Case of Study of the Electrification of a Tractor: Electric Motor Performance Requirements and Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Powertrain Electrification
2.1. Electrification Purpose and Constraints
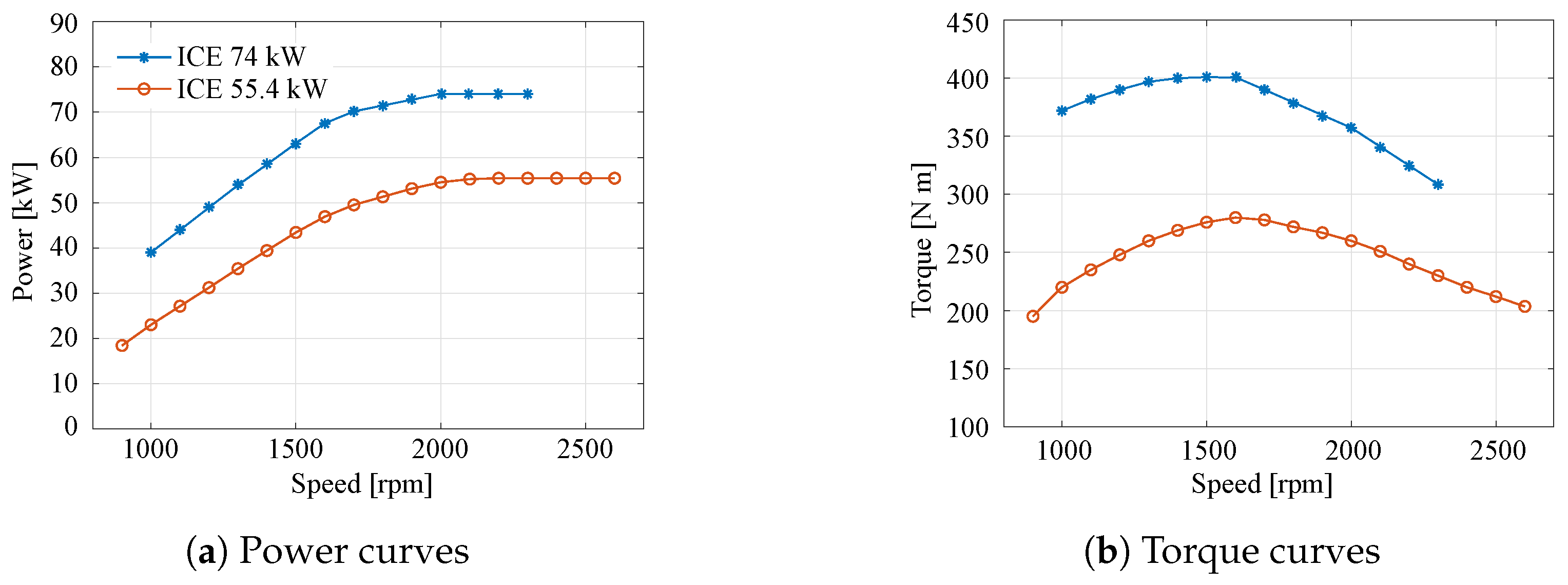
2.2. Traditional Powertrain
- The shaft connects the pump to operate the hydraulic oil circuit; this is required for hydraulic steering and hydraulic lifting. Moreover, there are instruments which need to be connected with the tractor hydraulic circuit.
- The shaft is required to power external instruments through the PTO. This shaft is connected to the ICE with a speed reducer. The clutch allows the shaft to be decoupled if not required.
- The shaft provides power to the rear wheel axle for traction, and eventually also to the front axle in the case of 4WD traction. The schema shows the clutch and a gearbox.
