Bioclimatic Architecture and Urban Morphology. Studies on Intermediate Urban Open Spaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Surface heat islands: the infrared radiation emitted and reflected by surfaces, which allow the portions of building where the surfaces are hottest to be identified, must be measured.
- Canopy-level heat islands: which exist in the air stratum where human activities are performed, from the ground to beneath the tree canopy and building roofs.
- Urban and boundary layer heat islands: which start from the level of building roofs and tree canopies, extending to the point where the urban landscapes no longer influence the atmosphere. This region generally extends no more than a mile from the surface [5].
2. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies toward Urban Resilience
2.1. Cool Materials
2.2. Green Infrastructures
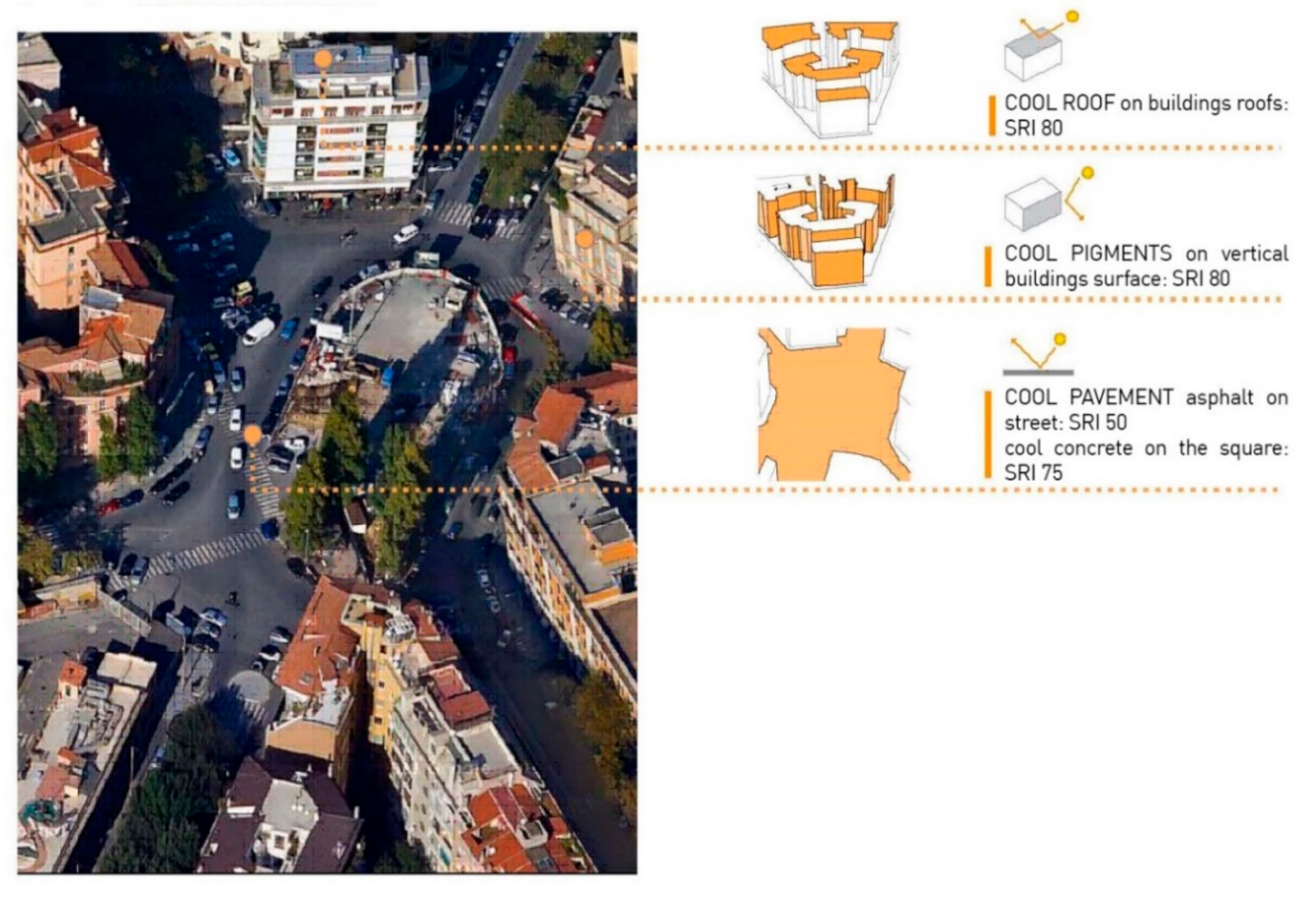
3. Case Study Piazza Bainsizza, Rome
3.1. Analysis of Initial Meteorological Conditions and Simulated Models
- 1.
- The grid cell dimension used for the ENVI-met models measures 2 m × 2 m.
- 2.
- Walls and roofs were modelled in the Database Manager specifying their three characteristic layers.
- 3.
- In the exterior layer of walls and roofs it was chosen to apply the prevalent material, that is concrete tiles for the roofs and brick block covered with lime plaster for the walls.
3.2. Definition of Scenario Simulation
- Optimization of possible nonmirrored reflectivity to solar radiation on the surfaces involved in the intervention.
- Optimization of the emissivity factor.
- Aesthetic value and integration due to the consolidated urban context.
- Planting with trees having medium-high leaf area density (LAD).
- Planting implemented in keeping with the consolidated urban and Mediterranean context.
