Experimental Investigation of a Mechanically Stable and Temperature/Salinity Tolerant Biopolymer toward Enhanced Oil Recovery Application in Harsh Condition Reservoirs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
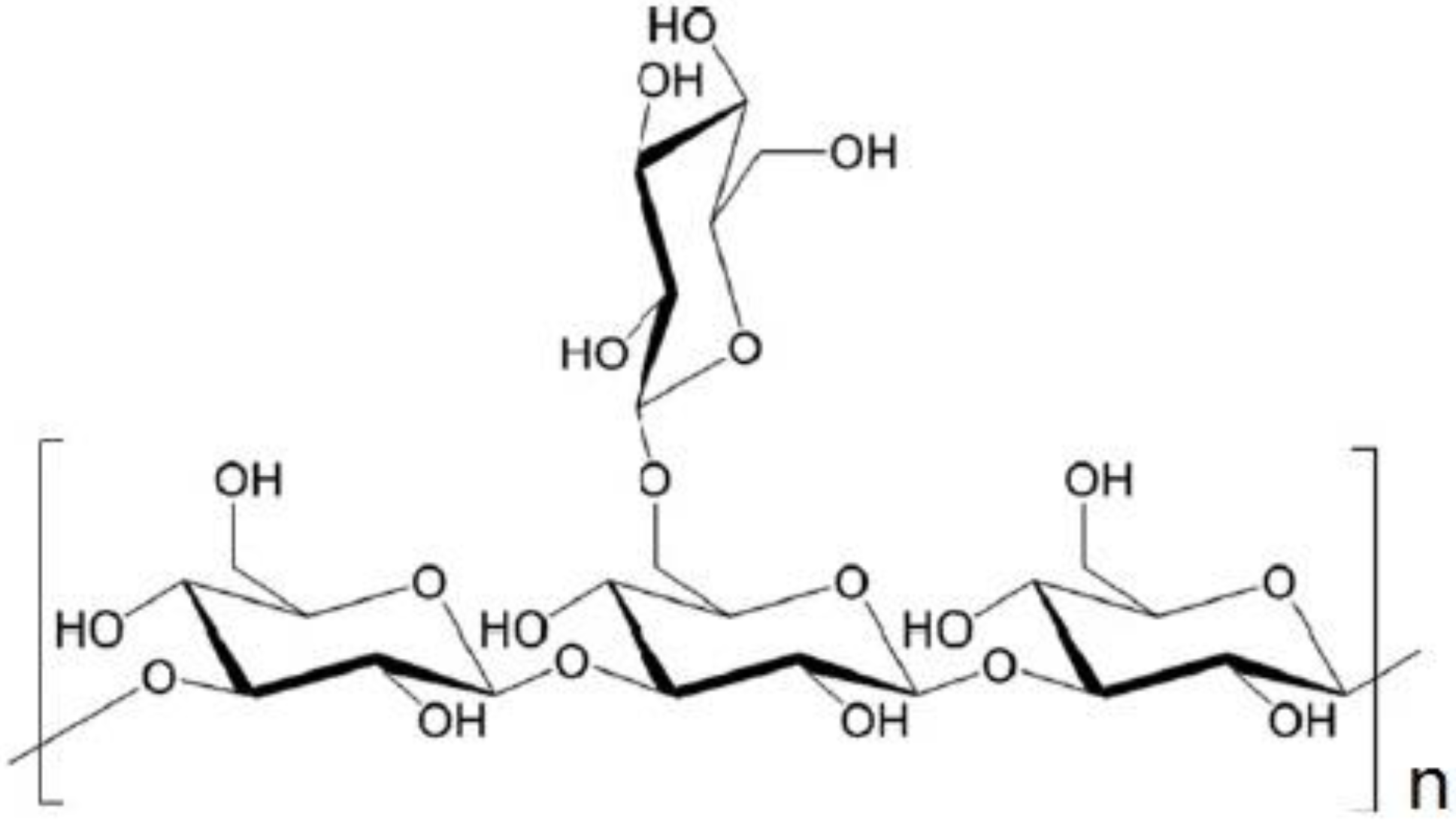
2.1. Materials
2.2. Steady and Dynamical Rheological Measurements
2.3. Mechanical Stability Test
2.4. Core Flood Test
3. Results and Discussion
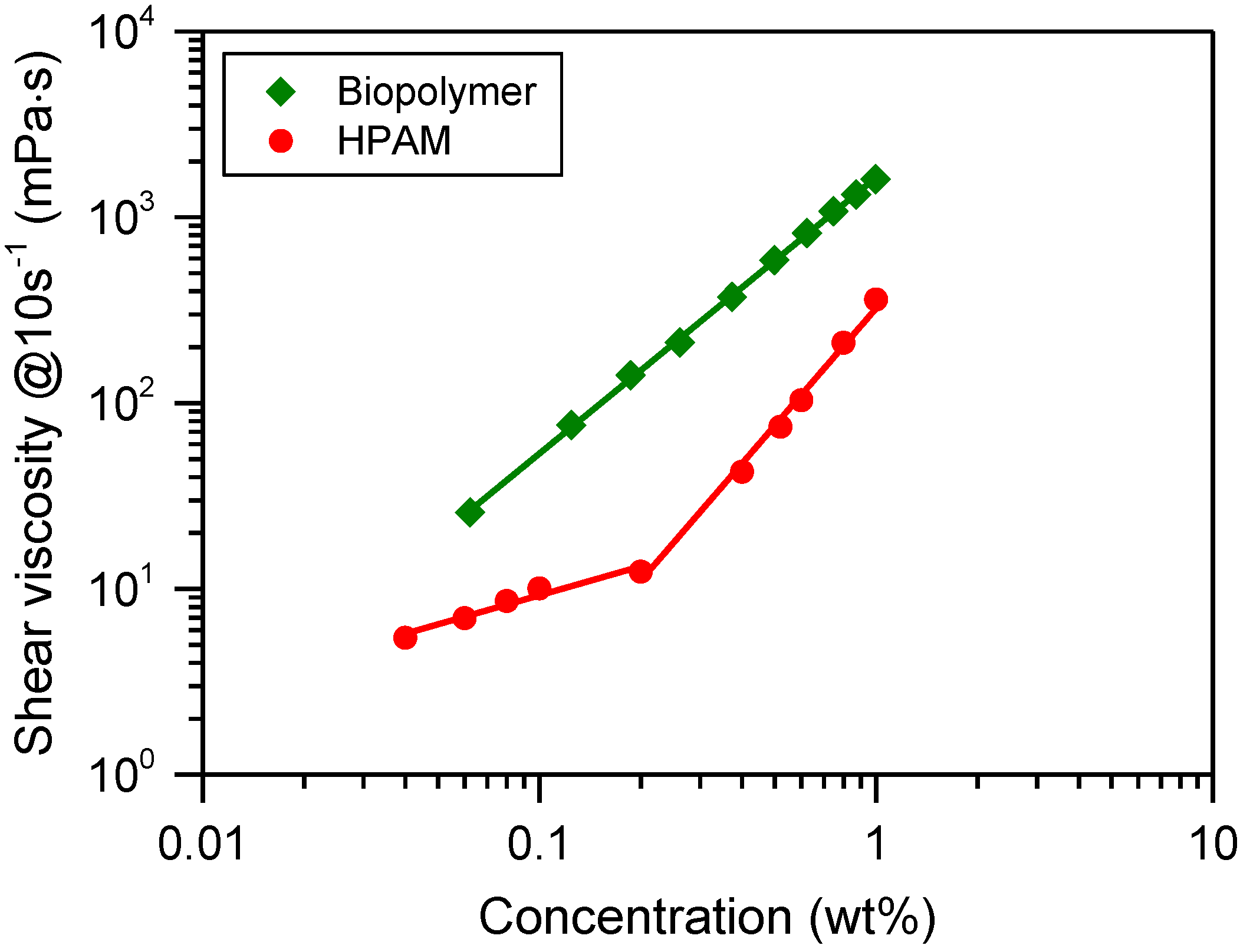
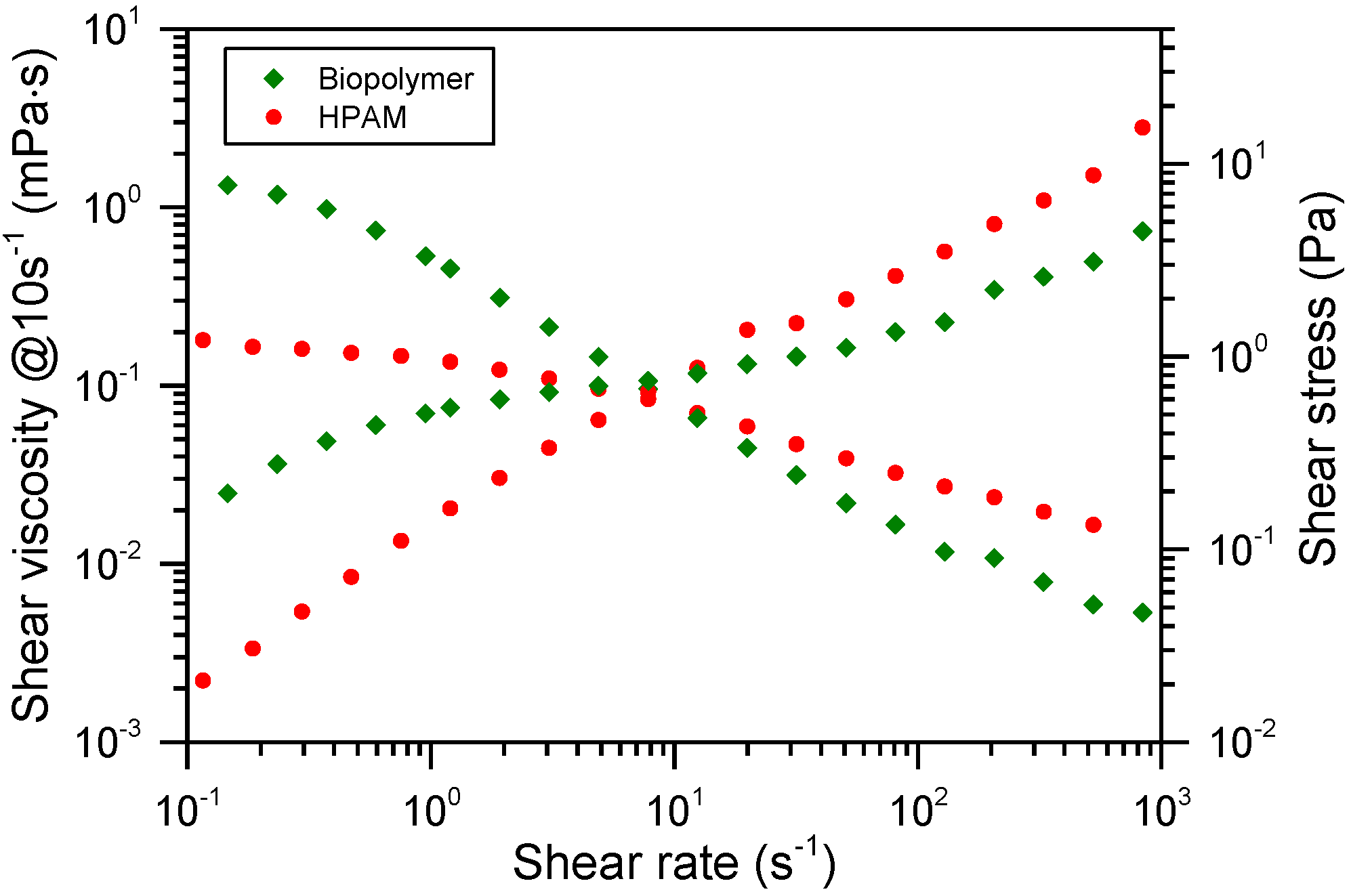
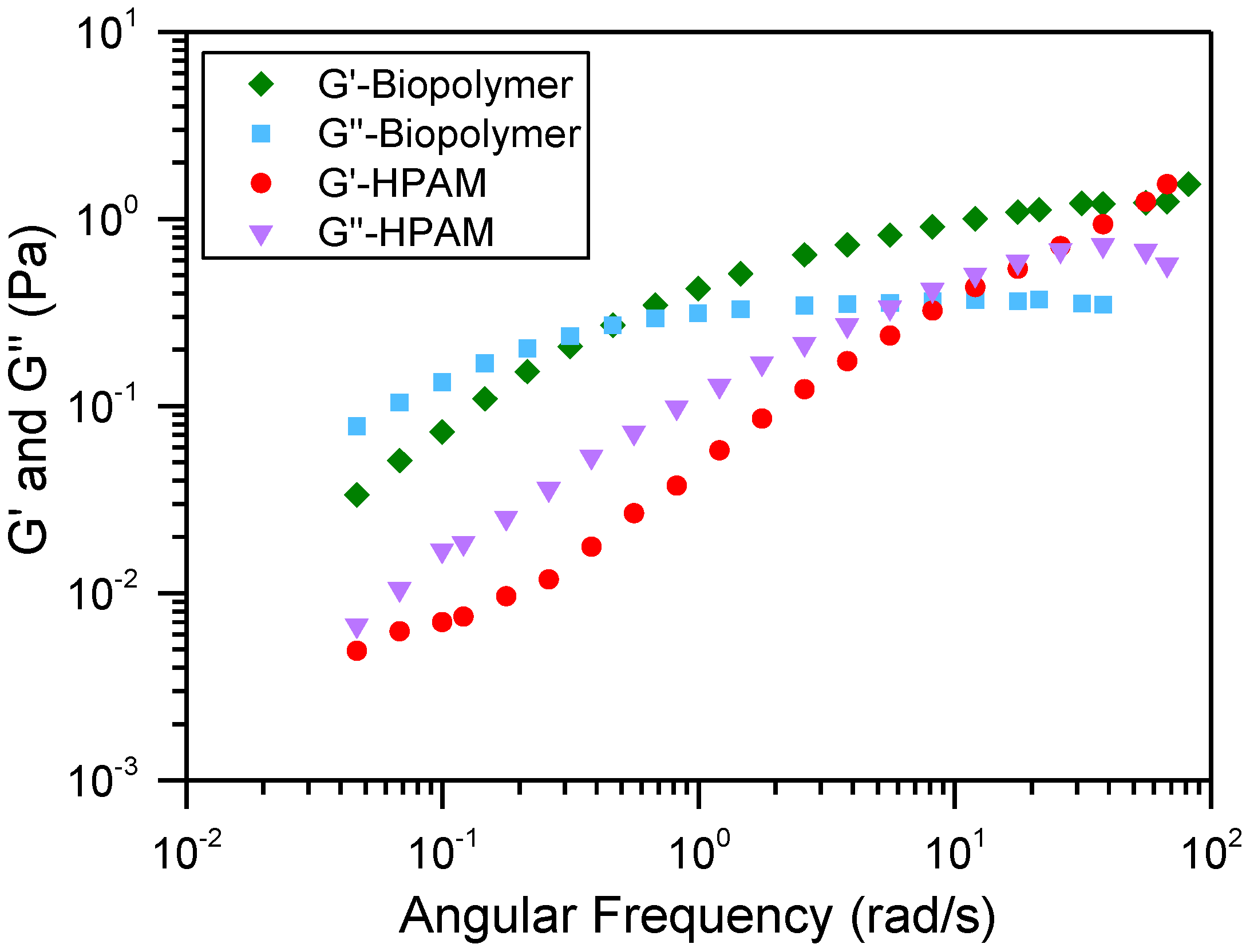
3.1. Thickening Capacity
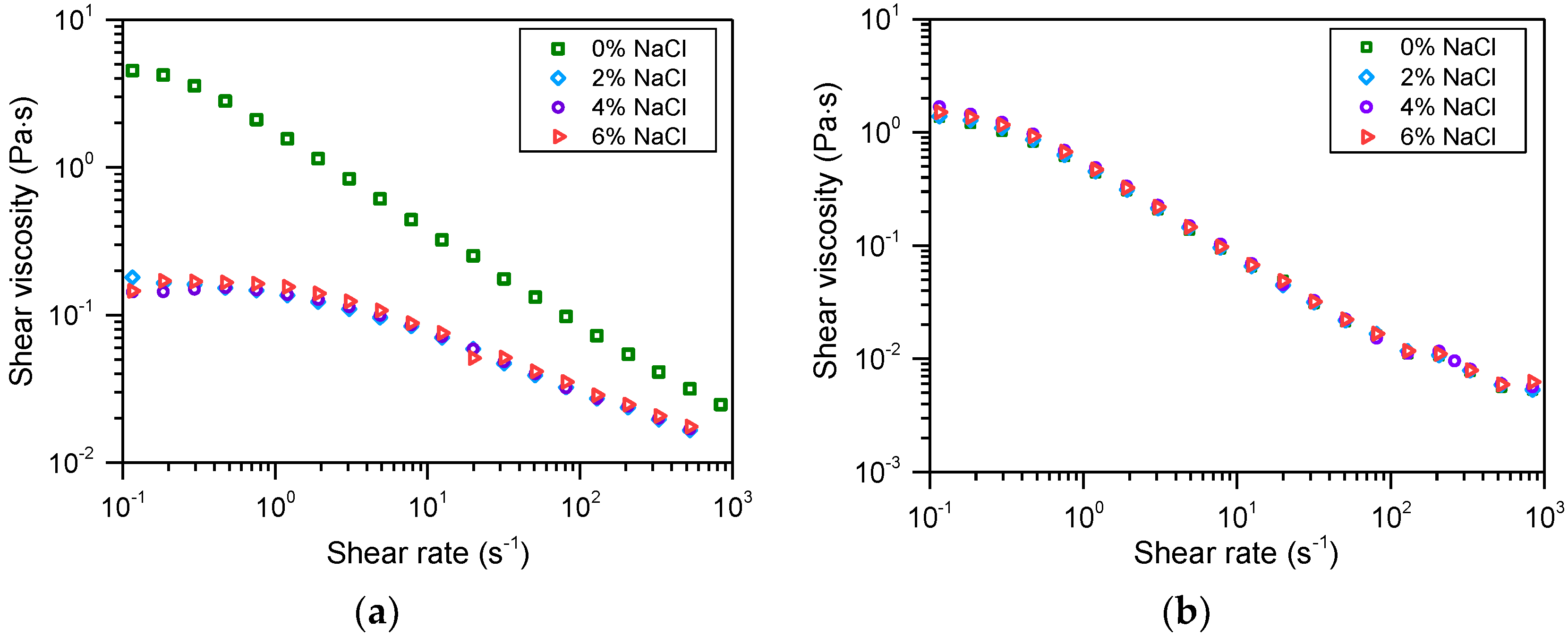
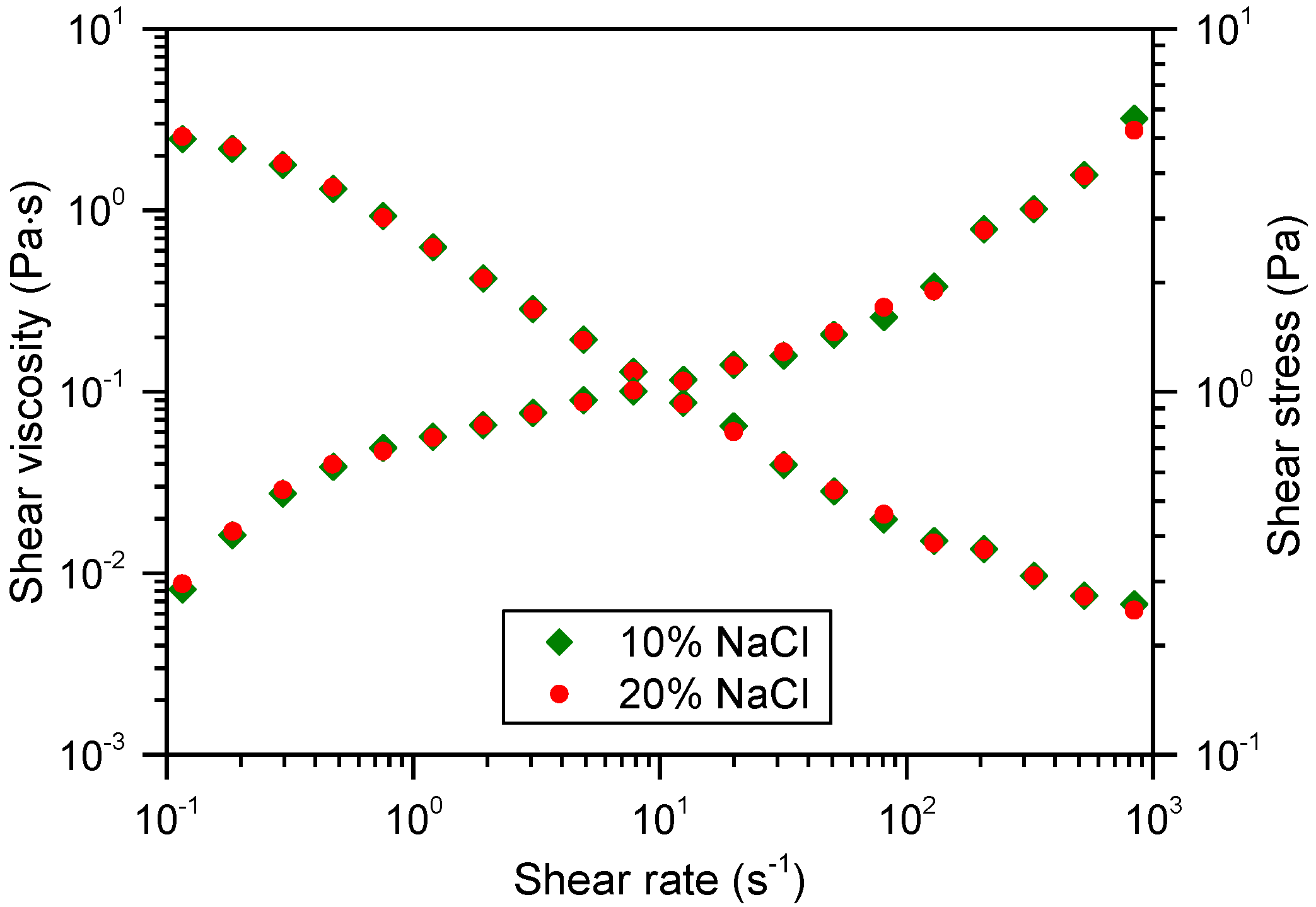
3.2. Salt Tolerance
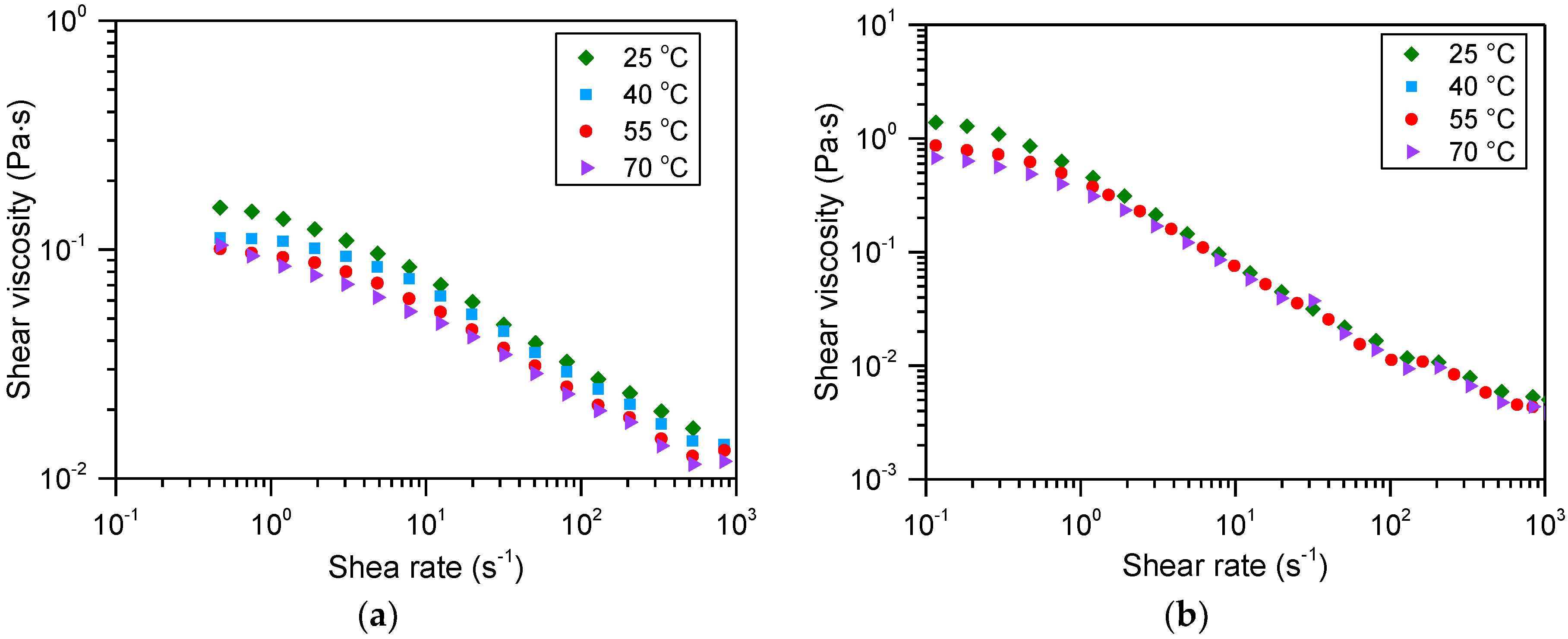
3.3. Temperature Resistance
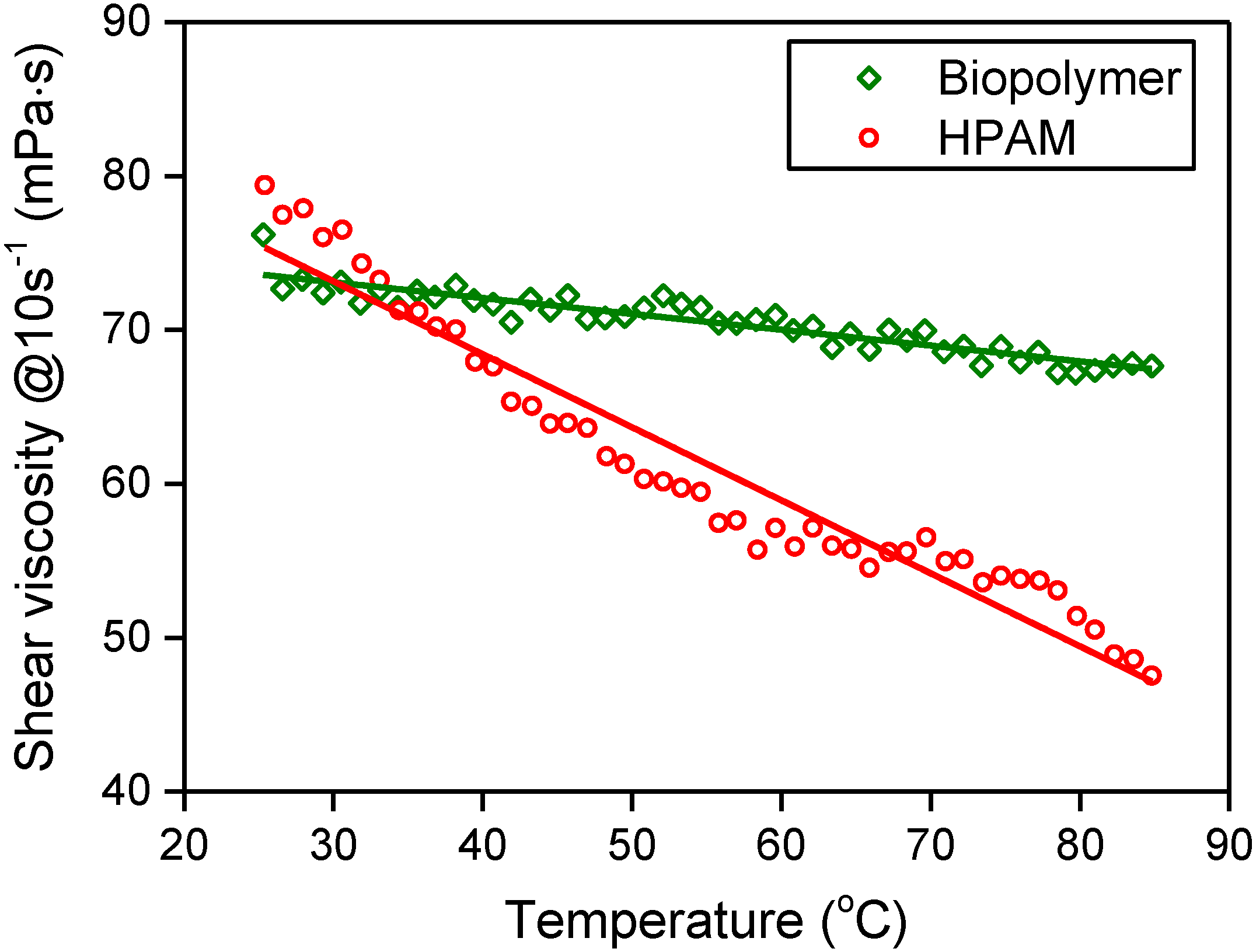
3.4. Mechanical Stability
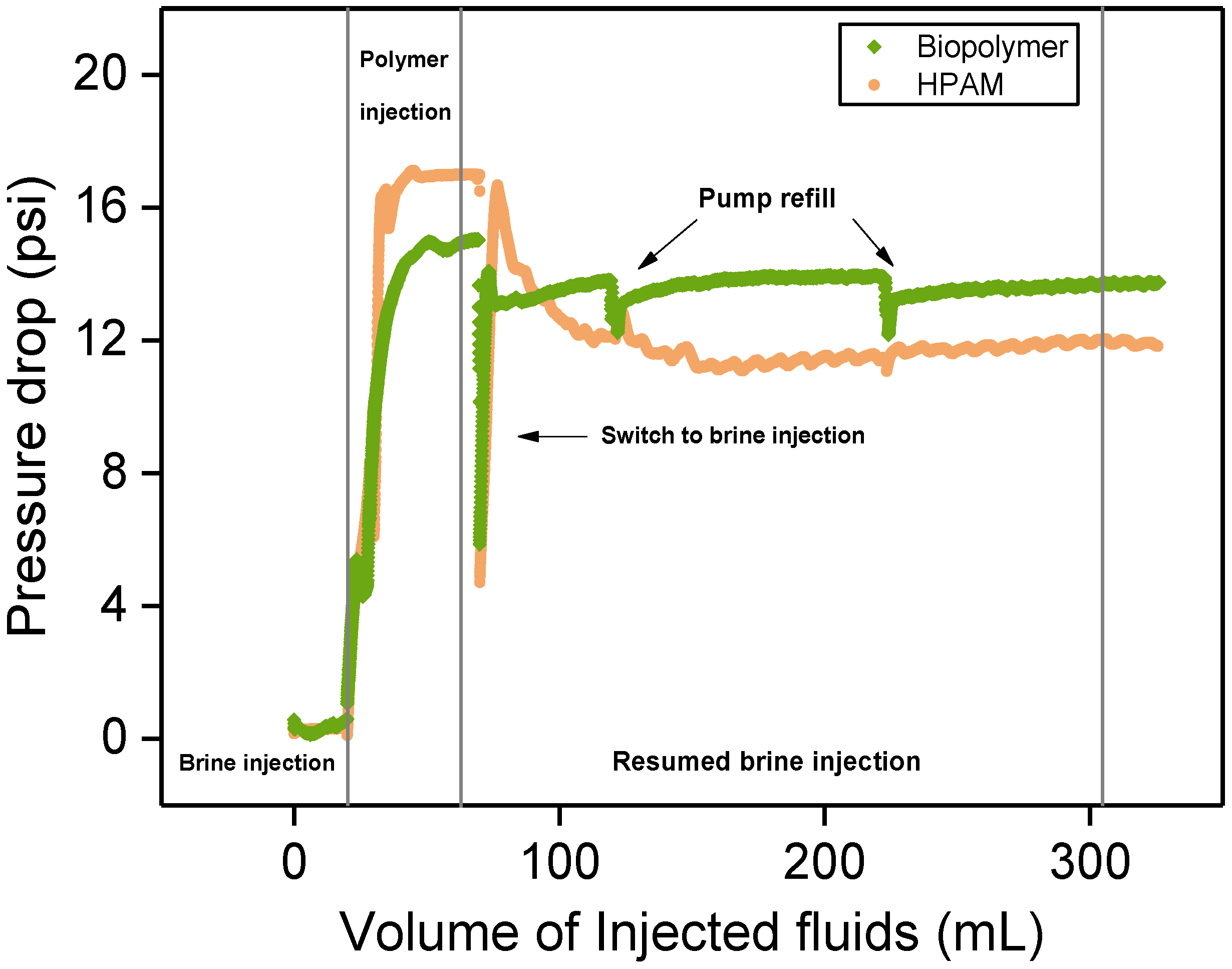
3.5. Flow Characteristics in Porous Media
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Shi, W.; Zang, L.; Wang, C.; Yu, S. Factors affecting the performance of forward osmosis treatment for oilfield produced water from surfactant-polymer flooding. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 615, 118457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alammar, A.; Park, S.H.; Williams, C.J.; Derby, B.; Szekely, G. Oil-in-water separation with graphene-based nanocomposite membranes for produced water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 118007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Peng, J.; Yuan, S.; Lin, D.; Zhang, M.; Xu, F.; Bao, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Bioinspired Hybrid Nanostructures for Wax Inhibition Coatings with Superhydrophilicity. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 4, 6178–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Han, P.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ma, M.; Lu, K.; Wei, C. In History Matching Method for High Concentration Viscoelasticity Polymer Flood Pilot in Daqing Oilfield. In Proceedings of the SPE Enhanced Oil Recovery Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–20 July 2011. SPE-144538-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.Z.; Fang, S.F.; Wang, D.M.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, Z.; Hong, W.H. Review of Practical Experience & Management by Polymer Flooding at Daqing. In SPE Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2008; pp. 1520–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Delamaide, E.; Zaitoun, A.; Renard, G.; Tabary, R. Pelican Lake Field: First Successful Application of Polymer Flooding in AHeavy Oil Reservoir. SPE Res. Eval. Eng. 2014, 17, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, G.A. Recent Developments and Remaining Challenges of Enhanced Oil Recovery. JPT J. Pet. Technol. 2011, 63, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Romero-Zerón, L.; Rodrigue, D. Oil Displacement Mechanisms of Viscoelastic Polymers in Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): AReview. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2014, 4, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, S.; Guo, Z. Necessity and Feasibility of Improving the Residual Resistance Factor of Polymer Flooding in Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Pet. Sci. 2010, 7, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, B.; Romero-Zerón, L.; Rodrigue, D. Novel Self-Assembling Polymeric System Based on AHydrophobic Modified Copolymer: Formulation, Rheological Characterization, and Performance in Enhanced Heavy Oil Recovery. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cheng, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, G. Experiences Learned after Production of more than 300 million Barrels of Oil by Polymer Flooding in Daqing Oil Field. In SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition; Society of Petroleum Engineers: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Demin, W.; Jiecheng, C.; Qingyan, Y.; Wenchao, G.; Qun, L. Viscous-Elastic Polymer Can Increase Microscale Displacement Efficiency in Cores. In SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2000; pp. 719–728. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Wu, J. Effect of Polymer Solution Viscoelasticity on Residual Oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2008, 26, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanpour, H.; Kuru, E. A New Look at the Viscoelastic Fluid Flow in Porous Media—A Possible Mechanism of Internal Cake Formation and Formation Damage Conrol. In SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2009; pp. 617–631. [Google Scholar]
