Abstract
In search of a more sustainable society, humanity has been looking to reduce the environmental impacts caused by its various activities. The energy sector corresponds to one of the most impactful activities since most energies produced come from fossil fuels, such as oil and coal, which are finite resources. Moreover, their inherent processes to convert energy into electricity emit various pollutants, which are responsible for global warming, eutrophication, and acidification of soil and marine environments. Biofuels are one of the alternatives to fossil fuels, and the raw material used for their production includes vegetable oils, wood and agricultural waste, municipal waste, and waste cooking oils (WCOs). The conventional route for WCO valorization is the production of biodiesel, which, as all recovery technologies, presents advantages and disadvantages that must be explored from a technical and economic perspective. Despite its successful use in the production of biodiesel, it should be noticed that there are other approaches to use WCO. Among them, thermochemical technologies can be applied to produce alternative fuels through cracking or hydrocracking, pyrolysis, and gasification processes. For each technology, the best conditions were identified, and finally, projects and companies that work with this type of technology and use WCO were identified.
1. Introduction
1.1. Consumption of Edible Oils in Europe
It is estimated that about 90% of cooking oils and fats used in the EU come from vegetable oils [1]. Since the sources and data refer to the flow of new and used edible oils in Portugal and Europe, the information is scarce, specifically on the quantities consumed, produced, collected, imported, and processed. Several sources of information, both at European and national levels, were consulted so that values can be estimated in some way.
In general, in the analysis carried out in this article, several types of edible oils (soybean, sunflower oils, etc.), vegetable fats, and olive oils were included since there is often no effective control over the residues that are deposited in containers for waste oil collected. The information collected refers, essentially, to the period from 2014 to 2018, making it possible to trace a temporal evolution whenever data are available [2].
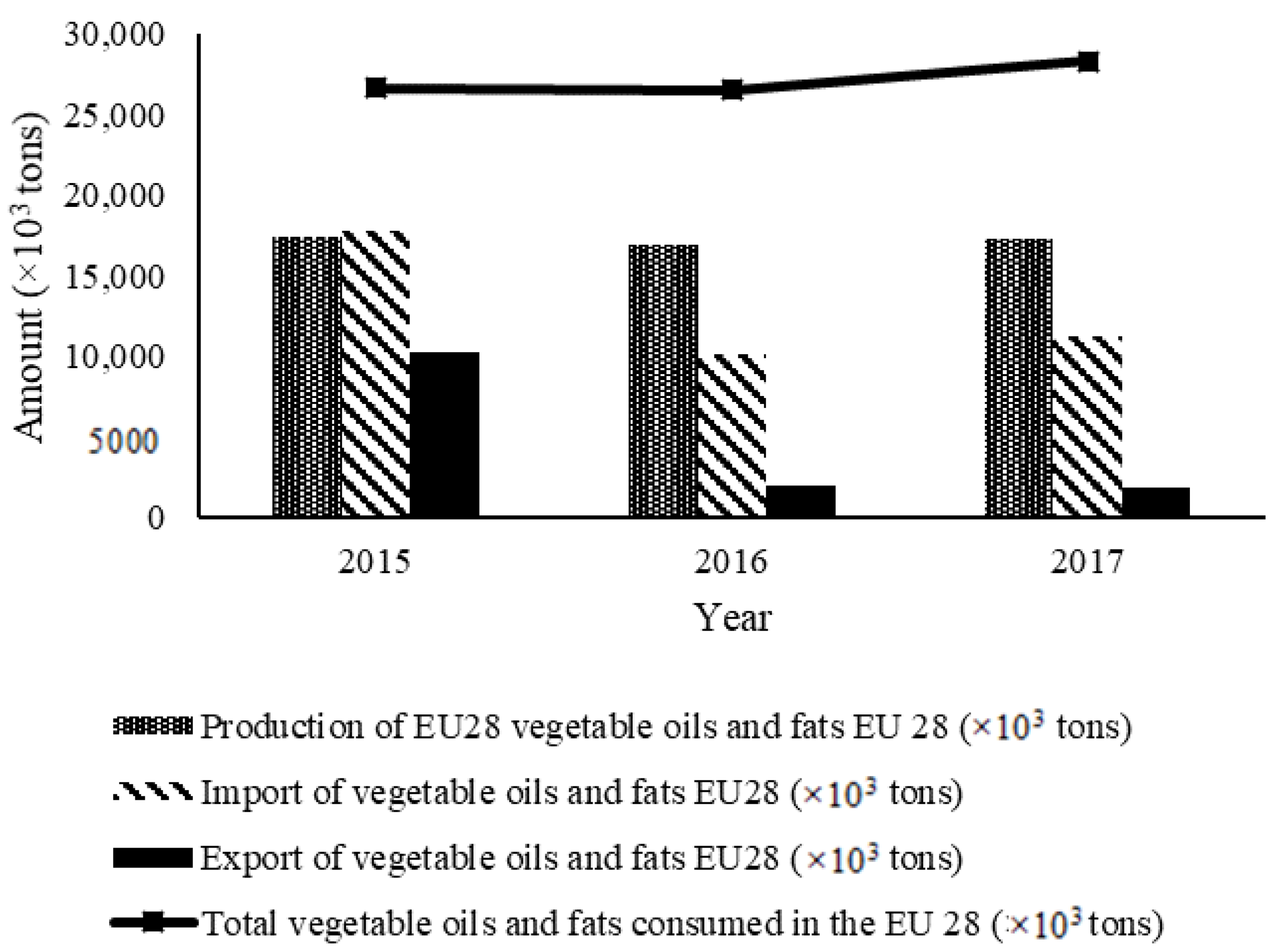
Thus, Figure 1 and Table 1 show the approximate amounts of vegetable oils and fats consumed at the European level by including vegetable oils and fats produced within the European Union and imported vegetable oils and fats, based on data obtained from the European Union Oil and Proteinmeal Industry, International Olive Council, and the National Institute of Statistics [2].
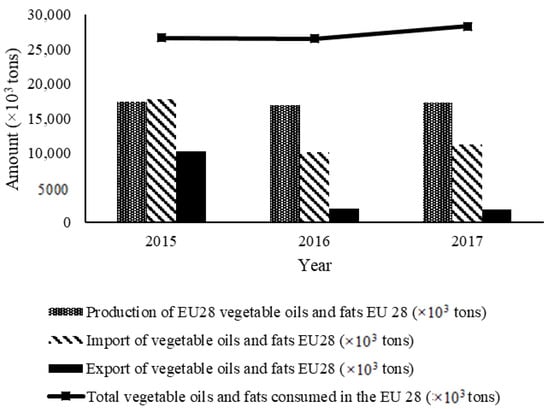
Figure 1.
Data on new vegetable oils and fats in the European Union [3].

Table 1.
Calculation of the total vegetable oils and fats consumed in the EU, in the years 2015–2018 [2].
1.2. Waste Cooking Oils
In general, it is difficult to estimate the global production of WCO due to the lack of reliable reports and the consequent difficulty in traceability (especially from the domestic sector) and the difficulties associated with estimating the production of WCO from consumption patterns. Nevertheless, several studies use indirect methods to estimate quantities based on consumption data for edible oils.
Estimates published in 2008 predicted that at least 16.54 million tons (Mt) of WCO would be produced each year among the largest producing countries and regions: China, Malaysia, the United States of America, Europe, Taiwan, Canada, and Japan [4].
According to the BioDieNet Project (2007–2009), the estimated annual WCO production for EU27 was 3.55 Mt, varying between 6.3–8.0 kg/capita and 5.6–7.2 kg/capita [5]. The estimated annual WCO contribution in the domestic sector would be 1.748 Mt [6,7], approximately 49% of total WCO production, with the remainder being attributed to the HORECA sector and a lesser extent to the industrial sector. Estimates published in 2016 predicted that 1.66 Mt of WCO would be available, 0.854 Mt from the domestic sector and 0.806 Mt from the commercial sector [8].
According to the European Biomass Industry Association, the potential estimated WCO to be collected is around 8 L WCO/capita/year. Extrapolated to the total EU population of around 500 million, this would mean an annual WCO production capacity of 4 Mt, approximately seven times more than the amount currently collected [9].
In a 2018 publication, the authors gathered data on the quantities of WCO produced, which can be subjected to recovery per year in different countries. Despite the relative degree of uncertainty resulting from the lack of reference in the studies consulted of the methods for obtaining the previous estimations, the figures give relevant information. According to the data presented, European countries, such as Denmark, Spain, Italy, and the United Kingdom, had annual productions between 0.1 Mt and 0.5 Mt of WCO. All other EU countries had annual production below 0.1 Mt. Analyzing the same data on a per capita basis, some EU countries, such as Portugal (up to 6.5 kg/capita/year), become major producers [10].
