Catalytic Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Carbon Pellets into Hydrocarbons-like Fuels in a Two-Stage Reactor: Analysis of Hydrocarbons Composition and Physical-Chemistry Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
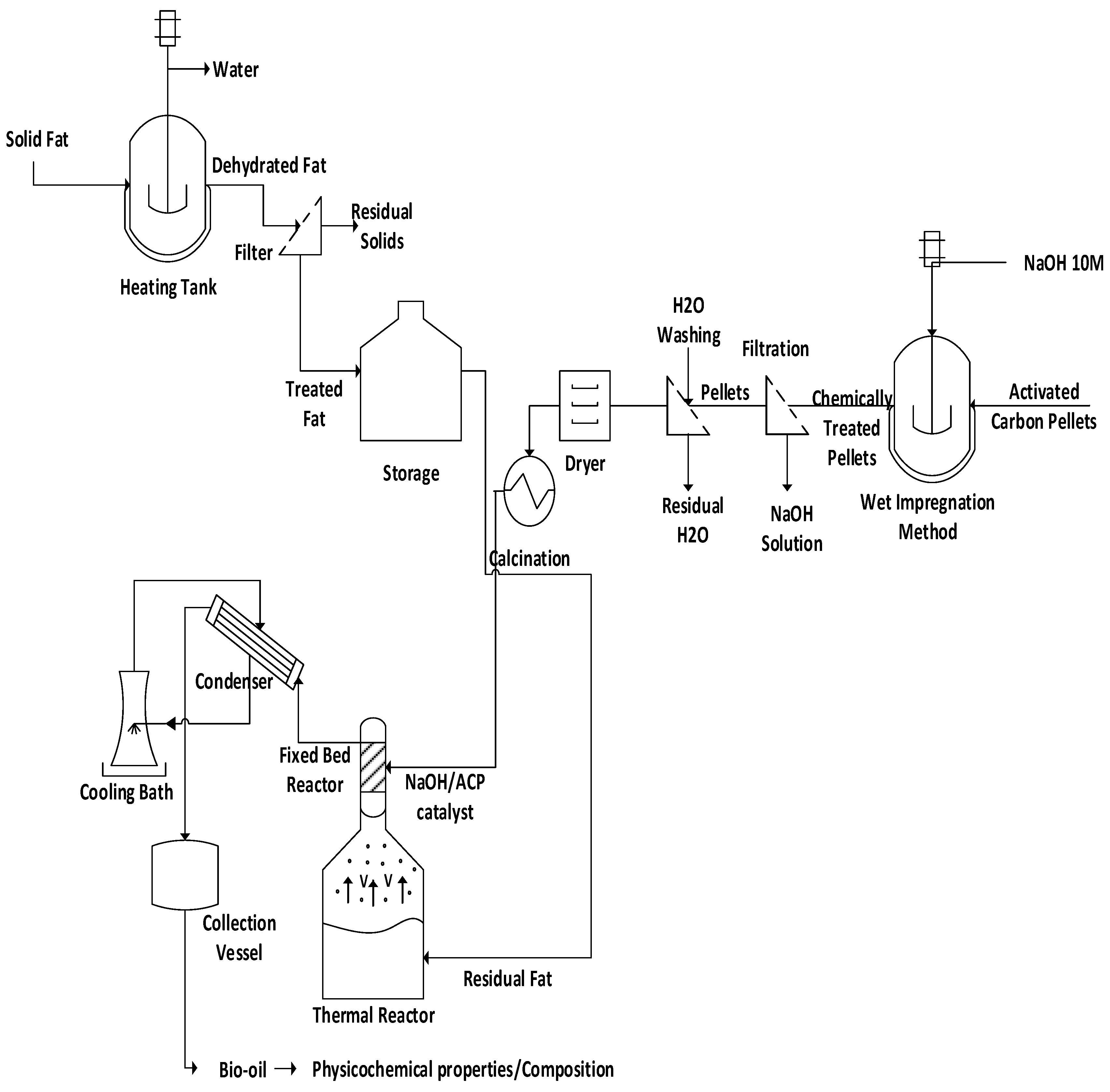
2.1. Methodology
2.2. Materials
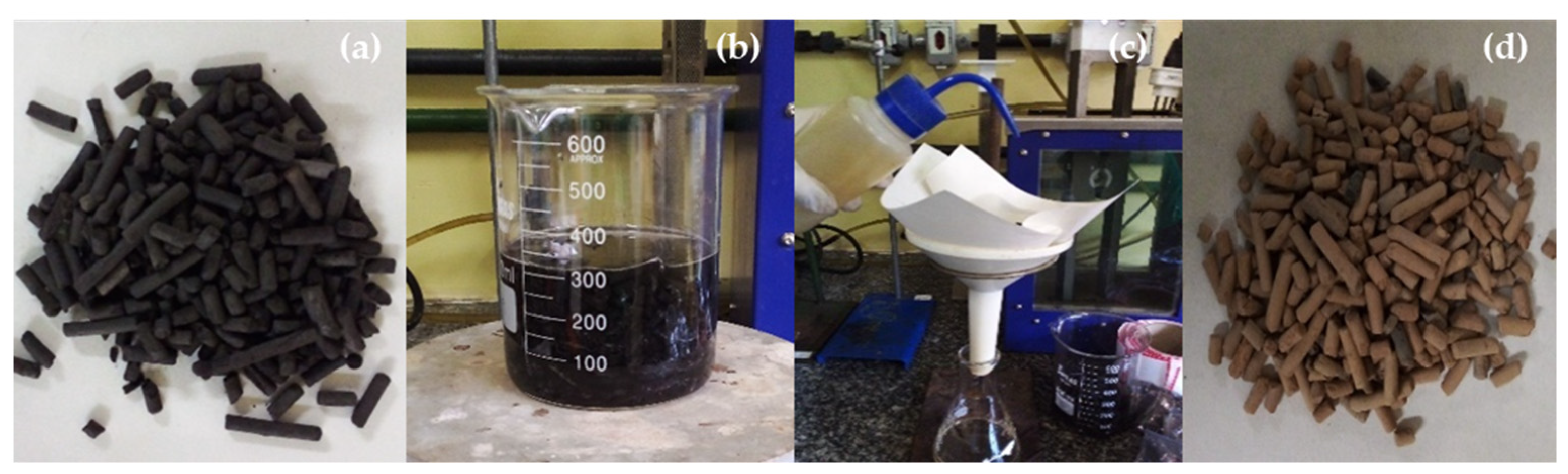
2.3. Chemical Activation of Commercial Activated Carbon Pellets
Wet Impregnation, Drying, and Calcination
2.4. Characterization of Residual Fat
2.5. Experimental Apparatus and Procedures
2.5.1. Experimental Apparatus
2.5.2. Experimental Procedures
Pyrolysis
Thermal Catalytic Cracking
2.6. Physicochemical and Chemical Composition of Bio-Oil
2.6.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Bio-Oil and Aqueous Phase
2.6.2. Chemical Composition of Bio-Oil and Aqueous Phase
2.7. Characterization of Activated Carbon Pellets
2.7.1. SEM and EDX Analysis
2.7.2. XRD Analysis
2.8. Mass Balances of Catalytic Cracking of Vapor-Phase Products
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Catalyst
3.1.1. SEM Analysis
3.1.2. EDX Analysis
3.1.3. XRD Analysis
3.2. Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Carbon Pellets
3.2.1. Process Conditions, Mass Balances, and Yields of Reaction Products
3.2.2. Effect of Catalyst-to-Residual Fat Ratio on the Yield of Bio-Oil
3.2.3. Effect of Reaction Time on the Physicochemical Properties of Bio-Oil
Effect of Reaction Time on the Density of Bio-Oil
Effect of Reaction Time on the Viscosity of Bio-Oil
Effect of Reaction Time on the Acidity of Bio-Oil
3.2.4. Effect of Reaction Time on the Selectivity of Hydrocarbons and Oxygenates in Bio-Oil
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zainan, N.H.; Srivatsa, S.C.; Fanghua, L.; Bhattacharya, S. Quality of bio-oil from catalytic pyrolysis of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Fuel 2018, 223, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Duan, D.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y.; Dai, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Ex-Situ Catalytic Upgrading of Vapors from Fast Microwave-Assisted Co-Pyrolysis of Chromolaena Odorata and Soybean Soapstock. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewpengkrow, P.; Atong, D.; Sricharoenchaikul, V. Selective Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis of Jatropha Curcas Residue with Metal Oxide Impregnated Activated Carbon for Upgrading Bio-Oil. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 18397–18409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewpengkrow, P.; Atong, D.; Sricharoenchaikul, V. Catalytic Upgrading of Pyrolysis Vapors from Jatropha Wastes Using Alumina, Zirconia and Titania Based Catalysts. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, L.