Edge Computing for IoT-Enabled Smart Grid: The Future of Energy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- ✓
- Indication of the inevitable trend of integrating EC with IoT-based SGs.
- ✓
- Provision of a comprehensive survey of recent EC–IoT-based SGs. The studies are detail analyzed according to three directions, power distribution, advanced metering, and micro-grid systems.
- ✓
- Proposal of a common framework for EC–IoT-based SGs.
- ✓
- Discussion of the challenges and open issues to drive EC–IoT-based SGs.
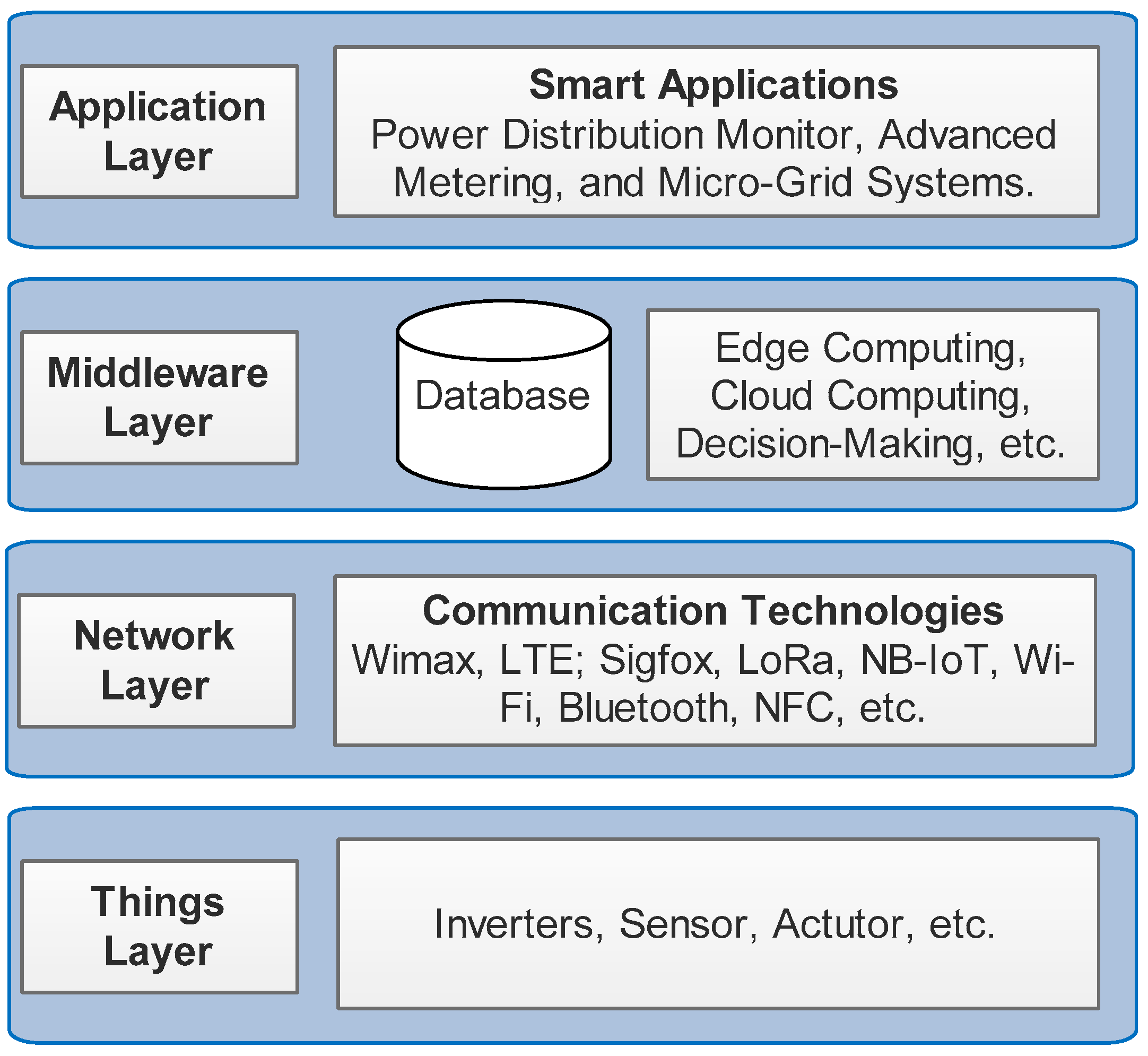
2. Architecture of EC–IoT-Based SGs
- (1)
- Things layer: Defined as all things, including terminals, smart sensors and actuators that aim to obtain data, then provide them to upper layers or execute sent tasks by upper layers.
