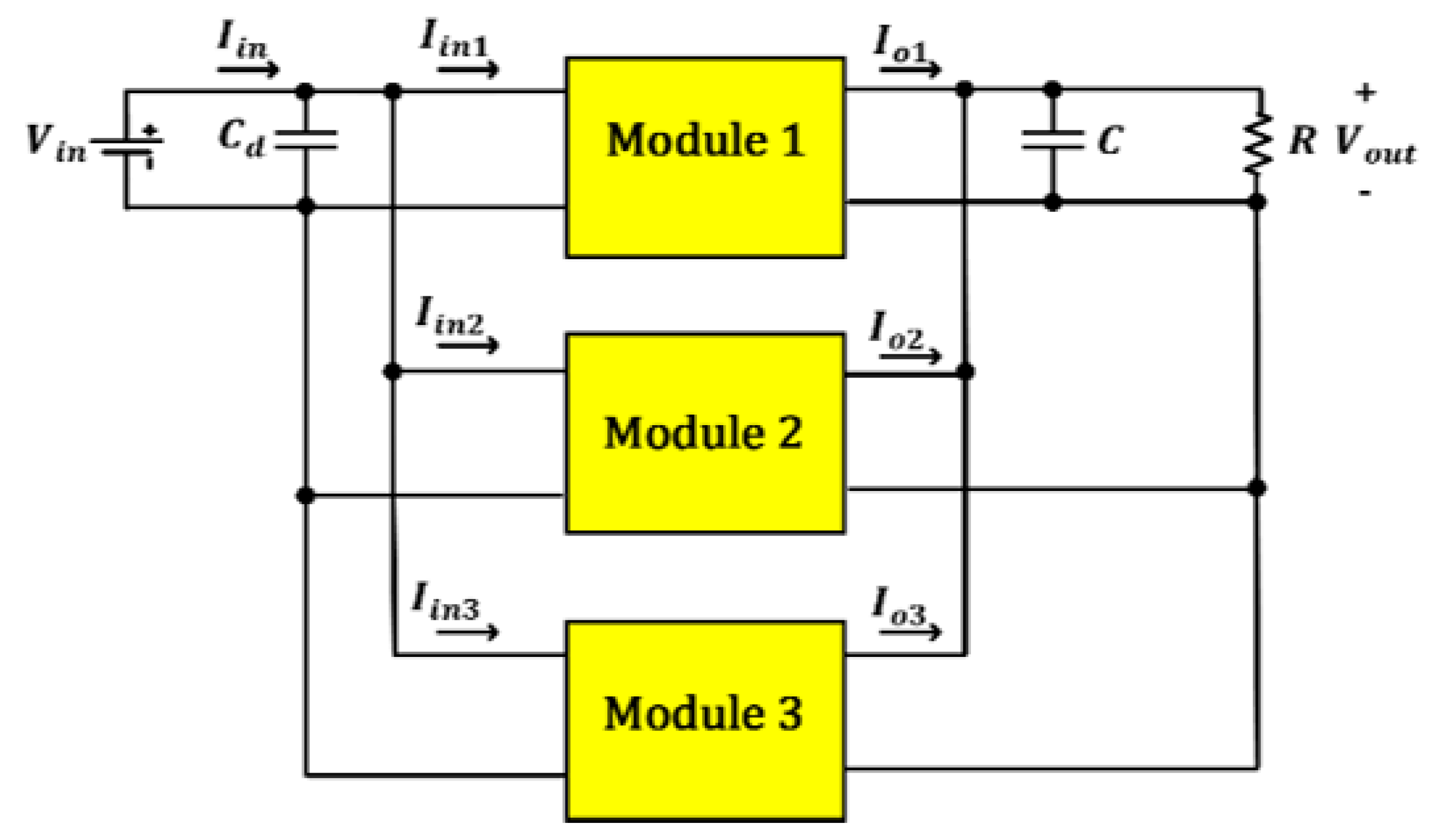
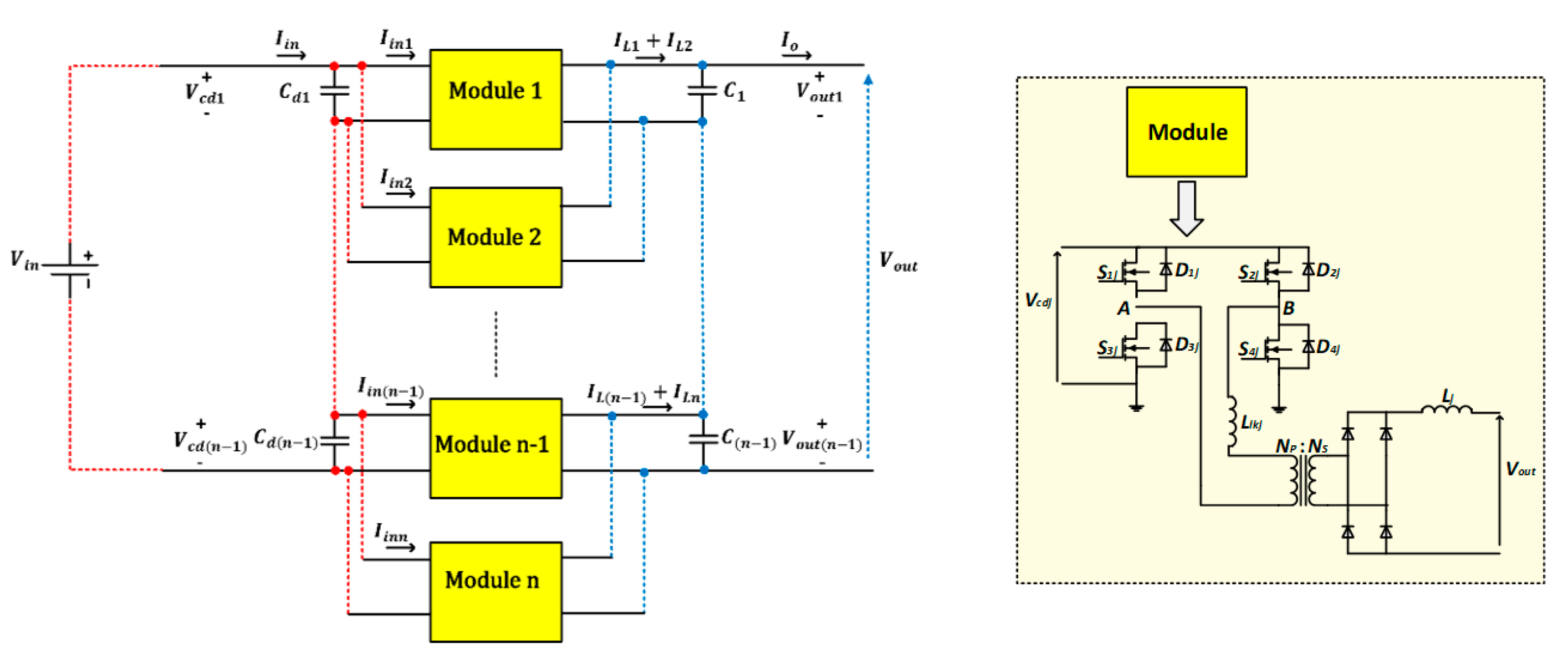
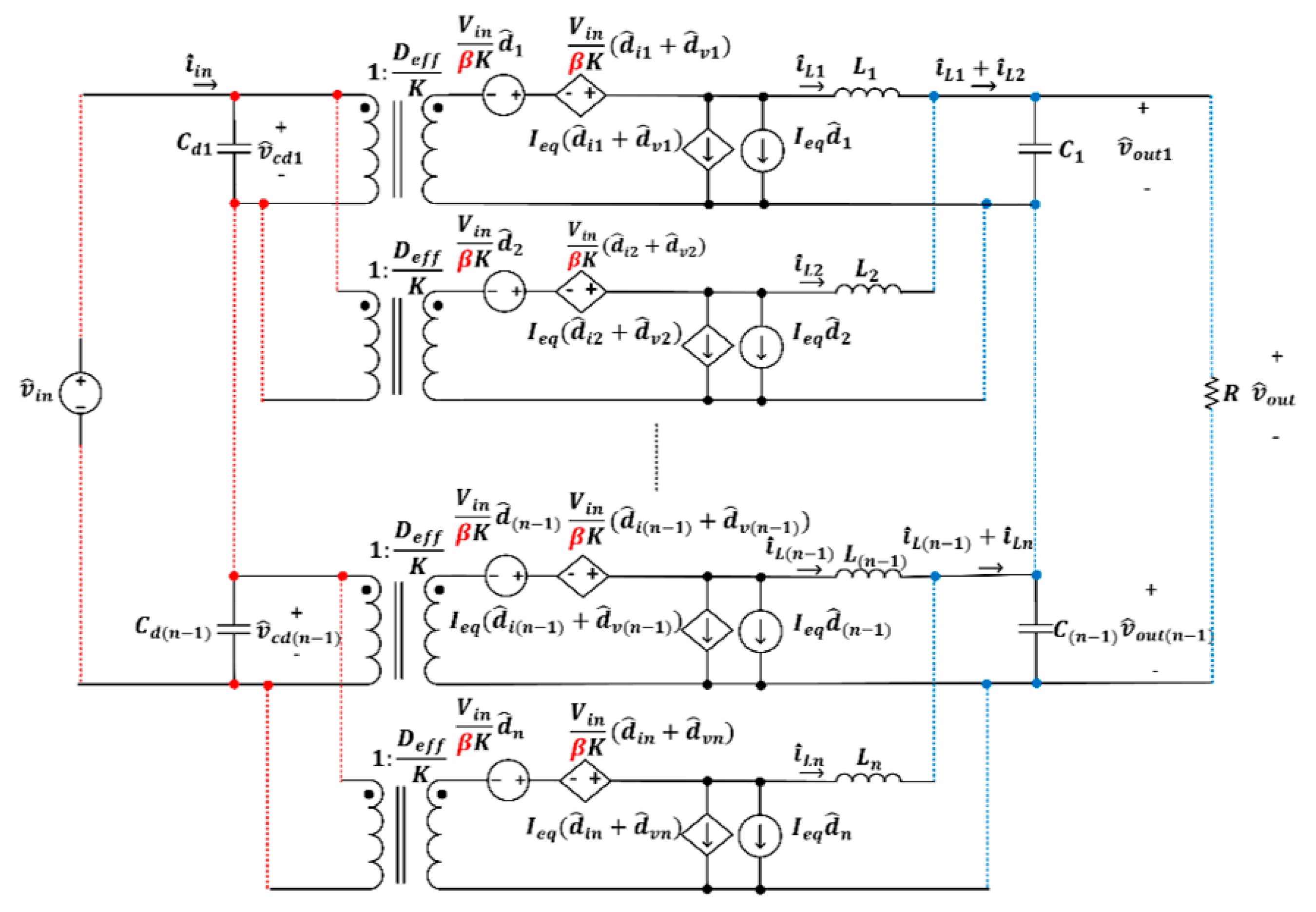
