Performance Improvement of PWM Control Methods for Voltage Step-Down in Series Resonant DC–DC Converters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
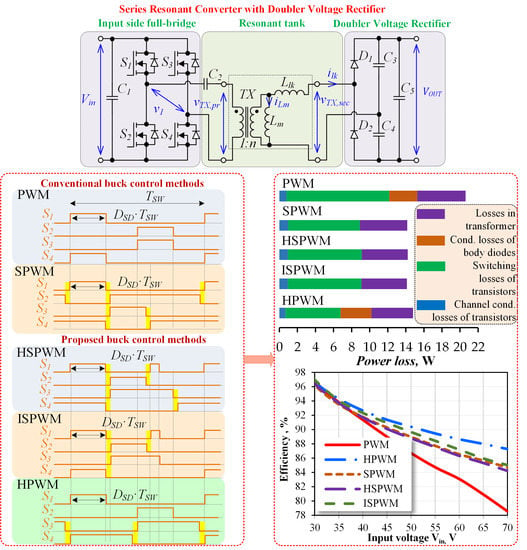
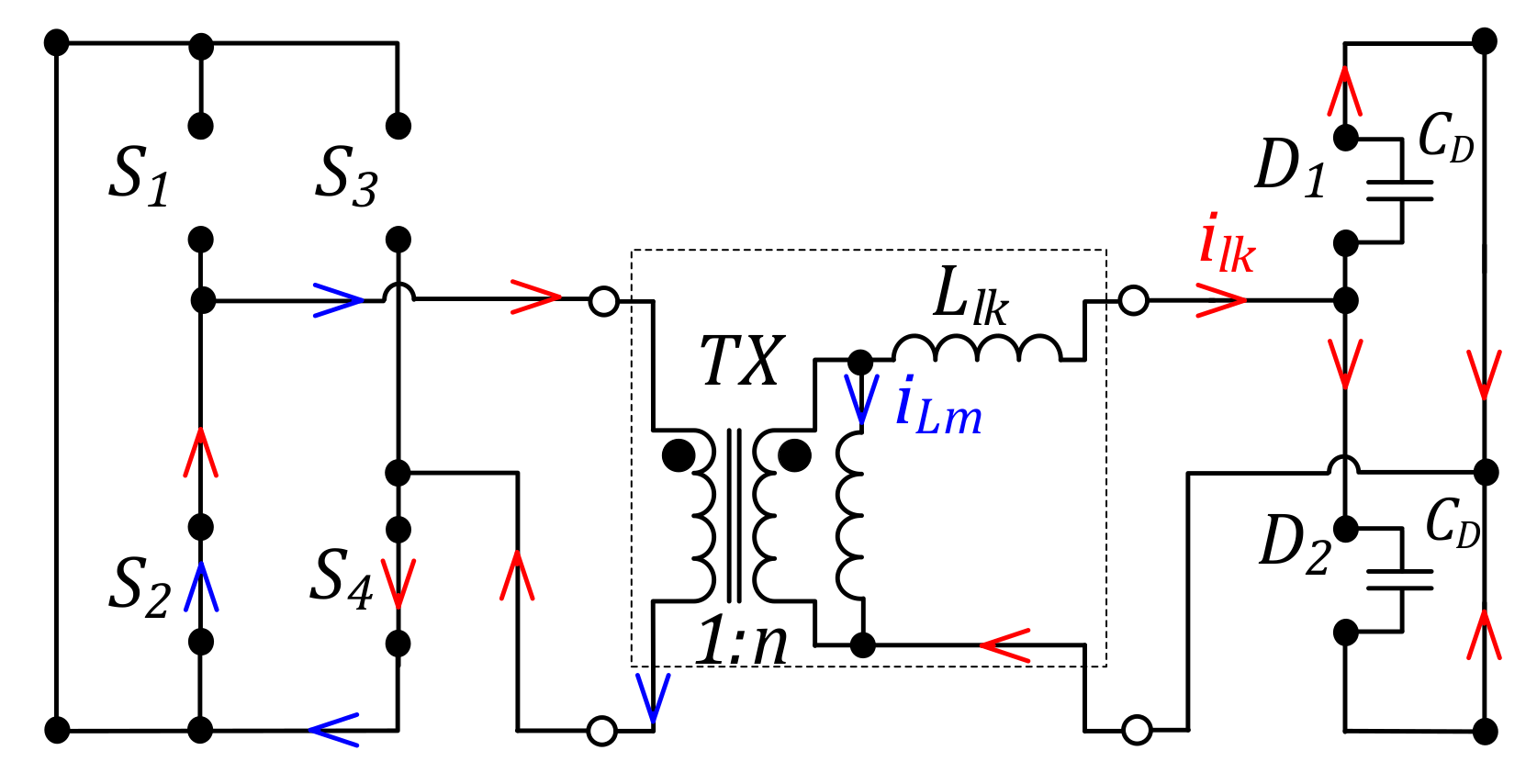
2. Description of the Series Resonant DC–DC Converter
3. Analysis of Existing PWM Methods
3.1. Methodology
3.2. Conventional PWM Method
3.3. Conventional Shifted PWM Method
4. Synthesis of New PWM Methods
4.1. Hybrid and Improved SPWM Methods
4.2. Hybrid PWM Method
5. Comparison of Existing and Proposed PWM Methods
5.1. Comparison of Current Stresses
- Turn-off current—as it defines the switching losses of the switches in the case of PWM of the SRC;
- The RMS current of the MOSFET channel (considering current flowing only when a switch is turned on)—as it influences the conduction losses of the switches;
- The average current of the body diode (considering negative current flowing when a MOSFET is turned off)—as it could increase the conduction losses in the switches significantly.
