Design, Analysis and Implementation of the Tapped-Inductor Boost Current Converter on Current Based System
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Switched Capacitor
1.2. Switched Inductor
1.3. Cascaded
1.4. Tapped Inductor
2. Family of the Tapped-Inductor Current Converters
2.1. Tapped-Inductor Buck Current Converter
2.2. Tapped-Inductor Boost Current Converter
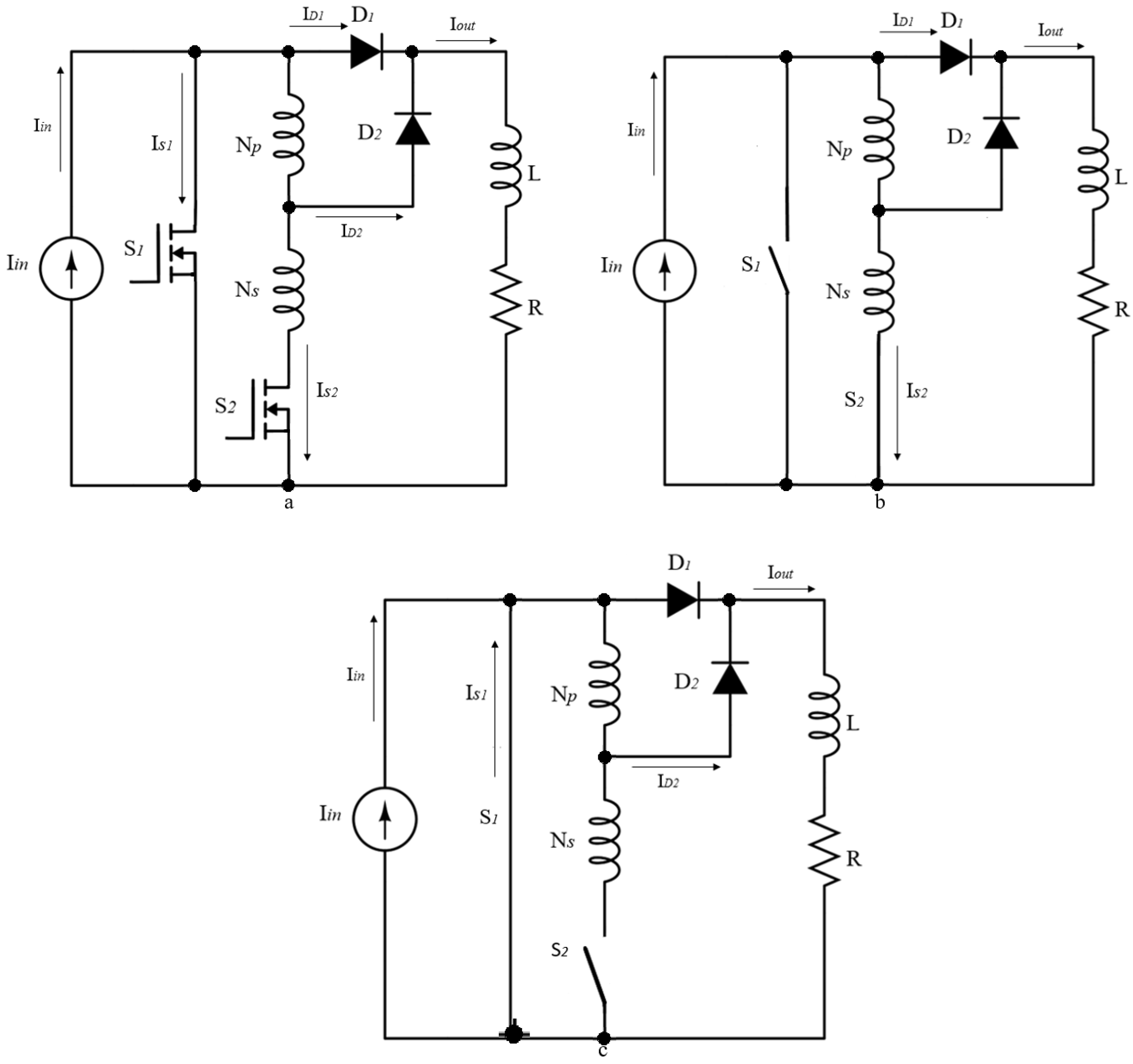
3. Circuit Description
3.1. Tapped-Inductor Buck-Boost Current Converter
3.2. Conventional Boost Current Converter
3.3. Tapped-Inductor Boost Current Converter
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Tapped-Inductor Boost Current Converter
4.2. Conventional Boost Current Converter
4.3. Current Conversion Ratio of Tapped-Inductor Boost Current Converter
4.4. Comparison of Power Conversion Efficiency
4.5. Comparison of Output Current Ripple
4.6. Loading Effect
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, S.; Tae, S.; Kim, R. Energy Demand Forecast Models for Commercial Buildings in South Korea. Energies 2019, 12, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aineto, D.; Iranzo-Sánchez, J.; Lemus-Zúñiga, L.G.; Onaindia, E.; Urchueguia, J.F. On the Influence of Renewable Energy Sources in Electricity Price Forecasting in the Iberian Market. Energies 2019, 12, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Calvet, R.; Martinez-Duart, J.M. On the Assessment of the 2030 Power Sector Transition in Spain. Energies 2019, 12, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger-Waldau, A. Snapshot of Photovoltaics—February 2019. Energies 2019, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Ouyang, C.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Gul, E. An Improved Mixed Integer Linear Programming Approach Based on Symmetry Diminishing for Unit Commitment of Hybrid Power System. Energies 2019, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuerl, S.; Herrmann, C.; Heiermann, M.; Grundmann, P.; Landwehr, N.; Kreidenweis, U.; Prochnow, A. The Future Agricultural Biogas Plant in Germany: A Vision. Energies 2019, 12, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifehei, K.; Azizyan, G.; Gualtieri, C. Analyzing the Performance of Wave-Energy Generator Systems (SSG) for the Southern Coasts of Iran, in the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea. Energies 2018, 11, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrenz, L.; Xiong, B.; Lorenz, L.; Krumm, A.; Hosenfeld, H.; Burandt, T.; Löffler, K.; Oei, P.Y.; Von Hirschhausen, C. Exploring Energy Pathways for the Low-Carbon Transformation in India—A Model-Based Analysis. Energies 2018, 11, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Hernández, J.M.; Velasco-Gómez, E.; San José-Alonso, J.F.; Tejero-González, A.; González-González, S.L.; Rey-Martinez, F.J. Monitoring Data Study of the Performance of Renewable Energy Systems in a Near Zero Energy Building in Spain: A Case Study. Energies 2018, 11, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Naegler, T.; Gils, H.C. Transformation towards a Renewable Energy System in Brazil and Mexico—Technological and Structural Options for Latin America. Energies 2018, 11, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, S.; Yao, L.; Smedley, K.M. A New Hybrid Boosting Converter for Renewable Energy Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, S.; Sathik, M.J.; Manoj, P.S.; Sundararajan, G. An assessment on performance of DC–DC converters for renewable energy applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, M.C.; Zhang, Z.; Knott, A.; Andersen, M.A.E. Analysis, Design, Modeling, and Control of an Interleaved-Boost Full-Bridge Three-Port Converter for Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 1138–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Agarwal, V. Design and Analysis of a High-Efficiency DC–DC Converter With Soft Switching Capability for Renewable Energy Applications Requiring High Voltage Gain. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2936–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, K.C.; Cheng, C.A.; Chen, C.T. High Step-Up Interleaved Boost Converter for Distributed Generation Using Renewable and Alternative Power Sources. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.W.E.; Ye, Y.-M. Duality approach to the study of switched-inductor power converters and its higher-order variations. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cheng, K.W.E.; Ye, Y.; Shi, Z. Wide input and wide output topology analysis for tapped-inductor converters with consideration of parasitic elements. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Feyzi, H.; Gholizadeh-Roshanagh, R. Generalized Switched-Inductor Based Buck-Boost Z-H Converter. Iran. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2017, 13, 340–352. [Google Scholar]
- Barzegarkhoo, R.; Moradzadeh, M.; Zamiri, E.; Madadi Kojabadi, H.; Blaabjerg, F. A New Boost Switched-Capacitor Multilevel Converter With Reduced Circuit Devices. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 6738–6754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Cheng, K.W.E.; Chen, S. A High Step-up PWM DC-DC Converter With Coupled-Inductor and Resonant Switched-Capacitor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 7739–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondzik, A.; Waradzyn, Z.; Stala, R.; Penczek, A. High efficiency switched capacitor voltage doubler with planar core-based resonant choke. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG), Bydgoszcz, Poland, 29 June–1 July 2016; pp. 402–409. [Google Scholar]
- Schaef, C.; Stauth, J.T. A Highly Integrated Series-Parallel Switched-Capacitor Converter With 12 V Input and Quasi-Resonant Voltage-Mode Regulation. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 6, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Cheng, K.W.E. Modeling and Analysis of Series-Parallel Switched-Capacitor Voltage Equalizer for Battery/Supercapacitor Strings. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, C.; Jose, B.R.; Mathew, J.; Evzelman, M. Modelling, simulation and experimental investigation of a new two input, series-parallel switched capacitor converter. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, K.S. Analysis and Design of the Ladder Resonant Switched-Capacitor Converters for Regulated Output Voltage Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7769–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishah, R.S.; Hosseini, S.H.; Babaei, E.; Sabahi, M. Optimal Design of New Cascaded Switch-Ladder Multilevel Inverter Structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2072–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Li, F. Novel High Step-Up DC-DC Converter With an Active Coupled-Inductor Network for a Sustainable Energy System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6476–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, F. A Novel High Step-up Converter with a Quasi-active Switched-Inductor Structure for Renewable Energy Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5030–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, M.; Poorali, B.; Adib, E. New cascade boost converter with reduced losses. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chincholkar, S.H.; Jiang, W.; Chan, C.Y. An Improved PWM-Based Sliding-Mode Controller for a DC-DC Cascade Boost Converter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 2018, 65, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Santos, O.; Martinez-Salamero, L.; Garcia, G.; Valderrama-Blavi, H.; Zambrano-Prada, D.A. Steady-State Analysis of Inductor Conduction Modes in the Quadratic Boost Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2253–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Resendiz, J.E.; Rosas-Caro, J.C.; Mayo-Maldonado, J.C.; Llamas-Terres, A. Quadratic boost converter based on stackable switching stages. IET Power Electron. 