2.3. Hybrid Powertrain
3. Hybrid-Powertrain Performance Investigation
3.1. Power-Management Strategy
3.2. Electric Motor Performance
3.3. Equivalent Thermal Torque
4. Design of the Electric Motor
4.1. Data and Performance
4.2. Thermal Analysis of the Electric Motor
4.3. Efficiency Map
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Lajunen, A.; Sainio, P.; Laurila, L.; Pippuri-Mäkeläinen, J.; Tammi, K. Overview of Powertrain Electrification and Future Scenarios for Non-Road Mobile Machinery. Energies 2018, 11, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) 2016/1628 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 September 2016 on requirements relating to gaseous and particulate pollutant emission limits and type-approval for internal combustion engines for non-road mobile machinery, amending Regulations (EU) No 1024/2012 and (EU) No 167/2013, and amending and repealing Directive 97/68/EC.
- Grammatico, S.; Balluchi, A.; Cosoli, E. A series-parallel hybrid electric powertrain for industrial vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Lille, France, 1–3 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, F.E.G.; Brandao, D.I.; Maia, T.; Braz de Filho, J.C. Off-Road Vehicle Hybridization Methodology Applied to a Tractor Backhoe Loader. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Detroit, MI, USA, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Brenna, M.; Foiadelli, F.; Leone, C.; Longo, M.; Zaninelli, D. Feasibility Proposal for Heavy Duty Farm Tractor. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference of Electrical and Electronic Technologies for Automotive, Milan, Italy, 9–11 July 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Barthel, J.; Gorges, D.; Bell, M.; Munch, P. Energy Management for Hybrid Electric Tractors Combining Load Point Shifting, Regeneration and Boost. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Coimbra, Portugal, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhitkova, S.; Felden, M.; Franck, D.; Hameyer, K. Design of an electrical motor with wide speed range for the in-wheel drive in a heavy duty off-road vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 1076–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Troncon, D.; Alberti, L.; Mattetti, M. A Feasibility Study for Agriculture Tractors Electrification: Duty Cycles Simulation and Consumption Comparison. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Detroit, MI, USA, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Troncon, D.; Alberti, L.; Bolognani, S.; Bettella, F.; Gatto, A. Electrification of agricultural machinery: A feasibility evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2019 Fourteenth International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER), Monte-Carlo, Monaco, 8–10 May 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin, B.; Magne, P.; Malysz, P.; Yang, Y.; Pantelic, V.; Preindl, M.; Korobkine, A.; Jiang, W.; Lawford, M.; Emadi, A. Making the Case for Electrified Transportation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajashekara, K. Present Status and Future Trends in Electric Vehicle Propulsion Technologies. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.C.; Bouscayrol, A.; Chen, K. Electric, Hybrid, and Fuel-Cell Vehicles: Architectures and Modeling. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmillan, R.H. The Mechanics of Tractor-Implement Performance: Theory and Worked Examples: A Textbook for Students and Engineers; University of Melbourne: Parkville, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.; Kim, Y.; Jung, I.; Jung, H. Permanent magnet synchronous motor for electric tractor of 35 horsepower. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE ECCE Asia Downunder, Melbourne, Australia, 3–6 June 2013; pp. 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhitkova, S.; Hameyer, K. Realization of a wide speed range for an agricultural tractor. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, L.; Bianchi, N.; Morandin, M.; Gyselinck, J. Finite-Element Analysis of Electrical Machines for Sensorless Drives With High-Frequency Signal Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, L.; Bianchi, N.; Bolognani, S. High Frequency d-q Model of Synchronous Machines for Sensorless Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3923–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottesi, O.; Alberti, L.; Sabariego, R.V.; Gyselinck, J. Finite Element Small-Signal Simulation of Electromagnetic Devices Considering Eddy Currents in the Laminations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engine Data-Sheet FPT N45 MSSX. Available online: https://www.fptindustrial.com/global/it/Pages/construction_nef45.aspx (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Engine Data-Sheet DEUTZ TCD2.2 L3. Available online: https://www.deutz.com/en/products/engines/detail/442/ (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Panzani, G.; Tanelli, M.; Savaresi, S.M.; Pirola, C.; Gavina, G.; Taroni, F. Transmission control for power-shift agricultural tractors. In Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 30 June–2 July 2010; pp. 2188–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirasingha, S.G.; Emadi, A. Classification and Review of Control Strategies for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Hybrid Electric Vehicle System Modeling and Control; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duty Cycle of the Electric Motor Driving a Weeder in Hybrid Mode. Available online: https://docs.google.com/document/d/e/2PACX-1vS7SpcbwXXuYrH3mdKuYEIxBPSqlZFueAgK7Q3QqZoa2P2IL_cHlbeetuGOuJG89ZLIaxdQZb8jwTp7/pub (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Duty Cycle of the Electric Motor Driving a Plant Lifting Plough in Pure Electric Mode. Available online: https://docs.google.com/document/d/e/2PACX-1vTeL8ZezHadvITaSIYSj-SQduoc5RFFlFaGZkKHiLpKgA-V_vGmLYZqm2RXxWiyc_D7AN6qnVyZGE8I/pub (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Deisenroth, D.; Ohadi, M. Thermal Management of High-Power Density Electric Motors for Electrification of Aviation and Beyond. Energies 2019, 12, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.S.; Sul, S.K.; Alberti, L.; Bianchi, N. Design and Control of an Axial-Flux Machine for a Wide Flux-Weakening Operation Region. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Alberti, L.; Barcaro, M. Design and Tests of a Four-Layer Fractional-Slot Interior Permanent-Magnet Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2234–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, P. Tooth-Coil Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Design for Special Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Nino, C.E.; Tariq, A.R.; Strangas, E.G. Thermal Analysis of Permanent Magnet Motor for the Electric Vehicle Application Considering Driving Duty Cycle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2493–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boglietti, A.; Cavagnino, A.; Staton, D.; Shanel, M.; Mueller, M.; Mejuto, C. Evolution and Modern Approaches for Thermal Analysis of Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.; Dorrell, D.; Alberti, L.; Bianchi, N.; Staton, D.; Hawkins, D. Thermal Analysis of Duplex Three-Phase Induction Motor Under Fault Operating Conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, L.; Fornasiero, E.; Bianchi, N. Impact of the Rotor Yoke Geometry on Rotor Losses in Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodetto, N.; Bianchi, N.; Alberti, L. Improved Analytical Estimation of Rotor Losses in High-Speed Surface-Mounted PM Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3548–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Duty Cycle Intensity | PTO | Experimental Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy cultivation | Weeder; Clod breaker | |
| Medium cultivation | ✓ | Atomizer; Grape harvester; Rotary cultivator |
| Light cultivation | Plant lifting plough; Tipping machine | |
| Light cultivation | ✓ | Tying machine |
| Heavy transportation | Road trailer |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Number of slots | 36 | - |
| Number of poles | 6 | - |
| Stator outer diameter | 200 | |
| Stator inner diameter | 135 | |
| Air gap thickness | 1 | |
| Stack length | 65 | |
| Magnet thickness | 6 | |
| Stator core mass | 6.47 | |
| Rotor core mass | 3.24 | |
| Copper mass | 2.55 | |
| Magnets mass | 0.94 | |
| Lamination material | M530-50A | - |
| Winding material | Cu | - |
| PM material | NdFeB | - |
| PM remanence | 1.21 | |
| PM coercivity | 883 | / |
| Slot copper-filling factor | 0.4 | - |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
| Rated torque | 40 | |
| Rated speed | 2600 | |
| Rated current density | 9.4 | / |
| Rated current | 24.5 | |
| Overload current | 420 | |
| Overload torque | 150 | |
| Winding peak voltage | 400 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Troncon, D.; Alberti, L. Case of Study of the Electrification of a Tractor: Electric Motor Performance Requirements and Design. Energies 2020, 13, 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092197
Troncon D, Alberti L. Case of Study of the Electrification of a Tractor: Electric Motor Performance Requirements and Design. Energies. 2020; 13(9):2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092197
Chicago/Turabian StyleTroncon, Diego, and Luigi Alberti. 2020. "Case of Study of the Electrification of a Tractor: Electric Motor Performance Requirements and Design" Energies 13, no. 9: 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092197
APA StyleTroncon, D., & Alberti, L. (2020). Case of Study of the Electrification of a Tractor: Electric Motor Performance Requirements and Design. Energies, 13(9), 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092197





