1. Introduction
The energy management of building systems and urban areas such as residential districts is assuming an increasingly relevant role in the control and assessment of urban development and refurbishment processes.
Digital predictive technologies and sensor-based control systems are becoming fundamental tools [
1] supporting policies to reach near-zero requirements and targets for buildings and urban districts. Nowadays, the integration of information communication technologies (ICT) has an important role in the configuration of smart cities and in defining digital strategies addressing social, public health, economic, environmental, and safety issues [
2].
The success of such digital transformations requires the ability to meet and manage new emerging challenges [
3]. Deep interactions between humans, infrastructures, and technologies are increasingly created over time by the global consequences of urbanization and the growth of human activities. Dealing with complexities related to sustainability matters, cities are implementing technological improvements achieving smarter performances through the definition of smart cities that adhere to a smart growth agenda [
4].
According to the above mentioned, it can be introduced the urban intelligence [
5] concept, providing insights into a number of issues currently faced by modern cities (i.e., air pollution, communication network demand, congested traffic, water floods, etc.) through the introduction of data from Internet of Things (IoT) sensors processed by intelligent and real-time advanced analytics. According to the United Nations prediction, 60% of cities will have at least half a million inhabitants by 2030, leading to issues in cities such as the increasing of network demand and crowd congestions [
6].
In the future, progressively current problems in cities will be necessarily managed through intelligent urban reasoning algorithms and suitable deployment data-model based on urban intelligence systems, pervasive computing, communication, big data management technologies, and artificial intelligence (AI), leading to a strong evolution in the management of urban environments as well as in the quality of life in smart cities [
7,
8].
The configuration of city digital twins represents a giant leap forward for urban sustainability from design to construction and maintenance basing on the implementation of Industry 4.0 principles [
9,
10]. It is defined as a digital replica of a physical asset, collecting information from sensors, drones, or other sensive IoT devices, applying advanced analytics, machine learning (ML), and AI obtaining real-time processed data about the lifecycle process of physical assets.
In particular, digital twin (DT) ecosystems are related to three main entities: a physical object, its virtual replica, and the connection between them in terms of collecting and connecting real-time information. Such a digital ecosystem can effectively contribute to the lifecycle management of both vertical and horizontal systems, in order to store, manage and process big data about the urban environment in a three-dimensional data model as a structured information system connected to the physical.
In this paper, the applications of such ICT-based digital approaches are related to energy management systems, in order to predict real time situations, enriching and leading to more effective decisions, obtaining the automation of repetitive tasks, and providing added value with the optimization of decision-making processes.
In particular, the objective concerns the configuration of a solid methodology for an increasingly intelligent system where the potential of ICT, IoT, big data and AI are combined interacting with BIM (building information modeling) models (
Figure 1), defining three-dimensional information and predictive systems for energy management.
In fact, the connection between IoT devices, digital information models (BIM), and AI defines an advanced smart-city ecosystem as an intelligent, ubiquitous, and sustainable digital urban context [
2] where real-time monitoring systems allow data connections and processing anytime and anyplace [
3,
4].
More specifically, the project developed by CITERA Interdepartmental Centre of Sapienza University of Rome explores the potential of digital-twin models integrated with AI systems finding a specific application as an opportunity to apply the developed methodology. The case study is related to the configuration of an effective DT model of a residential district in Rome, increasing energy efficiency and identifying a cost-optional solution for which both consumption and costs are expected to be reduced.
Therefore, the 3D information model was developed gradually from the territorial, infrastructural (using Autodesk InfraWorks for geographic information systems) up to the building scale (using Autodesk Revit for building information modeling). The model resulted both as a microscopic and macroscopic digital database, containing static, dynamic, geometric, and semantic data about buildings and their functional interactions.
As mentioned, a BIM approach was carried out focusing on energy management model-uses and leveraging interoperability using IFC (industry foundation classes) models for energy diagnosis purposes. Basing on such analysis, a smart-energy-grid management system was developed combining BIM as-built models with IoT and AI obtaining a substantial as-performed and up-to-date city digital twin.
2. Background
The objective of bringing the virtual and physical worlds together is focused to better support decision-making, reducing risks and configuring a citizen engagement tool, improving urban sustainability [
9]. The introduction of DT in construction processes addresses the improvement of decision-making focusing on well-informed and advanced real-time “what-if” scenario assessments, reducing wastes of time and resources that are typical in construction.
In this regard, the Newcastle University created a DT of the city dedicated to incidents and disasters responding and prevention, running simulations of incidents such as burst pipes, heavy rainfall or floods to evaluate the potential impact on communities over a 24 h period [
10].
Another effective example of smart-city DT currently ongoing is virtual Singapore, which provides capabilities from virtual experimentations, test-bedding, and decision-making up to research and development [
11].
Moreover, a relevant experience is carried out by the Centre for Digital Built Britain (CDBB) delivering a “smart digital economy for infrastructure and construction”, as a transformation of the UK AEC (architecture engineering and construction) industry’s approach about planning, building, maintenance and utilization of social and economic infrastructures [
12].
In addition, the ongoing project for the city digital twin of Atlanta creates a virtual reality (VR)-based platform (built basing on the unity interactive and data-driven cross-platform game engine) which contains a three-dimensional fully modeled city of Atlanta, reproducing the entire city into a virtual space, facilitating spatial-temporal feedbacks and interactions between the human/infrastructure systems and their virtual representations [
13].
Focusing on the energy implementations, three significant experiences related to DT developments integrated with AI systems can be mentioned, in order to define a systemic approach for the present study, aiming at integrating the objectives of the single experiences reported below.