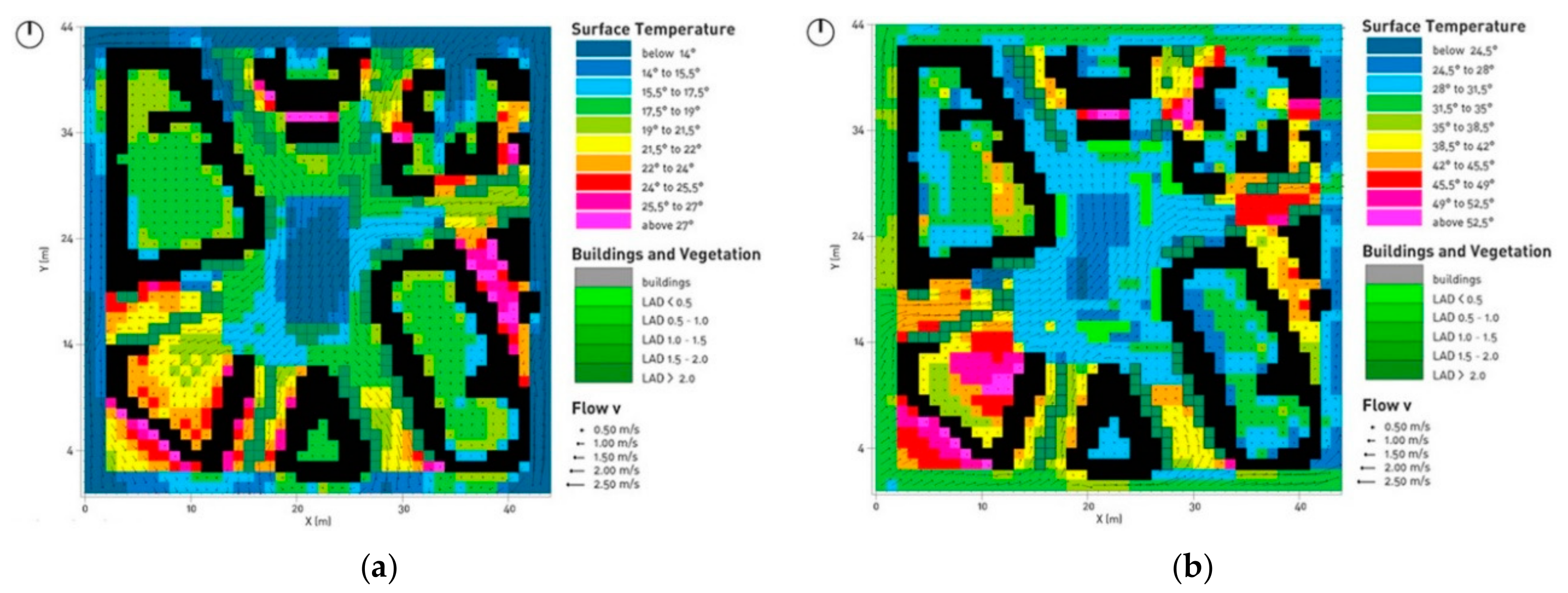
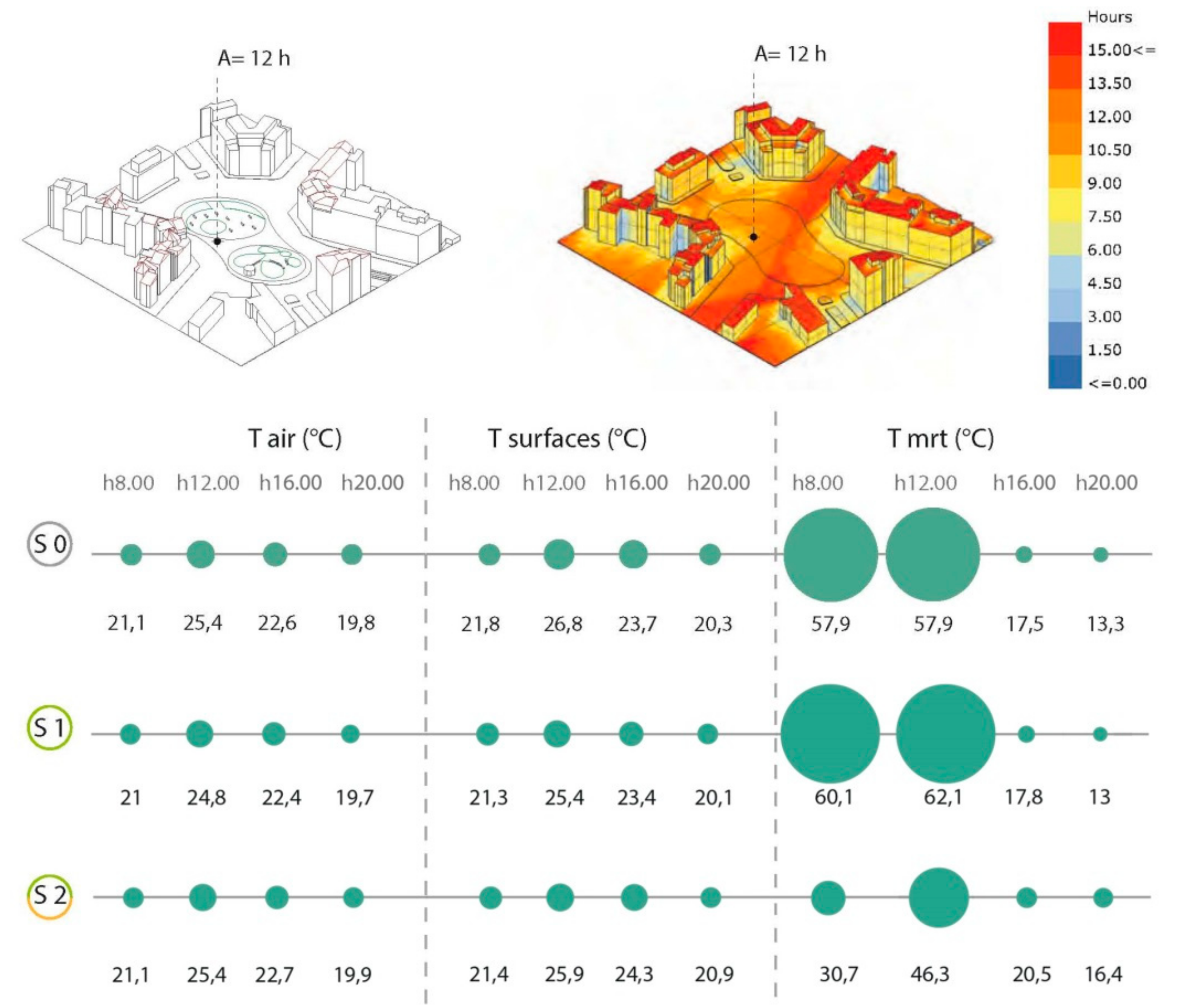
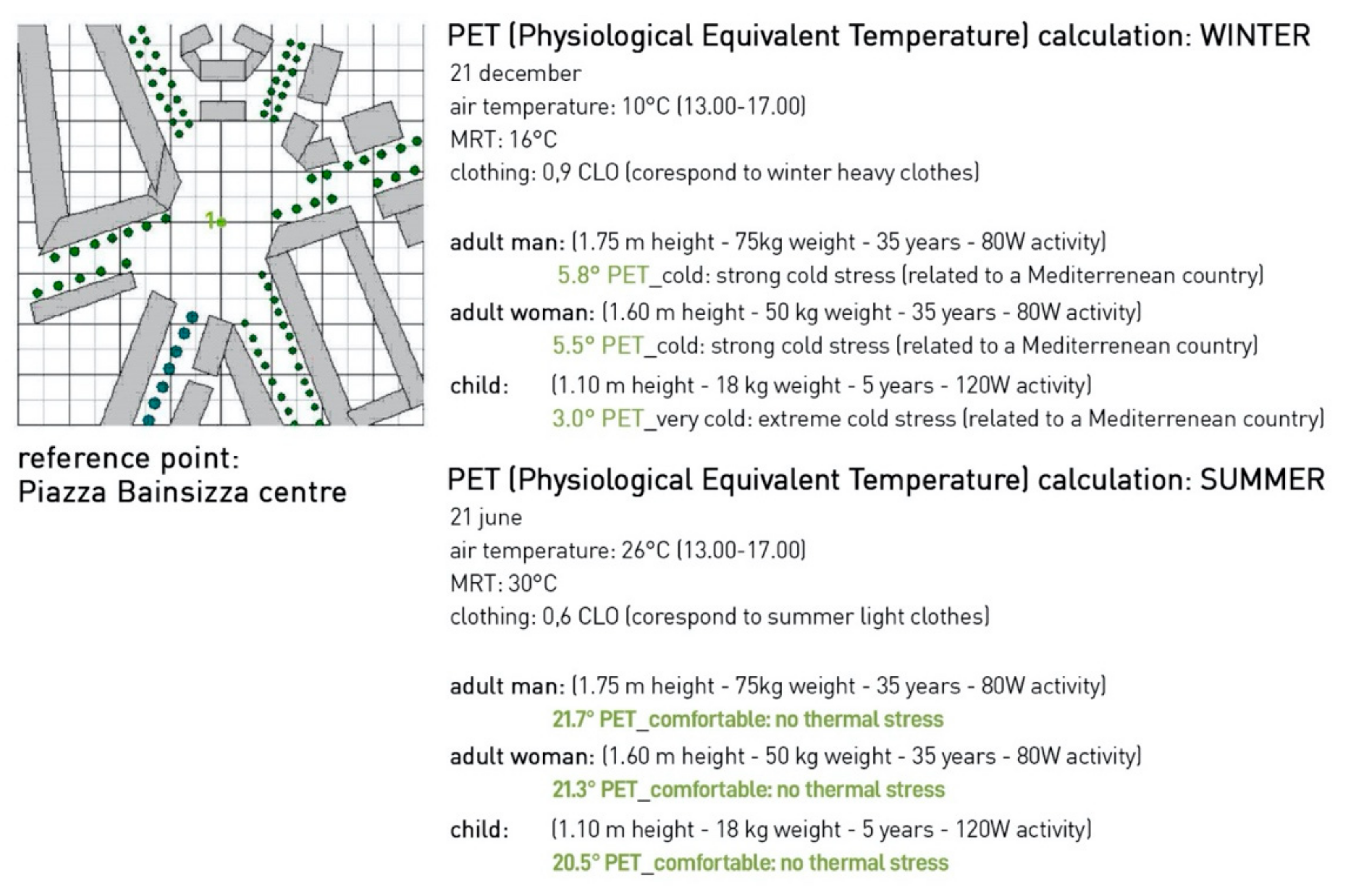
4. Discussion of Results
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change. IPCC Global Warming of 1.5 °C An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C Above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty, 1st ed.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-92-9169-151-7. [Google Scholar]
- UNFCCC. Yearbook of Global Climate Action 2019, 1st ed.; UNFCCC: Bonn, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-92-9219-186-3. [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg, H.E. The Urban Climate; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; ISBN 978-0-12-435960-4. [Google Scholar]
- Manley, G. On the frequency of snowfall in metropolitan England. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1958, 84, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Reducing Urban Heat Islands: Compendium of Strategies. 2009. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/heatisld/resources/compendium.html (accessed on 12 May 2019).
