The Online Parameter Identification Method of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine under Low-Speed Region Considering the Inverter Nonlinearity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Problem Statement
1.3. Previous Solutions
1.4. Main Contributions
1.5. Paper Structure
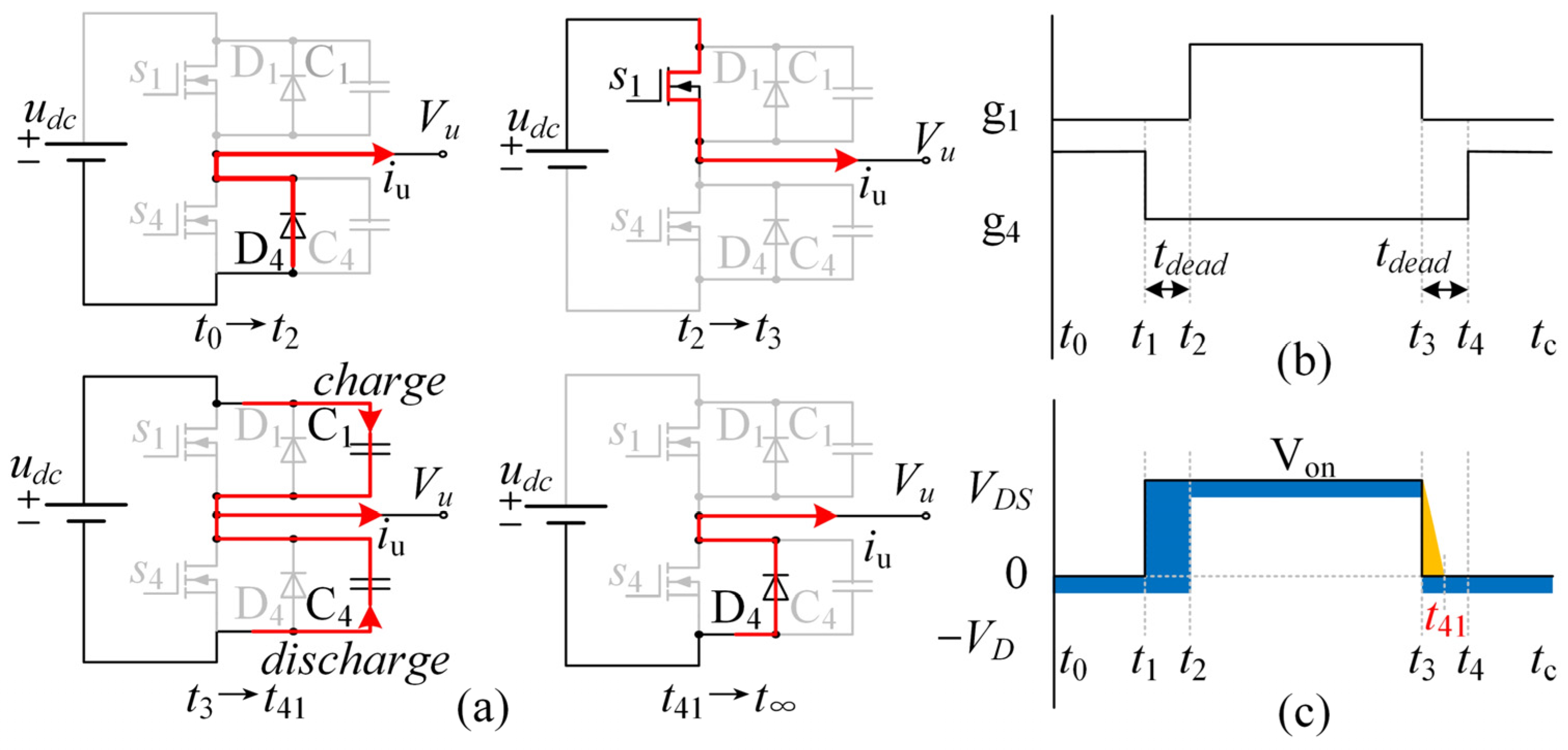
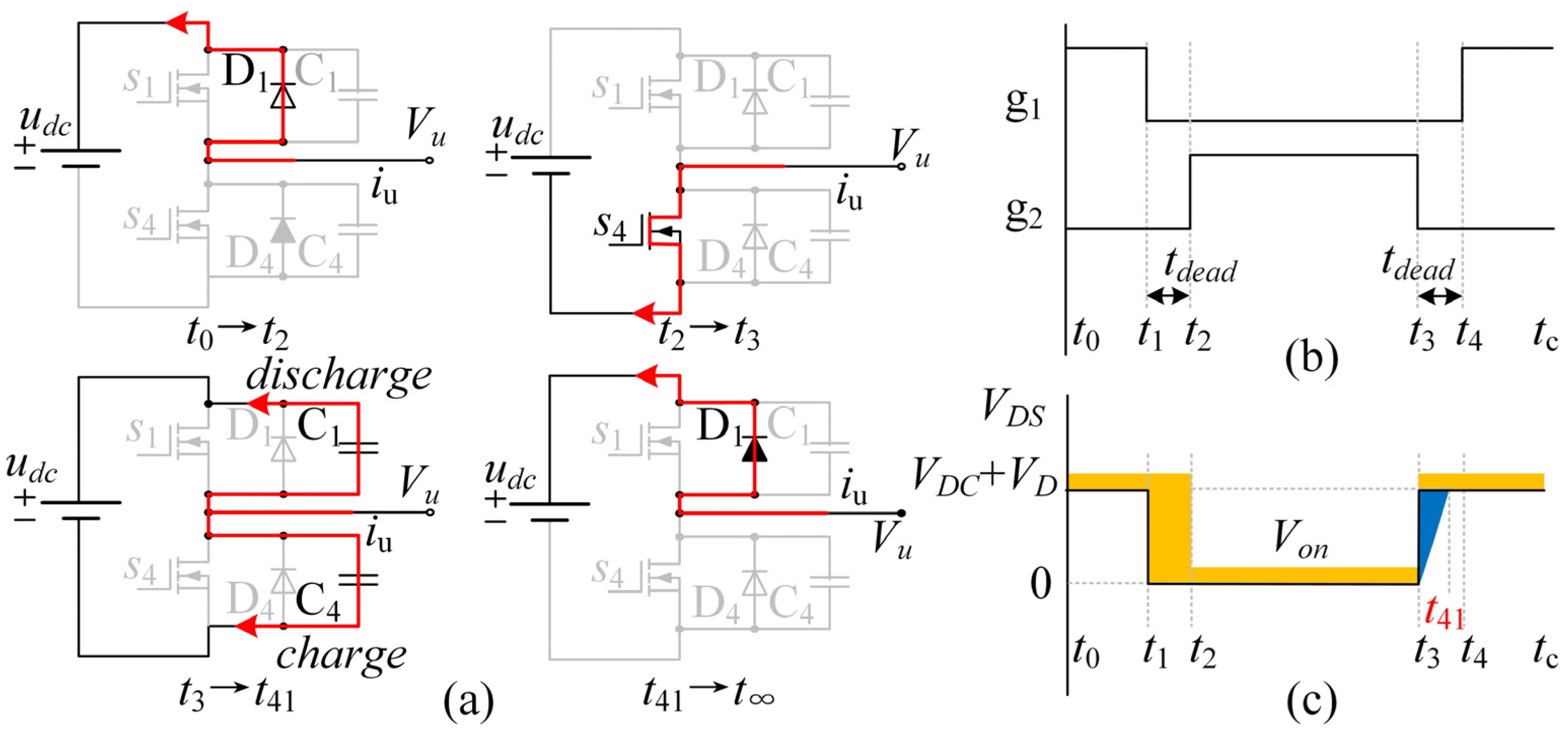
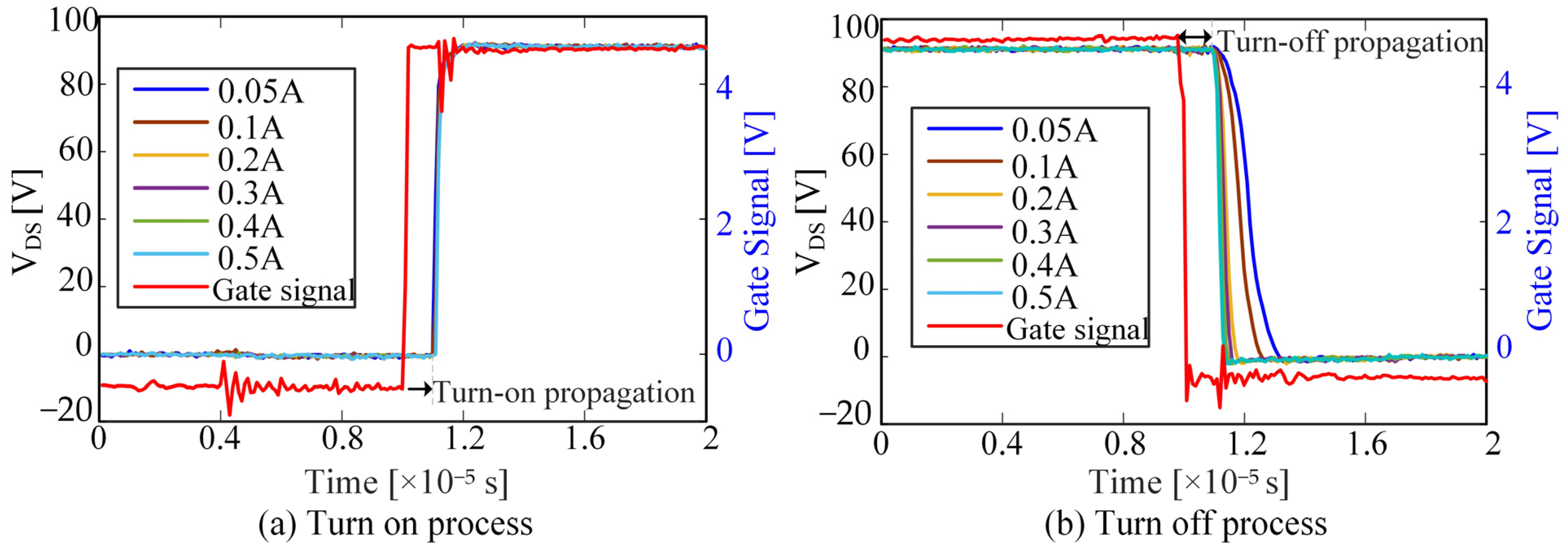