The first concerns a microclimatic study on urban scale carried out in the Kalasatama district by the Municipality of Helsinki, in which it is important to highlight the “Energy and Climate Atlas”, defined as a city information model for studying and developing strategies for the mitigation of climate changes and improving energy efficiency. The atlas includes a number of specific information about the buildings, such as heating systems, energy certification, electricity consumption, district heating, and water distribution. As configured, the model helps to analyze a series of technological scenarios, allowing users to define the solar energy potential of buildings, evaluating the possibility for reducing carbon dioxide emissions or outlining cost-impact scenarios for different interventions [
14].
In addition, it is important to investigate the behavior of energy-smart-grid systems serving differentiated users managed by ML. As known, the main issue to be resolved concerns the need to implement storage systems due to the characteristics of discontinuity of renewable energy production.
The ESS (energy storage system) management realized through a DT integrated with ML systems can bring significant improvements leading to consequent bill savings, if compared with the current systems based on predefined control systems of the electrical power supply from the batteries.
In addition, the development of an energy management system (EMS) is fundamental. As reported by Park, Byeon et al. [
15] “an EMS reinforces operational functions such as adjusting the amount and schedule of charging and discharging through the efficient control of the ESS and power conditioning system (PCS) and manages the overall power flow”. Moreover, it is connected with sensors and measurement equipment able to analyze and monitor consumption patterns, managing information about power activities and optimizing the overall efficiency.
Another extremely significant energy application of DT is the simulation and testing of scenarios for energy-efficiency interventions aiming to achieve nZEB (near zero energy buildings) requirements on buildings. Since most buildings today are already built, it is necessary to underline the essential application of nZEB parameters on existing built environments through the use of BIM-oriented 5D and 6D digital approaches [
16].
The fifth and sixth dimensions of BIM are used and developed to promote stakeholder’s collaboration, visualizing and evaluating different options with the configuration of nZEBs, in terms of sustainability and energy efficiency parameters (6D), estimating associated costs (5D) and technical issues [
16].
From there, the advances in building data interoperability both at a technical and organizational level enable relevant innovation in end–user energy delivery and optimization [
17] beside to open data availability, leveraging on technologies [
18] such as the IoT and cyber–physical systems.
3. Material and Methods
The case study of the present research analyzes digital ICT-based energy management techniques applied to a 16 eight-floor buildings residential district called Rione Rinascimento III, located in Rome, which represents the most significant Italian residential implementation of a geothermal source heat pump (GSHP) system, that is currently the largest in Europe.
3.1. The Urban Context
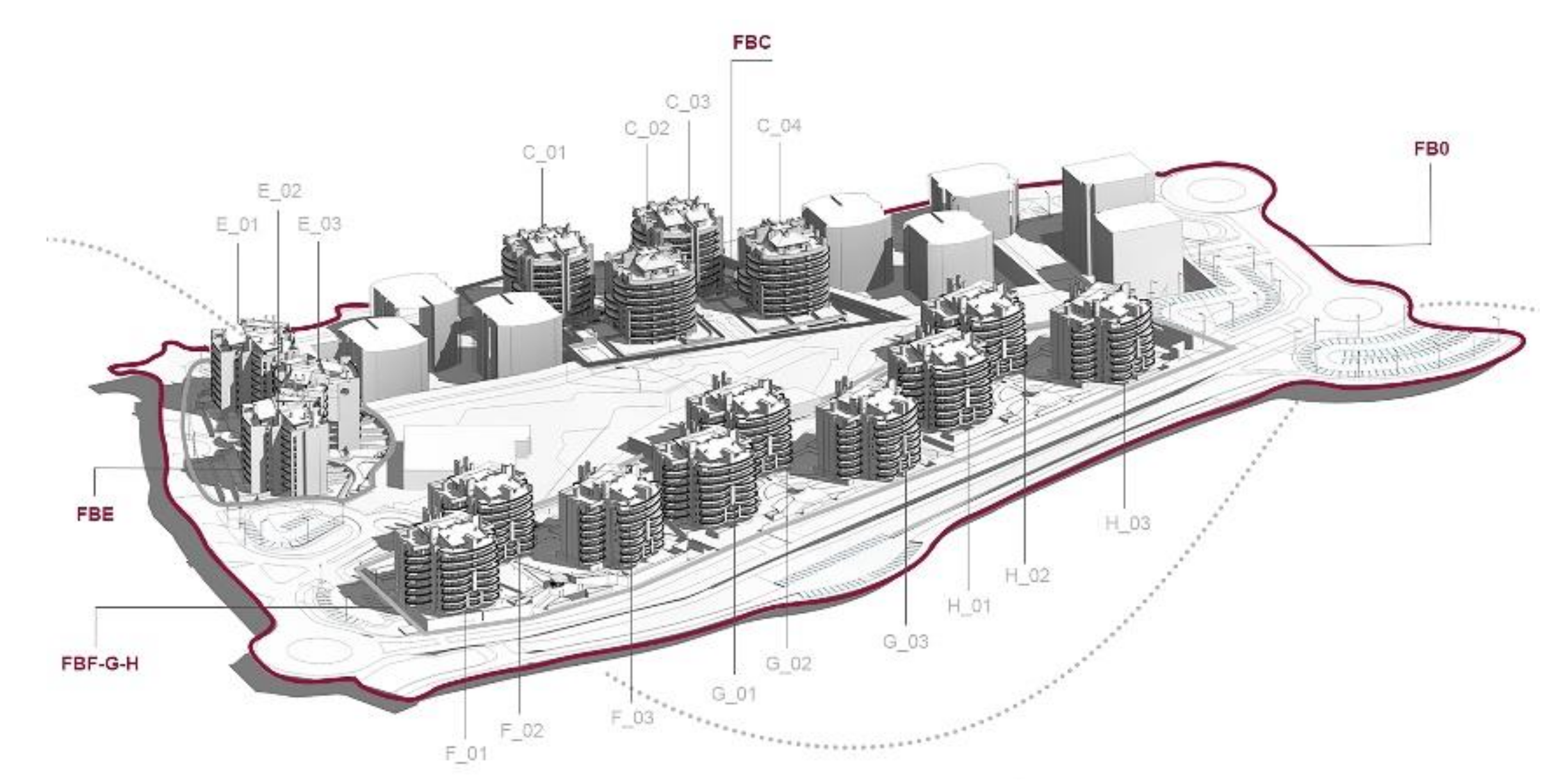
Rinascimento III (
Figure 2) is configured as a building intervention characterizing an energetically self-sufficient new portion of the city, integrated as much as possible with the surrounding areas in terms of urban planning and services, and it is considered of relevant significance since it is powered by a still not-commonly-deployed kind of renewable energy system.
