An Integrally Embedded Discrete Fracture Model for Flow Simulation in Anisotropic Formations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Basic Mathematical Method
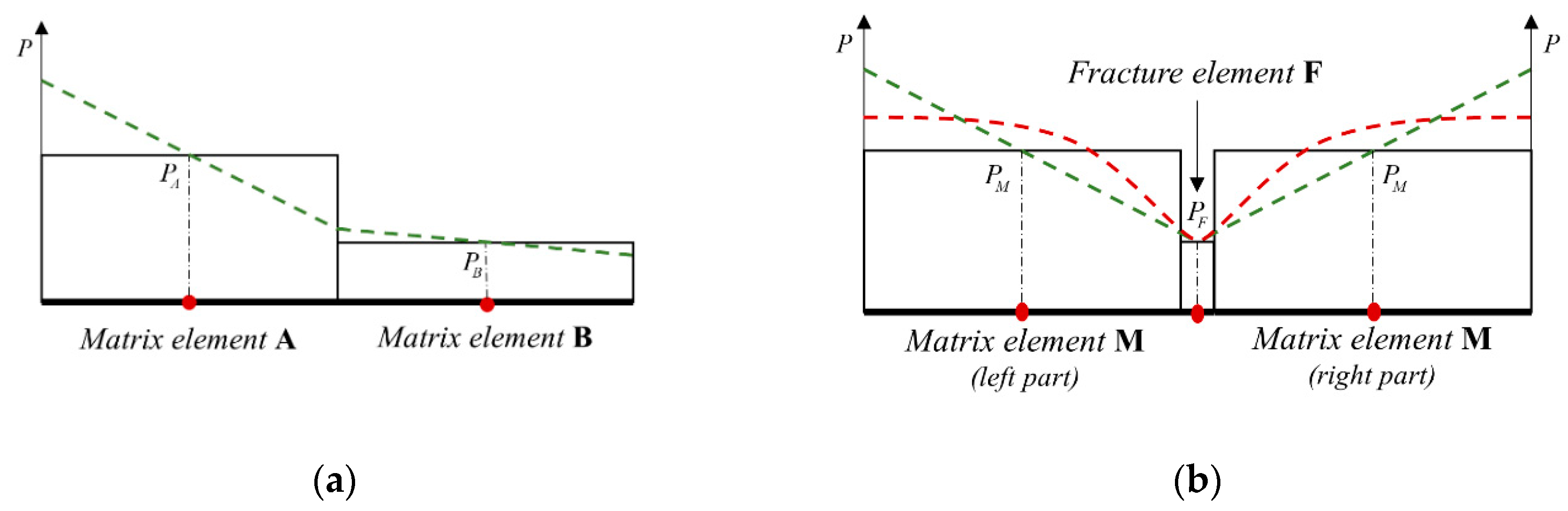
2.2. Integrally Embedded Discrete Fracture Model
2.3. Algorithm for the Embedding of Fractures into Anisotropic Formation
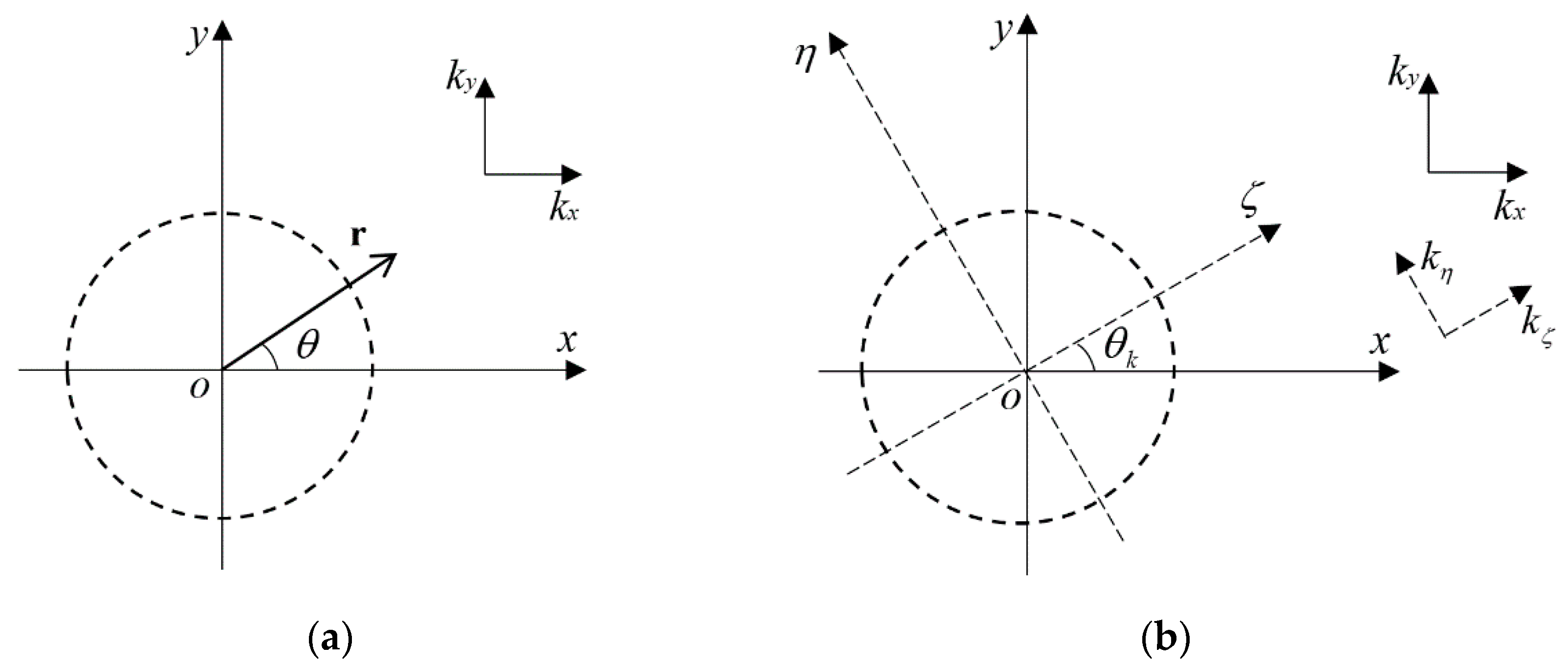
2.3.1. Analytic Point-Source Solution in Anisotropic Formation
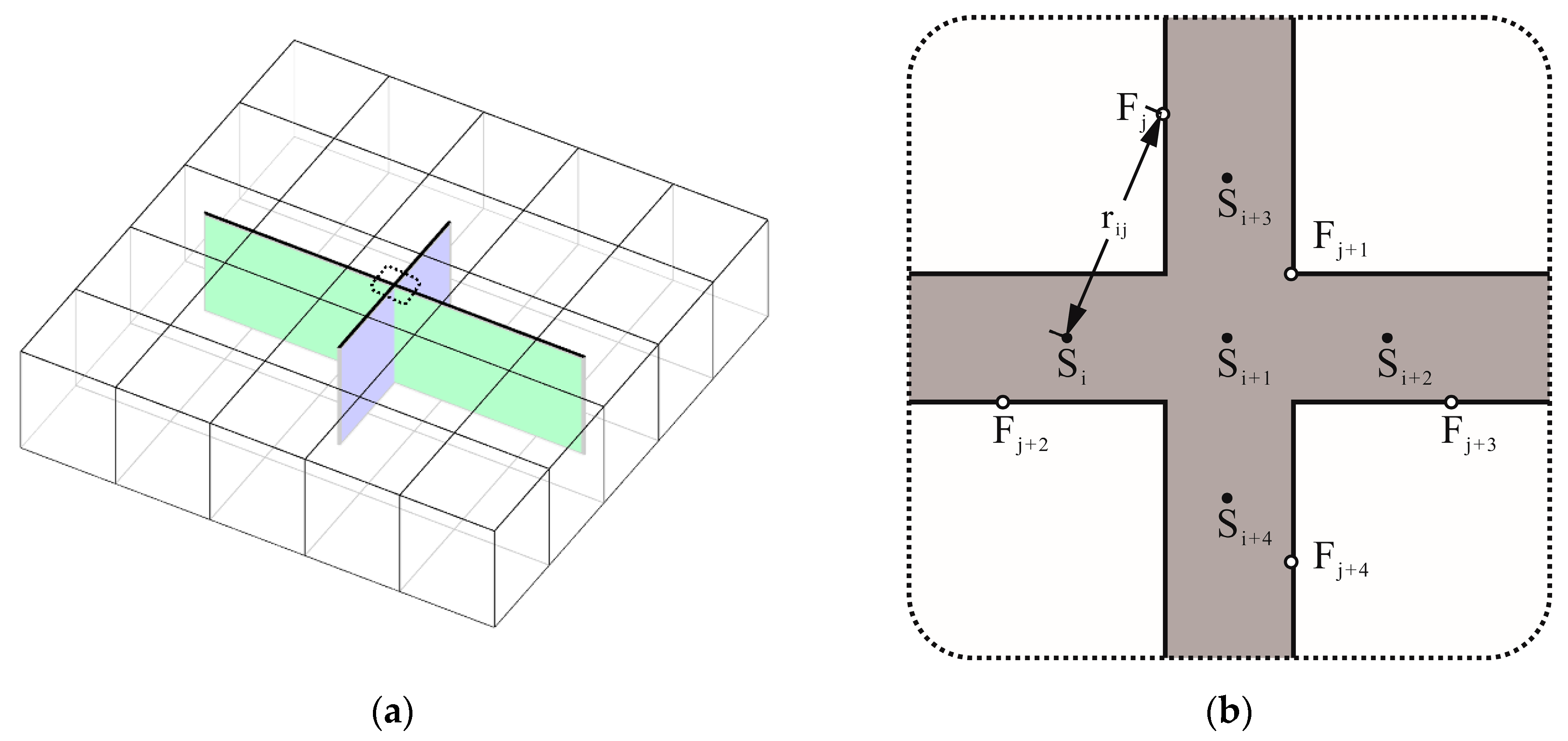
2.3.2. Calculation Methods for Matrix–Fracture Transmissibility
3. Model Validation
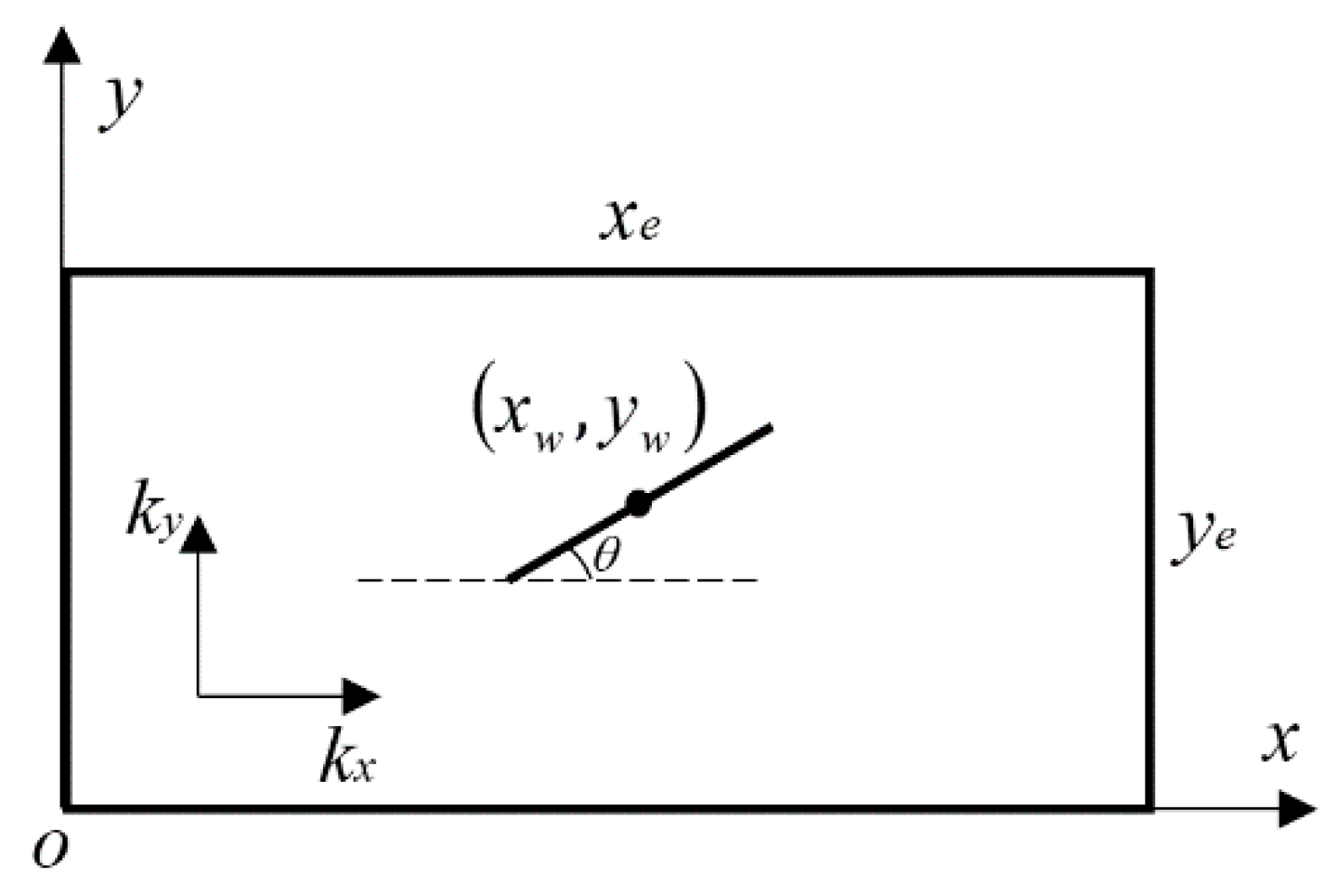
3.1. Case 1: Single-Phase Flow in Anisotropic Formation with Vertical Fractured Well
3.1.1. Analytic Solution of Quasi-Steady-State Flow
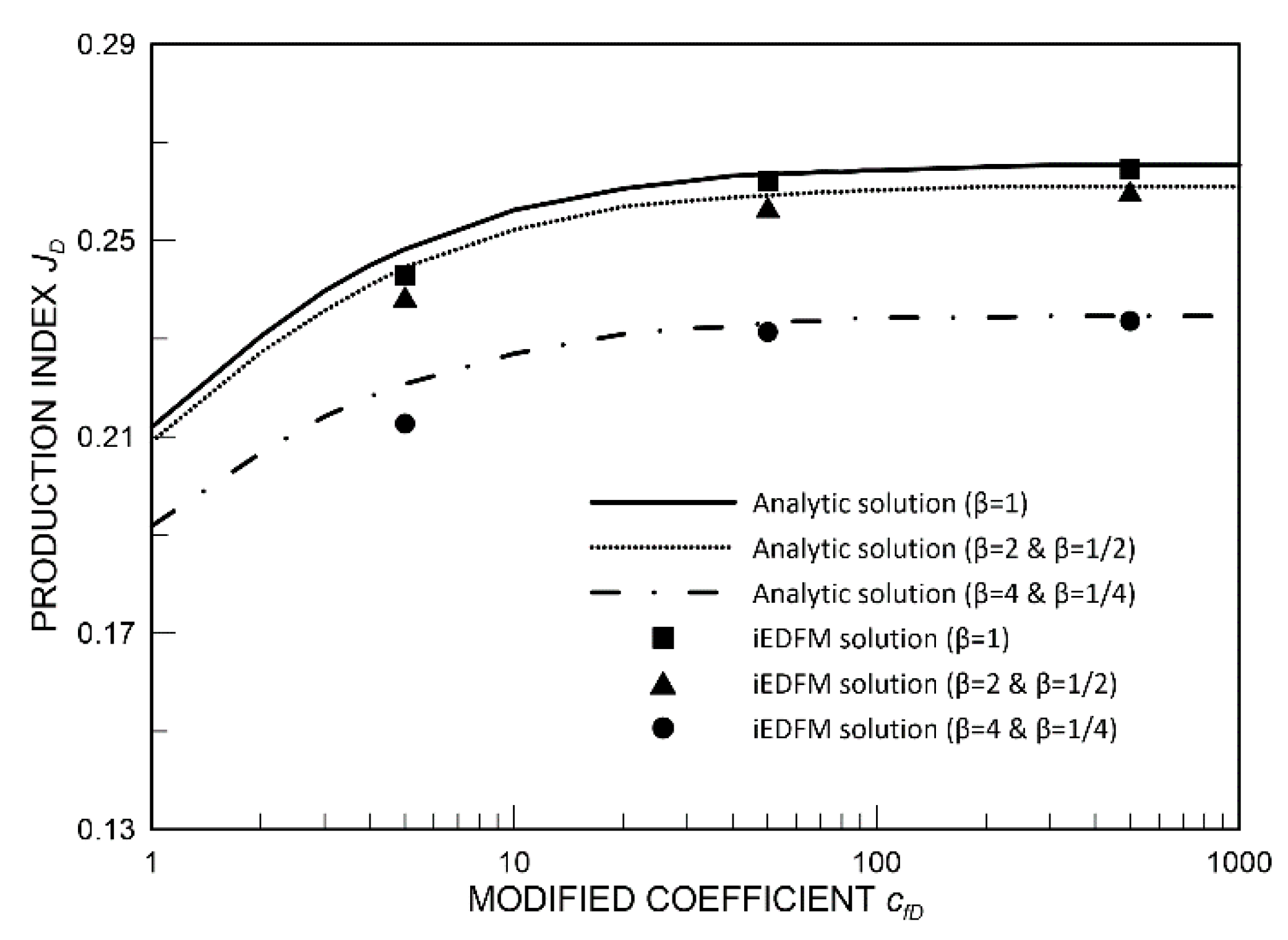
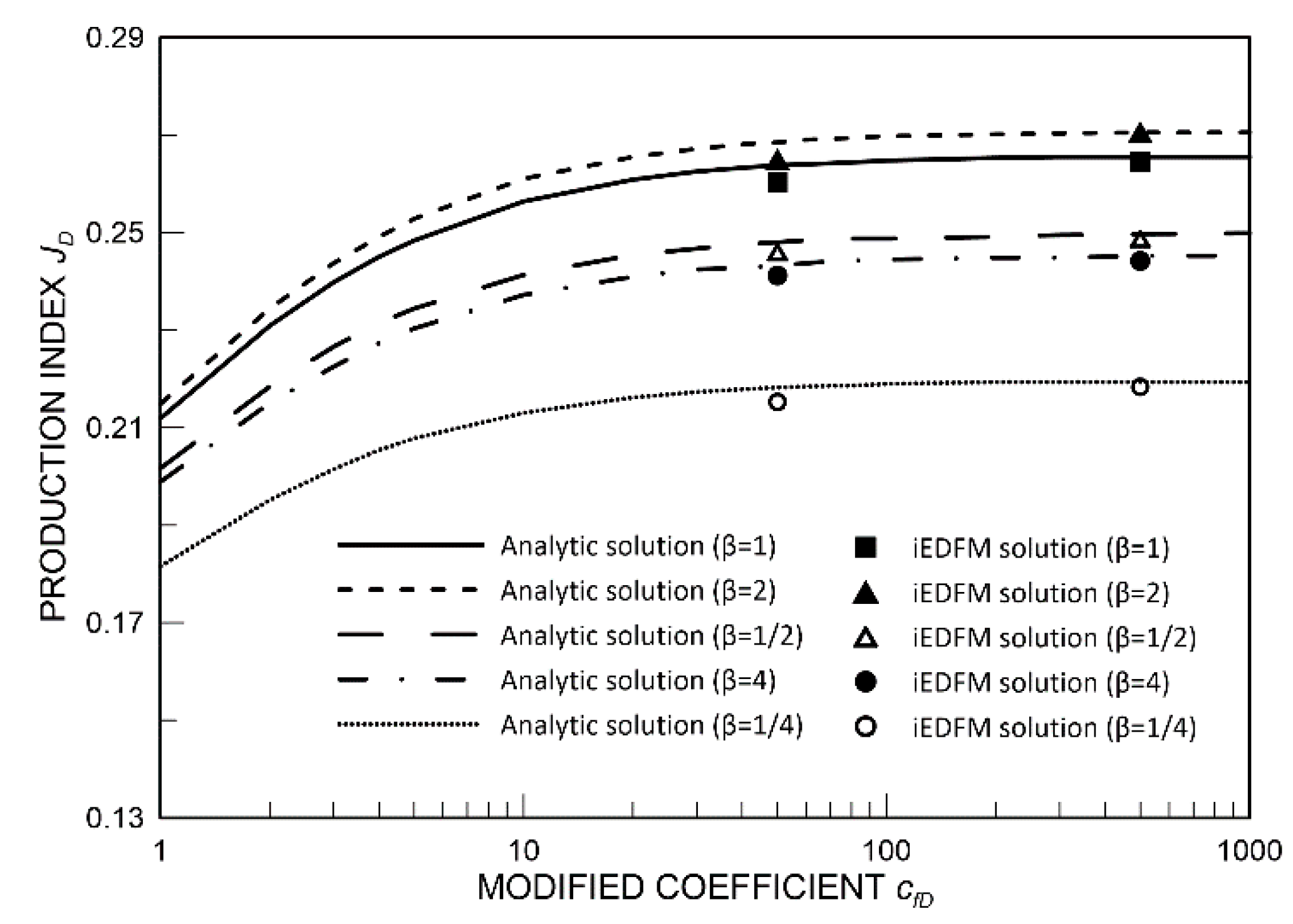
3.1.2. Comparison between Numerical and Analytic Solutions
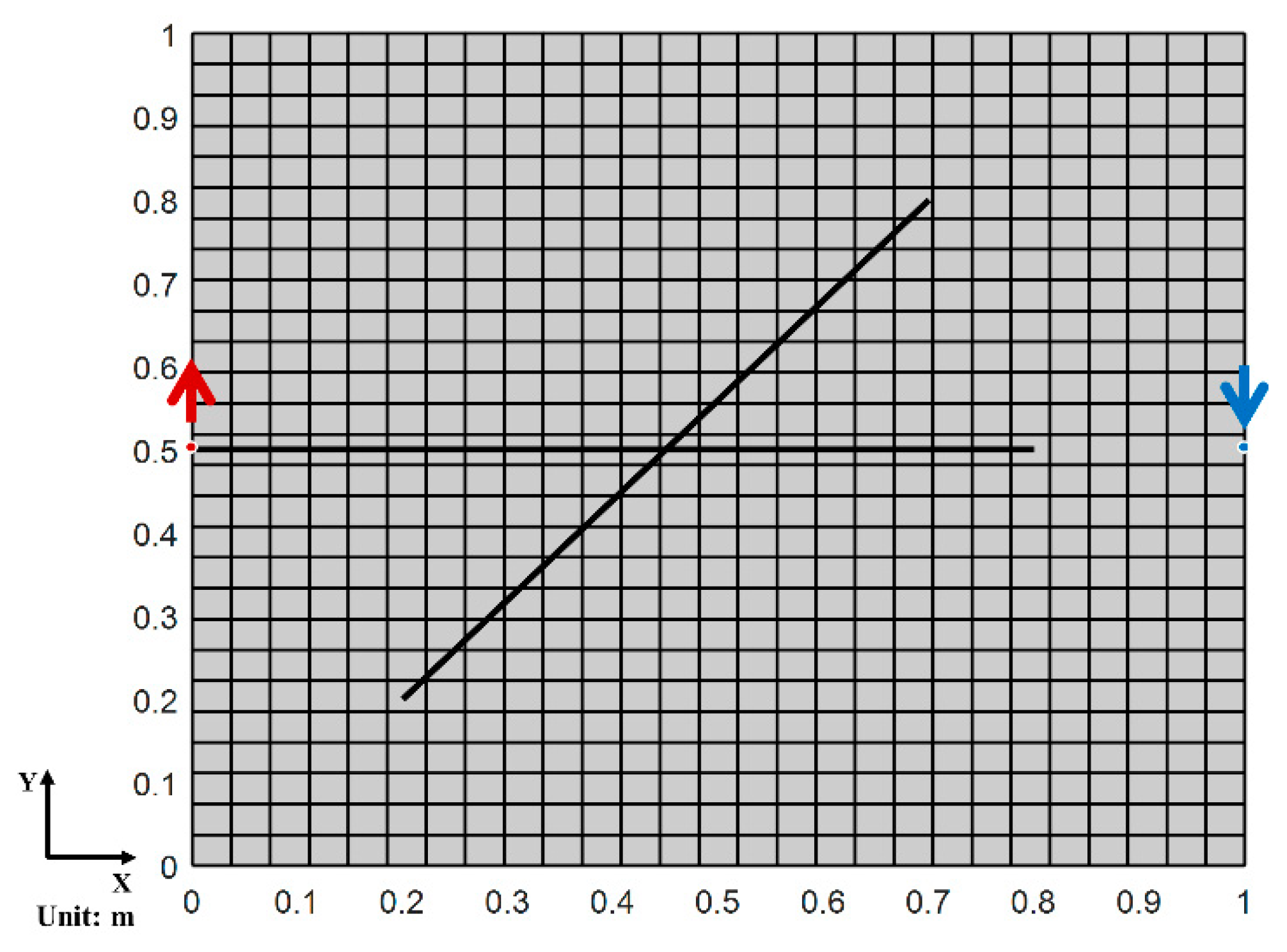
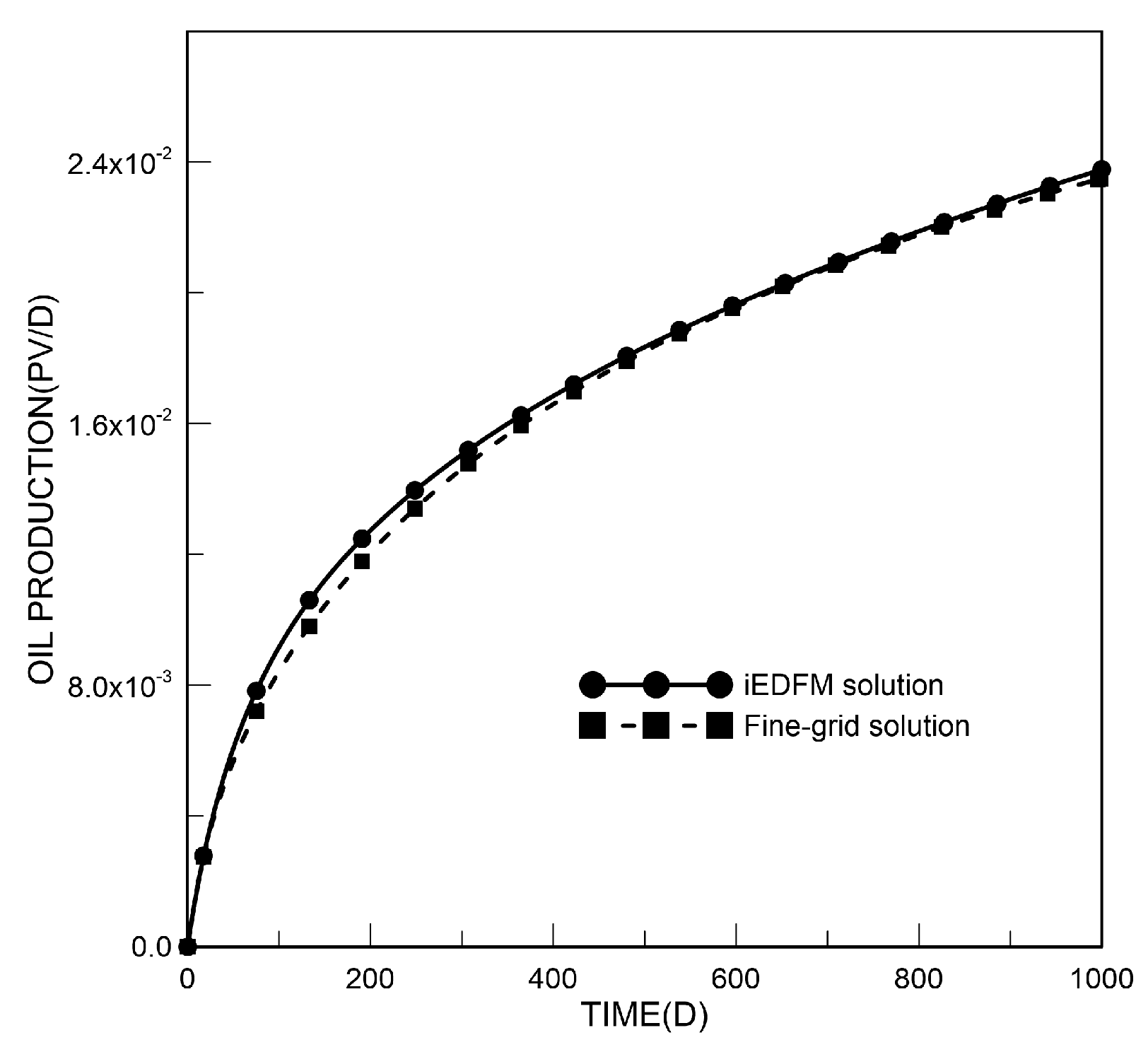
3.2. Case 2: Two-Phase Flow in Anisotropic Formation with Two Crossed Fractures
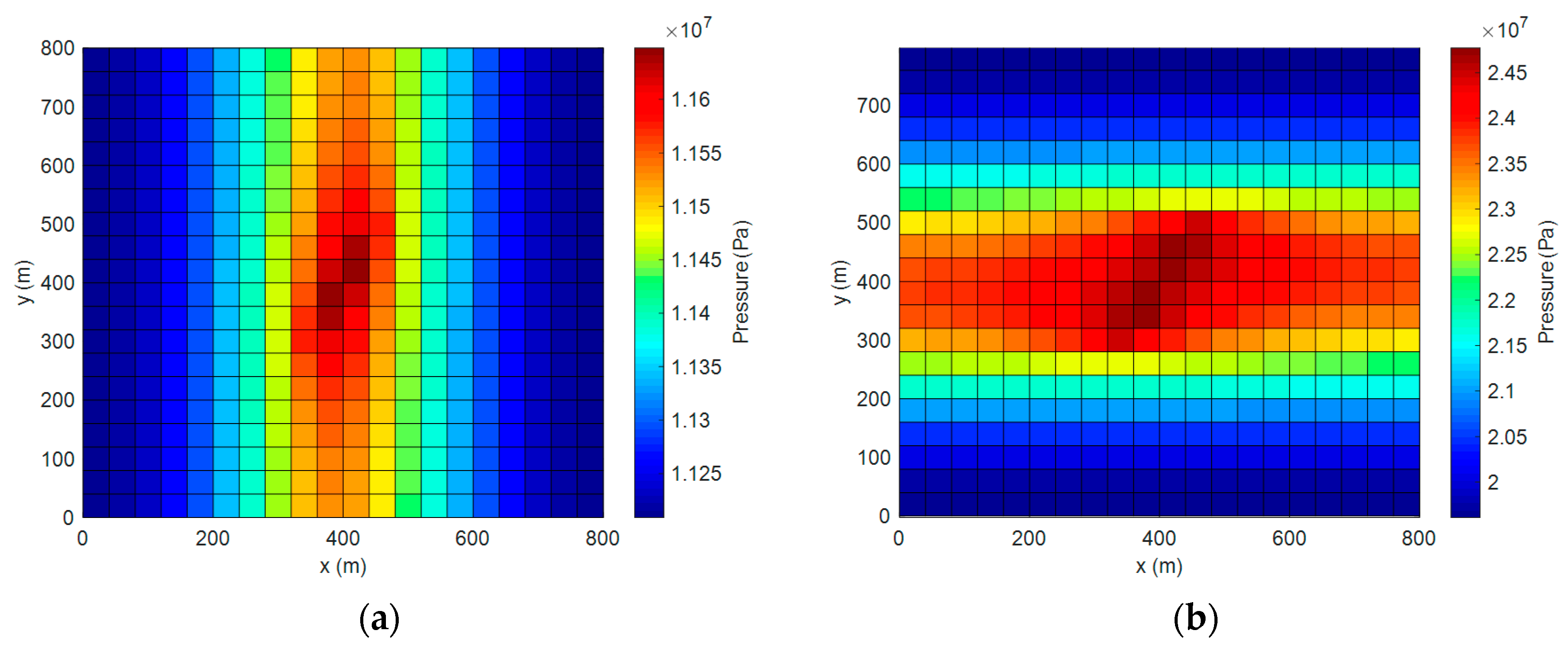
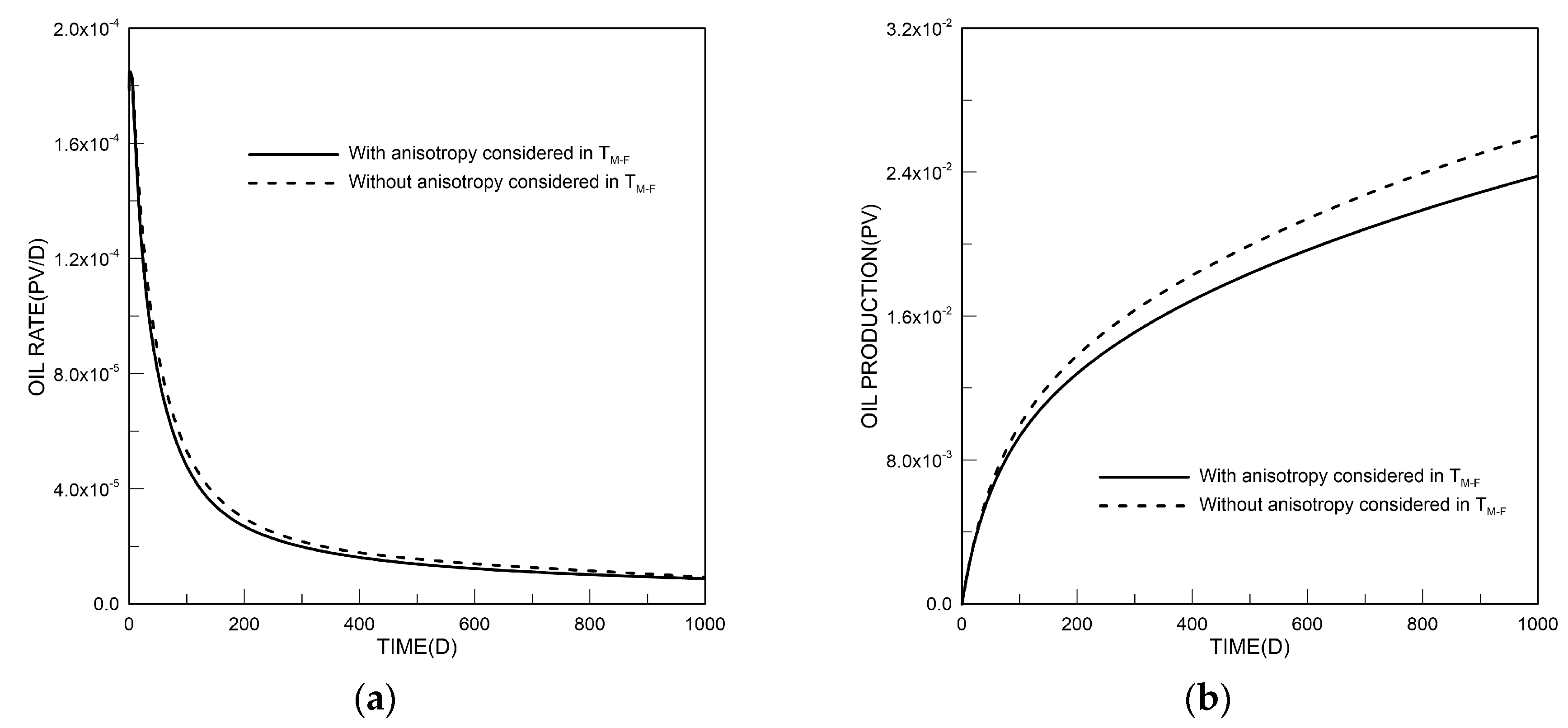
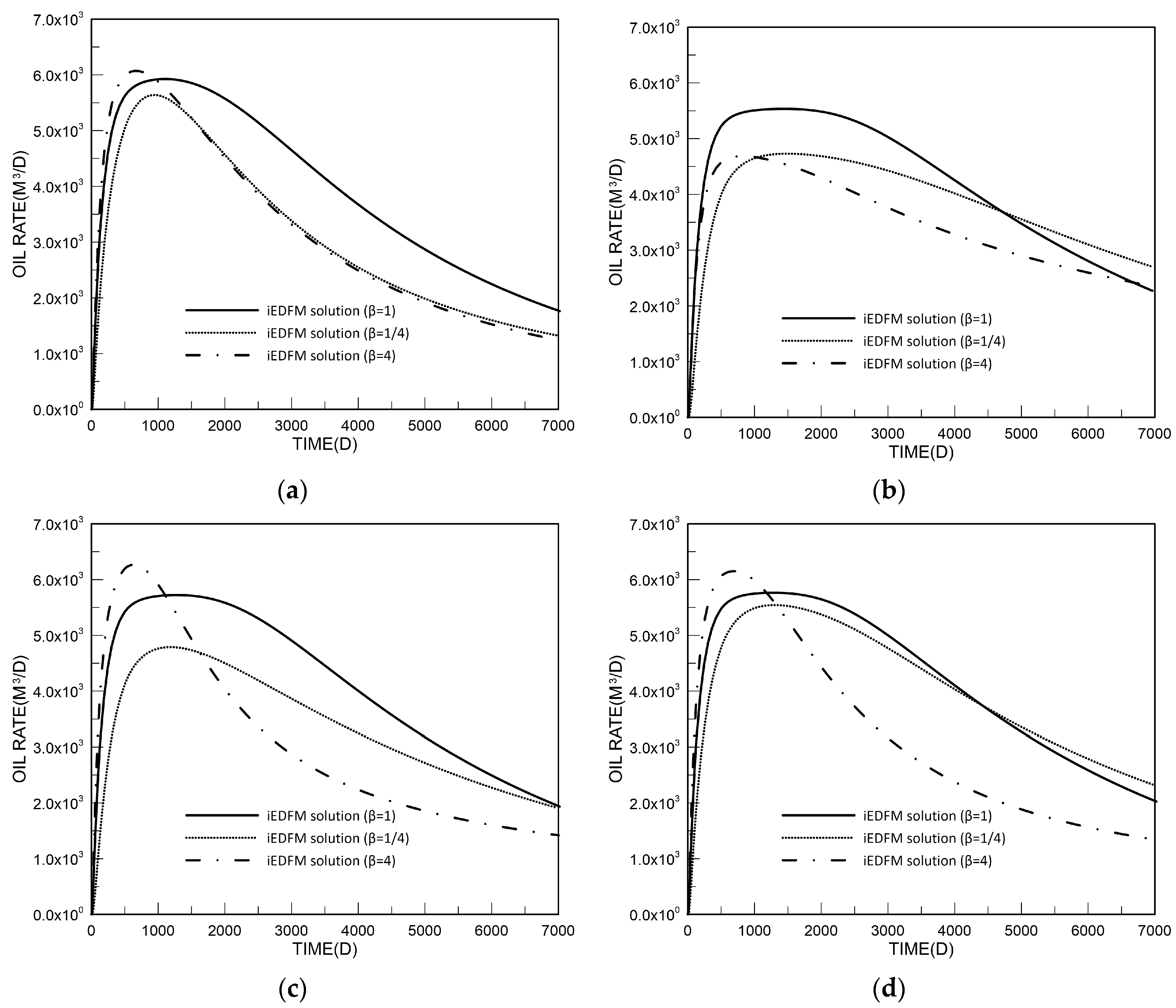
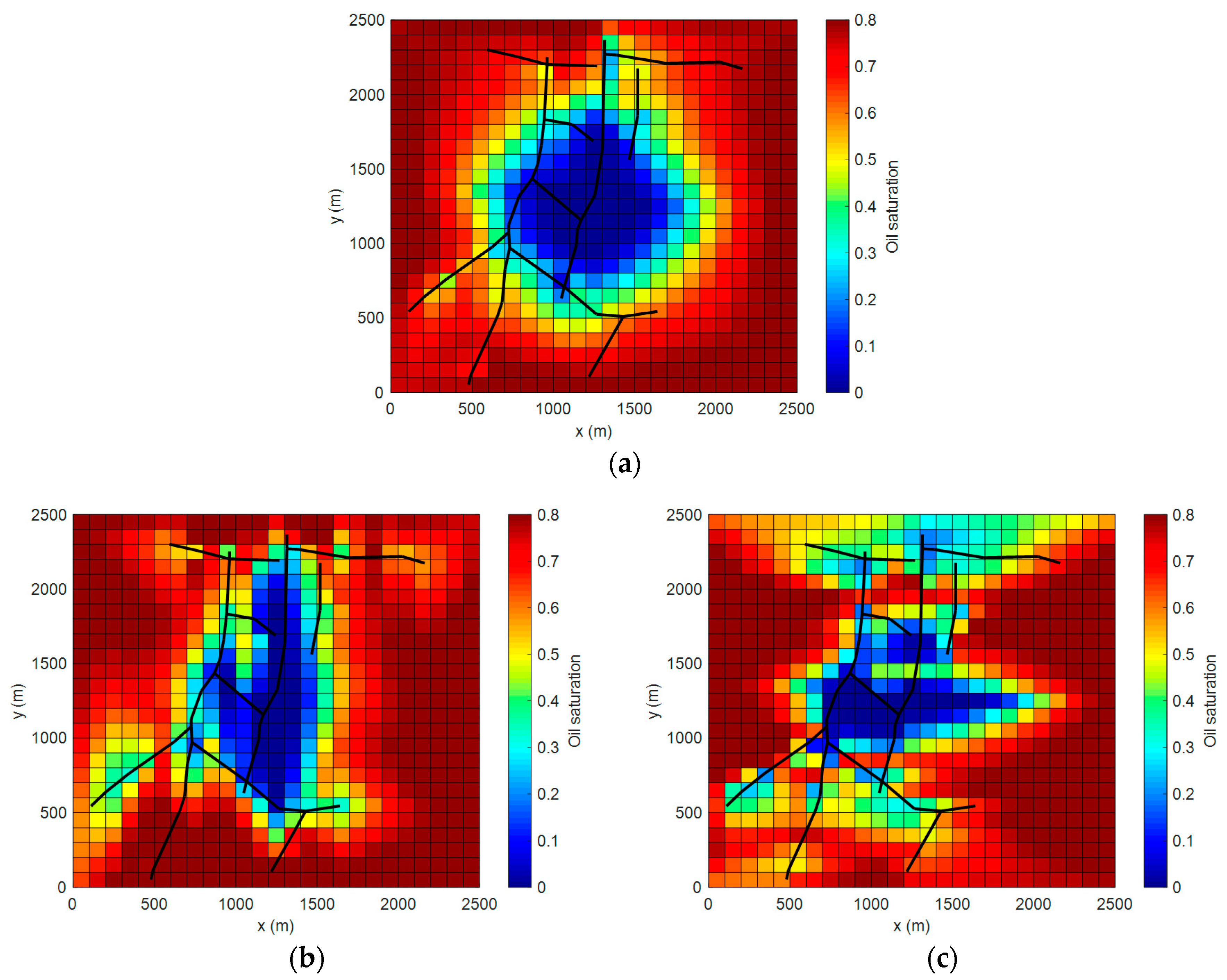
4. Model Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Saller, S.P.; Ronayne, M.J.; Long, A.J. Comparison of a Karst Groundwater Model with and without Discrete Conduit Flow. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurpinar, O.M.; Kossack, C.A. Realistic Numerical Models for Fractured Reservoirs. SPE J. 2000, 5, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.E.; Root, P.J. The Behavior of Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. SPE J. 1963, 33, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, H. Pressure Transient Analysis of Naturally Fractured Reservoirs with Uniform Fracture Distribution. SPE J. 1969, 9, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaan, A.D. Theory of Waterflooding in Fractured Reservoirs. SPE J. 1978, 18, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, J.R. Efficient Finite-Difference Method for Simulating Phase Segregation in the Matrix Blocks in Double-Porosity Reservoirs. SPE Reserv. Eng. 1986, 1, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, J.R.; Kazemi, H. Improved Calculations for Viscous and Gravity Displacement in Matrix Blocks in Dual-Porosity Simulators. J. Pet. Technol. 1988, 40, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruess, K.; Narasimhan, T.N. Practical Method for Modeling Fluid and Heat Flow in Fractured Porous Media. SPE J. 1985, 25, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Pruess, K. Multiple-porosity Method for Simulation of Naturally Fractured Petroleum Reservoirs. SPE Reserv. Eng. 1988, 3, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, L.S.K. Simulation of Block-to-Block Processes in Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. SPE Reserv. Eng. 1991, 6, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Di, Y.; Kang, Z.; Fakcharoenphol, P. A