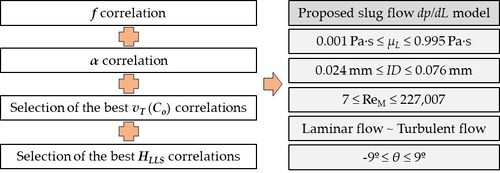
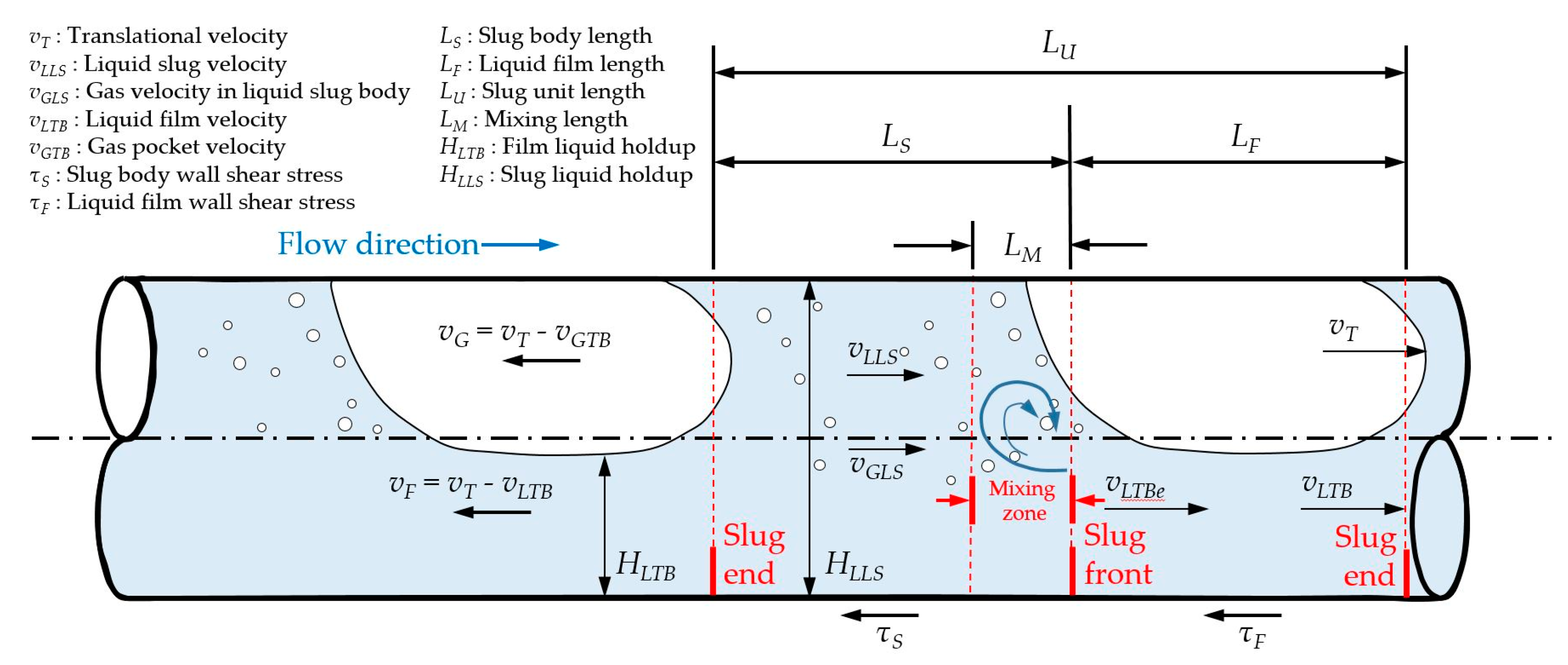
Optimization and Extended Applicability of Simplified Slug Flow Model for Liquid-Gas Flow in Horizontal and Near Horizontal Pipes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| AP | Pipe cross-sectional area, (m2) |
| Bo | Bond number, (-) |
| Co | Flow coefficient, (-) |
| d, I.D. | Pipe diameter, (m) |
| Frp | Relative performance factor, (-) |
| fS | Friction factor, (-) |
| g | Gravitational acceleration, (m/s2) |
| HL Avg. | Average liquid holdup of slug unit, (-) |
| HLLS | Slug liquid holdup, (-) |
| HLTB | Film liquid holdup, (-) |
| LF | Liquid film length, (m) |
| LM | Mixing length at liquid slug front, (m) |
| LS | Slug length, (m) |
| LU | Slug unit length, (m) |
| µL | Liquid viscosity, (Pa·s) |
| µG | Gas viscosity, (Pa·s) |
| NFr | Froude number, (-) |
| Nμ | Viscosity number, (-) |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination, (-) |
| ReM | Mixture Reynolds number, (-) |
| ρL | Liquid density, (kg/m3) |
| ρG | Gas density, (kg/m3) |
| ρS | Liquid slug body density, (kg/m3) |
| ρU | Slug unit density, (kg/m3) |
| σ | Surface tension, (N/m) |
| SF | Wetted perimeter of liquid phase (film region), (m) |
| SG | Wetted perimeter of gas phase (film region), (m) |
| τF | Liquid film wall shear stress, (Pa) |
| τS | Slug wall shear stress, (Pa) |
| τG | Gas (long bubble) wall shear stress, (Pa) |
| θ | Pipe inclination angle, (°) |
| vD | Drift velocity, (m/s) |
| vGLS | Gas bubble velocity in liquid slug body, (m/s) |
| vLLS | Liquid slug velocity, (m/s) |
| vLTB | Liquid film velocity, (m/s) |
| vM | Mixture velocity, (m/s) |
| vSL | Superficial liquid velocity, (m/s) |
| vSg | Superficial gas velocity, (m/s) |
| vT | Translational velocity, (m/s) |
| WL | Input liquid mass-flow rate, (kg/s) |
References
- Dukler, A.E.; Hubbard, M.G. A model for gas-liquid slug flow in horizontal and near horizontal tubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1975, 14, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Aydin, T.B.; Pereyra, E.; Sarica, C. Detailed flow filed measurements and analysis in highly viscous slug flow in horizontal pipes. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2018, 106, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, G.B. One-Dimensional Two-Phase Flow; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Taitel, Y.; Barnea, D. Two-phase slug flow. Adv. Heat Transf. 1990, 20, 83–112. [Google Scholar]