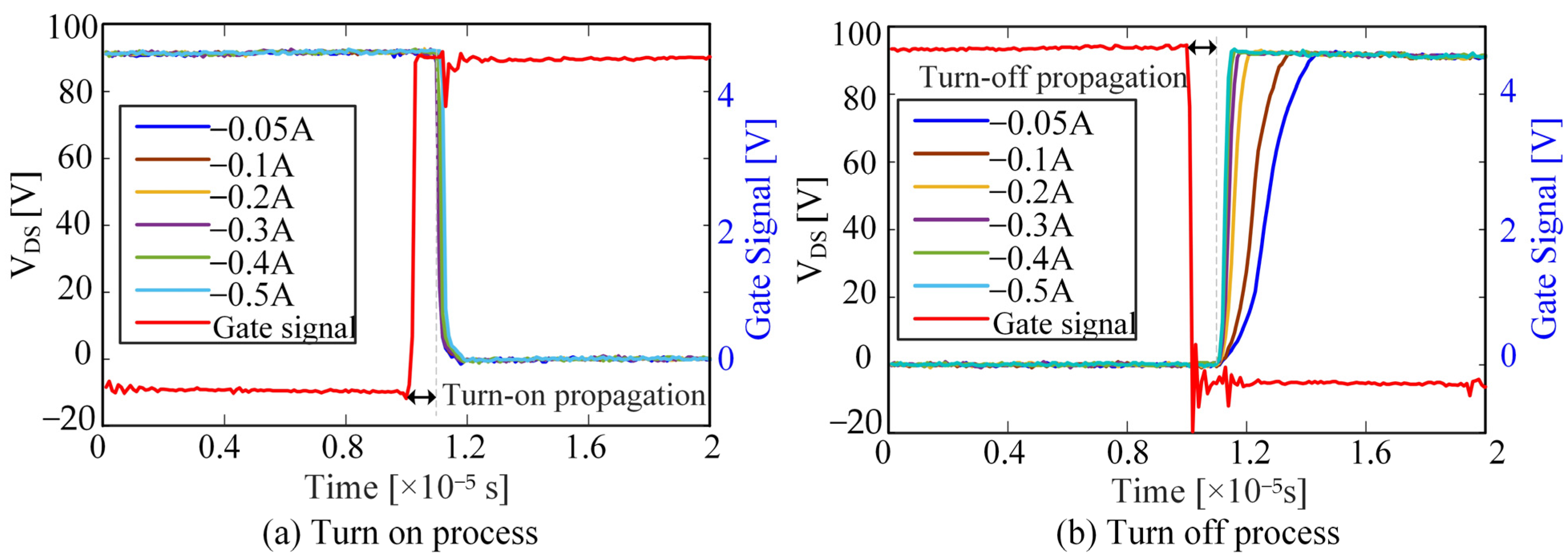
2. The Nonlinearity of Deadtime Effect
3. Offline Deadtime Compensation
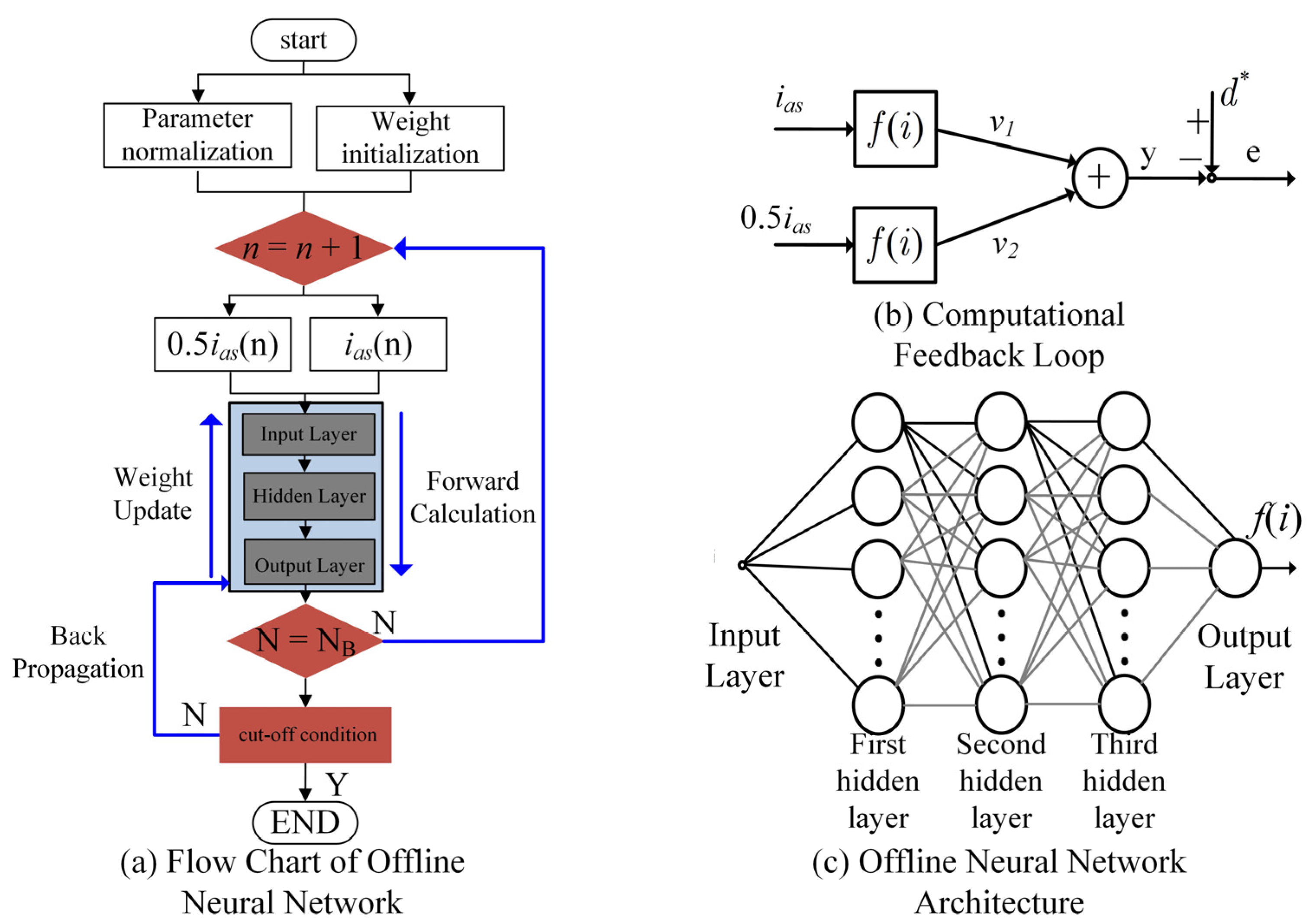
3.1. Equivalent Identification Model of Deadtime Effect
