Reducing the Power Consumption of the Electrodynamic Suspension Levitation System by Changing the Span of the Horizontal Magnet in the Halbach Array
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analytical Methods
3. Results
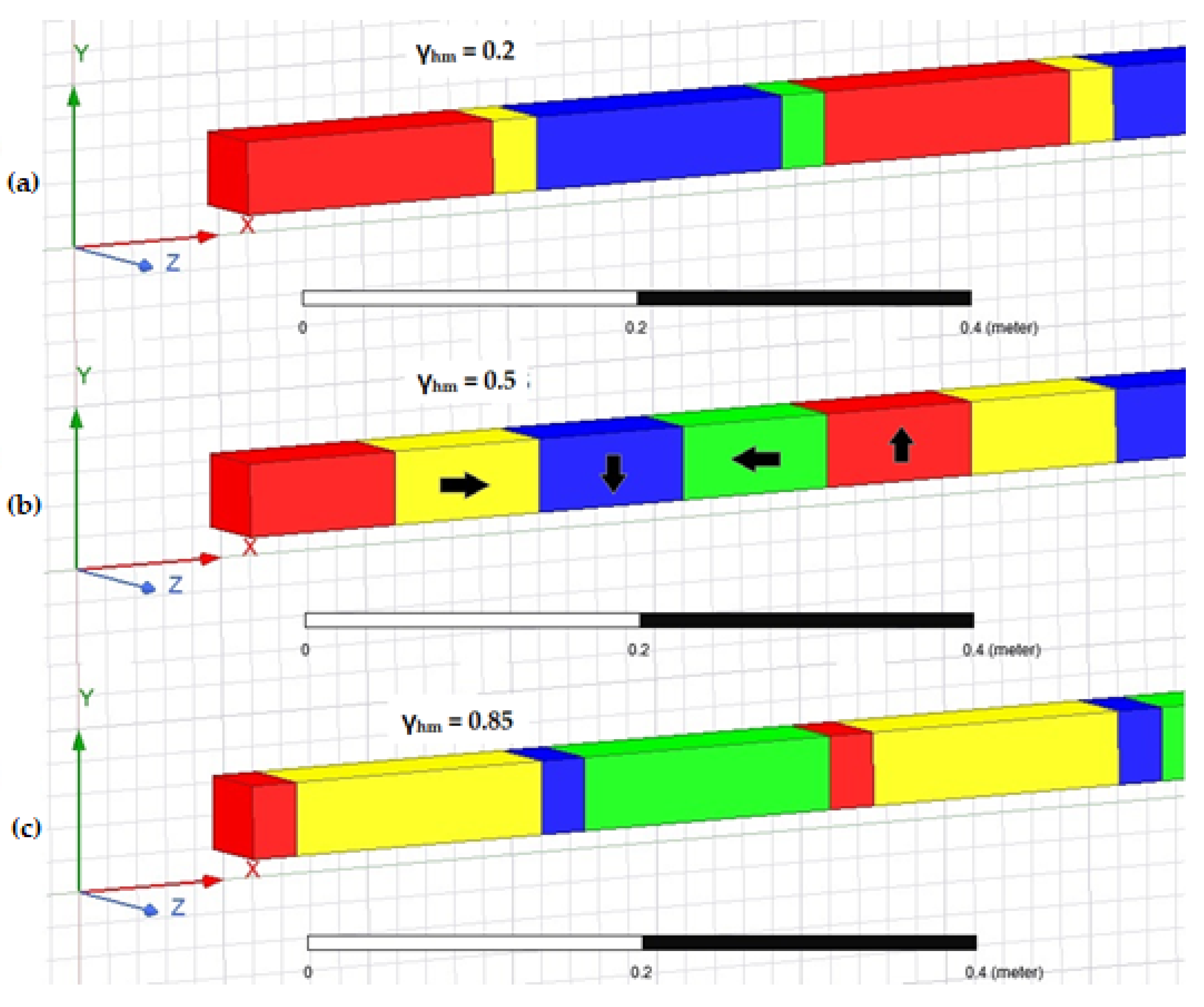
3.1. Magnetic Field Waveform
3.2. Transient Simulation Results
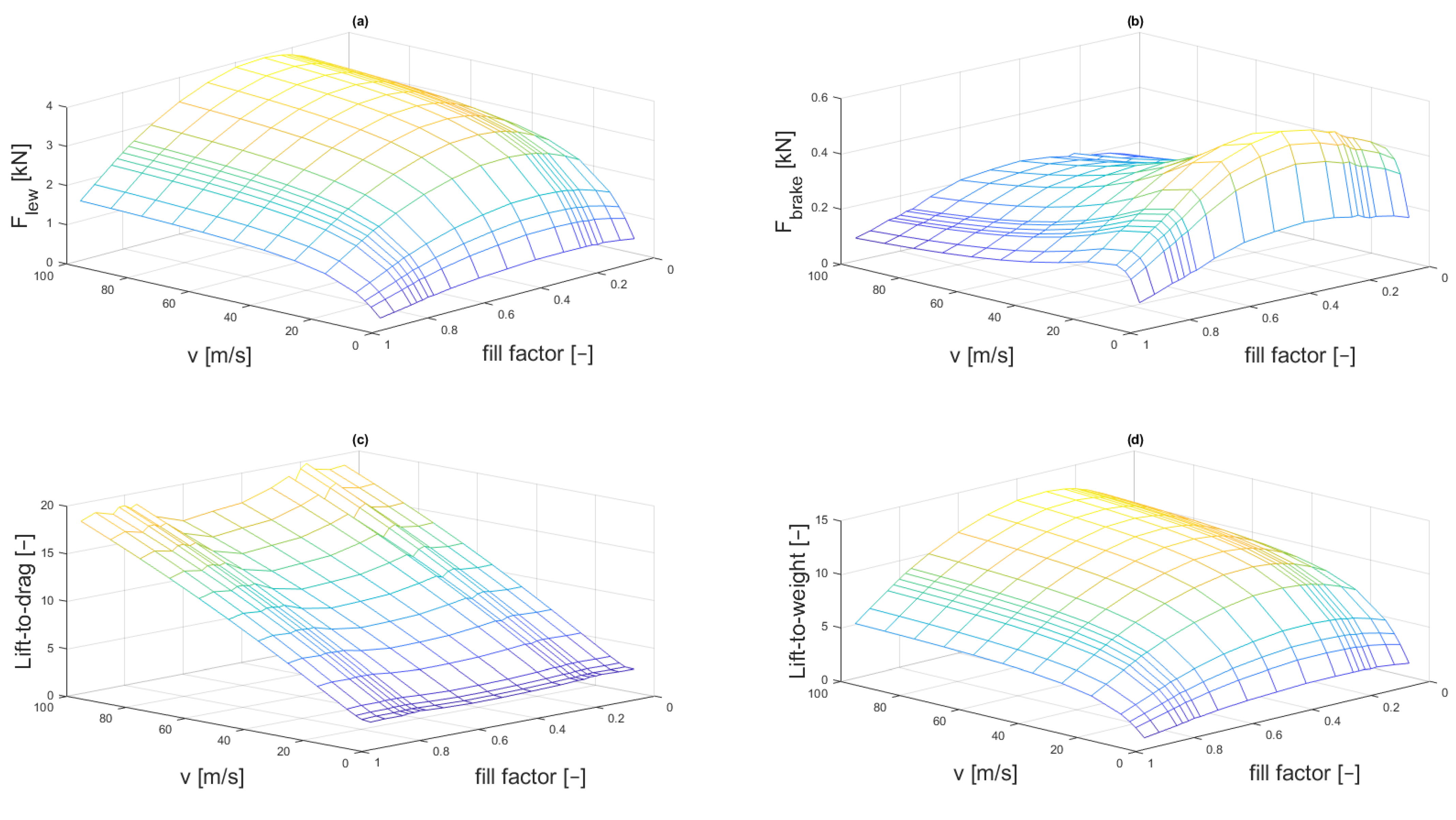
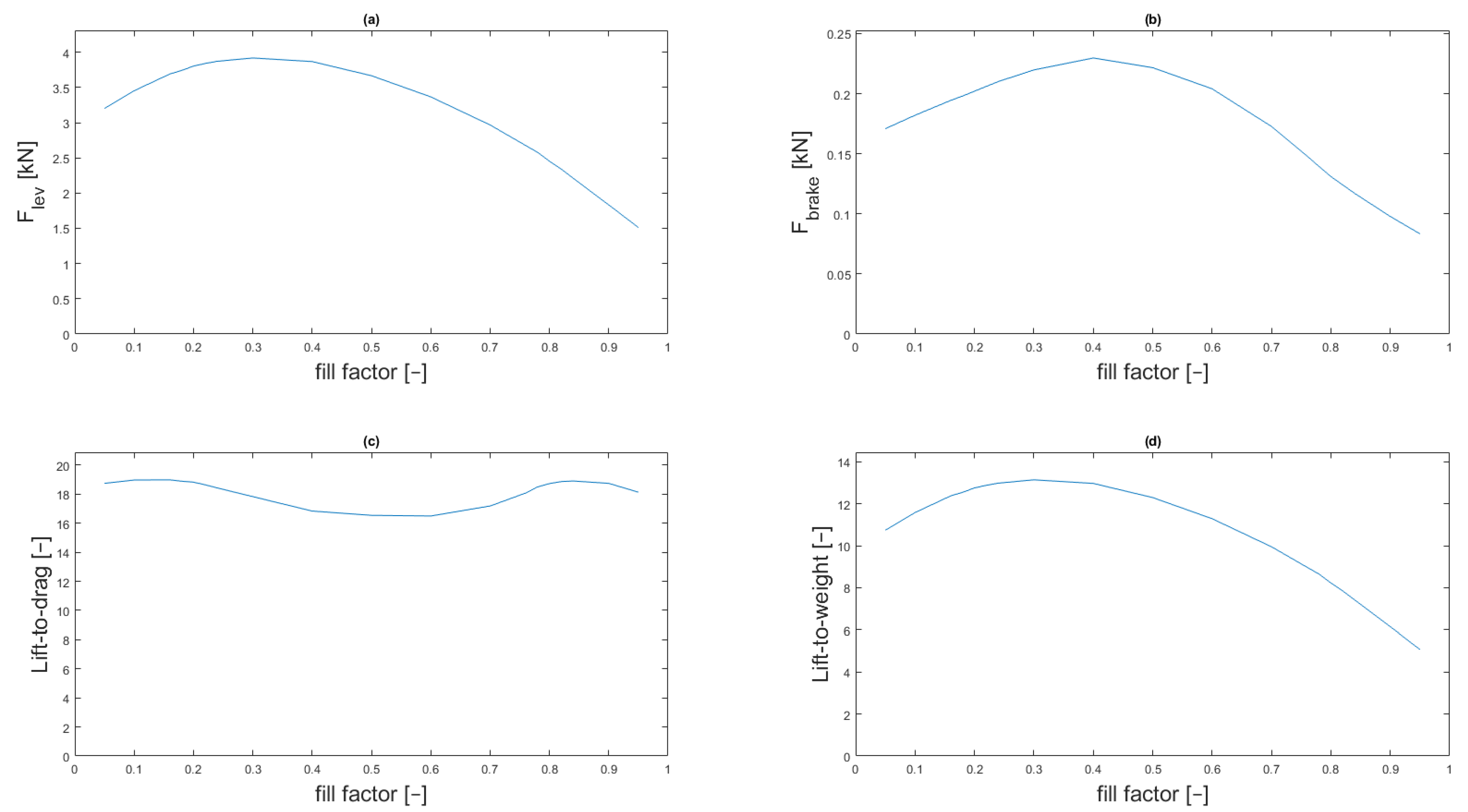
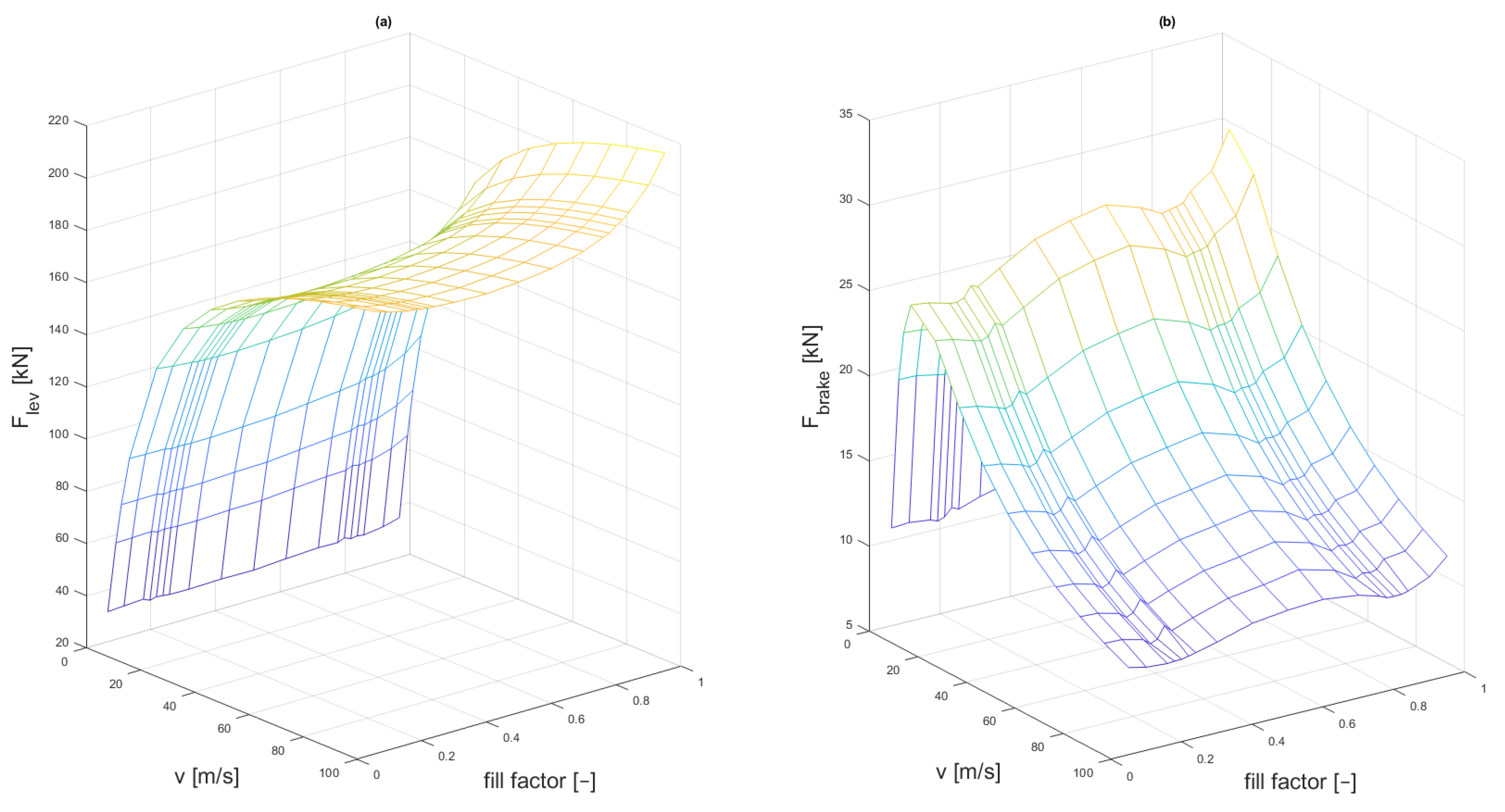
3.3. Calculation of the Required Levitation Force
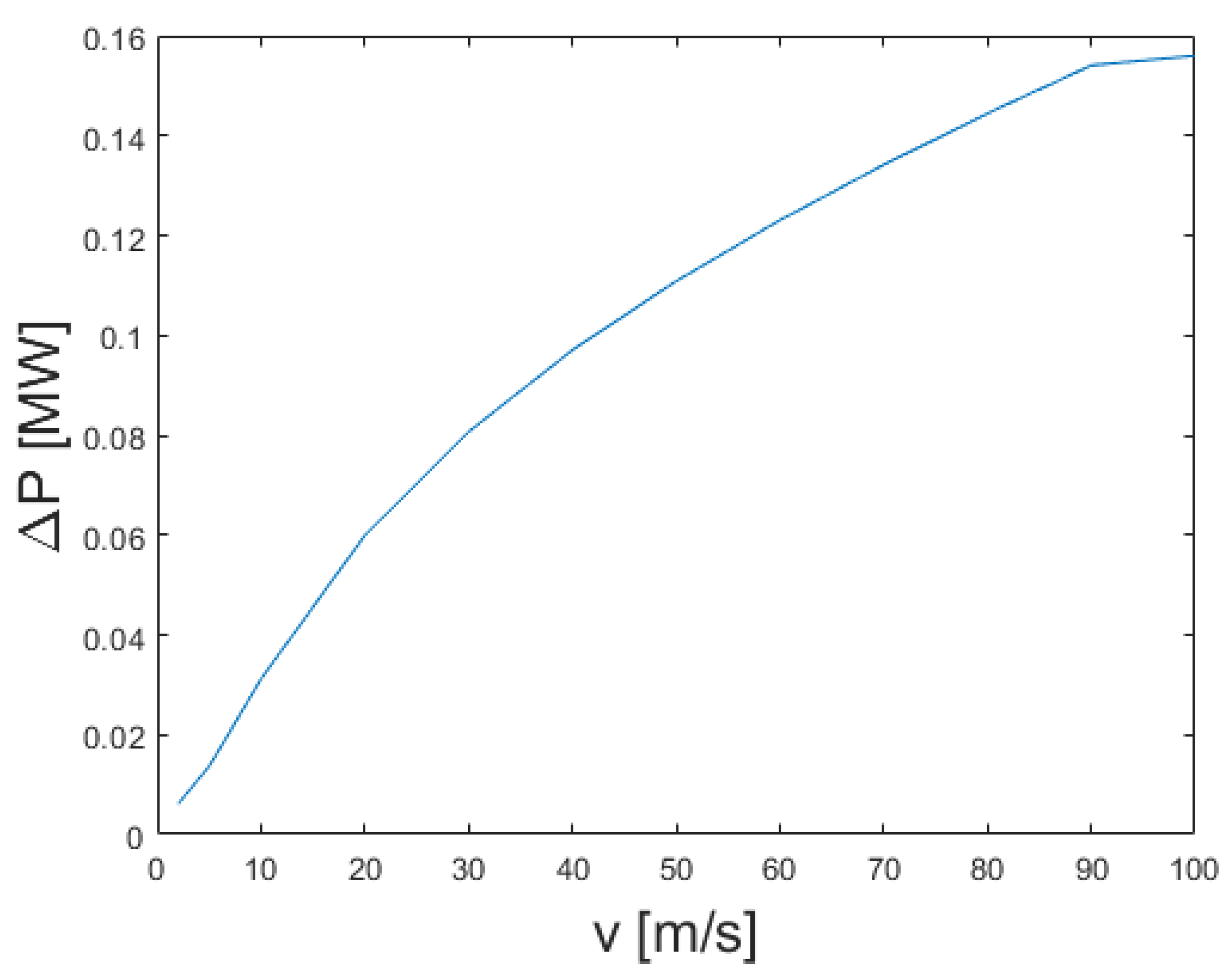
3.4. Power Consumption Analysis
4. General Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, H.-S.; Kim, D.-S. Magnetic Levitation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, G.; Steinmetz, G. The electromagnetic levitation and guidance technology of the ’transrapid’ test facility Emsland. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1984, 20, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.-Y.; Gieras, J.F. Incheon Airport Maglev Line. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2019, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.R.; Danby, G. MAGLEV Technology Development. In Transportation Technologies for Sustainability; Ehsani, M., Wang, F.Y., Brosch, G.