In the urban planning agreement between the Municipality of Rome and the private owner, primary and secondary public works were planned, as well as the completion of the Talenti Park area in front of the district. According to the Italian regulations, the new district is included in the category of bioenergetic improvement interventions, which aim at improving the bioclimatic performance of the settlement.
Moreover, the introduced Italian energy policies (such as Decree Law no. 63 of 4 June 2013) aim at a partial refunding up to 65% of the amount for energy requalification expenses, consistently improving the use of renewable sources such as the geothermal one.
The geological characteristics of the Italian territory are particularly favorable for the development of geothermal energy systems and could allow one to exploit low-enthalpy resources at different depths and in numerous areas of the country.
According to the above mentioned, a research activity was developed by the CNR (National Centre for Research) with a pilot project promoted in four Italian regions (Calabria, Campania, Apulia, and Sicily), contributing to the increase of knowledge about the use of geothermal resources, with the aim of providing useful information to start activities of exploration for the improvement of geothermal energy uses in the south of Italy [
19].
3.2. Linking Virtual to Physical
The concept of Construction 4.0 defines a framework where data-driven systems are able to manage physical processes by configuring a virtual replica of the physical world and achieving decentralized decision-making processes based on self-learning mechanisms [
20].
Therefore, BIM models containing data and information useful for processing assessments become able to communicate with the real systems using data from sensors, developing learning capabilities, and being able to process the received information.
The collaboration between 3D information models and IoT devices is highly necessary for a successful implementation of real-time DT purposes, as well as for energy management optimizations. However, the implementation of IoT in real-world environments configuring smart, ubiquitous, and live-interconnected systems (
Figure 3) is currently still restricted by technical barriers such as device battery life, network capacity, and maintenance costs.
The core functionality of IoT devices is to reliably collect and share data (such as flow rates, temperatures, pressures, physical movements, distance, mass, etc.) from its designated environment to the virtual world.
The hardware elements consist of a battery-powered sensor, an actuator, and a network communication system in which the collected data are processed and consequently sent to remote servers.
In the present application, the connection between the physical and virtual model is made through sensors [
21] able to monitor and communicate electrical power data such as power energy voltmeter ammeter for lighting and heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems and smart plugs for electromotive equipment such as computers, televisions, washing machines, and so forth (
Table 1) [
22].
In this case, AI systems allow the DT to develop predictive capabilities, learning from the events and improving outputs, ultimately taking and implementing autonomous decisions based on the analysis carried out without human interventions.
Moreover, the AI system achieves a balanced condition between energy consumption and energy production system’s performance parameters [
23], adapting itself to the environment in order to achieve the predefined objectives.
In other words, the system takes data from sensing devices, and it generates appropriate and specific actions through reasoning systems, modifying the behavior of the equipment in order to optimize energy consumptions. Specifically, it takes information from IFC-BIM and CityGML-GIS (geographic information systems) models, constantly updating them with real-time data as described in
Figure 4.
3.3. Data Interoperability
Principles of Industry 4.0 and data interoperability in the AEC sector are extensively applicable on linking GIS and BIM models, providing data for real-time multiscale object-oriented simulations of the built environment. As configured, GIS-BIM 3D city information models and applications require common communication standards introducing problems related to information integration and data interoperability at different domains and scales [
24].
In the specific case of information management in construction processes based on BIM methodologies, interoperability consists in exchanging data from models to different software and application platforms, implemented for different purposes and functionalities throughout to the whole lifecycle.
The main objective of interoperability is to facilitate the interaction between different and nonhomogeneous information systems, minimizing errors and aiming at reliability, effectiveness, and optimization of resources.
For the above mentioned, different levels and approaches on interoperability, are defined by the Information Technology Vocabulary (ISO/ISO/IEC 2382) [
25] as the “capability to communicate, execute programs, or transfer data among various functional units in a manner that requires the user to have little or no knowledge of the unique characteristics of those units” [
26,
27].
Industry foundation classes (IFC) were defined as a reference standard format for the building industry to develop different advanced processes based on spatial data relations between building components of a BIM model.
In the present application, specific processes can be scheduled for different activities, objectives and domains (
Table 2) since objects are connected to data entities and properties such as name, geometry, identifications, material parameters, etc.
In the GIS field, CityGML was developed as a model standard representing geometric and information relationships between geographic entities, being defined as the most appropriate territorial modeling standard in different levels of detail. In addition, IFC and CityGML standard were used, as they are currently the two semantic models dedicated to the configuration of object-oriented information management systems, even though research is still focused on information exchanging, linking IFC and CityGML toward an advanced 3D city information model [
28].
3.4. 6D BIM for Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
The study focuses on the Rinascimento III district (about 85,000 m2) which is a part of Rione Rinascimento, consisting of 16 eight-floor buildings hosting about 900 apartment units with 2500 inhabitants.
A significant part of the energy supplied to the building complex is self-produced using renewable geothermal sources. For this reason, the following case study is considered to be extremely relevant for approaching digital methodologies integrating DT and AI systems for an efficient energy-smart-grid management.