- Fabre, J.; Line, A. Modeling of two-phase slug flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1992, 24, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, J. Advancements of Two-Phase Slug Flow Modeling. In Proceedings of the University of Tulsa Centennial Petroleum Engineering Symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 29–31 August 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, M.J.C. Two-Phase Slug Flow Experiments with Viscous Liquids. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shoham, O. Mechanistic Modeling of Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flow in Pipes; SPE Publications: Richardson, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, R.; Pereyra, E.; Sarica, C.; Torres, C. A simplified slug flow model for highly viscous oil-gas flow in horizontal pipes. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 September–2 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gokcal, B. An Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of Slug Flow for High Oil Viscosity in Horizontal Pipes. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, R. Effect of Medium Oil Viscosity on Two-Phase Oil-Gas Flow Behavior in Horizontal Pipes. Master’s Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kora, C. Effects of High Oil Viscosity on Slug Liquid Holdup in Horizontal Pipes. Master’s Thesis, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T. Detailed Flow Field Analysis of Air and Highly Viscous Liquid Slug Flow in Horizontal Pipes. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kiger, K.T.; Duncan, J.H. Air-Entrainment Mechanisms in Plunging Jets and Breaking Waves. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2012, 44, 563–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, S.; Rensen, J.; Guet, S. Bubble Aspect Ratio and Velocity Measurement Using a Four-Point Fiber-Optical Probe. Exp. Fluids 2004, 36, 326–333. [Google Scholar]
- Cieslinski, J.T.; Mosdorf, R. Gas Bubble Dynamics-Experiment and Fractal Analysis. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 2005, 48, 1808–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Onodera, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Sussman, M. Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulations of a Rising Bubble in a Viscoelastic FENE-CR Model Fluid. AIP Conf. Proc. 2008, 1027, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Han, M.; Sha, Z.; Wang, J. Effect of Liquid Viscosity on Hydrodynamics and Bubble Behaviour of an External-Loop Airlift Reactor. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 91, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunner, B.; Tryggvason, G. Effect of Bubble Deformation on the Properties of Bubbly Flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2003, 495, 77–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Tryggvason, G. Effect of Bubble Deformability in Turbulent Bubbly Upflow in a Vertical Channel. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 040701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegenhein, T.; Lucas, D. Observations on Bubble Shapes in Bubble Columns under Different Flow Conditions. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2017, 85, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, G.A.; Nicholson, M.K.; Aziz, K. Correlation of the liquid volume fraction in the slug for horizontal gas-liquid slug flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1978, 4, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreussi, P.; Bendiksen, K. An investigation of void fraction in liquid slugs for horizontal and inclined gas-liquid pipe flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1989, 15, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felizola, H. Slug Flow in Extended Reach Directional Wells. Master’s Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul-Majeed, G.H. Liquid slug holdup in horizontal and slightly inclined two-phase slug flow. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2000, 27, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcano, R. Slug Characteristics for Two-Phase Horizontal Flow. Master’s Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T. On the Analysis of High Viscous Horizontal Slug Flow Characteristics by Changing Pipe Diameter. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ekinci, S. Pipe Inclination Effects on Slug Flow Characteristics of High Viscosity Oil-Gas Two-Phase Flow. Master’s Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, H. An Experiments Study of Inclined Two-Phase Flow. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kokal, S.S. An Experimental Study of Two Phase Flow in Inclined Pipes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Gokcal, B. Effects of High Oil Viscosity on Two-Phase Oil-Gas Flow Behavior in Horizontal Pipes. Master’s Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Al-safran, E.; Gokcal, B.; Sarica, C. Analysis and prediction of heavy oil two-phase slug length in horizontal pipes. In Proceedings of the SPE Heavy Oil Conference and Exhibition, Kuwait City, Kuwait, 12–14 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, J.R.; Hewitt, G.F. A Thermodynamic Non-Equilibrium Slug Flow Model. J. Heat Transf. 