Impacts of a LVRT Control Strategy of Offshore Wind Farms on the HTS Power Cable
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ▪
- Analyze the impact of various LVRT control techniques on the HTS cable operation. Two LVRT control strategies are focused on this study, which are the crowbar protection and the coordinated control of WTG converters;
- ▪
- Propose an effective coordinated control to improve the LVRT performance of offshore wind farms connected to the grid by the HTS cable.
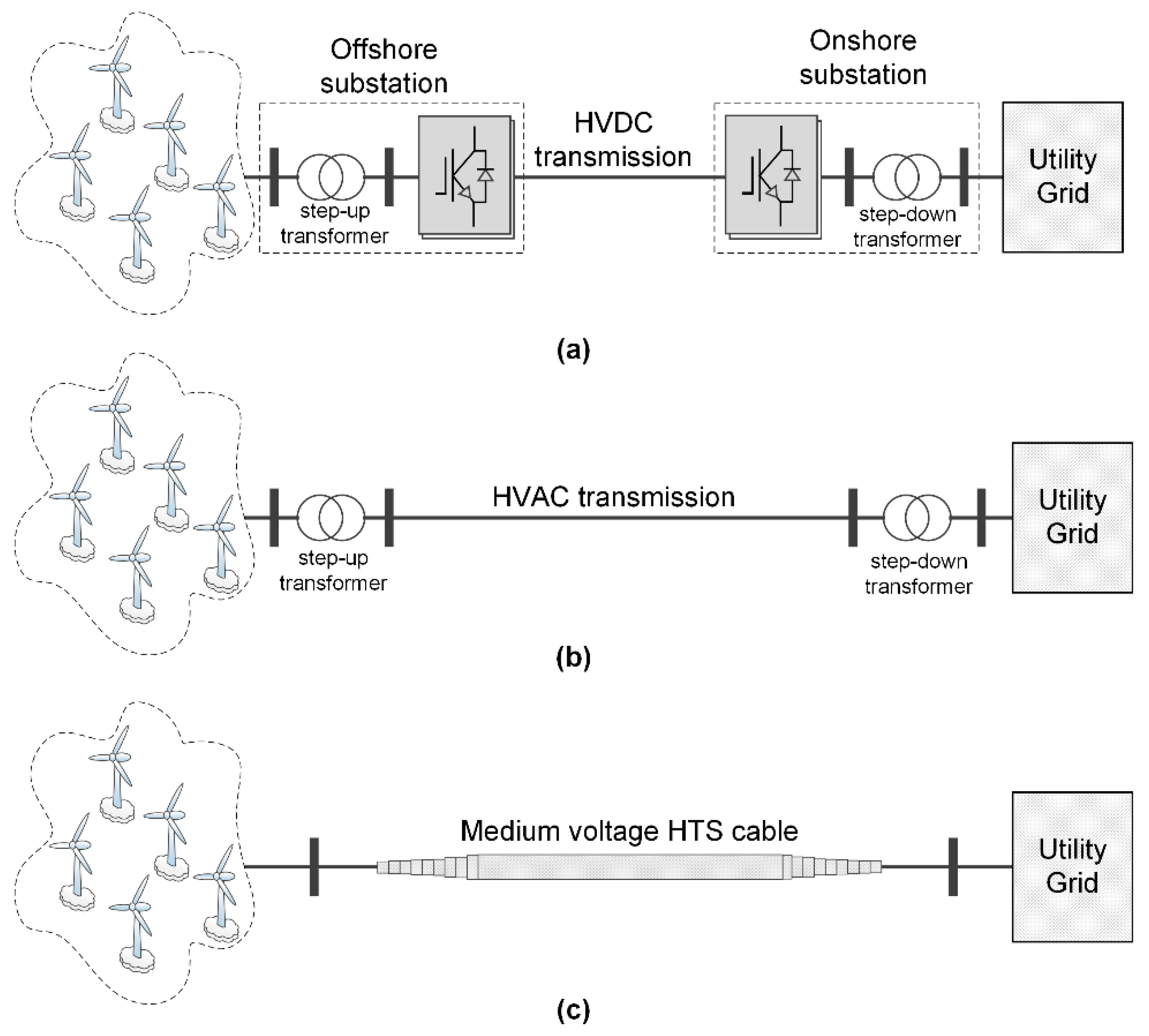
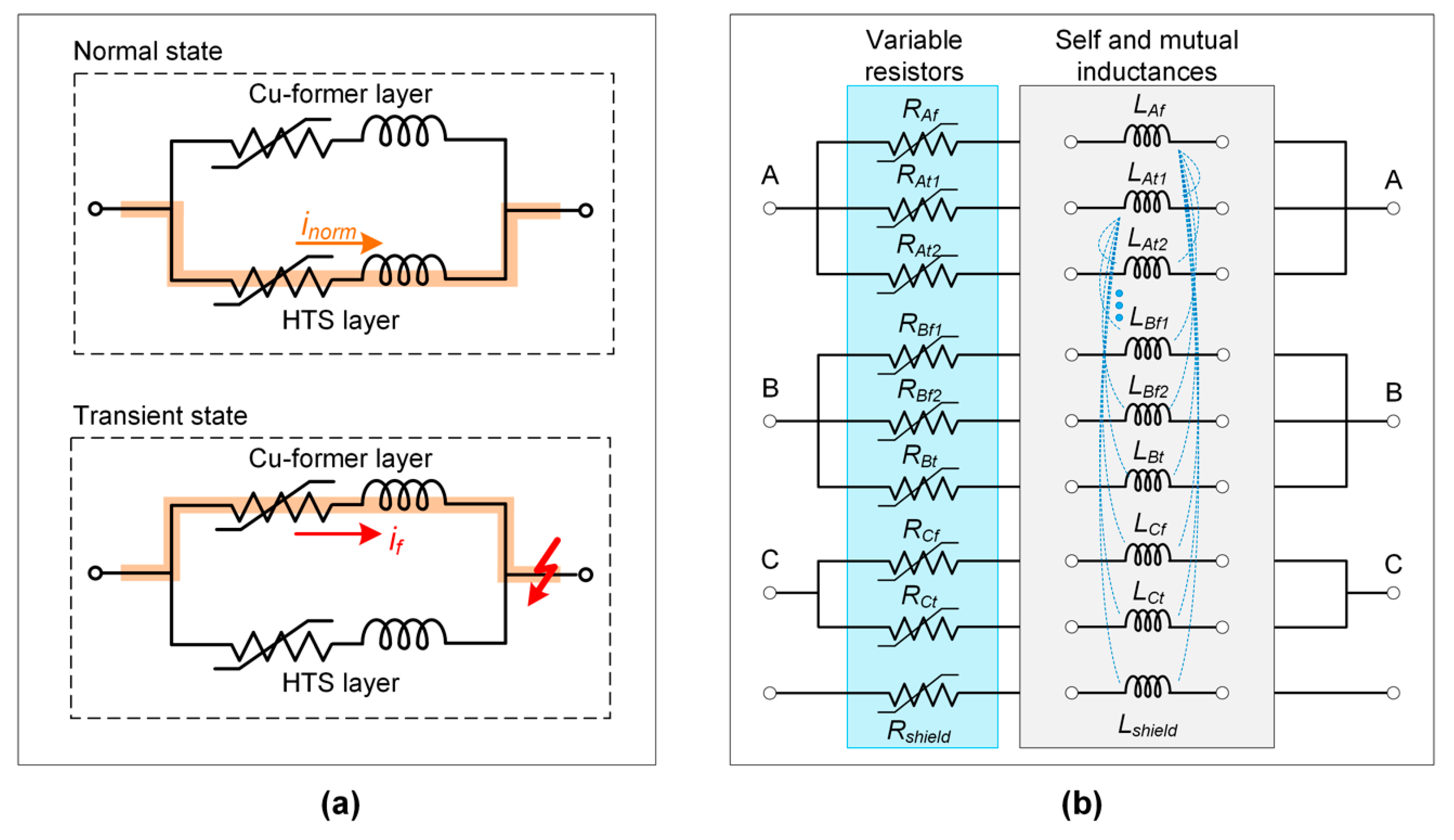
2. HTS Power Cable for Grid Connection of Offshore Wind Farm
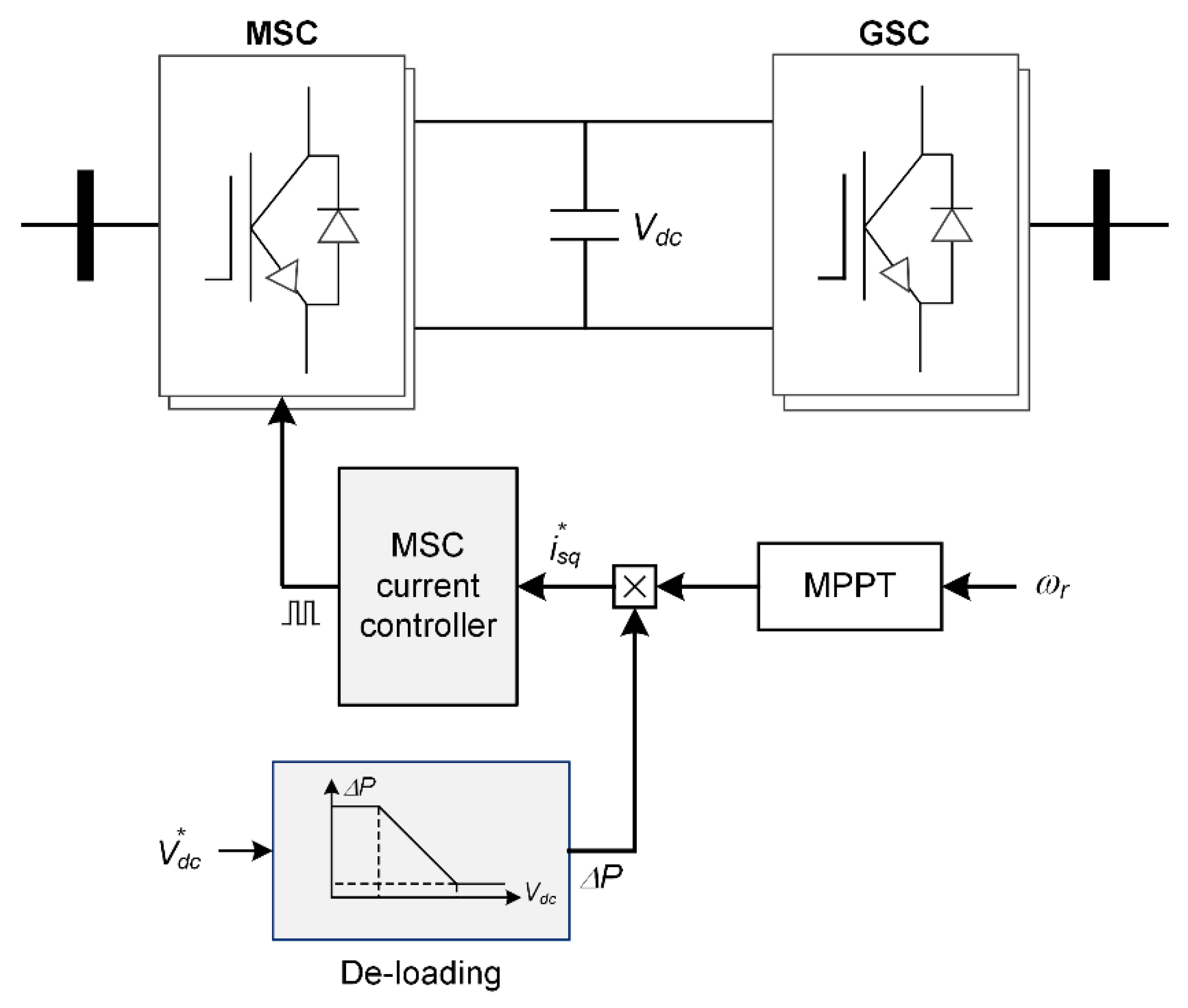
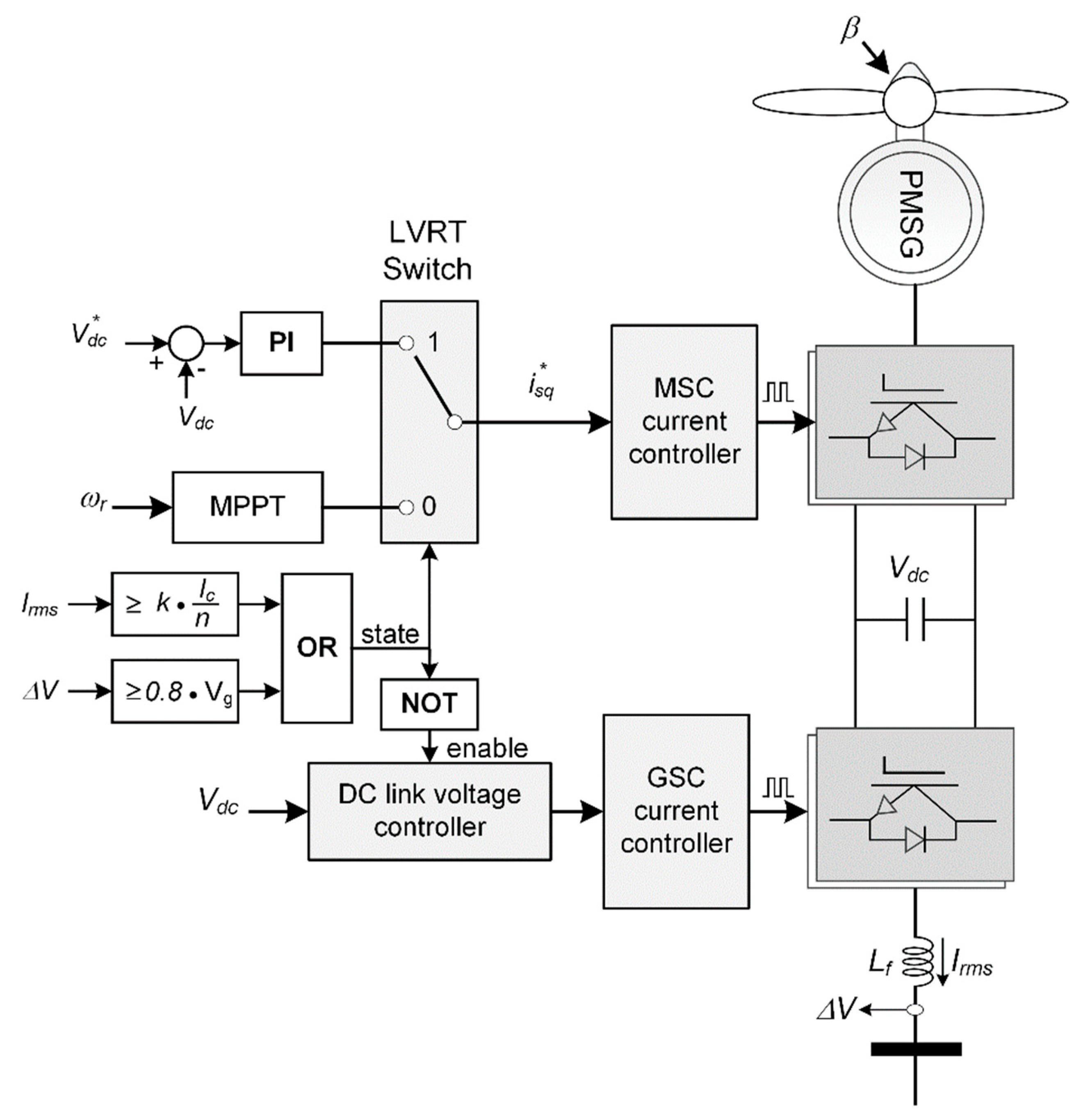
3. Converter Controller for LVRT Improvement
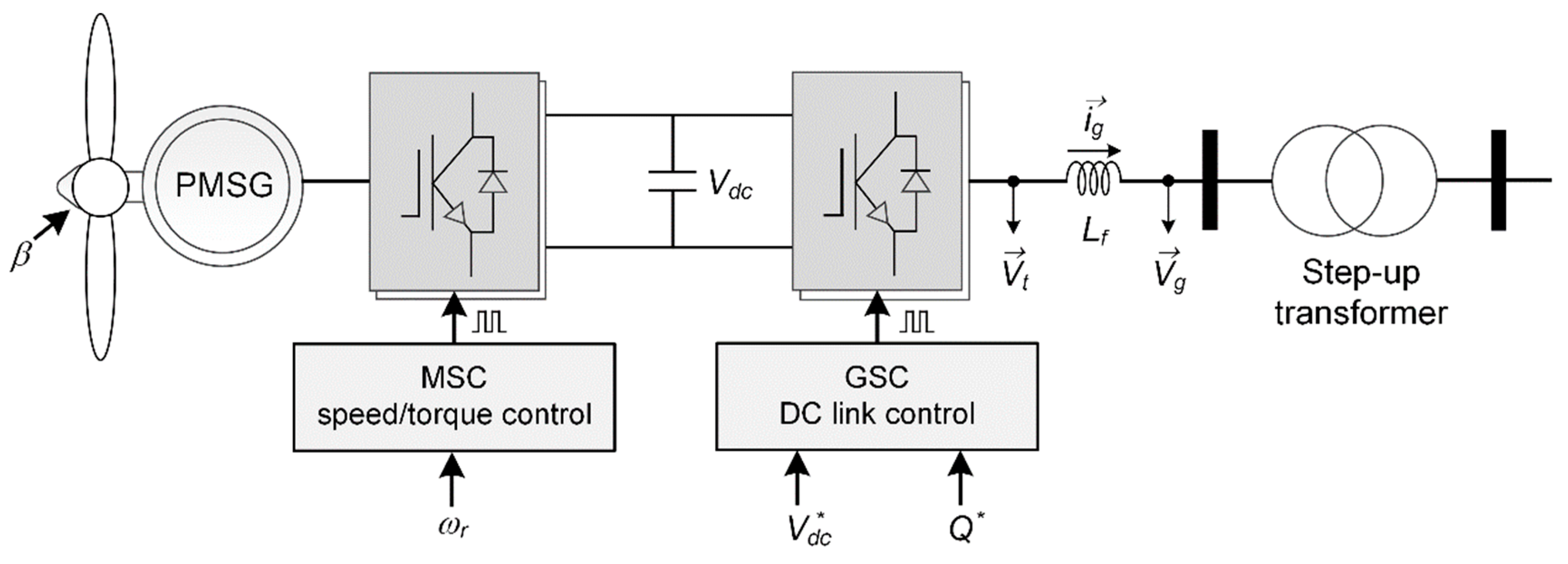
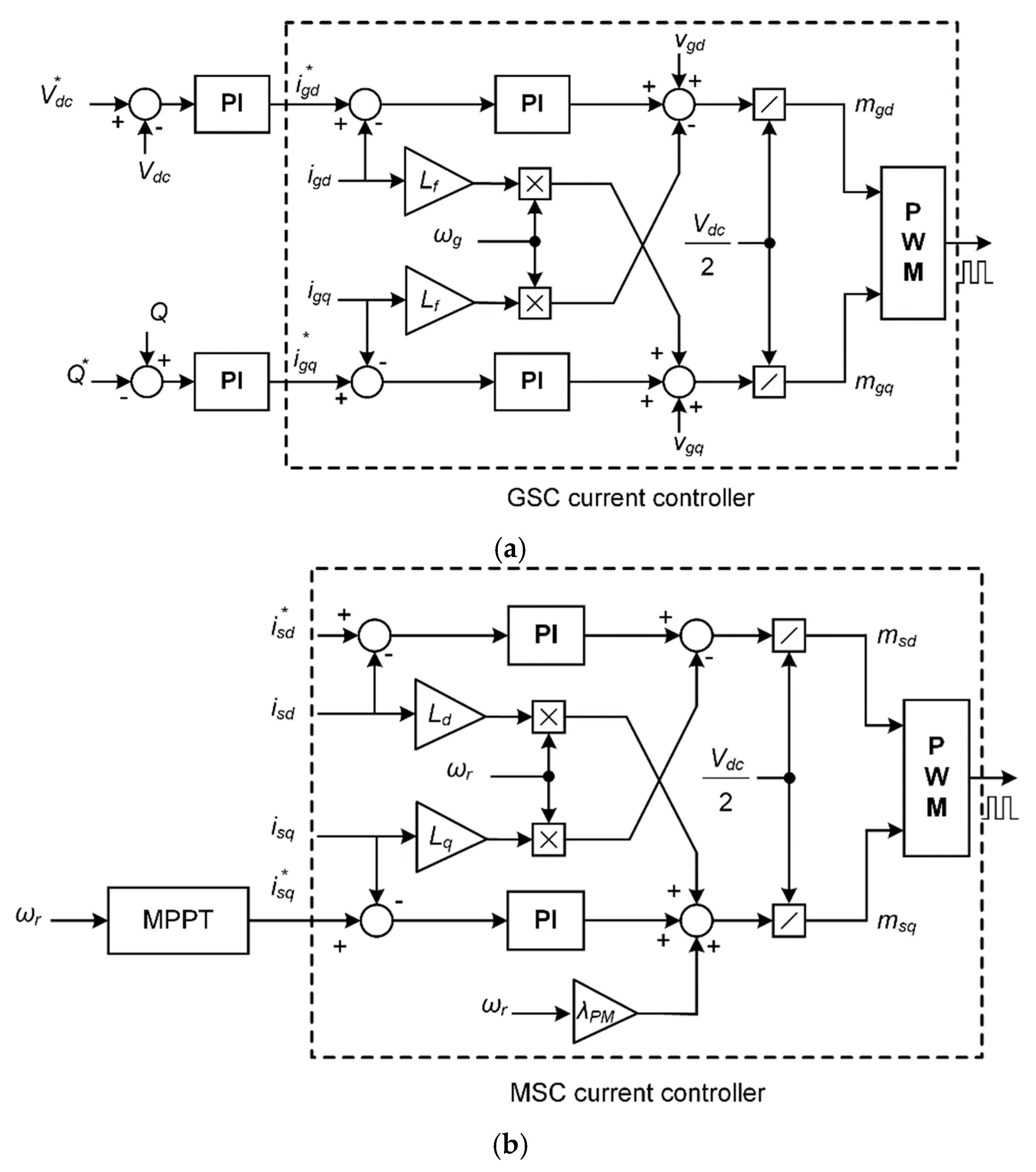
3.1. Converter Controller of Type-4 PMSG Wind Turbine Generator
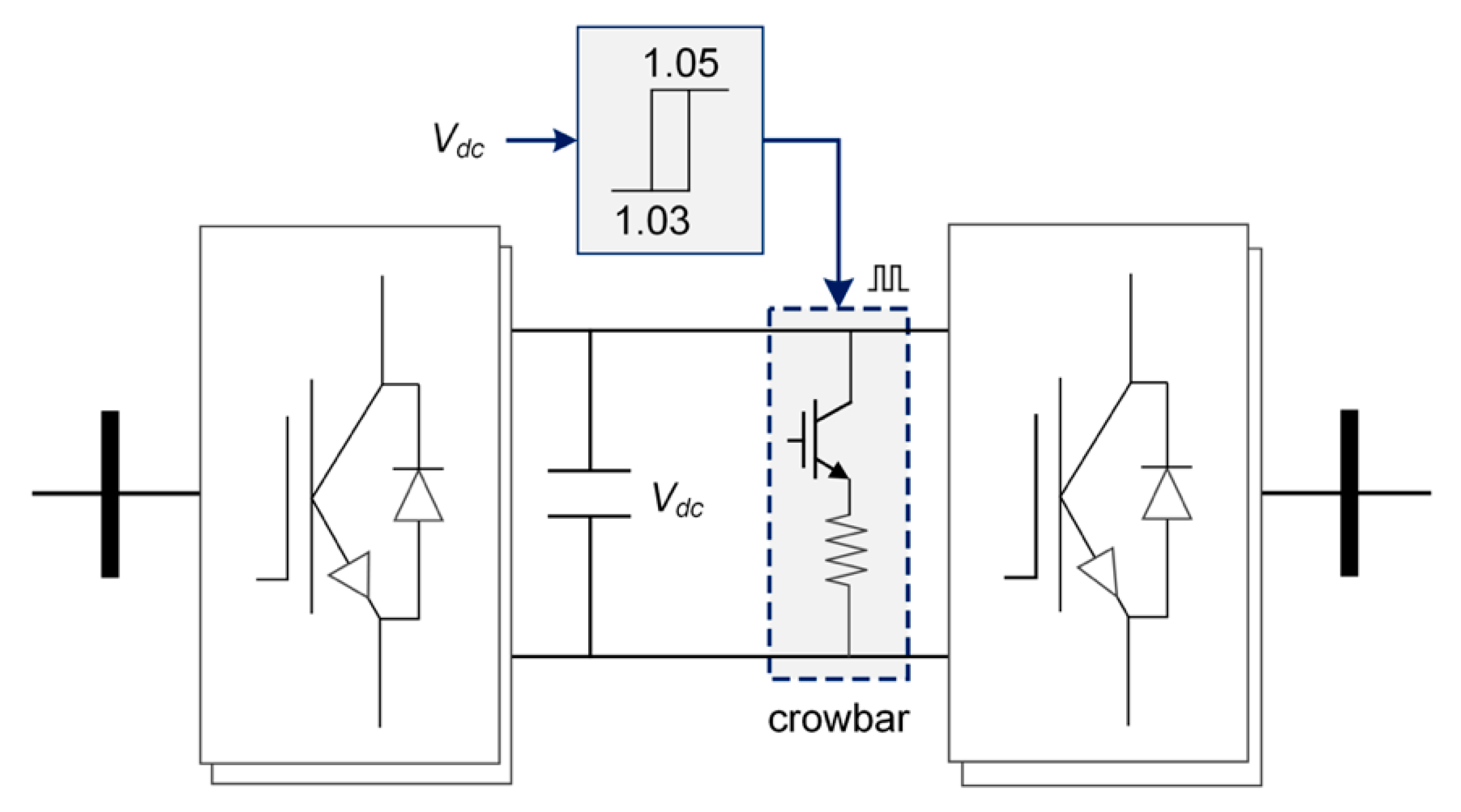
3.2. LVRT Control Strategies
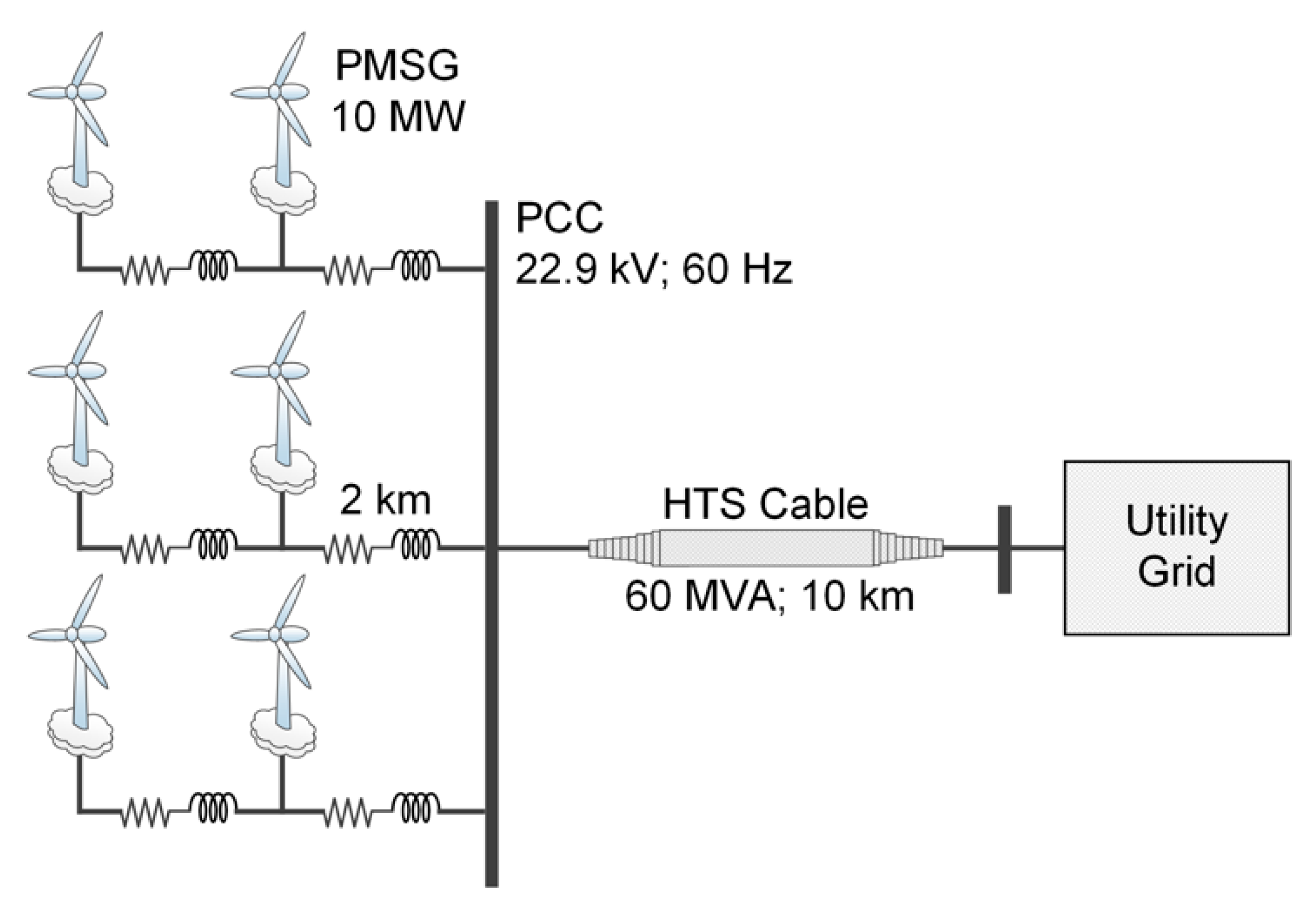
4. Simulation
4.1. System Description
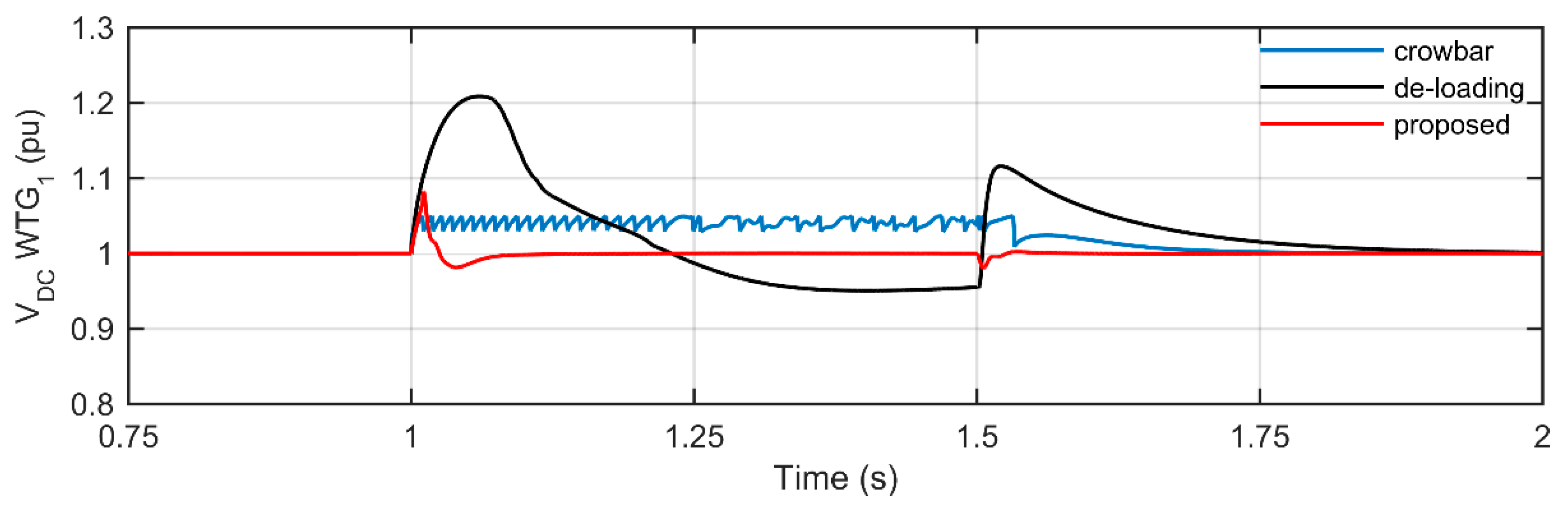
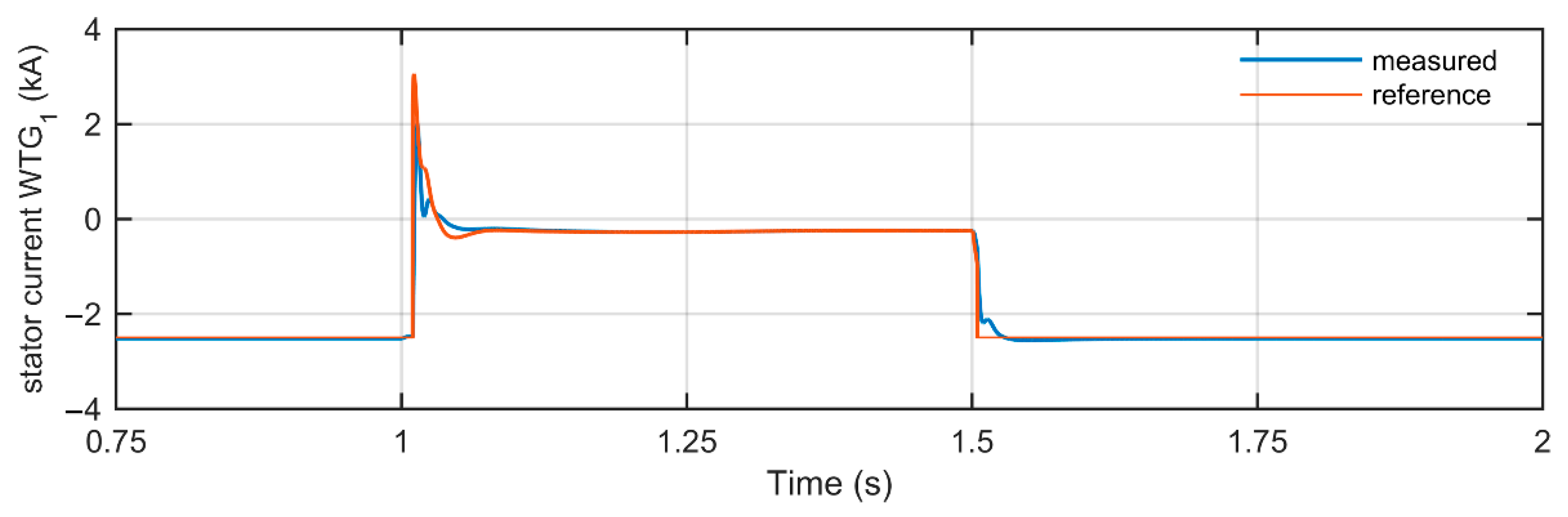
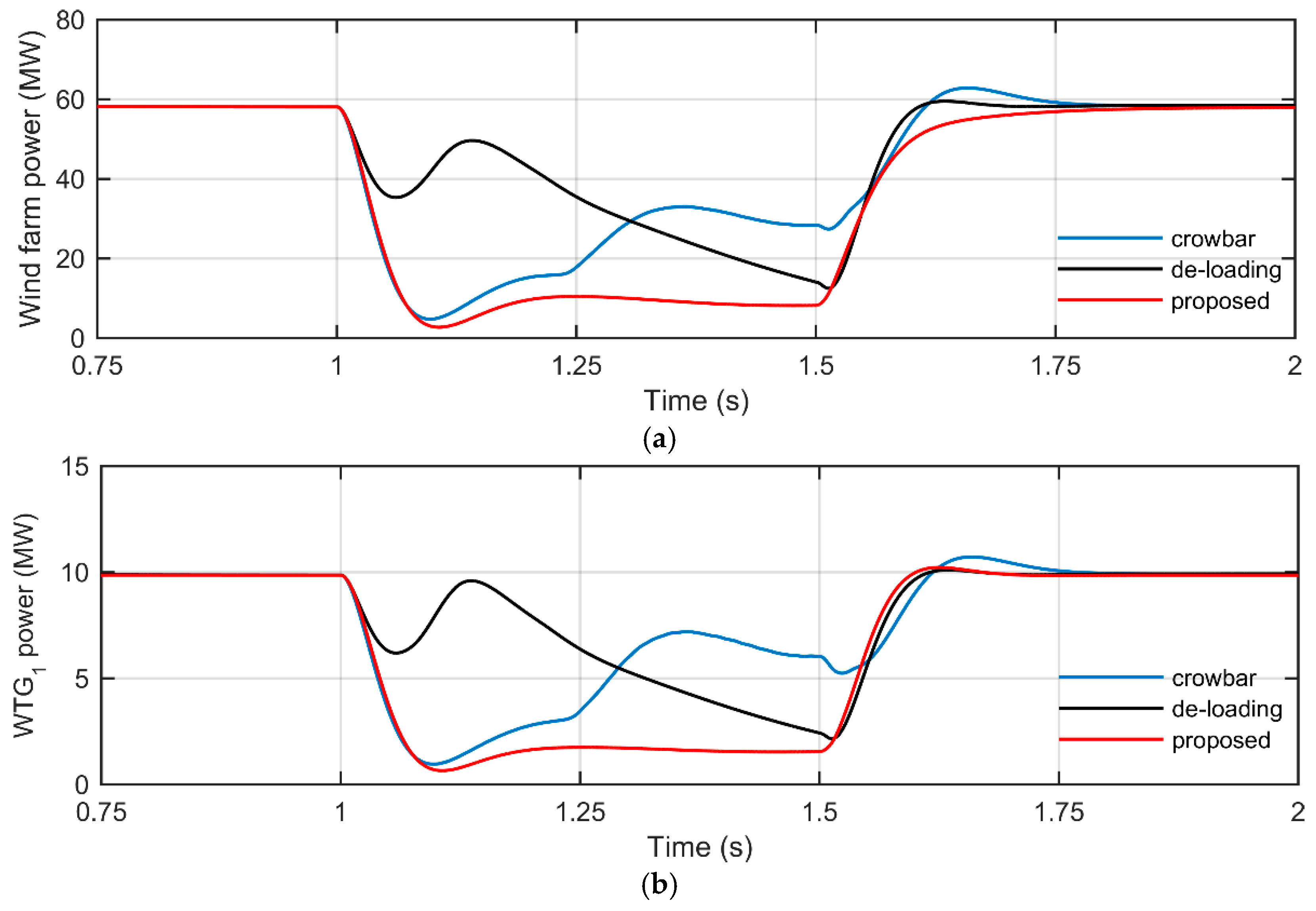
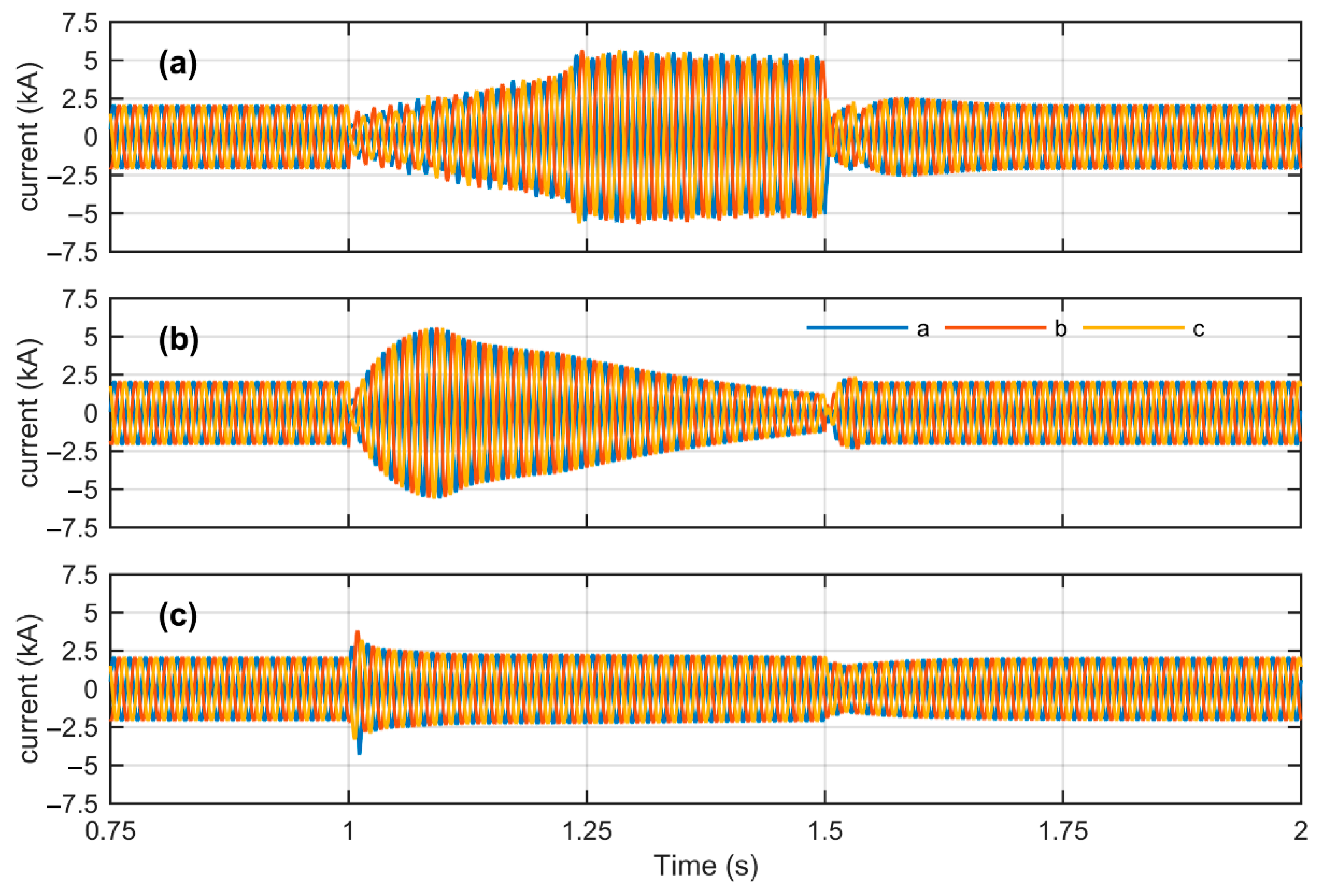
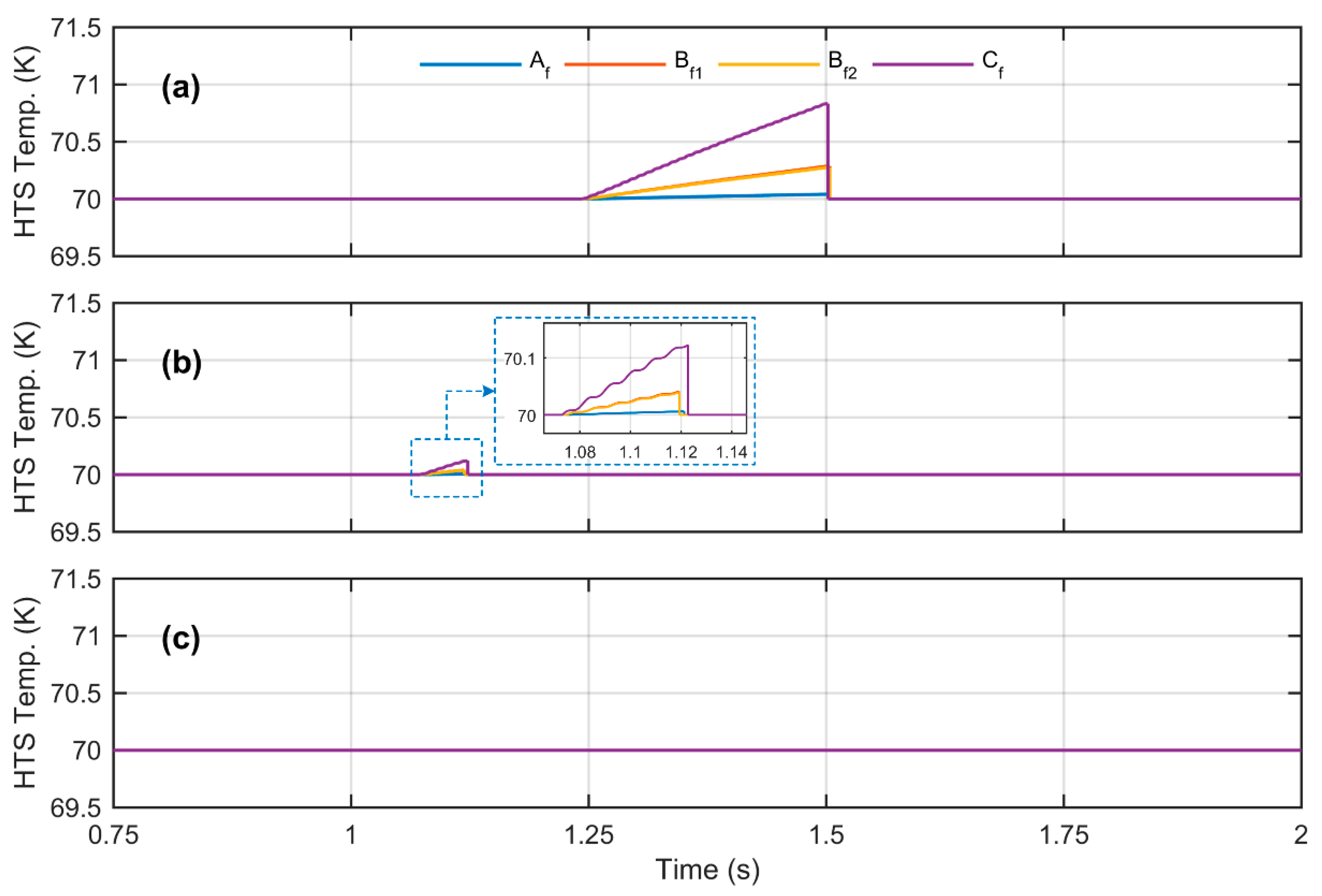
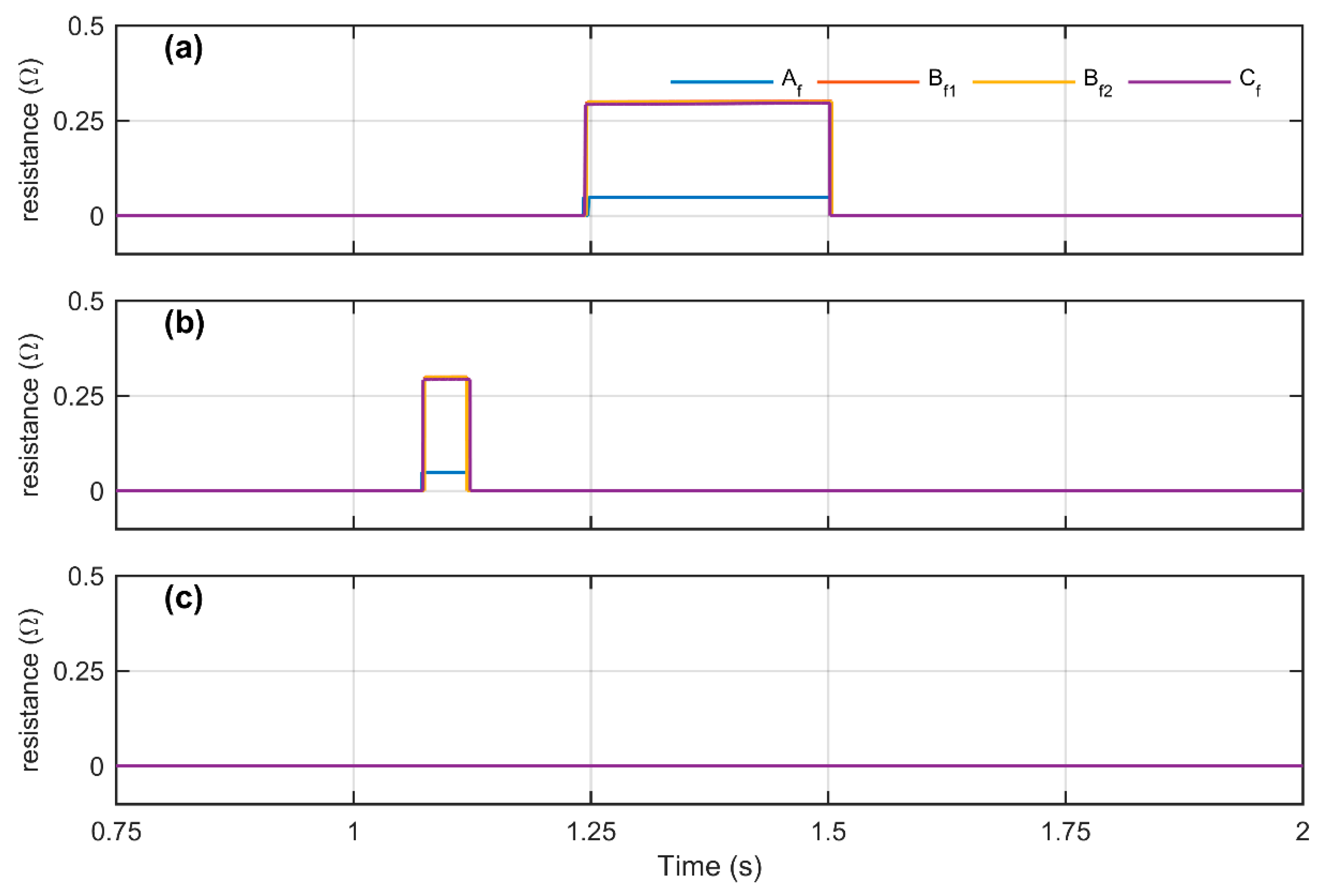
4.2. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Abbreviations | |