3.2. The Establishment of Neural Network
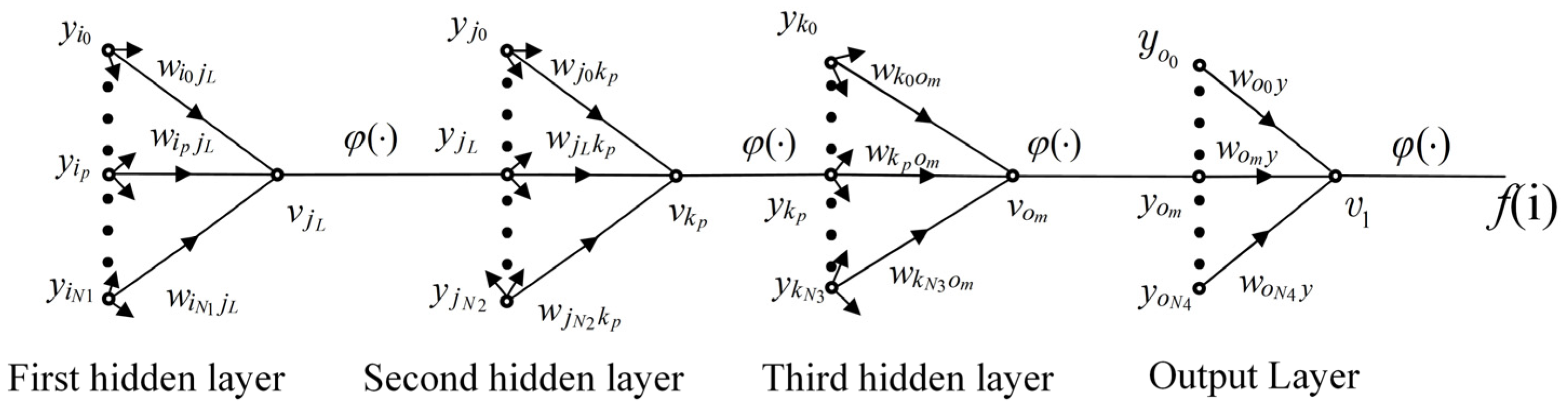
3.2.1. Forward Calculation Process
3.2.2. Back Propagation Process
- For the output layer
- 2.