- Pearlmutter, D. Patterns of sustainability in desert architecture. Arid Lands Newsl. 2000, 47, 1–12. Available online: http://ag.arizona.edu/oals/ALN/aln47/pearlmutter.html (accessed on 12 May 2019).
- US EPA. Smart Growth and Urban Heat Islands. 2009. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/heatisld/resources/pdf/smartgrowthheatislands.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2019).
- Oke, T.R. The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, J. The built environment induced urban heat island effect in rapidly urbanizing arid regions—A sustainable urban engineering complexity. Environ. Sci. 2004, 1, 249–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. Heat island research in Europe—The state of the art. ABER 2007, 1, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Mayer, H.; Chen, L. Contribution of trees and grasslands to the mitigation of human heat stress in a residential district of Freiburg, Southwest Germany. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 148, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piselli, C.; Castaldo, V.; Pigliautile, I.; Pisello, A.; Cotana, F. Outdoor comfort conditions in urban areas: On citizens’ perspective about microclimate mitigation of urban transit areas. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.S.; Costa, J.P. Addressing thermophysiological thresholds and psychological aspects during hot and dry mediterranean summers through public spacedesign: The case of Rossio. Build. Environ. 2017, 118, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, U.; Kohler, N. Resilience in the built environment. Build. Res. Inf. 2014, 42, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Myths of ecology and energy. In Perspectives on Energy: Issues, Ideas, and Environmental Dilemmas, 2nd ed.; Ruedisili, L.C., Firebaugh, M.W., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 3, pp. 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cretney, R. Resilience for whom? Emerging critical geographies of socio-ecological resilience. Geogr. Compass 2014, 8, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, S.H. Resilience and the neoliberal counter-revolution: From ecologies of control to production of the common. Resilience 2014, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderson, H.; Pritchard, L. Resilience and the Behavior of Large-Scale Systems, 1st ed.; Island Press: Covelo, CA, USA, 2002; ISBN 1-55963-970-9. [Google Scholar]
- Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Stults, M. Defining urban resilience: A review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 147, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Resilient Cities. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/cfe/regional-policy/resilient-cities.html (accessed on 21 July 2018).
- Santamouris, M. Cooling the cities—A review of reflective and green roof mitigation technologies to fight heat island and improve comfort in urban environments. Sol. Energy 2014, 103, 682–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. Urban Adaptation to Climate Change in Europe 2016: Transforming Cities in a Changing Climate, 1st ed.; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016; ISBN 978-92-9213-741-0. [Google Scholar]
- Shashua-Bar, L.; Hoffman, M.E. Vegetation as a climatic component in the design of an urban street: An empirical model for predicting the cooling effect of urban green areas with trees. Energy Build. 2000, 31, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisello, A.L. State of the art on the development of cool coatings for buildings and cities. Sol. Energy 2017, 144, 660–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Kaloush, K.E. Environmental impacts of reflective materials: Is high albedo a ‘silver bullet’ for mitigating urban heat island? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbari, H.; Cartalis, C.; Santamouris, M.; Synnefa, A.; Kolokotsa, D.; Muscio, A.; Pisello, A.L.; Rossi, F.; Wong, N.H.; Zinzi, M. Local climate change and urban heat island mitigation techniques—The state of the art. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2016, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santamouris, M.; Gaitani, N.; Spanou, A.; Saliari, M.; Giannopoulou, K.; Vasilakopoulou, K.; Kardomateas, T. Using cool paving materials to improve microclimate of urban areas—Design realization and results of the flisvos project. Build. Environ. 2012, 53, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erell, E.; Pearlmutter, D.; Boneh, D.; Kutiel, P.B. Effect of high-albedo materials on pedestrian heat stress in urban street canyons. Urban Clim. 2014, 10, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleghani, M.; Berardi, U. The effect of pavement characteristics on pedestrians’ thermal comfort in Toronto. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidimitriou, A.; Yannas, S. Microclimate development in open urban spaces: The influence of form and materials. Energy Build. 2015, 108, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidan, M.F.; Jones, P.J.; Gwilliam, J.; Salleh, E. An evaluation of outdoor and building environment cooling achieved through combination modification of trees with ground materials. Build. Environ. 2012, 58, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureti, F.; Martinelli, L.; Battisti, A. Assessment and mitigation strategies to counteract overheating in urban historical areas in Rome. Climate 2018, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolokotsa, D.; Maravelaki-Kalaitzaki, P.; Papantoniou, S.; Vangeloglou, E.; Saliari, M.; Karlessi, T.; Santamouris, M. Development and analysis of mineral based coatings for buildings and urban structures. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synnefa, A.; Santamouris, M.; Livada, I. A study of the thermal performance of reflective coatings for the urban environment. Sol. Energy 2006, 80, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlessi, T.; Santamouris, M.; Apostolakis, K.; Synnefa, A.; Livada, I. Development and testing of thermochromic coatings for buildings and urban structures. Sol. Energy 2009, 83, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretz, S.E.; Akbari, H. Long-term performance of high albedo roof coatings. Energy Build. 1997, 25, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saaroni, H.; Amorim, J.; Hiemstra, J.; Pearlmutter, D. Urban Green Infrastructure as a tool for urban heat mitigation: Survey of research methodologies and findings across different climatic regions. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Building a Green Infrastructure for Europe. Available online: https://www.worldcat.org/title/building-a-green-infrastructure-for-europe/oclc/875969246&referer=brief_results (accessed on 4 August 2018).