According to the BIM Use Classification System developed by Penn State University [
29] which basically categorizes BIM Uses (
Figure 5) as the main purpose to be achieved when implementing BIM in construction processes, specific purposes and objectives for BIM models were identified.
The definition of the main BIM purposes led to the identification of specific requirements for data implementation and model configuring.
Since the current application is based on the use of BIM and GIS models for energy management purposes, priority was given to the implementation of specific data such as well-defined technical parameters of the building envelope, thermal zones, rooms, HVAC systems, and equipment, as well as specific data about localization, climate [
30], boundary conditions, etc., as information coming directly from the BIM system in the interoperability process.
Moreover, BIM models can have different level of depth both geometrically and informatively, depending on the BIM Uses and related objectives. According to the ISO 19650 [
31] standard, LODs were defined, gradually moving toward a LOIN (level of information need) perspective shifting from a prescriptive to a performance approach, based on information granularity depending to predetermined specific BIM uses.
As mentioned, the production of the BIM models followed a number of phases coming from a low degree of definition (LOD 100 [
32]), useful in preliminary and outdoor concept stages, up to a LOD 400 (
Figure 4, right), according to the BIMForum, “2013 Level of Development Specification” (AIA/AGC, 2013), [
32] for indoor energy analysis and simulations purposes as described in
Figure 6.
As configured, the so-called sixth BIM dimension (6D) was achieved since the identified BIM use was connected to energy efficiency and sustainability analyses and simulations [
33]. Developing a BIM-oriented methodology allowed to assess the energy performance of the building system, providing relevant support to decision-making processes.
In this section, it is necessary to detail the data and boundary conditions necessary to run the energy analysis through the 6D BIM model [
33]. The thermal characteristics of the building envelope technical systems as well as the related data contained in the BIM model are reported in
Table 3.
In this case, DT reproduces the energy characteristics of the building envelope and technical plants, which combine a component of renewable energy as described in
Section 3.5. In
Table 4 the technical components of the main HVAC plants, as well as the controlled mechanical ventilation system are reported.
3.5. Building Energy Model (BEM)
The main objective of the DT-based developed methodology is using data models across different simulation and monitoring processes [
34], combining data from different sources (BIM, GIS, IoT, etc.) in a three-dimensional model, which is aligned almost in real-time with the reproduced system [
35,
36].
In order to create a building energy model (BEM) [
37], each component of the information model was associated with the corresponding products in a BEM software connected to BIM data (MC4 Suite for Revit), defining different thermal zones and boundary conditions.
Once the energy model was generated using a specific and authorized software, [
38] it followed the validation phase.
In particular, according to Italian regulation DLgs. 30 May 2008 on “calculation methodologies and requirements for the execution of energy diagnoses and energy certification of buildings” if the deviation between the values estimated by the model and the real consumption does not exceed 5% on average, then the model is validated.
In the pilot project described in the present study, the building complex is supplied by the largest European residential geothermal plant with GSHP (COP of 3.8 in winter configuration and 5.5 in summer configuration), equipped with 200 vertical geoprobes, 150 m deep.
The components of the total energy consumption of Rinascimento district are reported in the following schemes (
Figure 7) and divided into four main categories: (1) winter air conditioning; (2) summer air conditioning; (3) hot water; and (4) electric power supply.
In fact, the energy production coming from renewable energy sources (RES) and particularly from the geothermal plant could be estimated in about 6305 MWh/y on 9.979 MWh/y consumed, subdivided as shown in
Figure 7. Consequently, 63% of the total energy requirement of primary energy is produced by the geothermal system.
In this case study, the energy diagnosis was conducted on one single building (
Figure 8) of about 3648 m
2, using the Revit Suite of Mc4 Software through BIM data, for a dynamic simulation of the building behavior, supplied by a modular portion of the geothermal plant. Since the highlighted building is currently the only one being fully occupied by residents (who permitted the implementation of sensing devices for DT configuration), it was selected for energy modeling and real-time monitoring.
Moreover, since the geometry and spaces subdivision are almost identical for all the buildings, the modeled building is expected to share similar boundary conditions about solar radiation (
Figure 9) and ventilation with the other five highlighted in
Figure 8, positioned on the outer perimeter of the district without any shading.
The performed simulations led to the evaluation (according to the Italian classification of Legislative Decree 48, 10 July 2020) [
39] of an A2 class with a specific consumption of 26.8 kWh/m
2y; the comparison with the real value building consumptions coming from an average evaluation of 3 year bills (26.6 kWh/m
2y) validated the simulation model.
The aim of the DT model was also to simulate the increasing of the RES production percentage, in order to reach the goal for Rinascimento to become a near zero energy district (nZED). The energy simulation in the model were performed considering new installation of photovoltaic panels for the production of electricity and solar collectors for the production of domestic hot water.
In particular, the model was implemented with the integration of 312 kWp of monocrystalline photovoltaic modules in the building façade able to produce 276,000 kWh/y of electricity; and the realization of an area hosting 405 high-efficiency flat-plane solar collectors able to produce 410,000 kWh/y.
The simulations outputs lead to a final result of 6991 MWh/y of energy coming from renewable energy sources (RES) (geothermal+solar), which means about 70% of the district energy consumption directly produced in place by the RES microgrid of the complex.
However, the obtained results so far were focused on the building as a whole, specifying some different thermal zones created according to differences in use, occupation hours, types of HVAC installed, or types of external envelope and sun exposure.
Considering the analysis on a smaller scale, focusing on indoor environmental quality [
40] such as thermal-hygrometric conditions, the BIM model was detailed with HVAC systems to develop computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis [
41].