- Wever, D.A.Z.; Picchioni, F.; Broekhuis, A.A. Polymers for Enhanced Oil Recovery: A Paradigm for Structure-Property Relationship in Aqueous Solution. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1558–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, G.; Yu, L.; Gong, H.; Dong, M.; Li, Y. The Displacement Efficiency and Rheology of Welan Gum for Enhanced Heavy Oil Recovery. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, R.B.; Doe, P.H. Polymer Flooding Review. JPT J. Pet. Technol. 1987, 39, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Thermal Stability of High-Molecular-Weight Polyacrylamide Aqueous Solutions. Polym. Bull. 1981, 5, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hashmi, A.R.; Al Maamari, R.S.; Al Shabibi, I.S.; Mansoor, A.M.; Zaitoun, A.; Al Sharji, H.H. Rheology and Mechanical Degradation of High-Molecular-Weight Partially Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide during Flow through Capillaries. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 105, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seright, R.S. The Effects of Mechanical Degradation and Viscoelastic Behavior on Injectivity of Polyacrylamide Solutions. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1983, 23, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seright, R.S.; Henrici, B.J. Xanthan Stability at Elevated Temperatures. SPE Reserv. Eng. 1990, 5, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.H.; Li, W.D.; Tian, J.; Liu, Y.Z. Pilot Test of Xanthan Gum Flooding in Shengli Oilfield. In SPE Asia Pacific Improved Oil Recovery Conference; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kohler, N.; Chauveteau, G. Xanthan Poysaccharide Plugging Behavior in Porous Media—Preferential Use of Fermentation Broth. JPT J. Pet. Technol. 