- For the hidden layer
- 3.
- Cut-off condition
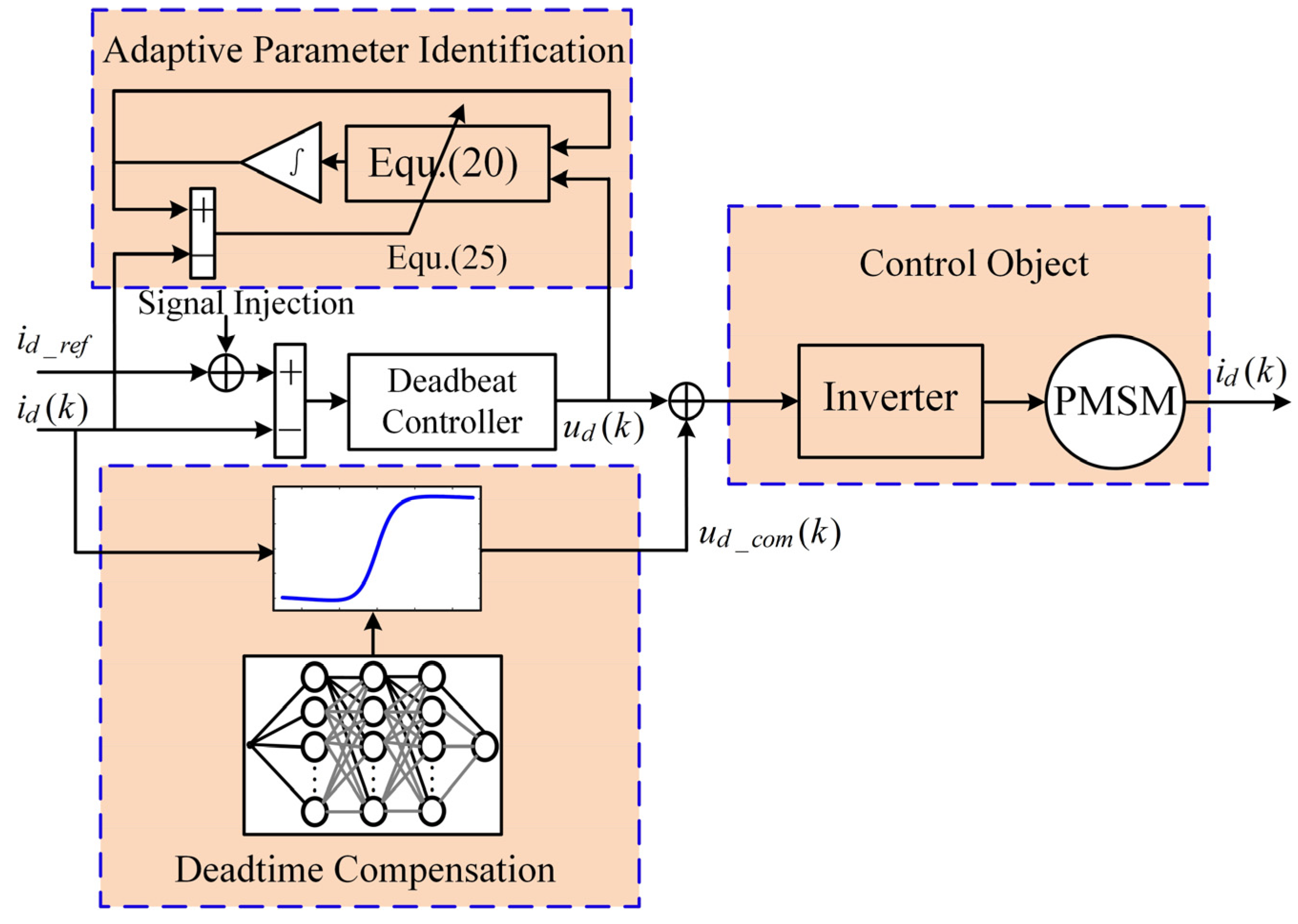