- United Nations Human Settlements Program (UN-Habitat). The State of European Cities 2016 Cities Leading the Way to a Better Future, 1st ed.; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2016; ISBN 978-92-79-64259-3. [Google Scholar]
- Human-Biometeorological Conditions and Thermal Perception in a Mediterranean Coastal Park. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00484-014-0944-z (accessed on 22 July 2018).
- Spronken-Smith, R.A.; Oke, T.R. The thermal regime of urban parks in two cities with different summer climates. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 2085–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.; Knight, T.M.; Pullin, A.S. Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketterer, C.; Matzarakis, A. Human-biometeorological assessment of heat stress reduction by replanning measures in Stuttgart, Germany. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 122, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analysis and Comparison of Shading Strategies to Increase Human Thermal Comfort in Urban Areas. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/9/3/91 (accessed on 22 July 2018).
- Upreti, R.; Wang, Z.H.; Yang, J. Radiative shading effect of urban trees on cooling the regional built environment. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 26, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Byrne, J.; Pickering, C. A systematic quantitative review of urban tree benefits, costs, and assessment methods across cities in different climatic zones. Urban For. Urban Green. 2012, 11, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.A.; Armson, D.; Ennos, A.R. A comparison of the growth and cooling effectiveness of five commonly planted urban tree species. Urban Ecosyst. 