Dynamic Equivalents in Power System Studies: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Historical Review of Research
- Disturbances, for example, short-circuits in the line, are forced, and measurements are made at various points in the system, e.g., at the place where the protection system is installed;
- Measurement devices connected to selected nodes record waveforms during disturbances (for which they are “waiting”).
- Modal analysis,
- Coherent grouping,
- Coherence–modal methods.
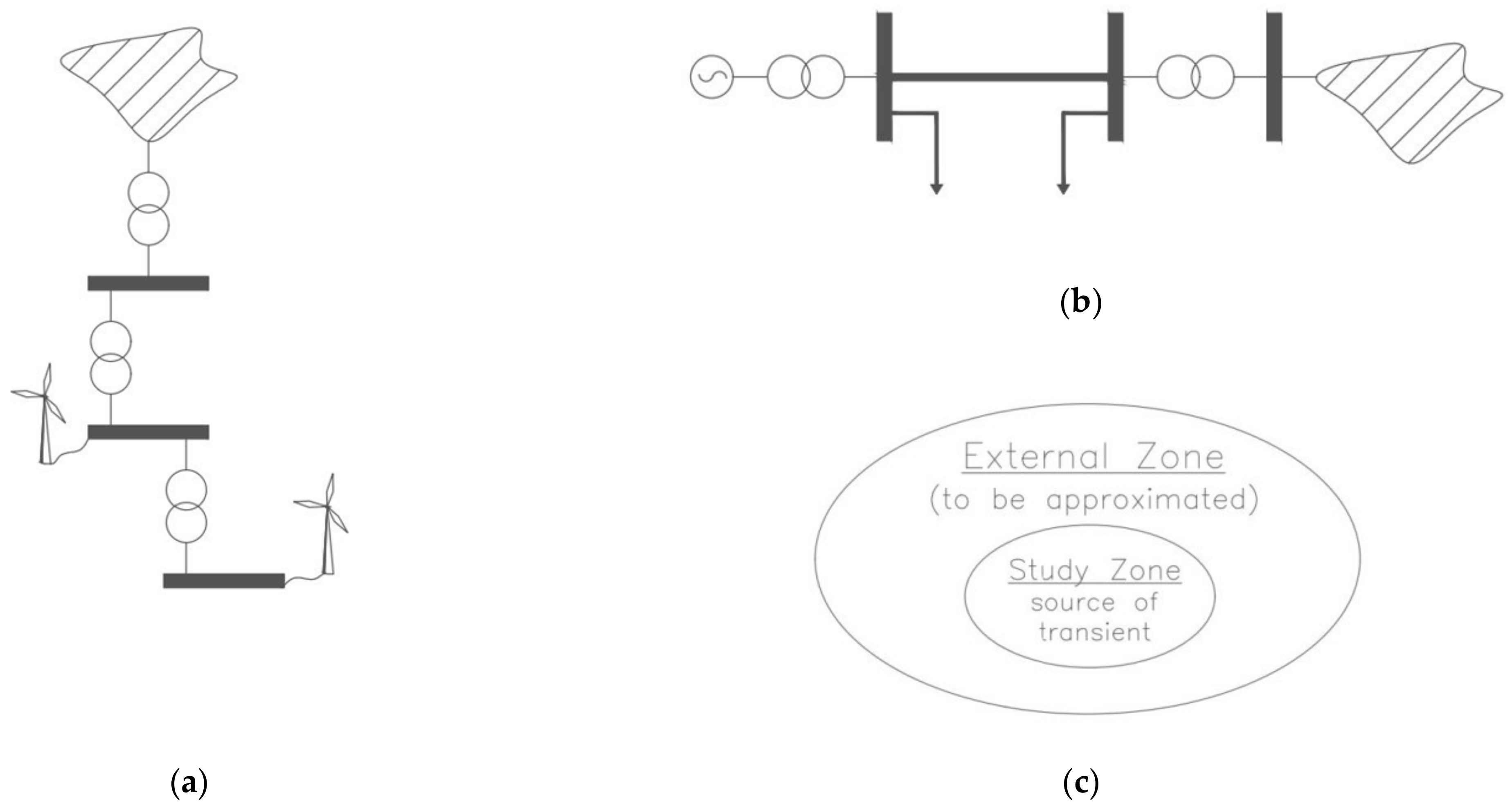
2. Searching for Structure of Equivalent Network
2.1. Principles and Conditions
- Measurements,
- Calculations in a layout with a complete and detailed representation of each element (without any simplifications),
- Calculations in an equivalent system.