| HTS | High temperature superconducting |
| FCL | Fault current limiter |
| ESS | Energy storage system |
| LVRT | Low voltage ride through |
| WTG | Wind turbine generator |
| BTB | Back-to-back converter |
| IGBT | Insulated-gate bipolar transistor |
| MSC | Machine-side converter |
| GSC | Grid-side converter |
| PMSG | Permanent magnet synchronous generator |
| PCC | Point of common coupling |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| MPPT | Maximum power point tracking |
| PLL | Phase-locked loop |
| Parameters | |
| Critical current of HTS cable | |
| Power change due to DC-link voltage drop | |
| DC-link power | |
| MSC power | |
| GSC power | |
| DC-link voltage | |
| DC-link voltage reference | |
| Space phasor | |
| Space phasor of grid current | |
| ; | dq-axis components of grid current |
| ; | dq-axis components of grid current reference |
| ; | dq-axis components of stator current reference |
| Space phasor of output filter voltage | |
| ; | dq-axis components of output filter voltage |
| Space phasor of terminal GCS voltage | |
| ; | dq-axis components of the terminal GSC voltage |
| ; | dq-axis components of the stator voltage |
| ; | dq-axis components of modulating signals of GSC |
| ; | dq-axis components of control inputs for the GSC |
| ; | dq-axis components of modulating signals of MSC |
| ; | dq-axis components of control inputs for the MSC |