6.1. ISIP-OSOP Generic DC-DC Converter Circuit Diagram
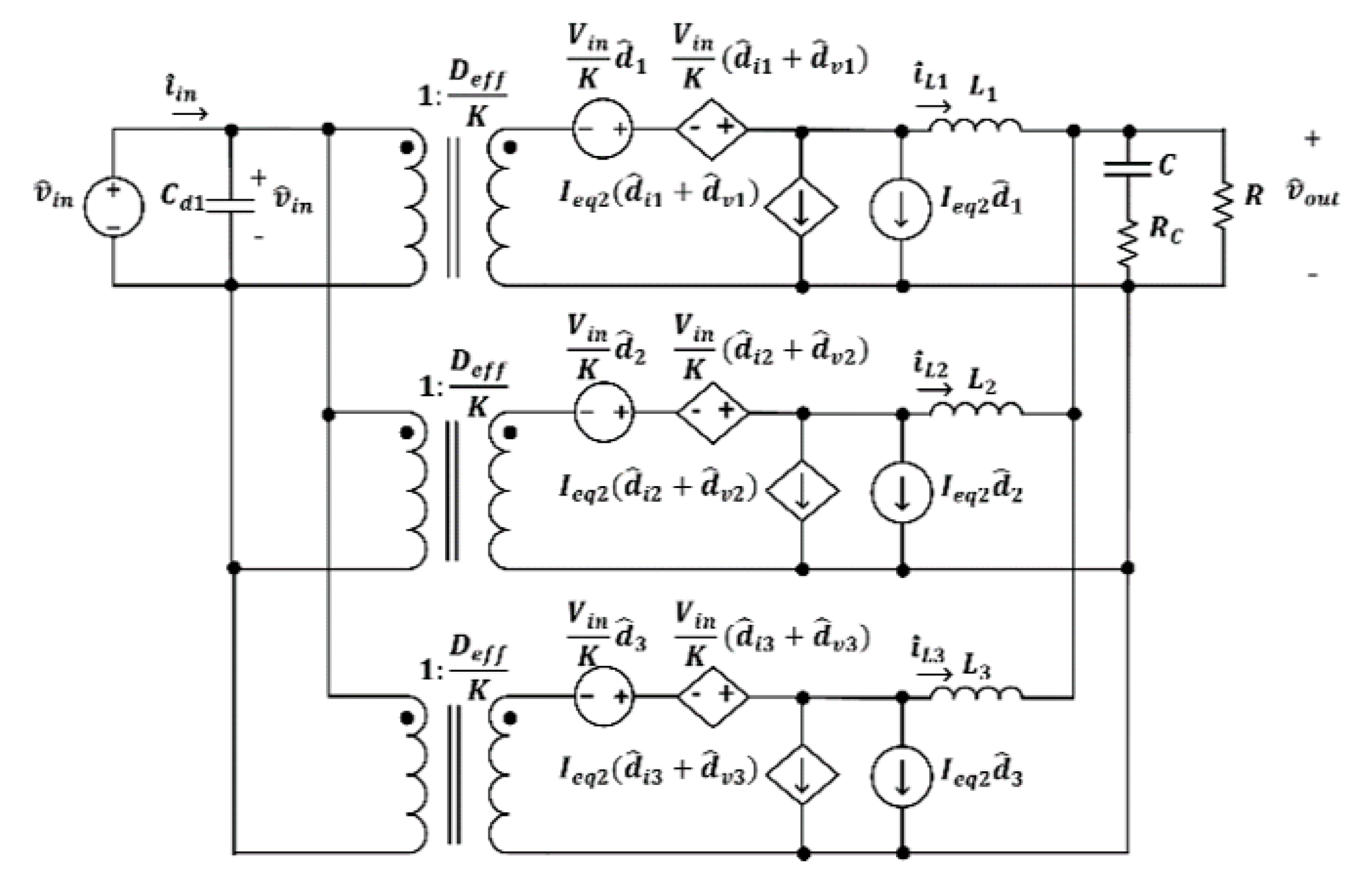
6.2. ISIP-OSOP Generic DC-DC Converter Small-Signal Analysis
- , if all the modules at the input side are connected in series.