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Man, G.; Yao, H. Prevention of CaO Deactivation Using Organic Calcium Precursor during Multicyclic Catalytic Upgrading of Bio-Oil. Fuel 2020, 271, 117692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichaphund, S.; Aht-ong, D.; Sricharoenchaikul, V.; Atong, D. Catalytic Upgrading Pyrolysis Vapors of Jatropha Waste Using Metal Promoted ZSM-5 Catalysts: An Analytical PY-GC/MS. Renew. Energy 2014, 65, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yang, S.; Yang, Q.; Wu, J.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yu, Z.; Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Microwave-Assisted Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis Coupled with Microwave-Absorbent of Soapstock for Bio-Oil in a Downdraft Reactor. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 185, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Q.; Ke, L.; Peng, Y.; Yang, S.; Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, R. Microwave-Assisted Catalytic Upgrading of Co-Pyrolysis Vapor Using HZSM-5 and MCM-41 for Bio-Oil Production: Co-Feeding of Soapstock and Straw in a Downdraft Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ke, L.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, L.; Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, R.; Xia, D.; et al. Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Waste Cooking Oil for Hydrocarbon Bio-Oil over Metal Oxides and HZSM-5 Catalysts. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 220, 113124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, B.; Zhang, R.; Gu, T.; Ji, X.; Zhong, L.; Chen, G.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Li, X. Co-Upgrading of Raw Bio-Oil with Kitchen Waste Oil through Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC). Appl. Energy 2018, 217, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, J.A.; de Sá, M.S.; Moral, A.; Bimbela, F.; Gandía, L.M.; Wisniewski, A. Renewable Hydrocarbon Production from Waste Cottonseed Oil Pyrolysis and Catalytic Upgrading of Vapors with Mo-Co and Mo-Ni Catalysts Supported on γ-Al2O3. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ke, L.; Yang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Xu, J.; Dai, L.; Wu, Q.; et al. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Woody Oil over SiC Foam-MCM41 Catalyst for Aromatic-Rich Bio-Oil Production in a Dual Microwave System. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, M.; Shadangi, K.P.; Mohanty, K. Effect of Catalytic Vapour Cracking on Fuel Properties and Composition of Castor Seed Pyrolytic Oil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 120, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.; Grubb, D.; Santillan-Jimenez, E.; Crocker, M. Conversion of Triglycerides to Hydrocarbons Over Supported Metal Catalysts. Top. Catal. 