5.2. Comparison of Power Losses in the SRC Controlled by PWM Methods
6. Experimental Results
6.1. Steady-State Waveforms
6.2. Normalized DC Voltage Gain
6.3. Efficiency
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez-Otero, M.A.; O’Neill-Carrillo, E. Efficient Home Appliances for a Future DC Residence. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Energy 2030 Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–18 November 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Marnay, C. On Voltage Standards for DC Home Microgrids Energized by Distributed Sources. In Proceedings of the 7th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Harbin, China, 2–5 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Fernandes, B.G. Optimal Voltage Level for DC Microgrids. In Proceedings of the IECON 2010—36th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Glendale, AZ, USA, 7–10 November 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragicevic, T.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Skrlec, D. Advanced LVDC Electrical Power Architectures and Microgrids: A Step toward a New Generation of Power Distribution Networks. IEEE Electr. Mag. 2014, 2, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Diaz, E.; Chen, F.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Burgos, R.; Boroyevich, D. Voltage-Level Selection of Future Two-Level LVdc Distribution Grids: A Compromise Between Grid Compatibiliy, Safety, and Efficiency. IEEE Electrif. Mag. 2016, 4, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannan, M.A.; Faisal, M.; Ker, P.J.; Mun, L.H.; Parvin, K.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Blaabjerg, F. A Review of Internet of Energy Based Building Energy Management Systems: Issues and Recommendations. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 38997–39014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, Z. A New Architecture for High Efficiency Maximum Power Point Tracking in Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 6th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Wuhan, China, 17–20 May 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.M.; Franquelo, L.G.; Bialasiewicz, J.T.; Galvan, E.; PortilloGuisado, R.C.; Prats, M.A.M.; Leon, J.I.; Moreno-Alfonso, N. Power-Electronic Systems for the Grid Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciato, M.; Consoli, A.; Attanasio, R.; Gennaro, F. Soft-Switching Converter With HF Transformer for Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.D.; Lee, J.P.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.J.; Yoo, D.W.; Song, E.H. A New Topology With High Efficiency Throughout All Load Range for Photovoltaic PCS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4427–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, D.; Chub, A.; Liivik, E.; Roasto, I. High-Performance Quasi-Z-Source Series Resonant DC–DC Converter for Photovoltaic Module-Level Power Electronics Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 3634–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Fei, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Lee, F.C. A GaN-Based DC–DC Module for Railway Applications: Design Consideration and High-Frequency Digital Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chub, A.; Husev, O.; Blinov, A.; Vinnikov, D. Novel Isolated Power Conditioning Unit for Micro Wind Turbine Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 5984–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krismer, F.; Biela, J.; Kolar, J.W. A Comparative Evaluation of Isolated Bi-Directional DC/DC Converters with Wide Input and Output Voltage Range. In Proceedings of the Fourtieth IAS Annual Meeting. Conference Record of the 2005 Industry Applications Conference, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China, 2–6 October 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragicevic, T.; Lu, X.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M. DC Microgrids—Part II: A Review of Power Architectures, Applications, and Standardization Issues. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 3528–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.-Y. A New Compact and High Efficiency Resonant Converter. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 March 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lee, F.C.; Zhang, A.J.; Huang, G. LLC Resonant Converter for Front End DC/DC Conversion. In Proceedings of the APEC. Seventeenth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (Cat. No.02CH37335), Dallas, TX, USA, 10–14 March 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Gao, Y.; Shang, P. Parameter Design Method of a Series-Parallel Resonant Converter. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 4th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 14–16 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.N.; Chiu, H.-J.; Hsieh, Y.-C. Design of Wide Input Voltage Range High Step-up DC-DC Converter Based on Secondary-Side Resonant Tank Full Bridge LLC. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Green Building and Smart Grid (IGBSG), Yi-Lan, Taiwan, 22–25 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chub, A.; Vinnikov, D.; Lai, J.-S. Input Voltage Range Extension Methods in the Series-Resonant DC-DC Converters. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 15th Brazilian Power Electronics Conference and 5th IEEE Southern Power Electronics Conference (COBEP/SPEC), Santos, Brazil, 1–4 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, C.; Lai, J.-S. Comparison of Secondary Topology of the LLC Converter for Photovoltaic Application. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Portland, OR, USA, 23–27 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, D.; Chub, A.; Kosenko, R.; Zakis, J.; Liivik, E. Comparison of Performance of Phase-Shift and Asymmetrical Pulsewidth Modulation Techniques for the Novel Galvanically Isolated Buck–Boost DC–DC Converter for Photovoltaic Applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelac, J.-P.; Ziogas, P.D. A DC to DC PWM Series Resonant Converter Operated at Resonant Frequency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1988, 35, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopoulos, G.; Jain, P. A Series-Resonant DC/DC Converter with Asymmetrical PWM and Synchronous Rectification. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE 31st Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference. Conference Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37018), Galway, Ireland, 23–23 June 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, B.; Guo, X. Dual-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter With Fixed-Frequency PWM Control for Wide Input Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, B.-Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Li, X. Steady-State Analysis of a Series Resonant Converter with Modified PWM Control. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Siem Reap, Cambodia, 18–20 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.V.; Viswanathan, K.; Naik, R.; Sabate, J.A.; Lai, R. Analysis and Control of Phase-Shifted Series Resonant Converter Operating in Discontinuous Mode. In Proceedings of the 2013 Twenty-Eighth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Kwon, B.H. Zero-Voltage- and Zero-Current-Switching Full-Bridge Converter With Secondary Resonance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevani, M.; Pan, S.; Jain, P. A Hybrid Phase-Shift Modulation Technique for DC/DC Converters With a Wide Range of Operating Conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7498–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, D.; Chub, A.; Korkh, O.; Malinowski, M. Fault-Tolerant Bidirectional Series Resonant DC-DC Converter with Minimum Number of Components. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Baltimore, MD, USA, September 29–3 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graovac, D.; Purschel, M.; Kiep, A. “MOSFET Power Losses Calculation Using the Data-Sheet Parameters”, Infineon Application Note, July 2006. Available online: https://application-notes.digchip.com/070/70-41484.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2020).









| Operating Parameters | |
| Input Voltage Range, Vin | 30–70 V |
| Output Voltage, Vout | 350 V |
| Switching Frequency, fSW | 100 kHz |
| Operating Power Range | 50–200 W |
| Components | |
| S1–S4 | On Semiconductor FDMS 86180 |
| D1, D2 | CREE C3D02060E |
| C1, C5 | 150 µF |
| C2 | 52.8 µF |
| C3, C4 | 43 nF |
| Llk | 28 µH |
| Lm | 1 mH |
| n | 6.3 |
| ON-State Resistance | 2.4 mΩ |
| Output Capacitor | 3730 pF |
| Rise Time | 12 ns |
| Fall Time | 7 ns |
| Total Gate Charge | 60 nC |
| Gate-Source Voltage | 10 V |
| Total Gate Resistance | 3.5 Ω |
| Gate-Drain Capacitance (VDS = 0 V) | 500 pF |
| Body Diode Forward Voltage | 0.8 V |
| Body Diode on Resistance | 28 mΩ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sidorov, V.; Chub, A.; Vinnikov, D. Performance Improvement of PWM Control Methods for Voltage Step-Down in Series Resonant DC–DC Converters. Energies 2020, 13, 4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174569
Sidorov V, Chub A, Vinnikov D. Performance Improvement of PWM Control Methods for Voltage Step-Down in Series Resonant DC–DC Converters. Energies. 2020; 13(17):4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174569
Chicago/Turabian StyleSidorov, Vadim, Andrii Chub, and Dmitri Vinnikov. 2020. "Performance Improvement of PWM Control Methods for Voltage Step-Down in Series Resonant DC–DC Converters" Energies 13, no. 17: 4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174569
APA StyleSidorov, V., Chub, A., & Vinnikov, D. (2020). Performance Improvement of PWM Control Methods for Voltage Step-Down in Series Resonant DC–DC Converters. Energies, 13(17), 4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174569