Enhanced Performance Modified Discontinuous PWM Technique for Three-Phase Z-Source Inverter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Only offering one degree of freedom from the control strategy point of view.
- A highly nonlinear performance at high-gain operating conditions.
- High sensitivity at low-modulation index operation.
- A common trade-off between extended operating conditions and voltage stresses.
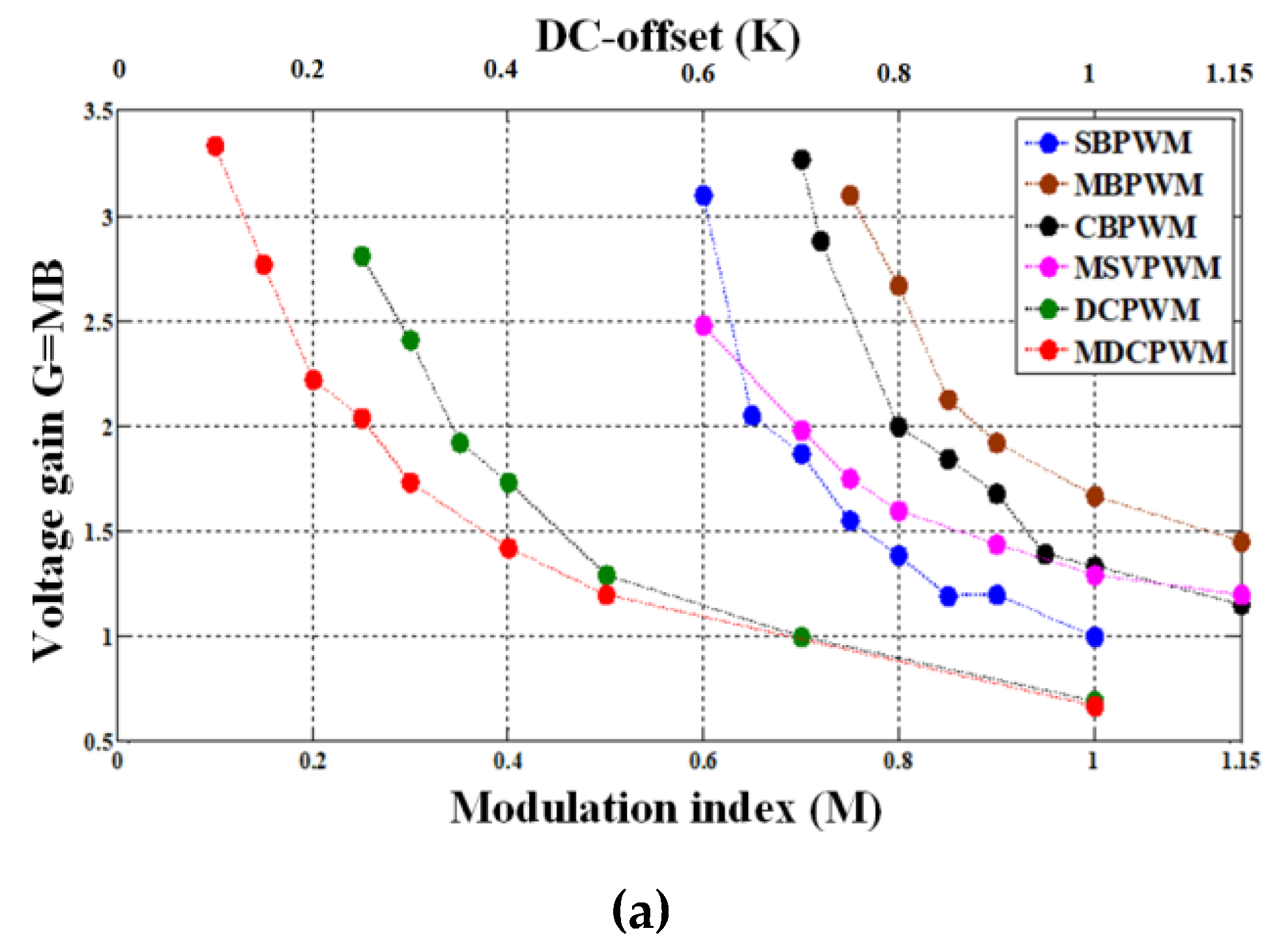
2. Conventional ZSI-PWM Techniques
3. Proposed Modified Discontinuous ZSI-PWM Techniques
4. Mathematical Analysis of the Proposed Modified Discontinuous ZSI-PWM Techniques
5. Simulation Analysis
6. Experimental Validation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaosuo, X.; Liuchen, C.; Baekhj, K.S.; Bordonau, J.; Shimizu, T. Topologies of single-phase inverters for small distributed power generators: An overview. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Amirahmadi, A.; Zhang, Q.; Kutkut, N.; Batarseh, I. Design and Implementation of Three-Phase Two-Stage Grid-Connected Module Integrated Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 3881–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. A High-Frequency Link Multilevel Cascaded Medium-Voltage Converter for Direct Grid Integration of Renewable Energy Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4167–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, U.R.; Rathore, A.K. Dual Three-Pulse Modulation-Based High-Frequency Pulsating DC Link Two-Stage Three-Phase Inverter for Electric/Hybrid/Fuel Cell Vehicles Applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, D.; Chatterjee, K. Two-Stage Solar Photovoltaic-Based Stand-Alone Scheme Having Battery as Energy Storage Element for Rural Deployment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 4148–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Xue, L.K.; Wang, C.S.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Interleaved High-Conversion-Ratio Bidirectional DC–DC Converter for Distributed Energy-Storage Systems—Circuit Generation, Analysis, and Design. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5547–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaer, S.B.; Pedersen, J.K.; Blaabjerg, F. A review of single-phase grid-connected inverters for photovoltaic modules. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Luo, F.; Zhang, X.; Boroyevich, D.; Mattavelli, P. Grid-Interface BidirectiGrid-Interface Bidirectional Converter for Residential DC Distribution Systems—Part One: High-Density Two-Stage Topology. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, R.O.; Barbi, I. A boost DC-AC converter: Analysis, design, and experimentation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1999, 14, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, P.; Ursaea, A.; Gubia, E.; Marroyo, L. Boost DC-AC inverter: A new control strategy. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.F. Z-source inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Jung, Y.G.; Lim, Y.C. Single-Phase AC–AC Converter Based on Quasi-Z-Source Topology. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.X.; Ming, Q.Z.; Zheng, P.F. Single-phase Z-source PWM AC-AC converters. IEEE Power Electron. Lett. 2005, 3, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, C. Z-source ac–ac converters solving commutation problem. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Duan, S.; Peng, F. Safe-commutation strategy for the novel family of quasi-Z-source AC–AC converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.F.; Cha, H.; Khan, A.A.; Kim, H.G. A Family of High-Frequency Isolated Single-Phase Z-Source AC–AC Converters with Safe-Commutation Strategy. IEEE Trans. Electron. 