Effects of Biodiesel Addition on the Physical Properties and Reactivity of the Exhaust Soot Particles from Diesel Engine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Engine and Fuels
2.2. Soot Sampling Method
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.4. Raman Spectroscopy
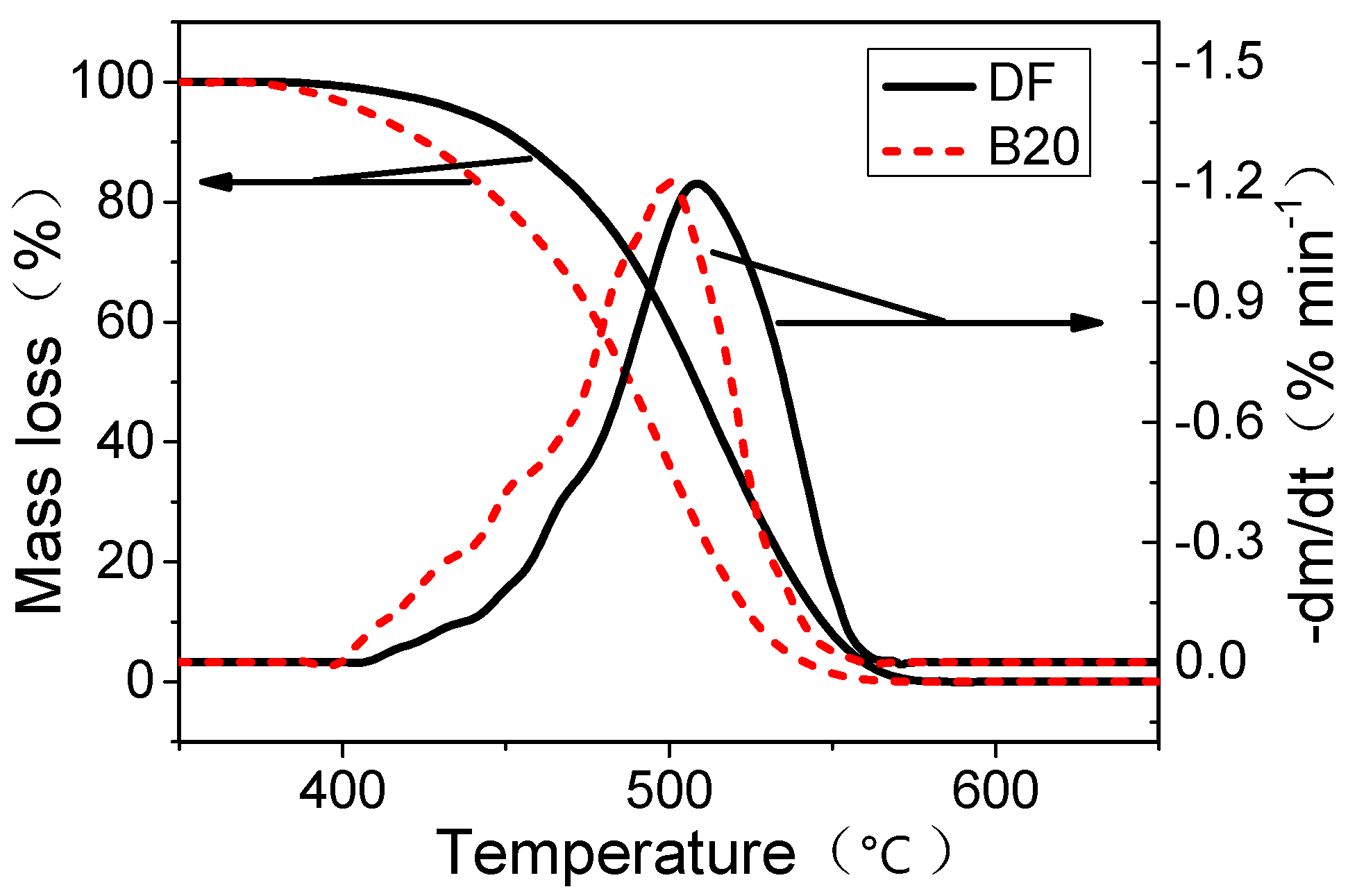
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
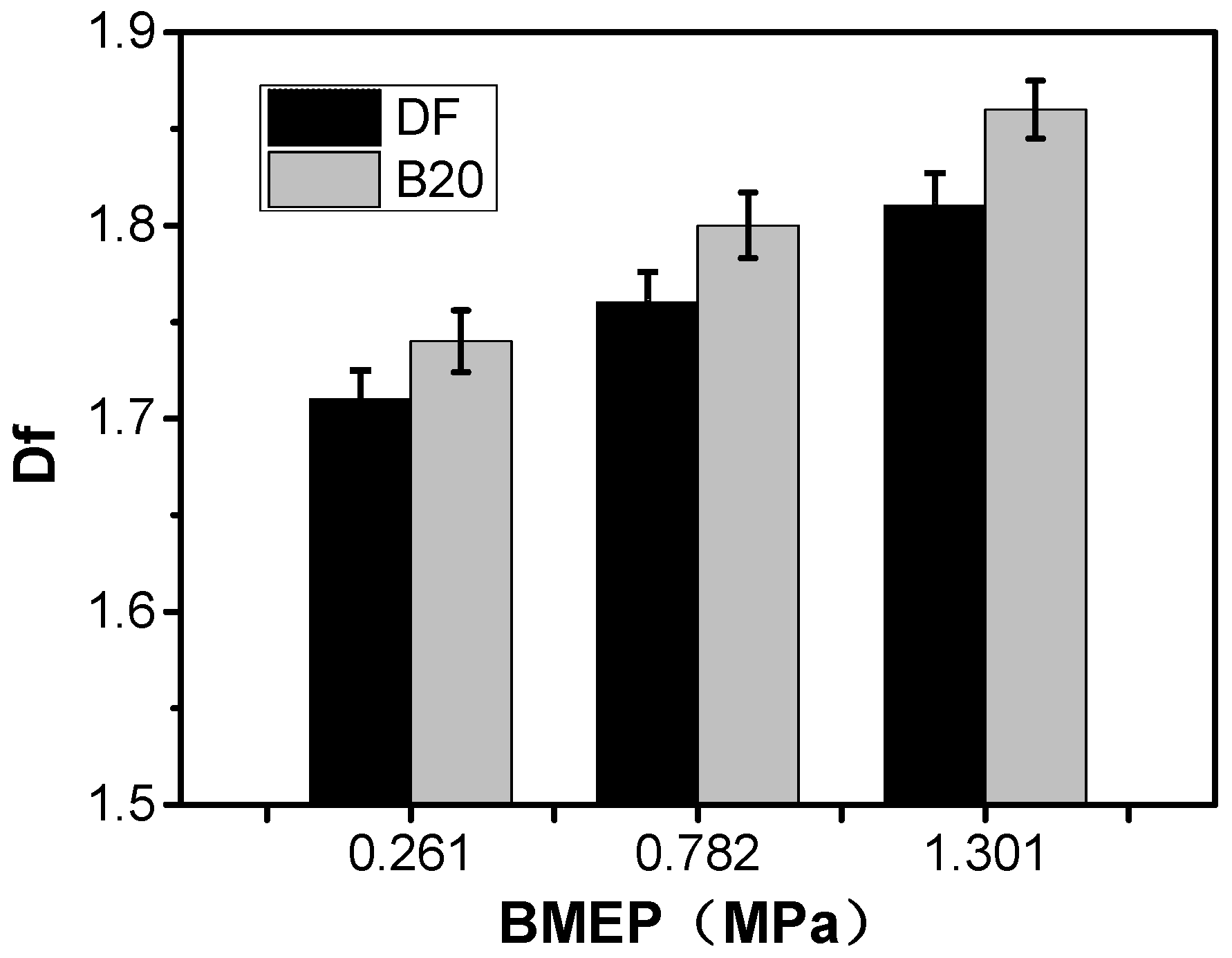
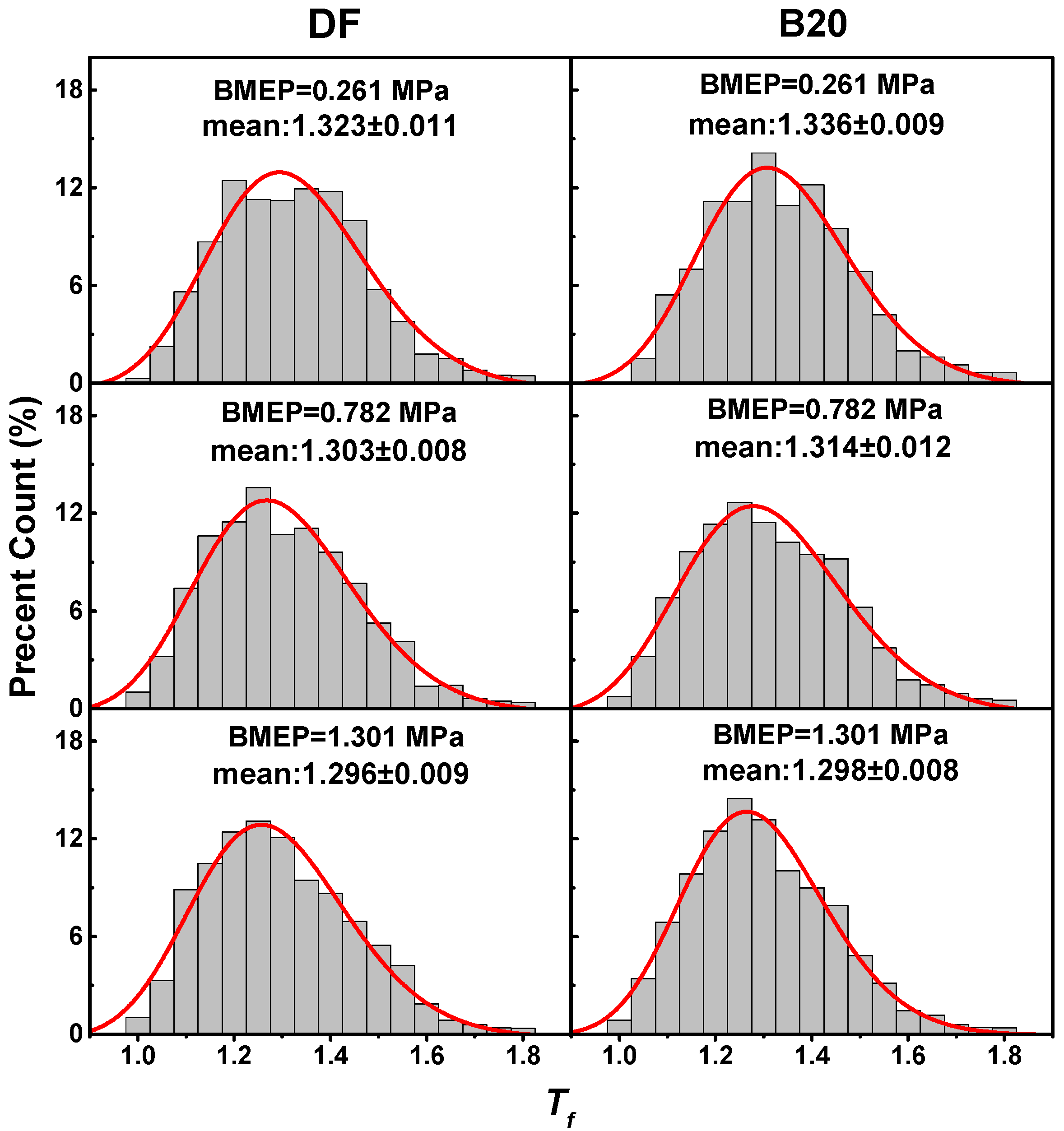
3.1. Fractal Morphology
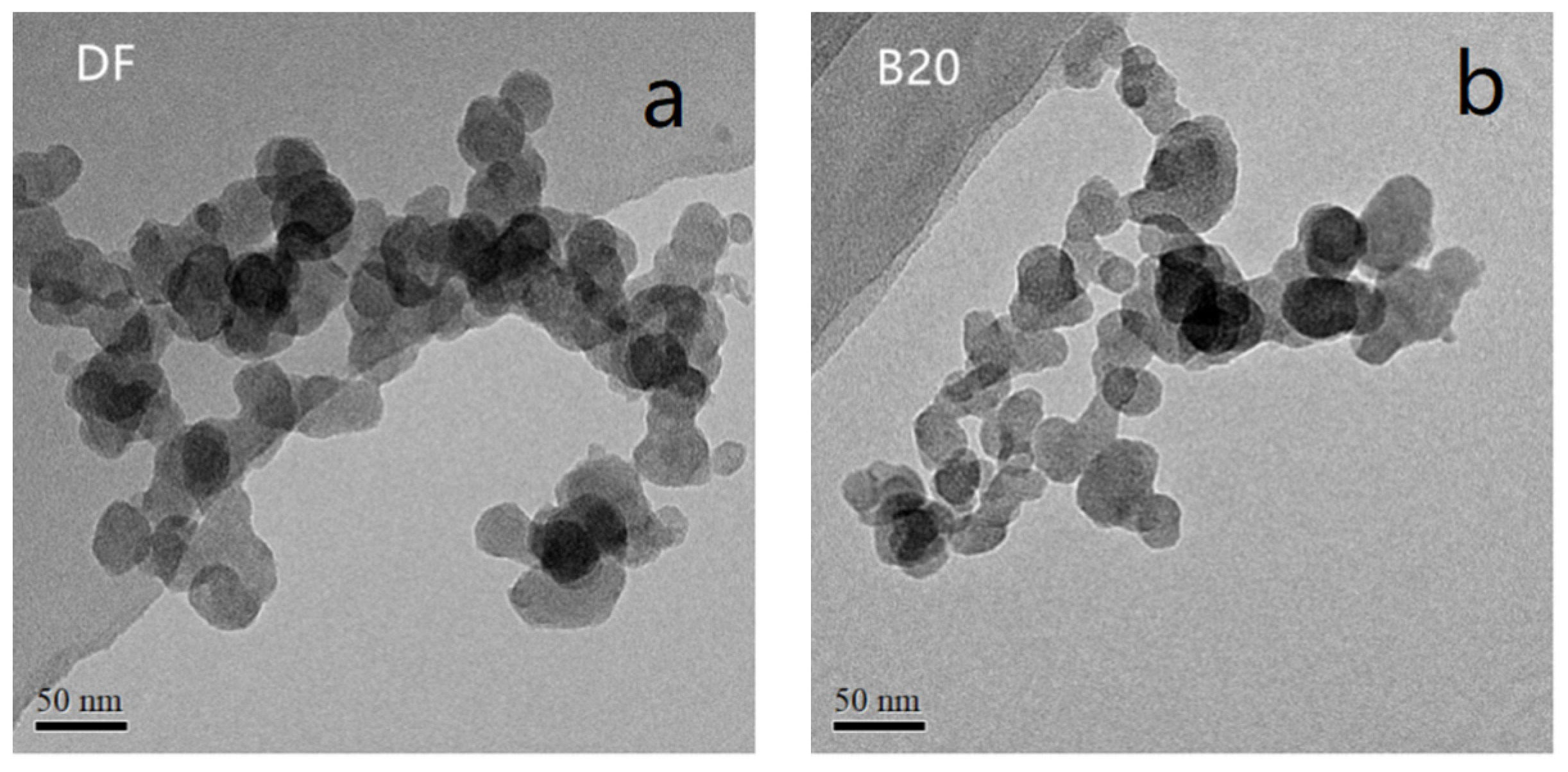
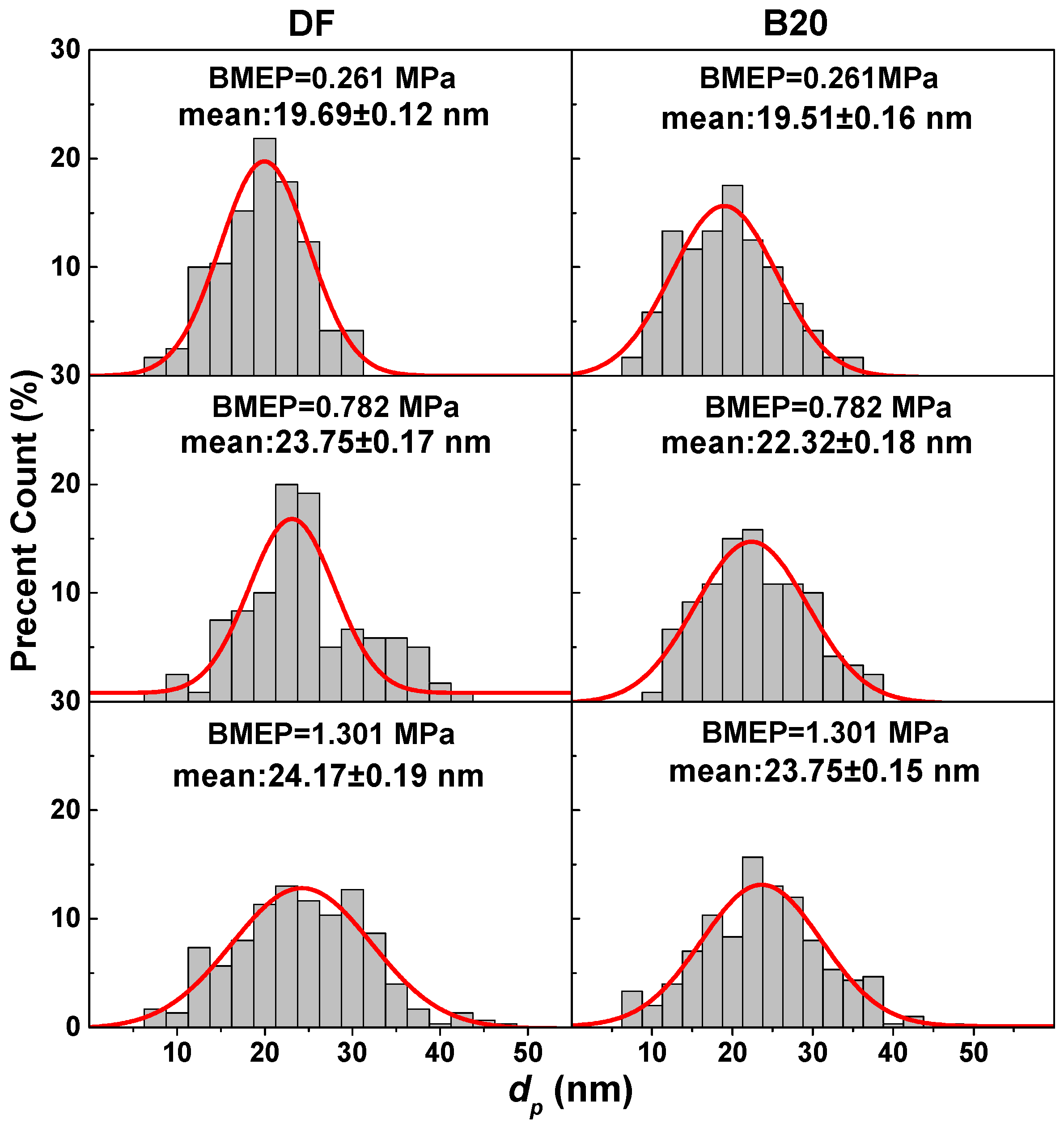
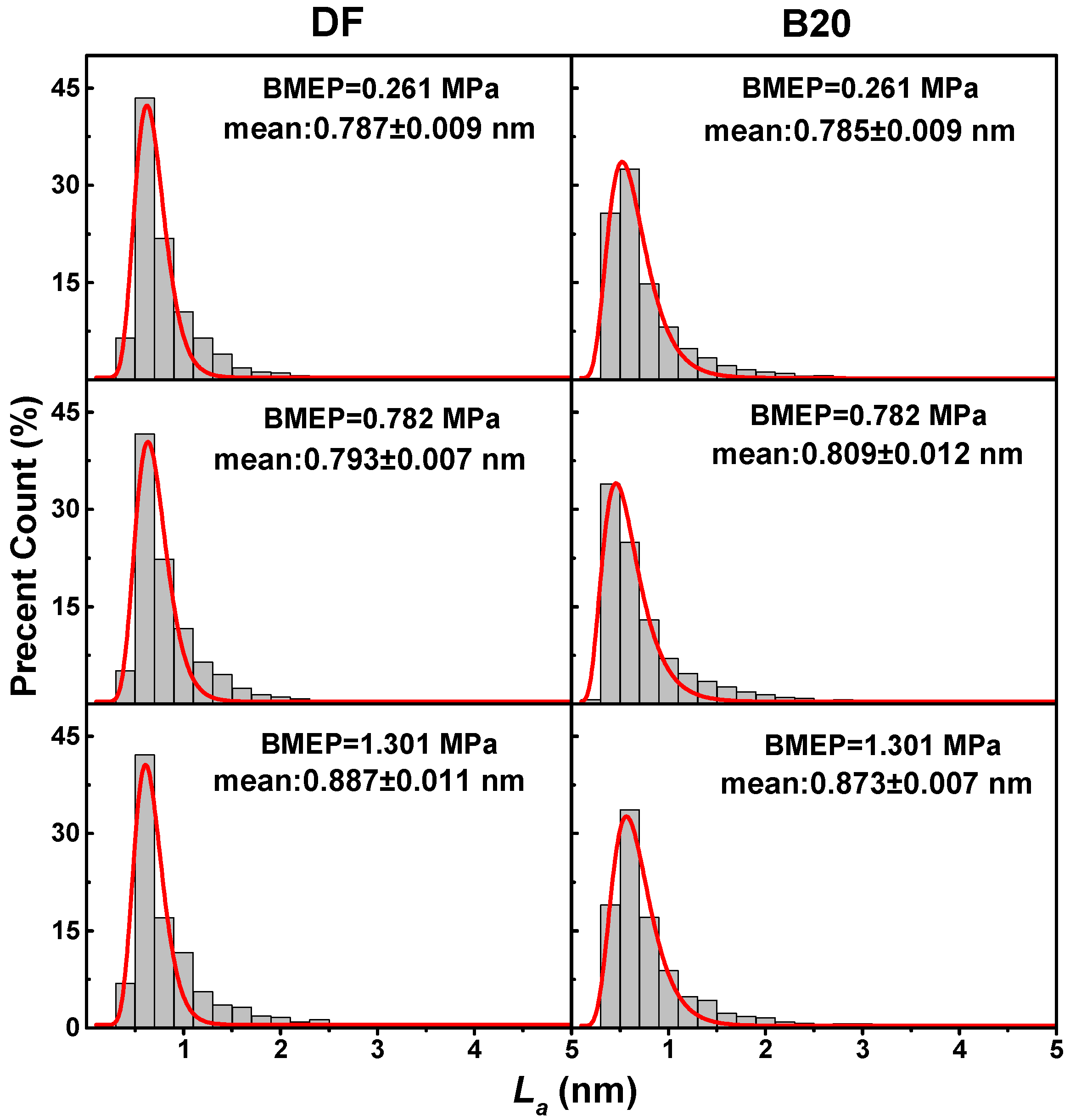
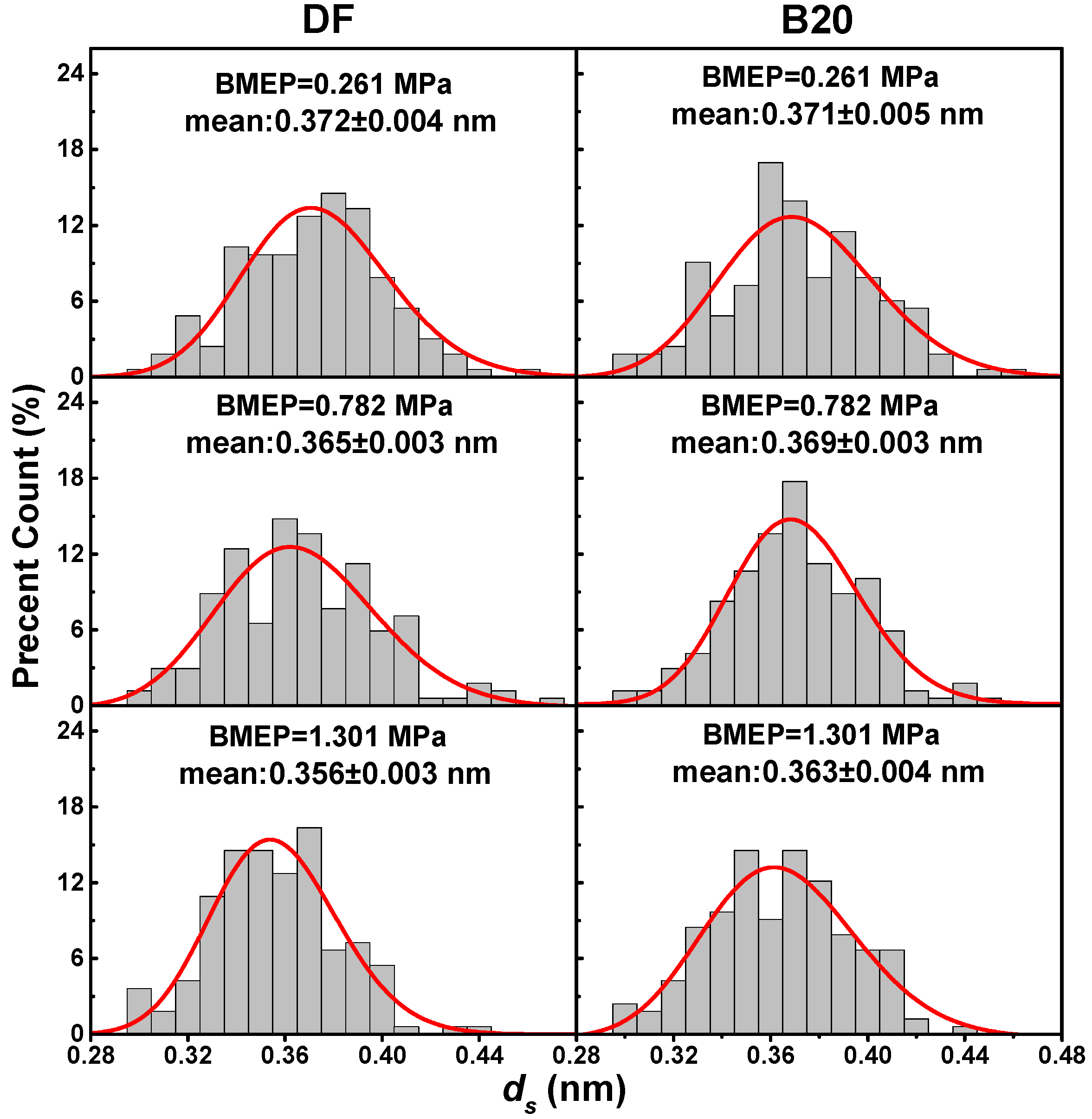
3.2. Primary Particle Size
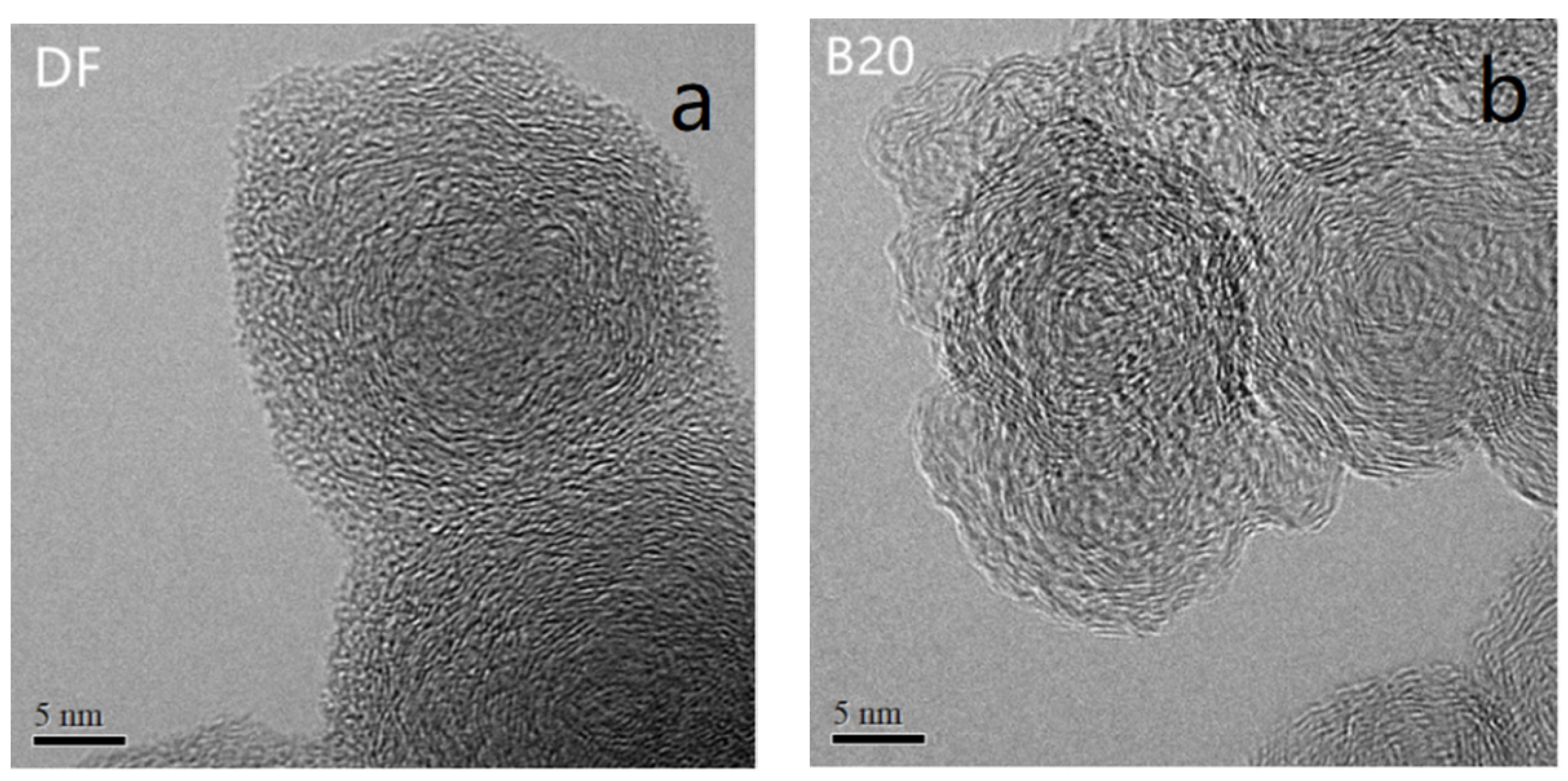
3.3. Nanostructure
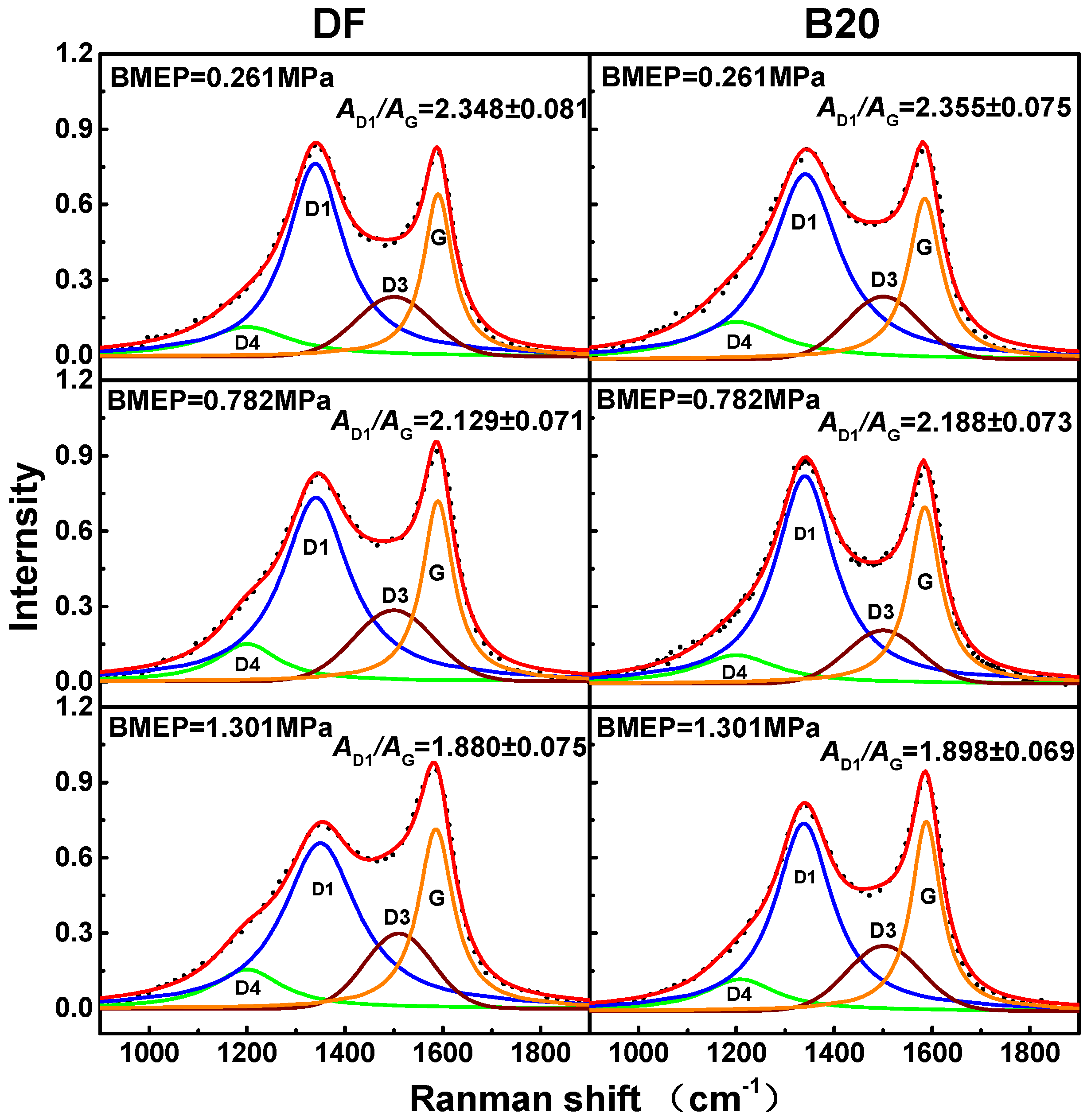
3.4. Soot Graphitization Degree
3.5. Soot Reactivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Directive 2009/28/EC, on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable sources and amending and subsequently repealing directives 2001/77/EC and 2003/30/EC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, 140, 16–62. [Google Scholar]
- Can, Ö.; Öztürk, E.; Solmaz, H.; Aksoy, F.; Çinar, C.; Yücesu, H.S. Combined effects of soybean biodiesel fuel addition and EGR application on the combustion and exhaust emissions in a diesel engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 95, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Lee, C.-F.F. Particulate matter emission characteristics of diesel engines with biodiesel or biodiesel blending: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhare, N.M.; Shelke, P.S.; Lahane, S. Experimental Investigation of Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation and Cottonseed B20 Biodiesel Fuel on Diesel Engine. Procedia Technol. 2016, 25, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassee, F.R.; Heroux, M.E.