Methodology of Excavator System Energy Flow-Down
Abstract
:1. Introduction
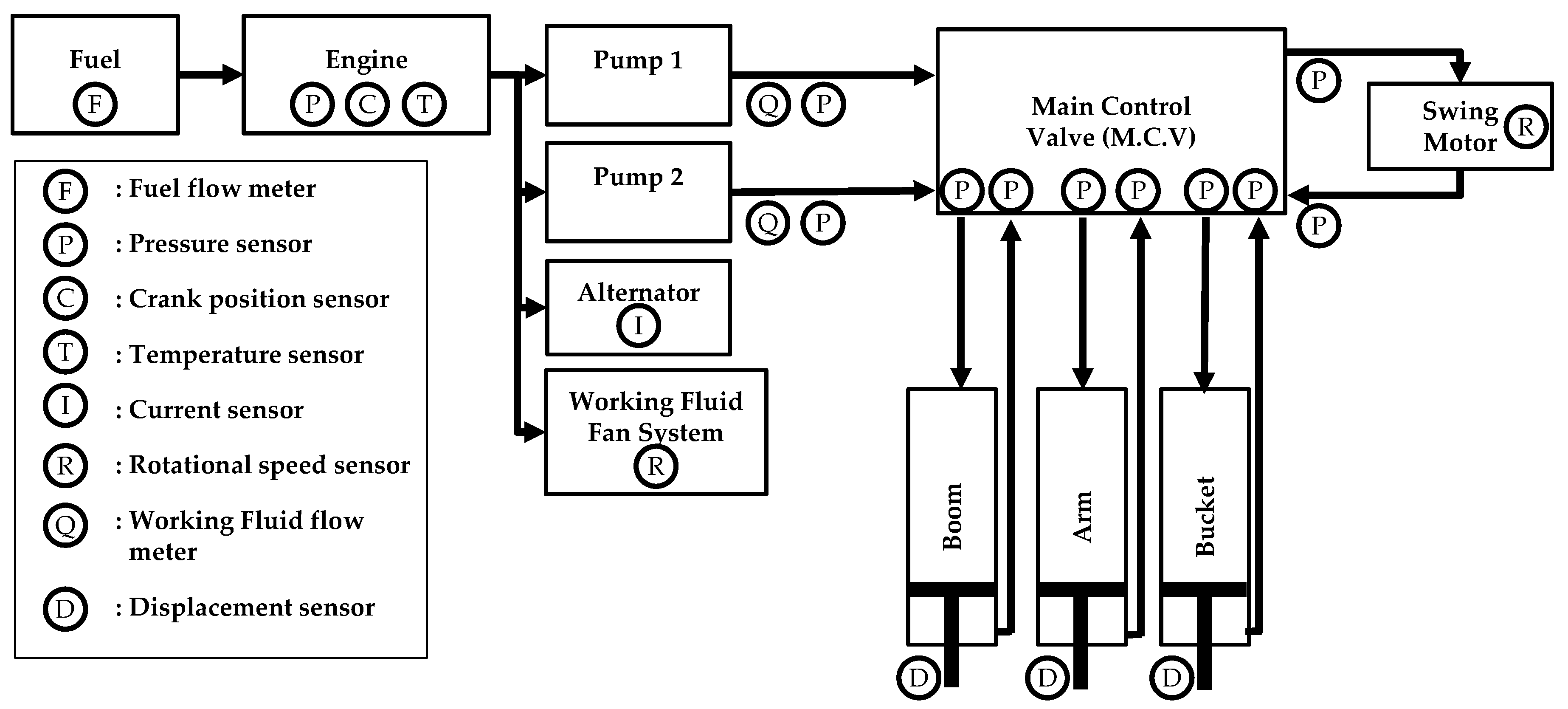
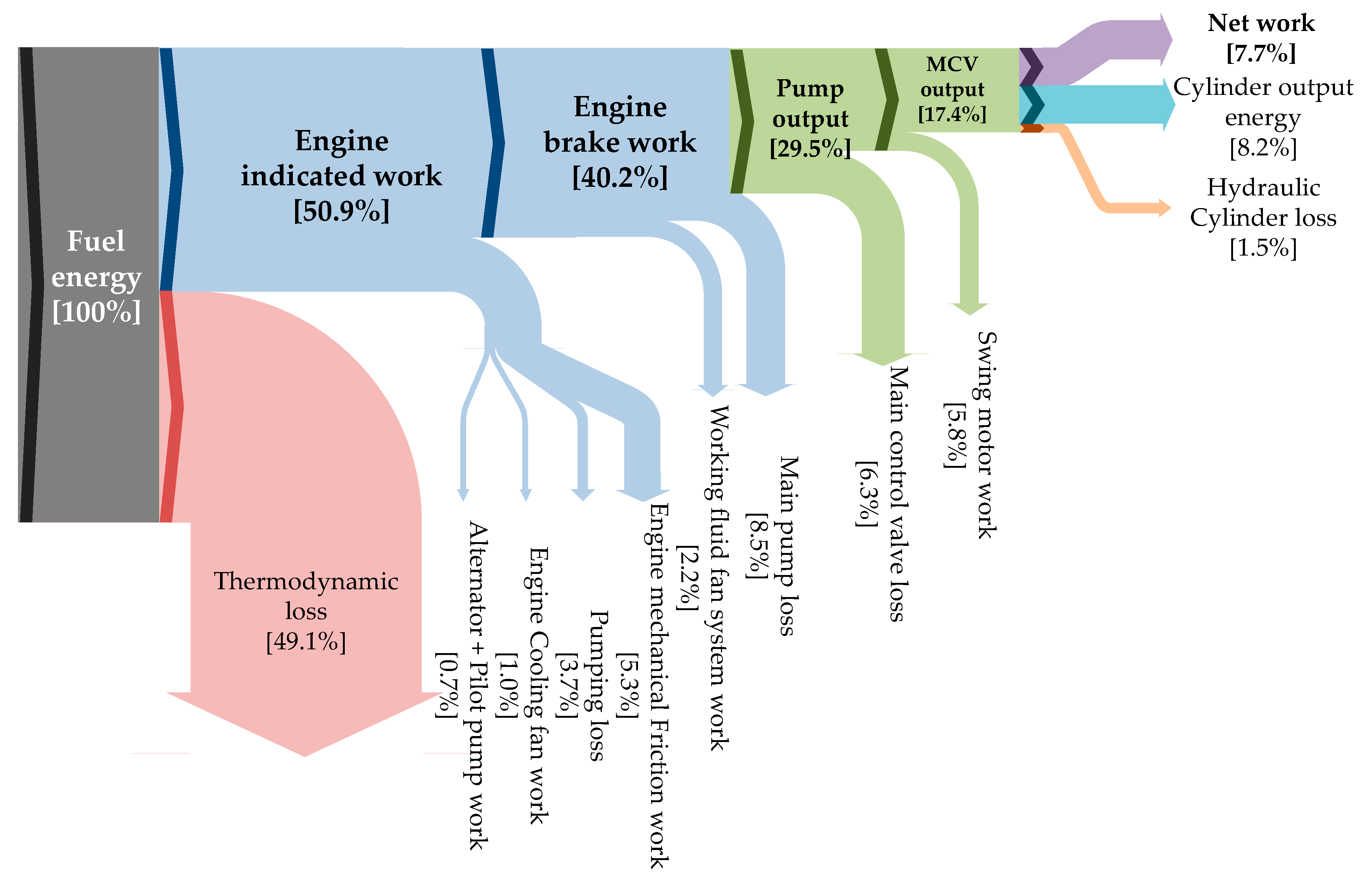
2. Excavator System Energy Flow
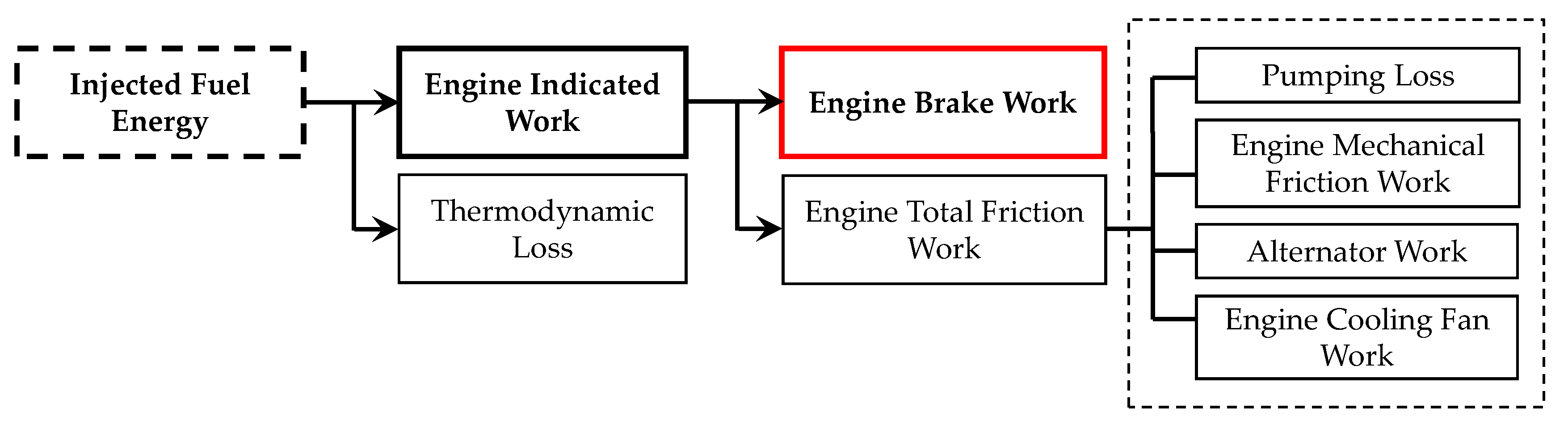
2.1. Energy Flow Model in the Engine System
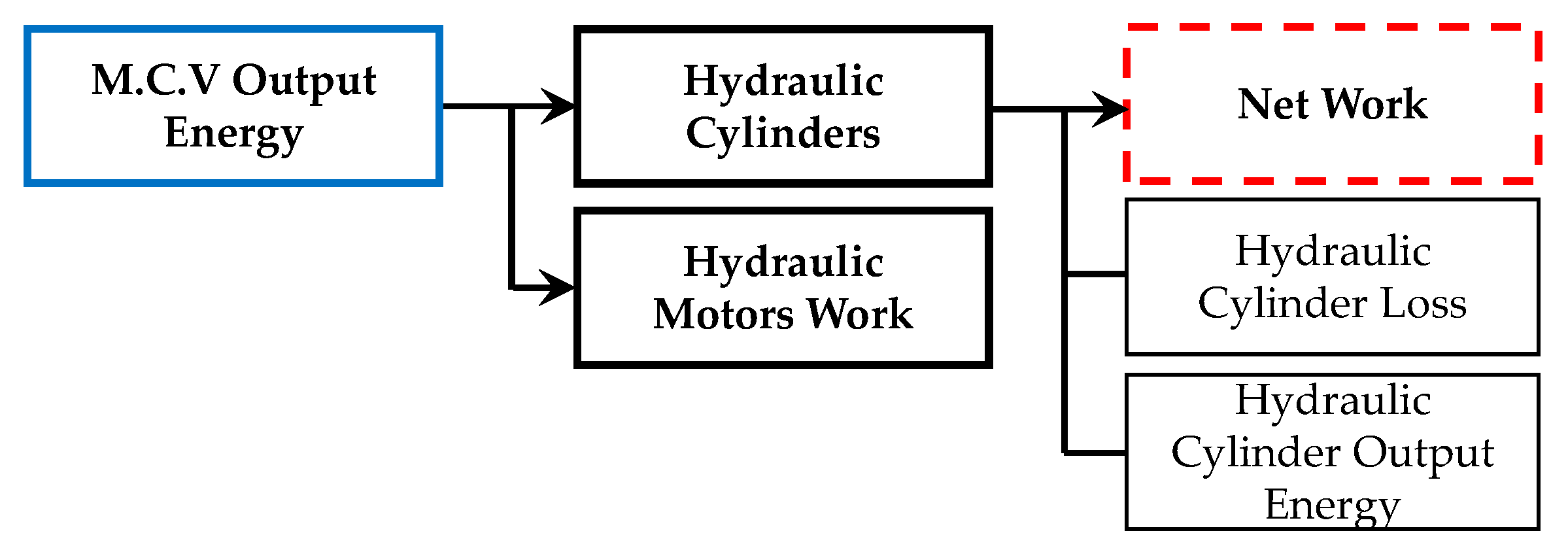
2.2. Energy Flow Model in the Hydraulic System
2.3. Energy Flow Model in the Hydraulic Actuation System
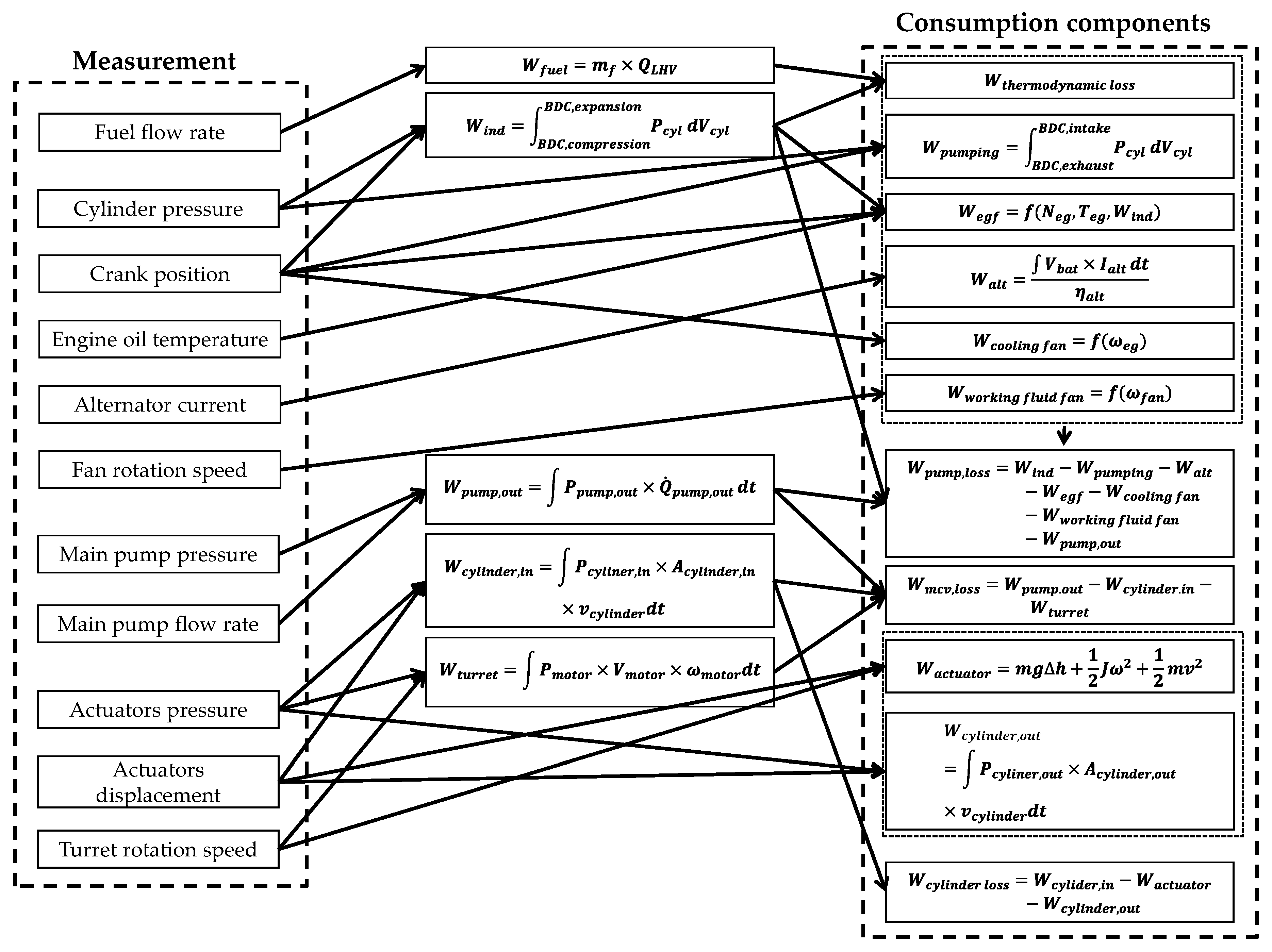
3. Modeling of Energy Consumption Component
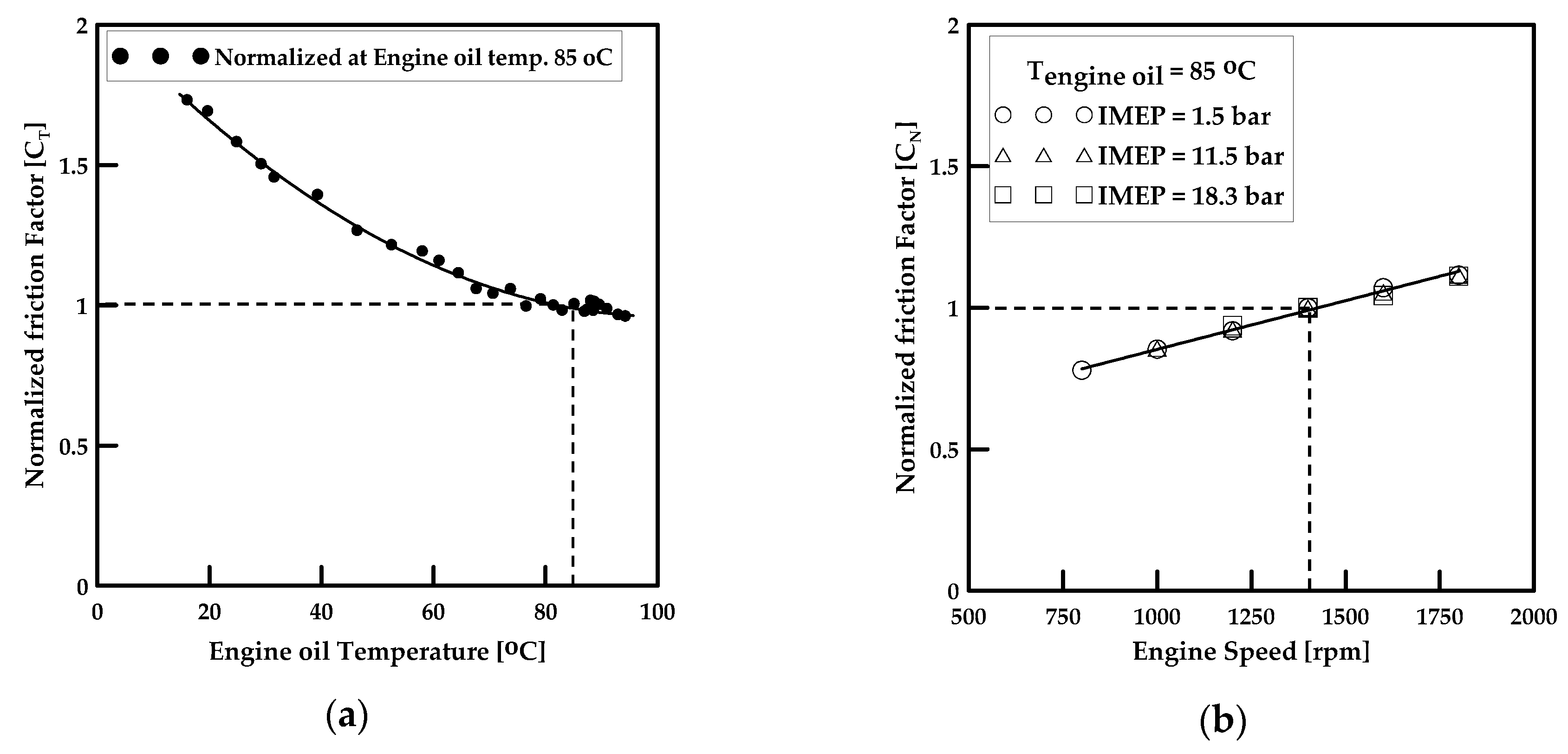
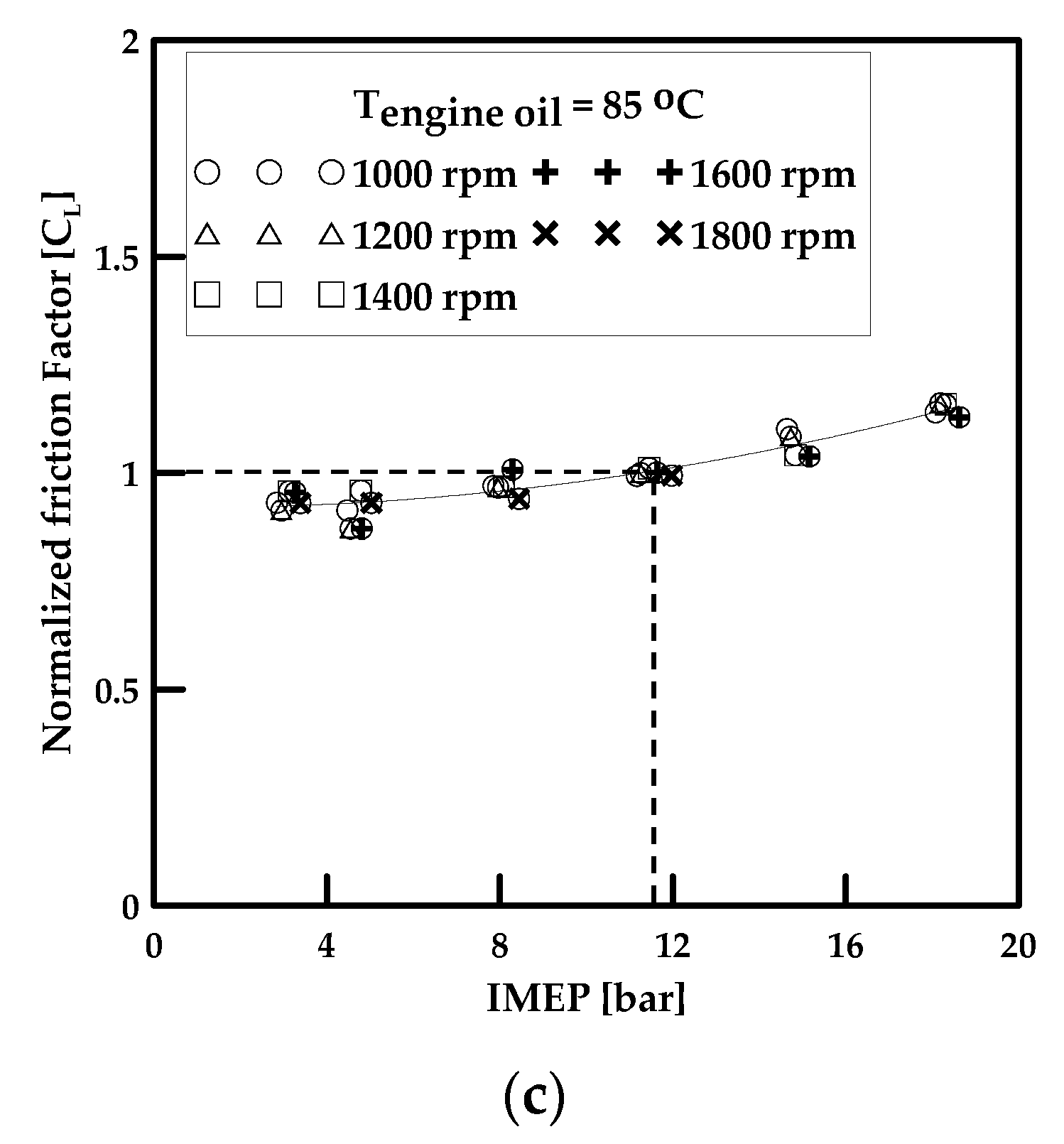
3.1. Modeling of Engine Total Friction
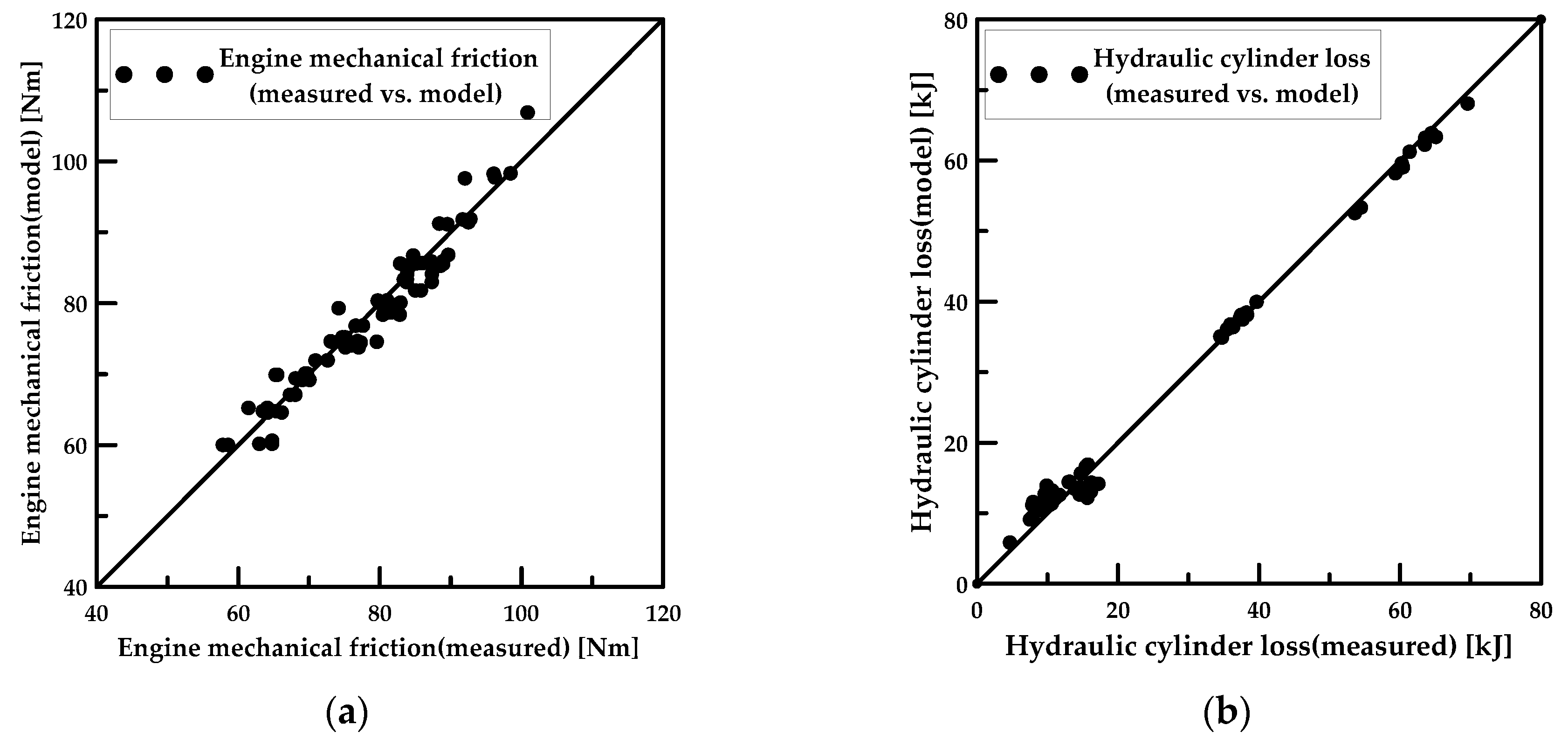
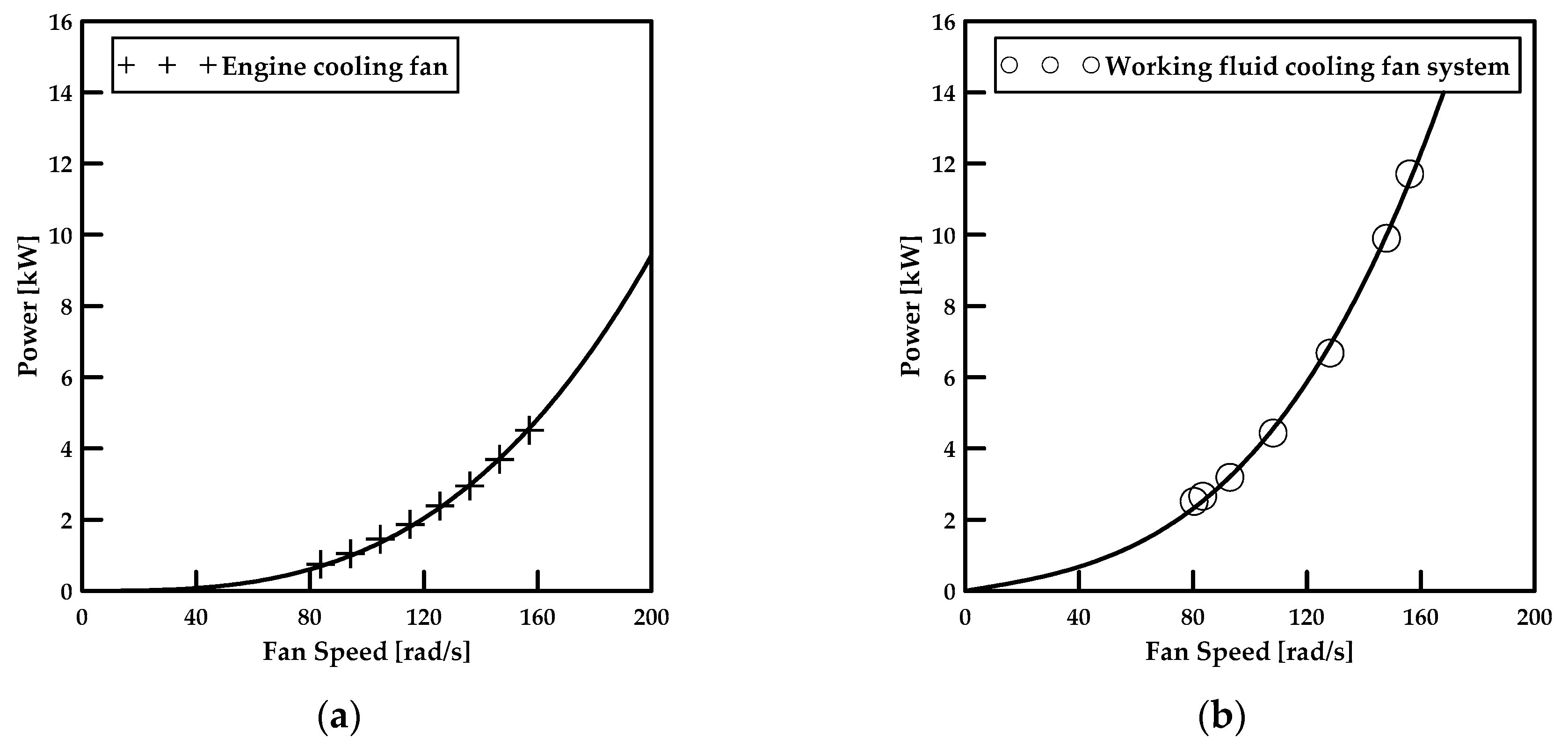
3.2. Modeling of the Hydraulic System
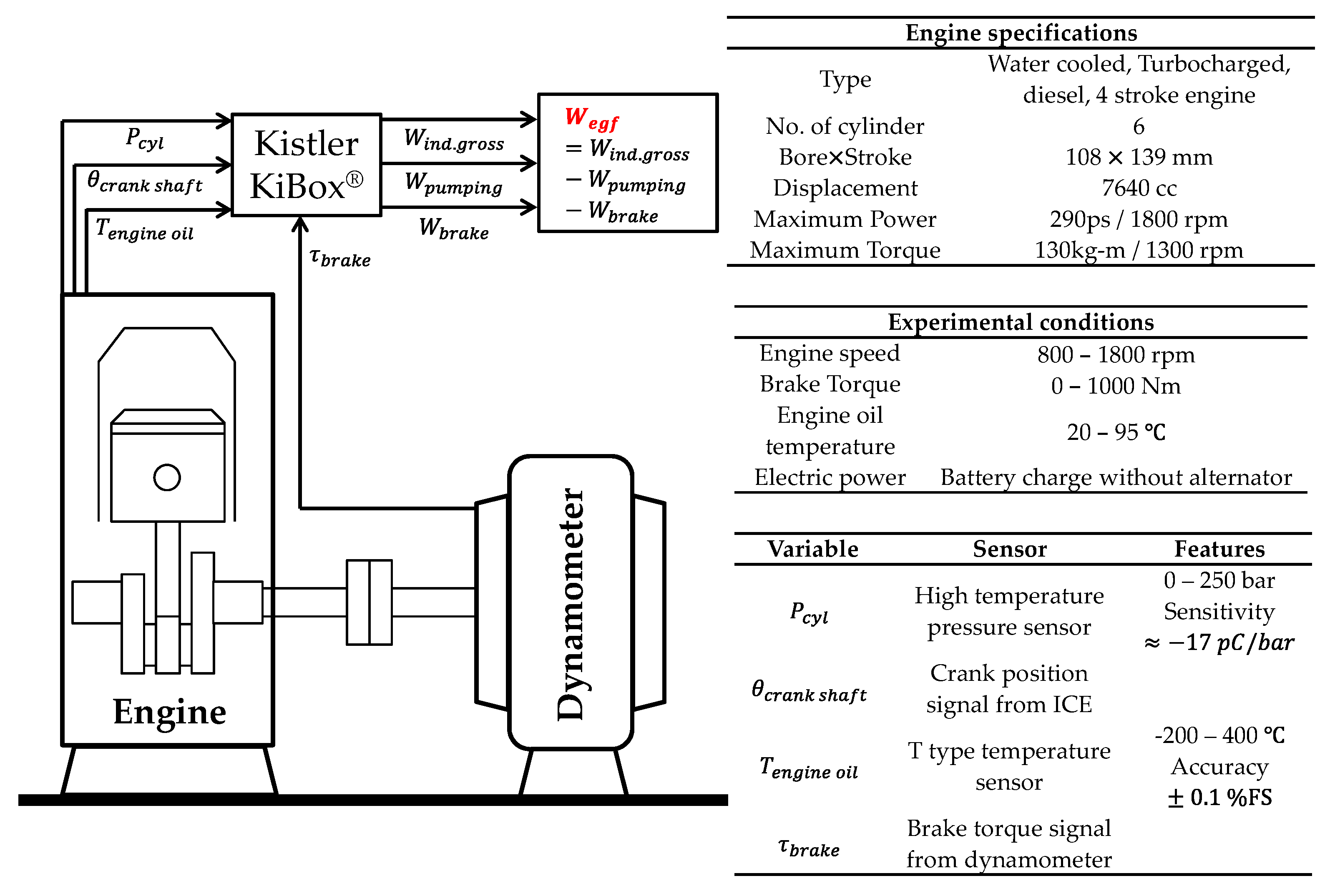
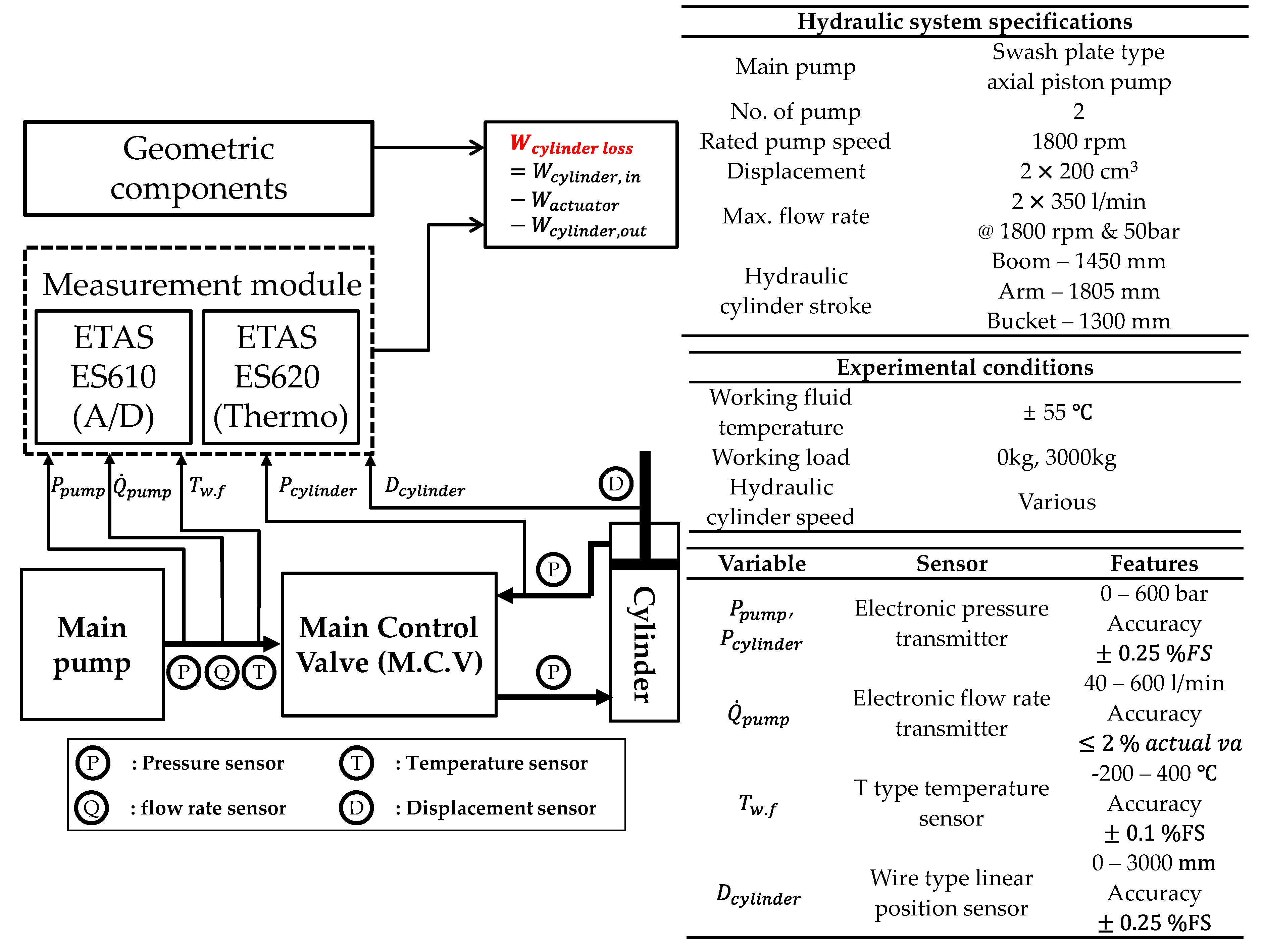
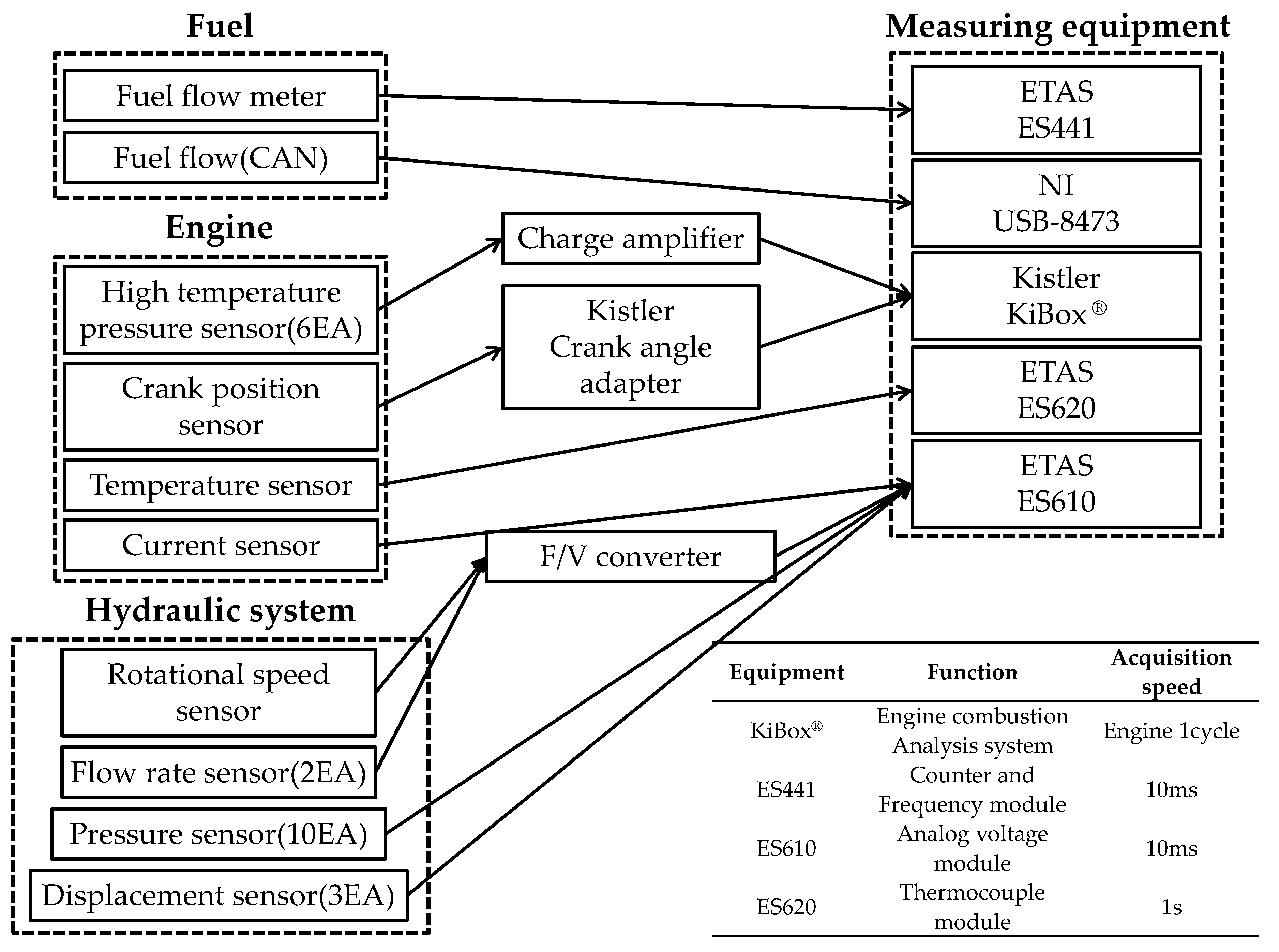
4. Real Time Data Measurement System
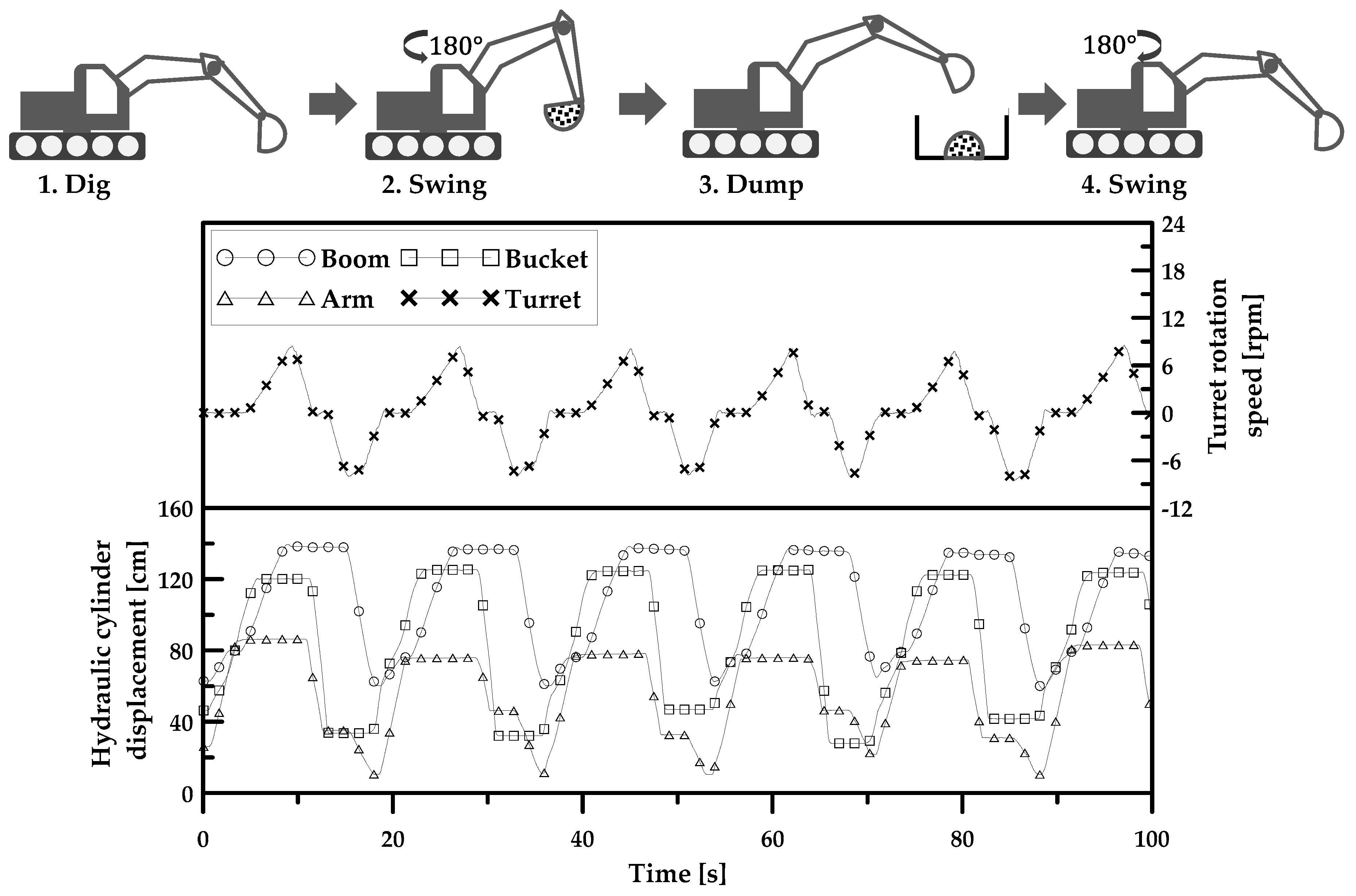
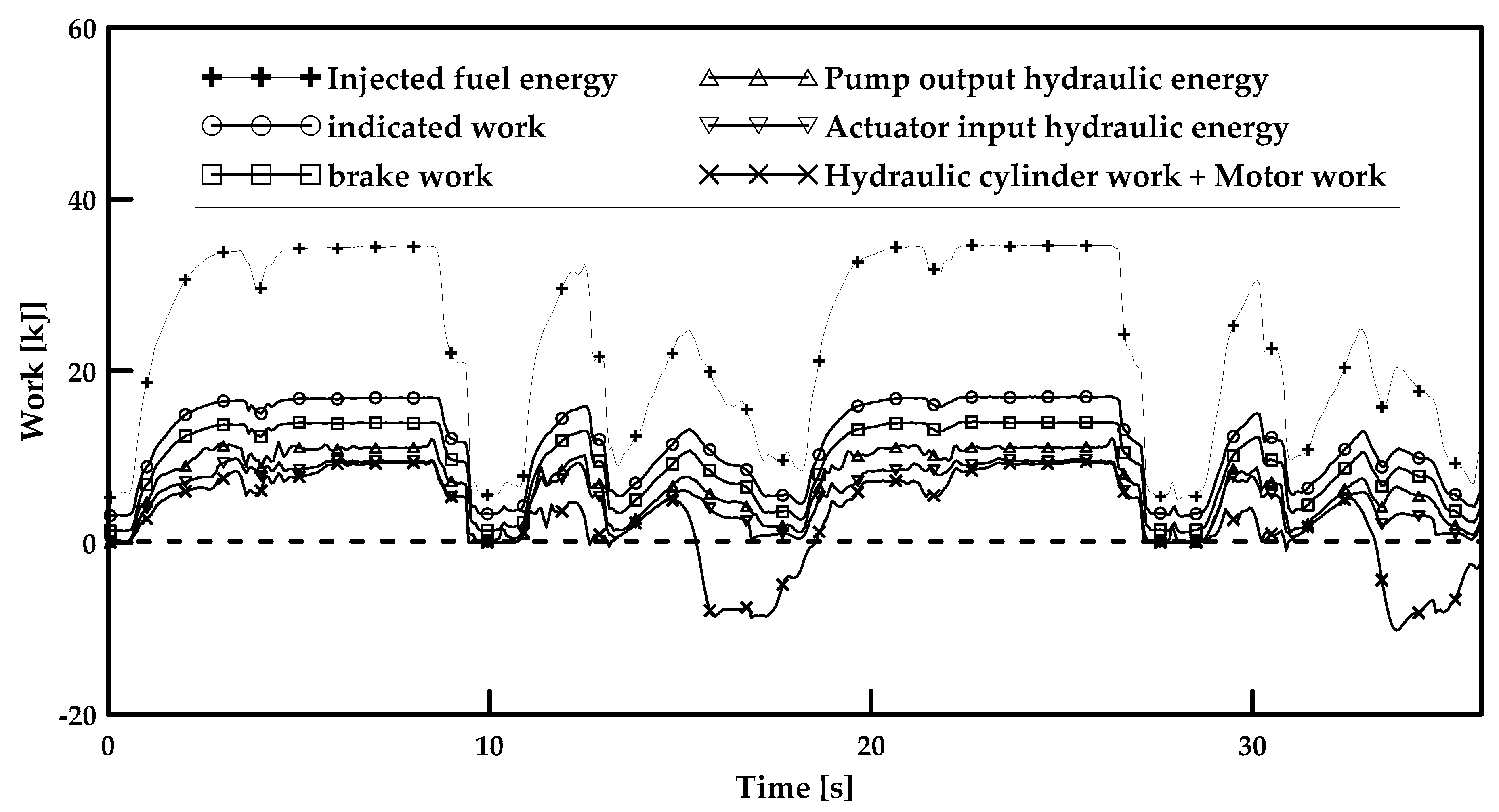
5. Dig and Dump Cycle Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trani, M.L.; Bossi, B.; Gangolells, M.; Casals, M. Predicting fuel energy consumption during earthworks. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3798–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abekawa, T.; Tanikawa, Y.; Hirosawa, A. Introduction of Komatsu Genuine Hydraulic Oil KOMHYDRO HE; Komatsu Technical Report; Yumpu: Komatsu, Japan, 2010; Volume 56. [Google Scholar]