2005, 127, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Perez, H.; Kim, T.W.; Pereyra, E.; Ratkovich, N. CFD Modeling of Air and Highly Viscous Liquid Two-Phase Slug Flow in Horizontal Pipes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 136, 638–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.; Garcia, R.; Padrino, J.C.; Mata, C.; Trallero, J.L.; Joseph, D.D. Power law and composite power law friction factor correlations for laminar and turbulent gas-liquid flow in horizontal pipelines. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2003, 29, 1605–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Pereyra, E.; Sarica, C.; Park, C.; Kang, J.M. An efficient drift flux closure relationship to estimate liquid holdups of gas-liquid two phase flow in pipes. Energies 2012, 5, 5294–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldesemayat, M.A.; Ghajar, A.J. Comparison of void fraction correlations for different flow patterns in horizontal and upward inclined pipes. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2007, 33, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, P.; Macian, R. A study of the performance of void fraction correlations used in the context of drift-flux two-phase flow model. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2002, 215, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumazeilles, P. An Experimental Study of Downward Slug Flow in Inclined Pipes. Master’s Thesis, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mishima, K.; Hibiki, T. Some characteristics of air-water two-phase flow in small diameter vertical tubes. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1996, 22, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petalas, N.; Aziz, K. A mechanistic model for multiphase flow in pipes. J. Can. Petrol. Technol. 2000, 39, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibiki, T.; Ishii, M. One-dimensional drift-flux model for two-phase flow in a large diameter pipe. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 46, 1773–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, L.E.; Shoham, O.; Schmidt, Z.; Chokshi, R.N.; Northug, T. Unified mechanistic model for steady-state two-phase flow: Horizontal to vertical upward flow. SPE J. 2000, 5, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Safran, E. Prediction of slug liquid holdup in horizontal pipes. J. Energ. Resour. ASME 2009, 131, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
