Optimum Electrical and Dielectric Performance of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Doped Disposed Transformer Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
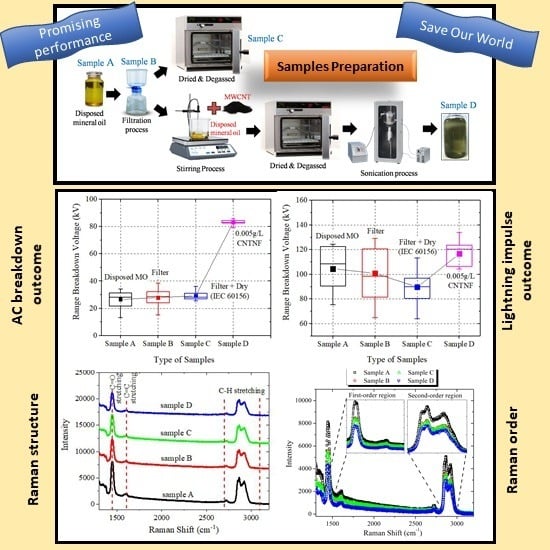
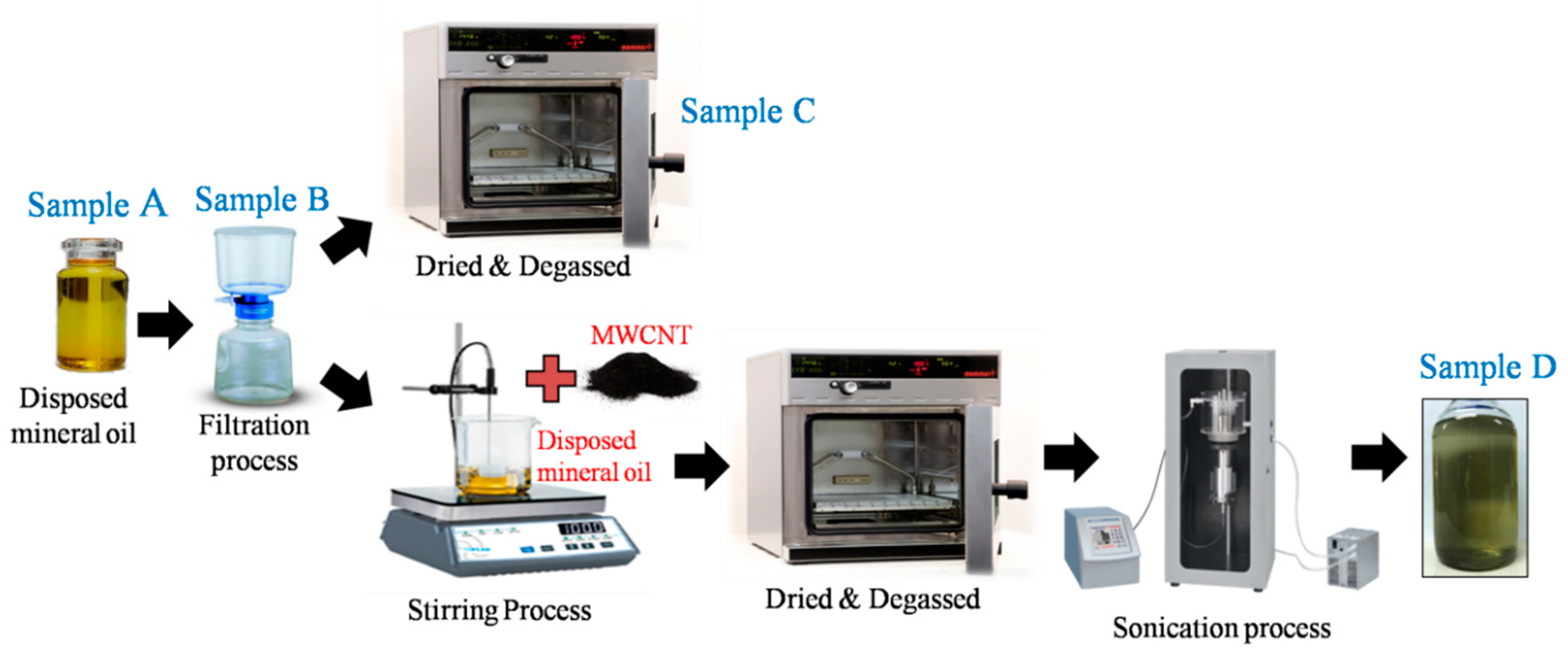
2.1. Sample Preparation
- Date of transformer oil: 15th October 2009
- Manufacturer: Shell
- Brand Name: DIALA S3 ZX-I
- Viscosity, kinematic (40 °C): 8.0
- Viscosity, kinematic (100 °C): 720
- Density (15 °C): 0.881
- Flash Point, open cup: 139 °C
- Pour Point: −60 °C
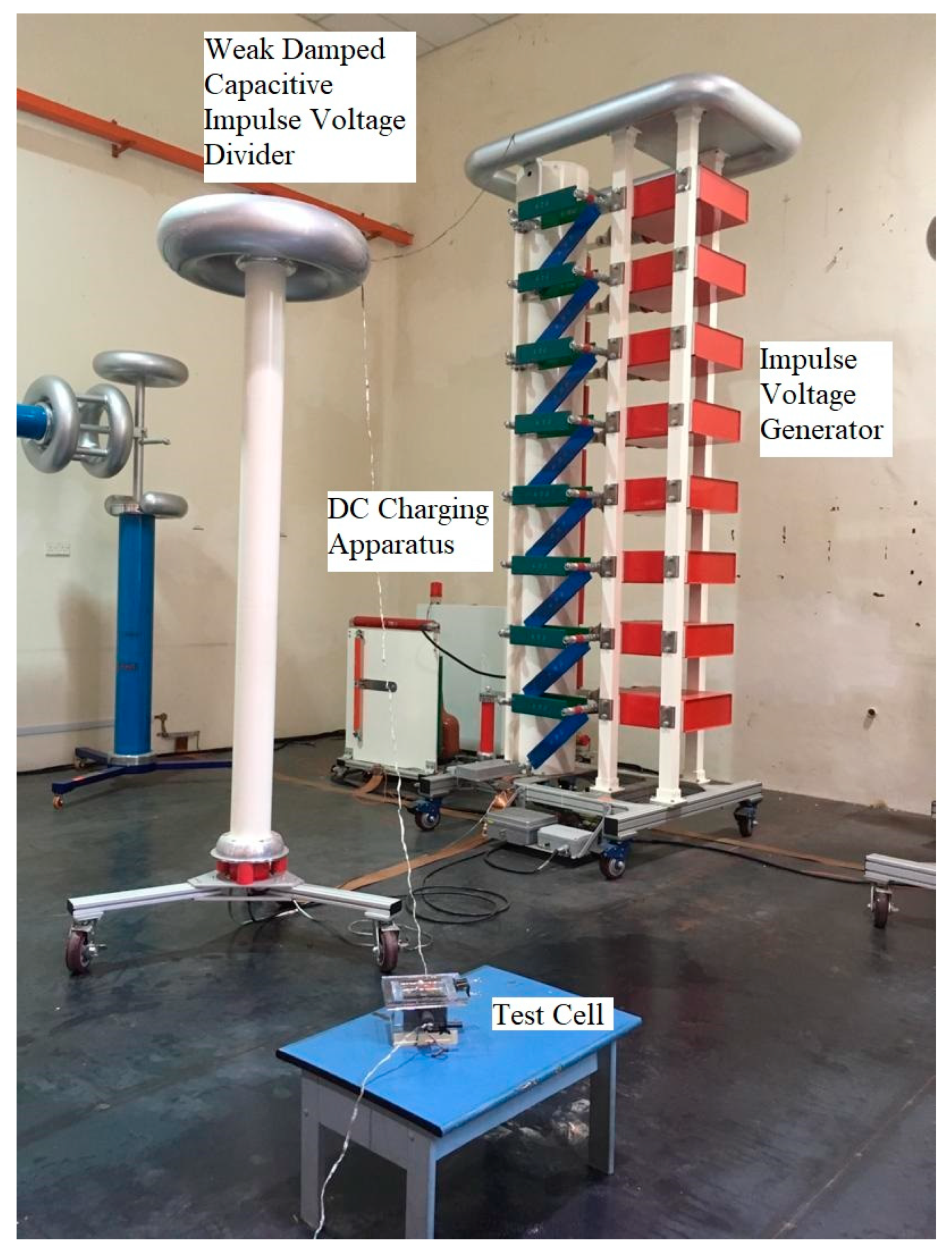
2.2. Alternating Current Breakdown Voltage Measurement
2.3. Lightning Impulse Test Setup
2.4. Dielectric Measurements
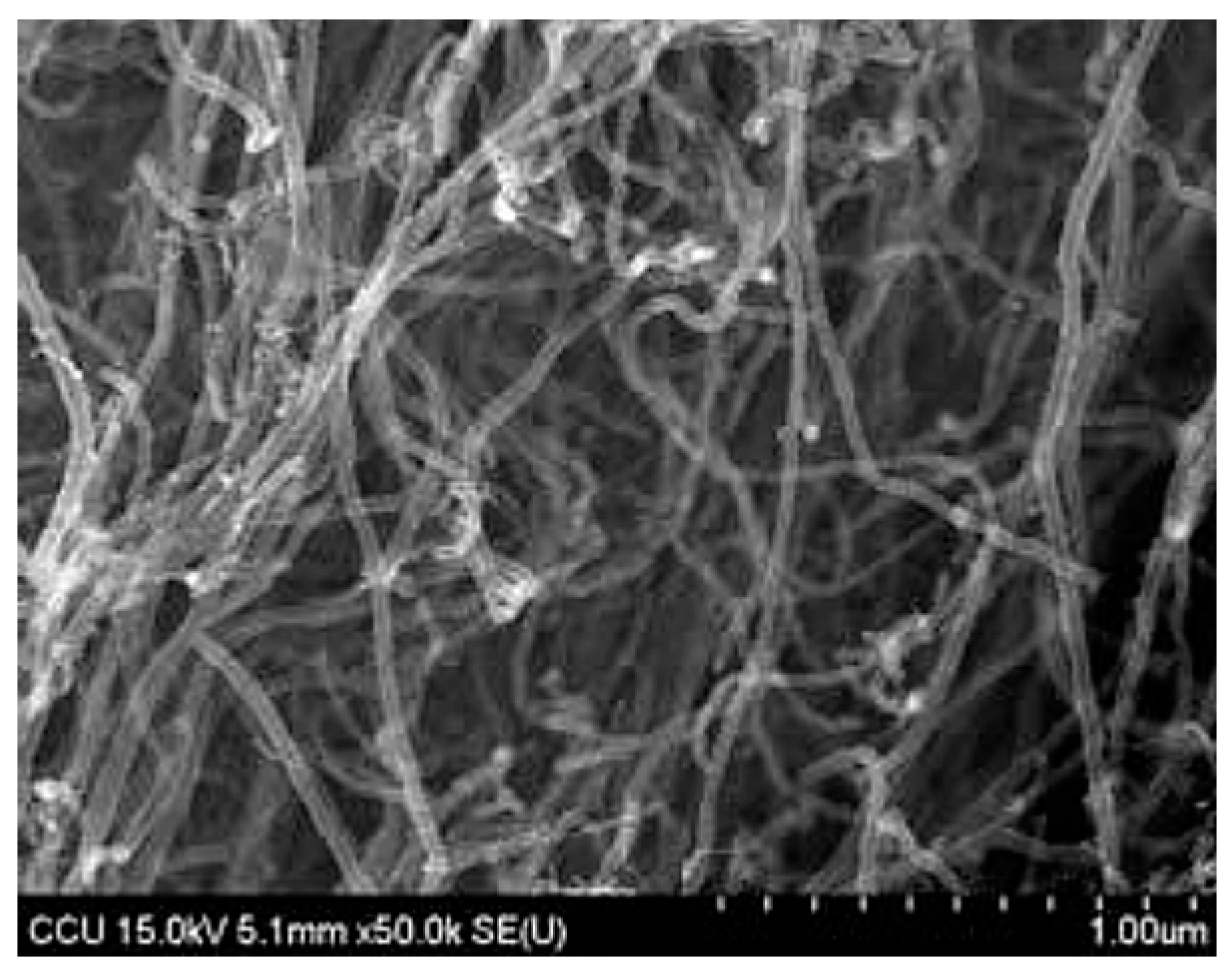
2.5. Raman Spectroscopy Analysis
3. Experimental Setup
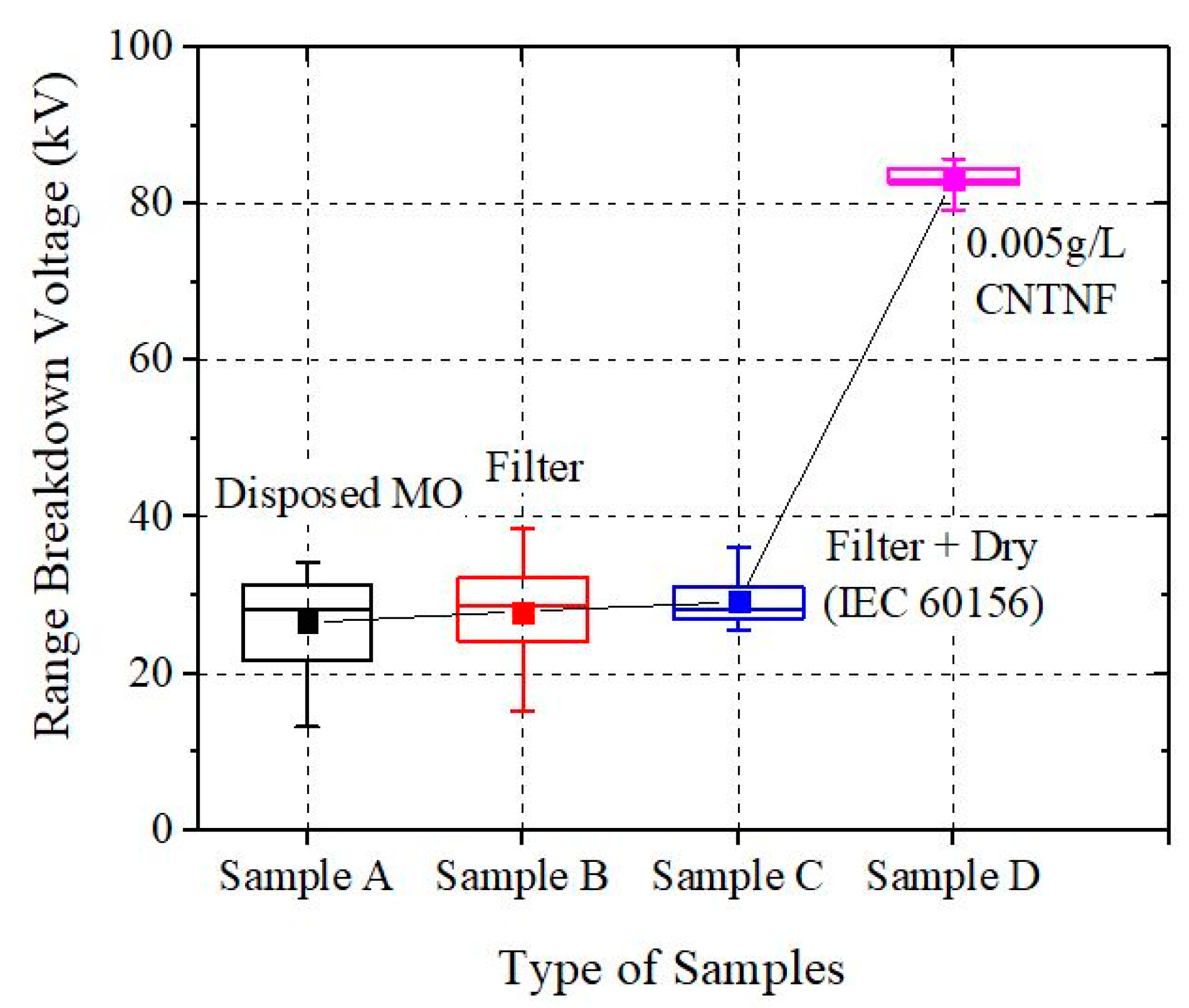
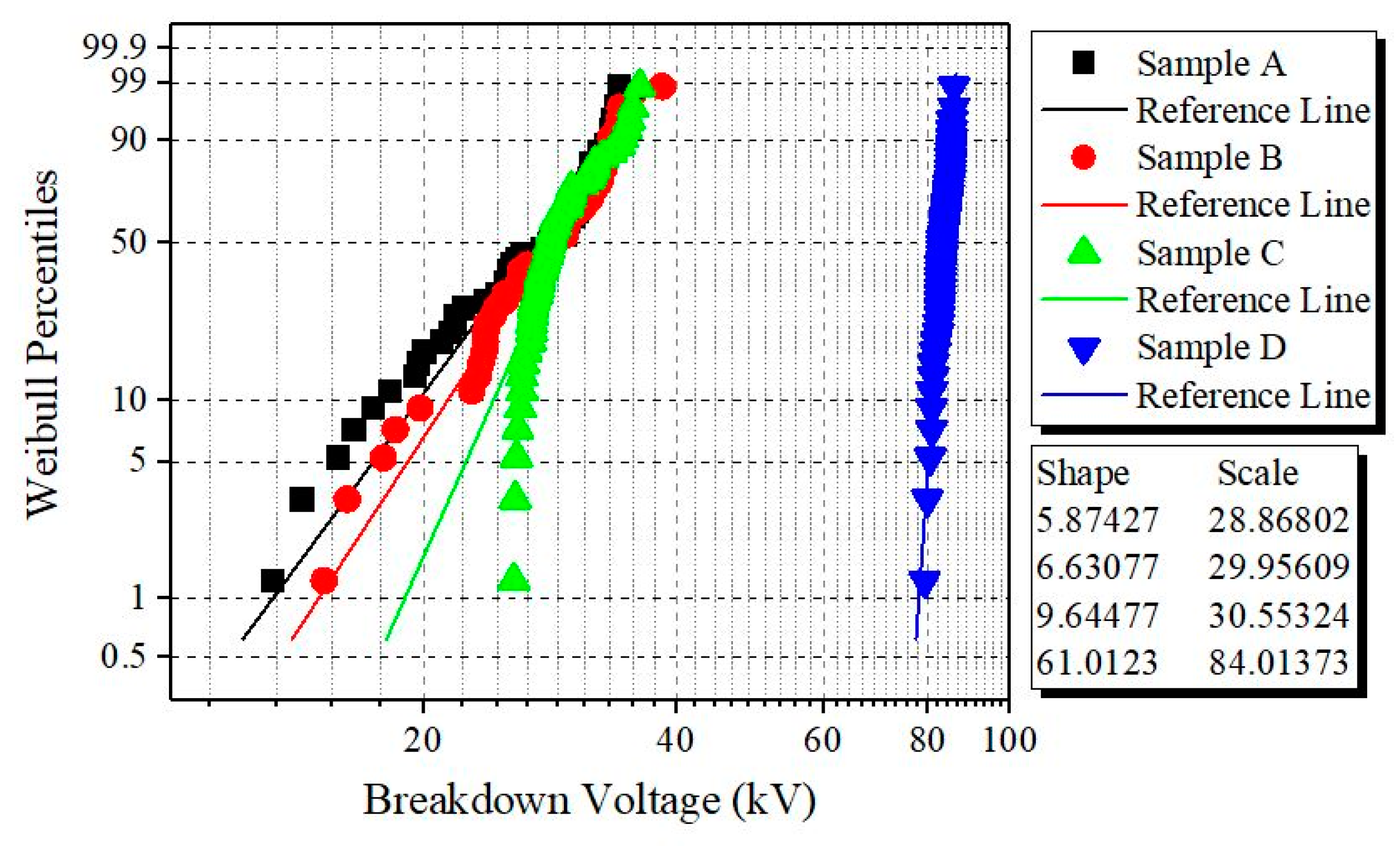
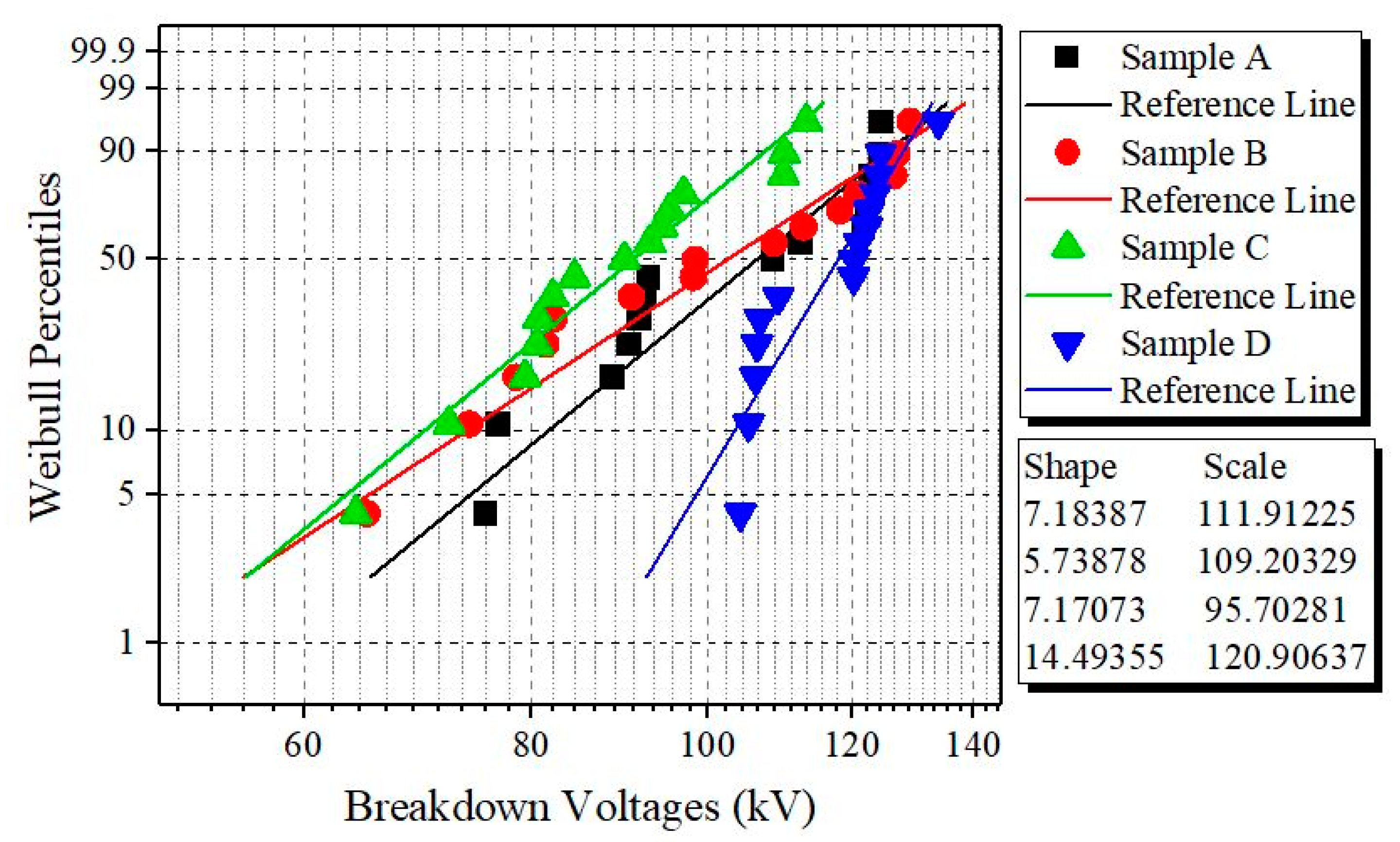
3.1. Weibull Analysis of AC BDV Measurements
3.2. Weibull Analysis of LI Measurements
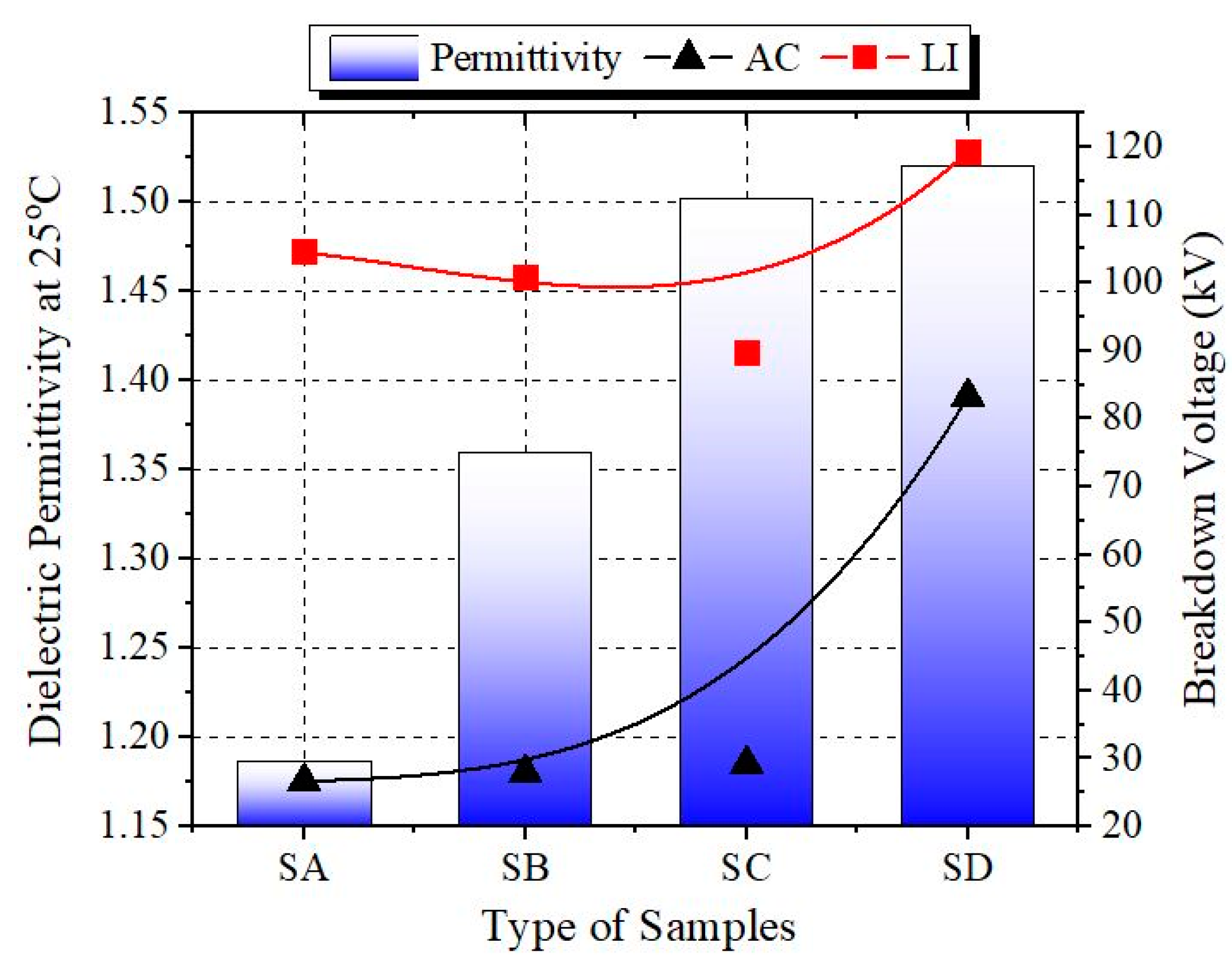
3.3. Dielectric Permittivity
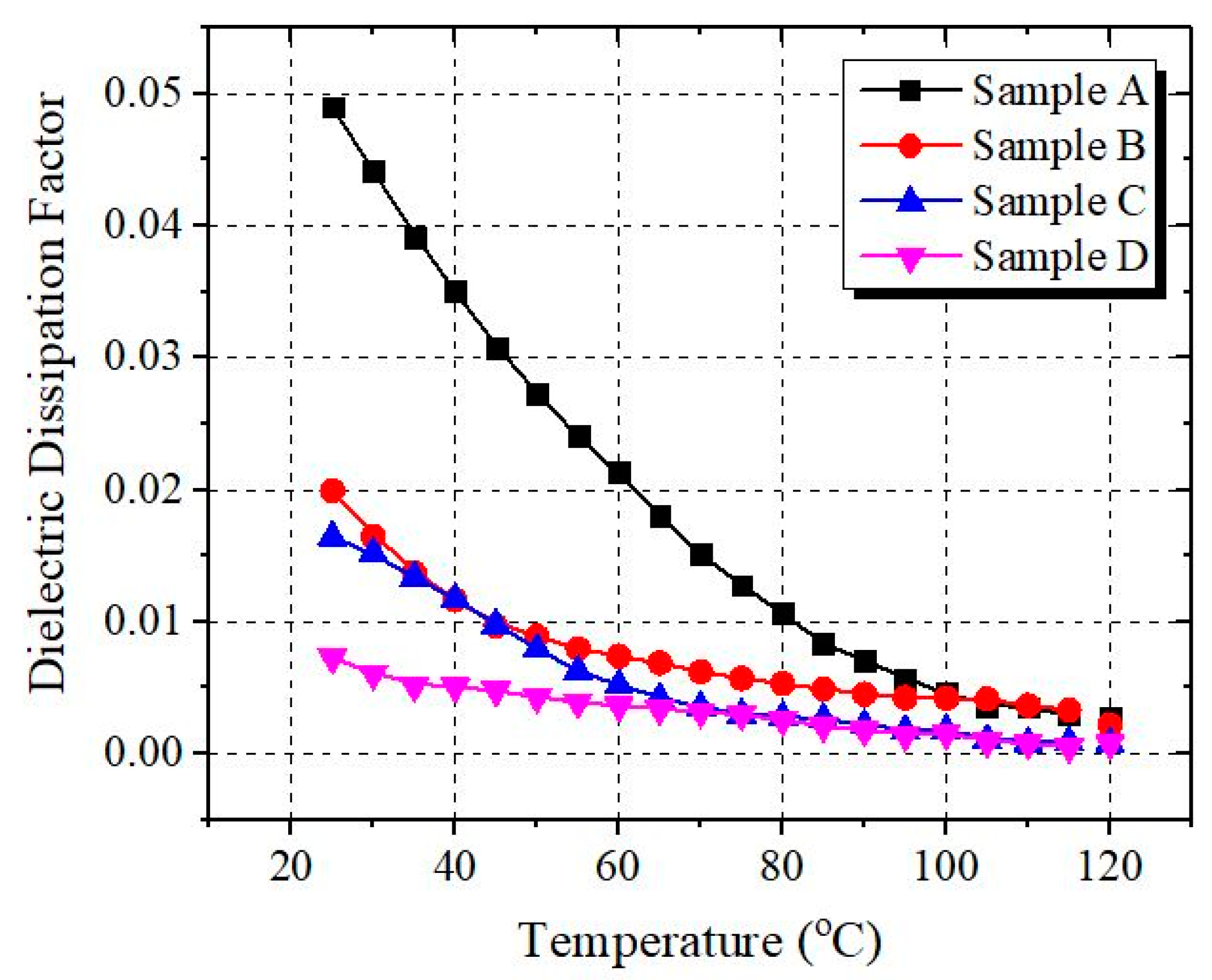
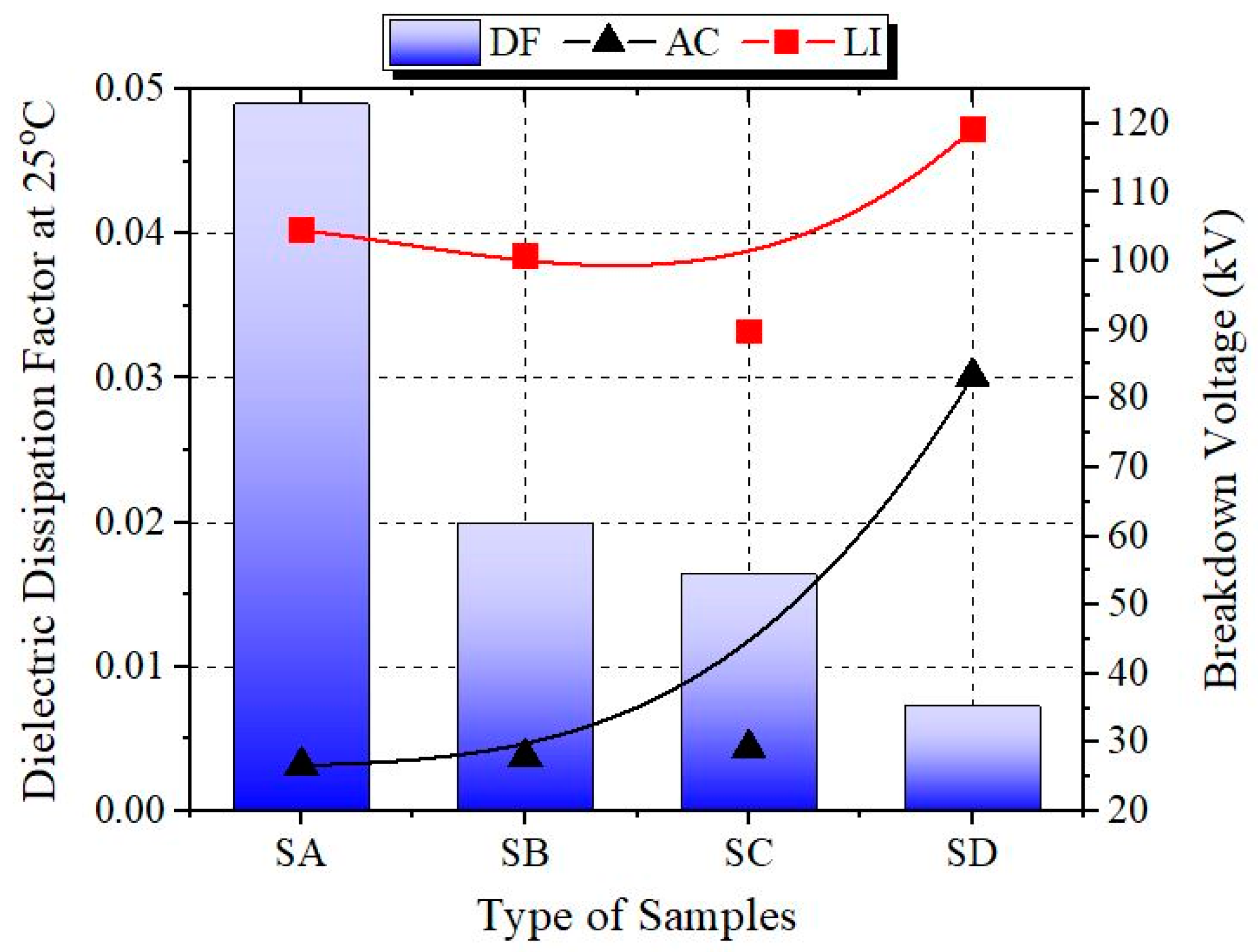
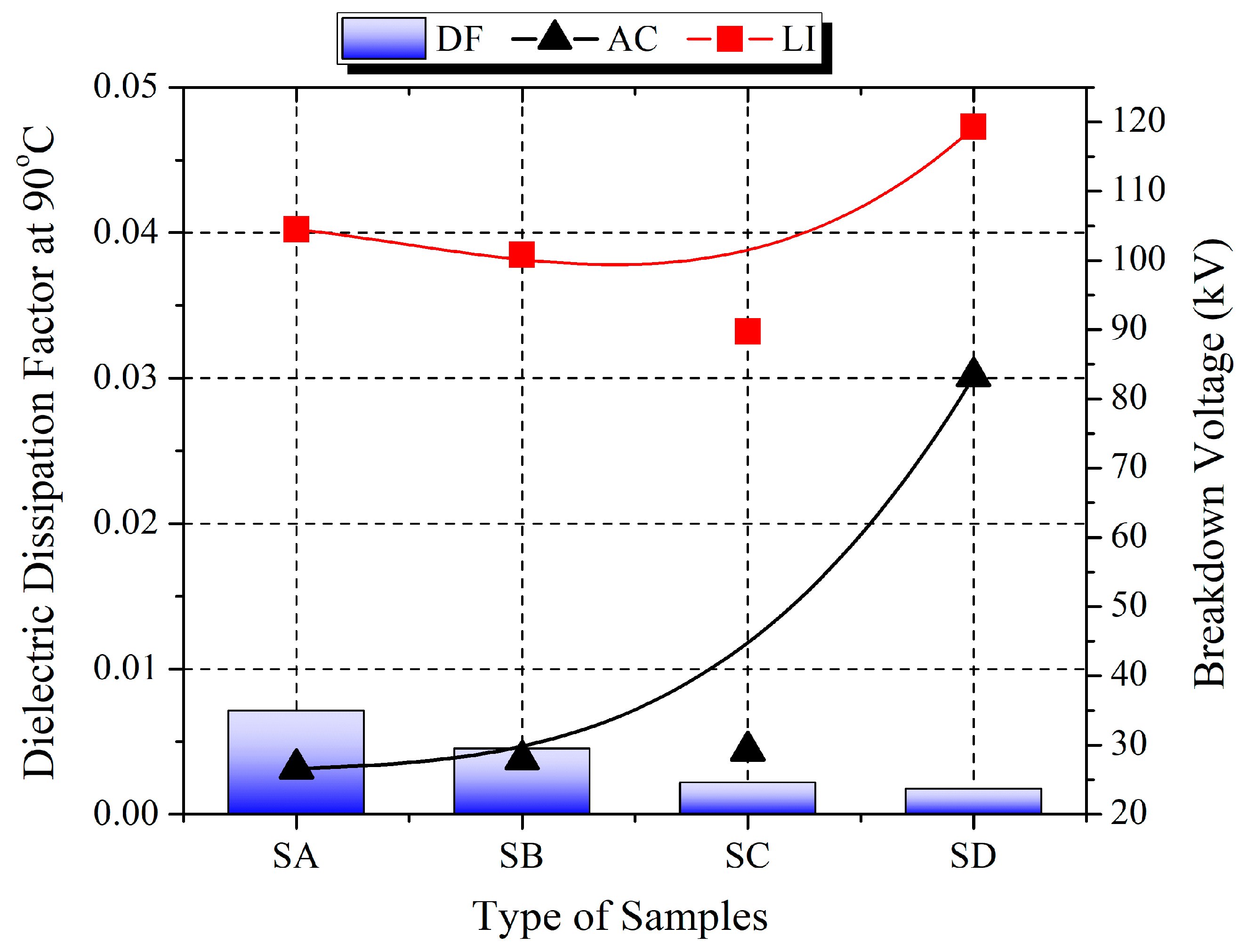
3.4. Dissipation Factor
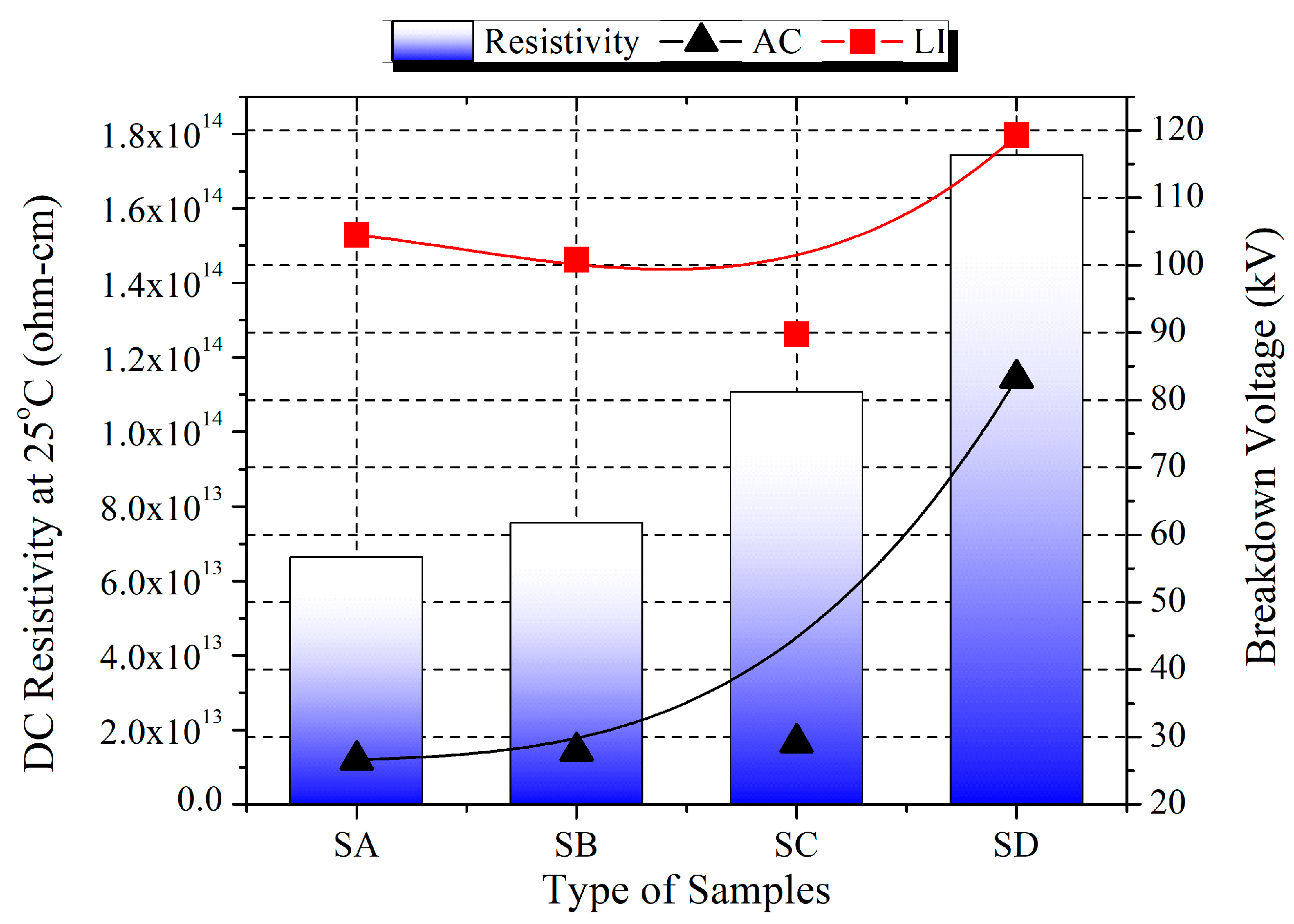
3.5. DC Resistivity
3.6. Raman Structural Information