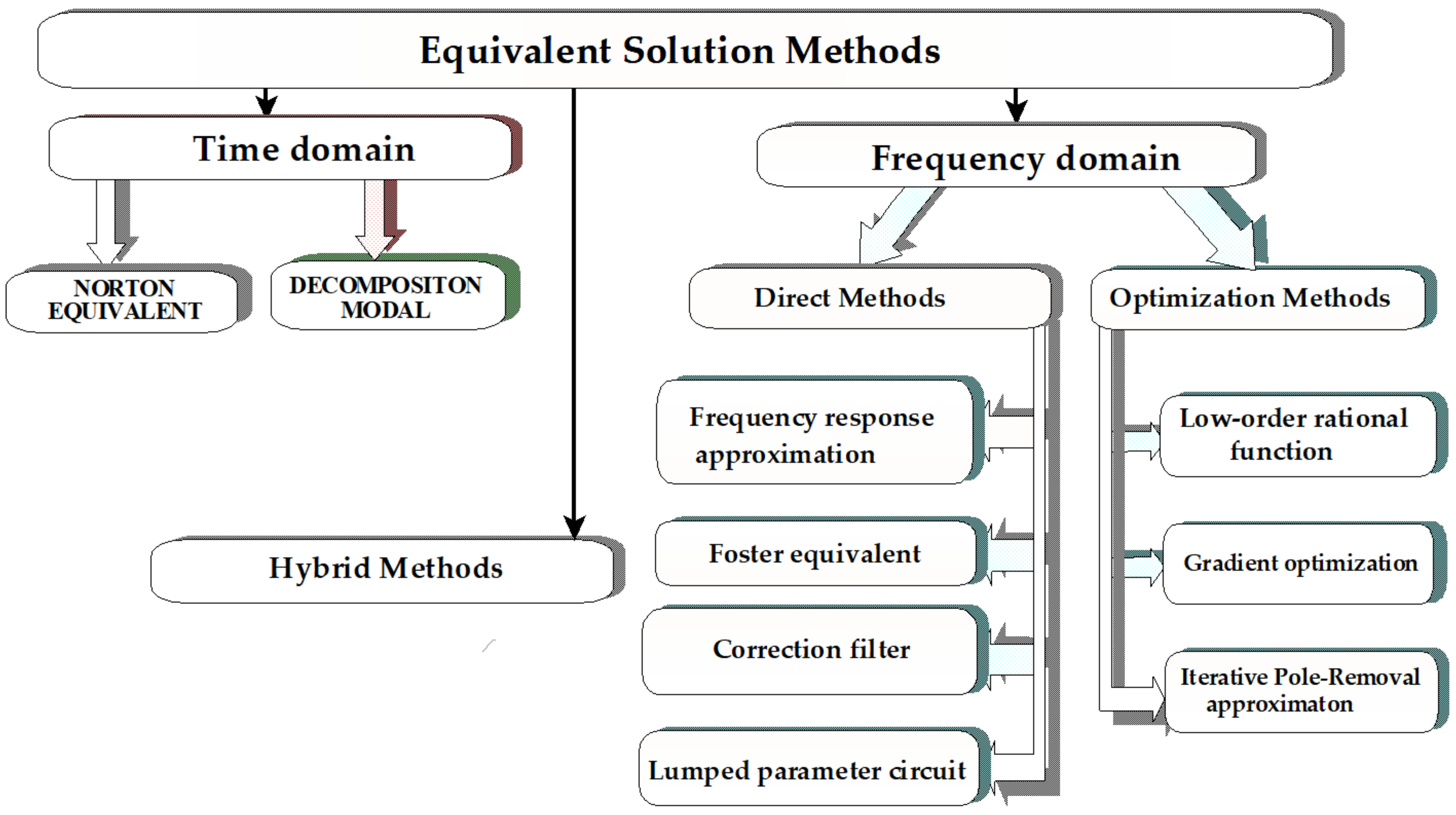
2.2. Methods of Searching for Optimal Structures
- There is no simple method to determine resonance frequencies for determining the parameters of the created equivalent diagrams;
- The location of the resonance frequencies is performed by approximation, and therefore, in order to increase the accuracy, the resolution of the characteristic should be increased;
- The frequency response for any external system is unpredictable for the selected frequency range;
- The calculation of the resistance in the equivalent diagrams is not accurate.