- , if all the modules at the input side are connected in parallel.
- , if the modules at the input side are connected in series and parallel.
- , if all the modules at the output side are connected in series.
- , if all the modules at the output side are connected in parallel.
- , if the modules at the output side are connected in series and parallel.
6.2.1. Control-To-Output Voltage Transfer Function
6.2.2. Control-To-Filter Inductor Current Transfer Function
6.2.3. Output Impedance
6.2.4. Converter Gain
6.3. ISIP-OSOP DC-DC Converter SSM Verification
6.3.1. Generalized Model Verification with a Two-Module IPOS DC-DC Converter
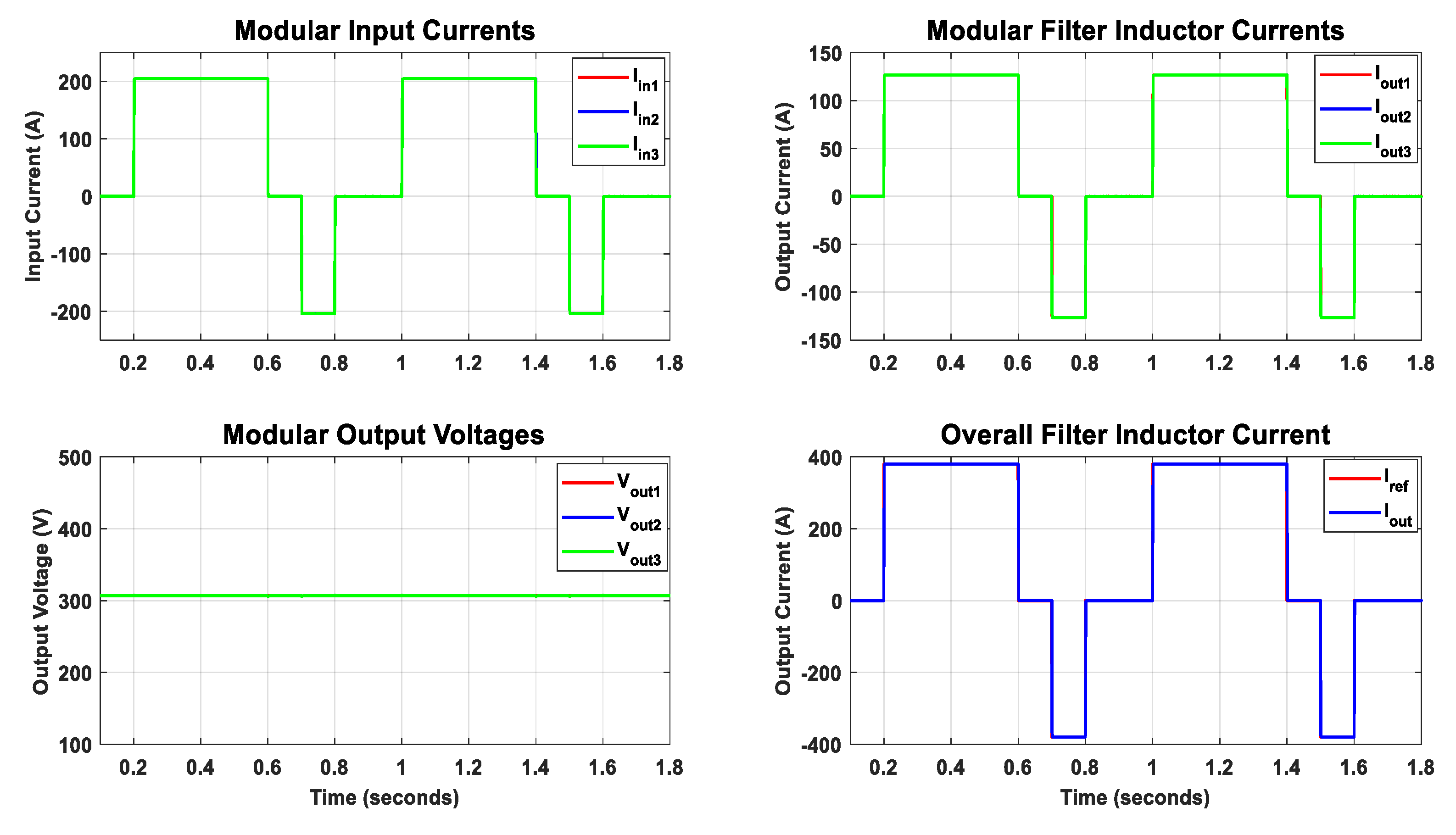
6.3.2. Generalized Model Verification with a Three-Module ISOP DC-DC Converter
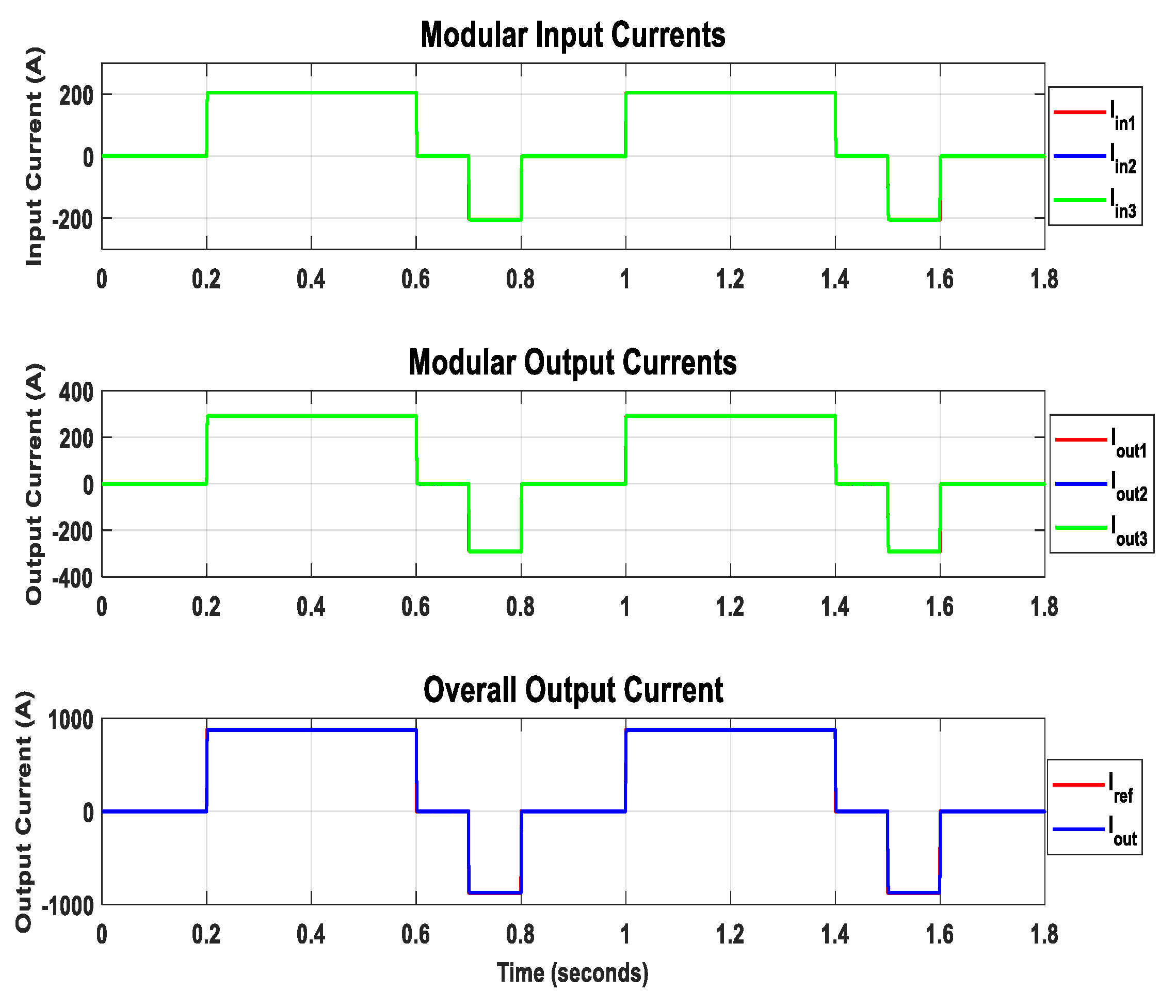
6.3.3. Generalized Model Verification with a Four-Module ISIPOS DC-DC Converter
7. Power Balancing in ISIP-OSOP DC-DC Converters
7.1. ISOS Control Strategy
7.2. ISOP Control Strategy
7.3. IPOP Control Strategy
7.4. IPOS Control Strategy
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EVs | Electric Vehicles |
| UFC | Ultra-Fast Charging |
| UF-EVC | Ultra-Fast EV Charging |
| SoC | State-of-Charge |
| DAB | Dual Active Bridge |
| DHB | Dual Half Bridge |
| ISOS | Input-Series Output-Series |
| IPOP | Input-Parallel Output-Parallel |
| ISOP | Input-Series Output-Parallel |
| IPOS | Input-Parallel Output-Series |
| SSM | Small-Signal Model |
| ISIP-OSOP | Input-Series Input-Parallel Output-Series Output-Parallel |
| FB-PS | Full-Bridge Phase-Shift |
| ISIPOS | Input-Series Input-Parallel Output-Series |
| RC | Reflex Charging |
| IVS | Input Voltage Sharing |
| OVS | Output Voltage Sharing |
| ICS | Input Current Sharing |
| OCS | Output Current Sharing |
| ESR | Equivalent Series Resistance |
| CFOCS | Cross Feedback Output Current Sharing |
References
