Agricultural Biogas—An Important Element in the Circular and Low-Carbon Development in Poland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Agricultural Biogas Market in the Context of Circular and Low-Carbon Development
- Additional opportunities for farmers to manage waste from agricultural production, which also allows reductions in the volume of bio-waste.
- Improvements in the efficiency of residues management from plant and animal production and waste from industrial processing of agricultural raw materials.
- Development of low-carbon energy sources in rural areas—biomass production on wasteland, etc.
- The modernization of road and storage infrastructure in rural areas.
- Development of distributed energy generation based on local energy resources.
- Improvement in the energy self-sufficiency of agricultural holdings.
- Additional sources of income for farmers and rural residents.
- Promoting the use of energy from renewable sources among residents of rural areas.
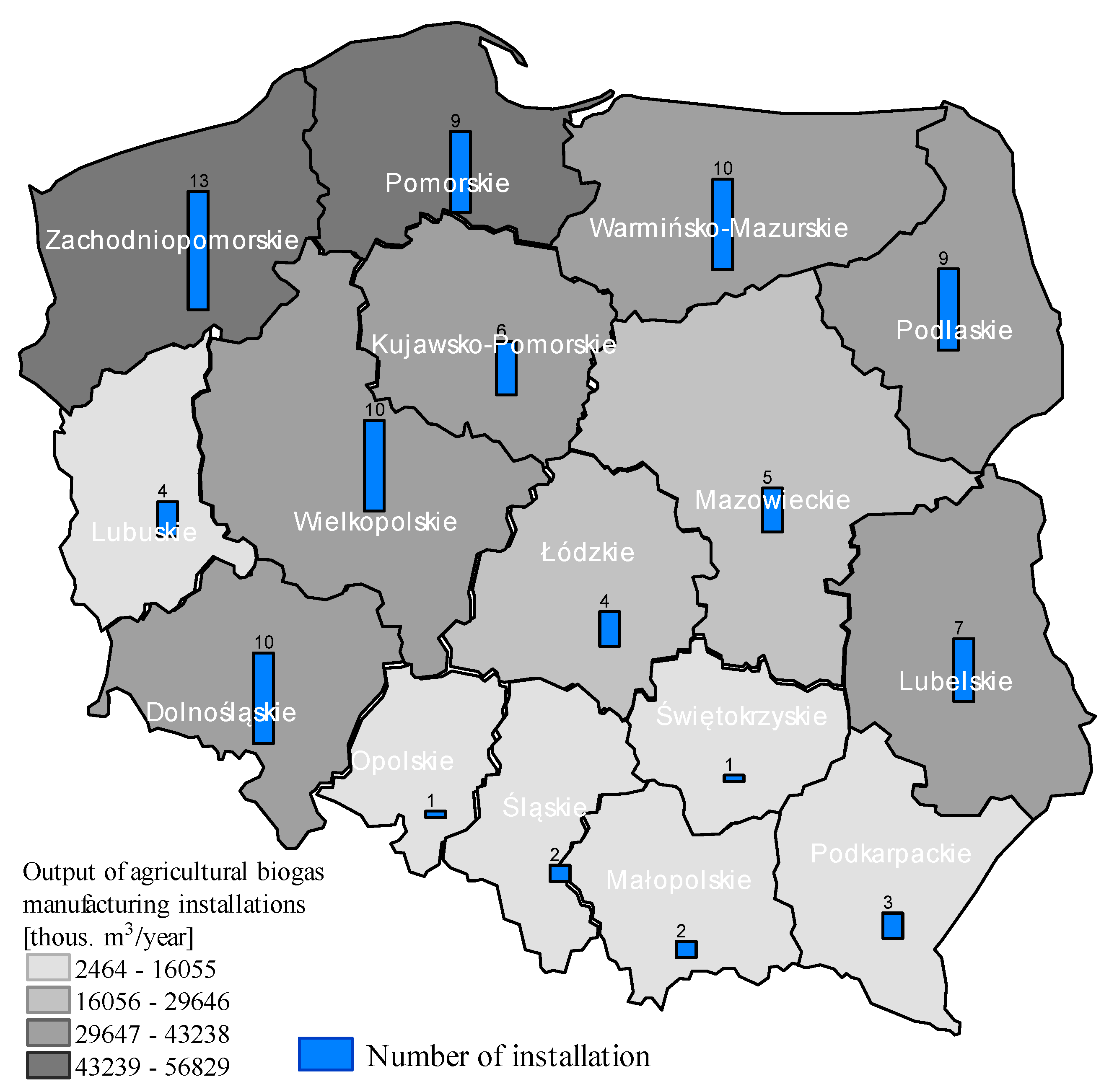
3. Current Status and Development Opportunities of the Agricultural Biogas Market in Poland—Production Volume, Feedstock, and Economic Conditions
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nevzorova, T.; Karakaya, E. Explaining the drivers of technological innovation systems: The case of biogas technologies in mature markets. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.; Harris, P.; McCabe, B.K. Biogas in the suburbs: An untapped source of clean energy? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowar, A. Low carbon agriculture in Poland - theoretical and practical challenges. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 2785–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowski, K.; Dach, J.; Lewicki, A.; Malińska, K.; do Carmo, I.E.P.; Czekała, W. Potential of biogas production from animal manure in Poland. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2019, 45, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Kucharski, P.; Białecka, B. Poultry manure as a substrate for agriculture and the chemical industry. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConf. SGEM 2019, 19, 611–618. [Google Scholar]
- Tłuczak, A. Potential and competitiveness of EU countries in terms of slaughter livestock production. Agric. Econ. Czech 2019, 65, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wisniewski, P.; Kistowski, M. Local-level agricultural greenhouse gas emissions in Poland. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 2255–2268. [Google Scholar]
- Sulewski, P.; Majewski, E.; Wąs, A. Supporting sustainable agriculture: The potential to reduce GHG emissions–the case of agricultural biogas Production in Poland. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2018, 20, 662–680. [Google Scholar]
- Jarosz, Z.; Faber, A. Ammonia emission from animal production in Poland on a regional scale. Ann. PAAAE 2019, 21, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka-Czubaszek, A.; Banaszuk, P.; Czubaszek, R. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from agriculture in the Podlaskie voivodeship in years 1999–2015. Pol. J. Nat. Sci. 2018, 33, 433–453. [Google Scholar]
- Piwowar, A. Challenges associated with environmental protection in rural areas of Poland: Empirical studies’ results. Econ. Sociol. 2020, 13, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowar, A. Attitudes and opinions of farmers in the context of environmental protection in rural areas in Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurowska, K.; Kryszk, H.; Marks-Bielska, R.; Mika, M.; Leń, P. Conversion of agricultural and forest land to other purposes in the context of land protection: Evidence from Polish experience. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowski, J. Attention: Smog alert! Citizen engagement for clean air and its consequences for fuel poverty in Poland. Energy Build. 2020, 207, 109525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikuć, M. Problems associated with the low emission limitation in Zielona Góra (Poland): Prospects and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernik, J.; Noszczyk, T.; Rutkowska, A. Towards a better understanding of the variables that influence renewable energy sources in eastern Poland. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnatowska, R.; Moryń-Kucharczyk, E. Current status of wind energy policy in Poland. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez, S.; Tobin, I.; Turco, M.; Jiménez-Guerrero, P.; Vautard, R.; Montávez, J.P. Future changes, or lack thereof, in the temporal variability of the combined wind-plus-solar power production in Europe. Renew. Energy 2019, 139, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igliński, B.; Buczkowski, R.; Iglińska, A.; Cichosz, M.; Piechota, G.; Kujawski, W. Agricultural biogas plants in Poland: Investment process, economical and environmental aspects, biogas potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4890–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzianowski, W.M.; Chasiak, I. The expansion of biogas fuelled power plants in Germany during the 2001-2010 decade: Main sustainable conclusions for Poland. J. Power Technol. 2011, 91, 102–113. [Google Scholar]
- Piwowar, A.; Dzikuć, M.; Adamczyk, J. Agricultural biogas plants in Poland—Selected technological, market and environmental aspects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, D.; Lewandowska, A. Biogas power plants in Poland—Structure, capacity, and spatial distribution. Sustainability 2015, 7, 16801–16819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Energy and Climate Plan for the years 2021–2030. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/aktywa-panstwowe/national-energy-and-climate-plan-for-the-years-2021-2030 (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Osička, J.; Kemmerzell, J.; Zoll, M.; Lehotský, L.; Černoch, F.; Knodt, M. What’s next for the European coal heartland? Exploring the future of coal as presented in German, Polish and Czech press. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2020, 61, 101316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rečka, L.; Ščasný, M. Brown coal and nuclear energy deployment: Effects on fuel-mix, carbon targets, and external costs in the Czech Republic up to 2050. Fuel 2018, 216, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xue, B.; Cai, G.; Thomas, H.; Stückrad, S. Comparing the energy transitions in Germany and China: Synergies and recommendations. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muradin, M.; Foltynowicz, Z. Potential for producing biogas from agricultural waste in rural plants in Poland. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5065–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyytimäki, J. Renewable energy in the news: Environmental, economic, policy and technology discussion of biogas. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2018, 15, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijó, L.; Lorenzo-Toja, Y.; González-García, S.; Bacenetti, J.; Negri, M.; Moreira, M.T. Eco-efficiency assessment of farm-scaled biogas plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 237, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Biogas Association. Available online: https://www.europeanbiogas.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/EBA-AR-2019-digital-version.