2010, 53, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Shimouchi, M.; Asami, K.; Fujimoto, K. Selective Catalytic Decarboxy-Cracking of Triglyceride to Middle-Distillate Hydrocarbon. Catal. Today 2011, 164, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, J.; Fu, J.; Leidl, J.A.; Hou, Z.; Lu, X. Catalytic Decarboxylation of Fatty Acids to Aviation Fuels over Nickel Supported on Activated Carbon. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asikin-Mijan, N.; Ooi, J.M.; AbdulKareem-Alsultan, G.; Lee, H.V.; Mastuli, M.S.; Mansir, N.; Alharthi, F.A.; Alghamdi, A.A.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H. Free-H2 Deoxygenation of Jatropha Curcas Oil into Cleaner Diesel-Grade Biofuel over Coconut Residue-Derived Activated Carbon Catalyst. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altalhi, A.A.; Mohammed, E.A.; Morsy, S.S.M.; Negm, N.A.; Farag, A.A. Catalyzed Production of Different Grade Biofuels Using Metal Ions Modified Activated Carbon of Cellulosic Wastes. Fuel 2021, 295, 120646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Almeida, H.; Corrêa, O.A.; Eid, J.G.; Ribeiro, H.J.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Pereira, L.M.; de Andrade Mâncio, A.; Santos, M.C.; da Silva Souza, J.A.; et al. Production of Biofuels by Thermal Catalytic Cracking of Scum from Grease Traps in Pilot Scale. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 118, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Almeida, H.; Corrêa, O.A.; Eid, J.G.; Ribeiro, H.J.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Pereira, L.M.; de Andrade Aâncio, A.; Santos, M.C.; da Mota, S.A.; et al. Performance of Thermochemical Conversion of Fat, Oils, and Grease into Kerosene-like Hydrocarbons in Different Production Scales. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 120, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Almeida, H.; Corrêa, O.A.; Ferreira, C.C.; Ribeiro, H.J.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Pereira, M.S.; de Andrade Mâncio, A.; Santos, M.C.; da Mota, S.A.P.; da Silva Souza, J.A.; et al. Diesel-like Hydrocarbon Fuels by Catalytic Cracking of Fat, Oils, and Grease (FOG) from Grease Traps. J. Energy Inst. 2017, 90, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha de Castro, D.; da Silva Ribeiro, H.; Hamoy Guerreiro, L.; Pinto Bernar, L.; Jonatan Bremer, S.; Costa Santo, M.; da Silva Almeida, H.; Duvoisin, S.; Pizarro Borges, L.; Teixeira Machado, N. Production of Fuel-Like Fractions by Fractional Distillation of Bio-Oil from Açaí (Euterpe Oleracea Mart.) Seeds Pyrolysis. Energies 2021, 14, 3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Mota, S.A.P.; Mancio, A.A.; Lhamas, D.E.L.; de Abreu, D.H.; da Silva, M.S.; dos Santos, W.G.; de Castro, D.A.R.; de Oliveira, R.M.; Araújo, M.E.; Borges, L.E.P.; et al. Production of Green Diesel by Thermal Catalytic Cracking of Crude Palm Oil (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq) in a Pilot Plant. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 110, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Velraj, R.; Lynch, I.; Saidur, R.; Pandey, A.K.; Sharshir, S.W.; Ma, Z.; GaneshKumar, P.; Kabeel, A.E. Sea-Water Desalination Using a Desalting Unit Integrated with a Parabolic Trough Collector and Activated Carbon Pellets as Energy Storage Medium. Desalination 2021, 516, 115217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, W.G.; Gibson, J.W.; Good, G.M. Coke Formation in Catalytic Cracking. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process. Des. Dev. 1962, 1, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillan-Jimenez, E.; Crocker, M. Catalytic Deoxygenation of Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives to Hydrocarbon Fuels via Decarboxylation/Decarbonylation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertani-Gmati, M.; Brahim, K.; Khattech, I.; Jemal, M. Thermochemistry and Kinetics of Silica Dissolution in NaOH Solutions: Effect of the Alkali Concentration. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 594, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerse, M.; Keune, K.; Iedema, P.; Woutersen, S.; Hermans, J. Evolution of Zinc Carboxylate Species in Oil Paint Ionomers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 5674–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Wang, Y.; Dai, L.; Ruan, R.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.; Tayier, M.; Liu, Y. Ex-Situ Catalytic Co-Pyrolysis of Lignin and Polypropylene to Upgrade Bio-Oil Quality by Microwave Heating. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrão, A.C.M.; Silva, C.M.S.; da Costa Assunção, F.P.; da Silva Ribeiro, H.J.; Santos, M.C.; da Silva Almeida, H.; Junior, S.D.; Borges, L.E.P.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Machado, N.T. Análise do processo de pirólise de sementes de açaí (euterpe oleracea, mart): Influência da temperatura no rendimento dos produtos de reação e nas propriedades físico-químicas do bio-óleo / process analysis of pyrolise of açaí (euterpe oleracea, mart) see. Braz. J. Dev. 2021, 7, 18200–18220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, S.A.P.; Mancio, A.A.; Santanna, J.S.; de Jesus Pantoja Gama, V.; Machado, N.T. Influence of the Reaction Time on the Quality (Physical-Chemical Properties) of Biofuels Obtained through Catalytic Cracking of Crude Palm Oil. Sci. Plena 2021, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valois, F.P.; Cardoso, A.R.B.; da Costa França Neto, R.; Pereira, L.M.; Lhamas, D.E.L.; da