- Ohira, S.; Suehiro, M.; Ota, K.; Kawamura, K. Use of emission rights for construction machinery to help prevent global warming. Hitachi Rev. 2013, 62, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Park, K. Analysis of the fuel economy factor of the commercial vehicle. In Proceedings of the KSAE 2005 Annual Conference and Exhibition, Pyeongtaek, Korea, 24–26 November 2005; pp. 522–526. [Google Scholar]
- Filla, R. Quantifying Operability of Working Machines. Ph.D. Thesis, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Filla, R. Operator and Machine Models for Dynamic Simulation of Construction Machinery. Ph.D. Thesis, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Quan, L.; Yang, Y. Excavator energy-saving efficiency based on diesel engine cylinder deactivation technology. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2012, 25, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu-dong, F. Analysis and Computing of Load Sensing System in Hydraulic Excavator. J. Tongji Univ. 2001, 29, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, C.; Stangl, M. Application of power regenerative boom system to excavator. In Proceedings of the 10th International Fluid Power Conference, Dresden, Germany, 8–10 March 2016; pp. 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.; Seo, J.; Nam, Y.; Kim, K.U. Energy-saving in excavators with application of independent metering valve. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C. Power Management for Multi Actuator Mobile Machines with Displacement Controlled Hydraulic Actuators. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, L.; Dong, Z.; Quan, L.; Li, Y. Potential energy regeneration method and its engineering applications in large-scale excavators. Energy Convers Manag. 