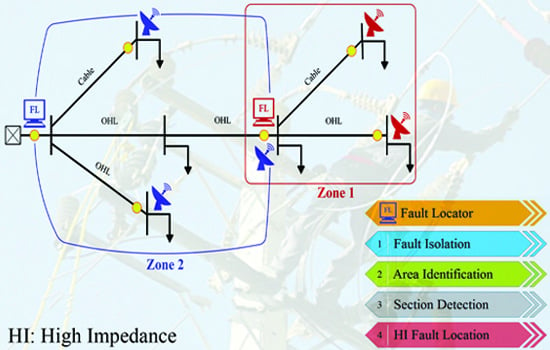
1. Introduction
Power distribution networks are vulnerable to different faults. This is mainly due to conditions such as a harsh working environment, operating conditions, and system aging. Such faults can compromise the security of electricity supply and the reliability in our cities [
1]. Fast automatic fault location is important in the process of power restoration and repair. After faults have been located and isolated, restoration plans are designed to maximize the re-energized loads [
2,
3].
Methods for automatic fault location in distribution networks can be categorized into two groups: (1) conventional automatic methods and (2) methods based on artificial intelligence [
4]. The first is represented by impedance based methods [
1,
5,
6], traveling wave methods [
7,
8,
9], etc. The second is represented by intelligence methods, such as artificial neural networks (ANN) [
10], support vector machines (SVM) [
11], fuzzy logic [
12,
13,
14], genetic algorithms (GA) [
15,
16], the matching approach [
17], etc. The performance of intelligence methods is highly dependable on the training data [
8]. Moreover, any network configuration changes require new data acquisition and update of the algorithm. The traveling wave method has a better performance in multi-branched radial topologies compared with the impedance based method [
18].
The current fault location practice in distribution systems consists of network switching, subscriber notification to the dispatching center, use of protective and smart equipment, and deployment of fault indicators on the network and substations. Fault location is challenging for distribution networks because feeders are distributed over wide branched areas composed of several overhead lines and underground cables.
Fault location has been extensively studied, and different methods have been proposed, which can be classified into four main categories according to [
19]. One of the main categories is the measurement based methods, which can be classified into three important groups: (1) power frequency signals [
1,
5,
6,
20,
21,
22], (2) high frequency signals [
7,
8,
9,
23,
24], and (3) artificial intelligence [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17].
Among shunt faults, high impedance (HI) faults are the most critical. When a high impedance fault occurs, the voltage and current levels in power systems do not increase significantly [
7,
25]. On the other hand, the HI faults may not be detected by the relay protection. Therefore, different methods have been proposed [
1,
7,
9,
25,
26,
27]. Fault location and parameters can be estimated within the first cycles after fault occurrence [
9]. In the traveling wave method, Discrete wavelet transform (DWT) based multi-resolution analysis (MRA) gives better signal representation because its resolution is balanced at any time and frequency [
7]. For characterization and extraction of transient signals with DWT transform, db4 has the best performance in the Daubechies family based on its detection and discrimination rates [
25]. Furthermore, power line communication (PLC) technology can be utilized for communication and monitoring of lines [
26,
28].
In this paper, an accurate fault location framework is proposed by using over-current relays and an MRA wavelet transform. Compared with the traveling wave method [
8,
29], the proposed technique needs only half of the signal cycle to locate the HI fault section position. After the fault data are sampled and processed, the mutual effects of electromagnetic transient signals are decomposed into their modal signals by the alpha-beta (
) transformation. Finally, the arrival time of the traveling waves can be defined using DWT and the
mother wavelet.
The method supports distribution grids that are equipped with data loggers. The data loggers have the ability to record voltage and current data and relevant harmonic information. Furthermore, they have the event recorder module, which records the voltage and current in one cycle before and after the occurring event time with a step of 400 s.
For the evaluation of the proposed method, different types of short-circuit faults with various resistances are simulated in a combined overhead line and underground cable smart distribution network with tapped lines. The proposed method is simulated by DigSILENT and MATLAB in balanced and unbalanced configurations. The results confirm the high efficiency and accuracy of the proposed method.
This paper is structured into five sections. Besides the Introduction section,
Section 2 describes the state-of-the-art on traveling wave fault location methods. The proposed extensions are discussed in
Section 3. The evaluation of the proposed method and the results are presented in
Section 4.
Section 5 presents the conclusion of this paper.
4. Results
A 13 node network, which is a combined overhead line and underground cable distribution network, is modeled according to
Figure 7. High impedance fault location is performed in the balanced and unbalanced conditions by MATLAB and DigSILENT software. The simulated network contained 12 loads and 12 lines with 9 overhead lines and 3 underground cables of a 20 kV voltage level. Load values and their distribution on both configuration are presented in
Table 2.