Due to this large amount of WCO produced, it is essential to recycle this waste to transform it into a “new product” with economic value. One way to recycle this waste is to convert it into biofuel [11,12,13].
2. Production of Alternative Fuels through Thermochemical Conversion Processes
The planet Earth faces several problems in the social, economic, and environmental spheres. Those are critical problems that correlate, for example, with the consumption of fossil fuels, which is responsible for causing numerous environmental impacts, such as the greenhouse effect, with direct impacts on human health. Transport depends on fossil fuels, specifically fuels derived from petroleum, gasoline, diesel, liquefied petroleum gas, and natural gas. In turn, automobiles are the leading polluting gases, with high associated fuel costs [14].
Recently, there has been widespread interest in learning more about obtaining liquid fuels from non-fossil sources, such as biofuels. Biofuels are an alternative way to replace fossil fuels since they are renewable and cause less environmental pollution. Biofuels are less polluting than fossil fuels as they emit fewer chemicals harmful to the environment during combustion and their production processes tend to be more sustainable [15].
The use of ethanol, a type of biofuel, can reduce global warming caused by fossil fuels. It reduces the emission of carbon dioxide (CO2), and much of the CO2 emitted by cars fueled with ethanol is reabsorbed in sugarcane plantations, which makes the CO2 emissions partially offset. On the other hand, biodiesel has remarkable environmental advantages when compared to diesel. According to a study performed by the United States National Biodiesel Council, burning biodiesel can emit, on average, 48% less carbon monoxide, 47% less particulate matter, and 67% less hydrocarbon than diesel from petroleum [15].
From the point of view of raw materials, biofuels are an asset because they use materials with cyclical availability, such as some plants (sugarcane, soybeans, palm, and others), algae, and several other residues. However, some experimental studies and projects investigate using waste streams to produce biofuel, even though they have high levels of contamination and heterogeneity. In addition, they have a more significant and faster continuity of raw material supplies for biofuel production. Thus, the literature generally classifies biofuels as first-, second-, and third-generation. Such classification is not yet entirely accepted, as it appears to consider the classification according to the technology used to produce the biofuel and the nature of the raw material [11].
First-generation biofuels are produced from sugar, starch, or vegetable oil, and their raw material is from vegetable or animal origin, competing with the production and distribution of food. Second-generation products are by-products, such as waste, biomass from tree pruning, used cooking oils, and others; these are more sustainable because they do not compete with food production [16].
Table 2 shows the relationship of raw material, technology, and types of biofuels produced.

Table 2.
Relationship of raw material, technology, and types of biofuels produced (adapted from [17]).
Due to the lack of information, this waste is discarded irregularly in the sewage collection system, which causes numerous environmental impacts, such as sea and lake contamination. It also has economic effects, as it increases the costs of wastewater treatment processes and can also damage the domestic pipe system [18,19].
According to Dias (2013), Juniper (2009), and Nascimento (2011), WCO can be valued in the manufacture of products in various segments of the industry, such as the production of soap, oil paints, and biofuels. Through the valorization of WCO, the production of biofuels appears as a solution to the energy problem to reduce the amount of waste generated and irregular deposition [17,20,21].
In addition, several studies reveal the potential of WCO to supplement the biofuel supply chain. Moreover, it is a good alternative that could contribute to solving fuel supply problems in more isolated places, such as rural areas [1,17,18,22].
Regarding the technologies and biofuel types produced, the state of the art performed indicates a predominance of studies for biodiesel production through transesterification. However, some studies use different technologies with other types of biofuels produced through the valorization of WCO, such as the production of hydrogen-rich syngas in gasification, bio-oils through various types of pyrolysis, and biokerosene, among others. Table 3 shows the leading technologies used to produce biofuel and the product of that technology [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34].

Table 3.
Alternative technologies used for biofuel production through WCO.
2.1. Hydrocracking
Hydrocracking is commonly used in the oil refinery to break down large molecules and remove sulfur (S), nitrogen (N), and metals from petroleum products [35]. This process requires a high amount of hydrogen for desulfurization. However, it also uses hydrogen (H2) to saturate the molecules, increasing the H2/C ratio of the compounds [36].
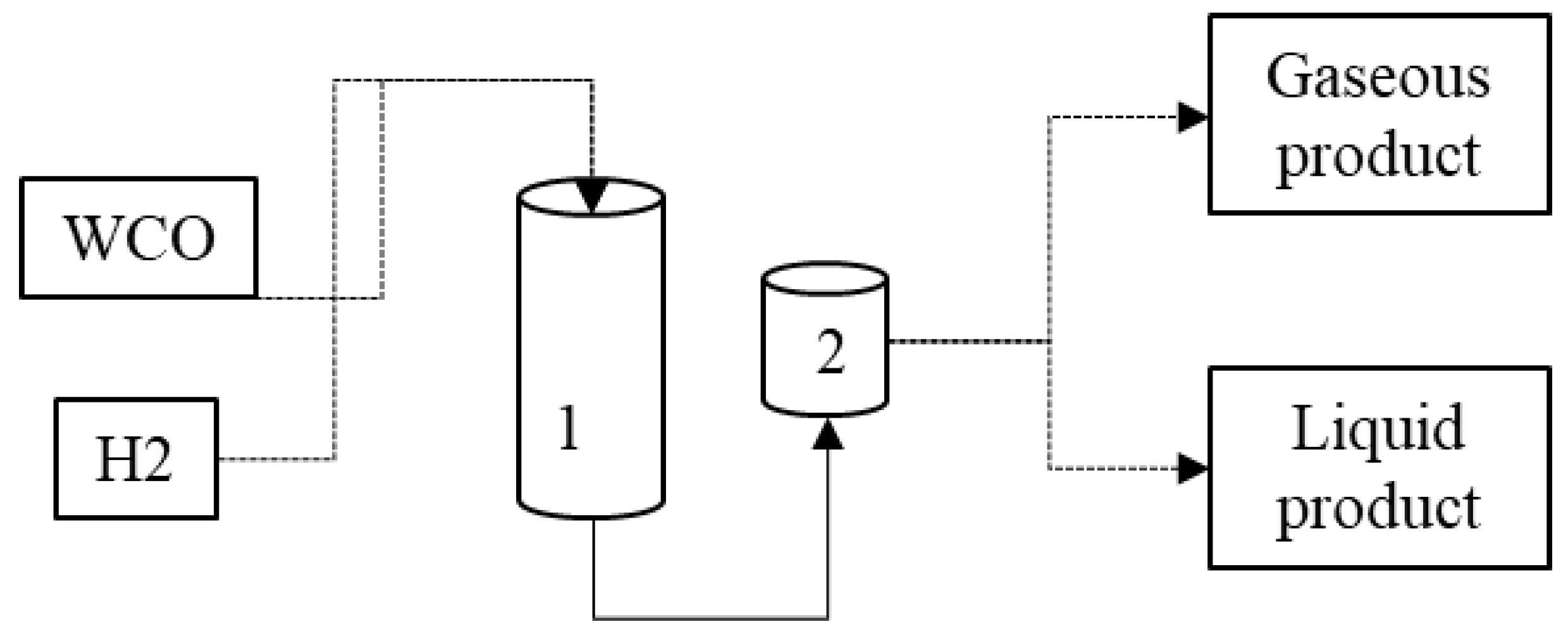
According to Tiwari (2011) and Melo (2016), the hydrocracking process is a good alternative for waste chemical recycling because of catalyst use. The waste can be used for deoxygenation, a complementary process that removes O2 atoms from the glyceride molecules and fatty acids in vegetable and animal oils, such as animal fat, used cooking oils, and others, to create purified and better-quality hydrocarbons [35,37]. In Figure 2, the hydrocracking process is represented.
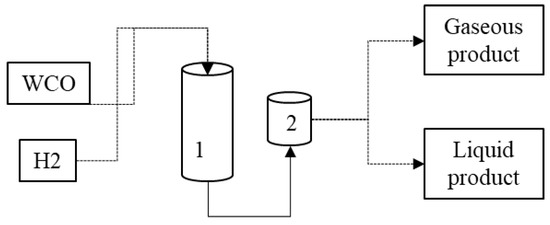
Figure 2.
Representation of the hydrocracking process. (1) Reactor; (2) vacuum separation of products. (Adapted from [24]).
