Silicone-Based Membranes as Potential Materials for Dielectric Electroactive Polymer Actuators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Silicone Mold Start 15 and Dragon Skin 10M (Smooth-On, Inc.);
- Carbon conductive grease (MG Chemicals 846);
- Copper tape;
- Rigid PMMA frame (Plexiglass®).
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K.J.; Tadokoro, S. Electroactive Polymers for Robotic Applicationss; Springer: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Cohen, Y. Electroactive Polymer (EAP) Actuators as Artificial Muscles: Reality, Potential, and Challenges; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rosset, S.; Araromi, O.A.; Schlatter, S.; Shea, H.R. Fabrication Process of Silicone-based Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 108, e53423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernat, J.; Kolota, J.; Rosset, S. Identification of a Nonlinear Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Based on the Harmonic Balance Method. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 2664–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffstadt, T.; Griese, M.; Maas, J. Online identification algorithms for integrated dielectric electroactive polymer sensors and self-sensing concepts. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavanne, J.; Civet, Y.; Perriard, Y. Modelling of a dielectric electroactive polymer tubular shape sensor for pressure measurements. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Banff, AB, Canada, 12–15 July 2016; pp. 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tairych, A.; Anderson, I.A. Capacitive Stretch Sensing for Robotic Skins. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallart, M.; Cottinet, P.J.; Guyomar, D.; Lebrun, L. Electrostrictive polymers for mechanical energy harvesting. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, T.; Rosset, S.; Anderson, I.; Shea, H. Dielectric elastomer generators that stack up. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, G.; Papini, G.; Righi, M.; Forehand, D.; Ingram, D.; Vertechy, R.; Fontana, M. Resonant wave energy harvester based on dielectric elastomer generator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat, J.; Kołota, J. DEAP Actuator Composed of a Soft Pneumatic Spring Bias with Pressure Signal Sensing. Energies 2021, 14, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaal, W.; Herold, S. Electroactive Polymer Actuators in Dynamic Applications. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, P.; Rizzello, G.; Seelecke, S. A novel biasing mechanism for circular out-of-plane dielectric actuators based on permanent magnets. Mechatronics 2018, 56, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Hussain, A.M.; Duduta, M.; Vogt, D.M.; Wood, R.J.; Clarke, D.R. Compact Dielectric Elastomer Linear Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lee, H.P.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Q. Control of a Soft Inchworm Robot with Environment Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 3809–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideris, E.; de Lange, H. Pumps operated by solid-state electromechanical smart material actuators—A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 307, 111915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.; Kogler, A.; Stadlbauer, J.M.; Foo, C.C.; Kaltseis, R.; Baumgartner, M.; Mao, G.; Keplinger, C.; Koh, S.J.A.; Arnold, N.; et al. A Lesson from Plants: High-Speed Soft Robotic Actuators. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Gao, X.; Conn, A.T. A Magnetically Coupled Dielectric Elastomer Pump for Soft Robotics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; Danielmeier, K.; Hitzbleck, J.; Krause, J.; Kridl, T.; Nowak, S.; Orselli, E.; Quan, X.; Schapeler, D.; Sutherland, W.; et al. Electroactive Polymers: Developments of and Perspectives for Dielectric Elastomers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9409–9421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Albuquerque, F.B.; Madsen, J.; Skov, A.L. Highly Stretchable Silicone Elastomer Applied in Soft Actuators. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, 2100732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochu, P.; Pei, Q. Advances in Dielectric Elastomers for Actuators and Artificial Muscles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 10–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, S.