2019, 195, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, P.; Murrenhoff, H. Boom potential energy regeneration scheme for hydraulic excavators. In Proceedings of the ASME/BATH 2016 Symposium on Fluid power and Motion Control, Bath, UK, 7–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, H. Simulation analysis of potential energy recovery system of hydraulic hybrid excavator. Int. J. Pr. Eng. Man. 2017, 18, 1575–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Q. Design and analysis of compound potential energy regeneration system for hybrid hydraulic excavator. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. I 2012, 226, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Control strategies of power system in hybrid hydraulic excavator. Autom. Constr. 2008, 4, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, N.; Seo, H.; Cha, S.; Lim, W. Fuel consumption analysis of hybrid excavator using electric swing motor. In Proceedings of the 24th International Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Symposium and Exhibition, Stavanger, Norway, 13–16 May 2009; pp. 879–886. [Google Scholar]
- Kagoshima, M.; Sora, T.; Komiyama, M. Development of hybrid power train control system for excavator. In Proceedings of the JSAE Annual Congress, Yokohama, Japan, 21–23 May 2003; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui, A.; Nanjyo, T.; Yoshimatsu, T. Development of the electro hydraulic actuator system on hybrid excavator. In Proceedings of the JSAE Annual Congress, Yokohama, Japan, 21–23 May 2003; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Jiang, J.; Su, X.; Karimi, H.R. Energy-saving analysis of hydraulic hybrid excavator based on common pressure rail. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hippalgaonkar, R.; Ivantysynova, M.; Zimmerman, J. Fuel-savings of a Mini-excavator through a hydraulic hybrid displacement controlled system. In Proceedings of the 8th international fluid power conference, Dresden, Germany, 26–28 March 2012; pp. 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Hippalgaonkar, R.; Ivantysynova, M. A Series-Parallel Hydraulic Hybrid Mini-Excavator with Displacement Controlled Actuators. In Proceedings of the 13th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power, Linköping, Sweden, 3–5 June 2013; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hippalgaonkar, R. Power Management for Hydraulic Hybrid Multi-Actuator Mobile Machines with DC Actuators. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hippalgaonkar, R.; Ivantysynova, M. Optimal power management of hydraulic hybrid mobile machines—Part I: Theoretical studies, modeling and simulation. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2016, 138, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minav, T.; Heikkinen, J.E.; Pietola, M. Direct driven hydraulic drive for new powertrain topologies for non-road mobile machinery. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 152, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minav, T.; Bonato, C.; Sainio, P.; Pietola, M. Direct driven hydraulic drive. In Proceedings of the 9th International Fluid Power Conference (IFK), Aachen, Germany, 24–26 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Minav, T.; Bonato, C.; Sainio, P.; Pietola, M. Efficiency of direct driven hydraulic drive for non-road mobile working machines. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 2431–2435. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Minav, T.; Pietola, M. Decentralized Hydraulics for Micro Excavator. In Proceedings of the 15th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power, Linköping, Sweden, 7–9 June 2017; pp. 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, J.D.; Pelosi, M.; Williamson, C.A. Energy consumption of an LS excavator hydraulic system. In Proceedings of the ASME international mechanical engineering congress and exposition, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 November 2007; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Casoli, P.; Riccò, L.; Campanini, F.; Lettini, A.; Dolcin, C. Mathematical model of a hydraulic excavator for fuel consumption predictions. In Proceedings of the ASME/BATH 2015 symposium on Fluid Power and Motion Control, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–14 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Altare, G.; Padovani, D.; Nervegna, N. A Commercial Excavator: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation of the Hydraulic Circuit. In Proceedings of the SAE 2012 Commercial Vehicle Engineering congress, Rosemont, IL, USA, 13–14 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Casoli, P.; Riccò, L.; Campanini, F.; Bedotti, A. Hydraulic hybrid excavator—Mathematical model validation and energy analysis. Energies 2016, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bedotti, A.; Campanini, F.; Pastori, M.; Riccò, L.; Casoli, P. Energy saving solutions for a hydraulic excavator. Energy Procedia 2017, 126, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukovic, M.; Leifeld, R.; Murrenhoff, H. Reducing fuel consumption in hydraulic excavators—A comprehensive analysis. Energies 2017, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.; Choi, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Ko, S.; Lee, D. A platform study of fuel consumption measurements for an excavator in motion. J. Drive Control 2017, 14, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Heywood, J.B. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York City, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 42–59, 712–745. [Google Scholar]
- Stotsky, A. Adaptive estimation of the engine friction torque. Eur. J. Control 2007, 13, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.; Busquets, E.; Ivantysynova, M. 40% Fuel Savings by Displacement Control Leads to Lower Working Temperatures-A Simulation Study and Measurements. In Proceedings of the 52nd National Conference on Fluid Power, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 23–25 March 2011; pp. 693–701. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, A. Fluid Power with Application, 7th ed.; Pearson Education: Upper saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 117–141. [Google Scholar]
- Earth-Moving Machinery—Fuel Consumption on Hydraulic Excavator—Test Procedure; JCMAS H020:2007; Japan Construction Machinery and Construction Association for Hydraulic Excavators: Tokyo, Japan, 2007.