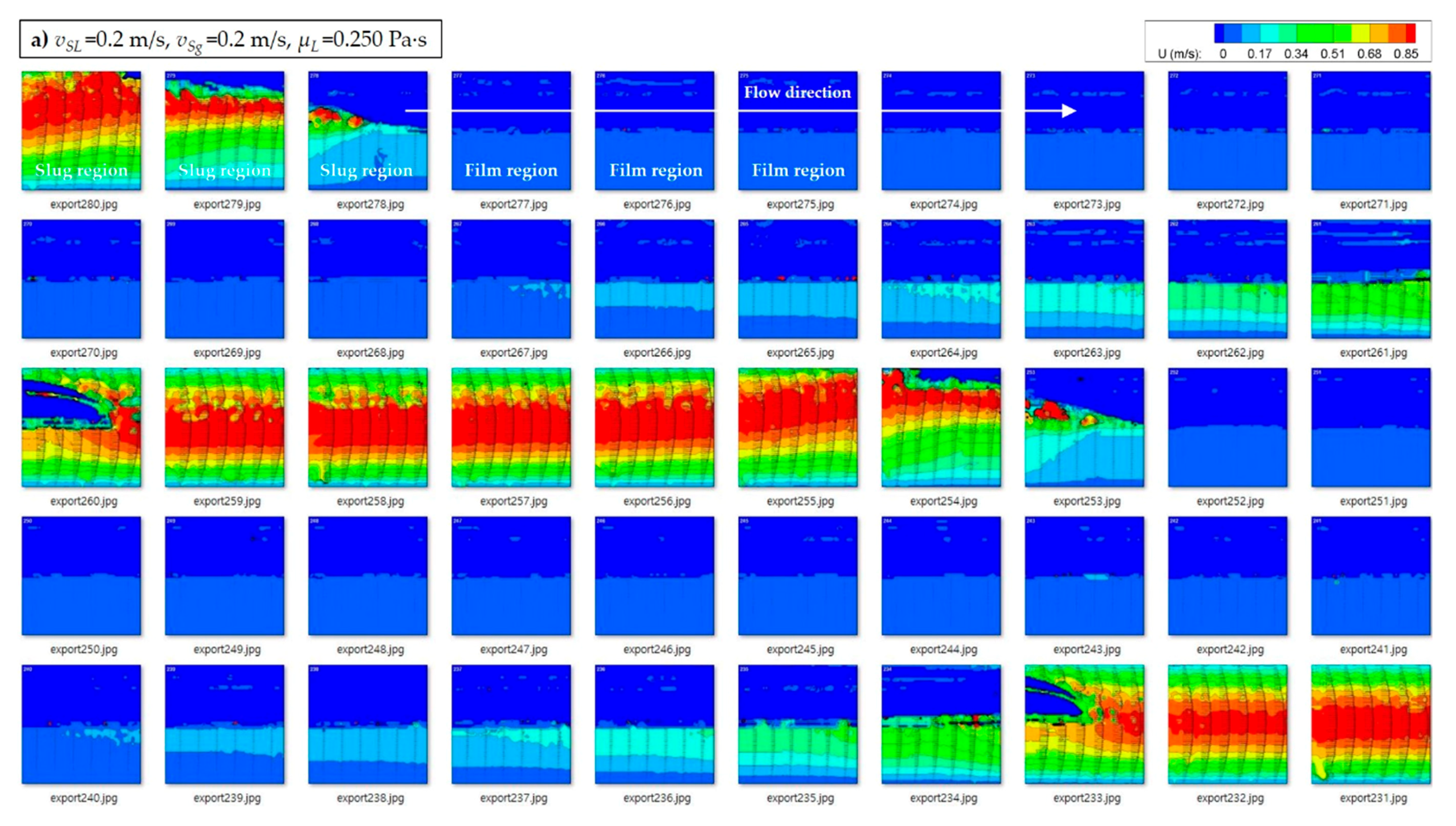

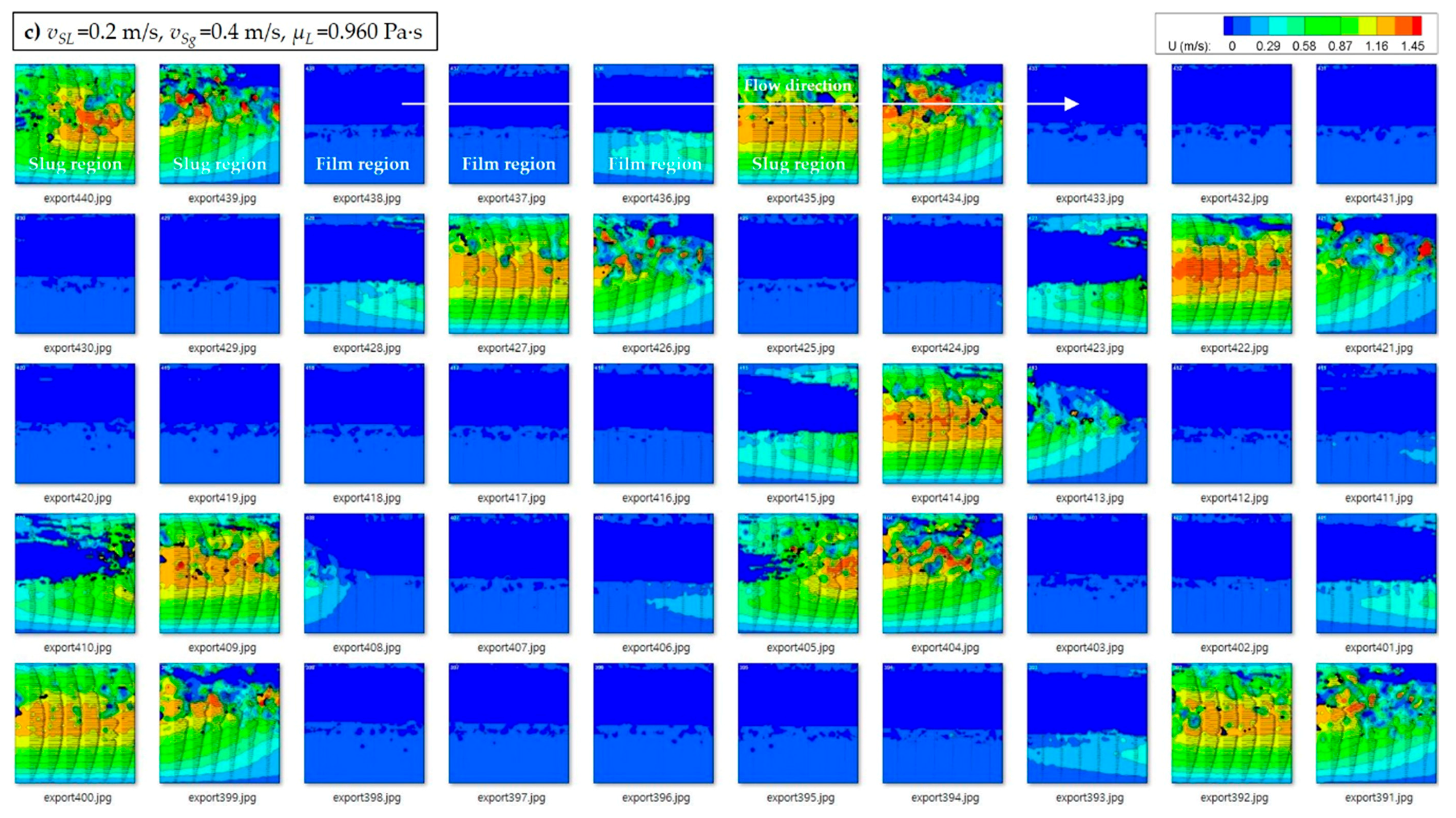
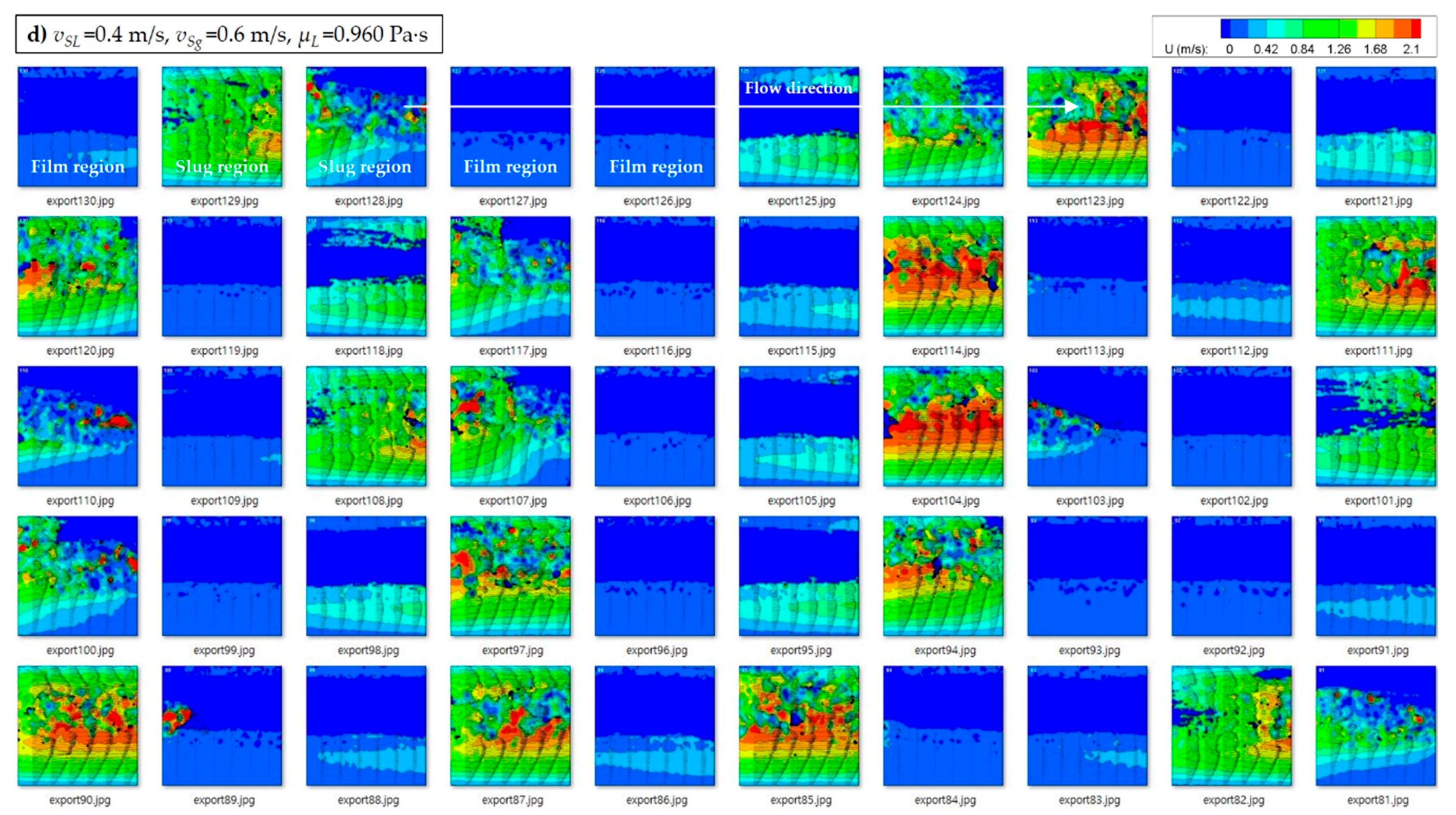
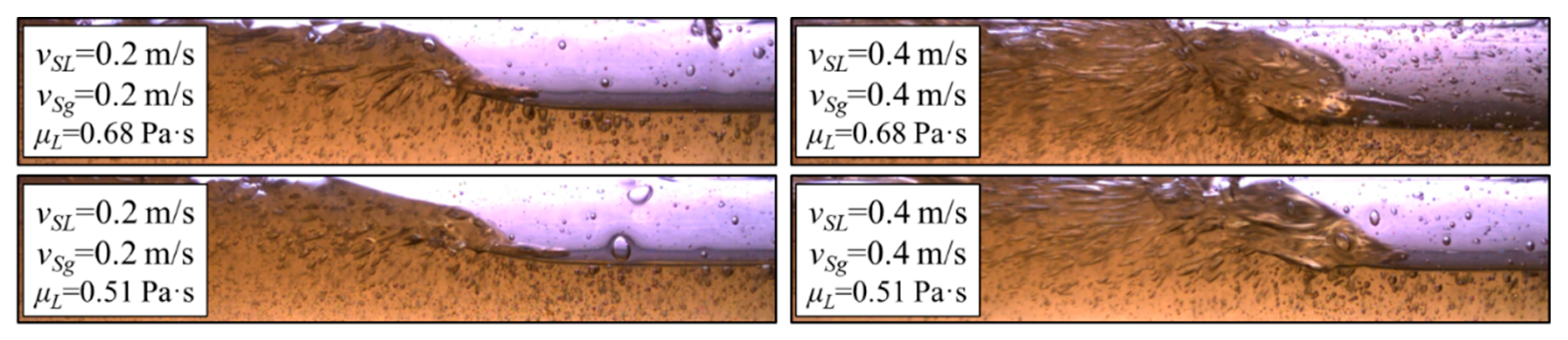
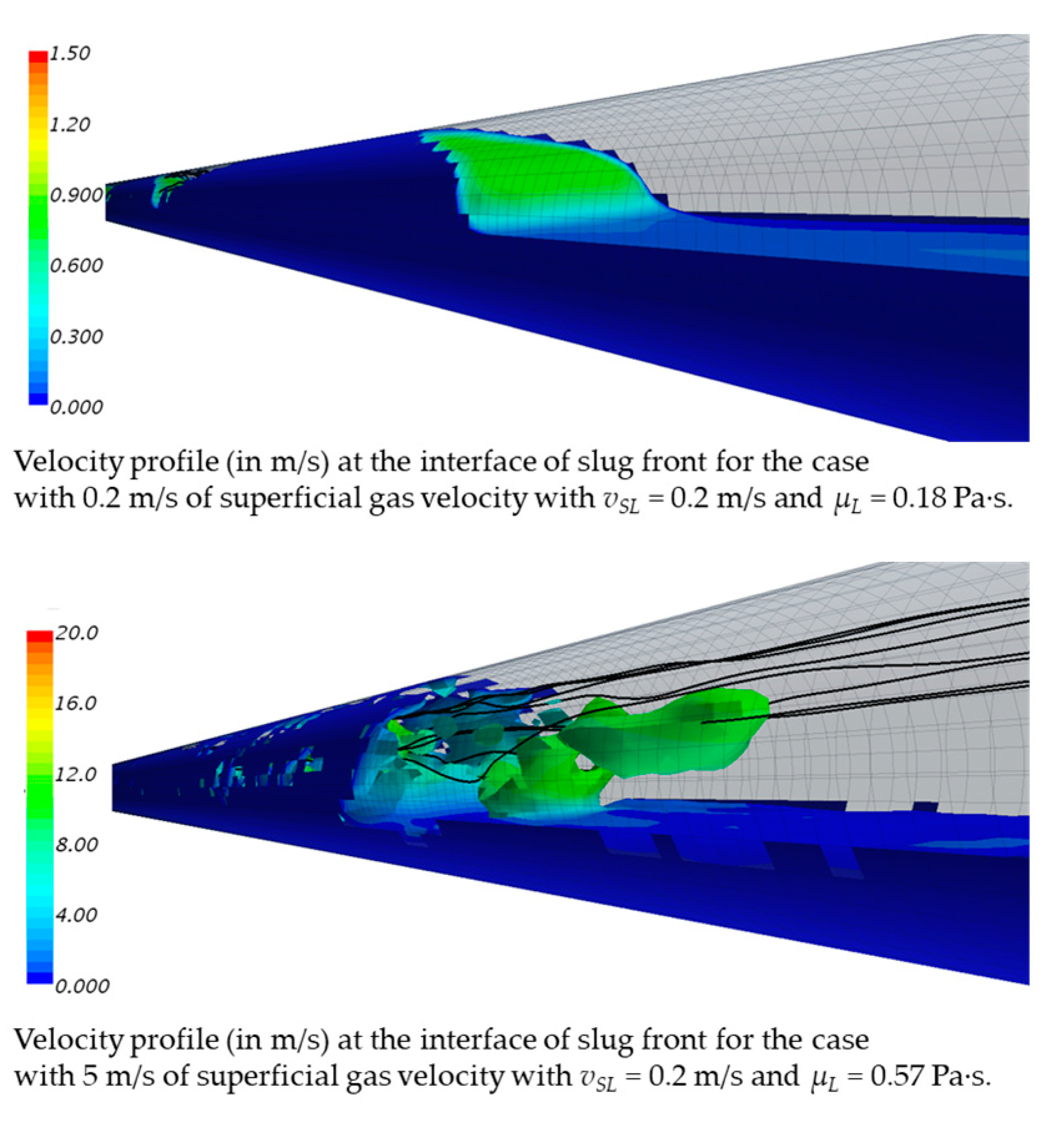
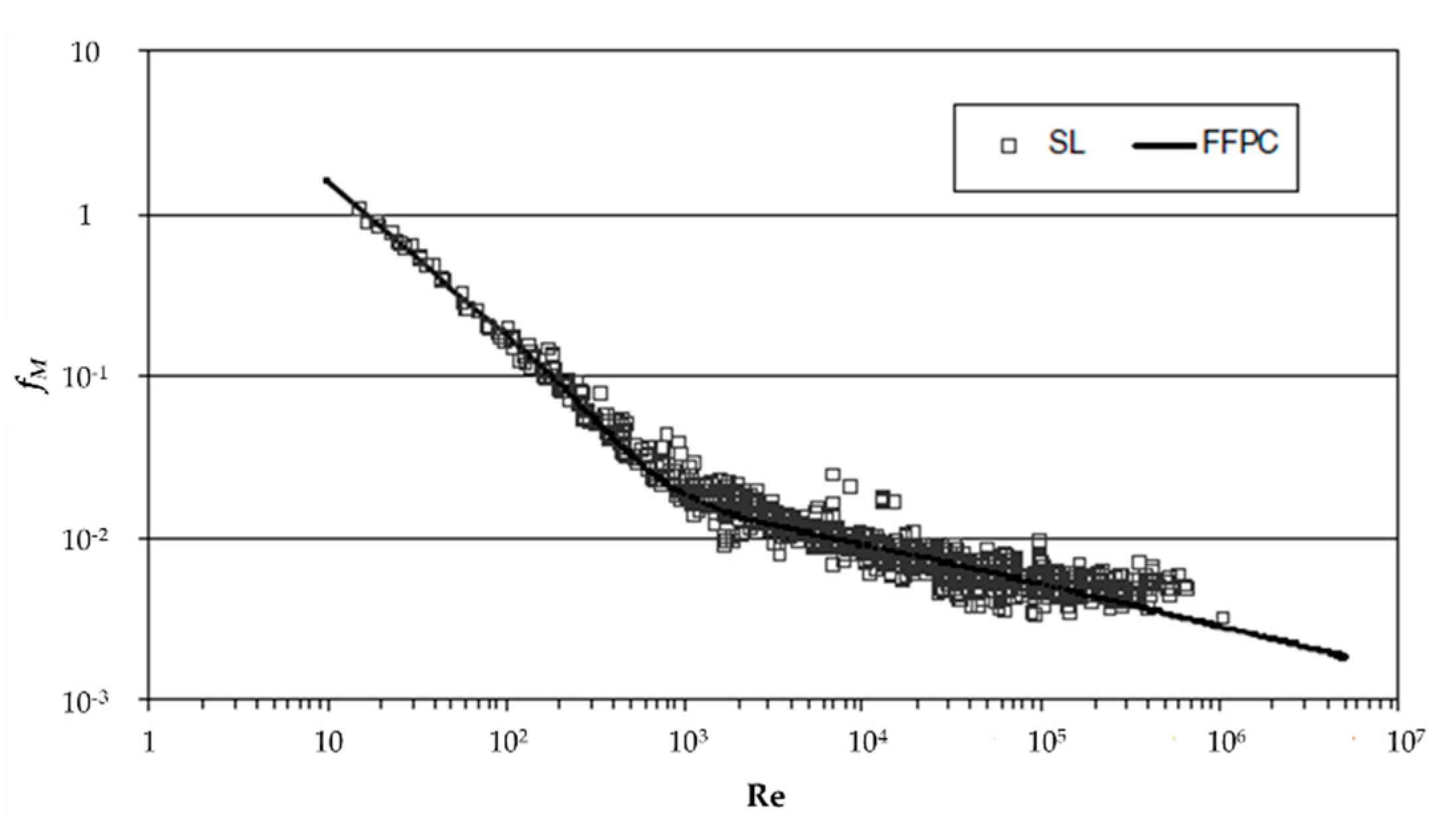

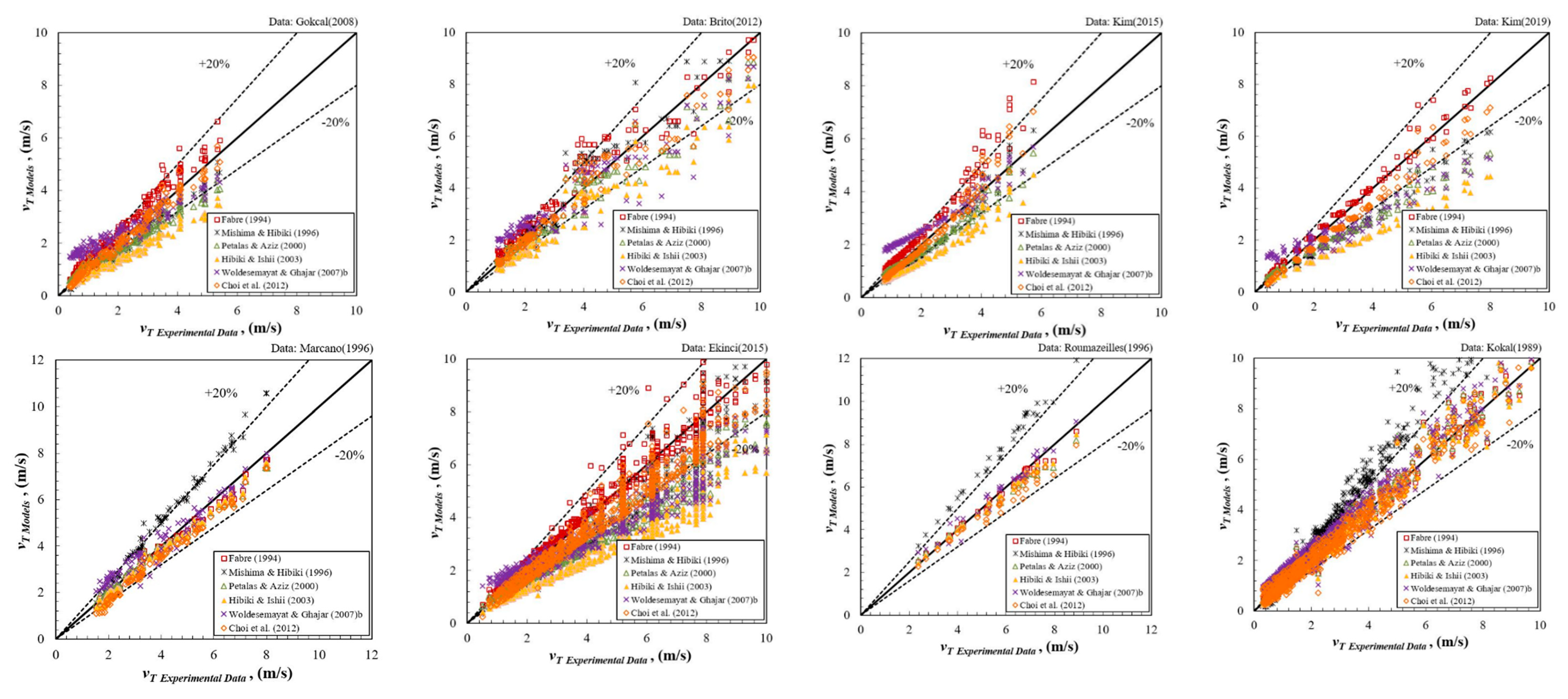
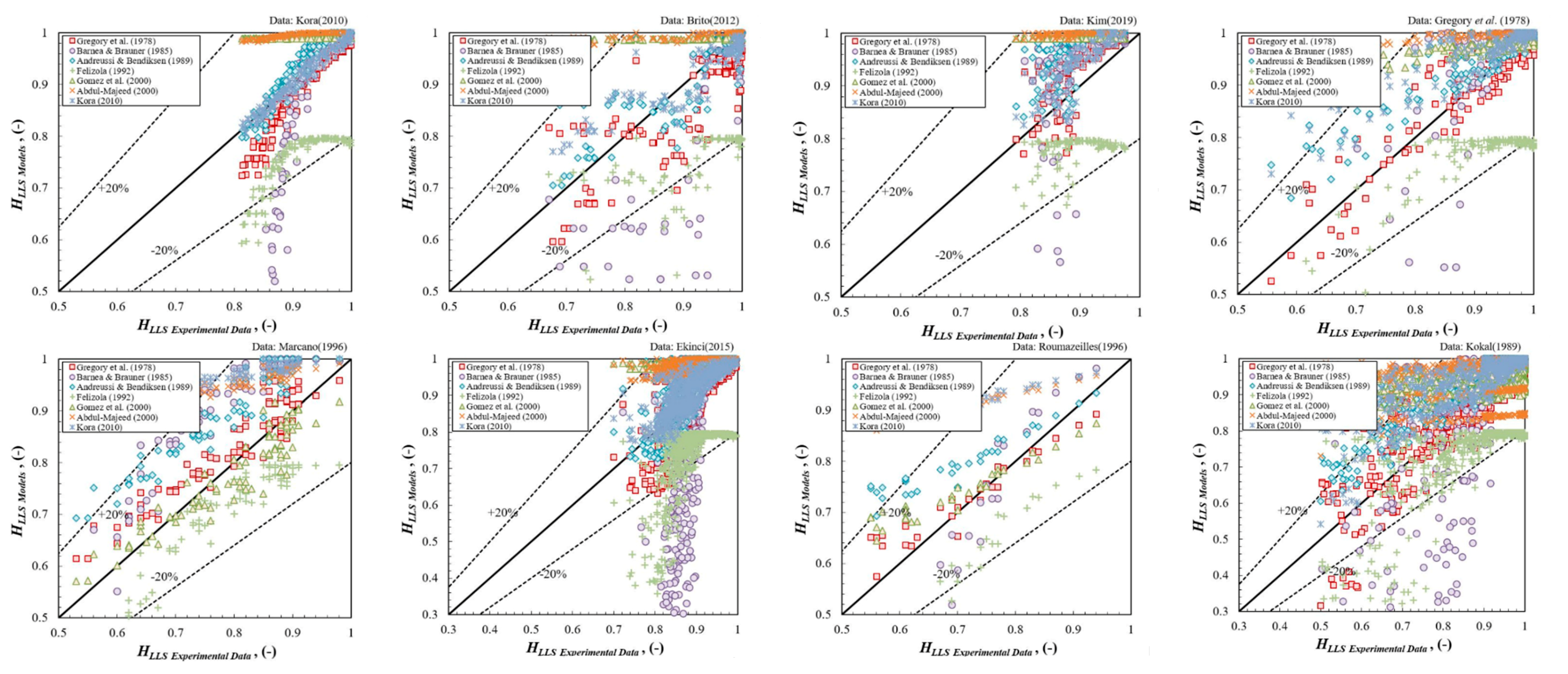
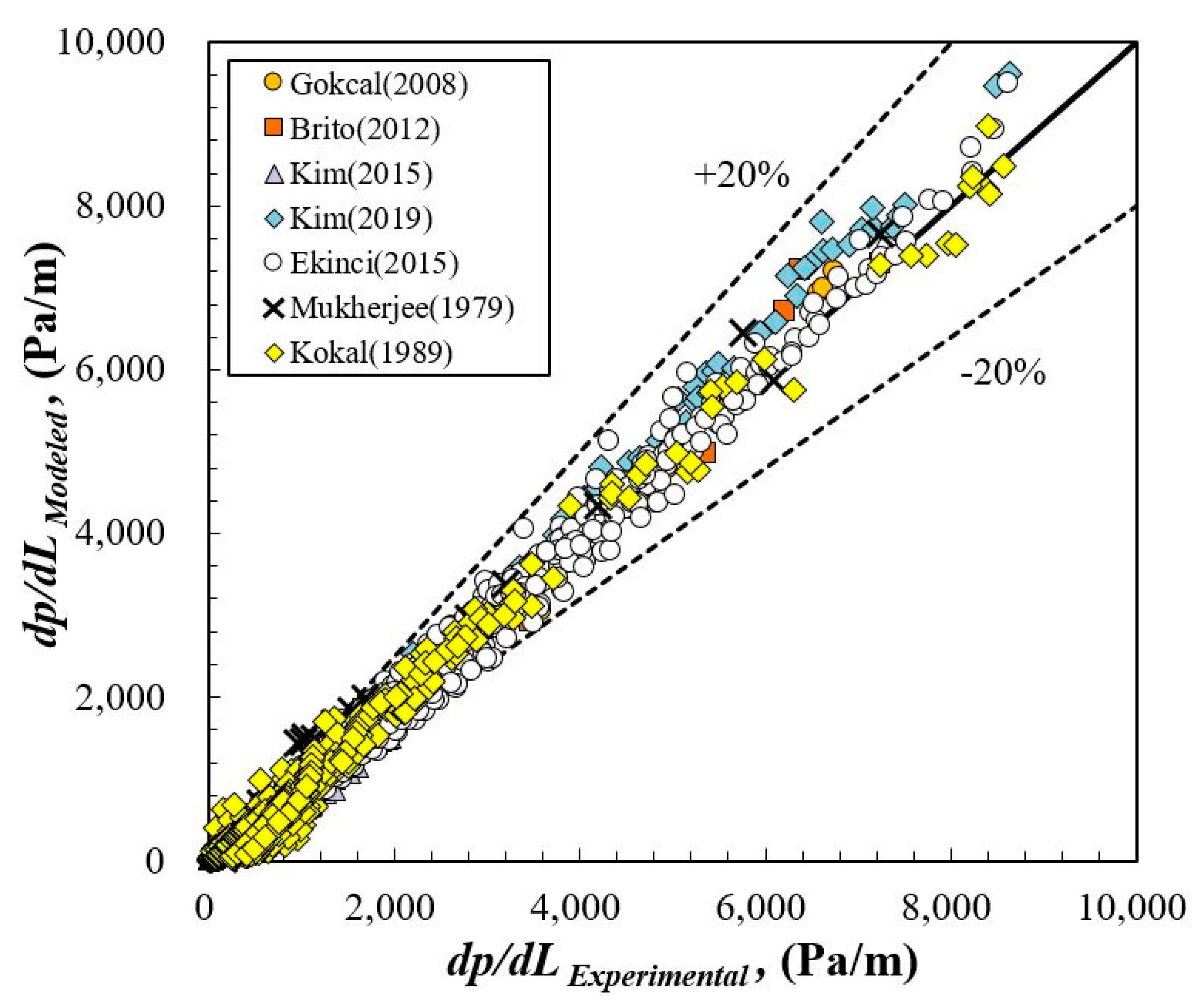
| Data Source | Fluid Types | No. of Data | I.D. | θ | vSL | vSg | ρL | ρG | μL | μG | σ | ReM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [m] | [º] | [m/s] | [m/s] | [kg/m3] | [kg/m3] | [Pa∙s] | [Pa∙s] | [N/m] | [-] | |||
| Gokcal [10] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 170 | 0.0508 | 0 | 0.05~0.80 | 0.10~2.17 | 872~885 | 1.12~2.08 | 0.178~0.601 | 0.000018 | 0.031 | 11~671 |
| Brito [11] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (medium and heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 126 | 0.0508 | 0 | 0.05~2.96 | 0.10~6.23 | 857~870 | 1.20~2.50 | 0.039~0.166 | 0.000010 | 0.031 | 148~1866 |
| Kim [27] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 485 | 0.0720 | 0 | 0.02~0.36 | 0.11~3.62 | 871~ 884 | 1.12~1.35 | 0.147~0.619 | 0.000010 | 0.033 | 30~1159 |
| Kim [13] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 107 | 0.0508 | 0 | 0.10~1.00 | 0.03~3.01 | 838~854 | 1.25~3.04 | 0.245~0.995 | 0.000010 | 0.033 | 7~312 |
| Marcano [26] | Liquid phase: Kerosene Gas phase: Air | 83 | 0.0780 | 0 | 0.14~2.07 | 0.45~6.00 | 808~819 | 2.07~6.38 | 0.002 | 0.000019 | 0.030 | 30,182~217,598 |
| Ekinci [28] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 584 | 0.0508 | −2, +2 | 0.10~0.80 | 0.10~5.14 | 871~884 | 1.21~2.78 | 0.153~0.614 | 0.000010 | 0.030 | 21~1742 |
| Roumazeilles [39] | Liquid phase: Kerosene Gas phase: Air | 33 | 0.0508 | −10~0 | 0.88~2.44 | 0.98~6.10 | 802~810 | 1.94~2.58 | 0.0015 | 0.000019 | 0.028 | 49,595~169,117 |
| Kokal [30] | Liquid phase: Light oil Gas phase: Air | 690 | 0.0258, 0.0512, 0.0763 | −9~+9 | 0.03~3.05 | 0.05~14.20 | 858 | 3.00 | 0.007 | 0.000018 | 0.031 | 364~70,419 |
| Correlation | Yr. | Flow Coefficient, Co, Correlation | Drift Velocity, vD, Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fabre [6] | 1994 | ||
| Mishima & Hibiki [40] | 1996 | ||
| Petalas & Aziz [41] | 2000 | ; | |
| Hibiki & Ishii [42] | 2003 | ||
| Woldesemayat & Ghajar [37] | 2007b | ||
| Choi et al. [36] | 2012 |