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Kelly, F.J. Particulate matter beyond mass: Recent health evidence on the role of fractions, chemical constituents and sources of emission. Inhal. Toxicol. 2013, 25, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, A.V.; Pereira, M.P.B.; De Oliveira Pontes, J.V.; De Luna, F.M.T.; Cavalcante, C.L. Performance and emissions characteristics of castor oil biodiesel fuel blends. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 125, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Armas, O.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, J. Effect of biodiesel fuels on diesel engine emissions. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 198–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca, M.; Mondragón, F.; Agudelo, J.R.; Benjumea, P.; Santamaría, A. Variations in the chemical composition and morphology of soot induced by the unsaturation degree of biodiesel and a biodiesel blend. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagu, K.; Venu, H.; Jayaraman, J.; Raju, V.D.; Subramani, L.; Appavu, P. Novel water hyacinth biodiesel as a potential alternative fuel for existing unmodified diesel engine: Performance, combustion and emission characteristics. Energy 2019, 179, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Cheung, C.S.; Ning, Z. Influence of waste cooking oil biodiesel on combustion, unregulated gaseous emissions and particulate emissions of a direct-injection diesel engine. Energy 2017, 127, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, X.J.; Cheung, C.S.; Ning, Z.; Yung, K.F. Effect of Waste Cooking Oil Biodiesel on the Properties of Particulate from a DI Diesel Engine. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Wal, R.L.; Tomasek, A.J. Soot oxidation: Dependence upon initial nanostructure. Combust. Flame 2003, 134, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Oliva, F.; Agudelo, J.R.; Boehman, A.L. Effect of fuel on the soot nanostructure and consequences on loading and regeneration of diesel particulate filters. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Seong, H. Oxidation characteristics of gasoline direct-injection (GDI) engine soot: Catalytic effects of ash and modified kinetic correlation. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 2371–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, P.; Pickering, E.; Jafari, M.; Guo, Y.; Stevanovic, S.; Fernando, J.F.S. Influence of fuel-oxygen content on morphology and nanostructure of soot particles. Combust. Flame 2019, 205, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Miljevic, B.; Saathoff, H.; Naumann, K.H.; Leisner, T. Influence of biodiesel fuel composition on the morphology and microstructure of particles emitted from diesel engines. Carbon 2016, 104, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yehliu, K.; Vander Wal, R.L.; Armas, O.; Boehman, A.L. Impact of fuel formulation on the nanostructure and reactivity of diesel soot. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 3597–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Alam, M.; Boehman, A.L. Impact of Alternative Fuels on Soot Properties and DPF Regeneration. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2007, 179, 1991–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchan-Merchan, W.; Abdihamzehkolaei, A.; Merchan-Breuer, D.A. Formation and evolution of carbon particles in coflow diffusion air flames of vaporized biodiesel, diesel and biodiesel-diesel blends. Fuel 2018, 226, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Park, S. Effect of injection pressure on soot formation/oxidation characteristics using a two-color photometric method in a compression-ignition engine fueled with biodiesel blend (B20). Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 131, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Hua, H. Performance of a common rail diesel engine using biodiesel of waste cooking oil and gasoline blend. J. Energy Inst. 2018, 91, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, A.M.; Farias, T.L.; Carvalho, M.G. A recipe for image characterization of fractal-like aggregates. J. Aerosol Sci. 1999, 30, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, C.; Song, J.; Lv, G.; Dong, S.; Zhao, Z. Evolution of the nanostructure, fractal dimension and size of in-cylinder soot during diesel combustion process. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, H.L. New methods for evaluating kinetic parameters from thermal analysis data. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Lett. 1969, 7, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lee, K.O.; Yozgatligil, A.; Choi, M.Y. Effects of engine operating conditions on morphology, microstructure, and fractal geometry of light-duty diesel engine particulates. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2005, 30, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, M.F.; Teng, Y.; Koylu, U.O. Diesel engine particulate emissions: A comparison of mobility and microscopy size measurements. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neer, A.; Koylu, U. Effect of operating conditions on the size, morphology, and concentration of submicrometer particulates emitted from a diesel engine. Combust. Flame 2006, 146, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, C.K.; Vander Wal, R.L. Physical and chemical characterization of SIDI engine particulates. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.A.; Cadrazco, M.; López, A.F.; Sanchez-Valdepeñas, J.; Agudelo, J.R. Impact of dual-fuel combustion with n-butanol or hydrous ethanol on the oxidation reactivity and nanostructure of diesel particulate matter. Fuel 2015, 161, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kook, S. Structural evolution of soot particles during diesel combustion in a single-cylinder light-duty engine. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 2720–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Hirner, F.S.; Bae, C.; Patel, C.; Gupta, T.; Agarwal, A.K. HRTEM evaluation of primary soot particles originated in a small-bore biofuel compression-ignition engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 159, 113899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Influence of waste cooking oil biodiesel on oxidation reactivity and nanostructure of particulate matter from diesel engine. Fuel 2016, 181, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z. Study on status characteristics and oxidation reactivity of biodiesel particulate matter. Fuel 2018, 218, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, J.R.; Álvarez, A.; Armas, O. Impact of crude vegetable oils on the oxidation reactivity and nanostructure of diesel particulate matter. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 2904–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Armas, O.; Hernández, J.J.; Tsolakis, A. Potential for reducing emissions in a diesel engine by fuelling with conventional biodiesel and Fischer-Tropsch diesel. Fuel 2010, 89, 3106–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanmore, B.R.; Brilhac, J.F.; Gilot, P. The oxidation of soot: A review of experiments, mechanisms and models. Carbon 2001, 39, 2247–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Guan, C.; Huang, Z. Effects of injection timing on exhaust particle size and nanostructure on a diesel engine at different loads. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 76, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfè, M.; Apicella, B.; Barbella, R.; Rouzaud, J.N.; Tregrossi, A.; Ciajolo, A. Structure-property relationship in nanostructures of young and mature soot in premixed flames. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Wal, R.L.; Tomasek, A.J. Soot nanostructure: Dependence upon synthesis conditions. Combust. Flame 2004, 136, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qurashi, K.; Boehman, A.L. Impact of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) on the oxidative reactivity of diesel engine soot. Combust. Flame 2008, 155, 675–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadezky, A.; Muckenhuber, H.; Grothe, H.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U.J.C. Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: Spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon 2005, 43, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, C.K.; Vander Wal, R.L.; Chen, X.; Yezerets, A.; Kamasamudram, K. Reconciliation of carbon oxidation rates and activation energies based on changing nanostructure. Carbon 2016, 98, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, M. Nanostructure and oxidative properties of soot from a compression ignition engine: The effect of a homogeneous combustion catalyst. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlbauer, W.; Zöllner, C.; Lehmann, S.; Lorenz, S.; Brüggemann, D. Correlations between physicochemical properties of emitted diesel particulate matter and its reactivity. Combust. Flame 2016, 167, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Boehman, A.L. Oxidation behavior of soot generated from the combustion of methyl 2-butenoate in a co-flow diffusion flame. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randy, L.; Vander Wal, C.J.M. Initial Investigation of Effects of Fuel Oxygenation on Nanostructure of Soot from a Direct-Injection Diesel Engine. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 2364–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Alam, M.; Boehman, A.; Kim, U. Examination of the oxidation behavior of biodiesel soot. Combust. Flame 2006, 146, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, C.; Song, J.; Lv, G.; Pang, H.; Zhang, W. Aliphatic C-H and oxygenated surface functional groups of diesel in-cylinder soot: Characterizations and impact on soot oxidation behavior. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ess, M.N.; Bladt, H.; Mühlbauer, W.; Seher, S.I.; Zöllner, C.; Lorenz, S. Reactivity and structure of soot generated at varying biofuel content and engine operating parameters. Combust. Flame 2015, 167, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bladt, H.; Schmid, J.; Kireeva, E.D.; Popovicheva, O.B.; Perseantseva, N.M.; Timofeev, M.A. Impact of Fe Content in Laboratory-Produced Soot Aerosol on its Composition, Structure, and Thermo-Chemical Properties. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, P.; Gupta, R. Effects of dual bio-fuel (Jatropha biodiesel and turpentine oil) on a single cylinder naturally aspirated diesel engine without EGR. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 115, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Properties | |
|---|---|
| Bore × Stroke (mm × mm) | 102 × 118 |
| Displacement volume (L) | 0.964 (single cylinder) |
| Compression ratio | 17:1 |
| Intake system | Turbocharged, intercooled, without exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) |
| Valves per cylinder | 4 |
| Rated power (kW)/speed (rpm) | 100/2800 |
| Maximum torque (Nm)/speed (rpm) | 400/1500–1700 |
| Injection system | Bosch Common rail |
| Maximum injection press (MPa) | 130 |
| Injector hole diameter (μm) | 153 |
| Properties | DF | B20 |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfur content (μg/g) | 42 | 31 |
| Density (g/mL, 20 °C) | 0.838 | 0.846 |
| Low heating value (MJ/kg) | 42.9 | 41.8 |
| Kinematic viscosity (40 °C, mm2/s) | 4.045 | 4.654 |