Table 3 shows the overhead and the cable line parameters of the network. The cables are between Nodes 2 and 3, 6 and 7, and 11 and 12, and the others are OHLs.
Figure 8 shows the three-phase transient voltage waveforms during a single-phase-to-ground short-circuit fault (BG) between Nodes 2 and 3 with 85
resistances and 11.58 km away from Node 2. The voltage waveforms in
Figure 8a–d are recorded at Nodes 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively.
4.1. Simulation
The simulation results included zone detection, section identification, and HI fault location based on the two terminals’ information. The results are presented in
Section 4.1.1,
Section 4.1.2 and
Section 4.1.3, respectively. The faults conditions in
Table 4 and
Table 5 are the same as those described in
Table 6.
4.1.1. Zone Detection
It was possible to identify and recognize the fault area, by implementing the proposed protection plan (
Section 3.1). Protection coordination of over current relays was done to isolate all types of short-circuit faults up to 100
from the network (isolation performance for all relays).
The test network had 12 lines with different lengths, which included seven different paths. Conservation coordination for all lines (OHLs and cables) was implemented seamlessly.
Table 4 shows the performance of the proposed coordination method for fault clearance and zone detection in balanced mode.
In the case of a fault, the relay responsible for the protection zone will isolate the faulty zone from other sectors in order to avoid the spreading of the disturbance and the collapse of the network.
4.1.2. Section Diagnosis
After the fault zone was identified by the operation of OCRs, the faulty line could be determined using the traveling wave timestamps inside the selected area. In this study, traveling times were extracted using DWT and the
mother wavelet in 10 levels. For this purpose,
and
were used for grounded and ungrounded faults, respectively.
Table 5 shows the section diagnosis simulation results.
4.1.3. Fault Location
Fault location results are presented in this section considering balanced and unbalanced configurations. Estimated fault location simulation outcomes were tested in different conditions, and the results are shown in
Table 6 for underground cables and overhead lines. As mentioned, these results were obtained for a distribution network (
Figure 7) using two terminals’ information. It should be noted that high impedance faults occurred in full load conditions.
4.2. Discussions
In [
27], the magnetic field sensors with a 3 km distance from each other were used for HI fault location in an overhead line distribution network. This method is not suitable for wide networks, especially with long-distance underground cables. The accuracy of the proposed method in [
1] decreased as fault resistance increased. To use the continuous wavelet transform for analyzing fault signals in [
8], high frequency sampling equipment (e.g., 1 GHz) is required. In addition, to have the same reference time for measurement units in [
8,
27], synchronization by a global positioning system (GPS) is required. The method that was presented in this paper improved the state-of-the-art as it did not have the weaknesses mentioned in [
1,
8,
27]. According to the results in
Table 7, it was also more accurate.
The works in [
1,
8,
27] were only tested in OHL distribution power network (DPN) using voltage and current and voltage and magnetic field measurement (see
Table 7) with a 1.5–2.8% error. However, in this paper, in addition to checking the validity of the proposed method in a combined overhead line and underground cable distribution network, the maximum error was −0.49%.
The high impedance fault usually presents a small fault current, which is not sufficient to trip the protection of the relay. However, in this work, the distribution zones were set by setting the sensitive relays or high impedance fault detection relays. The distribution network had data loggers on the nodes. The most common faults were unsymmetrical faults such as single phase fault to ground, double phase fault, and double phase fault to ground. The high impedance faults could be detected by sensitive EFrelays or high impedance fault detection relays. When the high impedance fault occurred, the mentioned relays detected the high impedance fault, and consequently, the faulty zone was determined. Based on the recorded time in the relays, the voltages of data loggers were extracted and converted, and WT was run and the transient times extracted. The one that had an earlier registration time determined the faulty section. Then, based on these times and the wave velocity, the fault distance was calculated. For this method, sensitive earth-fault relays were appropriate.
5. Conclusions
The purpose of the paper was to minimize outage in distribution networks. This study showed that the presented method was practical for area detection, faulty section identification, and high impedance short-circuit fault location in combined networks. The proposed method was tested on a 20 kV combined distribution network with 13 nodes in balanced and unbalanced conditions. The results confirmed that the proposed method was highly accurate in detecting faulty zones, sections, and location in a variety of OHLs, cables, and combined lines in different parts of the distribution networks. Comparing the proposed method with previous studies showed that the accuracy of the proposed method was higher, and more importantly, it was suitable for use in practical conditions. What distinguished this method from others was its ability to handle challenges such as unbalanced loads, combined lines, and HI faults. The accuracy of the proposed method in simulation was high, if all the data of relays and data loggers were provided and the communication service and GPS tags were available. However, some technical problems require further investigations in future work such as the effect of DGs, changing the network structure, and changing the system protection scheme by renewable energy resources, blinding, and false tripping in combined networks.