A Review of the External and Internal Residual Exhaust Gas in the Internal Combustion Engine
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- eEGR cooling: the flow is cooled to reduce exhaust gas temperatures before returning to the cylinder.
- -
- eEGR oxidation: The eEGR gases flow through a catalyst that oxidizes unburned combustibles into CO2 and H2O. This process extends the limits of eEGR.
- -
- eEGR fuel reforming: an eEGR reformer produces H2 and CO, increasing the premixed combustion rate.
2. External Exhaust Gas Recirculation
2.1. Effect of eEGR on Diesel Engine Performance and Emission Characteristics
2.2. Effect of eEGR on Alternative Fuel Engine Performance and Emission Characteristics
2.3. Effect of eEGR on Spark Ignition Engine Performance and Emission Characteristics
2.4. Control System and Prediction of eEGR Methods
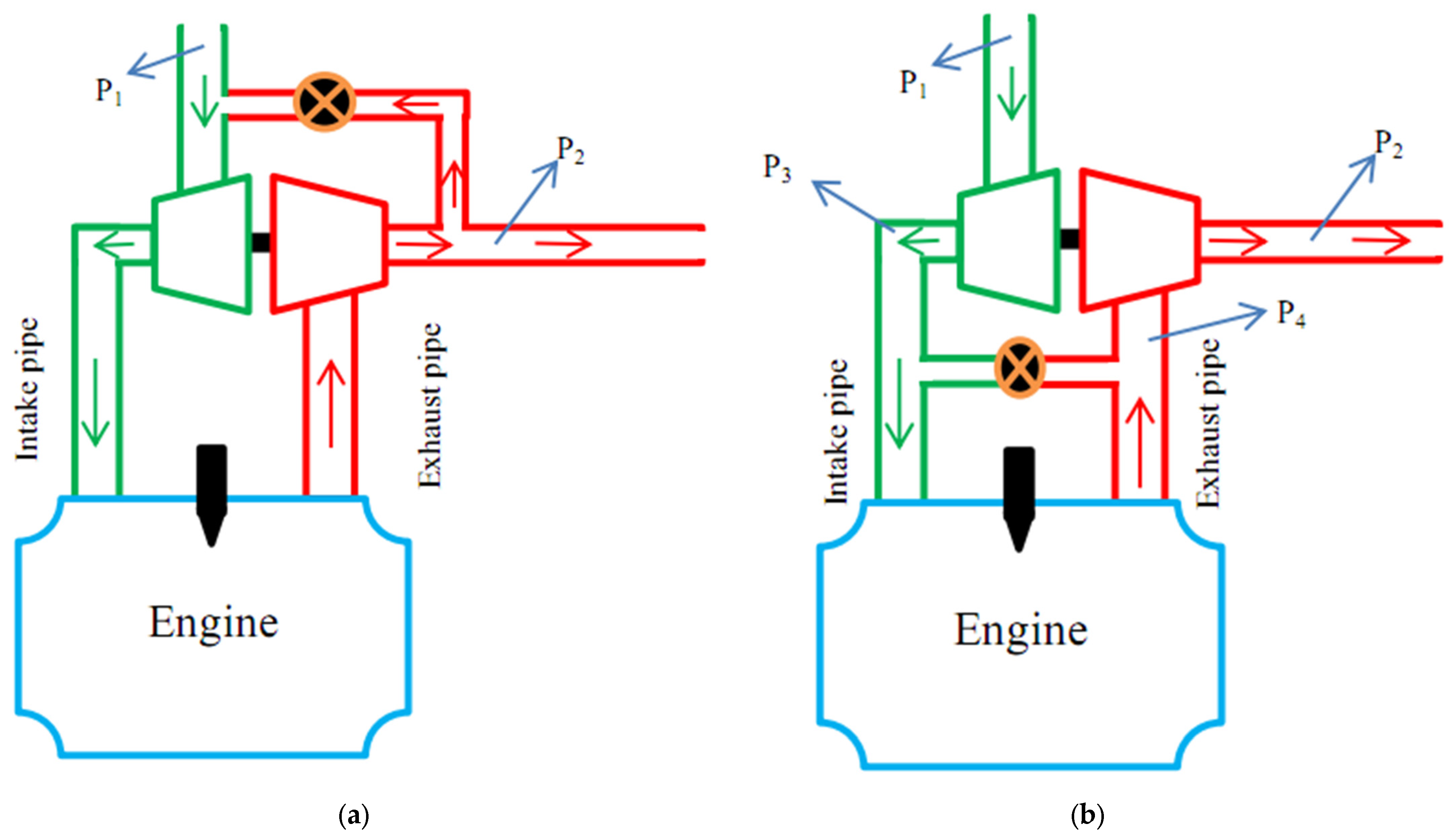
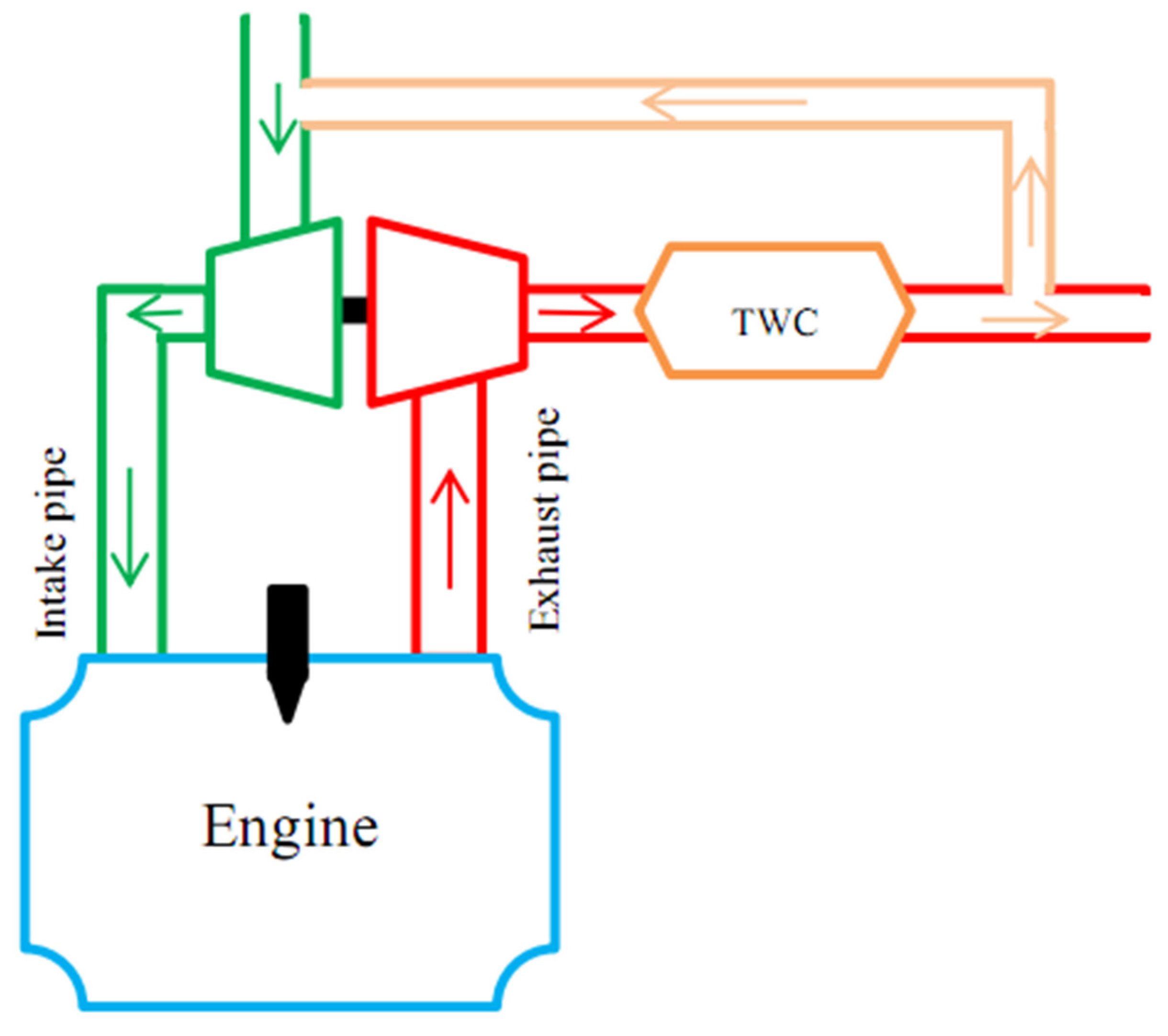
3. Internal Exhaust Gas Recirculation (iEGR)
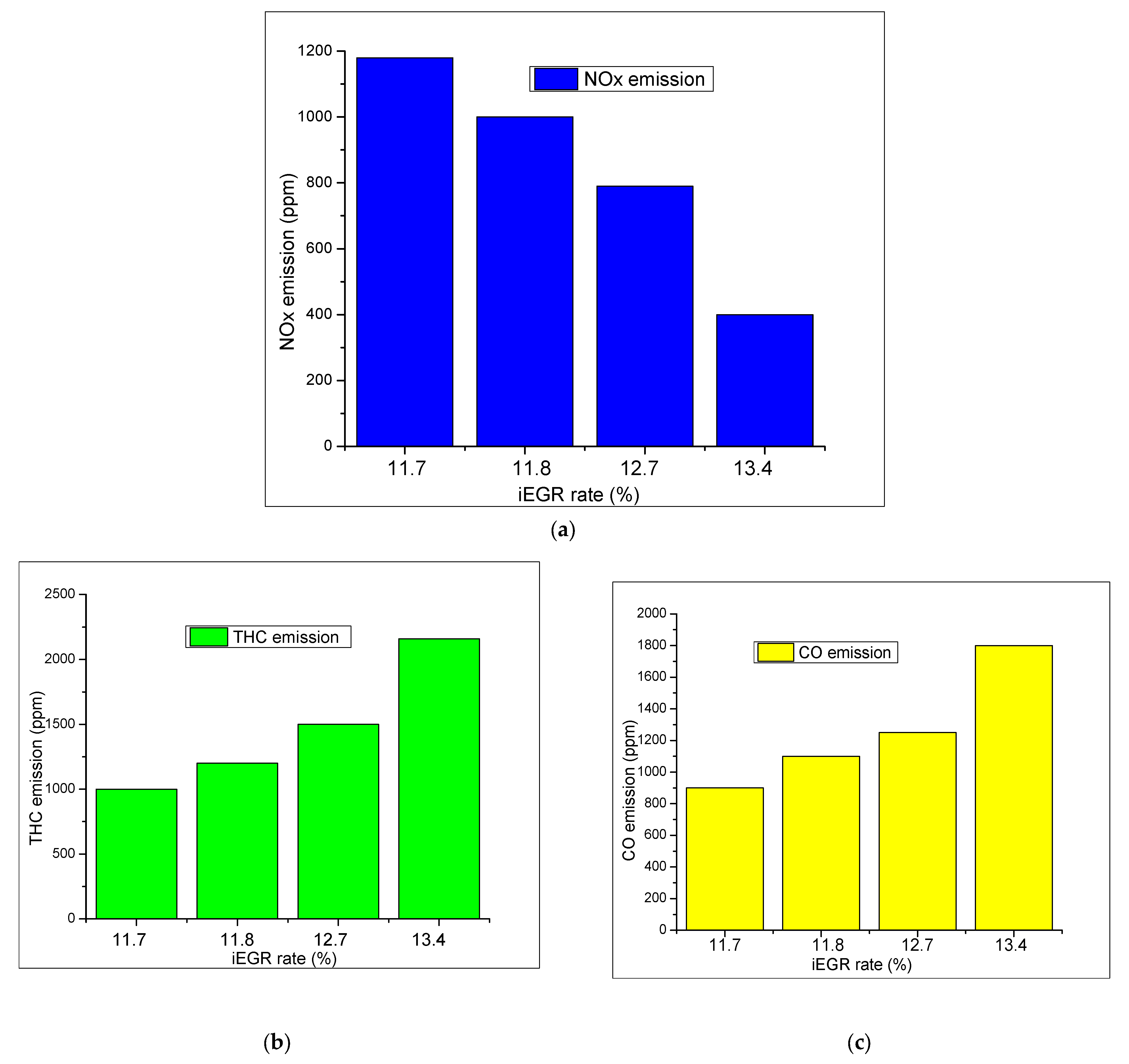
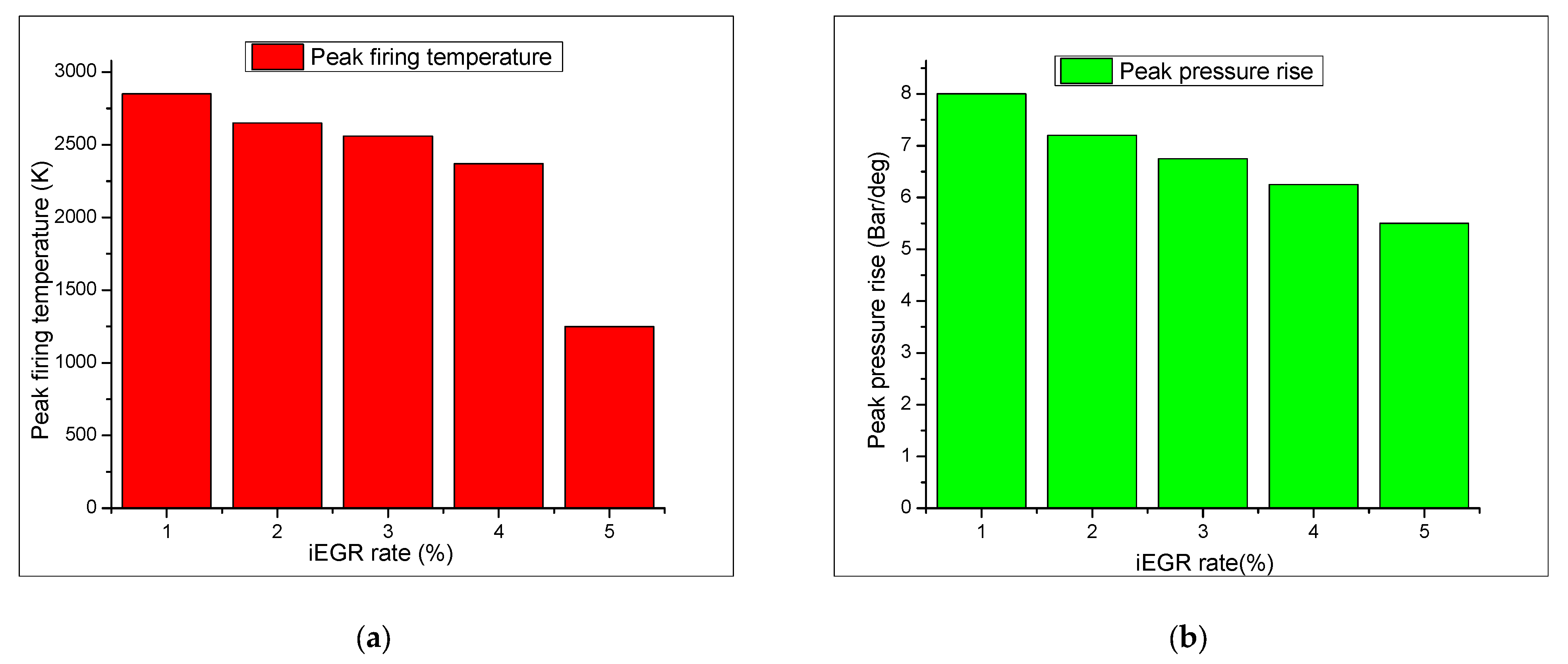
3.1. The Effect of iEGR on Engine Performance and Emission Characteristics
3.2. Control Strategies and Prediction of iEGR Methods
4. Conclusions
- Due to the benefits of reducing NOx emissions and improving ISFC and engine efficiency, both iEGR and eEGR are commonly used in modern internal combustion engines. Gasoline engines can improve ISFC and engine thermal efficiency at low loads, while hydrogen-fueled engines can operate without knock at a higher equivalence ratio. Exhaust gas recirculation can be used to suppress knock, improve engine efficiency, and reduce NOx emissions from a spark-ignition engine, but requires a high degree of precise technical control.
- Internal combustion engines using exhaust gas recirculation can reduce NOx emissions due to the resulting decrease in combustion temperatures, cylinder head flux, and oxygen concentrations. However, exhaust gas recirculation will increase hydrocarbon, CO, and soot emissions, ignition delays, and combustion duration. The increase in soot emission is due to increased carbon deposits, which also reduce the quality of lubricating engine oil and therefore causes an increase in engine wear. The increase in combustion duration is due to increased heat loss transfer.
- The iEGR method reduces NOx emissions to a lesser extent than the eEGR method because the exhaust gas recirculation rate is lower with iEGR. However, iEGR involves a lower initial cost, easier packaging and the potential for retrofits, lower maintenance cost, greater reliability, and a higher tolerance of high-sulfur fuels. It offers improved cold engine starts and warm-up periods.