4. Online Parameter Identification
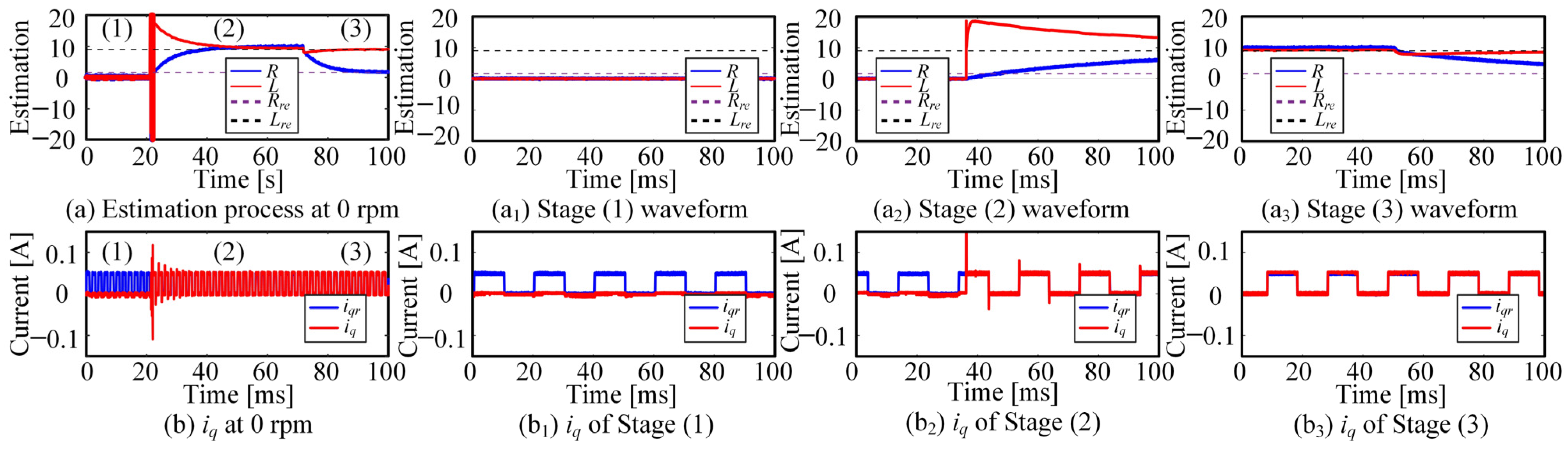
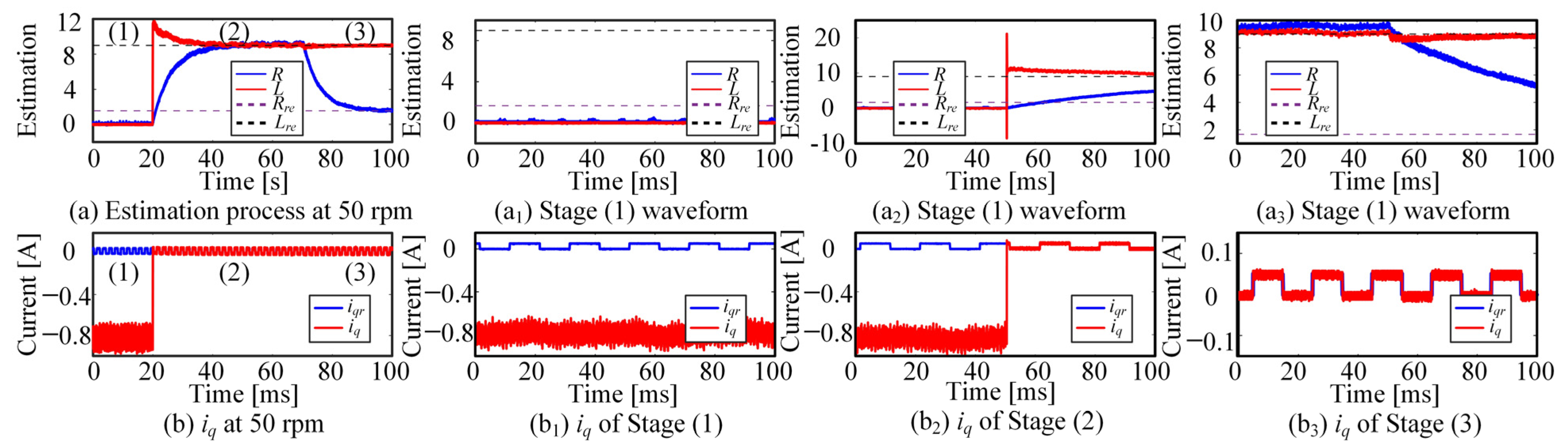