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herlenius, N.; Rasco, J.; Casserly, E. New IEC 60296 (ed.4) From a Transformer Oil Manufacturer’s Perspective. In Proceedings of the Transformer Life Management Conference, Hannover, Germany, 17–18 September 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Du, B.; Wang, F.; Yao, W.; Yao, S. The effect of nanoparticle surfactant polarization on trapping depth of vegetable insulating oil-based nanofluids. Phys. Lett. Sect. A Gen. At. Solid State Phys. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, A.; Shaaban, S.A.; Allam, M. Enhancing dielectric constant of transformer oils using multi-nanoparticles technique under thermal conditions. In Proceedings of the 2016 18th International Middle-East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON), Cairo, Egypt, 27–29 December 2016; pp. 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, C.O.; Diego, I.F.; Fernández, F.O.; Estébanez, C.R.; Remesal, S.P. Dielectric properties enhancement of vegetable transformer oil with TiO2,CuO and ZnO nanoparticles. Renew. Energy Power Qual. J. 2018, 1, 623–627. [Google Scholar]
- Suhaimi, N.S.; Ishak, M.T.; Din, M.F.; Ariffin, M.M.; Razali, S.; Amin, N.A.; Hashim, F.R. Breakdown strength of transformer oil filled with carbon nanotubes under various gap distances. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2017, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potivejkul, S.; Jariyanurat, K.; Pattanadech, N.; Wattakapaiboon, W. Electrical characteristics of natural ester based nanofluid. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Pattaya, Thailand, 8–10 March 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Li, C.; Ge, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yi, K. Effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticle concentrations on dielectric property of transformer oil. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application (ICHVE), Chengdu, China, 19–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Electrotechnical Commission. IEC 60156 Insulating Liquids—Determination of the Breakdown Voltage at Power Frequency—Test Method; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, I.H.; Ahmad, M.H.; Arief, Y.Z.; Awang, N.A.; Ahmad, N.A. Characteristics of mineral oil-based nanofluids for power transformer application. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, F.; Huang, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Significantly Improved Electrical Breakdown Strength of Natural Ester Liquid Dielectrics by Doping Ultraviolet Absorbing Molecules. IEEE Access 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, W.; Peng, N.; Chen, W. The impact of TiO2 nanoparticle concentration levels on impulse breakdown performance of mineral oil-based nanofluids. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katim, N.I.A.; Ishak, M.T.; Amin, N.A.M.; Hamid, M.H.A.; Ahmad, K.A.; Azis, N. Lightning Breakdown Voltage Evaluation of Palm Oil and Coconut Oil as Transformer Oil under Quasi-Uniform Field Conditions. Energies 2018, 11, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Electrotechnical Commission. IEC 60897-Methods for Determination of the Lightning Impulse Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Lv, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, M.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tu, Y. Effect of electron shallow trap on breakdown performance of transformer oil-based nanofluids. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Sima, W.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.; Hua, J. Accumulative effect of repeated lightning impulses on transformer insulation: Mechanism analysis. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 2430–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozga, P.; Hantsz, D. Influence of volume effect on electrical discharge initiation in mineral oil in the setup of insulated electrodes. Electr. Eng. 2017, 99, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, P.; Sima, W.; Shao, Q.; Ye, L.; Li, C. A promising nano-insulating-oil for industrial application: Electrical properties and modification mechanism. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, N.; Jarial, R.K.; Rao, U.M. Characterization of mineral oil based Fe3O4 nanofluid for application in oil filled transformers. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Electrotechnical Commission (Ed.) IEC 60422-Mineral Insulating Oils in Electrical Equipment-Supervision and Maintenance Guidance 4.0; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Somekawa, T.; Kasaoka, M.; Kawachi, F.; Nagano, Y.; Fujita, M.; Izawa, Y. Analysis of dissolved C2H2 in transformer oils using laser Raman spectroscopy. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Chen, W.; Gu, Z.; Zou, J.; Wan, F.; Wang, P.; Pan, C. Analysis of acetic acid dissolved in transformer oil based on laser Raman spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application (ICHVE), Chengdu, China, 19–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmatoła, M.; Chrobak, J.; Grabowski, R.; Iłowska, J.; Woch, J.; Szwach, I.; Semeniuk, I.; Drabik, J.; Wrona, M.; Kozdrach, R.; et al. Spectroscopic Methods in the evaluation of modified vegetable base oils from crambe abyssinica. Molecules 2018, 23, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Property | Unit | MWCNT |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Diameter | nm | 5–15 |