- Exhaust gas recirculation control strategies, and determination equations for eEGR and iEGR were also reported. Depending on an engine’s operating condition, a suitable combination of an exhaust gas recirculation control strategy and determination equation should be selected for optimal efficiency.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, G.; Lee, S.; Park, C.; Choi, Y.; Kim, C. Effect of ignition timing retard strategy on NOx reduction in hydrogen-compressed natural gas blend engine with increased compression ratio. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 2399–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.V.; García-Oliver, J.M.; García, A.; Pinotti, M. Effect of laser induced plasma ignition timing and location on Diesel spray combustion. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 133, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şöhret, Y.; Gürbüz, H.; Akçay, İ.H. Energy and exergy analyses of a hydrogen fueled SI engine: Effect of ignition timing and compression ratio. Energy 2019, 175, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Nagarajan, G.; Rao, G.L.N.; Sampath, S. Theoretical and experimental investigation on effect of injection timing on NOx emission of biodiesel blend. Energy 2014, 66, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Dhar, A.; Gupta, J.G.; Kim, W.I.; Lee, C.S.; Park, S. Effect of fuel injection pressure and injection timing on spray characteristics and particulate size-number distribution in a biodiesel fuelled common rail direct injection diesel engine. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljamali, S.; Abdullah, S.; Mahmood, W.M.F.W.; Ali, Y. Effect of fuel injection timings on performance and emissions of stratified combustion CNGDI engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 109, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, S.; Turner, J.W.; Sileghem, L.; Vancoillie, J. Methanol as a fuel for internal combustion engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2019, 70, 43–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartakovsky, L.; Sheintuch, M. Fuel reforming in internal combustion engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 67, 88–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, C.; Kim, Y.; Choi, Y.; Bae, J.; Lim, B. Effect of turbocharger on performance and thermal efficiency of hydrogen-fueled spark ignition engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 4350–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, S.; Maesschalck, P.; Rombaut, N.; Sierens, R. Increasing the power output of hydrogen internal combustion engines by means of supercharging and exhaust gas recirculation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 4406–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, R.K. Text Book “Internal Combusion Engine”; Laxmi-Publications: Delhi, India, 2008; Available online: https://www.kopykitab.com/A-Textbook-Of-Internal-Combustion-Engines-by-Er-R-K-Rajput (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Ganesan, V. Text Book “Internal Combustion Engine”; Tata McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Available online: https://books.google.com.vn/books?id=hfejAwAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=internal+combustion+engine+book&hl=vi&sa=X&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=internal%20combustion%20engine%20book&f=false (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Ayhan, V.; Ece, Y.M. New application to reduce NOx emissions of diesel engines: Electronically controlled direct water injection at compression stroke. Appl. Energy 2020, 260, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zheng, Z.; Peng, T. Effect of water injection on the knock, combustion, and emissions of a direct injection gasoline engine. Fuel 2020, 268, 117376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Cong, X.; Ma, Z.; Tang, C.; Meng, H.; Shi, C. Effects of direct water injection on engine performance in engine fueled with hydrogen at varied excess air ratios and spark timing. Fuel 2020, 269, 117209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Teng, Q.; He, B.; Chen, W.; Qian, Y. Investigation of water injection benefits on downsized boosted direct injection spark ignition engine. Fuel 2020, 264, 116765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Hu, B.; Akehurst, S.; Copeland, C.; Lewis, A.; Yuan, H.; Kennedy, I.; Bernards, J.; Branney, C. A review of water injection applied on the internal combustion engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 184, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, G.; Guo, F.; Xie, J. Development of wide-temperature vanadium-based catalysts for selective catalytic reducing of NOx with ammonia: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Dinesha, P.; Kumar, S. NOx reduction behaviour in copper zeolite catalysts for ammonia SCR systems: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Lee, M.; Jeong, B.