Effects of Injector Spray Angle on Performance of an Opposed-Piston Free-Piston Engine
Abstract
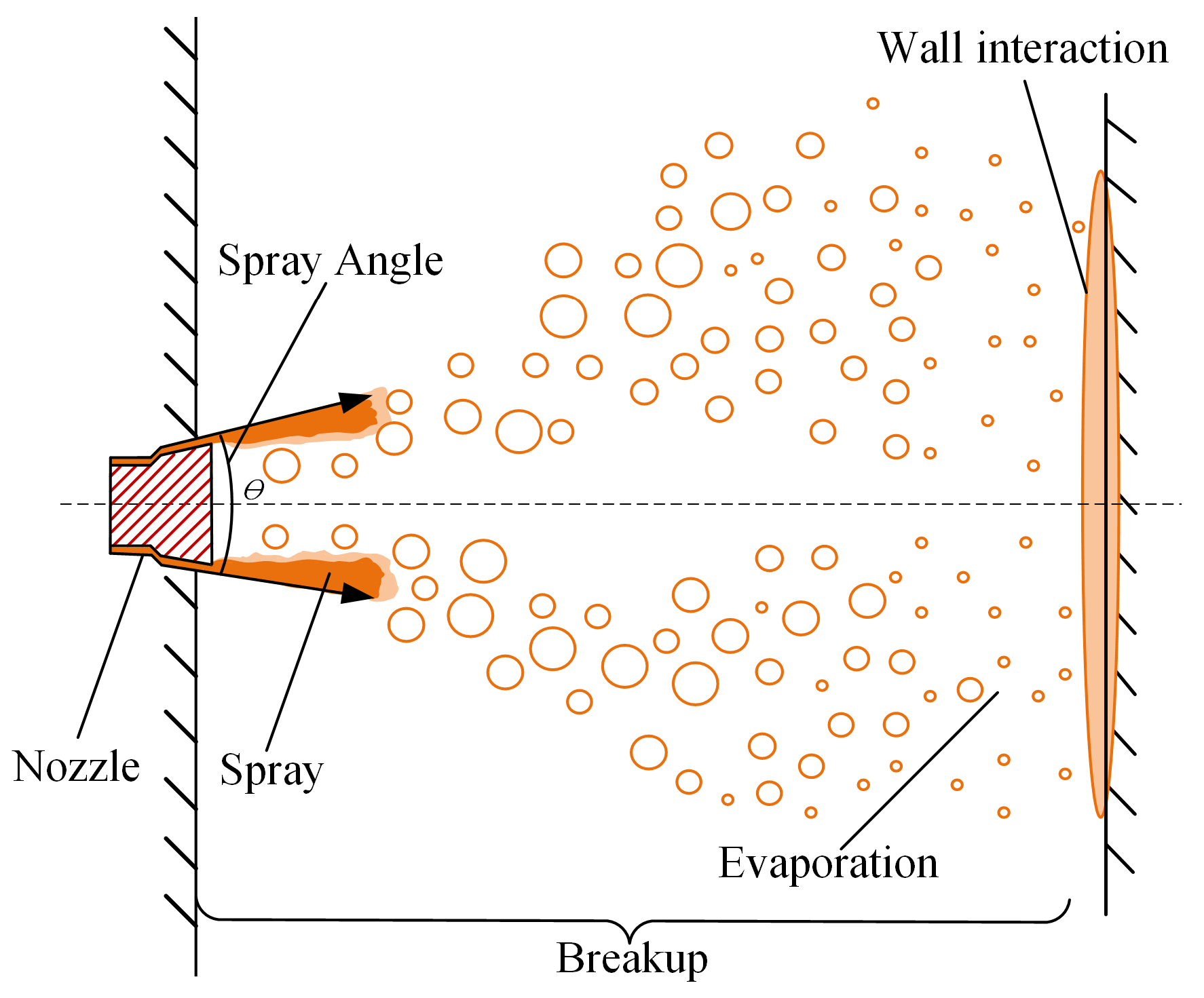
:1. Introduction
2. System Description
2.1. Working Principle of the Engine
2.2. Central Combustor of the Engine
3. CFD Model
3.1. Mesh Model of the Engine
3.2. Calculation Conditions of the Engine
3.3. Validation of Spray Models
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Effects of Spray Angle on Spray Process
4.2. Effects of Spray Angle on Combustion Process
4.3. Effects of Spray Angle on Combustion Characteristics
4.4. Effects of Spray Angle on Emissions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The spray angle had a slight influence on the fuel evaporation rate;
- (2)
- When the spray angle increased, the fuel concentration near the spark plug decreased, and that in the upper part of the cylinder became higher;
- (3)
- The heat release of smaller spray angle was faster in the early stage of the combustion process;
- (4)
- The peak in-cylinder pressure kept minor fluctuations as the spray angle was less than 45°, and it decreased when the spray angle reached 50°;
- (5)
- As the spray angle reached 40°, the combustion efficiency and indicated thermal efficiency achieve the highest value of 97.5% and 39.7% compared with other spray angles (30°, 35°, 45°, 50°);
- (6)
- From an emissions perspective, CO emissions decreased first and then increased with increasing spray angle. When the spray angle was 40°, the CO emissions achieved the lowest value. In order to obtain a better performance and keep lower CO emissions, the optimal spray angle should be approximately 40°.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.H.; Reitz, R.D. CFD simulations of diesel spray tip penetration with multiple injections and with engine compression ratios up to 100:1. Fuel 2013, 111, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculae, A.L.; Miron, L.; Chiriac, R. On the possibility to simulate the operation of a SI engine using alternative gaseous fuels. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, J.; Huang, R. Study on combustion characteristics and ignition limits extending of micro free-piston engines. Energy 2019, 179, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Han, C.; Xu, J. Numerical evaluation of pilot-ignition technology used for a hydrogen fuelled free piston engine generator. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 28599–28611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofianopoulos, A.; Zhou, Y.; Lawler, B.; Mamalis, S. Gas exchange processes of a small HCCI free piston engine—A computational study. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 127, 1582–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Guo, C.; Yuan, C.; Guo, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Roskilly, A.P.; Jia, B. Research on combustion process of a free piston diesel linear generator. Appl. Energy 2016, 161, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Wang, Y.; Xi, B.; Li, Z.; Zhen, X.; Fu, C.; Hu, Y. Study on HCCI combustion improvement by using dual assisted compression ignition (DACI) on a hydraulic free piston engine fueled with methanol fuel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 167, 114782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duronio, F.; De Vita, A.; Montanaro, A.; Villante, C. Gasoline direct injection engines—A review of latest technologies and trends. Part 2. Fuel 2020, 265, 116947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, V.R.K.; Rao, S.S. Effect of Fuel Injection Pressure and Spray Cone Angle in DI Diesel Engine Using CONVERGETM CFD Code. Procedia Eng. 2015, 127, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, Y.; Han, C.; He, Y. An investigation of mixture formation characteristics of a free-piston gasoline engine with direct-injection. Energy 2019, 173, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Song, Y.; Feng, H.; Zuo, Z.; Jia, B.; Zhang, Z.; Roskilly, A. Effect of fuel injection characteristics on the performance of a free-piston diesel engine linear generator: CFD simulation and experimental results. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 160, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Guo, X.; Huang, R.; Li, J.; Pan, M.; Chen, Y.; Pan, X. Assessment of n-pentanol additive and EGR rates effects on spray characteristics, energy distribution and engine performance. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 202, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Verma, T.N. Effect of fuel injection pressure on the characteristics of CI engine fuelled with biodiesel from Roselle oil. Fuel 2020, 265, 117005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Lee, C.-F.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bo, Y.; Liu, F. Effect of injection pressure on the impinging spray and ignition characteristics of the heavy-duty diesel engine under low-temperature conditions. Appl. Energy 2020, 262, 114552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Su, T.; Cong, X.; Wang, D.; Tang, C. Effects of second injection timing on combustion characteristics of the spark ignition direct injection gasoline engines with dimethyl ether enrichment in the intake port. Energy 2019, 180, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Singh, R.; Lavoie, G.; Woolridge, M.S.; Boehman, A.L. Multiple injection for improving knock, gaseous and particulate matter emissions in direct injection SI engines. Appl. Energy 2020, 262, 114578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, B.; Zeng, D. Effects of injector spray angle on combustion and emissions characteristics of a natural gas (NG)-diesel dual fuel engine based on CFD coupled with reduced chemical kinetic model. Appl. Energy 2019, 234, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmelev, V. An internal combustion alternator with both free piston and cylinder. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Mikalsen, R.; Smallbone, A.; Roskilly, A.P. A study and comparison of frictional losses in free-piston engine and crankshaft engines. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 140, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Hua, R. Two-Stroke Thermodynamic Cycle Optimization of a Single-Cylinder Free-Piston Engine Generator. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciampolini, M.; Bigalli, S.; Balduzzi, F.; Bianchini, A.; Romani, L.; Ferrara, G. CFD Analysis of the Fuel–Air Mixture Formation Process in Passive Prechambers for Use in a High-Pressure Direct Injection (HPDI) Two-Stroke Engine. Energies 2020, 13, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaidia, R.; Jemni, M.A.; Abid, M.S. Simulation and Empirical Studies of the Commercial SI Engine Performance and Its Emission Levels When Running on a CNG and Hydrogen Blend. Energies 2017, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Rourke, P.J.; Amsden, A.A. The Tab Method for Numerical Calculation of Spray Droplet Break-Up; SAE Paper 872089; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1987; Volume 87, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dukowicz, J.K. A particle-fluid numerical model for liquid sprays. J. Comput. Phys. 1980, 35, 