| Inner Diameter | nm | 2–5 |
| Length | µm | 10–30 |
| Purity | % | 95 |
| Specific Surface Area | m2/g | 220–300 |
| Tap Density | g/cm3 | 0.27 |
| True Density | g/cm3 | ~2.1 |
| Electrical Conductivity | s/cm | >100 |
| Making Method | - | CVD |
| Samples | Description of Samples |
|---|---|
| Sample 1 (SA) | Disposed mineral oil (base oil) |
| Sample 2 (SB) | After filtration process |
| Sample 3 (SC) | After filtration, thermal and degassed process |
| Sample 4 (SD) | Mineral oil with 0.005g/L CNT Nanofluid |
| Details | Sample A | Sample B | Sample C | Sample D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average BDV (kV) | 26.63 | 27.90 | 29.17 | 83.24 |
| Increment (%) | 0 | 4.55 | 9.54 | 212.58 |
| SD (kV) | 5.79209 | 5.13499 | 2.92297 | 1.65383 |
| Minimum | 13.20 | 15.20 | 25.60 | 79.20 |
| Median | 28.25 | 28.60 | 28.30 | 83.10 |
| Maximum | 34.20 | 38.50 | 36.20 | 85.80 |
| Q1 | 21.80 | 24.20 | 27.00 | 82.50 |
| IQ | 9.6 | 8.1 | 4 | 2.1 |
| Q3 | 31.40 | 32.30 | 31.00 | 84.60 |
| Range | 21 | 23.3 | 10.6 | 6.6 |