Mota, S.A.P.; da Silva Almeida, H.; Borges, L.E.P.; Machado, N.T.; Santos, M.C. Craqueamento Termo-Catalítico Da Borra de Neutralização Do Óleo de Palma Utilizando-Se CaCO3 Como Catalisador / Thermal Catalytic Cracking of Soap Phase Residue of Neutralization Process of Palm Oil Using CaCO3 as Catalyst. Braz. J. Dev. 2021, 7, 59461–59481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.M.; Rodrigues, E.C.; Cardoso, D.N.P.; Santos, W.G.; Machado, N.T. Thermocatalytic Cracking of Fat from Fat Boxes with Activated Red Mud. Braz. J. Dev. 2020, 6, 19876–19887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.M.; Machado, N.T.; da Silva Almeida, H.; da Costa Assunção, F.P.; dos Santos Rosa Junior, L. Caracterização de Biocarvão via Craqueamento Térmico Catalítico a Partir Do Blend Do Lodo de Esgoto e Gordura Residual Em Escala Piloto. Braz. J. Dev. 2020, 6, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancio, A.A.; da Mota, S.A.P.; Ferreira, C.C.; Carvalho, T.U.S.; Neto, O.S.; Zamian, J.R.; Araújo, M.E.; Borges, L.E.P.; Machado, N.T. Separation and Characterization of Biofuels in the Jet Fuel and Diesel Fuel Ranges by Fractional Distillation of Organic Liquid Products. Fuel 2018, 215, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mâncio, A.A.; da Costa, K.M.B.; Ferreira, C.C.; Santos, M.C.; Lhamas, D.E.L.; da Mota, S.A.P.; Leão, R.A.; de Souza, R.O.M.A.; Araújo, M.E.; Borges, L.E.P.; et al. Process Analysis of Physicochemical Properties and Chemical Composition of Organic Liquid Products Obtained by Thermochemical Conversion of Palm Oil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 123, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.; Lourenço, R.M.; de Abreu, D.H.; Pereira, A.M.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Almeida, H.S.; Mâncio, A.A.; Lhamas, D.E.L.; da Mota, S.A.P.; et al. Gasoline-like Hydrocarbons by Catalytic Cracking of Soap Phase Residue of Neutralization Process of Palm Oil (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq). J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 71, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillan-Jimenez, E.; Morgan, T.; Lacny, J.; Mohapatra, S.; Crocker, M. Catalytic Deoxygenation of Triglycerides and Fatty Acids to Hydrocarbons over Carbon-Supported Nickel. Fuel 2013, 103, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Qi, S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M. Deoxygenation of Octanoic Acid Catalyzed by Hollow Spherical Ni/ZrO2. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 529, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Specifications GC C-40 | Units |
|---|---|
| Particle size (mm) | 3.9–4.1 |
| Mean particle diameter (mm) | 4.0 |
| CCl4 activity (%) | 60 (minimum) |
| Butane activity (%) | 23 (typical) |