| Data Source | Fluid Types | No. of Data | I.D. | θ | vSL | vSg | ρL | ρG | μL | μG | σ | ReM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [m] | [º] | [m/s] | [m/s] | [kg/m3] | [kg/m3] | [Pa∙s] | [Pa∙s] | [N/m] | [-] | |||
| Kora [12] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 144 | 0.0508 | 0 | 0.10~0.82 | 0.10~3.51 | 880~888 | 1.28~3.49 | 0.179~0.601 | 0.000018 | 0.031 | 16~1047 |
| Brito [11] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (medium and heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 126 | 0.0508 | 0 | 0.05~2.96 | 0.10~6.23 | 857~870 | 1.20~2.50 | 0.039~0.166 | 0.000010 | 0.031 | 148~1,866 |
| Kim [13] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 107 | 0.0508 | 0 | 0.10~1.00 | 0.03~3.01 | 838~854 | 1.25~3.04 | 0.245~0.995 | 0.000010 | 0.033 | 7~312 |
| Gregory et al. [22] | Liquid phase: Light oil Gas phase: Air | 149 | 0.0258, 0.0512 | 0 | 0.03~2.32 | 0.05~6.05 | 858 | 1.25 | 0.007 | 0.000010 | 0.030 | 387~45,342 |
| Marcano [26] | Liquid phase: Kerosene Gas phase: Air | 83 | 0.0780 | 0 | 0.14~2.07 | 0.45~6.00 | 808~819 | 2.07~6.38 | 0.002 | 0.000019 | 0.030 | 30,182~217,598 |
| Ekinci [28] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 584 | 0.0508 | −2, +2 | 0.10~0.80 | 0.10~5.14 | 871~884 | 1.21~2.78 | 0.153~0.614 | 0.000010 | 0.030 | 21~1,742 |
| Roumazeilles [39] | Liquid phase: Kerosene Gas phase: Air | 33 | 0.0508 | −10~0 | 0.88~2.44 | 0.98~6.10 | 802~810 | 1.94~2.58 | 0.0015 | 0.000019 | 0.028 | 49,595~169,117 |
| Kokal [30] | Liquid phase: Light oil Gas phase: Air | 690 | 0.0258, 0.0512, 0.0763 | −9~+9 | 0.03~3.05 | 0.05~14.20 | 858 | 3.00 | 0.007 | 0.000018 | 0.031 | 364~70,419 |
| Correlation | Yr. | Slug Liquid Holdup, HLLS, Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| Gregory et al. [22] | 1978 | |
| Andreussi & Bendiksen [23] | 1989 | ; ; , |
| Felizola [24] | 1992 | |
| Gomez et al. [43] | 2000 | ; ; in radians |
| Abdul-Majeed [25] | 2000 | ; ; |
| Kora [12] | 2010 | ; ; |
| Data Source | Yr. | No. of Data | Best Correlation | ε1 | ε2 | ε3 | ε4 | ε5 | ε6 | Frp | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (m/s) | (m/s) | (m/s) | (-) | (-) | ||||
| Gokcal [10] | 2008 | 170 | Choi et al. [36] | −0.40 | 7.96 | 11.05 | −0.0373 | 0.1453 | 0.1982 | 0.08 | 0.975 |
| Brito [11] | 2012 | 126 | Mishima & Hibiki [40] | 1.65 | 12.30 | 15.03 | 0.1601 | 0.4448 | 0.6049 | 1.09 | 0.947 |
| Kim [27] | 2015 | 485 | Choi et al. [36] | −5.12 | 9.68 | 10.17 | −0.0519 | 0.2393 | 0.3265 | 0.48 | 0.951 |
| Kim [13] | 2019 | 107 | Choi et al. [36] | 11.39 | 11.74 | 11.54 | 0.1978 | 0.2186 | 0.2485 | 0.56 | 0.974 |