| Oil Samples | V1% | Increment (%) | V50% | Increment (%) | V90% | Increment (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 13.19 | 0 | 27.12 | 0 | 33.27 | 0 |
| B | 14.99 | 13.65 | 28.34 | 4.50 | 33.31 | 0.12 |
| C | 18.98 | 43.90 | 29.42 | 8.48 | 33.97 | 2.10 |
| D | 77.91 | 490.67 | 83.52 | 207.96 | 85.17 | 155.99 |
| Details | Sample A | Sample B | Sample C | Sample D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average BDV (kV) | 104.48 | 100.78 | 89.75 | 119.27 |
| Increment (%) | 0 | −3.54 | −14.09 | +14.16 |
| SD (kV) | 18.27079 | 21.38632 | 14.20893 | 11.40815 |
| Minimum | 75.46 | 64.96 | 64.03 | 104.18 |
| Median | 108.54 | 98.40 | 89.98 | 121.06 |
| Maximum | 124.53 | 129.14 | 113.25 | 144.87 |
| Q1 | 90.52 | 81.47 | 80.54 | 106.44 |
| IQ | 32.13 | 39.33 | 16.41 | 17.72 |
| Q3 | 122.65 | 120.80 | 96.95 | 124.16 |
| Range | 49.07 | 64.20 | 49.22 | 40.69 |
| Oil Samples | V1% | Increment (%) | V50% | Increment (%) | V90% | Increment (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 59.12 | 0 | 106.25 | 0 | 125.77 | 0 |
| B | 48.58 | −17.83 | 102.37 | −3.65 | 125.50 | −0.22 |
| C | 50.64 | +1.45 | 91.03 | −14.32 | 107.60 | −14.45 |
| D | 88.42 | +49.56 | 117.91 | +10.97 | 128.15 | +1.89 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suhaimi, N.S.; Md Din, M.F.; Abdul Rahman, A.R.; Abdul Hamid, M.H.; Mohamad Amin, N.A.; Wan Zamri, W.F.H.; Wang, J. Optimum Electrical and Dielectric Performance of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Doped Disposed Transformer Oil. Energies 2020, 13, 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123181
Suhaimi NS, Md Din MF, Abdul Rahman AR, Abdul Hamid MH, Mohamad Amin NA, Wan Zamri WFH, Wang J. Optimum Electrical and Dielectric Performance of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Doped Disposed Transformer Oil. Energies. 2020; 13(12):3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123181
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuhaimi, Nur Sabrina, Muhamad Faiz Md Din, Abdul Rashid Abdul Rahman, Mardhiah Hayati Abdul Hamid, Nur Aqilah Mohamad Amin, Wan Fathul Hakim Wan Zamri, and Jianli Wang. 2020. "Optimum Electrical and Dielectric Performance of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Doped Disposed Transformer Oil" Energies 13, no. 12: 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123181
APA StyleSuhaimi, N. S., Md Din, M. F., Abdul Rahman, A. R., Abdul Hamid, M. H., Mohamad Amin, N. A., Wan Zamri, W. F. H., & Wang, J. (2020). Optimum Electrical and Dielectric Performance of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Doped Disposed Transformer Oil. Energies, 13(12), 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123181