The hydrocracking procedure is carried out at high temperatures and pressures (52–300 °C and 0.1–20 MPa), being powered by H2, resulting in transport fuels and jet fuel, with the desired viscosity, low oxygen content, better atomization, and lubrication. For example, in the experimental study of Dujjanutat (2020), the researchers produced bio-hydrogenated kerosene with the desired molecular length, saturation, and branching level that had similar characteristics to the mineral kerosene [28].
Li et al. (2015) reported in their study that hydrocracking produces straight-chain alkanes from animal fatty acid triglycerides, WCO, and other vegetable oils. However, to have a better yield, lower production costs, and guarantee the removal of heteroatoms, it is necessary to use catalysts, such as Ni-Mo/Al2O3 and Co-Mo/Al2O3 [38].
Melo (2016) reported that temperature is a significant factor to be controlled as it directly influences the reaction and extent of the formation of alkane chains. If the temperature is too high, there will be a significant loss of CO2 and CO, producing lower hydrocarbons [37].
In the study led by Bezergianni (2009), biofuel production was carried out by the hydrocracking process, using WCO as raw material. Researchers realized that at the lower temperature (350 °C), more kerosene/jet fuel and naphtha were produced. On the other hand, when they increased the temperature to 390 °C, they observed a reduction in fuel production [23].
In another experimental study by Bezergianni (2009), the researchers concluded that high liquid hourly space velocity (LHSV) in the reactor associated with a moderate temperature (350 °C) promotes biodiesel production. On the other hand, the increase in temperature to 370 °C induces the production of other bio-oils [24].
Li (2015) tested three types of zeolites (Meso-Y, SAPO-34, and HY) with nickel, which were used to convert WCO as jet biofuel through hydrocracking. The experimental results show that the used cooking oil and the Meso-Y-catalyst obtained the best results since the combination mainly deoxygenated heptadecane (C17H36) and pentadecane (C15H30) chains by decarbonylation during the first three hours. The chains of long alkanes were broken into a range of C8–C16 alkanes. The researcher also verified the production of cycloalkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons through cyclization and dehydrogenation pathways [38].
Wijaya (2014) tested a Ni-bentonite catalyst to perform hydrocracking of WCO by temperature variation of 300, 350, 400, and 450 °C. The results show that the ideal temperature for biofuel production from cooking oil used with Ni-bentonite catalyst was 300 °C. The hydrocracking products contained 2-propanone, dodecane, octanoic acid, decanoic acid, dodecanoic acid, and 1,2 benzene dicarboxylic acid. These compounds are similar to those found in fossil gasoline and diesel [39].
2.2. Gasification
Gasification is a thermochemical conversion process in which substances containing carbon and hydrogen, such as biomass and solid urban waste, are partially oxidized at high temperatures (800–1100 °C). This process occurred in the presence of a gasifying agent (air, steam, and oxygen) and converted into gaseous products [40].
Gasification produces gas from fossil fuels, biomass, and waste, usually known as synthesis gas. The synthesis gas (syngas) consists mainly of CO, H2, CO2 CH2, and H2O [41]. This process may contain traces of hydrocarbons of high molecular weight, inert gases, and other contaminants. This gas is used in the production of electricity or steam. The gasification process reduces the possibility of dioxin and furan products and prevents compounds such as SO2 and NOX [42,43,44,45,46].
The H2 and CO content of the gasification reactions can be modified depending on the reaction conditions. To promote the hydrogen product, several catalytic treatments with Ni-based catalysts have been studied. These catalysts have proved to be the most effective in producing hydrogen from biowaste gasification so far [40,47].
Usually, syngas is used as a fuel for stationary power and heat generation or associated with catalytic conversion to produce other liquid fuels and chemical intermediates. Syngas can also produce biomass fuels in liquid through the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, which requires an H2/CO ratio of around 2.15. However, the H2/CO ratio of syngas produced is typically between 1.0 and 2.2 and may require additional adjustments to be achieved by gas exchange reactions in water or reverse exchange [40,43,48].
A significant challenge of biomass gasification is tar formation, leading to corrosion, scale, and blockage. Biomass tar is a light mixture of hydrocarbons and phenolic compounds that can be converted into gaseous products through steam injection and several types of catalysts to promote tar conversion.
Catalysts are classified into three groups: (1) naturally occurring catalysts (i.e., dolomite, olivine); (2) metal catalysts (i.e., nickel and alkali metals); and (3) alkaline catalysts (potassium hydroxide (KOH), potassium bicarbonate (KHCO3)). To reduce the biochar formation in syngas, operating parameters must be optimized [40,49,50].
Regarding the gasifier, the literature review describes three commonly used models: fluidized bed gasifiers, fixed bed gasifiers, and plasma gasifiers.
2.2.1. Fluidized Bed Gasifier
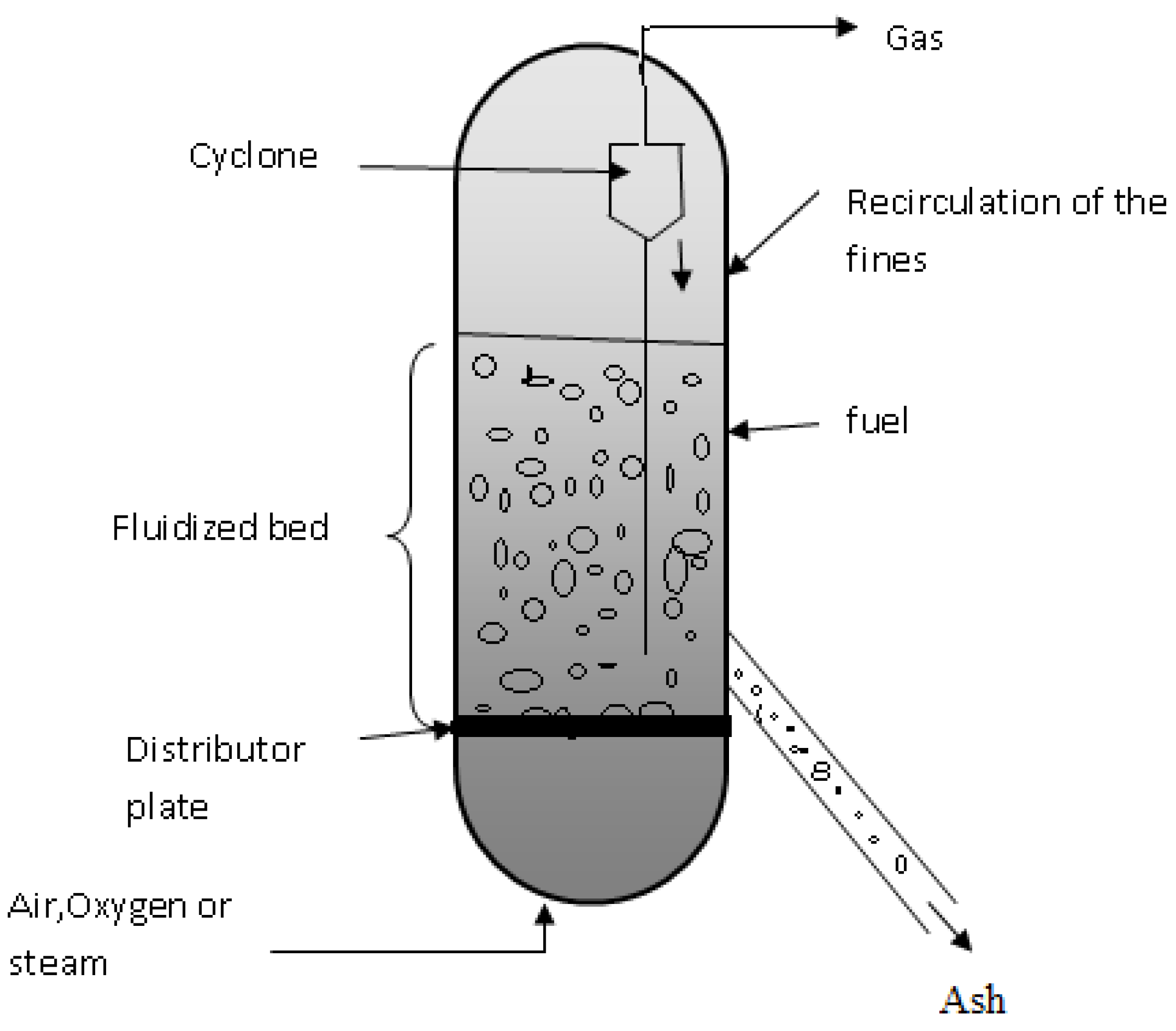
There are no distinct reaction zones in the fluidized bed gasifier (Figure 3). In this case, drying, pyrolysis, and gasification occur together, across the reactor bed, which, being well fluidized, leads to practically isothermal conditions. The bed is regularly made up of silica walls to maintain the ability to retain heat [51].