2015, 18, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Pomerantz, M.; Taha, H. Cool surfaces and shade trees to reduce energy use and improve air quality in urban areas. Sol. Energy 2001, 70, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, A.; Frangi, P.; Mori, J.; Donzelli, D.; Ferrini, F. Nature based solutions to mitigate soil sealing in urban areas: Results from a 4-year study comparing permeable, porous, and impermeable pavements. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kala, J.; De Kauwe, M.G.; Pitman, A.J.; Medlyn, B.E.; Wang, Y.P.; Lorenz, R.; Perkins-Kirkpatrick, S.E. Impact of the representation of stomatal conductance on model projections of heatwave intensity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- A Practical Guide to Cool Roofs and Cool Pavements. Available online: https://www.coolrooftoolkit.org/read-the-guide/ (accessed on 22 July 2018).
- Liu, K.; Baskaran, B. Thermal performance of green roofs through field evaluation. In Proceedings of the first North American Green Roof Infrastructure Conference, Awards and Trade Show: Greening Rooftops for Sustainable Communities, Chicago, IL, USA, 29–30 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarin, R.M.; Castellotti, F.; Busato, F. Experimental measurements and numerical modelling of a green roof. Energy Build. 2005, 37, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U. The outdoor microclimate benefits and energy saving resulting from green roofs retrofits. Energy Build. 2016, 121, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Roebber, P.J. Green roof mitigation potential for a proxy future climate scenario in Chicago, Illinois. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Solecki, W.; Parshall, L.; Gaffin, S. Mitigating New York City’s Heat Island with Urban Forestry, Living Roofs and Light Surfaces, 1st ed.; Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Asaeda, T.; Ca, V.T.; Wake, A. Heat storage of pavement and its effect on the lower atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Nastasi, B. Solar energy data analytics: PV deployment and land use. Energies 2020, 13, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolopoulou, M.; Steemers, K. Thermal comfort and psychological adaptation as a guide for designing urban spaces. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessì, V.; Rogora, R. Il Comfort Ambientale Degli Spazi Aperti; EdicomEdizioni: Gorizia, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]

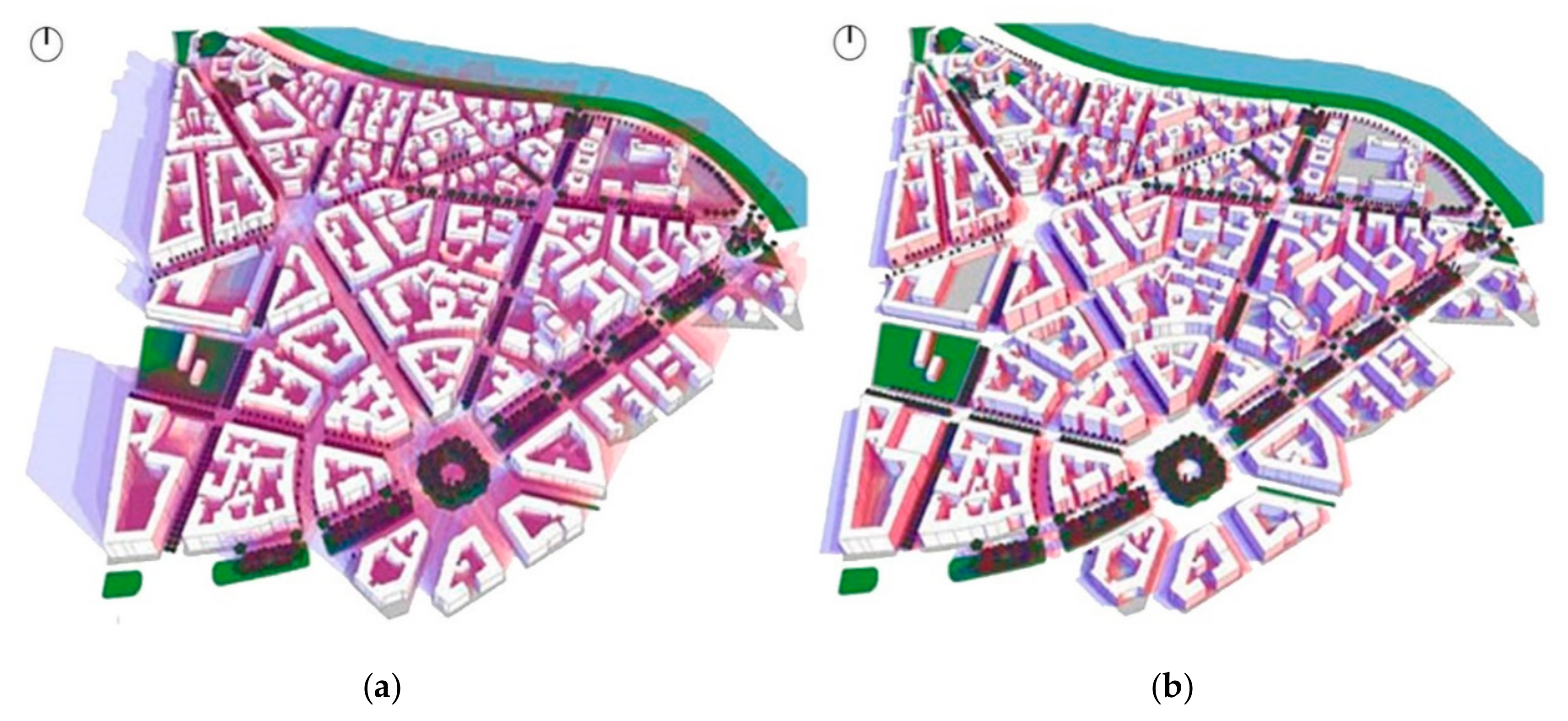
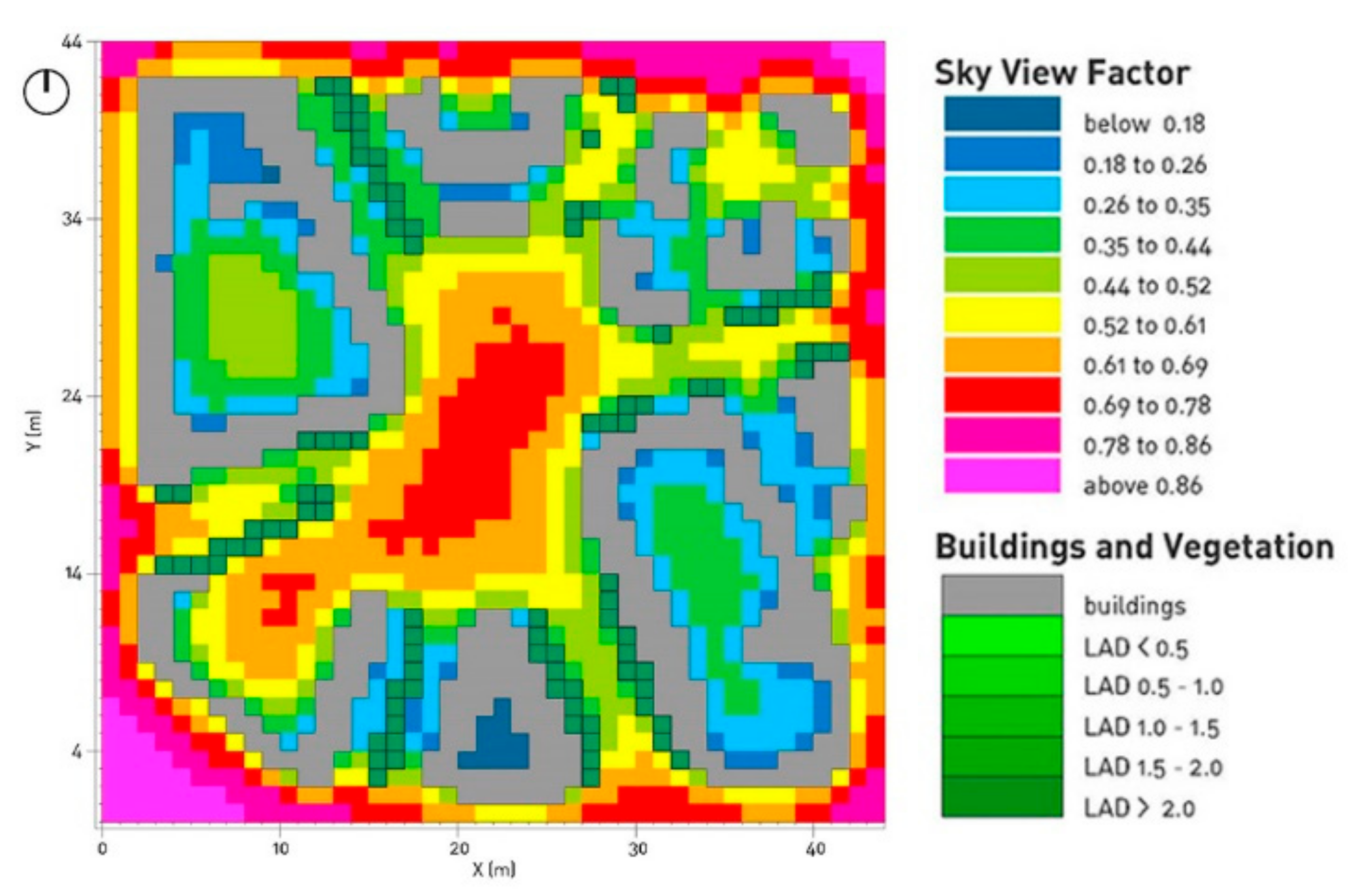
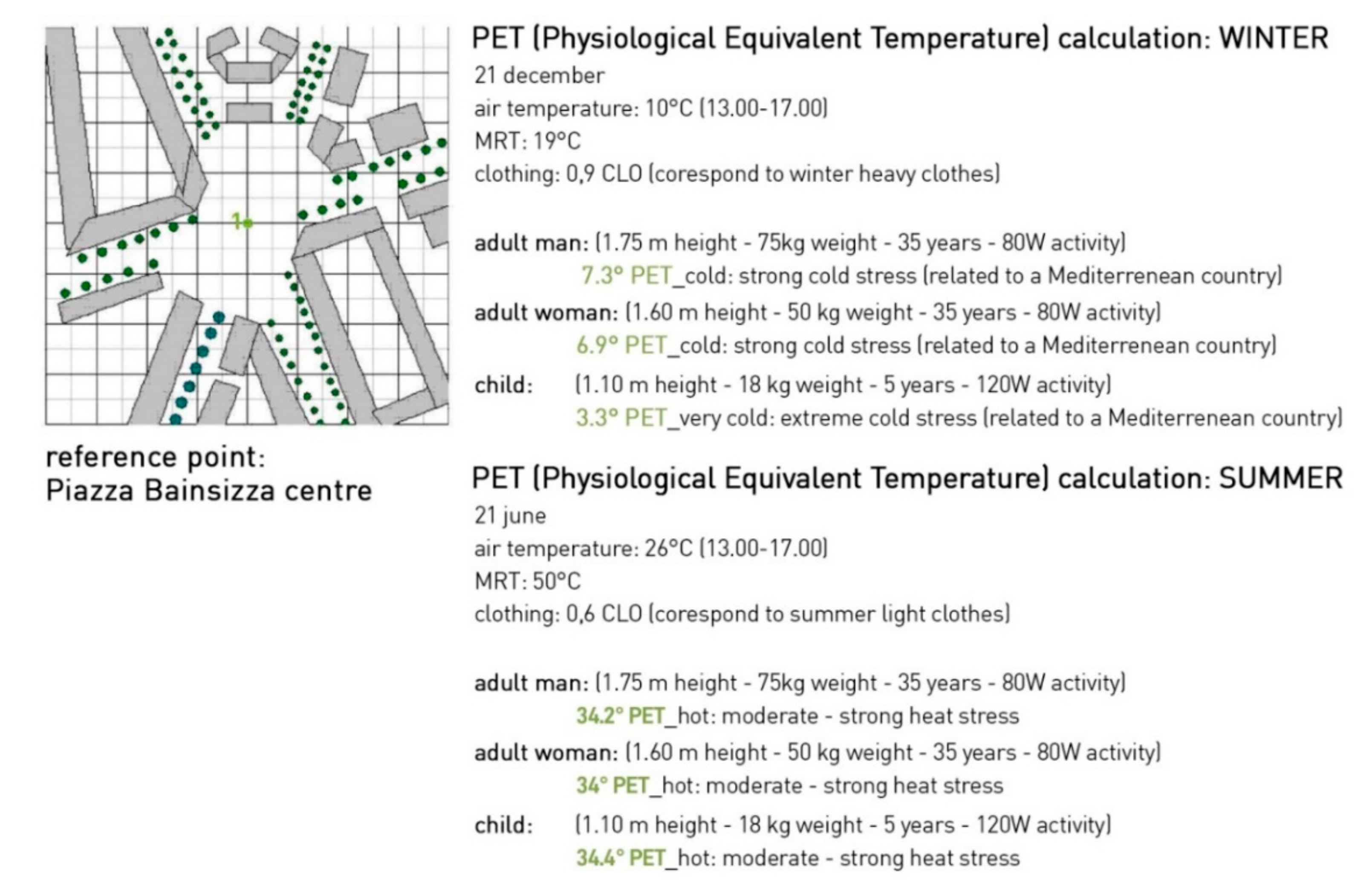
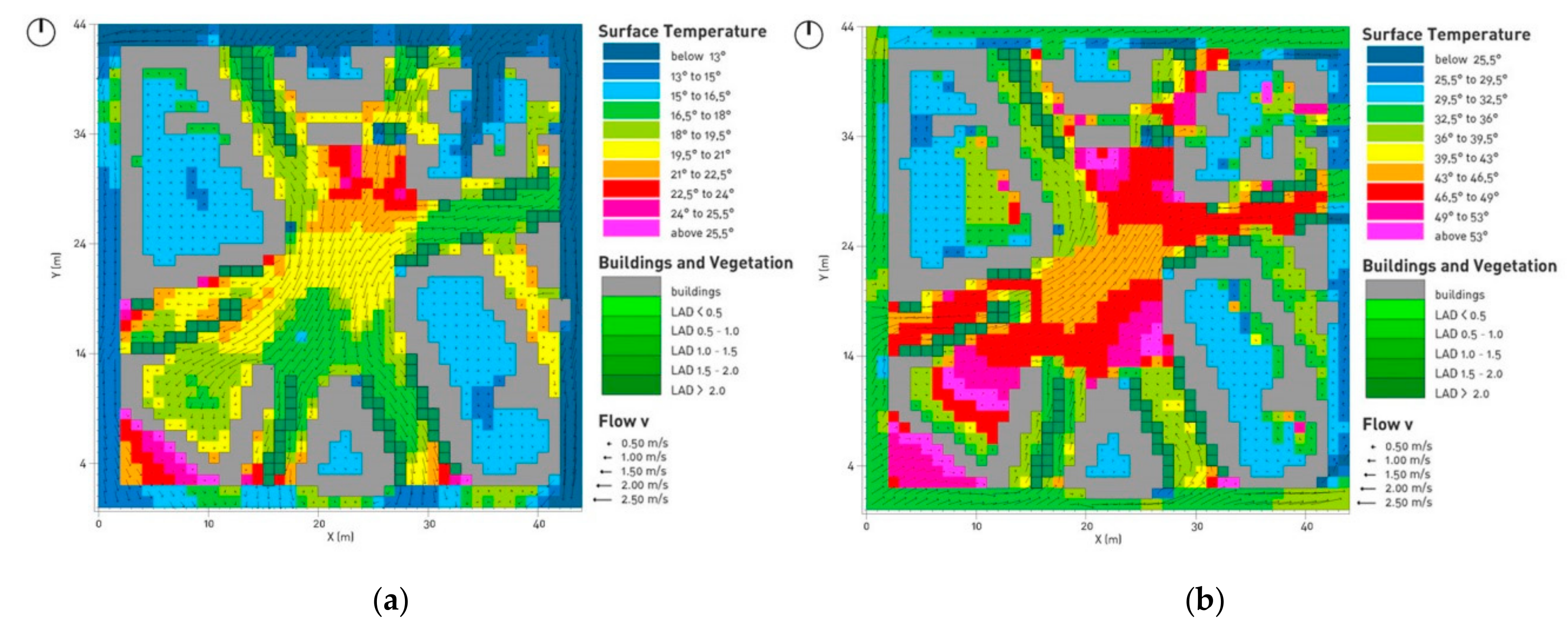





| Input Data | Winter Simulation | Summer Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| Starting date and time | 21 December 2015, 8:00 a.m. | 21 June 2015, 8:00 a.m. |
| Total simulation time | 12 h | 12 h |
| Wind speed in 10 m (v) | 0.9 m/s | 1.3 m/s |
| Wind direction | 50° | 230° |
| Initial air temperature (Tair) | 9 °C | 25 °C |
| Relative humidity (RH) | 81% | 69% |
| Roughness length (z0) | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Number x grid cells | 44 | 44 |
| Number y grid cells | 44 | 44 |
| Number z grid cells | 30 | 30 |
| Dimension of the grid in dx | 2 m | 2 m |
| Dimension of the grid in dy | 2 m | 2 m |
| Dimension of the grid in dz | 2 m | 2 m |
| Cloud cover (cc) | 3 | 0 |