The standard k-ε model was deployed according to the limited need of calculation power and time for iterations (less than 300) as well as for the absence of high-pressure gradients in the rooms.
The following input conditions have been set:
Average outdoor air temperature equal to 5 °C; radiant floor water temperature equal to 40 °C; underfloor heating surface temperature is between 24 and 29 °C; radiative model discrete ordinates; and 1 s timestep.
Four control probes were temporary fixed and positioned in the center of each room in a typical apartment at 1.50 m from the ground, which is the same height of the DT temperature and humidity monitors fixed in all the apartment rooms (
Figure 10).
Fluid-dynamics analyses were developed from the BIM model to study the temperature gradient and convective air flows in rooms, triggered by the operation of radiant floors in winter heating mode in order to evaluate comfort parameters in each room, experimenting data interoperability from BIM model to CFD analysis (
Figure 11).
3.6. Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning is a form of AI providing systems the capability to learn from data without the use of explicit programming. ML produces models where there are some kind of regularity in data [
42]. Like human children’s learning processes, it is driven by “experience” [
43].
As a general rule, training a model requires computer resources which are orders of magnitude bigger than those required to execute the model [
44,
45].
In this specific case, data are collected and analyzed in order to devise one or more model for energy-efficiency purposes using AI while allowing normal comfort and living habits. The general architecture of the system is shown in
Figure 12.
The goal was achieved through two phases: (1) design and implementation of the infrastructure and (2) obtaining data, training, and model testing.
3.6.1. Design and Implementation of the Infrastructure
Energy data are simple time series of power consumption or production, coming from real sensors in a given time lapse, each one transmitting data with its own application programming interface (API); moreover, they are obviously located close to energy loads or near power sources.
This means that data are not all in the same place at the same time, which is a necessary condition to perform the analysis that led to the desired algorithms.
The first problem is therefore to plan and deploy a cost-effective IT (information technology) infrastructure able to provide reliable data to be processed.
Each apartment was implemented with monitoring sensors, so that every device energy consumption could be considered to define the control solution of the overall energy requirement in each apartment.
All the implemented metering sensors produce a huge amount of data requiring significative computational resources to obtain acceptable analysis performances; therefore, the best solution for reducing installation expenses would be to control the system acquiring all the information in a data center or a service in a data center.
This architecture leads to the necessity of setting a local system for interconnecting IoT sensors and actuators over a geographical network (such as the Internet), executing sort of local computation and buffering data in case of connection blackout, using the known “ubiquitous and pervasive computing” [
46] techniques to deal with the computational problems of centralized intelligence.
Following this approach, two distinct problems had to be solved designing the infrastructure:
The first element in the infrastructure is a subsystem able to cope with several transmission protocols and time frames, whose output is the synchronized power consumption (or production) of the smart metered devices. This subsystem accepts instruction from the second element to switch on and off some of the controlled devices.
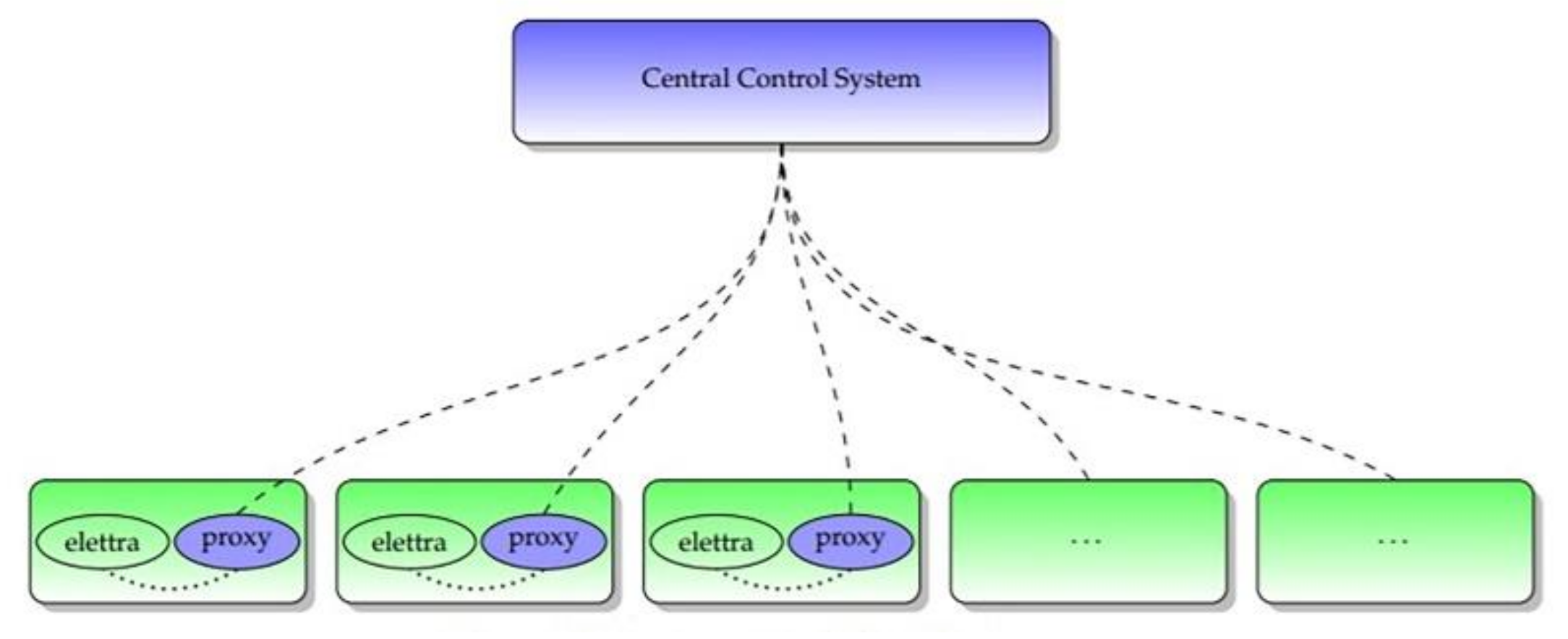
This element needs to be connected with all sensor networks; therefore, it has to be physically placed next to them, minimizing transmission problems and monitoring local environment even in absence of communication with the central control system. This kind of elements is called “elettra” in the following section.