| Marcano [26] | 1996 | 83 | Fabre [6] | −4.55 | 5.42 | 5.00 | −0.1815 | 0.2070 | 0.1886 | 0.39 | 0.974 |
| Ekinci [28] | 2015 | 584 | Fabre [6] | 7.17 | 9.47 | 10.59 | 0.1664 | 0.3355 | 0.4530 | 0.49 | 0.959 |
| Roumazeilles [39] | 1996 | 33 | Fabre [6] | −1.21 | 3.30 | 3.87 | −0.1131 | 0.1880 | 0.2189 | 0.19 | 0.972 |
| Kokal [30] | 1989 | 690 | Choi et al. [36] | 4.54 | 15.80 | 25.35 | 0.0133 | 0.2639 | 0.3855 | 1.21 | 0.974 |
| Data Source | Yr. | No. of Data | Best Correlation | ε1 | ε2 | ε3 | ε4 | ε5 | ε6 | Frp | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (-) | ||||
| Kora [12] | 2010 | 144 | Kora [12] | −0.07 | 0.82 | 1.03 | −0.0007 | 0.0075 | 0.0094 | 0.00 | 0.971 |
| Brito [11] | 2012 | 126 | Gregory et al. [22] | −4.35 | 6.34 | 6.65 | −0.0407 | 0.0554 | 0.0541 | 0.65 | 0.728 |
| Kim [13] | 2019 | 107 | Gregory et al. [22] | 3.76 | 5.12 | 4.42 | 0.0336 | 0.0455 | 0.0382 | 0.57 | 0.637 |
| Gregory et al. [22] | 1978 | 149 | Gregory et al. [22] | 0.53 | 3.52 | 5.27 | 0.0026 | 0.0287 | 0.0403 | 0.00 | 0.872 |
| Marcano [26] | 1996 | 83 | Gomez et al. [43] | −1.98 | 4.14 | 4.82 | −0.0186 | 0.0330 | 0.0377 | 0.12 | 0.826 |
| Ekinci [28] | 2015 | 584 | Gregory et al. [22] | −1.31 | 5.38 | 7.20 | −0.0106 | 0.0459 | 0.0603 | 0.42 | 0.681 |
| Roumazeilles [39] | 1996 | 33 | Gregory et al. [22] | 3.53 | 5.82 | 7.15 | 0.0186 | 0.0369 | 0.0439 | 0.00 | 0.734 |
| Kokal [30] | 1989 | 690 | Gregory et al. [22] | 1.07 | 5.36 | 9.88 | 0.0049 | 0.0396 | 0.0638 | 0.00 | 0.780 |
| Data Source | Fluid Types | No. of Data | I.D. | θ | vSL | vSg | ρL | μL | ReM | Co Correlation | HLLS Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [m] | [º] | [m/s] | [m/s] | [kg/m3] | [Pa∙s] | [-] | |||||
| Gokcal [10] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 170 | 0.0508 | 0 | 0.05~0.80 | 0.10~2.17 | 872~885 | 0.178~0.601 | 11~671 | Choi et al. [36] | Gregory et al. [22] |
| Brito [11] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (medium and heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 126 | 0.0508 | 0 | 0.05~2.96 | 0.10~6.23 | 857~870 | 0.039~0.166 | 148~1866 | Mishima & Hibiki [40] | Gregory et al. [22] |
| Kim [27] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 485 | 0.0720 | 0 | 0.02~0.36 | 0.11~3.62 | 871~884 | 0.147~0.619 | 30~1159 | Choi et al. [36] | Gregory et al. [22] |
| Kim [13] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 107 | 0.0508 | 0 | 0.10~1.00 | 0.03~3.01 | 838~854 | 0.245~0.995 | 7~312 | Choi et al. [36] | Gregory et al. [22] |