- Fecke, M. Standardisierung definierter Lastzyklen und Messmethoden zur Energieverbrauchsermittlung von Baumaschinen. In Proceedings of the 5th Fachtgaung Baumaschinentechnik, Dresden, Germany, 17–19 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, C. Bewertung der Energieeffizienz von Antriebssystemen mobiler Arbeitsmaschinen am Beispiel Bagger. Ph.D. Thesis, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]



| Symbol | Definition | Unit | Symbol | Definition | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normalized friction factor for engine load | - | Hydraulic cylinder output energy | J | ||
| Normalized friction factor for engine speed | - | Engine mechanical friction work | J | ||
| Normalized friction factor for temperature | - | Engine mechanical friction work at base point | J | ||
| Alternator current | A | Engine total Friction work | J | ||
| Fuel mass | kg | Hydraulic cylinder input energy | J | ||
| Engine cylinder pressure | Pa | Hydraulic motor input energy | J | ||
| Hydraulic cylinder pressure | Pa | Gross indicated work | J | ||
| Hydraulic motor pressure | Pa | MCV loss | J | ||
| Main pump pressure | Pa | MCV output energy | J | ||
| Hydraulic cylinder flow rate | m3/s | Pumping loss | J | ||
| Low heating value | J/kg | Main pump input work | J | ||
| Hydraulic motor flow rate | m3/s | Main pump output energy | J | ||
| Main pump flow rate | m3/s | Main pump loss | J | ||
| Hydraulic cylinder displacement speed | cm/s | Thermodynamic loss | J | ||
| Battery voltage | V | Working fluid fan system work | J | ||
| Engine cylinder volume | m3 | Alternator efficiency | - | ||
| Alternator work | J | Cooling fan angular velocity | rad/s | ||