- (2)
- Network layer: Defined as an intermediate layer for the connection between the Things layer and the upper layers. The main tasks of the network layer are to access control and establish real-time, secure, and efficient end-to-end connections. This layer is divided into two sublayers: 5G’s backhaul connections and low-power wide area (LPWANs) technologies such as Sigfox, NB-IoT, ZigBee and LoRa.
- (3)
- Middleware layer: Defined as the heart of the IoT-based SG. This layer covers emerging advanced technologies and solutions such as fog computing, edge computing, big data processing and analysis. The AI vision is implemented on this layer.
- (4)
- Application layer: This layer covers IoT-based SG applications that are implemented in a series of domains such as cities, industrial factories, residential buildings, farms, traffic systems, and IoT ecosystems. This layer combines all solutions, technologies, and applications to interact with humans through network communications.
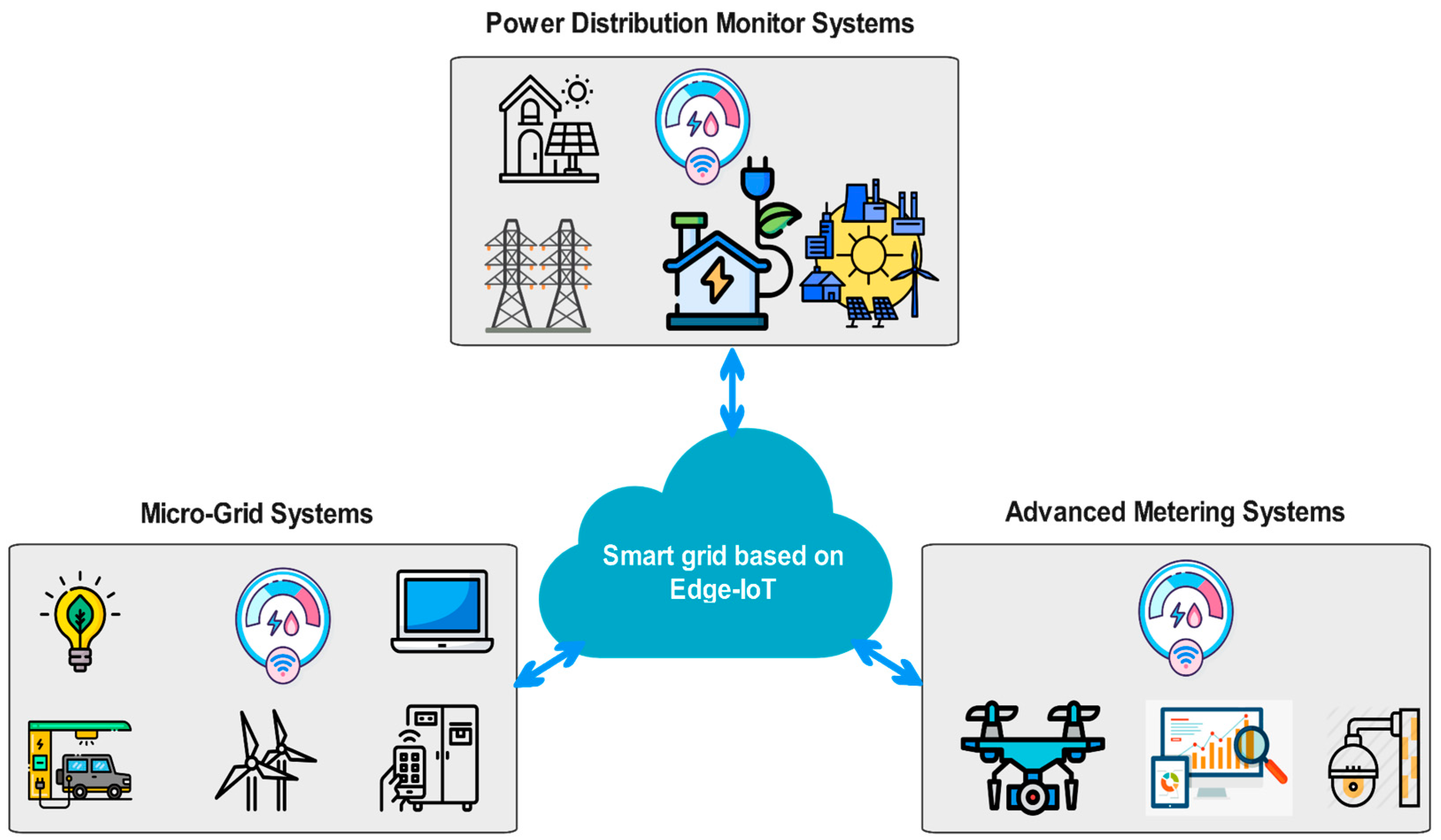
3. Survey of EC–IoT Smart Grids
3.1. Power Distribution Monitor Systems
3.2. Micro-Grid Systems
3.3. Advanced Metering Systems
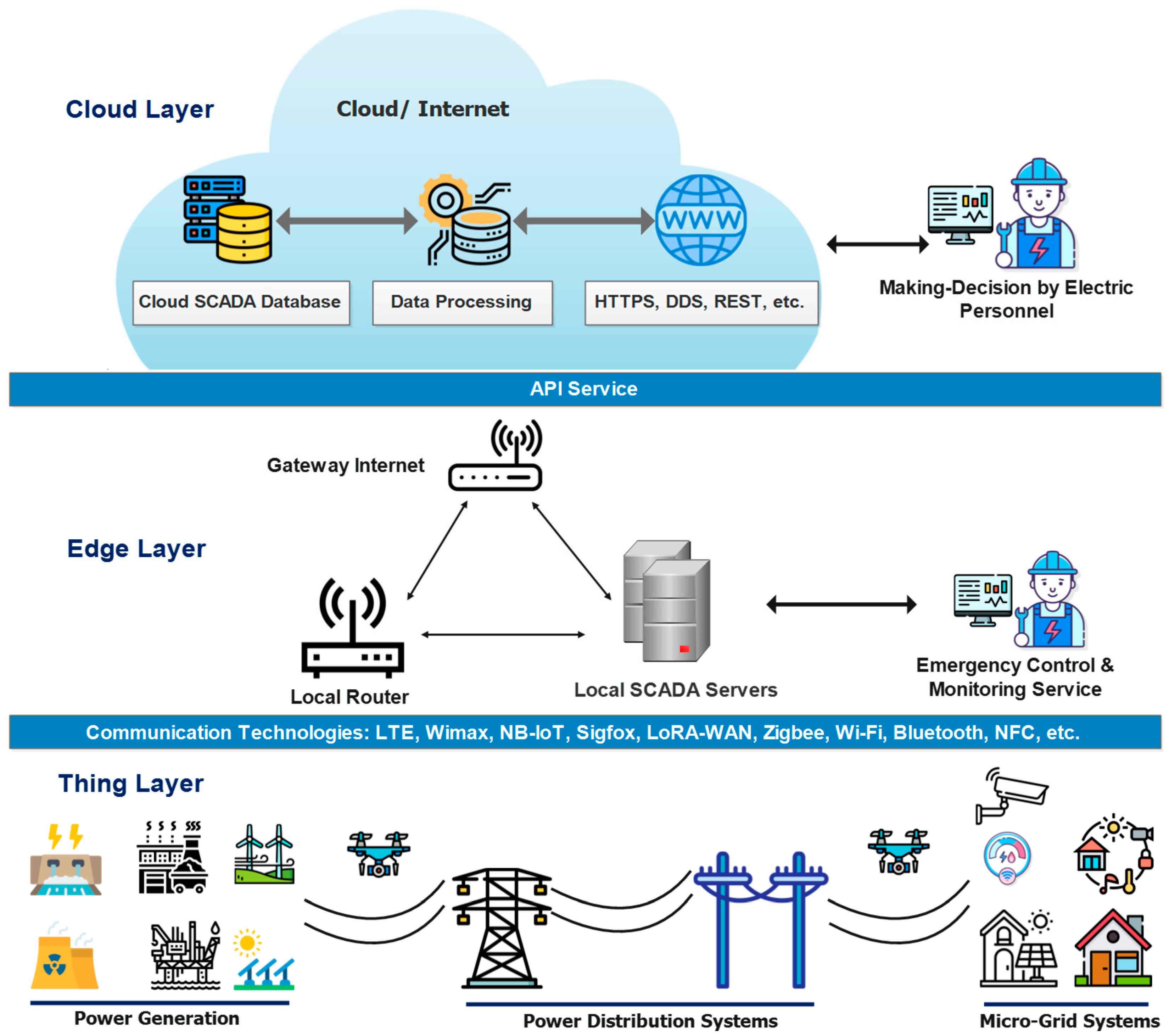
4. EC–IoT SCADA Application
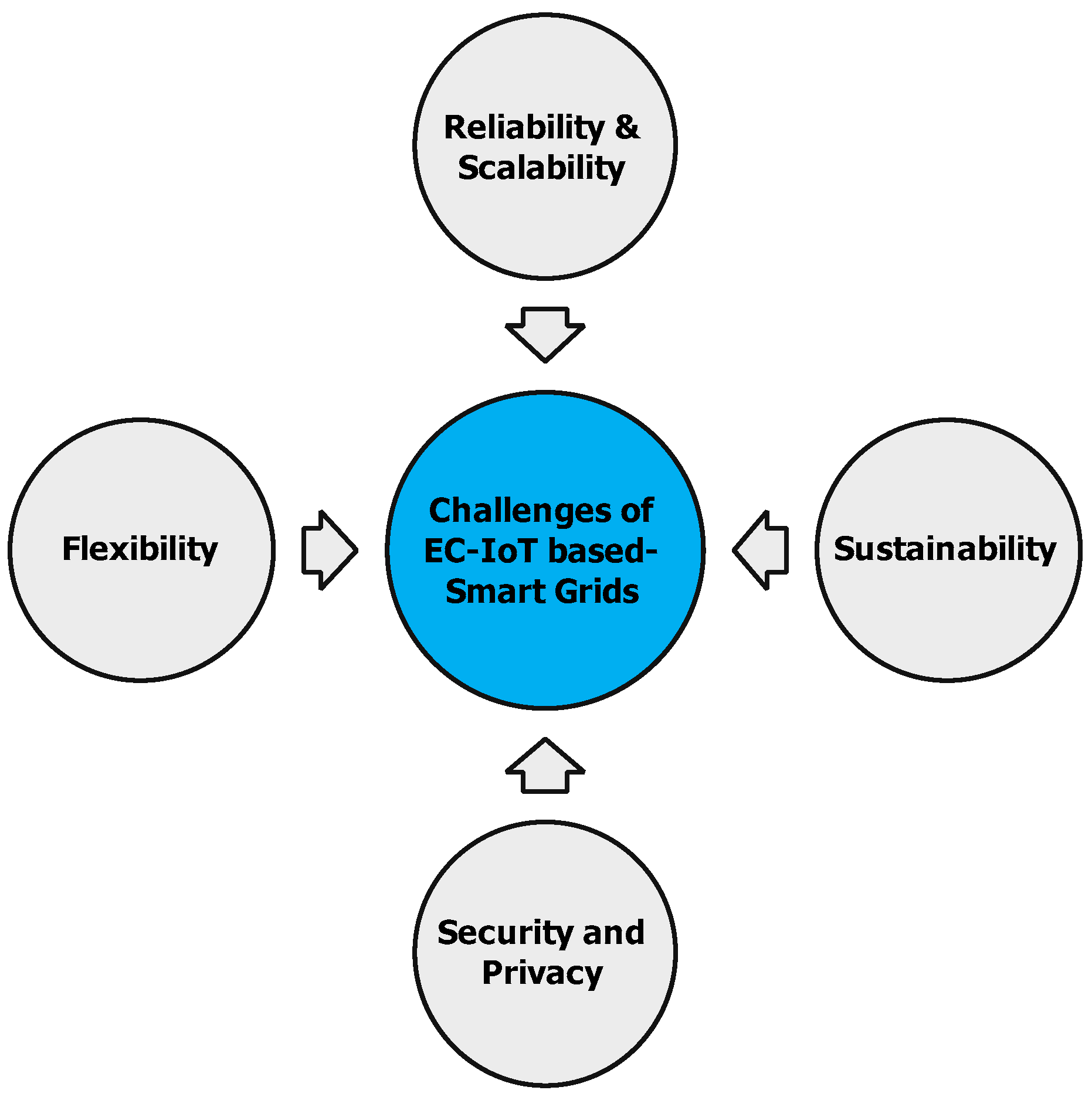
5. Challenges and Open Issues
5.1. Scalability and Reliability
5.2. Sustainability
5.3. Security and Privacy
5.4. Flexibility
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acronym | Definition | ||
| 5G | 5th Generation Mobile Networks | ||
| 6LoWPAN | General Packet Radio Service | ||
| AI | Artificial Intelligence | ||
| API | Application Programming Interface | ||
| AR | Augmented Reality | ||
| BESSs | Battery Energy Storage Systems | ||
| BTM | Behind-The-Meter | ||
| CC | Cloud Computing | ||
| D2D | Device to Device | ||
| DDoS | Distributed Denial of Service | ||
| DERs | Distributed Energy Resources | ||
| DG | Distributed Generators | ||
| EG | Edge Computing | ||
| EMR | Electronic Medical Record | ||
| FC | Fog Computing | ||
| FDI | False Data-Injection | ||
| GIS | Geographic Information Systems | ||
| IaaS | Infrastructure as a Service | ||
| IIoT | Industrial Internet of Things | ||
| IoT | Internet of Things | ||
| IoTH | Internet of Health Things | ||
| IoV | Internet of Vehicles | ||
| M2M | Mechanism to Mechanism | ||
| MCC | Multi-Cloud Computing | ||
| MEC | Mobile Edge Computing | ||
| MILP | Mixed Integer Linear Programming | ||
| NDN | Named Data Networking | ||
| NILM | Nonintrusive load monitoring | ||
| Probability Density Function | |||
| PVs | Photovoltaics | ||
| QoS | Quality of Service | ||
| RPL | Routing Protocol for LoWPAN | ||
| SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition | ||
| SDN | Software-Defined Networking | ||
| SG | Smart Grid | ||
| VVC | Volt/VAR Control |
References
- Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/238610/projected-world-electricity-generation-by-energy-source (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Saleem, Y.; Crespi, N.; Rehmani, M.H.; Copeland, R. Internet of Things-Aided Smart Grid: Technologies, Architectures, Applications, Prototypes, and Future Research Directions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 62962–63003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.eia.gov/totalenergy/data/monthly/pdf/sec9_11.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Abir, S.M.A.A.; Anwar, A.; Choi, J.; Kayes, A.S.M. IoT-Enabled Smart Energy Grid: Applications and Challenges. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 50961–50981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmani, M.H.; Davy, A.; Jennings, B.; Assi, C. Software Defined Networks-Based Smart Grid Communication: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2637–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Empowering Things with Intelligence: A Survey of the Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities in Artificial Intelligence of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 7789–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, A.; Conti, M. Key Management Systems for Smart Grid Advanced Metering Infrastructure: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2831–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, X.; Srinivasan, P.; Formby, D.; Beyah, R.A. Di-PriDA: Differentially Private Distributed Load Balancing Control for the Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2019, 16, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Choo, K.-K.R. Fault-Tolerant Multisubset Aggregation Scheme for Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 4065–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.Y.; Oad, A.; Abrar, M.; Munir, H.M.; Hasan, S.F.; Muqeet, H.A.U. Noor-bakhsh Amiri Golilarz, Edge Computing for IoT-Enabled Smart Grid. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 5524025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, E.; Abu-Dayya, A. Automatic meter reading in the smart grid using contention based random access over the free cellular spectrum. Comput. Netw. 2014, 59, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Misra, S.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Cloud Computing Applications for Smart Grid: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2015, 26, 1477–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol-Kantarci, M.; Mouftah, H.T. Energy-Efficient Information and Communication Infrastructures in the Smart Grid: A Survey on Interactions and Open Issues. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.U.; Usman, M.R.; Usman, M.A.; Politis, C. Design, Deployment and Performance Evaluation of an IoT Based Smart Energy Management System for Demand Side Management in Smart Grid. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 15261–15278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wen, H.; Wu, J.; Lei, W.; Hou, W.; Liu, W.; Xu, A.; Jiang, Y. Internet of Things Based Smart Grids Supported by Intelligent Edge Computing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 74089–74102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y. Permissioned Blockchain and Edge Computing Empowered Privacy-Preserving Smart Grid Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 7992–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wong, K.P. Cloud-Based Information Infrastructure for Next-Generation Power Grid: Conception, Architecture, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1896–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Du, X. Achieving Efficient and Secure Data Acquisition for Cloud-Supported Internet of Things in Smart Grid. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1934–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sureshkumar, V.; Anandhi, S.; Amin, R.; Selvarajan, N.; Madhumathi, R. Design of Robust Mutual Authentication and Key Establishment Security Protocol for Cloud-Enabled Smart Grid Communication. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 3565–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Liu, Z.; Yao, L.; Dai, F. Artificial intelligence for edge service optimization in Internet of Vehicles: A survey. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liang, F.; He, X.; Hatcher, W.G.; Lu, C.; Lin, J.; Yang, X. A Survey on the Edge Computing for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 6900–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, P.; Becvar, Z. Mobile Edge Computing: A Survey on Architecture and Computation Offloading. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1628–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, J. Deep Learning for Edge Computing Applications: A State-of-the-Art Survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58322–58336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X. Edge AI: On-Demand Accelerating Deep Neural Network Inference via Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor-A-Rahim, M.; Khyam, M.O.; Mahmud, M.A.; ul Huque, M.T.I.; Li, X.; Pesch, D.; Oo, A.M.T. Robust and Real-Time State Estimation of Unstable Microgrids Over IoT Networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Tang, L. Edge Intelligence for Real-Time Data Analytics in an IoT-Based Smart Metering System. IEEE Netw. 2020, 24, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamola, V.; Sancheti, A.; Chakravarty, S.; Kumar, N.; Guizani, M. An IoT and Edge Computing Based Framework for Charge Scheduling and EV Selection in V2G Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 10569–10580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Dillon, T.; Rahayu, W.; Li, M. Empowering IoT Predictive Maintenance Solutions With AI: A Distributed System for Manufacturing Plant-Wide Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuvo, S.S.; Yilmaz, Y. Home Energy Recommendation System (HERS): A Deep Reinforcement Learning Method based on Residents’ Feedback and Activity. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid. 2022, 13, 2812–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Yang, Q.; Li, S.; Wei, D.S.L.; Peng, M.; Memon, I.; Hong, P. PPSO: A Privacy-Preserving Service Outsourcing Scheme for Real-Time Pricing Demand Response in Smart Grid. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quy, K.V.; Hau, V.N.; Anh, V.D.; Ngoc, L.A. Smart healthcare IoT applications based on fog computing: Architecture, applications and challenges. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowley, F.; Pahl, C.; Jamshidi, P.; Fang, D.; Liu, X. A Classification and Comparison Framework for Cloud Service Brokerage Architectures. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2018, 6, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, R.; Ahmed, S.H.; Kim, B. Information-Centric Networking With Edge Computing for IoT: Research Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 73465–73488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.; Sankar, S.; Prasad, M.; Puthal, D.; Gupta, A.; Mohanty, M.; Lin, C.-T. Edge of things: The big picture on the integration of edge, IoT and the cloud in a distributed computing environment. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Jiang, L.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y. Intelligent Edge Computing for IoT-Based Energy Management in Smart Cities. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, R.J.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Aggregator based RPL for an IoT-fog based power distribution system with 6LoWPAN. China Commun. 2020, 17, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Ramezani, M.; Xiao, Y. Artificial Neural Networks for Volt/VAR Control of DER Inverters at the Grid Edge. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 5564–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekpour, A.R.; Annaswamy, A.M.; Shah, J. Hierarchical Hybrid Architecture for Volt/Var Control of Power Distribution Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, Y.; Shadmand, M.B. Multitimescale Three-Tiered Voltage Control Framework for Dispersed Smart Inverters at the Grid Edge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.N.; Pota, H.R.; Tran, Q.N.; Hu, J. Designing Constraint-Based False Data-Injection Attacks Against the Unbalanced Distribution Smart Grids. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 9422–9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Han, G.; Zhu, H.; Liu, L.; Guizani, M. Adaptive DE Algorithm for Novel Energy Control Framework Based on Edge Computing in IIoT Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 5118–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Chatterjee, D. An Improved Load Feature Extraction Technique for Smart Homes Using Fuzzy-Based NILM. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 2511209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, U.; Abbasi, U.; Mir, T.; Kanwal, S.; Alamri, S. Energy Management in Smart Buildings and Homes: Current Approaches, a Hypothetical Solution, and Open Issues and Challenges. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 94132–94148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markakis, K.E.; Nikoloudakis, Y.; Lapidaki, K.; Fiorentzis, K.; Karapidakis, E. Unification of Edge Energy Grids for Empowering Small Energy Producers. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajić, B.D.; Petrović, V.B.; Horvat, N.; Dragan, D.; Stanisavljević, A.; Katić, V.; Popović, J. A Distributed Ledger-Based Automated Marketplace for the Decentralized Trading of Renewable Energy in Smart Grids. Energies 2022, 15, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, F.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Q. Connectivity Verification in Distribution Systems Using Smart Meter Voltage Analytics: A Cloud-Edge Collaboration Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 3929–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Dehghanpour, K.