- Vasiladiotis, M.; Rufer, A. A Modular Multiport Power Electronic Transformer with Integrated Split Battery Energy Storage for Versatile Ultrafast EV Charging Stations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3213–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesler, M.; Kisacikoglu, M.C.; Tolbert, L.M. Vehicle-to-Grid Reactive Power Operation Using Plug-In Electric Vehicle Bidirectional Offboard Charger. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6778–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zou, C.; Tang, X.; Liu, T.; Hu, L. Cost-Optimal Energy Management of Hybrid Electric Vehicles Using Fuel Cell/Battery Health-Aware Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, F.; Ding, Z.; Hu, Z.; Sarikprueck, P. Technical Review on Advanced Approaches for Electric Vehicle Charging Demand Management, Part I: Applications in Electric Power Market and Renewable Energy Integration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.K.; Singh, M. Resonant controller of single-stage off-board EV charger in G2V and V2G modes. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, M.Z.; Imran, K.; Khattak, A.; Janjua, A.K.; Pal, A.; Nadeem, M.; Zhang, J.; Khan, S. Optimal Placement of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations in the Active Distribution Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 68124–68134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, D.; Tschannen, S.; Biela, J. Highly efficient and compact DC-DC converter for ultra-fast charging of electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 15th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (EPE/PEMC), Novi Sad, Serbia, 2–4 September 2012; pp. LS5d.3-1–LS5d.3-8. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, G.B.; Andrew, C.C.; Suzanne, M.; David, L.W. Vehicle Electrification: Status and Issues. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 1116–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, M.; Jemelin, C.; Louvet, N. Driving an Electric Vehicle: A sociological analysis on pioneer users. Proc. Energy Effic. 2011, 4, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidrue, M.; Parsons, G.; Kempton, W.; Gardner, M. Willingness to pay for electric vehicles and their attributes. Resour. Energy Econ. 2011, 33, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, M.; Krein, P.T. Review of battery charger topologies, charging power levels and infrastructure for plug-in electric and hybrid vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 2151–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaligh, A.; Dusmez, S. Comprehensive topological analysis of conductive and inductive charging solutions for plug-in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 3475–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Friedli, T.; Kolar, J.W. Three-phase unity power factor mains interfaces of high power EV battery charging systems. In Proceedings of the Workshop ECPE Power Electronics for Charging Electric Vehicles, Valencia, Spain, 21–22 March 2011; pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Intel. Revolutionizing Fast Charging for Electric Vehicles; Intel: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Crosier, R.; Chu, Y. Investigating the power architectures and circuit topologies for megawatt superfast electric vehicle charging stations with enhanced grid support functionality. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference, Greenville, SC, USA, 4–8 March 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Whitwam, R. BMW, Porsche Demo Super-Fast Electric Car Charger. ExtremeTech 2018. Available online: https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/282364-bmw-porsche-demo-super-fast-electric-car-charger (accessed on 9 March 2019).