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.H.; Baik, J.M.; Kim, H.D. Partially reduced graphene oxide as a support of Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Today 2018, 328, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, R.; Zhou, X.; Huang, H.; Pan, J.; Chen, Z. Reduction in PM and NOX of a diesel engine integrated with n-octanol fuel addition and exhaust gas recirculation. Energy 2019, 187, 115946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Shim, E.; Bae, C. Improvement of combustion and emissions with exhaust gas recirculation in a natural gas-diesel dual-fuel premixed charge compression ignition engine at low load operations. Fuel 2018, 235, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheeba, C.N.; Aghalayam, P. Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation in NOx Control for Compression Ignition and Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition Engines. Phys. Procedia 2015, 66, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Heffel, J.W. NOx emission and performance data for a hydrogen fueled internal combustion engine at 1500 rpm using exhaust gas recirculation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2003, 28, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, U.; Zheng, M. Exhaust gas recirculation for advanced diesel combustion cycles. Appl. Energy 2014, 123, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
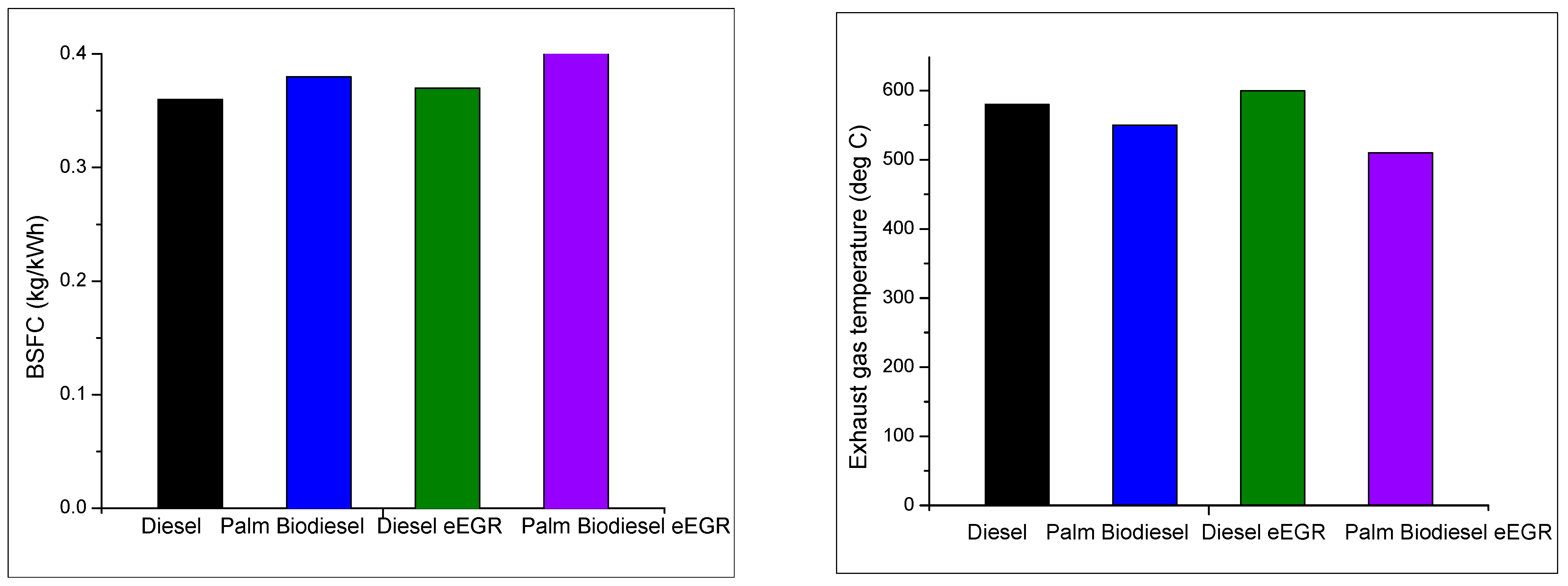
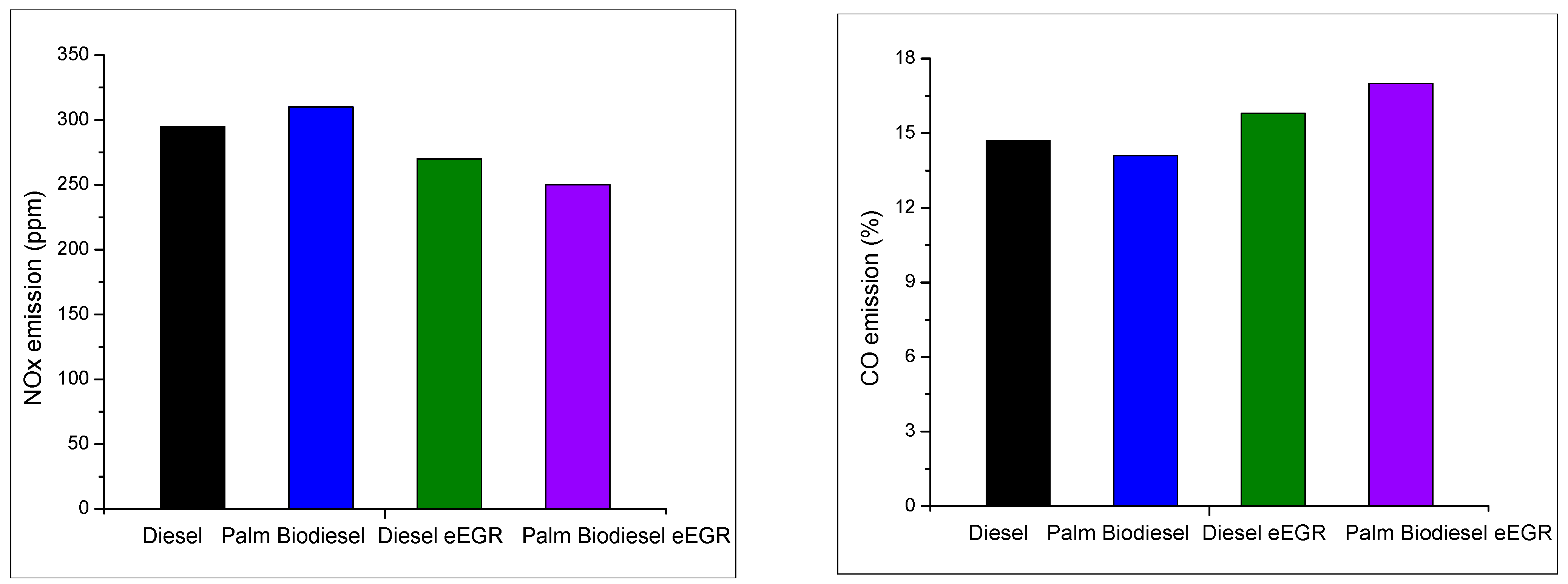
- Venu, H.; Subramani, L.; Raju, V.D. Emission reduction in a DI diesel engine using exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) of palm biodiesel blended with TiO2 nano additives. Renew. Energy 2019, 140, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.A.D.; di Nunno, D. Internal Exhaust Gas Recirculation for Efficiency and Emissions in a 4-Cylinder Diesel Engine. In Proceedings of the SAE 2016 International Powertrains, Fuels & Lubricants Meeting, Baltimore, MD, USA, 24–26 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Cui, Y.; Deng, K.; Peng, H.; Chen, Y. Study of low emission homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engine using combined internal and external exhaust gas recirculation (EGR). Energy 2006, 31, 2665–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimbo, T.; Hayakawa, Y. Model predictive control for automotive engine torque considering internal exhaust gas recirculation. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2011, 44, 12991–12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, C.; Triantopoulos, V.; Bares, P.; Bohac, S.; Stefanopoulou, A. Simultaneous Estimation of Intake and Residual Mass Using In-Cylinder Pressure in an Engine with Negative Valve Overlap. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. Four-stroke CAI engines with residual gas trapping. HCCI CAI Engines Automot. Ind. 2007, 103–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschaeren, R.; Schaepdryver, W.; Serruys, T.; Bastiaen, M.; Vervaeke, L.; Verhelst, S. Experimental study of NOx reduction on a medium speed heavy duty diesel engine by the application of EGR (exhaust gas recirculation) and Miller timing. Energy 2014, 76, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Shen, B. Effect of exhaust gases of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) coupling lean-burn gasoline engine on NOx purification of Lean NOx trap (LNT). Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 87, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, F.; Liu, J.; Xia, Y.; Wang, S. Experimental investigation on the influences of exhaust gas recirculation coupling with intake tumble on gasoline engine economy and emission performance. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 127, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, E. Handbook of Air Pollution From Internal Combustion Engines; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Alla, G.H. Using exhaust gas recirculation in internal combustion engines: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 1027–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Reader, G.T.; Hawley, J.G. Diesel engine exhaust gas recirculation—A review on advanced and novel concepts. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 883–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorathia, H.S.; Rahhod, P.P.; Sorathiya, A.S.; Engineering, M.; College, G.E.; Kutch, B. Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) on NOx emission CI engine—A review study. Ijaers 2012, 1, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Thangaraja, J.; Kannan, C. Effect of exhaust gas recirculation on advanced diesel combustion and alternate fuels—A review. Appl. Energy 2016, 180, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Das, L.M.; Kaushik, S.C.; Bhatti, S.S. The effects of compression ratio and EGR on the performance and emission characteristics of diesel-biogas dual fuel engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 150, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavuri, C.; Kokjohn, S.L. Computational optimization of a reactivity controlled compression ignition (RCCI) combustion system considering performance at multiple modes simultaneously. Fuel 2017, 207, 702–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, H. Physical characterization of particulate emissions from diesel engines: A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 896–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Jia, M.; Li, Y.; Chang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, T. Evaluation of variable compression ratio (VCR)and variable valve timing (VVT)strategies in a heavy-duty diesel engine with reactivity controlled compression ignition (RCCI)combustion under a wide load range. Fuel 2019, 253, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirkude, J.; Belokar, V.; Randhir, J. Effect of Compression Ratio, Injection Pressure and Injection Timing on Performance and Smoke Emissions of CI engine Fuelled with Waste Fried Oil Methyl Esters—Diesel Blend. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Harley, R.A.; Kreisberg, N.M.; Stolzenburg, M.R.; Hering, S.V. On-road measurement of fine particle and nitrogen oxide emissions from light- and heavy-duty motor vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2955–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torregrosa, A.J.; Broatch, A.; Olmeda, P.; Salvador-Iborra, J.; Warey, A. Experimental study of the influence of exhaust gas recirculation on heat transfer in the firedeck of a direct injection diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 153, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, D.; Singh, S.K.; Agarwal, A.K. Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) on performance, emissions, deposits and durability of a constant speed compression ignition engine. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2900–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, A.J.; Garner, C.P.; Taylor, D.H.C. The Effect of EGR on Diesel Engine Wear. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- George, S.; Balla, S.; Gautam, M. Effect of diesel soot contaminated oil on engine wear. Wear 2006, 262, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, L.; Zhu, S.; Liu, B.; Qian, Y.; Deng, K. Numerical and thermodynamic study on effects of high and low pressure exhaust gas recirculation on turbocharged marine low-speed engine. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, O.I.; Mamat, R.; Ali, O.M.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Yusaf, T.; Kadirgama, K.; Kettner, M. Alcohol and ether as alternative fuels in spark ignition engine: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 82, 2586–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, R.; Sani, M.S.M.; Sudhakar, K.; Kadarohman, A.; Sardjono, R.E. An overview of Higher alcohol and biodiesel as alternative fuels in engines. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balki, M.K.; Sayin, C. The effect of compression ratio on the performance, emissions and combustion of an SI (spark ignition) engine fueled with pure ethanol, methanol and unleaded gasoline. Energy 2014, 71, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosha, P.; Mohapatra, S.K.; Mahla, S.K.; Cho, H.M.; Chauhan, B.S.; Dhir, A. Effect of compression ratio on combustion, performance, and emission characteristics of compression ignition engine fueled with palm (B20)biodiesel blend. Energy 2019, 178, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, C.; Bae, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, Y.; Lim, B. Effect of different excess air ratio values and spark advance timing on combustion and emission characteristics of hydrogen-fueled spark ignition engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 25021–25030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, D.B.; Misra, A.; Medhekar, S. Investigations on the combustion parameters of a dual fuel diesel engine with hydrogen and LPG as secondary fuels. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 13808–13819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.C.; Belgiorno, G.; di Blasio, G.; Agarwal, A.K. Alcohol as an Alternative Fuel for Internal Combustion Engines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Jia, M.; Chang, Y.; Fan, W.; Xie, M.; Wang, T. Evaluation of the necessity of exhaust gas recirculation employment for a methanol/diesel reactivity controlled compression ignition engine operated at medium loads. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 101, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Kumar, N.M.; Ettappan, M.; Dhanagopal, R.; Vishnupriyan, J. Effect of exhaust gas re-circulation on performance, emission and combustion characteristics of ethanol-fueled diesel engine. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 20, 100643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Ju, D.; Tang, Q.; Fang, X.; Zhou, F. Experimental study of effects of exhaust gas recirculation on combustion, performance, and emissions of DME-biodiesel fueled engine. Energy 2020, 197, 117233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Lei, X.; Liu, S. Combustion and emission characteristics of a DME (dimethyl ether)-diesel dual fuel premixed charge compression ignition engine with EGR (exhaust gas recirculation). Energy 2014, 72, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, B.L.; Subramanian, K.A. Experimental investigation on effects of compression ratio and exhaust gas recirculation on backfire, performance and emission characteristics in a hydrogen fuelled spark ignition engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 5842–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
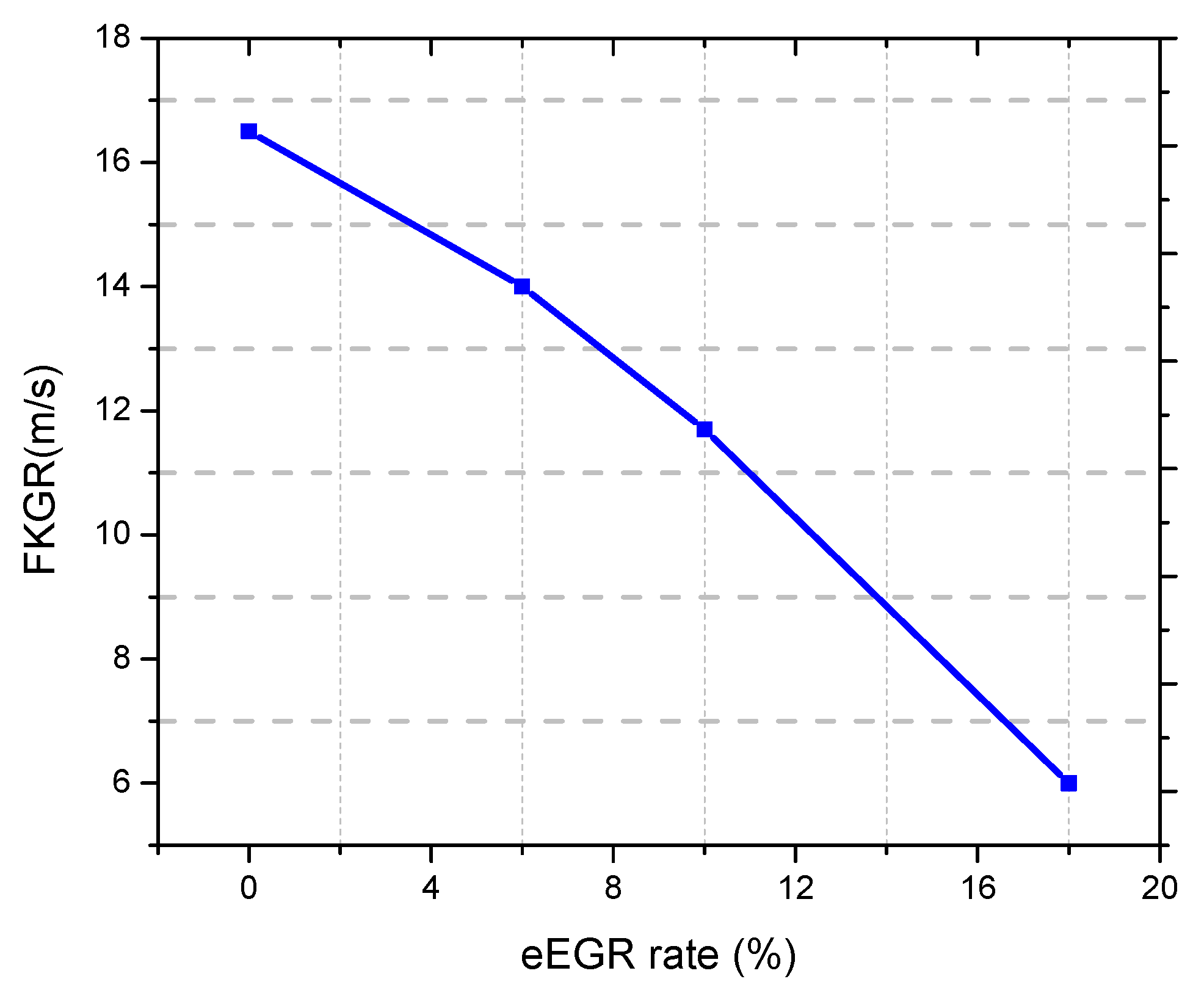
- Salvi, B.L.; Subramanian, K.A. Experimental investigation on effects of exhaust gas recirculation on flame kernel growth rate in a hydrogen fuelled spark ignition engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 107, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.M.; Mathur, R. Exhaust gas recirculation for Nox control in a multicylinder hydrogen-supplemented S.I. engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1993, 18, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, M.H.M.; Mamat, R.; Yusop, A.F.; Paruka, P.; Yusaf, T.; Najafi, G. Effects of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) on a Diesel Engine fuelled with Palm-biodiesel. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Lee, S. An investigation on the potential of dedicated exhaust gas recirculation for improving thermal efficiency of stoichiometric and lean spark ignition engine operation. Appl. Energy 2018, 228, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, F.; de Bellis, V.; Teodosio, L. Potentials of cooled EGR and water injection for knock resistance and fuel consumption improvements of gasoline engines. Appl. Energy 2016, 169, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.; Kim, C.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, Y.; Park, C. Comparative study on EGR and lean burn strategies employed in an SI engine fueled by low calorific gas. Appl. Energy 2014, 129, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimore, T.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Wyszynski, M.L.; Shuai, S. Investigation of EGR Effect on Combustion and PM Emissions in a DISI Engine. Appl. Energy 2016, 161, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, D.; Tsuchida, H.; Kobara, T.; Akagi, M.; Tsuyuki, T.; Nagamine, M. Study of an egr system for downsizing turbocharged gasoline engine to improve fuel economy. SAE Tech. Pap. 2014, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean-burn, C.B. Comparison Between Lean-Burn and Stoichiometric Technologies for CNG Heavy-Duty Engines. In SAE Transactions; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Abdel-Gayed, R. Qualitative Governing Approach of a Spark Ignition Engine Using Exhaust Gas Recirculation. Phys. Procedia 2015, 66, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Ramalingam, A.; Minwegen, H.; Heufer, K.A.; Pitsch, H. Impact of exhaust gas recirculation on ignition delay times of gasoline fuel: An experimental and modeling study. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhu, T.; Shu, G.; Tan, L.; Wang, Y. Gasoline engine exhaust gas recirculation—A review. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladommatos, N.; Abdelhalim, S.M.; Zhao, H.; Hu, Z. The dilution, chemical, and thermal effects of exhaust gas recirculation on diesel engine emissions-part 2: Effects of carbon dioxide. SAE Trans. 1996, 1844–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohketsu, S.; Mori, K.; Sakai, K.; Hakozaki, T. EGR technologies for a turbocharged and intercooled heavy-duty diesel engine. SAE Trans. 1997, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, R.S.G.; Beckman, D.E.; Veen, A. Efficient EGR technology for future HD diesel engine emission targets. SAE Trans. 1999, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, K.; Elonheimo, A.; Häkkinen, K.; Sarjovaara, T.; Larmi, M. Emission reduction using hydrotreated vegetable oil (HVO) with miller timing and EGR in diesel combustion. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2011, 5, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andwari, A.M.; Aziz, A.A.; Said, M.F.M.; Latiff, Z.A. Experimental investigation of the influence of internal and external EGR on the combustion characteristics of a wcontrolled auto-ignition two-stroke cycle engine. Appl. Energy 2014, 134, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, M.; Finesso, R.; Misul, D.; Spessa, E. Comparison between Internal and External EGR Performance on a Heavy Duty Diesel Engine by Means of a Refined 1D Fluid-Dynamic Engine Model. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1977–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozarac, D.; Vuilleumier, D.; Saxena, S.; Dibble, R.W. Analysis of benefits of using internal exhaust gas recirculation in biogas-fueled HCCI engines. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 87, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwaja, S.; Ansari, E.; Rao, S.; Szwaja, M.; Grab-Rogalinski, K.; Naber, J.D.; Pyrc, M. Influence of exhaust residuals on combustion phases, exhaust toxic emission and fuel consumption from a natural gas fueled spark-ignition engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 165, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa RB, R.; Hernández, J.J.; Teixeira, A.F.; Netto NA, D.; Valle, R.M.; Roso, V.R.; Coronado, C.J. Combustion, performance and emission analysis of a natural gas-hydrous ethanol dual-fuel spark ignition engine with internal exhaust gas recirculation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 195, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hua, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, F.; Feng, D.; Wei, H. Effect of internal exhaust gas recirculation on the combustion characteristics of gasoline compression ignition engine under low to idle conditions. Energy 2018, 164, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa, N.X.; Lim, O. Comparative Study of the Effective Release Energy, Residual Gas Fraction, and Emission Characteristics with Various Valve Port Diameter-Bore Ratios (VPD/B) of a Four-Stroke Spark Ignition Engine. Energies 2020, 13, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
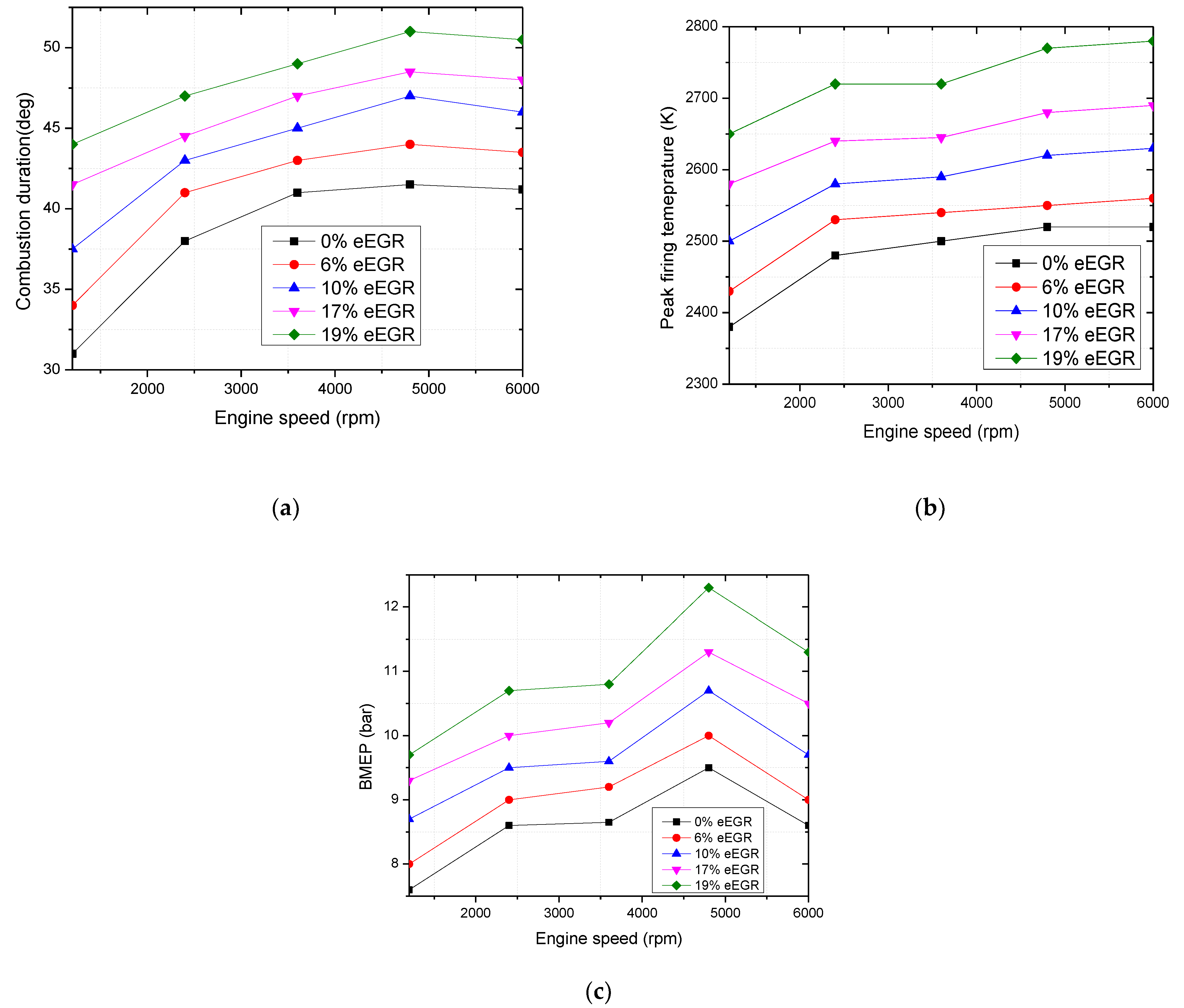
- Khoa, N.X.; Kang, Y.; Lim, O. The effects of combustion duration on residual gas, effective release energy and engine power of motorcycle engine at full load. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa, N.X.; Lim, O. The effects of combustion duration on residual gas, effective release energy, engine power and engine emissions characteristics of the motorcycle engine. Appl. Energy 2019, 248, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
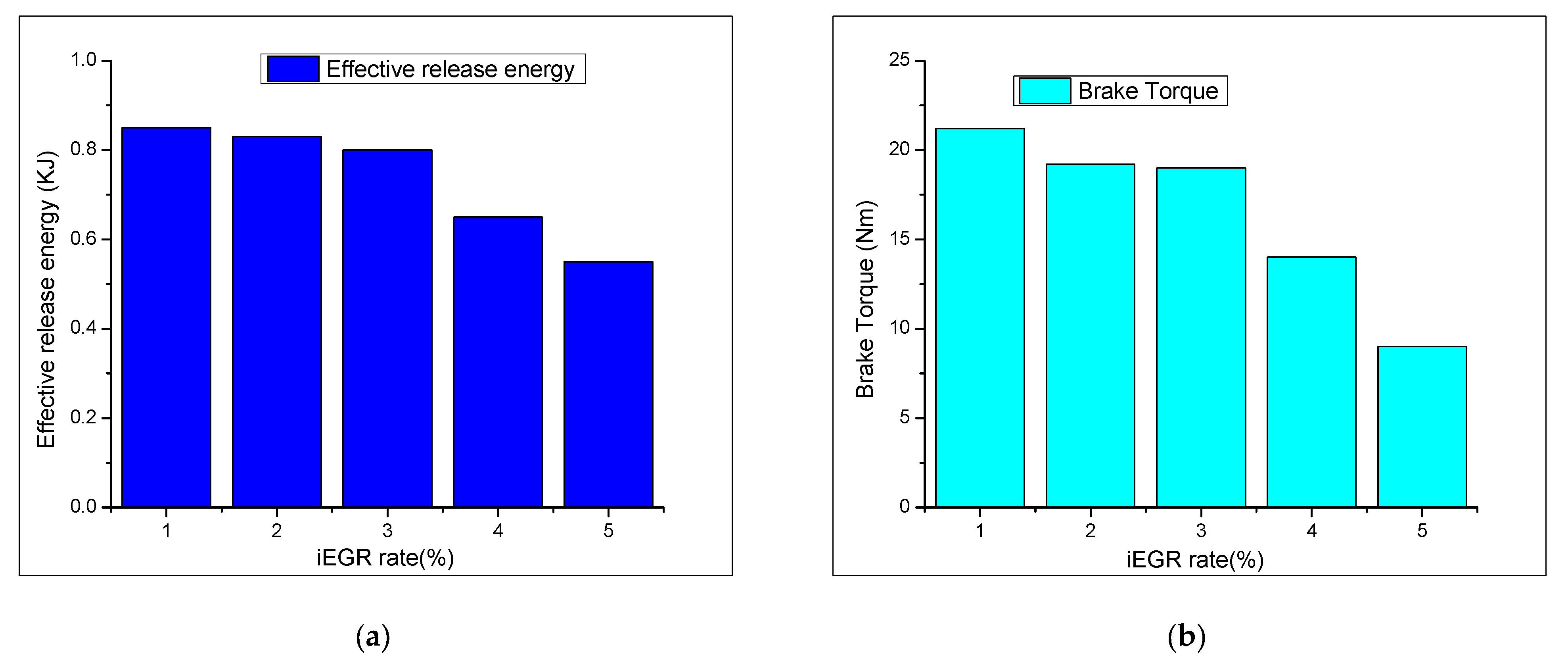
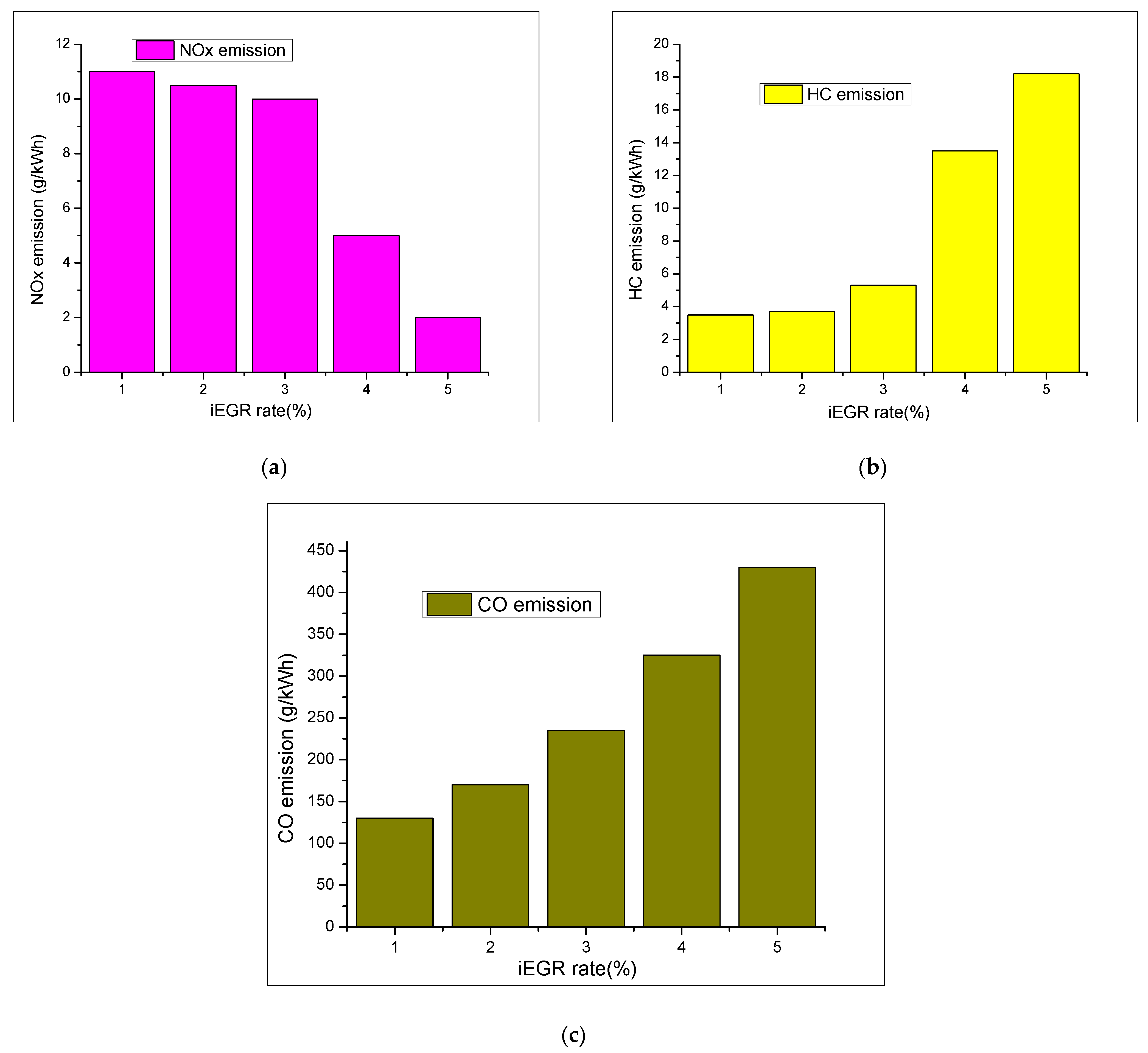