229–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naber, J.; Reitz, R.D. Modeling Engine Spray/Wall Impingement. SAE Tech. Pap. Ser. 1988, 88, 118–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, P.J. Statistical properties and numerical implementation of a model for droplet dispersion in a turbulent gas. J. Comput. Phys. 1989, 83, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Hiroyasu, H. Simplified Three-Dimensional Modeling of Mixture Formation and Combustion in a D.I. Diesel Engine. SAE Tech. Pap. Ser. 1989, 1, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, R.I.; Cervantes, T. Direct Injection System for a Two Stroke Engine. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, J. Effect of flash boiling on microscopic and macroscopic spray characteristics in optical GDI engine. Fuel 2017, 190, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Parameters | Content |
|---|---|
| Engine speed | 3500 r/min |
| Cylinder bore | 50 mm |
| Exhaust port position | 22 mm |
| Intake port position | 26 mm |
| Intake port width | 12 mm |
| Exhaust port width | 12 mm |
| Inner dead center (IDC) | 2.3 mm |
| Outer dead center (ODC) | 38 mm |
| Area of intake port | 562 mm2 |
| Area of exhaust port | 562 mm2 |
| Parameters | ECA (°CA) |
|---|---|
| Exhaust port open | 80 |
| Intake port open | 95 |
| Outer dead center | 154 |
| Intake port close | 223 |
| Exhaust port close | 241 |
| Inner dead center | 360 |
| Parameters | Content |
|---|---|
| Intake pressure | 1.3 bar |
| Intake temperature | 320 K |
| Exhaust pressure | 1.1 bar |
| Exhaust temperature | 700 K |
| Cylinder pressure | 5.7 bar |
| Cylinder temperature | 1680 K |
| Exhaust gas recycle (EGR) | 1 |
| Sub-Models | Content |
|---|---|
| Breakup | Taylor analogy breakup (TAB) |
| Evaporation | Dukowicz |
| Wall interaction | Walljet1 |
| Particle interaction | Schmidt |
| Parameters | Content |
|---|---|
| Flame model | Coherent flame/Extended coherent flame model (ECFM) |
| Stretch factor | 1.6 |
| Initial flame surface density | 630 |
| Parameters | Content |
|---|---|
| Injection fuel | Gasoline |
| Injection time | 220 °CA |
| Injection mass | 6.4 mg |
| Injection flow | 12.5 mg/ms |
| Ambient pressure | 1.5 bar |
| Ambient temperature | 293 K |
| Start velocity | 90 m/s |
| Particle sizes | 20 um |
| Spray Angle (°) | CA10 (°CA Before Inner Dead Center) | CA50 (°CA After Inner Dead Center) | CA90 (°CA After Inner Dead Center) | Combustion Efficiency (%) | Indicated Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 6.2 | 2.4 | 23.0 | 95.0 | 38.2 |
| 35 | 6.0 | 2.4 | 20.5 | 97.0 | 39.3 |
| 40 | 6.2 | 3.2 | 19.2 | 97.5 | 39.7 |
| 45 | 5.2 | 4.8 | 19.8 | 96.7 | 39.6 |
| 50 | 2.2 | 9.8 | 30.0 | 93.3 | 37.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, L. Effects of Injector Spray Angle on Performance of an Opposed-Piston Free-Piston Engine. Energies 2020, 13, 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143735
Zhang Q, Xu Z, Liu S, Liu L. Effects of Injector Spray Angle on Performance of an Opposed-Piston Free-Piston Engine. Energies. 2020; 13(14):3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143735
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qinglin, Zhaoping Xu, Shuangshuang Liu, and Liang Liu. 2020. "Effects of Injector Spray Angle on Performance of an Opposed-Piston Free-Piston Engine" Energies 13, no. 14: 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143735
APA StyleZhang, Q., Xu, Z., Liu, S., & Liu, L. (2020). Effects of Injector Spray Angle on Performance of an Opposed-Piston Free-Piston Engine. Energies, 13(14), 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143735