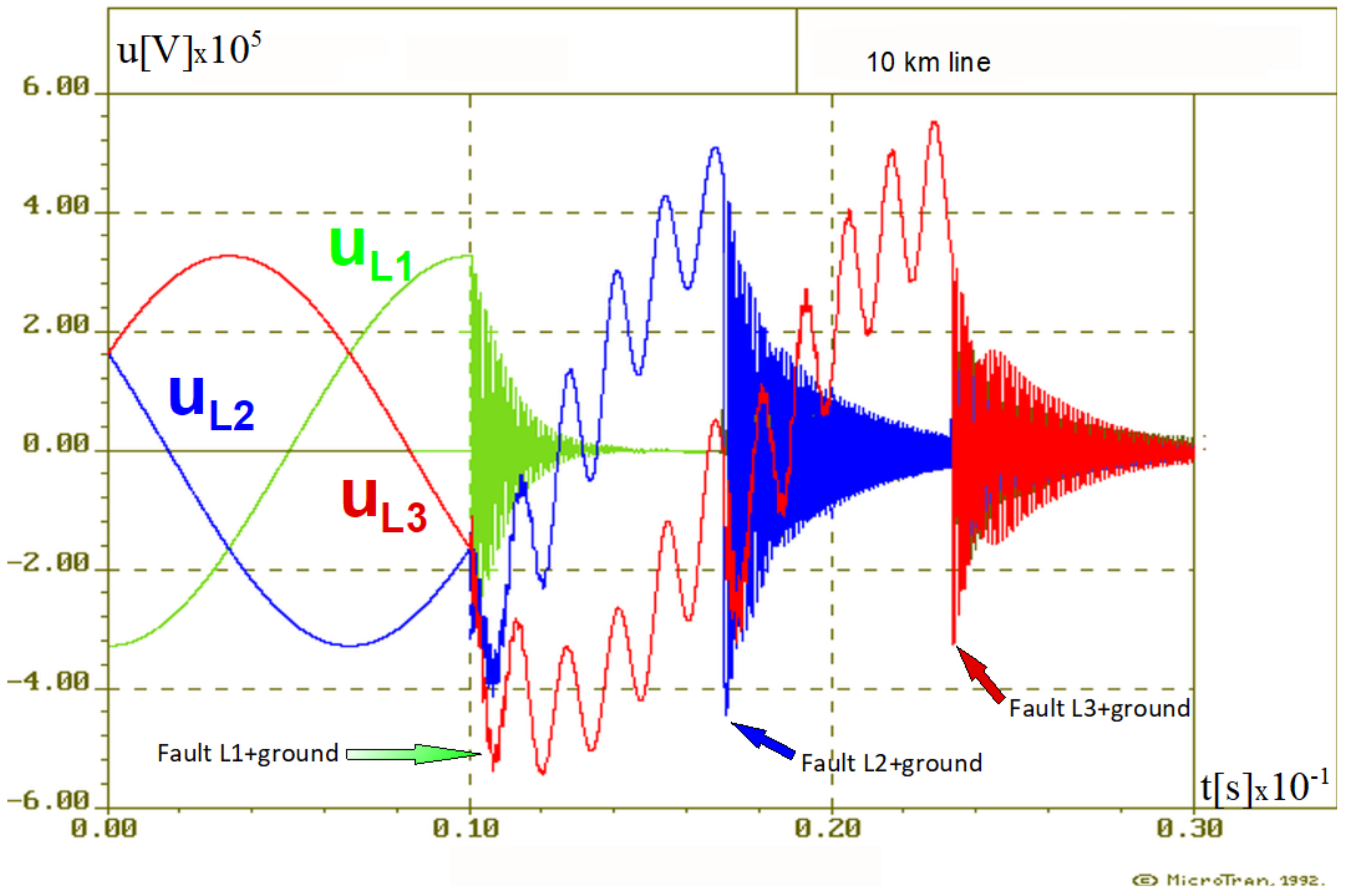
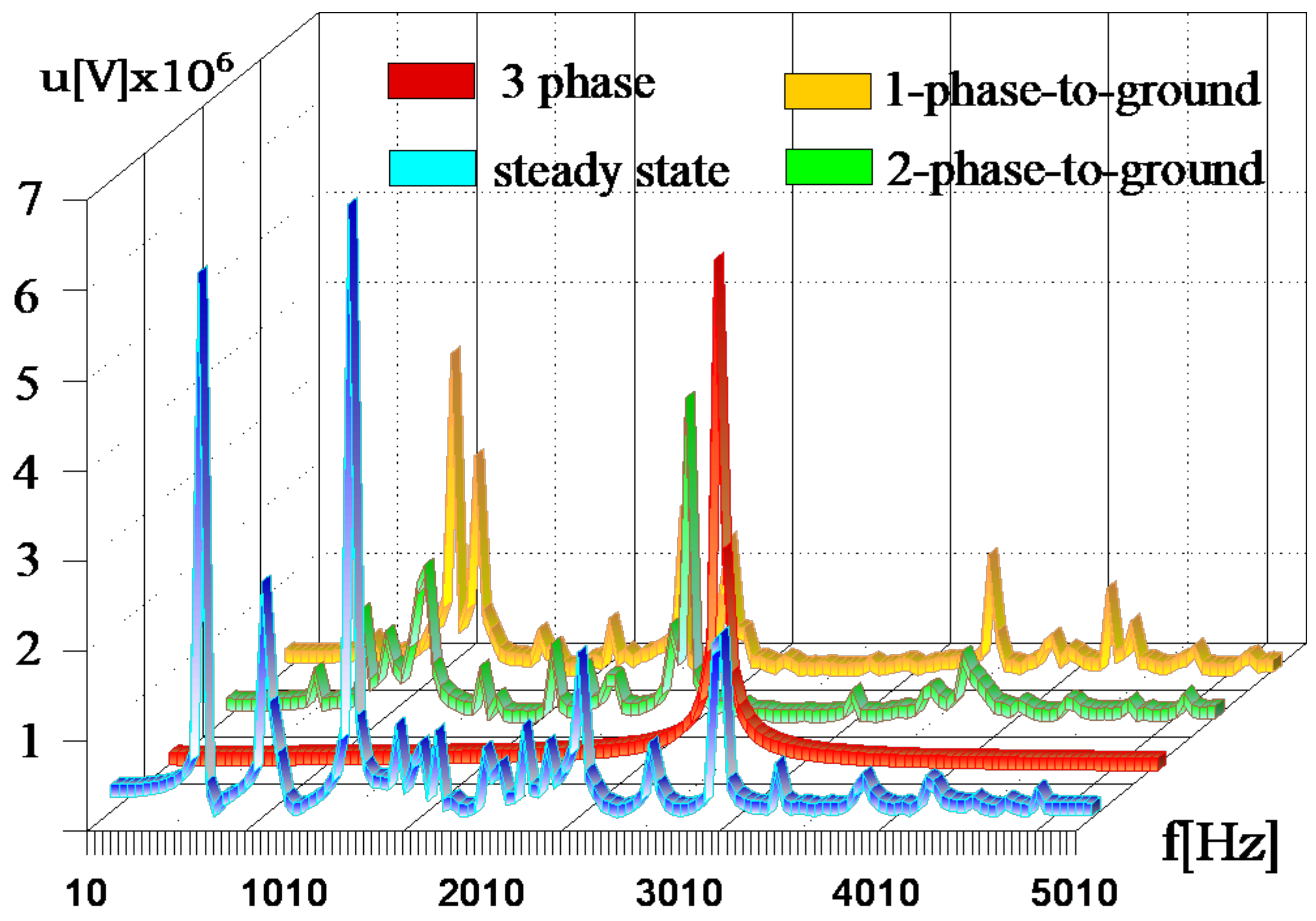
2.3. Contraindications to the Search for Equivalents in the Frequency Domain for the Study of Electromagnetic States
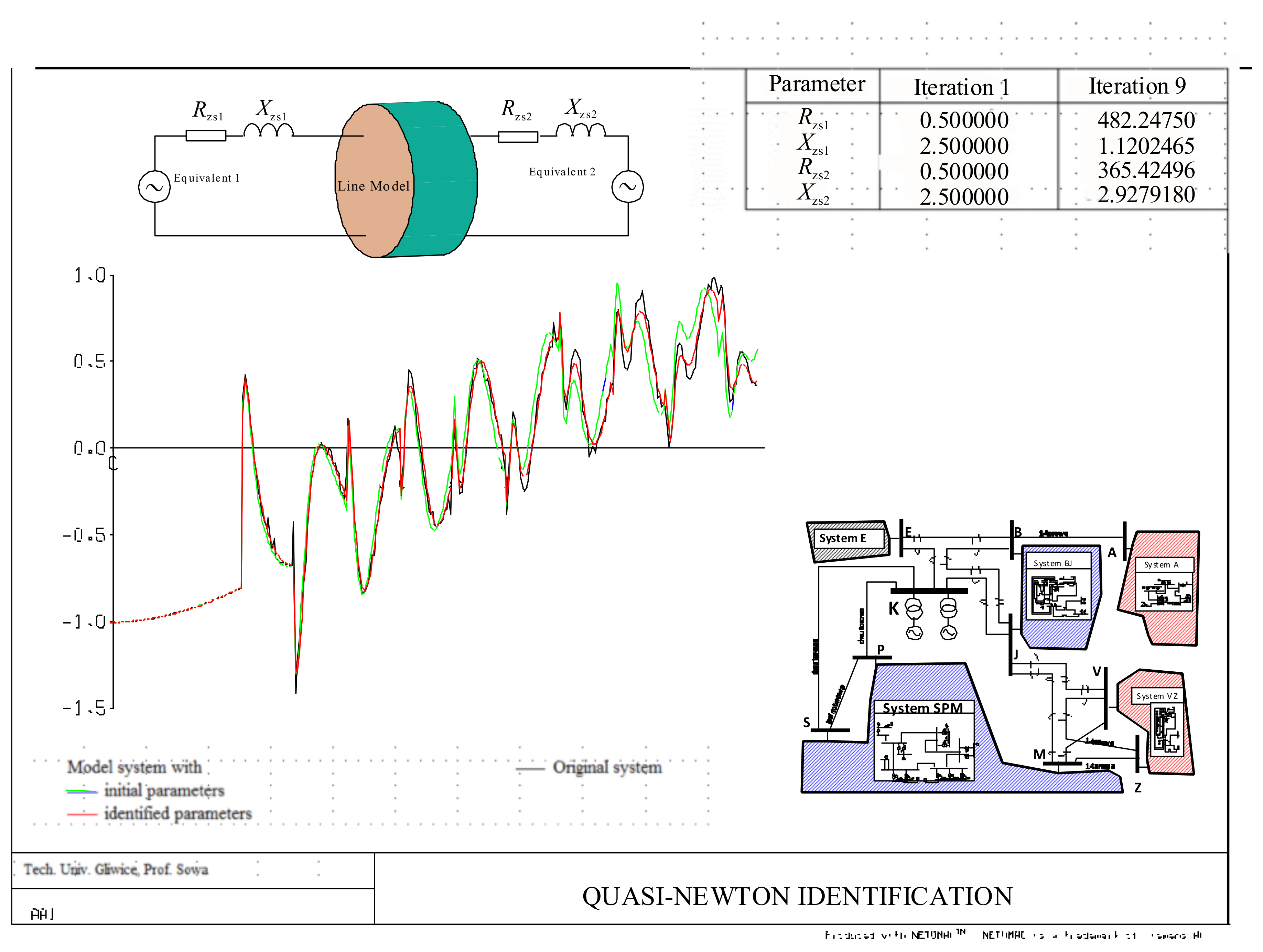
3. Identification of Equivalent System Parameters
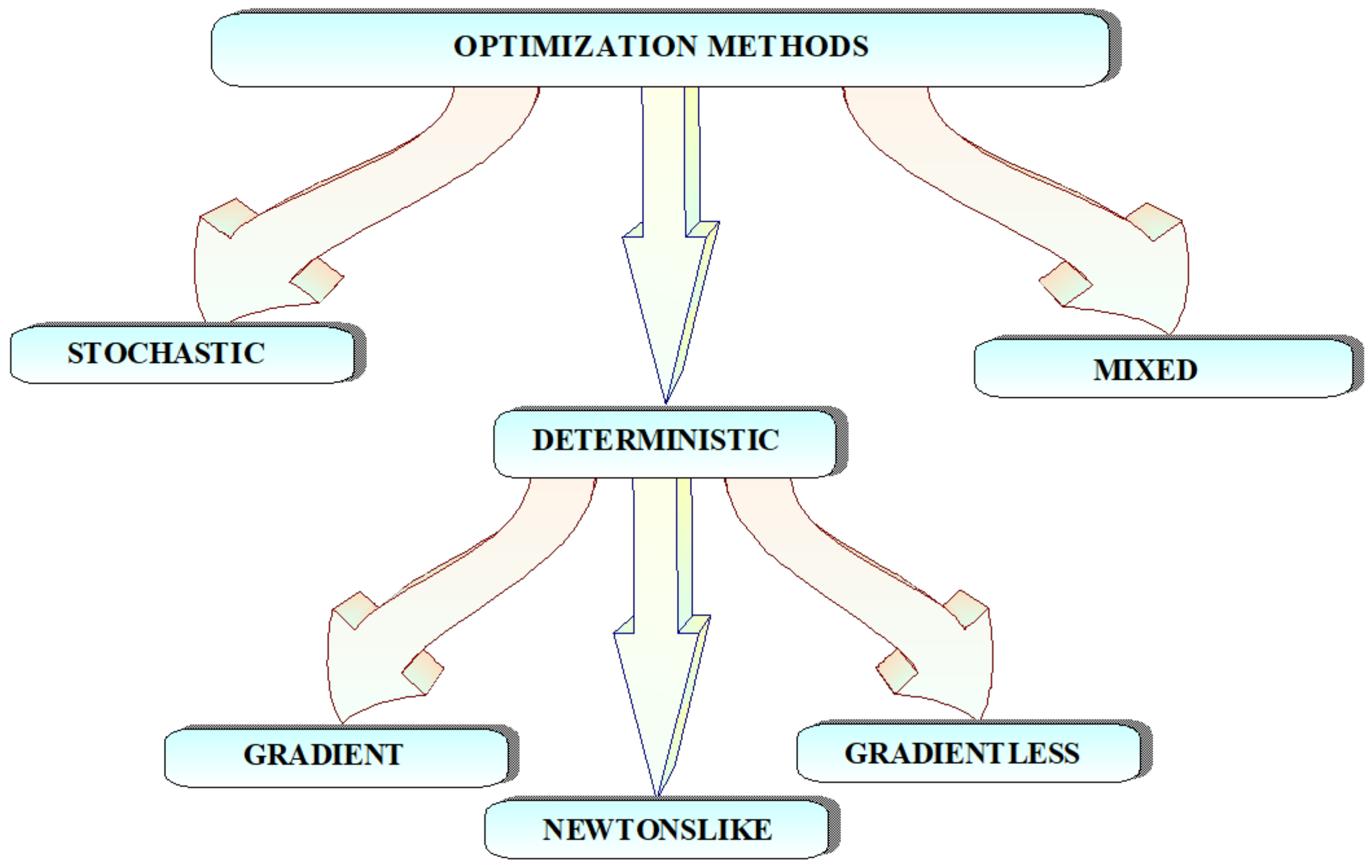
3.1. Description of Methods
3.2. Discussion of the Parameter Identification Method Selection
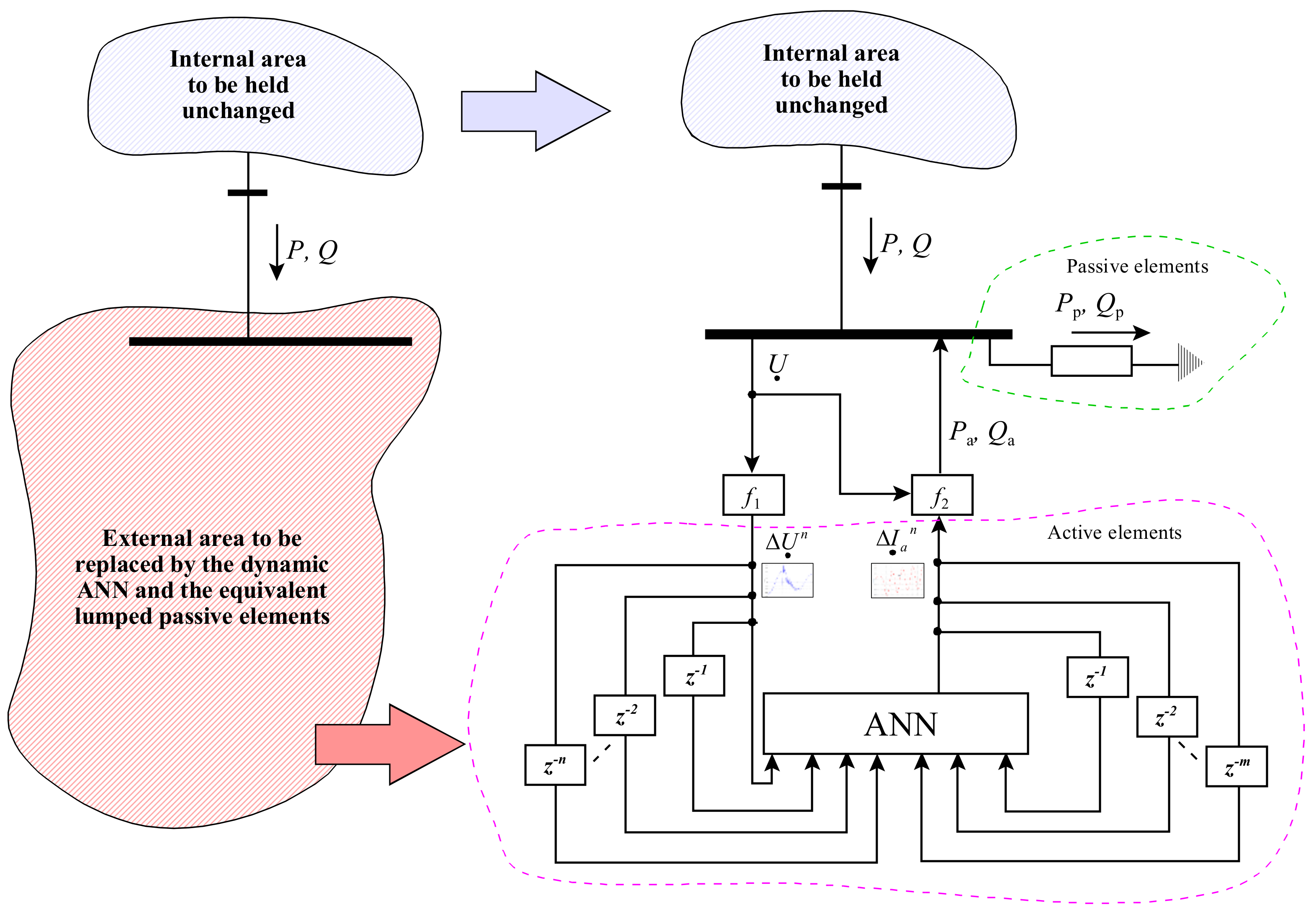
4. Application of ANN to Replace Complex System Structures
5. Summary and Conclusions
- The complexity of the structure,
- The number of identified parameters,
- The number of minimum local objective functions that appear,
- The time (calculation) step.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cipra, B.A. An introduction to the Ising model. Am. Math. Mon. 1987, 94, 937–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeves, S. A modal-coherency technique for deriving dynamic equivalents. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1988, 3, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housos, E.C.; Irisarri, G.; Porter, R.M.; Sasson, A.M. Steady State Netwrork Equivalents for Power System Planning Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1980, 6, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morched, A.S.; Brandwajn, V. Transmission Network Equivalents for Electromagnetic Transient Studies. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1983, 9, 2984–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Jung, B.T.; Park, J.K.; Kim, S.H.; Ahn, B.S. Transmission Network Equivalents in Time-Domain for Electromagnetic Transients Analysis. In Proceedings of the ICDS ’95, College Station, TX, USA, 5–7 April 1995; pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.F. Testing of the Modal Dynamic Equivalents Technique. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1978, PAS-97, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, N.R.; Arrillaga, J. Frequency-dependent AC system equivalents for harmonic and transient converter simulation. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1988, 3, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinney, W.F.; Bright, J.M. Adaptive Reductions for Power Flow Equivalents. IEEE Trans. 1987, PWRS-2, 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- Dimo, P. Modal Analysis of Power Systems; Abacus Press: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Duran, H.; Arvanitidis, N. Simplification for Area Security Analysis: A New Look at Equivalencing. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1972, 2, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, A.; Deckmann, S.; Garcia, A.; Stott, B. Real-Time External Equivalents for Static Security Analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1979, 2, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.T.; Cloues, W.J. Combination Load-Flow and Stability Equivalent for Power System Representation on A-C Network Analyzers. Trans. Am. Inst. Electr. Eng. Part III Power Appar. Syst. 1955, 74, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, M.; Srivastava, K. Dynamic REI equivalents for short circuit and transient stability analyses. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2009, 79, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.; Rodrigues, A.; Prada, R.; da Silva, M.G. External Equivalent for Electric Power Distribution Networks With Radial Topology. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PSS/E 30.1, Program Application Guide. Tech. Rep., Siemens, March 2005. Available online: http://www.pit-us.com (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Machowski, J.; Bialek, J.W.; Bumby, J.R. Power System Dynamics. Stability and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Barquin, J.; Rouco, L.; Vargas, H.R. Generalized Selective Modal Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/PES Winter Meeting: Panel Session on Recent Applications of Linear Analysis, New York, NY, USA, 27–31 January 2002; pp. 1194–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Verghese, G.C.; Perez-Arriaga, J.; Schweppe, F.C. Selective Modal Analysis with Applications to Electric Power Systems, Part II: The Dynamic Stability Problem. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1982, 9, 3126–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveiras, E.M.; De Queirozje, F.; Massaud, A.G. Modal Dynamic Equivalent for Electric Power Systems: Parts 26 I and II. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1988, 3, 1723–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arturi, C.M. Transient Simulation and Analysis of a Three-Phase Five-Limb Step-Up Transformer Following an out-of-Phase Synchronization. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1991, 6, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podmore, R. Identification of Coherent Generators for Dynamic Equivalents. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1978, 4, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.-K.; Liu, C.-C.; Jones, L.; Choe, J.-W. Coherency and Aggregation Techniques Incorporating Rotor and Voltage Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2004, 19, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machowski, J. Dynamic equivalents for transient stability studies of electrical power systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 1985, 7, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, J.S.; Schlueter, R.A. Computational Algorithms for Compucting Modal-Coherent Dynamic Equivalents. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1982, 5, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.B. Equivalent Circuits For Power Flow Studies. AIEE Trans. 1949, 68, 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Klein, M.; Yirga, S.; Kundur, P. Dynamic reduction of large power systems for stability studies. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1997, 12, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.; Stubbe, M. EUROSTAG—A Single Tool for Power System Simulation. Transm. Distrib. Int. 1992, 3, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- DIgSILENT GmbH, DIgSILENT GmbH, Power System Engineering and Software. 2007. Available online: http://digsilent.de (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Kulicke, B. Simulationsprogram Netomac: Differenzen-Leitwertverfahren bei kontinuierlichen und diskontinuierlichen Systemen. Siemens Forschungs–und Entwickl. Ber Bd 1981, 10, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Hingorani, N.G.; Burbey, M.F. Simulation of AC system impedance in HVDC system studies. IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst. 1970, 89, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, A.; Mario, L. Coordinated use of TNA and Digital Computer for Switching Surge Studies: Transient Equivalent of a Complex Network. IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst. 1970, 8, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morched, A.S.; Ottevangers, J.H.; Marti, L. Multi-Port Frequency Dependent Network Equivalents for the EMTP. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1993, 8, 1402–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlyen, A.; Iravani, M. Frequency domain modeling of external systems in an Electro-Magnetic Transients Program. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1993, 8, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.M.; Medina, E.; Mahseredjian, J.; Ramirez, A.; Sheshyekani, K.; Kocar, I. Frequency-Domain Fitting Techniques: A Review. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2020, 35, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.I.; Salama, M.M.A. Frequency Dependent Network Equivalent for AC Power System Using the QZ Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 1995 Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Montreal, QC, Canada, 5–8 September 1995; pp. 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kizilcay, M. Low-order network equivalents for electromagnetic transients studies. Eur. Trans. Electr. Power 1993, 3, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsen, B.; Semlyen, A. Rational approximation of frequency domain responses by vector fitting. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1999, 14, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavrilovic, M.M.; QueDo, V. An Iterative Pole-Removal Method for Synthesis of Power System Equivalent Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1984, 8, 2065–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T. Identification of a Multiphase Network Equivalent for Electromagnetic Transient Calculations Using Partitioned Frequency Response. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2005, 20, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, P. Search of Optimum Equivalent Representation for Transient Investigations during non-Simultaneous Faults. In Proceedings of the IASTED, International Conference Modeling and Simulation, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1–4 May 1998; IASTED/ACTA Press: Calgary, AB, Canada, 1998; pp. 466–470, ISBN 0-88986-252-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sowa, P. Optimization of Equivalent Networks for Transient Simulation in H.V. Transmission Systems. In Proceedings of the IASTED, International Conference—Modeling, Simulation and Optimization, Gold Coast, Australia, 6–9 May 1996; pp. 205–242. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, S.; Wood, A.R.; Bodger, P.S.; Smith, B.C. Rational functions as frequency dependent equivalents for transient studies. In Proceedings of the IW7 International Conference on Power Systems Transients, Seattle, WA, USA, 22–26 June 1997; pp. 