| Ekinci [28] | Liquid phase: Synthetic (heavy) oil Gas phase: Air | 584 | 0.0508 | −2, +2 | 0.10~0.80 | 0.10~5.14 | 871~884 | 0.153~0.614 | 21~1742 | Fabre [6] | Gregory et al. [22] |
| Mukherjee [29] | Liquid phase: Kerosene Gas phase: Air | 29 | 0.0240, 0.0350 | 0 | 0.03~3.40 | 0.28~6.76 | 786~858 | 0.001~0.045 | 351~227007 | Fabre [6] | Gomez et al. [43] |
| Kokal [30] | Liquid phase: Light oil Gas phase: Air | 690 | 0.0258, 0.0512, 0.0763 | −9~+9 | 0.03~3.05 | 0.05~14.20 | 858 | 0.007 | 364~70,419 | Choi et al. [36] | Gregory et al. [22] |
| Data Source | Yr. | No. of Data | ε1 | ε2 | ε3 | ε4 | ε5 | ε6 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (Pa/m) | (Pa/m) | (Pa/m) | (-) | |||
| Gokcal [10] | 2008 | 170 | −3.41 | 5.49 | 7.01 | −27.6606 | 74.2059 | 122.9432 | 0.992 |
| Brito [11] | 2012 | 126 | −16.08 | 17.08 | 11.48 | −86.0896 | 118.3163 | 158.4460 | 0.982 |
| Kim [27] | 2015 | 485 | −9.28 | 16.83 | 20.82 | −77.7965 | 81.5857 | 93.7674 | 0.880 |
| Kim [13] | 2019 | 107 | 7.37 | 7.38 | 5.27 | 270.9229 | 271.1362 | 259.4484 | 0.976 |
| Ekinci [28] | 2015 | 584 | −3.14 | 7.42 | 9.54 | −53.5043 | 146.2949 | 194.3485 | 0.988 |
| Mukherjee [29] | 1979 | 29 | 4.90 | 21.74 | 29.21 | 136.8585 | 214.8965 | 238.6554 | 0.981 |
| Kokal [30] | 1989 | 690 | 2.05 | 13.06 | 25.79 | −15.2850 | 61.5354 | 96.9182 | 0.994 |
| Total | 2191 | −3.01 | 11.87 | 19.64 | −28.3507 | 105.0804 | 165.0222 | 0.991 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.-W.; Woo, N.-S.; Han, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-J. Optimization and Extended Applicability of Simplified Slug Flow Model for Liquid-Gas Flow in Horizontal and Near Horizontal Pipes. Energies 2020, 13, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040842
Kim T-W, Woo N-S, Han S-M, Kim Y-J. Optimization and Extended Applicability of Simplified Slug Flow Model for Liquid-Gas Flow in Horizontal and Near Horizontal Pipes. Energies. 2020; 13(4):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040842
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tea-Woo, Nam-Sub Woo, Sang-Mok Han, and Young-Ju Kim. 2020. "Optimization and Extended Applicability of Simplified Slug Flow Model for Liquid-Gas Flow in Horizontal and Near Horizontal Pipes" Energies 13, no. 4: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040842
APA StyleKim, T.-W., Woo, N.-S., Han, S.-M., & Kim, Y.-J. (2020). Optimization and Extended Applicability of Simplified Slug Flow Model for Liquid-Gas Flow in Horizontal and Near Horizontal Pipes. Energies, 13(4), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040842