Multiple-Continuum Model for Simulating Single-phase and Multiphase Flow in Naturally Fractured Vuggy Reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2011, 78, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chawathe, A.; Hoteit, H.; Shi, X.; Li, L. Understanding Shale Gas Flow Behavior Using Numerical Simulation. SPE J. 2015, 20, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Alfi, M.; An, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Killough, J.E. General Multi-porosity Simulation for Fractured Reservoir Modeling. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 33, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M. On Equivalence of Dual-Porosity Poroelastic Parameters. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1999, 104, 10461–10466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorishad, J.; Mehran, M. An Upstream Finite-Element Method for Solution of Transient Transport-Equation in Fractured Porous-Media. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Fard, M.; Firoozabadi, A. Numerical Simulation of Water Injection in Fractured Media Using the Discrete-Fracture Model and the Galerkin Method. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2003, 6, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo, J.; Firoozabadi, A. Control-Volume Method for Numerical Simulation of Two-phase Immiscible Flow in Two- and Three-Dimensional Discrete-Fractured Media. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W07405.1–W07405.20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoteit, H.; Firoozabadi, A. Compositional Modeling of Discrete-Fractured Media without Transfer Functions by the Discontinuous Galerkin and Mixed Methods. SPE J. 2006, 11, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthai, S.K.; Mezentsev, A.; Belayneh, M. Finite Element-Node-Centered Finite-Volume Two-Phase-Flow Experiments with Fractured Rock Represented by Unstructured Hybrid-Element Meshes. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2007, 10, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandve, T.H.; Berre, I.; Nordbotten, J.M. An Efficient Multi-Point Flux Approximation Method for Discrete Fracture-Matrix Simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 2012, 231, 3784–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidane, A.; Firoozabadi, A. An efficient numerical model for multicomponent compressible flow in fractured porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 74, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidane, A.; Firoozabadi, A. Fracture-Cross-Flow Equilibrium in Compositional Two-Phase Reservoir Simulation. SPE J. 2017, 22, 950–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidane, A.; Firoozabadi, A. Higher-order simulation of two-phase compositional flow in 3D with non-planar fractures. J. Comput. Phys. 2020, 402, 108896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, Z.; Lei, G. Integrating Embedded Discrete Fracture and Dual-Porosity, Dual-Permeability Methods to Simulate