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Banja, M.; Jégard, M.; Motola, V.; Sikkema, R. Support for biogas in the EU electricity sector–A comparative analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 128, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlat, N.; Dallemand, J.F.; Fahl, F. Biogas: Developments and perspectives in Europe. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo-Romero, M.D.P.; Sánchez-Braza, A.; Salvador-Ponce, J.; Sánchez-Labrador, N. An overview of feed-in tariffs, premiums and tenders to promote electricity from biogas in the EU-28. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 1366–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA Bioenergy Task 37, Seoul, November 13-15, 2013, Country Report, Germany. Available online: http://www.biogas.cn/UpLoadEditor/file/20140116/20140116162141_1930.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Thrän, D.; Schaubach, K.; Majer, S.; Horschig, T. Governance of sustainability in the German biogas sector—Adaptive management of the Renewable Energy Act between agriculture and the energy sector. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2020, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuerl, S.; Herrmann, C.; Heiermann, M.; Grundmann, P.; Landwehr, N.; Kreidenweis, U.; Prochnow, A. The future agricultural biogas plant in Germany: A vision. Energies 2019, 12, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernas, J.; Moudrý, J., Jr.; Kopecký, M.; Konvalina, P.; Štěrba, Z. Szarvasi-1 and Its Potential to Become a Substitute for Maize Which Is Grown for the Purposes of Biogas Plants in the Czech Republic. Agronomy 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koryś, K.A.; Latawiec, A.E.; Grotkiewicz, K.; Kuboń, M. The Review of Biomass Potential for Agricultural Biogas Production in Poland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6515. [Google Scholar]
- Karaca, C. Determination of biogas production potential from animal manure and GHG emission abatement in Turkey. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 11, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, G.; Yilmaz, E. Waste Management in Dairy Cattle Farms in Aydın Region. Potential of Energy Application. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, B.; Kapetanaki, A.B.; Wang, P. Circular agri-food approaches: Will consumers buy novel products made from vegetable waste? Rural. Sociol. 2019, 28, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, N.; Monlau, F.; Sambusiti, C.; Ficara, E.; Barakat, A.; Zabaniotou, A. Contribution to Circular Economy options of mixed agricultural wastes management: Coupling anaerobic digestion with gasification for enhanced energy and material recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkovska, N.; Horabik-Pyzel, J.; Bun, R.; Danylo, O.; Nahorski, Z.; Jonas, M.; Xiangyang, X. High-resolution spatial distribution and associated uncertainties of greenhouse gas emissions from the agricultural sector. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. 2019, 24, 881–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dzikuć, M.; Piwowar, A. Ecological and economic aspects of electric energy production using the biomass co-firing method: The case of Poland. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikuć, M. Life cycle assessment technique as a support tool to determine the impact of thermal energy production on the environment. Przem. Chem. 2018, 97, 584–586. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowar, A.; Dzikuć, M. Outline of the economic and technical problems associated with the co-combustion of biomass in Poland. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energia ze źródeł odnawialnych w 2018 r. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/download/gfx/portalinformacyjny/pl/defaultaktualnosci/5485/10/2/1/energia_ze_zrodel_odnawialnych_w_2018.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2020).
