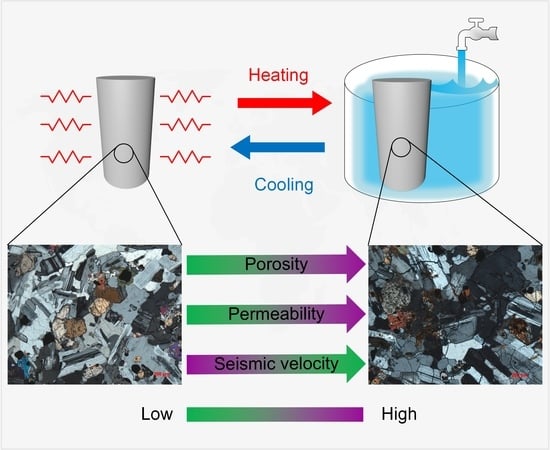
Effects of Cyclic Heating and Water Cooling on the Physical Characteristics of Granite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Rock Samples
2.2. Methodology of Heating and Cooling
2.3. Ultrasonic Wave Velocity Measurements
2.4. Porosity and Gas Permeability Measurements
2.5. Microscopic Observation
2.6. Image Processing
3. Results
3.1. Porosity
3.2. Gas Permeability
3.3. P- and S-Wave Velocity
3.4. Rock Microstructure
3.5. Microcrack Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Physical characteristics changed significantly after flowing water cooling at high heating temperatures versus the number of thermal cycles. P- and S-waves reduced with the increase of thermal cycles. Porosity did not change substantially at heating temperatures of less than 400 °C. The permeability increased by four orders of magnitude compared to the samples without thermal treatment, which is susceptible than porosity.
- (2)
- Both grain boundary microcracks and transgranular microcracks were found. The primary effect of heating was grain boundary cracking during the first thermal cycle. Increasing the number of thermal cycles, transgranular microcracks also developed in the rock. Both types of grain boundary microcracks and transgranular microcracks coalesced to form a fracture network.
- (3)
- Quantification of the crack morphology from CTS images indicated that the large number of microcracks that developed in the granite during high-temperature treatment changed the rocks physical properties. The length of microcracks increased by one order of magnitude.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, W.; Cao, W.; Jiang, F. A novel single-well geothermal system for hot dry rock geothermal energy exploitation. Energy 2018, 162, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breede, K.; Dzebisashvili, K.; Liu, X.; Falcone, G. A systematic review of enhanced (or engineered) geothermal systems: Past, present and future. Geotherm. Energy 2013, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomac, I.; Sauter, M. A review on challenges in the assessment of geomechanical rock performance for deep geothermal reservoir development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-Y.; Gao, M.; Shah, K.J.; Zheng, J.; Pei, S.-L.; Chiang, P.-C. Establishment of enhanced geothermal energy utilization plans: Barriers and strategies. Renew. Energy 2019, 132, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelkar, S.; WoldeGabriel, G.; Rehfeldt, K. Lessons learned from the pioneering hot dry rock project at Fenton Hill, USA. Geothermics 2016, 63, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, J. Forecast and evaluation of hot dry rock geothermal resource in China. Renew. Energy 2005, 30, 1831–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, W.G.P.; Ranjith, P.G.; Perera, M.S.A.; Chen, B.K.; Abdulagatov, I.M. Temperature-dependent mechanical behaviour of Australian Strathbogie granite with different cooling treatments. Eng. Geol. 2017, 229, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yin, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Bai, L. Dynamic Properties of Thermally Treated Granite Subjected to Cyclic Impact Loading. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, J.; Hu, D.; Skoczylas, F.; Shao, J. Laboratory Investigation on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Granite After Heating and Water-Cooling Treatment. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 51, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Z. Real-time permeability evolution of thermally cracked granite at triaxial stresses. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 133, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Hu, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, X.; Li, C. Influence of different thermal cycling treatments on the physical, mechanical and transport properties of granite. Geothermics 2019, 78, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Rong, G.; Cai, M.; Yao, M.-D.; Zhou, C.-B. Physical and mechanical behaviors of a thermal-damaged coarse marble under uniaxial compression. Eng. Geol. 2016, 200, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ni, J.; Shao, W.; Azzam, R. Experimental study on the influence of temperature on the mechanical properties of granite under uni-axial compression and fatigue loading. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2012, 56, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.K.; Verma, A.K.; Jha, M.K.; Sharma, P.; Singh, T.N. Effect of high temperature on physical and mechanical properties of Jalore granite. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 159, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ranjith, P.G.; Jing, H.-W.; Tian, W.-L.; Ju, Y. An experimental investigation on thermal damage and failure mechanical behavior of granite after exposure to different high temperature treatments. Geothermics 2017, 65, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Ji, J.; Shen, Z. Experiment investigation of granite damage under the high-temperature and high-pressure supercritical water condition. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 180, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Q.; Hao, S.; Geng, J.; Lv, C. Experimental study on the variation of physical and mechanical properties of rock after high temperature treatment. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 98, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Li, X.; Cao, W.; Xia, K. Effects of Thermal Treatment on Tensile Strength of Laurentian Granite Using Brazilian Test. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuze, F.E. High-temperature mechanical, physical and Thermal properties of granitic rocks—A review. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1983, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrich, J.T.; Wong, T.-F. Micromechanics of thermally induced cracking in three crustal rocks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 12743–12764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Kuriki, Y.; Kusuda, H.; Mabuchi, M. Observation of microstructures in granite samples subjected to one cycle of heating and cooling. J. Jpn. Soc. Eng. Geol. 2008, 49, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arena, A.; Delle Piane, C.; Sarout, J. A new computational approach to cracks quantification from 2D image analysis: Application to micro-cracks description in rocks. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 66, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Piane, C.; Arena, A.; Sarout, J.; Esteban, L.; Cazes, E. Micro-crack enhanced permeability in tight rocks: An experimental and microstructural study. Tectonophysics 2015, 665, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Kant, M.A.; Madonna, C.; Saar, M.O.; Rudolf von Rohr, P. The Effects of High Heating Rate and High Temperature on the Rock Strength: Feasibility Study of a Thermally Assisted Drilling Method. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018, 51, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, G. Evolution of thermal damage and permeability of Beishan granite. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Pu, H.; Li, X. Effect of Thermal Treatment on Brazilian Tensile Strength of Granites with Different Grain Size Distributions. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018, 51, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, B.; Gamage, R.; Rathnaweera, T.; Perera, M.; Chandrasekharam, D.; Kumari, W. An Influence of Thermally-Induced Micro-Cracking under Cooling Treatments: Mechanical Characteristics of Australian Granite. Energies 2018, 11, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarout, J.; Cazes, E.; Delle Piane, C.; Arena, A.; Esteban, L. Stress-dependent permeability and wave dispersion in tight cracked rocks: Experimental validation of simple effective medium models. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 6180–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qian, Z.; Wu, Z. Micro/macro physical and mechanical variation of red sandstone subjected to cyclic heating and cooling: An experimental study. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 78, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirdesai, N.N.; Mahanta, B.; Ranjith, P.G.; Singh, T.N. Effects of thermal treatment on physico-morphological properties of Indian fine-grained sandstone. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 78, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hu, B. Creep and Long-Term Permeability of a Red Sandstone Subjected to Cyclic Loading After Thermal Treatments. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018, 51, 2981–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, P.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y. Experimental investigation on triaxial mechanical and permeability behavior of sandstone after exposure to different high temperature treatments. Geothermics 2017, 69, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotóns, V.; Tomás, R.; Ivorra, S.; Alarcón, J.C. Temperature influence on the physical and mechanical properties of a porous rock: San Julian’s calcarenite. Eng. Geol. 2013, 167, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräf, V.; Jamek, M.; Rohatsch, A.; Tschegg, E. Effects of thermal-heating cycle treatment on thermal expansion behavior of different building stones. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2013, 64, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmutoglu, Y. Mechanical Behaviour of Cyclically Heated Fine Grained Rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 1998, 31, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, G.; Peng, J.; Cai, M.; Yao, M.; Zhou, C.; Sha, S. Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of bedrocks in geothermal fields. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 141, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Song, H.; Zhao, X. Effects of cyclic heating and LN2-cooling on the physical and mechanical properties of granite. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 156, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire-Lista, D.; Fort, R.; Varas-Muriel, M. Thermal stress-induced microcracking in building granite. Eng. Geol. 2016, 206, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwivedi, R.D.; Goel, R.K.; Prasad, V.V.R.; Sinha, A. Thermo-mechanical properties of Indian and other granites. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2008, 45, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, B.L.A.; Ranjith, P.G.; Rathnaweera, T.D.; Perera, M.S.A.; Silva, V.R.S.D. Quantification of thermally-induced microcracks in granite using X-ray CT imaging and analysis. Geothermics 2019, 81, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaki, S.; Takarli, M.; Agbodjan, W.P. Influence of thermal damage on physical properties of a granite rock: Porosity, permeability and ultrasonic wave evolutions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, Z.; Song, H.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Li, R.; Wen, H.; Huang, P.; Dai, X. Variations of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Heated Granite After Rapid Cooling with Liquid Nitrogen. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 2123–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, N.; Xie, X.; Li, M.; Yu, S. α-β phase transition of quartz based on molecular dynamics simulations. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials, Harbin, China, 19–23 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Duffrene, L. Molecular dynamic simulations of the alpha; -beta; phase transition in silica cristobalite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1998, 59, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, L.; Heap, M.J.; Baud, P.; Schmittbuhl, J. Quantification of microcrack characteristics and implications for stiffness and strength of granite. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 100, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Bonner, B.P.; Carlson, S.R.; Kowallis, B.J.; Heard, H.C. Thermal stress cracking in granite. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]























| Temperature (°C) | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cycles | 1 | A1, B1 | A2, B2 | A3, B3 | A4, B4 | A5, B5 | A6, B6 | A31, B31 (No thermal treatment) |
| 2 | A7, B7 | A8, B8 | A9, B9 | A10, B10 | A11, B11 | A12, B12 | ||
| 4 | A13, B13 | A14, B14 | A15, B15 | A16, B16 | A17, B17 | A18, B18 | ||
| 8 | A19, B19 | A20, B20 | A21, B21 | A22, B22 | A23, B23 | A24, B24 | ||
| 16 | A25, B25 | A26, B26 | A27, B27 | A28, B28 | A29, B29 | A30, B30 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.; Gao, L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, C.; Chen, S.; Zhuo, X. Effects of Cyclic Heating and Water Cooling on the Physical Characteristics of Granite. Energies 2020, 13, 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092136
Shi X, Gao L, Wu J, Zhu C, Chen S, Zhuo X. Effects of Cyclic Heating and Water Cooling on the Physical Characteristics of Granite. Energies. 2020; 13(9):2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092136
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xiangchao, Leiyu Gao, Jie Wu, Cheng Zhu, Shuai Chen, and Xiao Zhuo. 2020. "Effects of Cyclic Heating and Water Cooling on the Physical Characteristics of Granite" Energies 13, no. 9: 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092136
APA StyleShi, X., Gao, L., Wu, J., Zhu, C., Chen, S., & Zhuo, X. (2020). Effects of Cyclic Heating and Water Cooling on the Physical Characteristics of Granite. Energies, 13(9), 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092136