5. Results
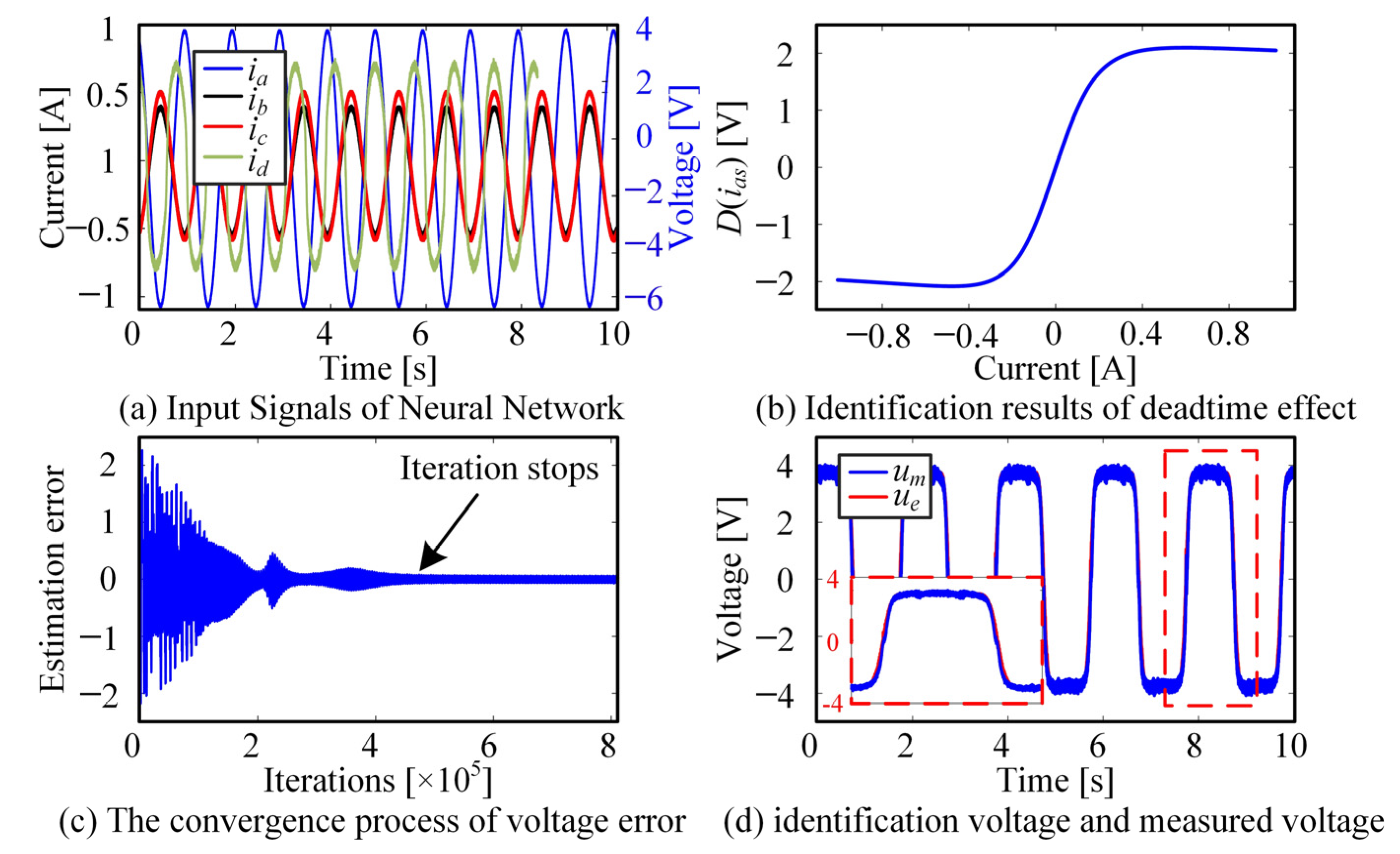
- Identification of inverter nonlinearity
- 2.