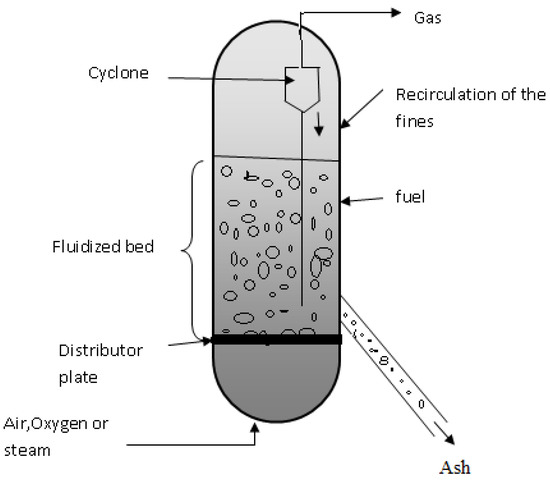
Figure 3.
Fluidized bed gasifier model [52].
According to Tamošiūnas (2019), fluidized bed gasification was developed to solve operational problems, such as a mixture of gas–solid contact, uniformity, temperature control, and efficiency. This gasifier model has the advantage of reaching a higher coal conversion rate, producing a gas with a lower concentration of tar [53].
The incoming biomass is pre-treated and added via an entrance inlet to the gasifier. After feeding, mixing with the bed material occurs and the drying, pyrolysis, and gasification phases take place. An oxidizing agent is added to the bottom of the gasifier, being fed at a speed sufficient to keep the bed material in a suspended state, thus acquiring characteristics like a fluid. The bed temperature depends on the type of material to be gasified, for example, in the case of biomass, due to high volatile content and with a low melting point, the bed temperature must be between 800 and 900 °C. In the treatment of waste, some processes operate at higher temperatures to guarantee their complete decomposition. The ashes produced during this process are removed from the bottom of the gasifier [40,43,51,54].
Kim (2015) carried out WCO valuation studies of soy oil to produce syngas gasified with air in a fluidized bed reactor. The gas produced was filtered with activated charcoal. It was observed that oxidation at low temperature (808.5 °C) significantly changed the composition of the fuel, making the WCO more favorable to the gasification reaction, producing a more significant amount of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. In addition, with the filtration of activated charcoal, the gas (WCO product) fulfilled the tar requirement (<0.1 g/Nm3) for the energy production of an engine by syngas [30].
Li (2009) studied the valorization of used palm oil to obtain syngas rich in hydrogen in a fluidized bed. The authors realized that the higher the temperature, the greater the quantity of syngas produced. However, this loses calorific power [55].
Sakaguchi (2010) studied the valorization of WCO, charcoal, and bio-oil from the pyrolysis of wood biomass to produce syngas in a fluidized bed gasifier with a maximum temperature of 840 °C. The authors concluded that for these materials and at this temperature, the carbon conversion is incomplete, and some mixed hydrocarbons are present in the gases produced. This occurred due to the catalysis of the water–gas displacement reaction, and steam gasification significantly affected the product’s gas yields, which led to higher H2 yields and lowered CO and hydrocarbon yields [56].
2.2.2. Fixed Bed Gasifier
The fixed bed gasifier (Figure 4) refers to the conditions at the ends of the bed, which do not change under stationary conditions. The combustible material is fed through the upper part of the gasifier, moving to the lower part of the aerator through the force of gravity, while the oxidizing material is added through the lower part of the reactor. In relation to the products generated in the system, the gas rises through the bed, and the ashes are extracted from the bottom of the bed. Thus, this configuration characterizes this reactor model as the counter current gasifier because the waste and the oxidizing agent roam in opposite directions [40,51].
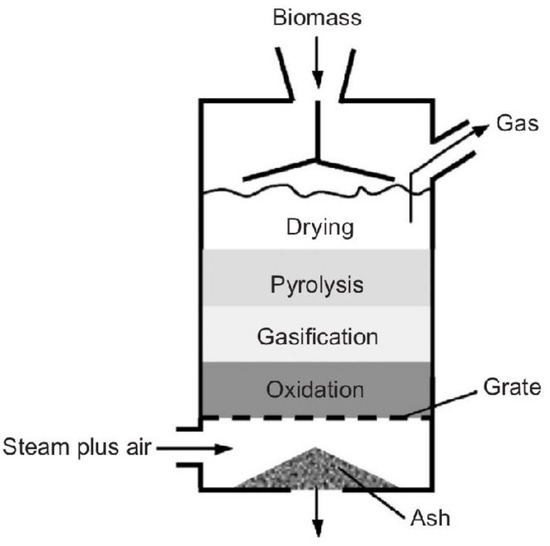
Figure 4.
Fixed bed gasifier [57].
Fixed bed gasifiers are a simple, reliable, and robust small-size technology. Due to the small size of the reactor and the low cost of its construction, it becomes an attractive solution in small-scale applications [53].
Nanda (2019) used WCO in gasification at variable temperatures (375–675 °C), feed concentration of 25–40% by weight, and reaction time of 15–60 min to investigate their effects on syngas yield and composition. The maximum hydrogen yields obtained were 5.16 mol/kg and total gases 10.5 mol/kg. It was observed that the ideal temperature, feed concentration, and reaction time with the best yields were 675 °C, 25% by weight, and 60 min, respectively [29].
Li (2013) evaluated the use of catalysts to produce syngas rich in H2. The catalysts Fe2O3, Al2O3, CaO, and activated charcoal were tested to evaluate the catalytic breakdown performance of the oil used in a fixed bed reactor. Fe2O3 was considered the most effective catalyst compared to the others to produce hydrogen, carbon deposit, and conversion of WCO. When the temperature rose, the syngas content and the conversion of used oil to Fe2O3 increased. The conversion of WCO to syngas occurred at 750 °C and reached 100%, and, at the same time, the content of H2 and CO was 48% and 10%, respectively [27].
Given that temperature influences the results for syngas production, [58] carried out studies to value the ash produced in the gasification process as catalysts to produce syngas with more quality and to value the ashes produced. The reaction conditions carried out were a catalyst concentration of 4% by weight, 12:1 molar ratio of methanol/oil, and operating time of 90 min. These catalysts optimized the conversion of fatty acids and methyl esters to hydrocarbons, converting 97% of the fatty acids.
Ahmad (2018) evaluated the use of an acid catalyst from charcoal gasification ashes for WCO methanolysis and to produce more liquid biofuel. The ideal reaction conditions were a 9:1 ratio of methanol/oil, 6% by weight of catalyst load (g), reaction of 130 min at 65 °C, and allowed the conversion of 96% of ester [59].