1981, 33, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, H.; Fang, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O. Schizophyllan: A Review on Its Structure, Properties, Bioactivities and Recent Developments. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2013, 1, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Norisuye, T.; Fujita, H. Triple Helix of Schizophyllum Commune Polysaccharide in Dilute Solution. 5. Light Scattering and Refractometry in Mixtures of Water and Dimethyl Sulfoxide. Macromolecules 1983, 16, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgelos, P.N.; Torkelson, J.M. The Role of Solution Structure in Apparent Thickening Behavior of Dilute Peo/Water Systems. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1988, 27, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitoun, A.; Kohler, N. Two-Phase Flow through Porous Media: Effect of An Adsorbed Polymer Layer. In SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 1988; pp. 297–310. [Google Scholar]
- Veerabhadrappa, S.K. Study of Effects of Polymer Elasticity on Enhanced Oil Recovery by Core Flooding and Visualization Experiments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.Y.; Zhang, K.; Chon, B.H.; Choi, H.J. Enhanced Oil Recovery Performance and Viscosity Characteristics of Polysaccharide Xanthan Gum Solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 21, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochi, T. Flow of Non-newtonian Fluids in Porous Media. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 2437–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirao, T.; Sato, T.; Teramoto, A.; Matsuo, T.; Suga, H. Solvent Effects on the Cooperative Order-Disorder Transition of Aqueous Solutions of Schizophyllan, ATriple-Helical Polysaccharide. Biopolymers 1990, 29, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Bera, A.; Ojha, K.; Mandal, A. Effects of Alkali, Salts, and Surfactant on Rheological Behavior of Partially Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide Solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4315–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quy, N.M.; Ranjith, P.G.; Choi, S.K.; Giao, P.H.; Jasinge, D. Analytical Assessment of Horizontal Well Efficiency with Reference to Improved Oil Recovery of the South-East Dragon Oil Field Southern Offshore of Vietnam. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2009, 66, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaki, T.; Tabata, K.; Kojima, T. Melting Behaviour of ATriple Helical Polysaccharide Schizophyllan in Aqueous Solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 1985, 5, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitoun, A.; Makakou, P.; Blin, N.; Al-Maamari, R.S.; Al-Hashmi, A.R.; Abdel-Goad, M.; Al-Sharji, H.H. Shear Stability of EOR Polymers. SPE J. 2012, 17, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Müller, A.J.; Odell, J.A. Entanglements in Semi-Dilute Solutions as Revealed by Elongational Flow Studies. Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1987, 75, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Romero-Zerón, L.; Rodrigue, D. Mechanical Properties and Flow Behavior of Polymers for Enhanced Oil Recovery. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2014, 53, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Romero-Zerón, L.; Rodrigue, D. Improved Viscoelasticity of Xanthan Gum through Self–Association with Surfactant: β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Applications in Enhanced Oil Recovery. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 3, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, R.H.; Middleman, S. Power-Law Flow through APacked Tube. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1965, 4, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Christ, F.R. Polymer Retention and Adsorption in the Flow of Polymer Solutionsthrough Porous Media. SPE Reserv. Eng. 1986, 1, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.J. Polymer Flooding; Gulf Professional Publishing, Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 101–129. [Google Scholar]
- Wever, D.A.Z.; Picchioni, F.; Broekhuis, A.A. Comblike Polyacrylamides as Flooding Agent in Enhanced Oil Recovery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 16352–16363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, G.; Rousseau, D.; Tabary, R.; Grassi, B. Flow of Hydrophobically Modified Water-Soluble-Polymer Solutions in Porous Media: New Experimental Insights in the Diluted Regime. SPE J. 2011, 16, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Flow Rate (mL/min) | Shear Rate (×103 s−1) |
|---|---|
| 2 | 3.49 |
| 4 | 6.98 |
| 6 | 10.47 |
| 8 | 13.96 |
| 10 | 17.45 |
| 12 | 20.94 |
| 14 | 24.43 |
| 16 | 27.92 |