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y. Disaggregating Customer-Level Behind-the-Meter PV Generation Using Smart Meter Data and Solar Exemplars. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 5417–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliatsios, D.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Lagkas, T.; Sarigiannidis, A.G. A Survey on SCADA Systems: Secure Protocols, Incidents, Threats and Tactics. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1942–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakaria, A.H.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Gokhale, A. Resiliency-Aware Deployment of SDN in Smart Grid SCADA: A Formal Synthesis Model. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2021, 18, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Sousa, P.; Mendes, J.; Danishvar, M.; Mousavi, A. Real-Time Event-Driven Learning in Highly Volatile Systems: A Case for Embedded Machine Learning for SCADA Systems. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 50794–50806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, G.; Caldera, C.; Shrobe, H. IIoT Cybersecurity Risk Modeling for SCADA Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 4486–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, D.; Zaman, M.; Joshi, R.; Sampalli, S. An Efficient Key Management and Multi-Layered Security Framework for SCADA Systems. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2022, 19, 642–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sampalli, S. A Survey of Security in SCADA Networks: Current Issues and Future Challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 135812–135831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, U.; Aseeri, A.O.; Alkatheiri, M.S.; Zhuang, Y. Context-Aware Autonomous Security Assertion for Industrial IoT. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 191785–191794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, M.; Cusman, A.; Stîngă, F.; Ionică, D.; Popescu, D. Experimenting with Digital Signatures over a DNP3 Protocol in a Multitenant Cloud-Based SCADA Architecture. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 156484–156503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wu, W.; Guo, Q.; Satpute, M.N.; Znati, T.; Du, D.Z. Reliability-Aware Offloading and Allocation in Multilevel Edge Computing System. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2021, 70, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dai, H.-N.; Wang, H. Convergence of Blockchain and Edge Computing for Secure and Scalable IIoT Critical Infrastructures in Industry 4.0. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 2300–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzler, K.; Maier, S.D.; Jäger, M.; Horn, R. SDG-Based Sustainability Assessment Methodology for Innovations in the Field of Urban Surfaces. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, Z.; Shah, M.A.; Maple, C.; Khattak, H.A.; Ameer, Z.; Asghar, M.N.; Mussadiq, S. Towards Energy Efficient Smart Grids Using Bio-Inspired Scheduling Techniques. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 158947–158960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Ni, W.; Wang, X.; Hossain, E. Modeling and Analysis of Energy Harvesting and Smart Grid-Powered Wireless Communication Networks: A Contemporary Survey. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2020, 4, 461–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.B.; Qureshi, M.A.; Javaid, N.; Alquthami, T. Dynamic Pricing Mechanism with the Integration of Renewable Energy Source in Smart Grid. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 16876–16892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.-F.; Wen, H.; Wu, J.; Pan, F.; Xu, A.; Song, H.; Xie, F.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, M. Security Enhancement for Mobile Edge Computing Through Physical Layer Authentication. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116390–116401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.; Rizzetti, T.A. A Review of Privacy-Preserving Aggregation Schemes for Smart Grid. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2021, 19, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Dong, M.; Miao, W.; Zhang, M.; Tang, H. A Data-Driven Approach for Blockchain-Based Smart Grid System. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 70061–70070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadali, A.; Haghighi, M.S. A Privacy-Preserving Homomorphic Scheme with Multiple Dimensions and Fault Tolerance for Metering Data Aggregation in Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 5212–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, M.; Wang, W. Distributed Extremum Seeking for Optimal Resource Allocation and Its Application to Economic Dispatch in Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3161–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Mondal, A.; Kumar, P.V.S.; Pal, S.K. SEED: QoS-Aware Sustainable Energy Distribution in Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2022, 7, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, G.M.; Bellalta, B.; Oechsner, S. The impact of dual prediction schemes on the reduction of the number of transmissions in sensor networks. Comput. Commun. 2017, 112, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arani, M.G.; Jabbehdari, S.; Pourmina, M.A. An autonomic resource provisioning approach for service-based cloud applications: A hybrid approach. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 78, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, N.C.; Sotiriadis, S.; Bessis, N. Adaptive Microservice Scaling for Elastic Applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 4195–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriadis, S.; Bessis, N.; Amza, C.; Buyya, R. Elastic Load Balancing for Dynamic Virtual Machine Reconfiguration Based on Vertical and Horizontal Scaling. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2019, 12, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Ref. No | Scenarios | Key Technologies | Case Study: Key Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| [36] | Power Distribution | Edge computing & 6LoWPAN protocol | This research proposed an aggregator to support communication between the smart meters far from edge servers to improve the grid performance. |