| Engine brake work | J | Working fluid fan angular velocity | rad/s | ||
| Cooling fan work | J | Time | s | ||
| Hydraulic cylinder loss | J | Hydraulic cylinder displacement | m |
| Actuator | c1 | c2 | c3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boom | 11.04 | 173.46 | 6371.11 |
| Arm | 7.45 | 88.05 | 3229.47 |
| Bucket | 17.11 | 111.78 | 4970.35 |
| Consumption Component | Boom | Arm | Bucket | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel Energy | (%) | Fuel Energy | (%) | Fuel Energy | (%) | |
| Net work | 2.1% | (24.9%) | 3.2% | (72.2%) | 2.4% | (50.0%) |
| Cyl. out energy | 5.7% | (70.9%) | 0.9% | (21.0%) | 1.6% | (34.0%) |
| Hyd. cylinder loss | 0.4% | (4.2%) | 0.3% | (6.8%) | 0.8% | (16.0%) |
| Total | 8.2% | - | 4.5% | - | 4.7% | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, K.; Kang, H.; An, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, J. Methodology of Excavator System Energy Flow-Down. Energies 2020, 13, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040951
An K, Kang H, An Y, Park J, Lee J. Methodology of Excavator System Energy Flow-Down. Energies. 2020; 13(4):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040951
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Kwangman, Hyehyun Kang, Youngkuk An, Jinil Park, and Jonghwa Lee. 2020. "Methodology of Excavator System Energy Flow-Down" Energies 13, no. 4: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040951
APA StyleAn, K., Kang, H., An, Y., Park, J., & Lee, J. (2020). Methodology of Excavator System Energy Flow-Down. Energies, 13(4), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040951