Fluid Flow in Shale Oil Reservoirs. Energies 2017, 10, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lough, M.F.; Jensen, C.L. Hierarchical Modeling of Flow in Naturally Fractured Formations with Multiple Length Scales. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lee, S.H. Efficient Field-Scale Simulation of Black Oil in a Naturally Fractured Reservoir through Discrete Fracture Networks and Homogenized Media. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2008, 11, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cavalcante Filho, J.S.A.; Yu, W.; Sepehrnoori, K. Discrete-Fracture Modeling of Complex Hydraulic-Fracture Geometries in Reservoir Simulators. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2017, 20, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wu, K.; Sepehrnoori, K. Simulation of Shale Gas Transport and Production with Complex Fractures Using Embedded Discrete Fracture Model. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 2251–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Huang, Z.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Fan, D. Numerical Simulation of Hydro-Mechanical Coupling in Fractured Vuggy Porous Media Using the Equivalent Continuum Model and Embedded Discrete Fracture Model. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 126, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Di, Y. An Integrally Embedded Discrete Fracture Model with a Semi-Analytic Transmissibility Calculation Method. Energies 2018, 11, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Mi, L.; Chai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Killough, J.E. An Enhanced Discrete Fracture Network Model for Multiphase Flow in Fractured Reservoirs. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2018, 161, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Cheng, L.; Cao, R.; Jia, P.; Liu, H.; Du, X. A Modified Projection-Based Embedded Discrete Fracture Model (pEDFM) for Practical and Accurate Numerical Simulation of Fractured Reservoir. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2020, 187, 106852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tene, M.; Bosma, S.B.M.; Al Kobaisi, M.S.; Hajibeygi, H. Projection-Based Embedded Discrete Fracture Model (pEDFM). Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 105, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Yao, J.; Shao, J. Study of Hydraulic Fracturing in an Anisotropic Poroelastic Medium via a Hybrid EDFM-XFEM Approach. Comput. Geotech. 2019, 105, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Xing, G.; Wang, J. Pressure-Transient Analysis for a Vertically Fractured Well at an Arbitrary Azimuth in a Rectangular Anisotropic Reservoir. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2017, 159, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, D.P.; Blasingame, T.A. Constant-Rate Drawdown Solutions Derived for Multiple Arbitrarily-Oriented Uniform-Flux, Infinite-Conductivity, or Finite-Conductivity Fractures in an Infinite-Slab Reservoir. In Proceedings of the SPE Gas Technology Symposium, Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–18 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Spivey, J.P.; Lee, W.J. Estimating the Pressure-Transient Response for a Horizontal or a Hydraulically Fractured Well at an Arbitrary Orientation in an Anisotropic Reservoir. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 1999, 2, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, F.; Brigham, W.E. Transient Flow in Elliptical Systems. SPE J. 1979, 19, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Ding, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, C. Rate Decline Curves Analysis of a Vertical Fractured Well with Fracture Face Damage. J. Energ. Resour. Asme. 2012, 134, 032803.1–032803.9. [Google Scholar]
- Gringarten, A.C.; Ramey, H.J.; Raghavan, R. Unsteady-State Pressure Distributions Created by a Well with a Single Infinite Conductivity Vertical Fracture. SPE J. 1974, 14, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, B.; Li, J.; Li, H. Discrete Fracture Modeling of 3D Heterogeneous Enhanced Coalbed Methane Recovery with Prismatic Meshing. Energies 2015, 8, 6153–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuck, E.L.; Davis, T.L.; Benson, R.D. Multicomponent 3-D Characterization of a Coalbed Methane Reservoir. Geophysics 1996, 61, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Anisotropic Formation | Equivalent Isotropic Formation |
|---|---|
| Anisotropy coefficient | |