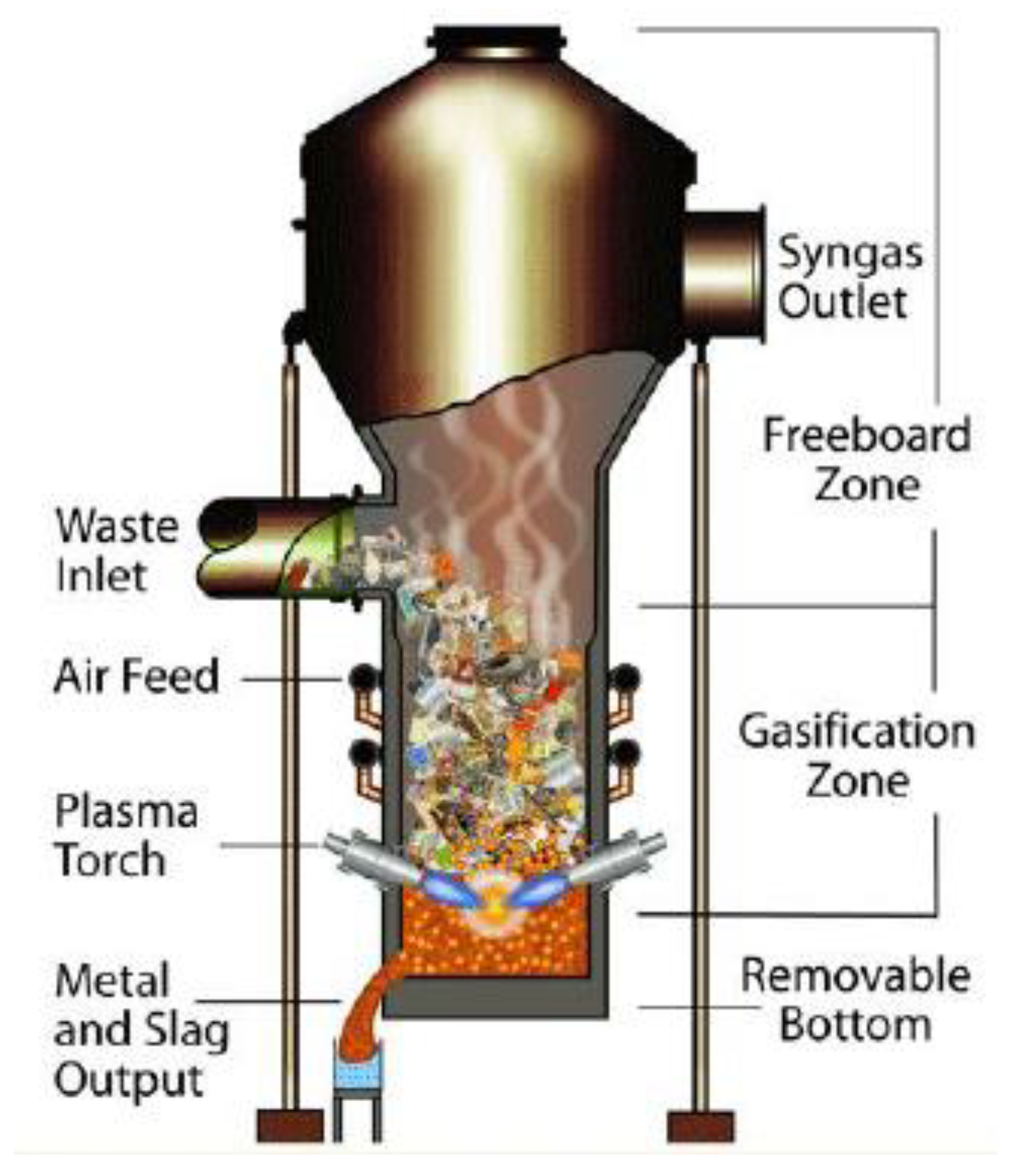
2.2.3. Plasma Gasifier
Plasma gasification (Figure 5) is a new and promising thermochemical treatment method. The core of the technology is in the installation of the gasifier, called the plasma torch, which heats the raw material to high temperatures (from several thousand to tens of thousands of degrees). These high temperatures are reached due to the burning of the electric arc between two electrodes in the discharge chamber of plasma. The central part of the gasifier is fed into the discharge chamber passing through the region of the burning arc, where it is heated. The material to be treated will be in contact with a plasma stream, where temperatures will reach 2000–5000 °C. Therefore, one of the main advantages of plasma gasification is its ability to treat any dangerous or non-dangerous organic and inorganic raw material, breaking it down into elementary molecules. The organic matter is converted into high-quality syngas with a small amount of tar, while the inorganic fraction is glazed in inert slag and leaves the reactor at the bottom [38].
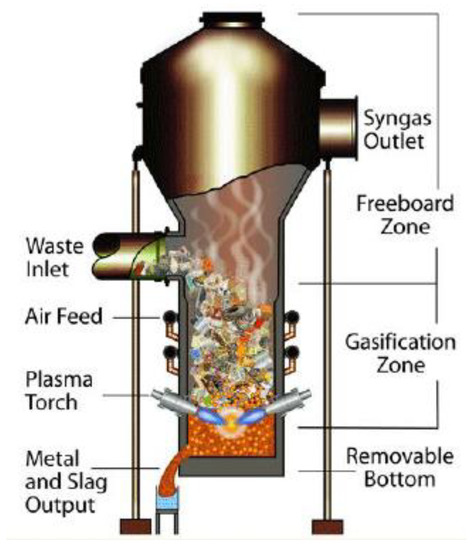
Figure 5.
Plasma gasification model [53].
Tamošiūnas (2019) investigated the valorization of WCO by gasification of plasma for obtaining syngas. The best efficiency of the gasification process was obtained at a ratio of gasifying agent/raw material (S/WCO) of 2.33. For this reason, the highest concentration of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, the H2/CO ratio, the lowest heating value, carbon conversion efficiency, energy conversion efficiency, specific energy requirements, and the tar content in the syngas were 47.9%, 22.42%, 2.14, 12.7 MJ/Nm3, 41.3% 85.42%, 196.2 kJ/mol (or 1.8 kWh/kg), and 0.18 g/Nm3, respectively. The study concluded that the thermal arc plasma method used in this study can be effectively used for the gasification of cooking oil residues in high-quality syngas with an incredibly low tar content [53].
Rafiq (2011) studied the valuation of WCO to produce a bio syngas through a plasma gasifier; a Ni-based catalyst was used and propane and air as oxidants. The results show that in the test that lasted 10 h at a temperature of 920 °C, with a WCO flow of 38 mL/h where the plasma stabilized, the concentrations of CO, H2, CO2, and CH4 increased from 8.4 to 13.8%, 7.1 to 15%, 3.2 to 4.2%, and 0.6 to 2.5%, respectively, and the concentrated CO2 decreased from 5.32 to 2.7%. However, a high proportion of H2/CO indicates syngas suitable to produce hydrogen or biomethane [60].
Table 4 shows some global companies that use gasification to produce biofuels through waste, forest biomass, MSW, and others. Gasification is a recommended technology because it can be used in a wide variety of organic foods (biodegradable and non-biodegradable), the materials produced have good qualities, and this technology is highly recommended to produce bio syngas and bio-oil.

Table 4.
Companies that use gasification to produce biofuels.
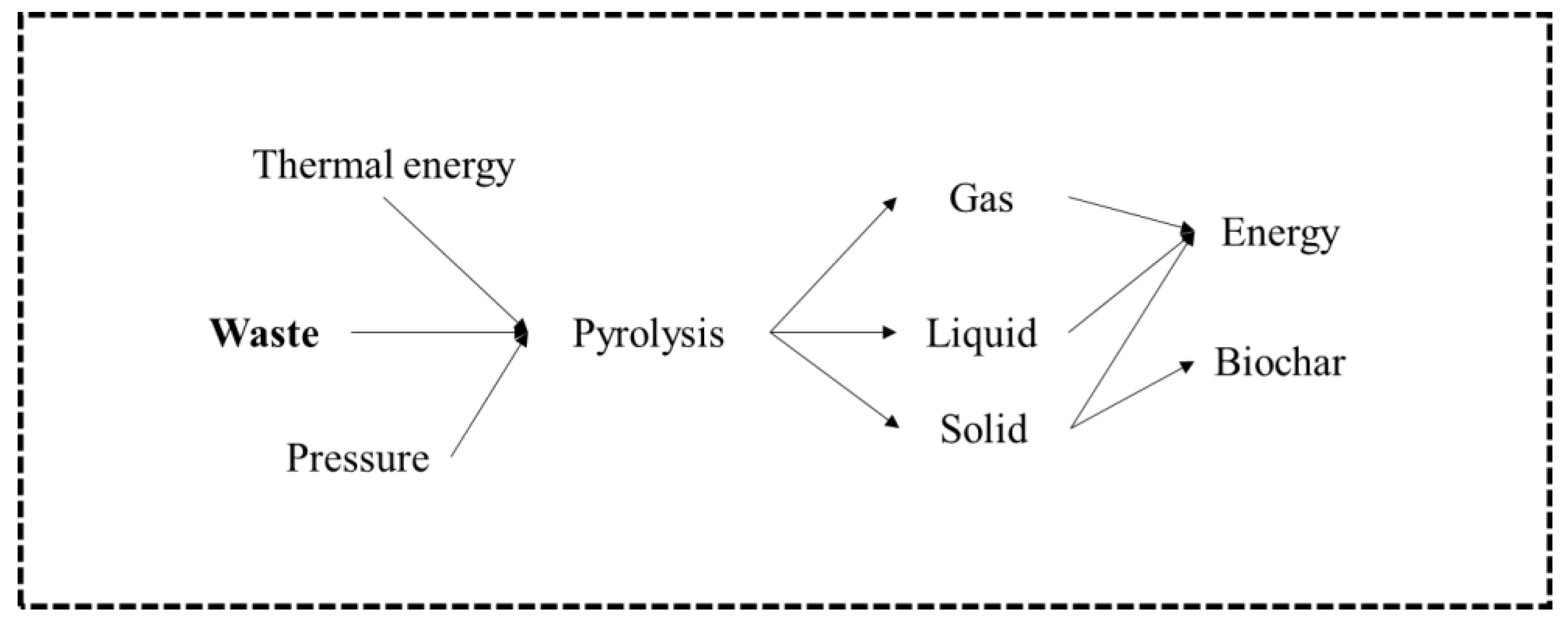
3. Pyrolysis
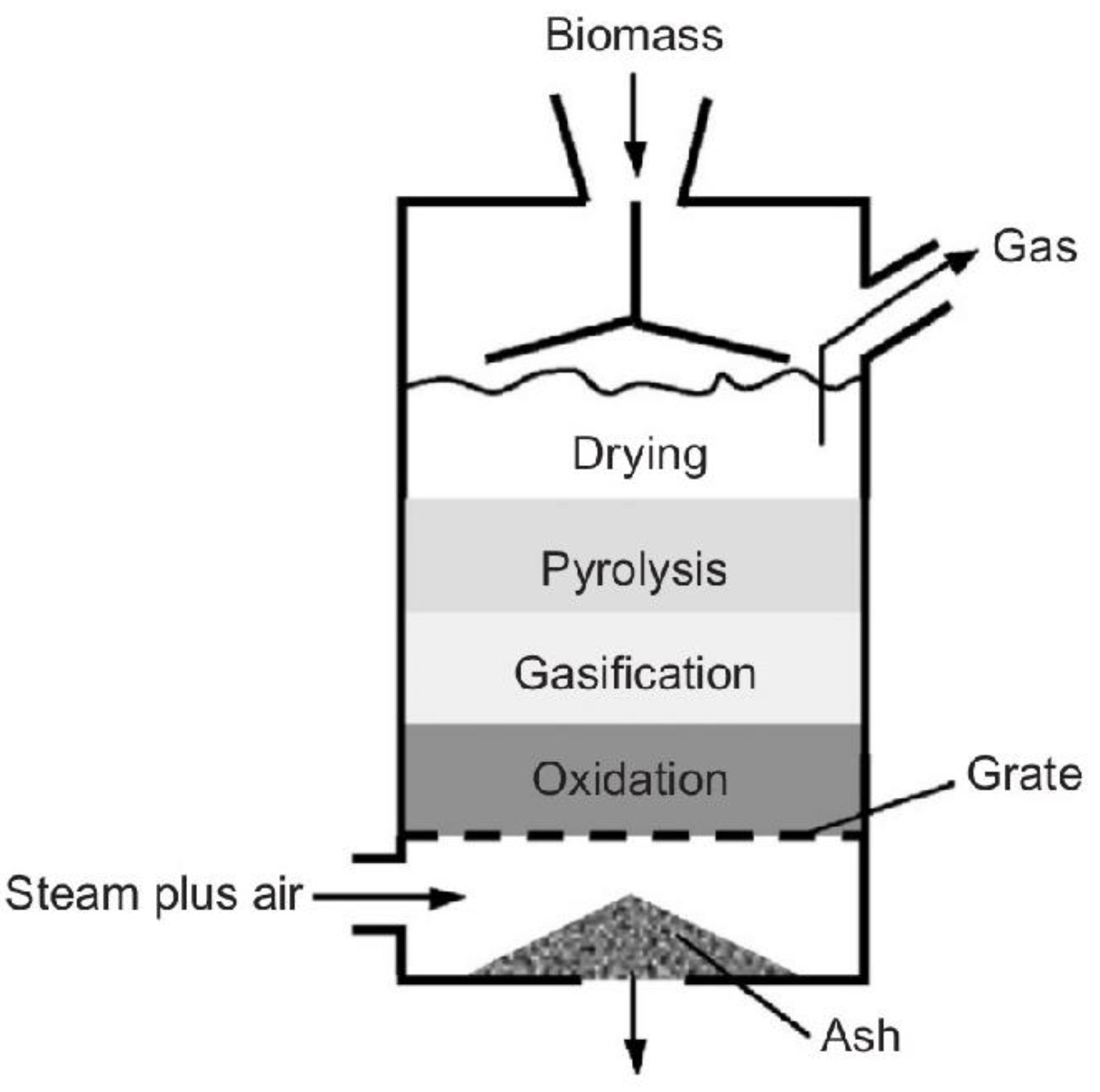
Pyrolysis is the thermal degradation of carbonaceous material at a temperature between 400 and 800 °C, in the complete absence of oxygen, or with a supply so limited that gasification does not occur to any appreciable extent. In this process, devolatilization and the decomposition of solid materials occur because of temperature, and, consequently, no combustion is possible. The products of the pyrolysis process (Figure 6) are gas, liquid (oil), and solid coal, the relative proportions of which vary according to the materials used, the pyrolysis method, and the reaction parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and length of stay [17,40,51]. Pyrolysis is characterized by endothermic processes, where the atmosphere is inert, and energy is supplied through the reactor walls. At the levels of reactors used in this process, they are identical