- Identification of PMSM parameters
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Zou, J. Integral Sliding Mode Control Based Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for PMSM Drives With Disturbance Rejection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 37, 2845–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, M. Enhancing Low-Speed Sensorless Control of PMSM Using Phase Voltage Measurements and Online Multiple Parameter Identification. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 10700–10710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Q.J.; Kawamura, A. An accurate approach of nonlinearity compensation for VSI inverter output voltage. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Narayanan, G. Small-Signal Stability Analysis of an Open-Loop Induction Motor Drive Including the Effect of Inverter Deadtime. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 52, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, Q.; Geng, X.; Lin, K. Analysis of the Effect of the Parasitic Capacitance of Switch Devices on Current Distortions of Voltage Source Rectifier. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Chengdu, China, 1–4 August 2021; pp. 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, D. Inverter Nonlinear Error Compensation Using Feedback Gains and Self-Tuning Estimated Current Error in Adaptive Full-Order Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Garcia, A.; Lipo, T.A. On-line dead time compensation technique for open-loop PWM-VSI drives. In Proceedings of the APEC ‘98 Thirteenth Annual Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 15–19 February 1998; pp. 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.M.; Zhu, Z.Q. Modeling and compensation of inverter nonlinearity effects in carrier signal injection-based sensorless control methods from positive sequence carrier current distortion. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 3434–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Shen, Z.; Mattavelli, P.; Boroyevich, D.; Karimi, K.J. Small-Signal Model of Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) and Voltage Source Converter (VSC) Considering the DeadTime Effect and Space Vector Modulation Types. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 4145–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Niu, W.; Xu, H.; Fang, C.; Shi, L. Analysis on dead-time compensation method for direct-drive PMSM servo system. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Busan, Korea, 26–29 October 2013; pp. 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Jiang, D. Dead-Time Effect Compensation Method Based on Current Ripple Prediction for Voltage-Source Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, W.; Rho, M.-S.; Park, S.-Y. Effective Dead-Time Compensation Using a Simple Vectorial Disturbance Estimator in PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, N.; Wang, G.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. An Offline Parameter Self-Learning Method Considering Inverter Nonlinearity With Zero-Axis Voltage. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 14098–14109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Ahn, J.-W. A Simple and Direct Dead-Time Effect Compensation Scheme in PWM-VSI. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3017–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Yoon, Y.-D. Compensation for inverter nonlinearity considering voltage drops and switching delays of each leg’s switches. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, K.D.; Aorith, H.K.A. Online Control of IPMSM Drives for Traction Applications Considering Machine Parameter and Inverter Nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Daleel, M.; Mahgoub, A. Accurate and simple improved lookup table compensation for inverter dead time and nonlinearity compensation. In Proceedings of the 2017 Nineteenth International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON), Cairo, Egypt, 19–21 December 2017; pp. 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, N.; Senjyu, T.; Kinjo, T.; Funabashi, T.; Sekine, H. Dead-time compensation strategy for permanent magnet synchronous motor drive taking zero-current clamp and parasitic capacitance effects into account. IEE Proc.-Electr. Power Appl. 2004, 152, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, L. Dead-Time Compensation of Inverters Considering Snubber and Parasitic Capacitance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 3179–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, P.; Jin, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, M. Influences on Output Distortion in Voltage Source Inverter Caused by Power Devices’ Parasitic Capacitance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 4261–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yao, W.; Chen, B.; Wang, K.; Lee, K.; Lu, Z. Automeasurement of the Inverter Output Voltage Delay Curve to Compensate for Inverter Nonlinearity in Sensorless Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 5542–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xia, C.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, T. Disturbances Attenuation of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Using Cascaded Predictive-Integral-Resonant Controllers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 1514–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Q.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, K. An Adaptive Strategy to Compensate Nonlinear Effects of Voltage Source Inverters Based on Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 129992–130002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Wen, X.; Zhao, F.; Feng, Z. Adaptive Linear Neuron Based Dead Time Effects Compensation Scheme. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 2530–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, N.; Senjyu, T.; Uezato, K.; Funabashi, T. Adaptive Dead-Time Compensation Strategy for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-H.; Kim, J.-M. Dead Time Compensation Method for Voltage-Fed PWM Inverter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Akin, B. A New LMS Algorithm Based Deadtime Compensation Method for PMSM FOC Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 6472–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Sul, S.-K. Inverter Nonlinearity Compensation Through Deadtime Effect Estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 10684–10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoo, J.; Sul, S.-K. Stator Resistance Estimation using DC Injection Robust to Inverter Nonlinearity in Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Detroit, MI, USA, 11–15 October 2020; pp. 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Units | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Rated voltage Udc | V | 220 |
| Rated power P | kW | 0.4 |
| Stator resistance Rs | Ω | 1.7 |
| Rated speed n | r/min | 3000 |
| Torque T | N·m | 1.27 |
| inductance L | mH | 6 |
| Flux linkage of PM ψf | Wb | 0.071 |
| Rotational inertia J | Kg·m2 | 0.000029 |
| Sampling period Ts | s | 0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Fan, Y. The Online Parameter Identification Method of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine under Low-Speed Region Considering the Inverter Nonlinearity. Energies 2022, 15, 4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124314
Zhang Q, Fan Y. The Online Parameter Identification Method of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine under Low-Speed Region Considering the Inverter Nonlinearity. Energies. 2022; 15(12):4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124314
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiushi, and Ying Fan. 2022. "The Online Parameter Identification Method of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine under Low-Speed Region Considering the Inverter Nonlinearity" Energies 15, no. 12: 4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124314
APA StyleZhang, Q., & Fan, Y. (2022). The Online Parameter Identification Method of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine under Low-Speed Region Considering the Inverter Nonlinearity. Energies, 15(12), 4314. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124314