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. Performance prediction of circular dielectric electro-active polymers membrane actuators with various geometries. In Proceedings of the Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD), San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 March 2015; Volume 9430, pp. 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Review of Dielectric Elastomer Actuators and Their Applications in Soft Robots. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Werth, H.; Goldman, A.; Hida, Y.; Diesner, C.; Lane, L.; Menezes, P.L. Recent Progress on Electroactive Polymers: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Ceramics 2021, 4, 516–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, M.; Liu, D.; Sue, H.J. 2—Mechanical properties of thermosets. In Thermosets; Guo, Q., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 28–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Farajollahi, M.; Choi, Y.S.; Lin, I.T.; Marshall, J.E.; Thompson, N.M.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Madden, J.D.W.; Smoukov, S.K. Electroactive polymers for sensing. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 20160026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Anderson, I.; Bauer, S.; Frediani, G.; Gallone, G.; Gei, M.; Graaf, C.; Jean-Mistral, C.; Kaal, W.; Kofod, G.; et al. Standards for dielectric elastomer transducers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 105025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Soft Robotics Toolkit. Available online: https://softroboticstoolkit.com/book/dielectric-elastomer-actuators (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Rizzello, G.; Naso, D.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. Modeling, Identification, and Control of a Dielectric Electro-Active Polymer Positioning System. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Pei, Q.; Joseph, J. High-Speed Electrically Actuated Elastomers with Strain Greater Than 100%. Science 2000, 287, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perju, E.; Shova, S.; Opris, D.M. Electrically Driven Artificial Muscles Using Novel Polysiloxane Elastomers Modified with Nitroaniline Push–Pull Moieties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 23432–23442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheima, Y.; Caspari, P.; Opris, D.M. Artificial Muscles: Dielectric Elastomers Responsive to Low Voltages. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1900205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