- BMW. Ultra-Fast Charging Technology Ready for Future of Electric Vehicles. Electron. Compon. News 2018. Available online: https://www.ecnmag.com/news/2018/12/ultra-fast-charging-technology-ready-future-electric-vehicles (accessed on 9 March 2019).
- Yuan, Z.; Xu, H.; Chao, Y.; Zhang, Z. A novel fast charging system for electrical vehicles based on input-parallel output-parallel and output-series. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Harbin, China, 2–5 August 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Beldjajev, V. Research and Development of the New Topologies for the Isolation Stage of the Power Electronic Transformer. Master’s Thesis, Tallinn University of Technology, Tallinn, Estonia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, S.P.; Stieneker, M.; Soltau, N.; Rabiee, S.; Stagge, H.; de Doncker, R.W. Comparison of the Modular Multilevel DC Converter and the Dual-Active Bridge Converter for Power Conversion in HVDC and MVDC Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, H.I. DC/DC Converters for Multi-terminal HVDC Systems Based on Modular Multilevel Converter; Norwegian University of Science and Technology: Kongeriket, Norway, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Modular and Scalable DC-DC Converters for Medium-/High-Power Applications. Master’s Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Li, H. A high-frequency medium-voltage DC-DC converter for future electric energy delivery and management systems. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Power Electronics—ECCE Asia, Jeju, Korea, 30 May–1 June 2011; pp. 1031–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Papadakis, C. Protection of HVDC Grids Using DC Hub. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Carrizosa, M.J.; Benchaib, A.; Alou, P.; Damm, G. DC transformer for DC/DC connection in HVDC network. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE), Lille, France, 2–6 September 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, C.C.; Trainer, D.R. Innovative concepts for hybrid multi-level converters for HVDC power transmission. In Proceedings of the 9th IET International Conference on AC and DC Power Transmission (ACDC 2010), London, UK, 19–21 October 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Alatalo, M. Module Size Investigation on Fast Chargers for BEV; Chalmers University of Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jalakas, T.; Roasto, I.; Vinnikov, D. Electric vehicle fast charger high voltage input multiport converter topology analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference-Workshop Compatibility and Power Electronics, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 5–7 June 2013; pp. 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, S.; Wu, B. Electric Vehicle Charging Station with an Energy Storage Stage for Split-DC Bus Voltage Balancing. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2376–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Wu, B.; Kouro, S.; Yaramasu, V.; Wang, J. Electric Vehicle Charging Station Using a Neutral Point Clamped Converter with Bipolar DC Bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srdic, S.; Liang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, W.; Lukic, S. A SiC-based high-performance medium-voltage fast charger for plug-in electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Aggeler, D.; Canales, F.; Zelaya, H.; La Parra, D.; Coccia, A.; Butcher, N.; Apeldoorn, O. Ultra-fast DC-charge infrastructures for EV-mobility and future smart grids. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT Europe), Gothenburg, Sweden, 10–13 October 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, T.; Liu, C.; Shan, R.; Wang, Y.; Kong, D.; Guo, J. A Novel Phase-Shift Full-Bridge Converter with Separated Resonant Networks for Electrical Vehicle Fast Chargers. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Power Electronics and Application Conference and Exposition (PEAC), Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Justino, J.C.G.; Parreiras, T.M.; Filho, B.J.C. Hundreds kW Charging Stations for e-Buses Operating Under Regular Ultra-Fast Charging. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Huang, A.Q.; Teng, H.; Lu, J.; Bai, K.H.; Brown, A.; McAmmond, M. A novel energy balanced variable frequency control for input-series-output-parallel modular EV fast charging stations. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiladiotis, M.; Rufer, A.; Béguin, A. Modular converter architecture for medium voltage ultra fast EV charging stations: Global system considerations. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference, Greenville, SC, USA, 4–8 March 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Vlatkovic, V.; Sabate, J.A.; Ridley, R.B.; Lee, F.C.; Cho, B.H. Small-signal analysis of the phase-shifted PWM converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1992, 7, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Adam, G.; Holliday, D.; Finney, S. Modular input-parallel output-series DC/DC converter control with fault detection and redundancy. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, X.; Chen, W.; Cheng, L.; Tse, C.K.; Yan, H.; Zhang, T. Control Strategy for Input-Series–Output-Parallel Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMenshawy, M.; Massoud, A. Multimodule ISOP DC-DC Converters for Electric Vehicles Fast Chargers. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Smart Grid and Renewable Energy (SGRE), Doha, Qatar, 19–21 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, Y.; Adam, G.P.; Holliday, D.; Finney, S.J. Medium-voltage DC/DC converter for offshore wind collection grid. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2016, 10, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMenshawy, M.; Massoud, A. Multimodule DC-DC Converters for High-Voltage High-Power Renewable Energy Sources. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Smart Grid and Renewable Energy (SGRE), Doha, Qatar, 19–21 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, D.; Guo, Z.; Luo, T.; Liao, X. A General Control Strategy for Input-Series–Output-Series Modular DC-DC Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 3766–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Shi, J.; He, X. A novel input-parallel output-parallel connected DC-DC converter modules with automatic sharing of currents. In Proceedings of the 7th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Harbin, China, 2–5 June 2012; pp. 1871–1876. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Ruan, X.; Yan, H.; Tse, C.K. DC/DC Conversion Systems Consisting of Multiple Converter Modules: Stability, Control, and Experimental Verifications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, D.; Guo, Z.; Liao, X. Cross-Feedback Output-Current-Sharing Control for Input-Series-Output-Parallel Modular DC–DC Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2762–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Lin, C.H.; Lai, S.-Y. Development of Fast Large Lead-Acid Battery Charging System Using Multi-state Strategy. Int. J. Comput. Consum. Control. (IJ3C) 2013, 2, 56–65. [Google Scholar]





| Charging Level | Input Voltage | Phase | Power | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | (Single) AC | h | ||
| Level 2 | (Single) AC | h | ||
| Level 3 (DC Fast Charging) | (Three) DC | min | ||
| Ultra-fast/Super-fast Charging | or Medium Voltage ranging from | (Three) DC | min |
| Defined Variables | ||
|---|---|---|
| Input Side | 2 | |
| 1 | ||
| 2 (same as ) | ||
| Output Side | 1 | |
| 2 | ||
| 1 | ||
| Transfer Functions for Two-Module IPOS DC-DC Converter | |
|---|---|
| Defined Variables | ||
|---|---|---|
| Input Side | 1 | |
| 3 | ||
| 1 | ||
| Output Side | 3 | |
| 1 | ||
| 3 | ||
| Transfer Functions for Three-Module ISOP DC-DC Converter | |
|---|---|
| Defined Variables | ||
|---|---|---|
| Input Side | 2 | |
| 2 | ||
| 2 | ||
| Output Side | 1 | |
| 4 | ||
| 1 | ||
| Transfer Functions for Four-Module ISIPOS DC-DC Converter | |
|---|---|
| Parameters | First Module | Second Module | Third Module 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall converter rated power | |||
| Rated power per module | |||
| Overall input voltage | |||
| Input voltage per module | |||
| Overall output voltage | |||
| Output voltage per module | |||
| Modules Number | |||
| Turns ratio | |||
| Leakage inductance | |||
| Effective duty cycle | |||
| Input Capacitance | |||
| Output filter inductor | |||
| Output capacitance | |||
| Load resistance | |||
| Switching frequency | |||
| Parameters | First Module | Second Module | Third Module 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall converter rated power | |||
| Rated power per module | |||
| Overall input voltage | |||
| Input voltage per module | |||
| Overall output voltage | |||
| Output voltage per module | |||
| Modules Number | |||
| Turns ratio | |||
| Leakage inductance | |||
| Effective duty cycle | |||
| Input Capacitance | |||
| Output filter inductor | |||
| Output capacitance | |||
| Load resistance | |||
| Switching frequency | |||
| Parameters | First Module | Second Module | Third Module 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall converter rated power | |||
| Rated power per module | |||
| Overall input voltage | |||
| Input voltage per module | |||
| Overall output voltage | |||
| Output voltage per module | |||
| Modules Number | |||
| Turns ratio | |||
| Leakage inductance | |||
| Effective duty cycle | |||
| Input Capacitance | |||
| Output filter inductor | |||
| Output capacitance | |||
| Load resistance | |||
| Switching frequency | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
ElMenshawy, M.; Massoud, A. Modular Isolated DC-DC Converters for Ultra-Fast EV Chargers: A Generalized Modeling and Control Approach. Energies 2020, 13, 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102540
ElMenshawy M, Massoud A. Modular Isolated DC-DC Converters for Ultra-Fast EV Chargers: A Generalized Modeling and Control Approach. Energies. 2020; 13(10):2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102540
Chicago/Turabian StyleElMenshawy, Mena, and Ahmed Massoud. 2020. "Modular Isolated DC-DC Converters for Ultra-Fast EV Chargers: A Generalized Modeling and Control Approach" Energies 13, no. 10: 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102540
APA StyleElMenshawy, M., & Massoud, A. (2020). Modular Isolated DC-DC Converters for Ultra-Fast EV Chargers: A Generalized Modeling and Control Approach. Energies, 13(10), 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13102540