| Iodine number (mg/g) | 900 |
| Surface area (m2/g) | 900 |
| Hardness (%) | 95 |
| Moisture (%) | 5.0 (maximum) |
| Density (g/cm3) | 0.45–0.55 |
| pH | 9.0–11.0 |
| Catalyst | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activated Carbon Pellets (ACP) | ACP Impregnated with 10.0 M NaOH | Used ACP Impregnated with 10.0 M NaOH | |||||||
| Chemical Elements | Mass [wt.%] | Atomic Mass [wt.%] | SD | Mass [wt.%] | Atomic Mass [wt.%] | SD | Mass [wt.%] | Atomic Mass [wt.%] | SD |
| C | - | - | - | - | - | - | 43.28 | 56.58 | 0.37 |
| O | 58.21 | 72.00 | 0.11 | 61.67 | 74.58 | 0.08 | 31.67 | 31.08 | 0.30 |
| Mg | 0.94 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 1.01 | 0.80 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.02 |
| Al | 10.93 | 8.02 | 0.04 | 10.77 | 7.73 | 0.03 | 4.20 | 2.44 | 0.04 |
| Si | 22.49 | 15.85 | 0.07 | 17.88 | 12.32 | 0.04 | 8.67 | 4.85 | 0.07 |
| K | 2.05 | 1.04 | 0.02 | 1.93 | 0.96 | 0.01 | 1.18 | 0.47 | 0.02 |
| Ca | 1.40 | 0.69 | 0.01 | 1.72 | 0.83 | 0.01 | 4.84 | 1.90 | 0.04 |
| Fe | 3.07 | 1.09 | 0.02 | 2.20 | 0.76 | 0.01 | 3.50 | 0.98 | 0.04 |
| Ti | 0.45 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.01 |
| Na | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 1.82 | 1.53 | 0.02 | 2.05 | 1.40 | 0.04 |
| Mn | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Process Parameters | 400 (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0% (wt.) | 5.0% (wt.) | 7.5% (wt.) | 10.0% (wt.) | |
| Mass of residual fat (g) | 1200 | 700.4 | 700 | 700 |
| Cracking time (min) | 90 | 100 | 90 | 120 |
| Initial cracking temperature (°C) | 360 | 370 | 395 | 396 |
| Mechanical system stirring speed (rpm) | 100 | 600 | 600 | 600 |
| Mass of solid (Coke) (kg) | 50 | 59.95 | 68.25 | 73.8 |
| Mass of liquid (Bio-oil) (kg) | 917.0 | 424.09 | 353.07 | 211.55 |
| Mass of H2O (kg) | 78.66 | 19.8 | 22.35 | 21.00 |
| Mass of gas (kg) | 154.34 | 196.49 | 256.36 | 393.65 |
| Yield of Bio-oil (wt.%) | 76.41 | 60.55 | 50.44 | 30.22 |
| Yield of H2O (wt.%) | 6.55 | 2.83 | 3.19 | 3.00 |
| Yield of Coke (wt.%) | 4.17 | 8.56 | 9.75 | 11.18 |
| Yield of Gas (wt.%) | 12.87 | 27.89 | 36.62 | 55.60 |
| Temperature/Catalyst | tReaction [min] | Physicochemistry Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ [g/cm³] | I.A [mg KOH/g] | ν [mm²/s] | ||
| 400 °C | 50 | 0.8520 | 135.26 | 8.10 |
| 60 | 0.8372 | 54.24 | 5.70 | |
| 70 | 0.8299 | 7.12 | 3.60 | |
| 80 | 0.8220 | 2.37 | 3.03 | |
| 400 °C, 5% ACP (wt.) | 50 | 0.9266 | 144.14 | 7.74 |
| 60 | 0.8956 | 133.98 | 7.64 | |
| 80 | 0.8864 | 131.36 | 4.36 | |
| 100 | 0.8436 | 75.4 | 2.89 | |
| 400 °C, 7.5% ACP (wt.) | 70 | 0.8957 | 143.39 | 2.72 |
| 90 | 0.8688 | 134.32 | 2.68 | |
| 120 | 0.8507 | 51.71 | 2.65 | |
| 400 °C, 10% ACP (wt.) | 60 | 0.8599 | 143.39 | 3.74 |
| 70 | 0.8493 | 132.49 | 3.69 | |