| Coordinate , | , |
| Matrix permeability , | |
| Fracture azimuth | |
| Fracture Half-length | |
| Fracture aperture |
| Reservoir | Size (m): | |
| Matrix | Meshes: | Permeability in x direction (m2): |
| Fracture | Permeability : | Half-length (m): for ; for |
| Vertical Well | Production (m3/s): | Position : |
| Reservoir | Size (m): | |
| Matrix | iEDFM mesh: Fine grid mesh: | Permeability (m2): (m2): |
| Fracture | Permeability : | |
| Injection Well | Injection (m3/d): | Position: |
| Producing Well | Pressure (MPa): | Position: |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, R.; Di, Y.; Wu, D.; Wu, Y.-S. An Integrally Embedded Discrete Fracture Model for Flow Simulation in Anisotropic Formations. Energies 2020, 13, 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123070
Shao R, Di Y, Wu D, Wu Y-S. An Integrally Embedded Discrete Fracture Model for Flow Simulation in Anisotropic Formations. Energies. 2020; 13(12):3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123070
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Renjie, Yuan Di, Dawei Wu, and Yu-Shu Wu. 2020. "An Integrally Embedded Discrete Fracture Model for Flow Simulation in Anisotropic Formations" Energies 13, no. 12: 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123070
APA StyleShao, R., Di, Y., Wu, D., & Wu, Y.-S. (2020). An Integrally Embedded Discrete Fracture Model for Flow Simulation in Anisotropic Formations. Energies, 13(12), 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123070