2016, 31, 7522–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evran, F.; Aydemir, M.T. Isolated High Step-Up DC–DC Converter with Low Voltage Stress. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 3591–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwakoti, Y.P.; Loh, P.C.; Blaabjerg, F.; Town, G. Y-source impedance network. 2014 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition—APEC 2014. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 3362–3366. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Yu, Q.; Leng, Z.; Chen, X. Switched Z-Source Isolated Bidirectional DC–DC Converter and Its Phase-Shifting Shoot-Through Bivariate Coordinated Control Strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 4657–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, D.; Roasto, I.; Strzelecki, R.; Adamowicz, M. Step-Up DC/DC Converters with Cascaded Quasi-Z-Source Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 3727–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Yang, S.; Peng, F.Z.; Inoshita, R. Steady state and transient analysis of a three phase current-fed Z-source PWM rectifier. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Dearborn, MI, USA, 7–10 September 2009; pp. 426–432. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Shuitao, Y.; Peng, F.Z.; Inoshita, R. Three phase current-fed Z-source PWM rectifier. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–24 September 2009; pp. 1569–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Qian, Z.; Xie, Y.; Peng, F.Z. A novel ZVS Z-source rectifier. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition 2006 APEC’06, Dallas, TX, USA, 19–23 March 2006; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kala-Konga, C.L.; Gitau, M.N.; Bansal, R.C. Steady-state and small-signal models of a three-phase quasi-Z-source AC–DC converter for wind applications. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2016, 10, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Peng, F.Z.; Chen, L.; Wen, X. Analysis and design of Bi-directional Z-source inverter for electrical vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2008 Twenty-Third Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Austin, TX, USA, 24–28 February 2008; pp. 1252–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.; Peng, F.Z. Four quasi-Z-Source inverters. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 15–19 June 2008; pp. 2743–2749. [Google Scholar]
- Gajanayake, C.J.; Luo, F.L.; Gooi, H.B.; So, P.L.; Siow, L.K. Extended-Boost Z-Source Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2642–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yu, K.; Luo, F.L. Switched Inductor Z-Source Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Lim, Y.C.; Cho, G.B. Switched-Inductor Quasi-Z-Source Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.F.; Cha, H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.G. Switched-Coupled-Inductor Quasi-Z-Source Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, P.C.; Li, D.; Blaabjerg, F. Γ-Z-Source Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 4880–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Lim, Y.C.; Kim, Y.G. TZ-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5686–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Peng, F.Z.; Cha, H. Trans-Z-Source Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3453–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossam-Eldin, A.; Abdelsalam, A.K.; Refaey, M.; Ali, A.A. A topological review on recent improvements of three-phase impedance source inverter. In Proceedings of the 2017 Nineteenth International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON), Cairo, Egypt, 19–21 December 2017; pp. 1106–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Joseph, A.; Wang, J.; Peng, F.Z.; Adams, D.J. Comparison of