to those of gasification, distinguishing themselves in the operating temperature, as well as in the volume of oxygen used during the process, which is almost zero [61]. The increase in temperature in pyrolysis causes the breakdown of covalent bonds of chemical compounds, thus resulting in the formation of smaller molecular fragments, called free radicals. If the test takes place at relatively low pressures, where free radicals are diluted, they can return to pyrolysis until smaller radicals and even hydrogen are formed. Radicals, when agglomerated with hydrogen, tend to produce gaseous hydrocarbons such as methane, ethane, and propane, among others. These free radicals, in turn, can collide, causing a molecular restructuring that gives rise to more stable compounds and with larger dimensions to the point of forming macromolecules, giving rise to coal [61].
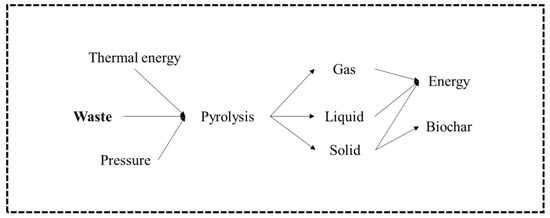
Figure 6.
Pyrolysis process model [51].
The main product resulting from the pyrolysis process below 500 °C is bioliquid. This product after the refining process can be used as a substitute for fossil fuels, namely as a substitute for diesel [17,40]. However, if pyrolysis is carried out at temperatures above 800 °C, the primary product formed is syngas, like that produced in a gasification installation. As the process is carried out in the absence of air, the product contains a variety of hydrocarbon materials, as well as carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Small amounts of pyrolysis oil are produced and, in addition, a solid coal that will contain any inorganic material from the waste [62].
Thus, pyrolysis can be classified into two types, depending on the temperature used. Slow pyrolysis occurs at temperatures up to 650 °C. In turn, fast pyrolysis occurs at temperatures above 800 °C [25,51,62]. The gas acquired in the pyrolysis process has calorific value, varying between 13 and 21 MJ/Nm3, and the liquids, called pyrolysis oils, are a complex mixture of hydrocarbons with the potential to be used as liquid fuel or to produce energy [51].
3.1. Studies of Recovery by Slow Pyrolysis
This process is quite old and is used to produce coal at low temperatures and low heating rates. The residence time of the gas is long (5 to 30 min), and the components in the vapor phase can react with each other, resulting in the formation of solid coal or other liquids [63]. In the study by Dong and Zhao (2018), WCOs and pieces of tire rubbers were valued by the process of pyrolysis at low temperatures (280 °C) to obtain a product like the bitumen used in asphalt paving [64]. In studies carried out by Moreira (2015), the author performed slow pyrolysis to evaluate cashew peels at a temperature that varied between 400 and 500 °C [65]. The results show that the solid obtained (biochar), the liquid (aqueous phase + bio-oil), and the gas phase had a yield of around 30, 40, and 50% by weight, respectively. In the study carried out by [63] on a laboratory scale, he carried out the valuation of 200 g of WCO to produce bio-oils and coal by pyrolysis at 400 °C for 85 minutes. The results show that 130 g of a bio-oil and 40 g of coal were obtained. Borges (2019) studied the valorization of coffee husk pellets in a fixed bed reactor to produce biofuel. Pyrolysis occurred at a temperature range of 400–500 °C. The main compounds identified were phenol, 2-methylphenol (O-cresol), 3-methylphenol (M-cresol) and naphthalene, caffeine, and adipic acid bis (ethylhexyl) ester. According to the authors, this material has the potential to be used as energy [66]. Lam (2019) carried out vacuum microwave pyrolysis of WCOs in an activated carbon bed at a temperature of 580 °C. The results demonstrate that the biofuel produced obtained a yield of up to 84% by weight of liquid oil, containing light hydrocarbons and greater calorific value (49 MJ/kg) when compared to diesel and gasoline, presenting great potential for application as a fuel [26].