The second architecture element is another subsystem, composed of a different “proxy”, and each proxy receives the outputs of the first subsystem as an input. The proxies deliver the data to the central unit and receive back data from the same device, taking care of bandwidth problems and unreliability of the network.
These proxies have to be physically close to the first subsystem while the central unit can be remote; the central control system is a centralized unit able to store and process data, operating building digital simulation models and delivering commands back to the proxies.
The logic model of the designed infrastructure is based on three elements, as shown in
Figure 13.
Following this logic infrastructure, a series of “cheap” small computer or SoC (system on chip) had to be equipped, containing both the “elettra” and “proxy” subsystems; all those computers are connected to a high-performing server in a data centre able to run the software of the central control system. The operative concept of this infrastructure is exemplified in
Figure 14, where only a few energy consumer devices are reported as an example.
Elements e1, e2, e3, e4, and e5 are the cheap computing containing the elettra subsystem and the proxy, while elements c1 to c10 are energy load examples, and P1, P2 are photovoltaic panels for electric power production and geothermal plant.
3.6.2. Obtain Data, Train, and Test Models
Once the data are stored in the central control system, they can be analyzed to build digital numerical models able to simulate and optimize all the main parameters of the smart energy grid. All data have a similar form, so that they can be viewed as a series of {location, date-time, object, value}.
Considering a single location, using ML techniques and rule-based methods such as association rule learning, it is possible to deduce which device is active at a certain time for each selected location [
46].
In the present application, it was not possible to consider all the locations as equivalent one to the other, as detailed in
Section 4.
A possible general solution is the adoption of best practices, which are hard to define due to the different final uses (home, office, and mixed use) and layouts; if grouped by location and similarities parameters, AI becomes able to automatize processes attributing each location to the most appropriate group or cluster. Therefore, it is necessary to run a ML technique known as “clustering” to automatically create groups of similar apartments used for mathematical representation of each unit: to create the feature vector of each unit, each and every energy consumer and producer was counted and grouped together by type [
47].
Given the vector representation of each apartment, we used the well-known unsupervised technique known as K-means, to automatically extract groups of energy-similar apartments.
After a period of observation, a sample for each homogeneous group in a single location was chosen. These local samples were used to extract behavioral rules to be applied to the others belonging to the sample group.
Analyzing the configuration of each location at a given time, it is possible to compare any apartment “Ai” with the sample one “As”. As an example, a general association rule can be expressed as follows: “at time tk, make a comparison of device type dj of flat i (dAij) with the correspondent device type of the reference one (d As j). If they are in a similar status, then do nothing; otherwise, switch it on or off, so that it is in the same state of the reference one’s.”.
An association rule is something in the form X → Y that in a smart grid should assume the simplified form TheSolarPanel IsOn → TheWashingMachineIsOn. We achieved this using the “Apriori Algorithm” which is an influential algorithm for mining frequent item for Boolean association rules. It identifies the frequency of individual items in the dataset, extending them to larger item sets, according to their appearance in the dataset [
48].
Nevertheless, every automated system can easily fail if the digital representation of the built environment does not match reality. Assuming that, inevitably during the lifetime of an apartment, some smart plug will be connected to different devices, affecting the digital model reliability and accuracy.
In order to keep the digital model continuously up-to-date, AI techniques transform a power absorption curve of a single device in a sequence of characters named “energy words of the device” [
48], using analytical processes similar to those of text analyses; then, a supervised learning method named “Naïve Bayes classifier” automatically identifies the type of each energy load, so that the system can detect a mismatch between the digital representation and what is actually connected to the network.
The dictionary of different energy words exceeded the size of 60,000, with the major number appearing less than three time in the energy footprint; therefore, we set this threshold to avoid dimensionality problems. The resulting predictive model elaborated using the Naïve Bayes classifier was validated using both a 66% train 33% test split and a 10-fold cross validation technique, taking advantage of the tool named “Weka”, an open source ML software (using the class weka.classifier.bayes.NaiveBayes).
4. Results
As a consequence of the energy efficiency improvement based on the implementation of renewable energy systems, in winter conditions, the geothermal power plant supplies every building both with heating and domestic hot water; solar collectors integrate the system, while the photovoltaic system powers the external lighting system around the perimeter of the buildings. In summer conditions, domestic hot water is produced through solar collectors covering 100% of the actual needs, while the geothermal power plant only works for the production of chilled water for cooling (through the absorber), while the photovoltaic system powers the entire lighting system of the complex.
The energy diagnosis conducted on a single building using the BIM model through the Revit Suite of Mc4 Software led to the transition from an A2 class (with a specific consumption of 26.8 kWh/m
2y) to an A4 class (with a specific consumption of 16.1 kWh/m
2y). Moreover, in order to further validate the results and the obtained energy diagnosis, the calculation was also repeated with two other numerical simulation tools: (1) Termus BIM, basing on the BIM model and (2) ArchiEnergy, a semidynamic software developed by Sapienza University of Rome (
Table 5).
Once the results and deviation values were obtained, they were evaluated and compared to the following chart in
Figure 15, which reports results from other energy diagnosis conducted on similar building systems.
From the analysis, it is shown that the diagnoses made with the energy software led to similar results with a maximum deviation of 12%, and the difference between the two BIM-based, Mc4 Suite for Revit and Termus BIM, is 5% (
Table 5).