- Khoa, N.X.; Nhu, Y.Q.; Lim, O. Estimation of parameters affected in internal exhaust residual gases recirculation and the influence of exhaust residual gas on performance and emission of a spark ignition engine. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, B.P. Residual Gas Effects on Combustion in an Air-Cooled Utility Engine. Master’s Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khoa, N.X.; Lim, O.T. Effective release energy, residual gas, and engine emission characteristics of a V-twin engine with various exhaust valve closing timings. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.W.G.; Bassett, M.D.; Pearson, R.J.; Pitcher, G.; Douglas, K.J. New operating strategies afforded by fully variable valve trains. In 2004 SAE World Congress; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Milovanovic, N.; Dave, B.; Gedge, S.; Turner, J. Cam Profile Switching (CPS) and phasing strategy vs Fully Variable Valve Train (FVVT) strategy for transitions between spark ignition and controlled auto ignition modes. In 2005 SAE World Congress; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2005; Volume 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Sichuan, X.; Du, A. Research on a New Electromagnetic Valve Actuator Based on Voice Coil Motor for Automobile Engines. In SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwoerer, J.; Dodi, S.; Fox, M.; Huang, S.; Yang, Z. Internal EGR systems for NOx emission reduction in heavy-duty diesel engines. In SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2004; Volume 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millo, F.; Mallamo, F.; Arnone, L.; Bonanni, M.; Franceschini, D. Analysis of different internal EGR solutions for small diesel engines. In SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007; Volume 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benajes, J.; Reyes, E.; Luján, J.M. Intake valve pre-lift effect on the performance of a turbocharged diesel engine. In SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1996; Volume 96, pp. 1407–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, W. Potential of Variable Valve Actuation in Diesel Engines for Light Duty Vehicles. In Proceedings of the ATA International Symposium on the Future of Diesel Engine Technology for Passenger Cars, Costa Smerelda, Italy, 12–13 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vafidis, C.; Piccinini, A.; Gianolio, L. Variable Valve Actuation for In-Cylinder Charge and Combustion Control in D.I. Diesel Engines. In Proceedings of the IFP International Congress a New Generation of Engine Combustion Processes for the Future, Rueil Malmaison, France, 26–27 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzanova, T.D.M.; Nora, M.D.; Martins, M.E.S.; Machado, P.R.M.; Pedrozo, V.B.; Zhao, H. The effects of residual gas trapping on part load performance and emissions of a spark ignition direct injection engine fuelled with wet ethanol. Appl. Energy 2019, 253, 113508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.; Moon, G.; Jeong, D.; Bae, C. Effects of internal exhaust gas recirculation on controlled auto-ignition in a methane engine combustion. Fuel 2009, 88, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lai, M.C.; Jansons, M.; Guo, G.; Zhang, S.; Tang, Q. Experimental and numerical investigation of the effects of low-pressure, high-pressure and internal EGR configurations on the performance, combustion and emission characteristics in a hydrogen-enriched heavy-duty lean-burn natural gas SI engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 195, 1319–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

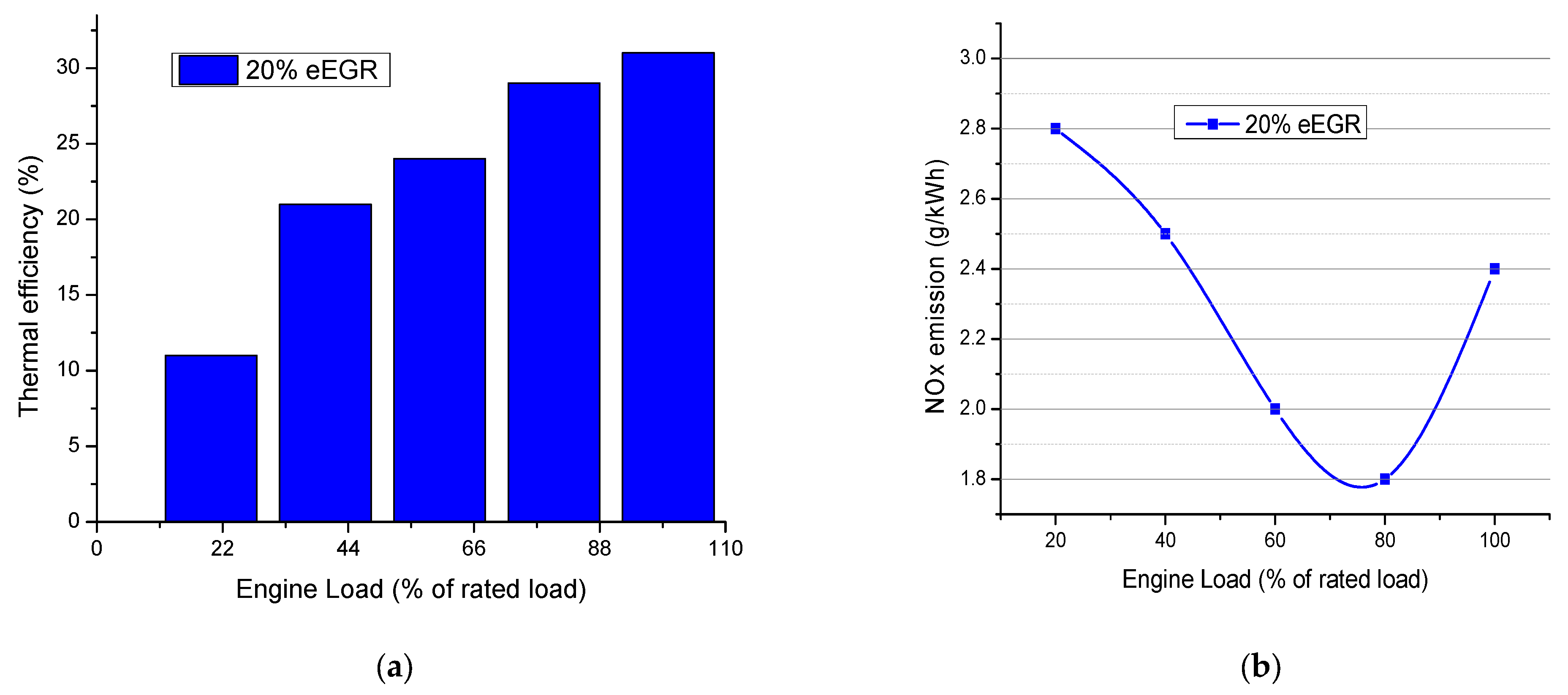
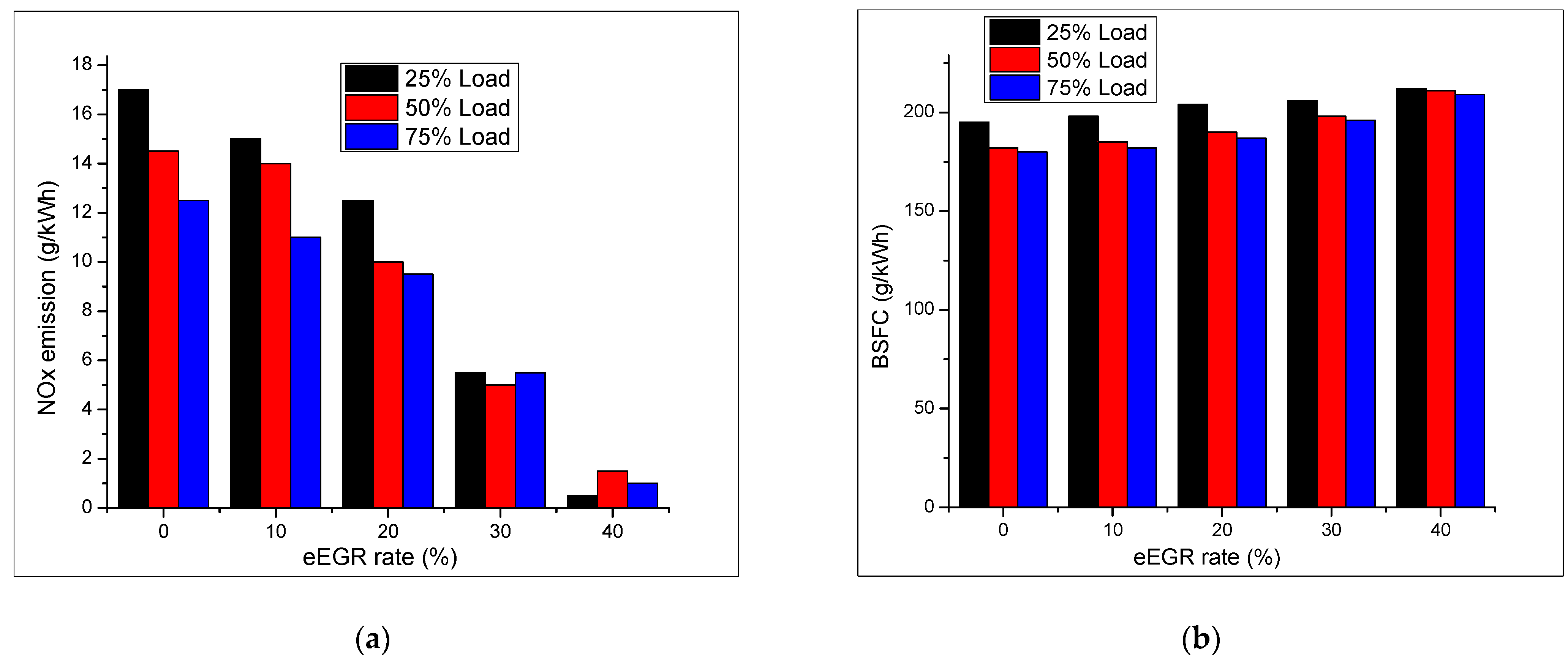
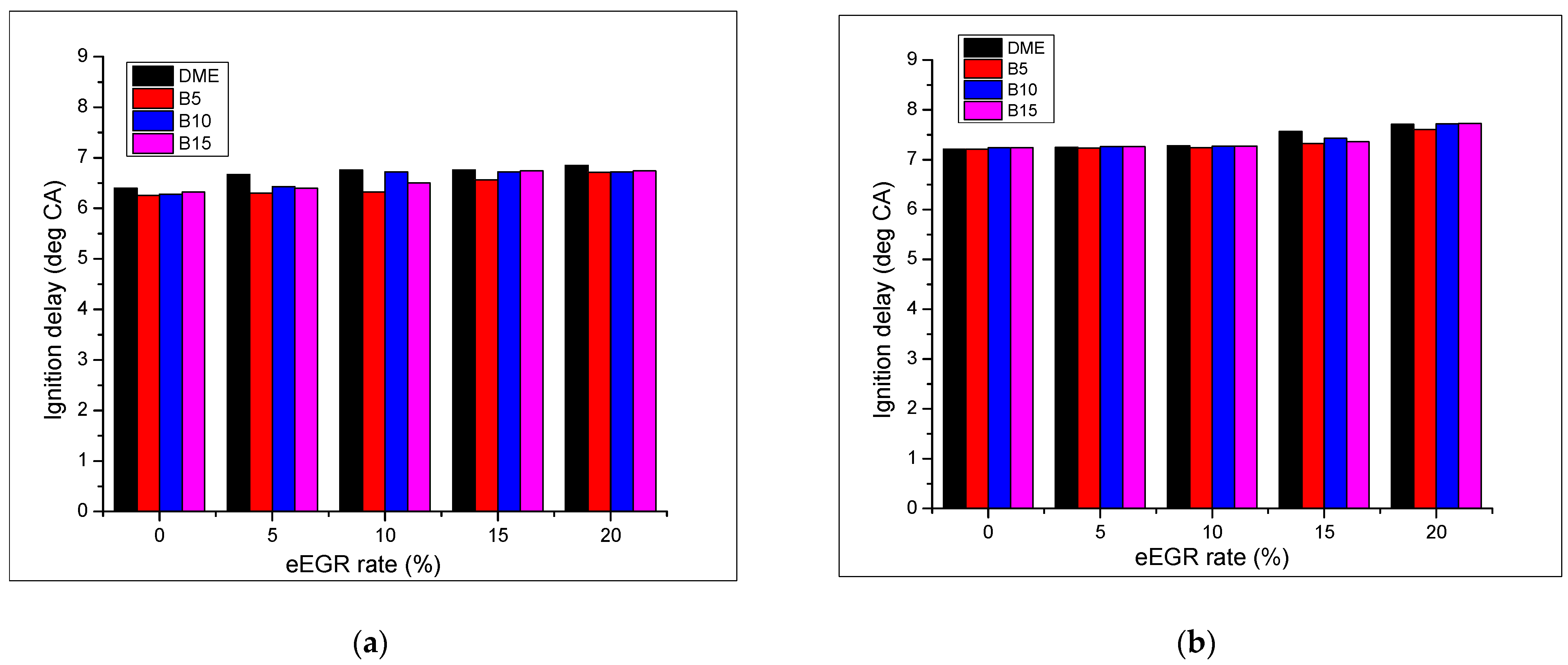
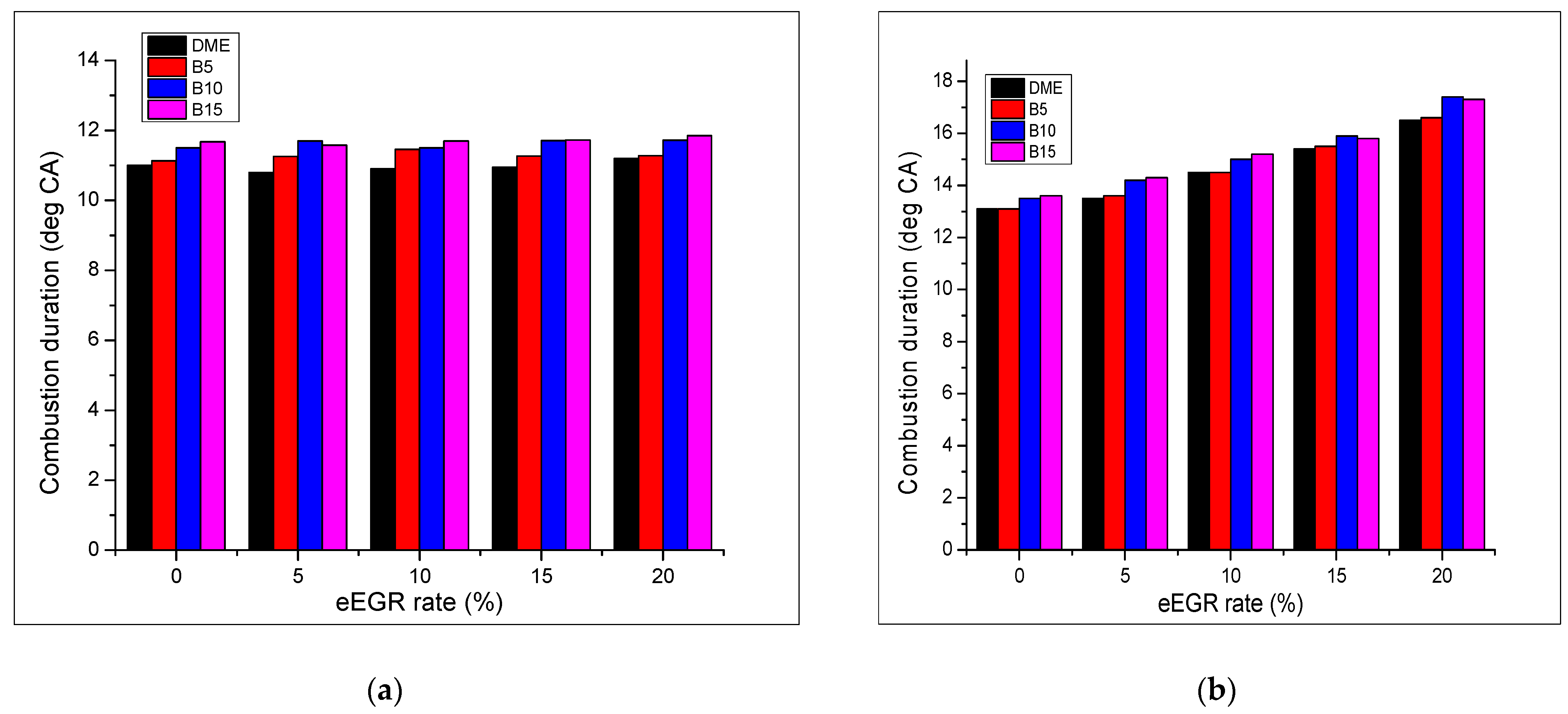

| Piston Ring Order | % Weight Loss | |
|---|---|---|
| With eEGR | Without eEGR | |
| 1 | 0.35 | 0.45 |
| 2 | 0.62 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 0.8 | 0.35 |
| Oil ring | 0.9 | 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khoa, N.X.; Lim, O. A Review of the External and Internal Residual Exhaust Gas in the Internal Combustion Engine. Energies 2022, 15, 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031208
Khoa NX, Lim O. A Review of the External and Internal Residual Exhaust Gas in the Internal Combustion Engine. Energies. 2022; 15(3):1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031208
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhoa, Nguyen Xuan, and Ocktaeck Lim. 2022. "A Review of the External and Internal Residual Exhaust Gas in the Internal Combustion Engine" Energies 15, no. 3: 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031208
APA StyleKhoa, N. X., & Lim, O. (2022). A Review of the External and Internal Residual Exhaust Gas in the Internal Combustion Engine. Energies, 15(3), 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031208