3.2. Valorisation Studies by Fast Pyrolysis
Demirbas (2008) studied the valorization of the olive core by means of fast pyrolysis, and its results demonstrate that 780 °C was the ideal temperature to produce bio-oil, with a conversion rate of 43% [67]. Meier (2015) carried out fast WCO pyrolysis to produce biofuels in a temperature range of 400, 475, and 525 °C; the WCO was reduced to smaller carbon chains producing a heavy bio-oil (C12–C18), light bio-oils (C4–C11), and a biogas (C2–C4) in a residence time of 15–80 s. The authors concluded that the material has a good calorific value, being like compounds of petroleum origin [34]. Wiggers (2009) studied the fast and continuous pyrolysis of soybean oil and soybean WCO, where the material was heated up to 600 °C. The results show that two biofuel fractions were produced, one heavy with C22 carbon chains and the other light with C11 carbon chains. In addition, in the light fraction, in small amounts, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylene, and other aromatic compounds were found. Thus, they demonstrated that the biofuels obtained contain compounds such as fractions of gasoline and diesel oil [33]. Singhabhandhu (2010) studied the valorization of WCO with car engine oils to produce a biofuel; the technology used was fast pyrolysis at 780 °C. The results obtained show that it was possible to convert 1514.81 t/year of WCO and 2.168 t/year of lubricating oil into biofuel, obtaining performances like conventional fuels [32]. Alcalá (2013) carried out a study on the production of biodiesel with different materials and methods. However, regarding pyrolysis, the biodiesel produced comes from the WCO, where a small production of coal and gas was also observed. The reaction took place at a temperature of 500 °C, and 75% biodiesel, 12% coal, and 13% biogas were obtained. It was also observed that biodiesel (38 MJ/kg) showed a lower heating value than conventional diesel [68].
3.3. Valorization Studies by Catalytic Pyrolysis
Catalytic pyrolysis uses a compound that generally has alkaline properties (Na, K, Ca, Al, and others), called a zeolitic catalyst. These catalysts assist in the removal of coal that contaminates liquid biofuel. In addition to assisting in the production of biofuels, catalysts can produce other products by WCO valorization, such as compounds of organic solvents, toluene, xylene, and others. Wang (2018) valued WCOs through fast pyrolysis to produce aromatic compounds (benzene, toluene, xylene, naphthalene, and ethylbenzene), olefins (2-butene, 2-pentene, and propene), and acids (n-hexadecanoic acid, 9,12-octadecadienic acid, and 6-octadecenoic acid), with the aid of an alkaline catalyst (HZSM-5) [69]. The results show that 58,56% of WCO was converted into aromatic compounds (toluene and xylene), 24.69% into olefins, and 16.75% into acids. The pyrolysis temperature was 600 °C. Araújo (2017) studied a Si/Al catalyst in the proportion of 1:1, to valorize sunflower oil by pyrolysis. Two reaction products were created: first, a bio-oil with hydrocarbons such as mineral diesel; the second was an acidic fraction, composed mainly of low-acidity components due to the catalyst [25]. Pyrolysis has the advantage of producing pyrolysis oil (bio-oil) that can completely or partially replace petroleum-derived fuels, as the studies presented show that bio-oil has similar properties to conventional fuels and also produces biochar which contains a good calorific value.
4. Final Remarks on the Production of Alternative Biofuels through the WCO
In view of the new environmental paradigms and the search for more sustainable products, the production of biofuels is an important path toward the pursuit of this objective for having a cleaner and greener production when compared to fossil fuels, in addition to the fact that biofuels can come from wastes such as WCO. The technologies to produce these biofuels are varied, as previously described, and each technology can be used to create a specific type of fuel, with unique properties, having as its common denominator the enormous potential for replacing fossil fuels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.N., A.R. and A.F.; methodology, A.F.; software, V.P.; validation, J.C., C.V. and J.A.; formal analysis, L.N., A.R. and A.F.; investigation, N.V. and V.P.; resources, N.V. and V.P.; data curation, L.N., A.R. and A.F.; writing—original draft preparation, L.N.; writing—review and editing, L.N., A.R. and N.V.; visualization, J.C.; supervision, J.C.; project administration, J.C., C.V. and J.A.; funding acquisition, C.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was co-financed by the FITEC—Fund for Innovation, Technology and Circular Economy, Interface Program, within the scope of the project CVR—Base Funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Peters, J.; Thielmann, S. Promoting biofuels: Implications for developing countries. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Study on the Implementation of Conformity Checks in the Olive Oil Sector throughout the European Union; European Union. Publications Office: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; ISBN 9789276092643. [Google Scholar]
- EU. European Union Oil and Protein Meal Industry, International Olive Council; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, M.M.; Lee, K.T.; Bhatia, S. Feasibility of edible oil vs. non-edible oil vs. waste edible oil as biodiesel feedstock. Energy 2008, 33, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderssen, I.M.; Webber, C.; Kelly, R.; Andersen, O. Localized Production and Supply of Biodiesel from Used Cooking Oils. State of the Art in Europe; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2007; ISSN nr: 0803-4354. Available online: https://www.vestforsk.no/sites/default/files/migrate_files/rapport12-07-biodienet_wp2_rpt_v12.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- EUBIA. Transformation of Used Cooking Oil into Biodiesel: From Waste to Resource; European Biomass Industry Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2015; Available online: https://www.eubren.com/UCO_to_Biodiesel_2030_01.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Tsoutsos, T.D.; Tournaki, S.; Paraíba, O.; Kaminaris, S.D. The Used Cooking Oil-to-biodiesel chain in Europe assessment of best practices and environmental performance. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GREENA. “Market Watch”. 2020. Available online: https://www.greenea.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Greenea-Market-Watch-October-2020-_-EN.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- European Biomass Industry Association. Available online: https://www.eubia.org/ (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Teixeira, M.R.; Nogueira, R.; Nunes, L.M. Quantitative assessment of the valorisation of used cooking oils in 23 countries. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, W.; Azimov, U.; Gauthier-Maradei, P.; Molano, L.C.; Combrinck, M.; Munoz, J.; Esteves, J.J.; Patino, L. Waste-to-energy conversion technologies in the UK: Processes and barriers—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Yakoob, M.; Shah, M.P. Agricultural waste management strategies for environmental sustainability. Environ. Res. 2021; 112285, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Araby, R.; Abdelkader, E.; El Diwani, G.; Hawash, S.I. Bio-aviation fuel via catalytic hydrocracking of waste cooking oils. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2020, 44, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Biofuels securing the planet’s future energy needs. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy, Biofuel Basics-Biofuel BasicsBioenergy Technologies Office. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/bioenergy/biofuel-basics (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Saladini, F.; Patrizi, N.; Pulselli, F.M.; Marchettini, N.; Bastianoni, S. Guidelines for emergy evaluation of first, second and third generation biofuels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juniper. IOFUELS: A Decision Maker’s Guide to Opportunities for Converting Biomass and Wastes into Transport Fuels Independt Waste Technology Review; Juniper Consultancy Services Limited: Bolton, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker Lago, S.M.; Freire da Rocha, W., Jr. Logística reversa, legislação e sustentabilidade: O óleo de fritura residual como matéria-prima para produção de biodiesel. Gestão E Soc. 2016, 10, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraiba, O.; Tournaki, S.; Tsoutsos, T.; Antunes, D. Used cooking oil to biodiesel: Practical Guide. In Used Cooking Oil Recycling for Sustainable Biodiesel Production; Sustainable Cities: Designing for People and the Planet; Energy and Environment Agency of Arrábida: Coimbra, Portugal, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, D.J.B. Processos de Valorização Energética de Óleos e Gorduras. 2013. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10362/11340 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Nascimento, A.C.; Nascimento, R.M.; Caetano, R. Manual: A logística reversa do óleo de fritura usado como solução para problemas ambientais. 2011. Available online: https://www.setorreciclagem.com.br/images/oleo.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Tsita, K.G.; Kiartzis, S.J.; Ntavos, N.K.; Pilavachi, P.A. Next generation biofuels derived from thermal and chemical conversion of the Greek transport sector. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 17, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezergianni, S.; Voutetakis, S.; Kalogianni, A. Catalytic Hydrocracking of Fresh and Used Cooking Oil. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 8402–8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezergianni, S.; Kalogianni, A. Hydrocracking of used cooking oil for biofuels production. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3927–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, M.; Oliveira, M.R.; Gondim, A.D.; Souza, J.D.; Araujo, A.S. Thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of sunflower oil using AlMCM-41. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.S.; Mahari, W.A.