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-W.; Kim, K.-C.; Lee, J. Review of maglev train technologies. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurol, S.; Baldi, R.; Bever, D.; Post, R. Status of The General Atomics Low Speed Urban Maglev Technology Development Program. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Magnetically Levitated Systems and Linear Drives, Shanghai, China, 26–28 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.B. Overview of the 2004 Magplane Design Proceedings of The 18th International Conference on Magnetically Levitated Systems and Linear Drives, Maglev’2004, China, October, 2004. Available online: http://www2.iee.or.jp/~dld/maglev/maglev2004_Program.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Lim, J.; Lee, C.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; You, W.; Lee, K.-S.; Choi, S. Design Model of Null-Flux Coil Electrodynamic Suspension for the Hyperloop. Energies 2020, 13, 5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaidez, E.; Bhattacharyya, S.P.; Karpetis, A.N. Levitation Methods for Use in the Hyperloop High-Speed Transportation System. Energies 2019, 12, 4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janić, M. Estimation of direct energy consumption and CO2 emission by high speed rail, transrapid maglev and hyperloop passenger transport systems. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2021, 15, 696–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Jeong, S.-S. Characteristic analysis of eddy-current brake system using the linear Halbach array. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 2994–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-M.; Jeong, S.-S.; Cha, S.-D. The application of linear Halbach array to eddy current rail brake system. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 2627–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.L.; Rote, D.M.; Coffey, H.T. Study of Japanese Electrodynamic-Suspension Maglev Systems; Argonne National Lab.: Lemont, IL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musolino, A.; Raugi, M.; Rizzo, R.; Tripodi, E. Stabilization of a Permanent-Magnet MAGLEV System via Null-Flux Coils. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2015, 43, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, R.F.; Ryutov, D.D. The Inductrack Approach to Magnetic Levitation. In Proceedings of the MAGLEV 2000 The 16th International Conference on Magnetically Levitated Systems and Linear Drives, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 7–10 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Post, R.F.; Hoburg, J.F. A Laminated Track for the Inductrack System: Theory and Experiment; Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL): Livermore, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Saslow, W.M. Maxwell’s theory of eddy currents in thin conducting sheets, and applications to electromagnetic shielding and MAGLEV. Am. J. Phys. 1992, 60, 693–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R. Teaching electrodynamic levitation theory. IEEE Trans. Educ. 1990, 33, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miericke, J.; Urankar, L. Theory of electrodynamic levitation with a continuous sheet track—Part I. Appl. Phys. A 1973, 2, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urankar, L.; Miericke, J. Theory of electrodynamic levitation with a continuous sheet track—Part II. Appl. Phys. A 1974, 3, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangbo, W.; Chunsheng, L.; Wei, X.; Baofeng, Y. Optimization design of linear Halbach array for EDS Maglev. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Harbin, China, 3–5 September 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, K.; Jing, Y. A Novel 3-D Analytical Modeling Method of Trapezoidal Shape Permanent Magnet Halbach Array for Multi-objective Optimization. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2019, 14, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kou, B. Investigation of a novel 2-D Halbach magnet array for magnetically levitated planar motor. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sydney, Australia, 11–14 August 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovers, J.; Jansen, J.; Lomonova, E.; Ronde, M. Calculation of the Static Forces among the Permanent Magnets in a Halbach Array. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 4372–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. Novel Permanent Magnet Brushless Machines Having Segmented Halbach Array. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Halbach, K. Application of permanent magnets in accelerators and electron storage rings (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 3605–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
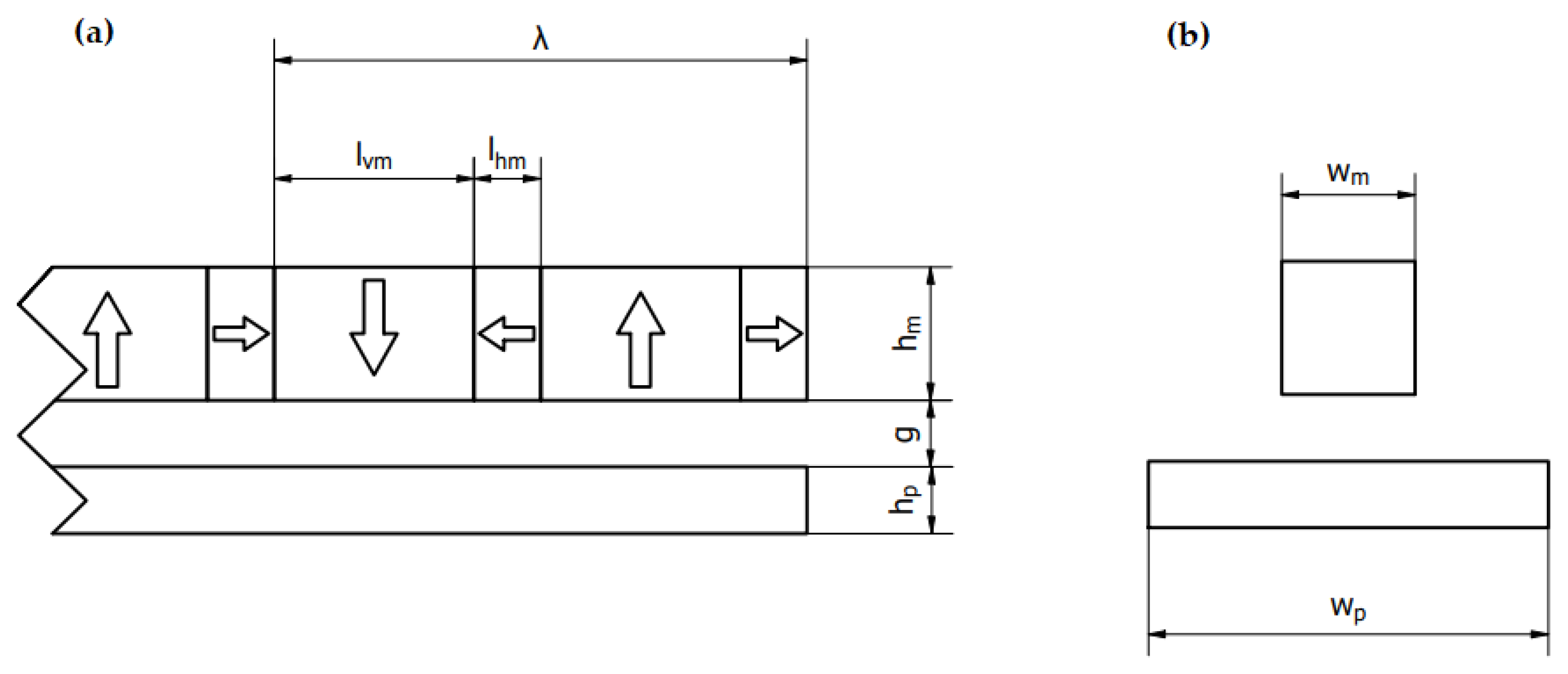




| Parameters Type | Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometrical parameters | Wavelength | λ | 400 mm |
| PM’s height | hm | 50 mm | |
| Conductive plate height | hp | 10 mm | |
| Air gap size | g | 30 mm | |
| PM’s width | wm | 50 mm | |
| Conductive plate width | wp | 120 mm | |
| Material parameters | Plate conductivity | s | 32.47 MS/m |
| PM’s remanence | Br | 1.4 T | |
| Dynamic parameters | Max vehicle velocity | vmax | 100 m/s |
| Levitation velocity | vlev | 10 m/s | |
| Mass of the vehicles body | mbody | 14,000 kg |
| γhm = 0.2 | γhm = 0.5 | γhm = 0.85 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bm_avg | 190 mT | 230 mT | 213 mT |
| Pγhm = 0.5/Pγhm = 0.2 | Pγhm = 0.5 − Pγhm = 0.2 |
|---|---|
| 115% | 0.156 MW |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kublin, T.; Grzesiak, L.; Radziszewski, P.; Nikoniuk, M.; Ordyszewski, Ł. Reducing the Power Consumption of the Electrodynamic Suspension Levitation System by Changing the Span of the Horizontal Magnet in the Halbach Array. Energies 2021, 14, 6549. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206549
Kublin T, Grzesiak L, Radziszewski P, Nikoniuk M, Ordyszewski Ł. Reducing the Power Consumption of the Electrodynamic Suspension Levitation System by Changing the Span of the Horizontal Magnet in the Halbach Array. Energies. 2021; 14(20):6549. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206549
Chicago/Turabian StyleKublin, Tomasz, Lech Grzesiak, Paweł Radziszewski, Marcin Nikoniuk, and Łukasz Ordyszewski. 2021. "Reducing the Power Consumption of the Electrodynamic Suspension Levitation System by Changing the Span of the Horizontal Magnet in the Halbach Array" Energies 14, no. 20: 6549. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206549
APA StyleKublin, T., Grzesiak, L., Radziszewski, P., Nikoniuk, M., & Ordyszewski, Ł. (2021). Reducing the Power Consumption of the Electrodynamic Suspension Levitation System by Changing the Span of the Horizontal Magnet in the Halbach Array. Energies, 14(20), 6549. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206549