Moreover, the fluids-dynamic analysis performed in specific rooms of a single apartment was confirmed by the data coming from sensors, showing that there is no discomfort in any area due to the configuration of the radiant floor equipment.
In fact, large masses of moving air can be observed as previously shown in
Figure 11. This is mainly due to the temperature difference between the floor and the environment. Convective motions affecting all the areas are generated; however, the temperature gradient is fully compliant with the regulation requirements, and the air velocities are very low, falling within the range of comfort conditions.
It was also monitored the temperature in each area, where the internal temperature was initially 5 °C (equal to the external temperature), until the achievement of the internal comfort temperature of 20 °C. The temperature transient is shown below (
Figure 16).
It can be noticed that the air heating trend is almost the same for all the rooms, and the comfort temperature is reached in about 1900 s (just over 30 min).
Moreover, another obtained result was the implementation of an intelligent energy management model, i.e., an automatic ML system capable of modulating loads (mainly electrical) according to the expected self-production of energy; for this purpose, information from the European Copernicus [
49] earth observation system are acquired in order to have accurate predictive meteorological data.
In this regard, the energy-smart-grid system realized with solar collectors and photovoltaic panels needs a set of rules to establish priorities regarding energy production and consumption loads:
Production: electricity from solar sources, being totally free, must be the first to be fed into the distribution network, followed by the energy coming from the geothermal power plant (which needs electricity to power the circulation pumps); as a last option, it is possible to use energy coming from the public electrical net or use gas.
Consumption: the priority of power supply must be given to the lighting system, followed by the electromotive force circuit, while the air conditioning systems can be regulated and modulated in the event of a lack of energy, by lowering or raising the optimal temperature up to 2 °C.
Therefore, the AI system contributed to reach the goal of increasing the efficiency of the entire energy system by more than 10%, limiting the dependence of the building complex from the electricity and gas distribution networks to a maximum of 20% of the total energy consumed. The system for energy loads forecasting and managing was created in a single apartment (
Figure 17) according to the following two logical steps: (a) the creation of a synthetic method to group the plants based on the similarity of results in terms of energy efficiency and (b) metering, evaluation, and analysis of consumption data of the selected plant.
The inevitable use mutability of the apartments was also considered, as well as the variations in energy loads over time; consequently, an algorithm able to automatically deduce which devices are used in each power outlet was adopted, analyzing the hourly trend of current absorption.
Some energy sensors (as detailed in Material and Methods) were applied, and data were collected in a central system. The different typology of energy loads was considered, and then submetering was performed, as shown in
Table 6 and
Figure 18.
Energy consumption of each device varies according to its power absorption, as shown in
Table 6 and
Figure 18 and
Figure 19, which report some controlled measures on a typical working day, detailing both the apartment and the single rooms.
The use of these energy sensors led to another result: the so-called “submetering” It was possible to detect the biggest single load both in the apartment and in a single room. In this way, the analysis and decision of how to save energy becomes simpler, devising strategies affecting the most consuming items, effectively contributing to the overall energy saving.
5. Discussion
The concept of DT is extremely transversal and widely suitable to both microscales such as apartments and macroscales at the district levels. As the new and future buildings will be directed to near-zero-energy building standards (nZEB), or even zero-energy buildings (ZEB), they therefore need tools suitable for the new design requirements, i.e., digital systems able to predict and simulate both global energy consumption and internal behavior [
50].
It is quite impossible to define a validation process able to ensure the reliability of the calculation method by 100%.
For a full comprehension of the model and interoperability process accuracy, it was necessary to proceed with a comparison methodology based on the overall final outputs, (kWh/m2y) between three different software (1) Termus BIM by Acca Software, (2) ArchiEnergy from Sapienza University of Rome, and (3) Mc4 Suite for Revit.
The developed analysis was focused on the comparison of results coming from different processes basing on both traditional and BIM approaches. On the one hand, Termus BIM used IFC BIM standards, while in Mc4 Software a plug-in approach was developed directly connecting the Revit BIM model with Mc4 analysis tools. On the other hand, the ArchiEnergy software is a traditional system calculating energy consumption based on inputs by the user about the plant and the building envelope.
Following the validation phase, the DT led to the evaluation of the smart-grid implementation effects. In particular, in
Figure 20, the reduced energy consumption and the relative reduced CO
2 consumption coming from the Mc4 Suite for Revit analysis are shown.
At the same time, the work carried out highlights how in highly urbanized contexts characterized, it is very difficult to achieve high performances as required by the nZEB Italian Decree [
51], even if significant energy requalification interventions are developed, improving both the building envelope and air conditioning systems.
As a consequence, it became necessary to consider building complexes not only as consumers, but also as energy producers in a local, block, district, or neighborhood smart grid: the concept of “prosumer”.
By such a logic, the role of AI in smart-grids management and optimization of both energy production and consumption becomes decisive, being able to make reliable forecasts on possible scenarios.
Analyzing similar energy efficiency interventions on buildings and residential complexes, it is shown how efficient technologies are now available, well defined, and widely known. Therefore, the parameters of selection between different interventions are essentially (a) climatic parameters, (b) regulatory restrictions and constraints on interventions, and (c) the availability of government grants for the use of RES, compensating the payback time, which is still too long for certain technologies.
As previously shown, the use of BIM-based systems [
16] for building energy efficiency drives no substantial improvements in terms of accuracy of results compared to traditional methodologies [
18].
However, the real innovation contribution of DT-enabled systems concerns the definition of digital technologies able to reduce the gap between the expected performance of buildings and their real behavior. These goals are mentioned in the strategies of National and International R&D Programs such as Next Generation EU (Recovery and Resilience Facilities) [
52], Strategic Energy Technology (SET) Plan [
53], and Italian National Integrated Energy and Climate Plan (Dimension 5 Research, Innovation and Competitiveness) [
54].