| Flash point (°C) | 64 | 84 |
| 50% distillation/°C | 247.0 | 253.2 |
| 95% distillation/°C | 331.5 | 333.6 |
| Aromatic content (wt%) | 9.8 | 7.79 |
| Cetane number | 51.8 | 53 |
| % C (wt) | 87.2 | 84.94 |
| % H (wt) | 12.8 | 12.68 |
| % O (wt) | 0 | 2.38 |
| Speed (rpm) | Torque (Nm) | Load (%) | BMEP (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1600 | 80 | 20 | 0.261 |
| 1600 | 240 | 60 | 0.782 |
| 1600 | 400 | 100 | 1.301 |
| BMEP | DF | B20 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tp (°C) | Tb (°C) | Ea (kJ/mol) | Tp (°C) | Tb (°C) | Ea (kJ/mol) | |
| 0.261 MPa | 505.8 | 532.6 | 144.2 | 483.7 | 498.8 | 134.3 |
| 0.782 MPa | 510.5 | 546.7 | 154.5 | 500.2 | 526.8 | 142.9 |
| 1.301 MPa | 566.5 | 607.3 | 163.9 | 519.8 | 550.2 | 154.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Lyu, G.; Song, C.; Qiao, Y. Effects of Biodiesel Addition on the Physical Properties and Reactivity of the Exhaust Soot Particles from Diesel Engine. Energies 2020, 13, 4206. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13164206
Zhang X, Lyu G, Song C, Qiao Y. Effects of Biodiesel Addition on the Physical Properties and Reactivity of the Exhaust Soot Particles from Diesel Engine. Energies. 2020; 13(16):4206. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13164206
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuyang, Gang Lyu, Chonglin Song, and Yuehan Qiao. 2020. "Effects of Biodiesel Addition on the Physical Properties and Reactivity of the Exhaust Soot Particles from Diesel Engine" Energies 13, no. 16: 4206. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13164206
APA StyleZhang, X., Lyu, G., Song, C., & Qiao, Y. (2020). Effects of Biodiesel Addition on the Physical Properties and Reactivity of the Exhaust Soot Particles from Diesel Engine. Energies, 13(16), 4206. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13164206