Traditional Inverters and Z -Source Inverter for Fuel Cell Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Fu, L.; Lin, C.H.; Li, C.; Choi, W.; Wang, J. Development of an 85-kW Bidirectional Quasi-Z-Source Inverter with DC-Link Feed-Forward Compensation for Electric Vehicle Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5477–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.Z.; Shen, M.; Holland, K. Application of Z-Source Inverter for Traction Drive of Fuel Cell—Battery Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiston, A.; Miliani, E.H.; Pierfederici, S.; Meibody-Tabar, F. Efficiency Improvement of a Quasi-Z-Source Inverter-Fed Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine-Based Electric Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2016, 2, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehghan, S.M.; Mohamadian, M.; Yazdian, A. Hybrid Electric Vehicle Based on Bidirectional Z-Source Nine-Switch Inverter. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 2641–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, H.P. Permanent-magnet synchronous motor drive system for electric vehicles using bidirectional z-source inverter. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2012, 2, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Cintron-Rivera, J.G.; Peng, F.Z. Modeling and Control of Quasi-Z-Source Inverter for Distributed Generation Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Abu-Rub, H.; Peng, F.Z.; Lei, Q.; De Almeida, A.T.; Ferreira, F.J.; Sun, D.; Liu, Y. An Energy-Stored Quasi-Z-Source Inverter for Application to Photovoltaic Power System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 4468–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rub, H.; Iqbal, A.; Ahmed, S.M.; Peng, F.Z.; Li, Y.; Baoming, G. Quasi-Z-Source Inverter-Based Photovoltaic Generation System with Maximum Power Tracking Control Using ANFIS. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajanayake, C.J.; Vilathgamuwa, D.M.; Loh, P.C.; Teodorescu, R.; Blaabjerg, F. Z-Source-Inverter-Based Flexible Distributed Generation System Solution for Grid Power Quality Improvement. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 24, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, N.; Zolghadri, M.R. Three-Phase Quasi-Z-Source Inverter with Constant Common-Mode Voltage for Photovoltaic Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 4790–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadian, S.; Ahmadi, R. Model Predictive-Based Maximum Power Point Tracking for Grid-Tied Photovoltaic Applications Using aZ-Source Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 7611–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, S.; Cao, D.; Peng, F.Z. A Digital Current Control of Quasi-Z-Source Inverter with Battery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, M.A.H.; G, F.L.; Puma, J.L.A.; A, J.A.T.; Filho, A.J.S. Battery Energy Storage System Applied to Wind Power System Based On Z-Source Inverter Connected to Grid. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 4035–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, P.; Shen, W.X. Single-Phase Uninterruptible Power Supply Based on Z-Source Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 2997–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahparasti, M.; Yazdian, A.; Mohamadian, M.; Larijani, A.S.; Fatemi, A. Parallel uninterruptible power supplies based on Z-source inverters. IET Power Electron. 2012, 5, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.F.; Miaosen, S.; Zhaoming, Q. Maximum boost control of the Z-source inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Miaosen, S.; Jin, W.; Joseph, A.; Zheng, P.F.; Tolbert, L.M.; Adams, D.J. Constant boost control of the Z-source inverter to minimize current ripple and voltage stress. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, H.; Khaburi, D.A. A new method for minimizing of voltage stress across devices in Z-source inverter. In Proceedings of the 2011 2nd Power Electronics, Drive Systems and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), Tehran, Iran, 16–17 February 2011; pp. 610–614. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.W.; Keyhani, A. Control of a Fuel Cell Based Z-Source Converter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agelidis, V.G.; Ziogas, P.; Joos, G. Dead-band’ PWM switching patterns. In Proceedings of the PESC ‘92 Record 23rd Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Toledo, Spain, 29 June–3 July 1992; Volume 1, pp. 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Steinke, J.K. Switching frequency optimal PWM control of a three-level inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1992, 7, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, M.S.; Elserougi, A.A.; Massoud, A.M.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Ahmed, S. A Pulsewidth Modulation Technique for High-Voltage Gain Operation of Three-Phase Z-Source Inverters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2016, 4, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhakim, A.; Blaabjerg, F.; Mattavelli, P. Modulation Schemes of the Three-Phase Impedance Source Inverters—Part I: Classification and Review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6309–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, M.S.; Rahim, N.A.; Ghazali, K.H.; Hanafi, A.H.M. Z-source inverter pulse width modulation: A survey. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Control and Computer Engineering 2011 (InECCE), Pahang, Malaysia, 21–22 June 2011; pp. 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Jain, S.K. A review on modulation techniques of Z-source network. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th India International Conference on Power Electronics (IICPE), Patiala, India, 17–19 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
















| PWM Technique | Shoot-Through Duty Ratio | Boosting Factor | Voltage Stress | Voltage Gain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBPWM | ||||
| MBPWM | ||||
| CBPWM | G) | |||
| MSVPWM | ) | G) | ||
| ZSI-DCPWM | ||||
| PROPOSED MODIFIED ZSI-DCPWM |
| Symbol | Definition | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Input DC voltage | 30 V | |
| L1, L2 | Z-network first and second inductor | 5 mH |
| C1.C2 | Z-network first and second capacitor | 3300 µF |
| f | Fundamental frequency | 50 Hz |
| Switching frequency | 10 kHz | |
| Load impedance | (10 + j3.1415) Ω |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hossameldin, A.A.; Abdelsalam, A.K.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Williams, B.W. Enhanced Performance Modified Discontinuous PWM Technique for Three-Phase Z-Source Inverter. Energies 2020, 13, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13030578
Hossameldin AA, Abdelsalam AK, Ibrahim AA, Williams BW. Enhanced Performance Modified Discontinuous PWM Technique for Three-Phase Z-Source Inverter. Energies. 2020; 13(3):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13030578
Chicago/Turabian StyleHossameldin, Ahmed A., Ahmed K. Abdelsalam, Ahmed A. Ibrahim, and Barry W. Williams. 2020. "Enhanced Performance Modified Discontinuous PWM Technique for Three-Phase Z-Source Inverter" Energies 13, no. 3: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13030578
APA StyleHossameldin, A. A., Abdelsalam, A. K., Ibrahim, A. A., & Williams, B. W. (2020). Enhanced Performance Modified Discontinuous PWM Technique for Three-Phase Z-Source Inverter. Energies, 13(3), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13030578





