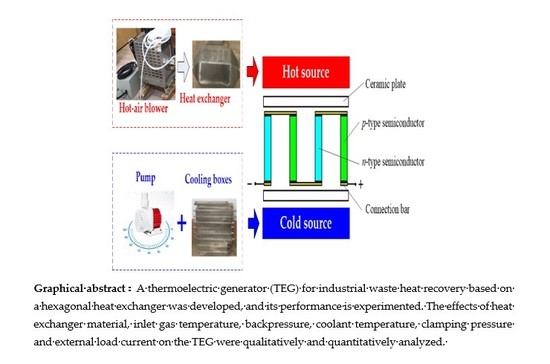
Experimental Study on a Thermoelectric Generator for Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Based on a Hexagonal Heat Exchanger
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup of a TEG System
3. Experimental Results and Discussions
3.1. Temperature Distribution
3.2. Influence of Heat Exchanger Material
3.3. Influence of Backpressure
3.4. Influence of Coolant Temperatures
3.5. Influence of Clamping Pressure
3.6. System Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Notations
| P1 | inlet gas temperature sensor |
| T1 | inlet gas temperature sensor |
| T2 | outlet gas temperature sensor |
| n | p-type and the n-type semiconductor galvanic arms number |
| VTEG | open circuit voltage of TEG |
| RTEG | internal resistance of TEG |
| αPNi | relative Seebeck coefficient |
| αpi | Seebeck coefficients of the p-type semiconductor galvanic arms |
| αni | Seebeck coefficients of the n-type semiconductor galvanic arms |
| THi | hot side temperature of TEM |
| TLi | cold side temperature of TEM |
| lp | leg length of a p-type semiconductor galvanic arm |
| σp | electricity resistivity of a p-type semiconductor galvanic arm |
| Ap | cross-sectional area of a p-type semiconductor galvanic arm |
| ln | leg length of a n-type semiconductor galvanic arm |
| σn | electricity resistivity of a n-type semiconductor galvanic arm |
| An | cross-sectional area of a p-type semiconductor galvanic arm |
| PTEG | maximum output power of TEG |
| Rm | external load resistance |
| Qh | heat input to the cylindrical heat exchanger |
| Gh | volume flow rate of inlet gas |
| ρh | density of inlet gas |
| Ch | heat capacity of inlet gas at constant pressure |
| Thi | inlet gas temperature |
| Tho | outlet gas temperature |
| η | maximum TEG system efficiency |
References
- Jaziri, N.; Boughamoura, A.; Müller, J.; Mezghani, B.; Tounsi, F.; Ismail, M. A comprehensive review of thermoelectric generators: Technologies and common applications. Energy Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W. High performance and integrated design of thermoelectric generator based on concentric filament architecture. J. Power Sources 2018, 393, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willars-Rodríguez, F.J.; Chávez-Urbiola, E.A.; Vorobiev, P.; Vorobiev, Y.V. Investigation of solar hybrid system with concentrating Fresnel lens, photovoltaic and thermoelectric generators. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, M.E.; Dincer, I. Performance assessment of a thermoelectric generator applied to exhaust waste heat recovery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 120, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.K.; Chen, L.G.; Feng, Y.L.; Xiong, B. Thermoelectric generator for industrial gas phase waste heat recovery. Energy 2017, 135, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proto, A.; Bibbo, D.; Cerny, M.; Vala, D.; Kasik, V.; Peter, L.; Conforto, S.; Schmid, M.; Penhaker, M. Thermal energy harvesting on the bodily surfaces of arms and legs through a wearable thermo-electric generator. Sensors 2018, 18, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Gu, H.M.; Kim, C.; Choi, H.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.; Yi, K.; Lee, S.; Cho, B. High-performance self-powered wireless sensor node driven by a flexible thermoelectric generator. Energy 2018, 162, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonov, V. Thermoelectric energy harvesting of human body heat for wearable sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgate, T.-C.; Bennett, R.; Hammel, T.; Caillat, T.; Keyser, S.; Sievers, B. Increasing the efficiency of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator. J. Electron. Mater. 2015, 44, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Cleary, M.; Wang, X.W.; Kempf, N.; Schoensee, L.; Yang, J.; Joshi, G.; Meda, L. High-temperature and high-power-density nanostructured thermoelectric generator for automotive waste heat recovery. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szybist, J.; Davis, S.; Thomas, J.F.; Kaul, B.C. Performance of a Half-Heusler thermoelectric generator for automotive application. SAE Tech. Pap. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Won, B.C.; Rhi, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yoo, J.H.; Jang, J.C. Thermoelectric power generation system for future hybrid vehicles using hot exhaust gas. J. Electron. Mater. 2011, 40, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkisz, J.; Fuc, P.; Lijewski, P.; Ziolkowski, A.; Galant, M.; Siedlecki, M. Analysis of an increase in the efficiency of a spark ignition engine through the application of an automotive thermoelectric generator. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 4028–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Yanez, P.; Armas, O.; Capetillo, A.; Martinez-Martinez, S. Thermal analysis of a thermoelectric generator for light-duty diesel engines. Appl. Energy 2018, 226, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Yanez, P.; Armas, O.; Kiwan, R.; Stefanopoulou, A.G.; Boehman, A.L. A thermoelectric generator in exhaust systems of spark-ignition and compression-ignition engines. A comparison with an electric turbo-generator. Appl. Energy 2018, 229, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.; Zhou, W.; Yang, G.Y.; Quan, S.H. A hybrid maximum power point tracking method for automobile exhaust thermoelectric generator. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 2676–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.; Liu, G.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Zhou, W.; Huang, L.; Deng, Y.D. Performance investigation of an exhaust thermoelectric generator for military SUV application. Coatings 2018, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraisse, G.; Ramousse, J.; Sgorlon, D.; Goupil, C. Comparison of different modeling approaches for thermoelectric elements. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 65, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.; Wang, C.J.; Wu, F.; Chang, Y.F.; Deng, Y.D. Parameter matching and optimization of an isg mild hybrid powertrain based on an automobile exhaust thermoelectric generator. J. Electron. Mater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Yu, J.L.; Wang, S.Z. Experimental study on low-temperature waste heat thermoelectric generator. J. Power Sources 2009, 188, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Dimension of TEM | 40 mm × 40 mm × 40 mm |
| Maximum operation temperature of TEM | 400 °C |
| Rated operation temperature of TEM | 330 °C |
| Maximum conversion efficiency of TEM | 6.5% |
| Dimension of cooling box | 250 mm × 50 mm × 20 mm |
| Material of cooling box | Aluminum |
| Thickness of cooling box | 1 mm |
| Thickness of heat exchanger | 2 mm |
| Maximum power of pump | 40 W |
| Maximum flow of pump | 5000 L/H |
| Rated power of radiator | 100 W (24V DC) |
| Rated power of hot-air blower | 2000 W |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quan, R.; Li, T.; Yue, Y.; Chang, Y.; Tan, B. Experimental Study on a Thermoelectric Generator for Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Based on a Hexagonal Heat Exchanger. Energies 2020, 13, 3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123137
Quan R, Li T, Yue Y, Chang Y, Tan B. Experimental Study on a Thermoelectric Generator for Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Based on a Hexagonal Heat Exchanger. Energies. 2020; 13(12):3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123137
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuan, Rui, Tao Li, Yousheng Yue, Yufang Chang, and Baohua Tan. 2020. "Experimental Study on a Thermoelectric Generator for Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Based on a Hexagonal Heat Exchanger" Energies 13, no. 12: 3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123137
APA StyleQuan, R., Li, T., Yue, Y., Chang, Y., & Tan, B. (2020). Experimental Study on a Thermoelectric Generator for Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Based on a Hexagonal Heat Exchanger. Energies, 13(12), 3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123137