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Peng, W.; Chong, C.T.; Ma, N.L.; Chase, H.A.; Liew, Z.; Yusup, S.; Kwon, E.E.; et al. Microwave vacuum pyrolysis of waste plastic and used cooking oil for simultaneous waste reduction and sustainable energy conversion: Recovery of cleaner liquid fuel and techno-economic analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 109359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhengshun, W.; Shaofei, X.; Xiaoyan, L.; Tingting, S.; Qiangxian, W.; Yu, Z. Catalytic Cracking of Waste Cooking Oil for the Production of Synthesis Gas. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2013, 7, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujjanutat, P.; Kaewkannetra, P. Production of bio-hydrogenated kerosene by catalytic hydrocracking from refined bleached deodorised palm/palm kernel oils. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Rana, R.; Hunter, H.N.; Fang, Z.; Dalai, A.K.; Kozinski, J.A. Hydrothermal catalytic processing of waste cooking oil for hydrogen-rich syngas production. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 195, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-D.; Jung, S.-H.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Yang, W.; Lee, U.-D. Production of producer gas from waste cooking oil in a fluidized bed reactor: Influence of low-temperature oxidation of fuel. Fuel 2015, 146, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonti, D.; Prussi, M.; Buffi, M.; Tacconi, D. Sustainable bio kerosene: Process routes and industrial demonstration activities in aviation biofuels. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhabhandhu, A.; Tezuka, T. Prospective framework for collection and exploitation of waste cooking oil as feedstock for energy conversion. Energy 2010, 35, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggers, V.R.; Meier, H.F.; Wisniewski Jr, A.; Barros, A.A.C.; Maciel, M.R.W. Biofuels from continuous fast pyrolysis of soybean oil: A pilot plant study. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6570–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.F.; Wiggers, V.R.; Zonta, G.R.; Scharf, D.R.; Simionatto, E.L.; Ender, L. A kinetic model for thermal cracking of waste cooking oil based on chemical lumps. Fuel 2015, 144, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Rana, B.S.; Kumar, R.; Verma, D.; Kumar, R.; Joshi, R.K.; Garg, M.O.; Sinha, A.K. Hydrotreating and hydrocracking catalysts for processing of waste soya-oil and refinery-oil mixtures. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregório, A. Catálise de Hydrocracking baseado em Zeólitos. Master’s Thesis, Department Engenharia Quimica Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2015. Available online: https://repositorio.ipl.pt/bitstream/10400.21/5392/1/Disserta%C3%A7%C3%A3o.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Melo, B.M.d.C. Hidrogenação Catalítica de Resíduos Para Produção de Biocombustíveis Líquidos; Department Ciências. University: Lisboa, Portugal, 2016; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10451/25623 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Li, T.; Cheng, J.; Huang, R.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Conversion of waste cooking oil to jet biofuel with nickel-based mesoporous zeolite Y catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijaya, K.; Syoufian, A.; Ariantika, S.D. Hydrocracking of Used Cooking Oil into Biofuel Catalyzed by Nickel-Bentonite. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 3785–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guran, S. Sustainable Waste-to-Energy Technologies: Gasification and Pyrolysis. In Sustainable Food Waste-To-Energy Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alauddin, Z.A.B.Z.; Lahijani, P.; Mohammadi, M.; Mohamed, A.R. Gasification of lignocellulosic biomass in fluidized beds for renewable energy development: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2852–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, A.C.; Pelagagge, P.M. RDF production plants: II Economics and profitability. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2002, 22, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higman, C. “Gasification”. In Combustion Engineering Issues for Solid Fuel Systems, 1st ed.; Miller, B.G., Tillman, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 423–468. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, P.; Cruz, S.F.; De, R. Recuperação energética e eliminação urbanos, resíduos sólidos. Master’s Thesis, Faculdade de Tecnologia de São Paulo-FATEC, São Paulo, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Monir, M.U.; Aziz, A.A.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yousuf, A. Gasification of lignocellulosic biomass to produce syngas in a 50 kW downdraft reactor. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 119, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monir, M.U.; Khatun, F.; Aziz, A.A.; Vo, D.-V.N. Thermal treatment of tar generated during co-gasification of coconut shell and charcoal. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Williams, P.T.; Shi, J.; Huang, J. Hydrogen production from biomass gasification with Ni/MCM-41 catalysts: Influence of Ni content. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 108–109, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, N.S.; Janse van Vuuren, M.; Claeys, M.; van Steen, E. Importance of the usage ratio in iron-based Fischer−Tropsch synthesis with recycle. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 8629–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Weller, C.L.; Jones, D.D.; Hanna, M.A. Contemporary issues in thermal gasification of biomass and its application to electricity and fuel production. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrenfeldt, J.; Thomsen, T.P.; Henriksen, U.; Clausen, L.R. Biomass gasification cogeneration–A review of state of the art technology and near future perspectives. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 50, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.; Cruz, F. Gaseificação: Processo alternativo para a recuperação energética e eliminação de resíduos sólidos urbanos. Master’s Thesis, Faculdade de Tecnologia de São Paulo -FATEC, São Paulo, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, L.; Anithamary, X. Lower Order Modeling and Control of Alstom Fluidized Bed Gasifier. In Gasification for Practical Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 313–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamošiūnas, A.; Jeguirim, M. Char gasification. In Char and Carbon Materials Derived from Biomass; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 187–228. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, L.; Silva, H.; Oliveira, J.; Fernandes, S.; Freitas, E.; Hilliou, L. Plastic waste use as aggregate and binder modifier in open-graded asphalts. In Proceedings of the 3rd Int Conference on Wastes: Solutions, Treatments, and Opportunities, Viana Do Castelo, Portugal, 14–16 September 2015; pp. 67–72. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1822/39125 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Li, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Yan, R. Hydrogen-rich gas production by steam gasification of palm oil wastes over supported tri-metallic catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 9108–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Watkinson, A.P.; Ellis, N. Steam Gasification of Bio-Oil and Bio-Oil/Char Slurry in a Fluidized Bed Reactor. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 5181–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacovsky, D.; Dallos, M.; Wörgetter, M. Status of 2nd Generation Biofuels Demonstration Facilities in June 2010; Report T-39; IEA Bioenergy: Vienna, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, J.; Rashid, U.; Patuzzi, F.; Alamoodi, N.; Choong, T.S.Y.; Soltani, S.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C.; Nehdi, I.A.; Baratieri, M. Mesoporous Acidic Catalysts Synthesis from Dual-Stage and Rising Co-Current Gasification Char: Application for FAME Production from Waste Cooking Oil. Materials 2020, 13, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, J.; Rashid, U.; Patuzzi, F.; Baratieri, M.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H. Synthesis of char-based acidic catalyst for methanolysis of waste cooking oil: An insight into a possible valorization pathway for the solid by-product of gasification. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 158, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.H.; Hustad, J.E. Biosyngas production by autothermal reforming of waste cooking oil with propane using a plasma-assisted gliding arc reactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 8221–8233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P. Produção de Hidrocarbonetos Líquidos e Gasosos por Pirólise de Resíduos Plásticos. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia, Univercity, Nova Lisboa, Lisboa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Breeze, P. Advanced Waste-to-Energy Technologies: Gasification, Pyrolysis, and Plasma Gasification. In Energy from Waste; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.M.S.P. Reaproveitamento de óleo queimado através do processo de Pirolise. Master’s Thesis, Department Mechanical Engenharia Mecanica Instituto Politécnico de Tomar, Tomar, Portugal, 2016. Available online: https://comum.rcaap.pt/handle/10400.26/28883?locale=en (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Dong, R.; Zhao, M. Research on the pyrolysis process of crumb tire rubber in waste cooking oil. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R. Estudo da pirólise lenta da casca da castanha de caju. Master’s Thesis, Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2015. Available online: https://teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/85/85134/tde-07102015-090727/pt-br.php (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Borges, F.A.; Oliveira, T.J.P.D.E.; Costa, K.L.S. Estudo Experimental De Pirólise Lenta De Pellets De Casca De Café Em Um Reator De Leito Fixo. Blucher Chem. Eng. Proc. 2019, VI, 672–678. [Google Scholar]
- Demirbas, A. Comparison of transesterification methods for production of biodiesel from vegetable oils and fats. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá, A.; Bridgwater, A. V Upgrading fast pyrolysis liquids: Blends of biodiesel and pyrolysis oil. Fuel 2013, 109, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Darensbourg, D.J. Carbon dioxide-based functional polycarbonates: Metal catalyzed copolymerization of CO2 and epoxides. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 372, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).