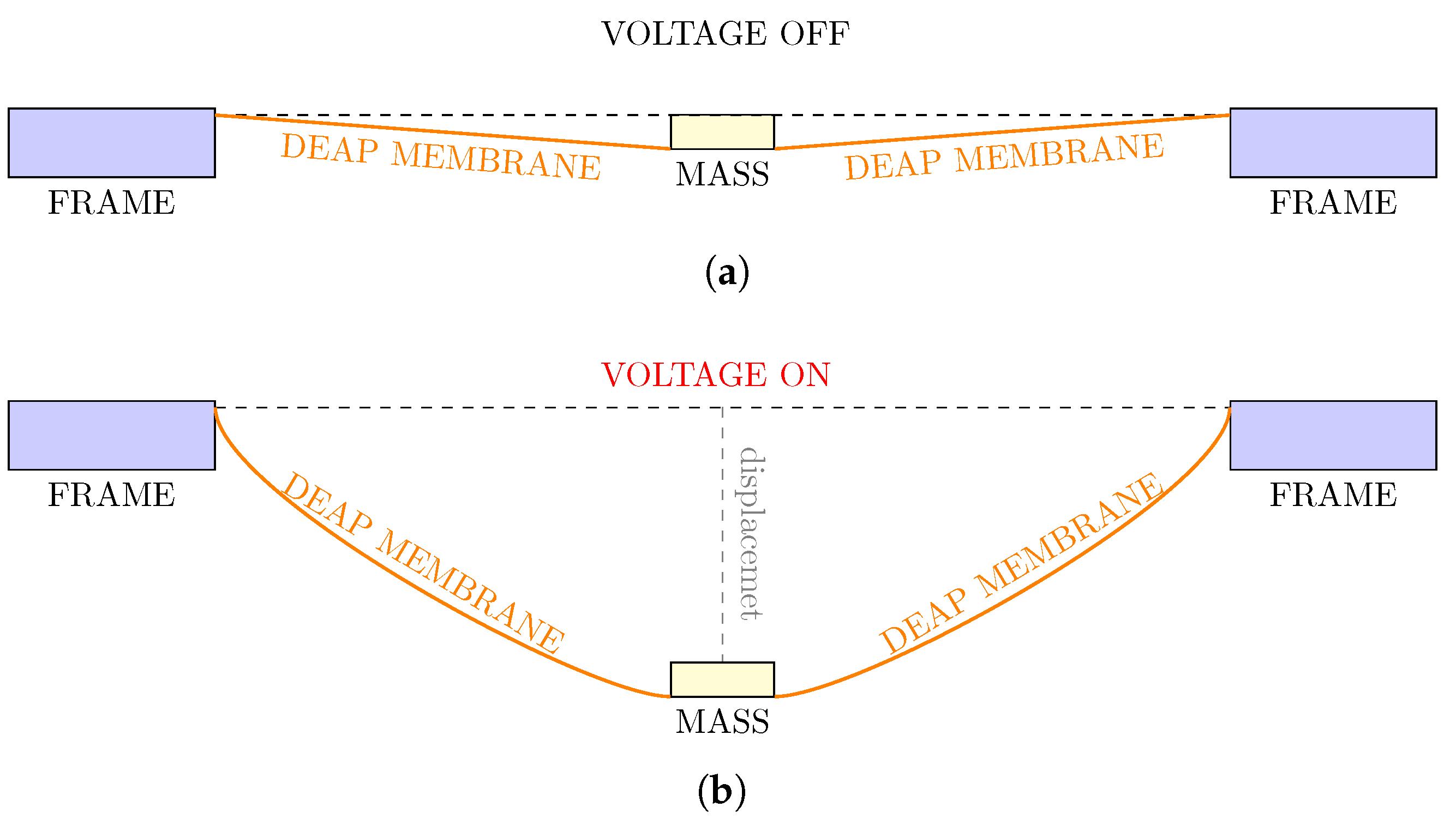

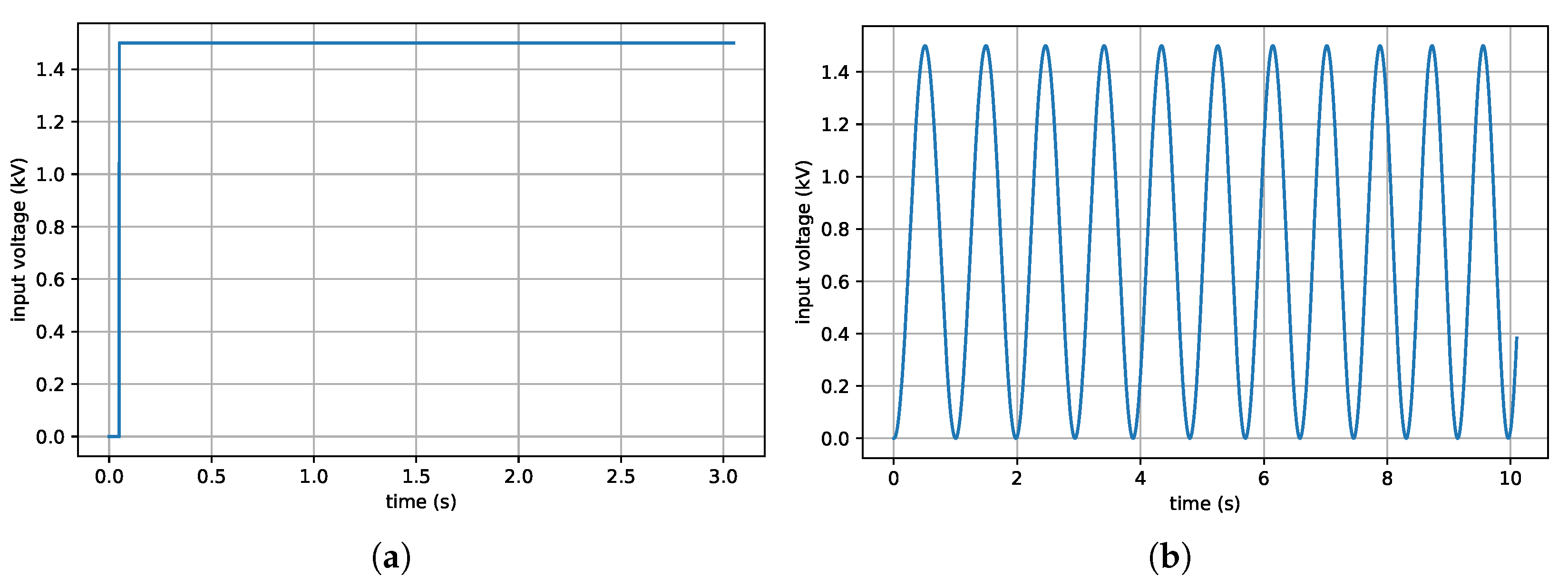

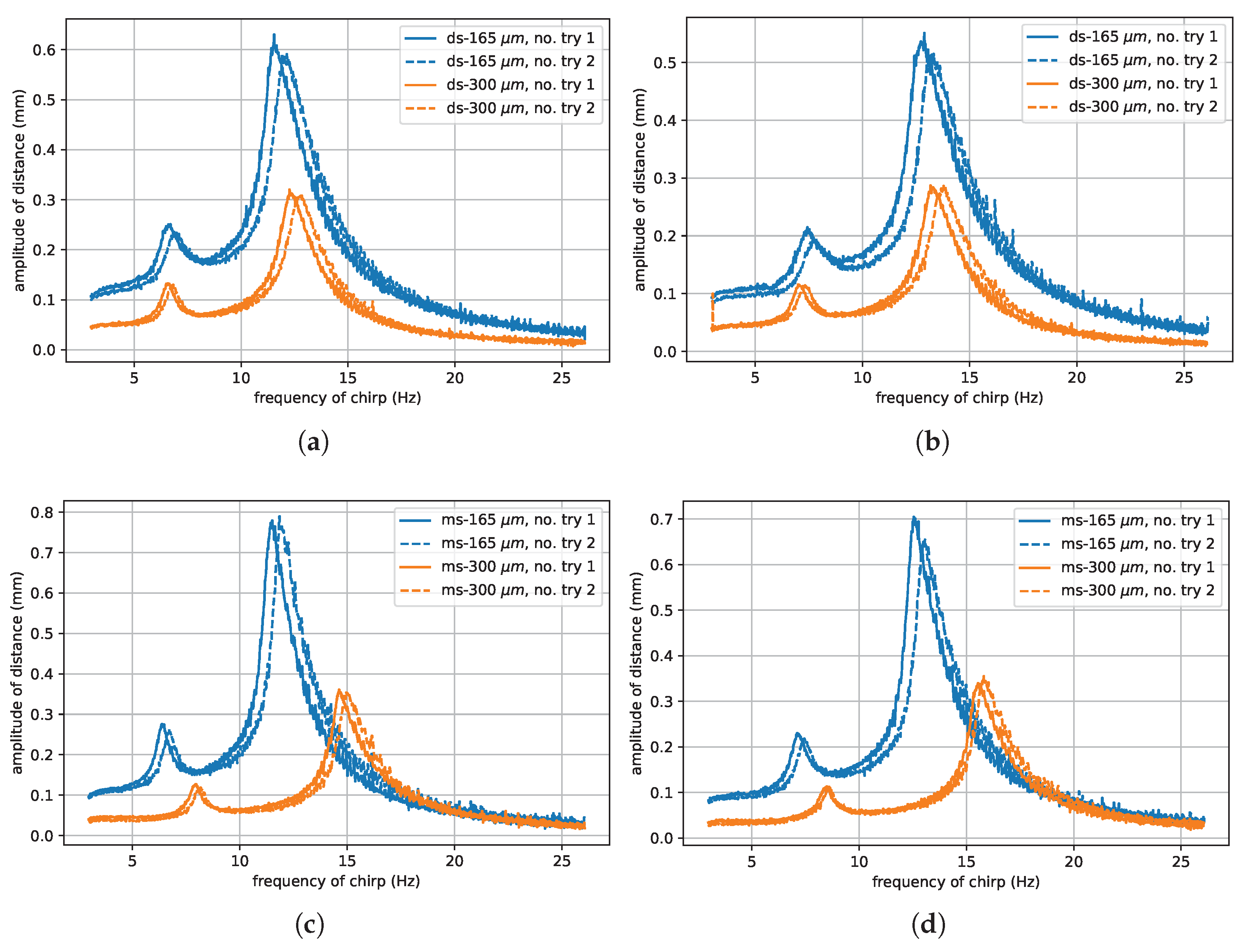
| Parameter | Mold Start 15 | Dragon Skin 10M |
|---|---|---|
| Modulus | 15 | 22 |
| Mixed Viscosity | 12,500 cPs | 23,000 cPs |
| Tensile Strength | 400 | 475 |
| Specific Gravity | / | / |
| Elongation at Breaks | 440% | 1000% |
| Shrinkage | < / | < / |
| Parameter | Dimension |
|---|---|
| Internal Diameter | 70 |
| External Diameter | 84 |
| Silicone Membrane Diameter | 100 |
| Silicone | Membrane Thickness | Capacity (pF) | Relative Permittivity (1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DS | 300 | 392.7 | 3.40 |
| DS | 165 | 613.4 | 3.02 |
| MS | 300 | 390.1 | 3.50 |
| MS | 165 | 691.9 | 3.36 |
| Silicone | Mean (mm) | Standard Deviation (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| DS 165 | 0.57 | 0.04 |
| DS 300 | 0.30 | 0.02 |
| MS 165 | 0.73 | 0.06 |
| MS 300 | 0.35 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernat, J.; Gajewski, P.; Kołota, J.; Marcinkowska, A. Silicone-Based Membranes as Potential Materials for Dielectric Electroactive Polymer Actuators. Energies 2022, 15, 6324. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176324
Bernat J, Gajewski P, Kołota J, Marcinkowska A. Silicone-Based Membranes as Potential Materials for Dielectric Electroactive Polymer Actuators. Energies. 2022; 15(17):6324. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176324
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernat, Jakub, Piotr Gajewski, Jakub Kołota, and Agnieszka Marcinkowska. 2022. "Silicone-Based Membranes as Potential Materials for Dielectric Electroactive Polymer Actuators" Energies 15, no. 17: 6324. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176324
APA StyleBernat, J., Gajewski, P., Kołota, J., & Marcinkowska, A. (2022). Silicone-Based Membranes as Potential Materials for Dielectric Electroactive Polymer Actuators. Energies, 15(17), 6324. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176324