2018, 11, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Bussa, V.K.; Singh, R.K.; Mahanty, R. Quadratic boost derived hybrid multi-output converter. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 2042–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sutanto, D.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, D. High-voltage-gain quadratic boost converter with voltage multiplier. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Ramos, J.; Mota-Varona, R.; Ortiz-Lopez, M.G.; Diaz-Saldierna, L.H.; Langarica-Cordoba, D. Control Strategy of a Quadratic Boost Converter With Voltage Multiplier Cell for High-Voltage Gain. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovitz, A.; Yao, J.; Smedley, K. Unified Modeling of PWM Converters With Regular or Tapped Inductors Using TIS-SFG Approach. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1702–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bez, F.; Bonanno, G.; Corradini, L.; Garbossa, C. Control Technique for Reliable Operation of the Synchronous Series Capacitor Tapped Inductor Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 8150–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, N.; Medina, F.; Hernández, C.; Arau, J.; Vázquez, E. Double tapped-inductor boost converter. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, G.; Kim, K.D.; Kang, F.S. Cascaded dc-to-dc converter employing a tapped-inductor for high voltage boosting ratio. In Proceedings of the IECON 2015—41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 932–937. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Sekiguchi, R.; Sano, Y. Study on Improving Precision of Analysis of Boost Ratio and Power Efficiency of Tapped-Inductor DC–DC Converter Circuit. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 2018, 202, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Duty Ratio | 0.1–0.9 |
| Load R () | 5 |
| Capacitance C (F) | 30 |
| Inductance L (mH) | 1.53 |
| Load R () | 5 |
| Switching frequency (kHz) | 100 |
| Turns Ratio of the tapped-inductor | 0.7 |
| Output Inductive filter L (mH) | 1.53 |
| (m) | 58 |
| (m) | 58 |
| () | 0.4 |
| () | 0.2 |
| () | 0.1 |
| (V) | 0.5 |
| (V) | 0.5 |
| Duty Ratio | 0.1–0.9 |
| Load R () | 5 |
| Switching frequency (kHz) | 100 |
| Turns Ratio of the tapped-inductor | 0.7 |
| Primary inductance, Np (mH) | 62 |
| Secondary inductance, Ns (mH) | 3 |
| Output inductive filter (mH) | 1.53 |
| Switches S1, Rds1 (m) | 58 |
| Switches S2, Rds2 (m) | 58 |
| Duty Ratio | 0.1–0.9 |
| Load R () | 5 |
| Switching frequency (kHz) | 100 |
| Capacitor C (F) | 30 |
| Output inductive filter L (mH) | 1.53 |
| Duty Ratio | 0.1–0.9 |
| Load R () | 10 |
| Switching frequency (kHz) | 100 |
| Turns Ratio of the tapped-inductor | 0.7 |
| Primary inductance, Np (mH) | 62 |
| Secondary inductance, Ns (mH) | 3 |
| Output inductive filter L (mH) | 1.53 |
| Switches S1,Rds1 (m) | 58 |
| Switches S2,Rds2 (m) | 58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leung, C.P.; Cheng, K.W.E. Design, Analysis and Implementation of the Tapped-Inductor Boost Current Converter on Current Based System. Energies 2021, 14, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14040888
Leung CP, Cheng KWE. Design, Analysis and Implementation of the Tapped-Inductor Boost Current Converter on Current Based System. Energies. 2021; 14(4):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14040888
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeung, Chim Pui, and Ka Wai Eric Cheng. 2021. "Design, Analysis and Implementation of the Tapped-Inductor Boost Current Converter on Current Based System" Energies 14, no. 4: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14040888
APA StyleLeung, C. P., & Cheng, K. W. E. (2021). Design, Analysis and Implementation of the Tapped-Inductor Boost Current Converter on Current Based System. Energies, 14(4), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14040888