| [37] | Power Distribution | Artificial Neural Network | This research proposed a novel Volt/VAR control strategy for optimal DER inverters at the edge layer. |
| [38] | Power Distribution | Hierarchical Hybrid Architecture | This research proposed three-layer architecture to optimal Volt/VAR control of power distribution grids to improve coordination of distributed generators. |
| [39] | Power Distribution | Hierarchical Hybrid Architecture | This research proposed a multi-time scale three-tiered voltage control schema for smart inverters at the grid edge to stabilize the voltage fluctuations. |
| [40] | Power Distribution | Security | This research designed a false data-injection attack schema into SE modules of the unbalanced power distribution grid systems to indicate challenges in the operator of smart grid systems. |
| [41] | Micro-Grid Systems | Edge computing, mutation strategy | Propose an evolution energy control algorithm based on edge computing and mutation strategy to trade off other metrics for optimal energy efficiency in smart factories. |
| [42] | Micro-Grid Systems | Harmonic signature analysis and Fuzzy rule | Propose the load feature extraction technique based on the support of the current harmonic signature analysis and the intelligent identification method to monitor different electrical loads. |
| [43] | Micro-Grid Systems | Energy Management Model | Propose the self-managing energy system model, called SES, to save energy for households and buildings. |
| [44] | Micro-Grid Systems | Blockchain | Propose an autonomous energy transactions model to sell excess power from solar grids. |
| [45] | Micro-Grid Systems | Private Distributed Ledger | Propose an autonomous energy binding mechanism to transaction households’ excess power. |
| [46] | Metering Systems | Cloud/Edge computing | Propose a collaboration mechanism to identify outlier users and correct connections. |
| [47] | Metering Systems | Probability and Gaussian model | Propose a solution to improve volatility of load and enhance disaggregation ability behind the smart meter. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minh, Q.N.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Quy, V.K.; Ngoc, L.A.; Chehri, A.; Jeon, G. Edge Computing for IoT-Enabled Smart Grid: The Future of Energy. Energies 2022, 15, 6140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176140
Minh QN, Nguyen V-H, Quy VK, Ngoc LA, Chehri A, Jeon G. Edge Computing for IoT-Enabled Smart Grid: The Future of Energy. Energies. 2022; 15(17):6140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176140
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinh, Quy Nguyen, Van-Hau Nguyen, Vu Khanh Quy, Le Anh Ngoc, Abdellah Chehri, and Gwanggil Jeon. 2022. "Edge Computing for IoT-Enabled Smart Grid: The Future of Energy" Energies 15, no. 17: 6140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176140
APA StyleMinh, Q. N., Nguyen, V.-H., Quy, V. K., Ngoc, L. A., Chehri, A., & Jeon, G. (2022). Edge Computing for IoT-Enabled Smart Grid: The Future of Energy. Energies, 15(17), 6140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176140