In this case, DT becomes a key element for research and development on second-generation smart buildings entirely based on electricity consumption and characterized by energy autonomy, high flexibility, block chain, and smart contract dialogue systems with the grid, assisted by digital monitoring methods.
Artificial Intelligence
Although optimizations on energy consumption have been studied in depth [
55], when dealing with residential compounds or SOHO (small office home office) buildings, we cannot directly borrow general solutions from research experiences [
56,
57]. In fact, the overall consumption in these environments is the sum of small contributions by a considerable amount and variety of devices [
58], while, mostly in industrial environments, there are generally few big powers draining that can be controlled one by one.
Moreover, these small consumers are operated by people which do not follow any procedure, since they have their personal habits: dealing with both technical and human factors through data analysis techniques becomes a fundamental strategy [
59].
DT was coupled with AI to investigate building behaviors as a whole, and supervised learning techniques are used to produce an efficient and intelligent storage system management in the whole complex.
The problem of energy savings in buildings is strictly connected to the need of measuring and controlling energy loads in an efficient way, which can evolve complex scenarios. For instance, if nobody is at home and it is already late morning, both the coffee machine in the kitchen and the air conditioning are wasting energy if they are still switched on, while if someone is still there then both appliances should be still operational. Consequently, several sensors and actuators can be involved and their data should be interconnected so that an ad hoc algorithm derives the correct energy saving policy (e.g., a motion sensor shares data with electrical relays able to switch on/off the correct devices).
Real-time building management system incorporate model-based control through ML [
60] to extend the use of mathematical models even to the management of human-related factors. In fact, thermal, humidity, acoustical comfort, and occupants model are combined and connected to ML.
While the first model depend on facts, the latter depend on humans: the behavioral model is a probabilistic one [
60]: the probability that an occupant takes specific behavioral decisions or actions is defined as a function of the occupant’s characteristic and the current environmental conditions, and “predicting the residents” actions toward a specific situation is not easy”.
Considering the apartment microscale, instead of the whole building, our approach was to envision the automatic definition of best practices [
61]; if grouped by location and similarities parameters, thanks to unsupervised learning techniques, it was possible to automatize the processes of attributing each location to the most appropriate group or cluster. In our approach, the most efficient and performing apartment for each group or cluster was found considering the energy bill over a few months, confirmed by the energy data collected over a given period [
62].
Given these “sample” location, personal actions in apartments can be modeled with behavioral rules [
63]: the definition of rules was given using a formal logic that allows exceptions [
48] through AI, using Apriori algorithm to automatically learn the rules.
The automatic update of the BIM model to ensure the validity of the DT, based on an up-to-date information model, was dealt with by using web services [
64]. Specifically, it was necessary to ensure that information about energy loads coming from smart plugs were up-to-date in the model. A supervised learning technique (named “Naïve Bayes classifier”) combined with a novel energy load information coding [
65] was used to achieve the goal.
6. Conclusions and Further Developments
The configured DT methodology gives buildings the capability of improving and enriching their knowledge and available data, receiving input and signals from sensors that constantly monitor them, developing self-learning capabilities and predictivity through the integration with AI systems.
Moreover, the paper focuses on how the concept of DT is extremely transversal and applicable both to macroscopic and microscopic scales (from district to apartment), as demonstrated for the use of energy management systems. It can be related, for example, to specific components of technological systems, to the digitalization of infrastructures and real estate assets, to technological systems, or networks of technological systems, etc.
The objective of the research was to exploit ML systems to manage and to simultaneously integrate self-production and supply system in an energy smart grid, in terms of both thermal and electrical loads.
The results of the DT-based real-time monitoring are able to reduce the gap between the energy performance of the buildings (simulated through energy diagnosis) and the real building performance. This is possible thanks to data analysis, which allows one to get more refined energy management strategies, even highlighting inadequate users’ behaviors and policies.
As far as load forecasting is concerned, the configured DT is able to calculate thermal loads on a daily basis [
60], integrating them with algorithms capable to calculate in advance building consumption based on historical data transmitted by sensors; in this way the system, on the one hand, acquires real-time data from smart metering [
61] and environmental quality sensors; on the other hand, it integrates historical data (bills, consumption, etc.) and IoT with a real-time simulation approach [
62]. The purpose is aimed at updating and refining the database, tailoring the energy profile of consumption on real users
These intelligent systems implemented also provide an active control on the energy balance; in fact, once the system becomes sufficiently confident, it takes control itself of the energy production systems, as well as of the loads modulation and regulation in order to optimize the energy balance system, limiting nonessential loads in case of production deficit.
Even the optimization of thermo-hygrometric wellbeing parameters in the indoor environment is considered as fundamental. In fact, through the analysis of data from environmental quality sensors and after an appropriate self-learning period, the DT becomes able even to set operations times and levels of the systems to optimize the thermo-hygrometric wellbeing of users.
Moreover, spreading the proposed research to an urban approach, developments in the BIM-GIS synergy, as both large- and small-scale digital information system configuration, would allow for the integration of each urban energy cell with the national power distribution grid, with particular focus on electric mobility and storage systems of smart grids, urban metabolism, etc. Predictions about the impacts on neighboring areas and profiling functional integrations would be performed, providing essential digital tools for the implementation and real-time monitoring of municipal and district energy plans.
In addition, in this regard, further developments of the present research would reach the optimization of the operations using a data model as a process core, replicating reality in real time, limiting or even eliminating system malfunctioning, grid unbalance, or even power breakdowns. With the aim of reducing malfunctions and breakdowns on energy services, the proposed methodology would be applied even to the facility management of HVAC and electrical plants toward configuring predictive maintenance systems.