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kulicke, B.; Hinrichs, H.J. Parameteridentifikation und Ordnungsreduktion mit Hilfe des Simulationsprogramms Netomac. Etz-Archiv 1988, 10, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Abur, A.; Singh, H. Time domain modeling of external systems for electromagnetic transients programs. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1993, 8, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaventura, W.; Semlyen, A.; Iravani, M.; Lopes, A. Robust Sparse Network Equivalent for Large Systems: Part I—Methodology. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2004, 19, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmy, A.; Erlich, I.; Sowa, P. Artificial neural network-based dynamic equivalents for distribution systems containing active sources. IEE Proc. Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2004, 151, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.; Al-Ramadhan, A. Dynamic equivalent of external power system and its parameter estimation through artificial neural networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2002, 24, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, P. Comparison of results of optimization by searching of equivalent system. In Proceedings of the 2008 40th North American Power Symposium, Calgary, AB, Canada, 28–30 September 2008; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Stankovic, A.; Saric, A. Transient Power System Analysis With Measurement-Based Gray Box and Hybrid Dynamic Equivalents. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2004, 19, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovicc, A.; Saric, A.; Milosevic, M. Identification of nonparametric dynamic power system equivalents with artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuglie, E.D.; Guida, L.; Torelli, F.; Lucarella, D.; Pozzi, M.; Vimercati, G. Identification of Dynamic Voltage-Current Power System Equivalents through Artificial Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Bulk Power System Dynamics and Control, VI, Cortina d’Ampezzo, Italy, 22–27 August 2004; pp. 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sowa, P. Representation of power system for electromagnetic transient calculation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. Eng. 2008, 1, 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Mahseredjian, J.; Dinavahi, V.; Martinez, J.A. Simulation Tools for Electromagnetic Transients in Power Systems: Overview and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2009, 24, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahseredjian, J. Computation of power system transients: Overview and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 24–28 June 2007; p. 