| Albedo ground | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Albedo roof | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Albedo wall | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Surface | S0 | S1 | S2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Albedo (a) | Name | Albedo (a) | Name | Albedo (a) | LAD (m2/m3) | |
| Roofs | concrete tile | 0.30 | cool pigment concrete tile | 0.65 | grass | 0.20 | - |
| Walls | concrete wall + cement plaster | 0.40 | concrete wall + cement plaster + cool pigmented | 0.60 | concrete wall + cement plaster + cool pigmented | 0.60 | - |
| Pavements | asphalt | 0.20 | cool pigment concrete tile | 0.65 | asphalt + grass | 0.20 | - |
| Vegetation | - | - | - | - | Cedrus Atlantica evergreen (Cat) | 0.18 | 0.70–0.80 |
| - | - | - | - | Pinus Pinea evergreen (Pp) | 0.18 | 0.70–0.80 | |
| - | - | - | - | Quercus ilex deciduous (Qi) | 0.20 | 0.80-0.90 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Battisti, A. Bioclimatic Architecture and Urban Morphology. Studies on Intermediate Urban Open Spaces. Energies 2020, 13, 5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13215819
Battisti A. Bioclimatic Architecture and Urban Morphology. Studies on Intermediate Urban Open Spaces. Energies. 2020; 13(21):5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13215819
Chicago/Turabian StyleBattisti, Alessandra. 2020. "Bioclimatic Architecture and Urban Morphology. Studies on Intermediate Urban Open Spaces" Energies 13, no. 21: 5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13215819
APA StyleBattisti, A. (2020). Bioclimatic Architecture and Urban Morphology. Studies on Intermediate Urban Open Spaces. Energies, 13(21), 5819. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13215819