| 90 | 0.8414 | 64.92 | 2.24 | |
| Temperature/Catalyst | tReaction [min] | Concentration [%area.] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocarbons | Oxygenates | ||
| 400 °C | 50 | 71.950 | 28.050 |
| 60 | 88.515 | 11.485 | |
| 70 | 90.966 | 9.034 | |
| 80 | 95.137 | 4.863 | |
| 400 °C, 5% ACP (wt.) | 50 | 27.855 | 72.145 |
| 60 | 43.619 | 56.381 | |
| 80 | 48.479 | 51.521 | |
| 100 | 68.333 | 31.667 | |
| 400 °C, 7.5% ACP (wt.) | 70 | 50.836 | 49.164 |
| 90 | 55.507 | 44.493 | |
| 120 | 68.364 | 31.636 | |
| 400 °C, 10% ACP (wt.) | 60 | 53.925 | 46.075 |
| 70 | 55.290 | 44.710 | |
| 90 | 75.764 | 24.236 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernar, L.P.; Ferreira, C.C.; Costa, A.F.d.F.; Ribeiro, H.J.d.S.; dos Santos, W.G.; Pereira, L.M.; Pereira, A.M.; Moraes, N.L.; Assunção, F.P.d.C.; Mota, S.A.P.d.; et al. Catalytic Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Carbon Pellets into Hydrocarbons-like Fuels in a Two-Stage Reactor: Analysis of Hydrocarbons Composition and Physical-Chemistry Properties. Energies 2022, 15, 4587. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15134587
Bernar LP, Ferreira CC, Costa AFdF, Ribeiro HJdS, dos Santos WG, Pereira LM, Pereira AM, Moraes NL, Assunção FPdC, Mota SAPd, et al. Catalytic Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Carbon Pellets into Hydrocarbons-like Fuels in a Two-Stage Reactor: Analysis of Hydrocarbons Composition and Physical-Chemistry Properties. Energies. 2022; 15(13):4587. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15134587
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernar, Lucas Pinto, Caio Campos Ferreira, Augusto Fernando de Freitas Costa, Haroldo Jorge da Silva Ribeiro, Wenderson Gomes dos Santos, Lia Martins Pereira, Anderson Mathias Pereira, Nathalia Lobato Moraes, Fernanda Paula da Costa Assunção, Sílvio Alex Pereira da Mota, and et al. 2022. "Catalytic Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Carbon Pellets into Hydrocarbons-like Fuels in a Two-Stage Reactor: Analysis of Hydrocarbons Composition and Physical-Chemistry Properties" Energies 15, no. 13: 4587. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15134587
APA StyleBernar, L. P., Ferreira, C. C., Costa, A. F. d. F., Ribeiro, H. J. d. S., dos Santos, W. G., Pereira, L. M., Pereira, A. M., Moraes, N. L., Assunção, F. P. d. C., Mota, S. A. P. d., de Castro, D. A. R., Santos, M. C., Mendonça, N. M., Duvoisin, S., Jr., Borges, L. E. P., & Machado, N. T. (2022). Catalytic Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Carbon Pellets into Hydrocarbons-like Fuels in a Two-Stage Reactor: Analysis of Hydrocarbons Composition and Physical-Chemistry Properties. Energies, 15(13), 4587. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15134587