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, M.; Ametani, A.; Martin, C.; Kocar, I.; Montenegro, A.; Goldsworthy, D.; Tobin, T.; Mahseredjian, J.; Ramos, R.; Marti, J.R.; et al. Simulation of Switching Overvoltages and Validation With Field Tests. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2018, 33, 2884–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavella, M. Power system transient stability assessment—Traditional vs modern methods. Control. Eng. Pract. 1998, 6, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wehenkel, L.; Pavella, M. SIME: A Comprehensive Approach to Fast Transient Stability Assessment. IEEJ Trans. Power Energy 1998, 118, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavella, M. Generalized one-machine equivalents in transient stability studies. IEEE Power Eng. Rev. 1998, 18, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Action | Structure Search in the Field | Parameter Identification | Reduction | Initial Struture | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge of the Structure of the Original System | ||||||
| YES | Single-sided power or unconnected systems | s * | Frequency | Necessary | Static | Unnecessary |
| w ** | Time | Not recommended | Unnecessary | |||
| Connected | s * | Frequency | Dynamic | Unnecessary | ||
| w ** | Time | Not recommended | Unnecessary | |||
| NO | Measurement results | Unnecessary | Unnecessary | ANN | ||
| Short-circuit power only (number of lines known) | Unnecessary | Unnecessary | ANN | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sowa, P.; Zychma, D. Dynamic Equivalents in Power System Studies: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041396
Sowa P, Zychma D. Dynamic Equivalents in Power System Studies: A Review. Energies. 2022; 15(4):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041396
Chicago/Turabian StyleSowa, Paweł, and Daria Zychma. 2022. "Dynamic Equivalents in Power System Studies: A Review" Energies 15, no. 4: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041396
APA StyleSowa, P., & Zychma, D. (2022). Dynamic Equivalents in Power System Studies: A Review. Energies, 15(4), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041396