| RMS current of GSC | |
| Voltage drop | |
| DC-link capacitor | |
| Inductance filter | |
| Grid angular frequency (rad/s) | |
| Rotor angular frequency (rad/s) | |
| Measured reactive power | |
| Reference reactive power | |
| Optimal torque reference | |
| Number of pole pairs | |
| Magnet flux of PMSG | |
| Angle of the space phasor | |
| Initial phase angle of grid voltage | |
| ; | dq components of stator inductance |
| Stator resistance of PMSG | |
| Turns ratio of the step-up transformer | |
| Number of WTGs in offshore wind farm | |
| Wind turbine parameters | |
| Optimal tip-speed ratio | |
| Turbine swept area | |
| Air mass density | |
| Turbine blade radius | |
| Maximum performance coefficient | |
| Pitch angle |
References
- Yang, B.; Kang, J.; Lee, S.; Choi, C.; Moon, Y. Qualification Test of a 80 kV 500 MW HTS DC Cable for Applying Into Real Grid. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2015, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukas, D.I.; Syrpas, A.; Labridis, D.P. Multiterminal DC Transmission Systems Based on Superconducting Cables Feasibility Study, Modeling, and Control. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2018, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Tang, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, A.; Li, J.; Cheng, S. Techno-economic feasibility study on hts power cables. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2009, 19, 1774–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, J.Y. Application Methodology for 22.9 kV HTS Cable in Metropolitan City of South Korea. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2007, 17, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Shu, B.; Han, X.; Ma, X.; Bian, B.; Li, J.; Liang, Z. Fault Analysis for 110 kV HTS Power Cables. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2014, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, M.-C.; Ju, C.-H.; Kim, J.-G.; Park, M.; Yu, I.-K.; Yang, B. Transient analysis of an HTS DC power cable with an HVDC system. Phys. C Supercond. 2013, 494, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytnikov, V.E.; Bemert, S.E.; Kopylov, S.I.; Romashov, M.A.; Ryabin, T.V.; Shakaryan, Y.G.; Lobyntsev, V.V. Status of HTS Cable Link Project for St. Petersburg Grid. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2015, 25, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Park, M.; Yu, I.-K.; Won, Y.; Kwak, Y.; Lee, C. Recent Status and Progress on HTS Cables for AC and DC Power Transmission in Korea. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2018, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, J.; Tønnesen, O.; Kaas-Pedersen, J.; Nielsen, A.H.; Træholt, C. A new concept for superconducting DC transmission from a wind farm. Phys. C Supercond. 2002, 372–376, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, A. HTS dc transmission and distribution: Concepts, applications and benefits. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2015, 28, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, A.; Gholizad, B.; Stieneker, M.; Stagge, H.; De Doncker, R.W. Technical and Economical Evaluation of DC High-Temperature Superconductor Solutions for the Grid Connection of Offshore Wind Parks. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.-H. A Feasibility Study on HTS Cable for the Grid Integration of Renewable Energy. Phys. Procedia 2013, 45, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Geschiere, A.; Willén, D.; Piga, E.; Barendregt, P. HTS cables open the window for large-scale renewables. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 97, 012183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, N.; Shinozaki, Y.; Nagasaki, Y.; Miyagi, D.; Tsuda, M. Configuration Method of Tri-Axial ReBCO Cable Suitable for Long Distance Power Transmission. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro Pereira, R.; Pereira, A.; Ferreira, C.; Barbosa, F. Influence of Crowbar and Chopper Protection on DFIG during Low Voltage Ride Through. Energies 2018, 11, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Shao, S.; Malliband, P.; Abdi, E.; McMahon, R.A. Crowbarless Fault Ride-Through of the Brushless Doubly Fed Induction Generator in a Wind Turbine Under Symmetrical Voltage Dips. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Z.; El-Naggar, A. Impact of Grid Impedance on LVRT Performance of DFIG System With Rotor Crowbar Technology. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 127999–128008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xiao, L.; Dai, S. Enhancing Low-Voltage Ride-Through Capability and Smoothing Output Power of DFIG With a Superconducting Fault-Current Limiter–Magnetic Energy Storage System. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2012, 27, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Song, N.; Gao, Z.; Xu, X.; Jing, L.; Teng, Y.; Zhu, Z. Development of a 1-MVA/1-MJ Superconducting Fault Current Limiter–Magnetic Energy Storage System for LVRT Capability Enhancement and Wind Power Smoothing. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2018, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-W.; Ke, D.-P.; Qiao, W.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Kirschen, D.S.; Wei, C. Transient Reconfiguration and Coordinated Control for Power Converters to Enhance the LVRT of a DFIG Wind Turbine With an Energy Storage Device. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1679–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Lim, S.-H.; Kim, J.-C. Application of a Superconducting Fault Current Limiter to Enhance the Low-Voltage Ride-Through Capability of Wind Turbine Generators. Energies 2019, 12, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Lim, S.-H. Enhancement on the Fault Ride through Capability of Power Distribution Systems Linked by Distributed Generation due to the Impedance of Superconducting Fault Current Limiters. Energies 2019, 12, 4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Abido, M.; El-Amin, I. Fault Current Limiters in Power Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2018, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Lin, Z.-W.; Niu, Y.-G. An Improved Flux Magnitude and Angle Control With LVRT Capability for DFIGs. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 3845–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.M.; Tiwari, A.N.; Singh, D. Low-voltage ride-through enhancement with the ω and T controls of PMSG in a grid-integrated wind generation system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Lee, W.-G.; Lee, S.; Park, M.; Kim, H.; Won, D.; Yoo, J.; Yang, H.S. A Simplified Model of Coaxial, Multilayer High-Temperature Superconducting Power Cables with Cu Formers for Transient Studies. Energies 2019, 12, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahela, O.P.; Gupta, N.; Khosravy, M.; Patel, N. Comprehensive Overview of Low Voltage Ride Through Methods of Grid Integrated Wind Generator. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 99299–99326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Symbol | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Rate power | 10 MW | |
| Machine side voltage | 6.6 kV | |
| Step-up transformer | 6.6 kV/22.9 kV | |
| Grid-side phase voltage | 22.9 kV | |
| DC-link voltage of BTB converter | 12 kV | |
| DC capacitor | 2000 µF | |
| Grid synchronous frequency | 60 Hz | |
| Rate wind speed | 11.4 m/s |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.-T.; Kim, H.-M.; Yang, H.S. Impacts of a LVRT Control Strategy of Offshore Wind Farms on the HTS Power Cable. Energies 2020, 13, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051194
Nguyen T-T, Kim H-M, Yang HS. Impacts of a LVRT Control Strategy of Offshore Wind Farms on the HTS Power Cable. Energies. 2020; 13(5):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051194
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thai-Thanh, Hak-Man Kim, and Hyung Suk Yang. 2020. "Impacts of a LVRT Control Strategy of Offshore Wind Farms on the HTS Power Cable" Energies 13, no. 5: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051194
APA StyleNguyen, T.-T., Kim, H.-M., & Yang, H. S. (2020). Impacts of a LVRT Control Strategy of Offshore Wind Farms on the HTS Power Cable. Energies, 13(5), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051194