- Overview of electricity production and use in Europe. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/overview-of-the-electricity-production-2/assessment-4 (accessed on 8 March 2020).
- Gawlik, L. The Polish power industry in energy transformation process. Miner. Econ. 2018, 31, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinat, S.; Mintalova, T.; Dvořák, P.; Navratil, J.; Klusáček, P.; Kunc, J. Does rural space benefit from location of anaerobic digestion plants? Perspective of communal administration. Geogr. Cassoviensis 2013, 7, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pawłowski, W. Biogazownia jako element mający pozytywny wpływ na zmiany środowiskowe przestrzeni wiejskich (Biogas plant as an element that has a positive influence on the environmental changes of rural space). Inżynieria Ekol. 2017, 18, 157–169. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Menna, F.; Malagnino, R.A.; Vittuari, M.; Segrè, A.; Molari, G.; Deligios, P.A.; Solinas, S.; Ledda, L. Optimization of agricultural biogas supply chains using artichoke byproducts in existing plants. Agric. Syst. 2018, 165, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blades, L.; Morgan, K.; Douglas, R.; Glover, S.; De Rosa, M.; Cromie, T.; Smyth, B. Circular biogas-based economy in a rural agricultural setting. Energy Proced. 2017, 123, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqui, S.; Zerhusen, B.; Zehetmeier, M.; Effenberger, M. Distribution of specific greenhouse gas emissions from combined heat-and-power production in agricultural biogas plants. Biomass Bioenerg. 2020, 133, 105443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curkowski, A.; Oniszk-Popławska, A.; Haładyj, A.; Wybór, B.-P. Co Powinien Wiedzieć Każdy Obywatel (Biogas–A deliberate choice. What every citizen should know); Fundacja Instytut na rzecz Ekorozwoju: Warszawa, Poland, 2013; pp. 10–11. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Modica, M. Does the construction of biogas plants affect local property values? Econ. Lett. 2017, 159, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheutz, C.; Fredenslund, A.M. Total methane emission rates and losses from 23 biogas plants. Waste Manag. 2019, 97, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacyna, M.; Wasiak, M.; Lewczuk, K.; Karoń, G. Noise and environmental pollution from transport: Decisive problems in developing ecologically efficient transport systems. J. Vibroeng. 2017, 19, 5639–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, S.; Knopik, L.; Markiewicz-Patalon, M.; Brzostek, A. Assessment of transport substrates for selected agricultural biogas plant. In Proceeding of 6th International Conference on Trends in Agricultural Engineering, Prague, Czech Republic, 7–9 September 2016; pp. 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sławiński, K.; Bujaczek, R.; Piskier, T. Ocena przydatności kalkulatorów biogazowni przy planowaniu budowy biogazowni rolniczej (Assessment of the usefulness of biogas calculators when planning the construction of agricultural biogas plants). Inżynieria Rol. 2012, 4, 369–375. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Pilarski, K.; Dach, J.; Janczak, D.; Zbytek, Z. Wpływ odległości transportowej na wydajność pracy agregatów i koszty zagospodarowania pofermentu z biogazowni rolniczej 1 MWel (The influence of transport distance on tank efficiency and management costs of post-digestate from 1 MW agricultural biogas plant). J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2011, 56, 109–113. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Piwowar, A. Development of the agricultural biogas market in Poland—Production volume, feedstocks, activities and behaviours of farmers. Probl. World Agric. 2019, 19, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chodkowska-Miszczuk, J. Institutional Support for Biogas Enterprises–The Local Perspective. Quest Geogr. 2019, 38, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Support Centre for Agriculture. Available online: http://bip.kowr.gov.pl/informacje-publiczne/odnawialne-zrodla-energii/biogaz-rolniczy/dane-dotyczace-dzialalnosci-wytworcow-biogazu-rolniczego-w-latach-2011-2018 (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- National Support Centre for Agriculture. Available online: http://www.kowr.gov.pl/uploads/pliki/oze/biogaz/Rejestr_wytw%C3%B3rc%C3%B3w_biogazu_rolniczego_z_dnia_24.01.2019_r.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2020).
- Florkowski, W.J.; Us, A.; Klepacka, A.M. Food waste in rural households support for local biogas production in Lubelskie Voivodship (Poland). Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszałek, A. Czy możliwe jest przezwyciężenie problemu marnotrawstwa żywności? (Is it possible to solve the food waste problem?). Nierówności Społeczne Wzrost Gospod. 2018, 54, 474–485. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Pilarski, K.; Pilarska, A.A.; Boniecki, P.; Niedbała, G.; Durczak, K.; Witaszek, K.; Mioduszewska, N.; Kowalik, I. The Efficiency of Industrial and Laboratory Anaerobic Digesters of Organic Substrates: The Use of the Biochemical Methane Potential Correction Coefficient. Energies 2020, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saad, M.F.M.; Rahman, N.A.A.; Yusoff, M.Z.M. Hydrogen and Methane Production from Co-digestion of Food Waste and Chicken Manure. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 2805–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugol, M.; Prask, H. Porównanie uzysku biogazu z trzech rodzajów kiszonek: Z kukurydzy, lucerny i trawy (Comparison of biogas yield from three types of silage: Maize, lucerne and grass silage). Inżynieria Rol. 2011, 9, 31–38. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Fugol, M.; Szlachta, J. Zasadność używania kiszonki z kukurydzy i gnojowicy świńskiej do produkcji biogazu (The reason for using corn and fermented liquid manure ensilage for biogas production). Inżynieria Rol. 2010, 1, 169–174. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sadecka, Z.; Suchowska-Kisielewicz, M. Co-fermentation of chicken manure. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2016, 18, 609–625. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Han, Y.; Ren, G.; Yang, G. Improved biogas production from chicken manure anaerobic digestion using cereal residues as co-substrates. Energy Fuel 2014, 28, 2490–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pečar, D.; Pohleven, F.; Goršek, A. Kinetics of methane production during anaerobic fermentation of chicken manure with sawdust and fungi pre-treated wheat straw. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busato, C.J.; Da Ros, C.; Pellay, R.; Barbierato, P.; Pavan, P. Anaerobic membrane reactor: Biomethane from chicken manure and high-quality effluent. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tańczuk, M.; Junga, R.; Kolasa-Więcek, A.; Niemiec, P. Assessment of the Energy Potential of Chicken Manure in Poland. Energies 2019, 12, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schommer, V.A.; Wenzel, B.M.; Daroit, D.J. Anaerobic co-digestion of swine manure and chicken feathers: Effects of manure maturation and microbial pretreatment of feathers on methane production. Renew. Energy 2020, 152, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurpaska, S.; Kiełbasa, P.; Sobol, Z. Innovative Methods of Obtaining Substrates and Pre-treatment in the Production of Biogas. In Renewable Energy Sources: Engineering, Technology, Innovation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Igliński, B.; Piechota, G.; Iwański, P.; Skarzatek, M.; Pilarski, G. 15 Years of the Polish agricultural biogas plants: Their history, current status, biogas potential and perspectives. Clean Technol. Environ. 2020, 22, 281–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, J.; Graczyk, M. Green certificates as an instrument to support renewable energy in Poland—Strengths and weaknesses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 6577–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | The Number of Entities Entered into the Register | The Number of Plants Included in the Register | The Amount of Agricultural Biogas Produced (thousand m3) | The Amount of Electricity Generated from Agricultural Biogas (MWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 4 | 8 | 36,646 | 73,433 |
| 2012 | 10 | 16 | 73,152 | 141,804 |
| 2013 | 21 | 28 | 112,412 | 227,890 |
| 2014 | 35 | 42 | 174,253 | 354,978 |
| 2015 | 50 | 58 | 206,236 | 429,400 |
| 2016 | 69 | 78 | 250,159 | 524,532 |
| 2017 | 84 | 94 | 291,742 | 608,269 |
| 2018 | 86 | 96 | 303,609 | 638,510 |
| Specification | Units | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Manure | (Mg) | 265,961 | 349,173 | 455,583 | 574,069 | 598,963 | 774,997 | 807,223 | 757,555 |
| (%) | 56.66 | 38.07 | 28.94 | 27.00 | 24.11 | 23.98 | 21.26 | 18.94 | |
| Residues from Fruit and Vegetables | (Mg) | 10,984 | 86,109 | 268,599 | 355,740 | 494,046 | 665,315 | 756,929 | 769,546 |
| (%) | 2.34 | 9.39 | 17.06 | 16.73 | 19.89 | 20.59 | 19.94 | 19.24 | |
| Distillers Grains with Solubles | (Mg) | 30,465 | 146,607 | 354,877 | 349,366 | 439,580 | 477,523 | 762,296 | 839,983 |
| (%) | 6.49 | 15.99 | 22.54 | 16.43 | 17.69 | 14.78 | 20.08 | 21.00 | |
| Maize Silage | (Mg) | 108,876 | 241,590 | 287,471 | 416,595 | 415,322 | 439,145 | 472,152 | 482,805 |
| (%) | 23.19 | 26.34 | 18.26 | 19.59 | 16.72 | 13.59 | 12.44 | 12.07 | |
| Bee Pulp | (Mg) | 6,922 | 37,082 | 101,661 | 189,811 | 189,016 | 222,157 | 280,209 | 291,768 |
| (%) | 1.47 | 4.04 | 6.46 | 8.93 | 7.61 | 6.87 | 7.38 | 7.29 | |
| Other | (Mg) | 46,207 | 56,560 | 105,988 | 240,796 | 347,574 | 652,622 | 718,121 | 858,499 |
| (%) | 9.84 | 6.17 | 6.73 | 11.32 | 13.99 | 20.19 | 18.91 | 21.46 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piwowar, A. Agricultural Biogas—An Important Element in the Circular and Low-Carbon Development in Poland. Energies 2020, 13, 1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071733
Piwowar A. Agricultural Biogas—An Important Element in the Circular and Low-Carbon Development in Poland. Energies. 2020; 13(7):1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071733
Chicago/Turabian StylePiwowar, Arkadiusz. 2020. "Agricultural Biogas—An Important Element in the Circular and Low-Carbon Development in Poland" Energies 13, no. 7: 1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071733
APA StylePiwowar, A. (2020). Agricultural Biogas—An Important Element in the Circular and Low-Carbon Development in Poland. Energies, 13(7), 1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071733