| 18 | 31.41 |
| 20 | 34.90 |
| Core Plug | HPMA | Biopolymer |
|---|---|---|
| Permeability | kbrine = 149 md | kbrine = 130 md |
| Length | 5 cm | 5 cm |
| Cross-sectional area | 11.81 cm2 | 11.81 cm2 |
| Pore volume (PV) | 16.43 cm3 | 15.56 cm3 |
| Porosity | 27.8% | 26.3% |
| Average pore radius | 2.07 µm | 1.98 µm |
| Shear rate (s−1) | 58.6 | 64.6 |
| Polymer | Shear Viscosity | Shear Stress | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | n | R2 | m | p | R2 | ||
| HPAM | 0.13 | 0.70 | 0.96 | 0.015 | 8.51 | 0.63 | 0.99 |
| Biopolymer | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.99 | 0.104 | 4.02 | 0.31 | 0.96 |
| Polymer | 0 wt% NaCl | 2 wt% NaCl | 4 wt% NaCl | 6 wt% NaCl | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | n | R2 | k | n | R2 | k | n | R2 | k | n | R2 | |
| HPAM | 1.58 | 0.38 | 0.99 | 0.13 | 0.70 | 0.96 | 0.12 | 0.72 | 0.93 | 0.13 | 0.71 | 0.93 |
| Biopolymer | 0.41 | 0.30 | 0.99 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.99 | 0.44 | 0.30 | 0.99 | 0.46 | 0.29 | 0.99 |
| Polymer | 25 °C | 40 °C | 55 °C | 70 °C | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | n | R2 | k | n | R2 | k | n | R2 | k | n | R2 | |
| HPAM | 0.13 | 0.70 | 0.96 | 0.12 | 0.68 | 0.97 | 0.10 | 0.69 | 0.98 | 0.09 | 0.68 | 0.99 |
| Biopolymer | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.99 | 0.38 | 0.32 | 0.99 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.99 | 0.27 | 0.36 | 0.99 |
| Polymer | RF e | Effective Viscosity (mPa∙s) | RRF e | r (μm) | e (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPAM | 56.3 | 56.3 | 38.2 | 2.07 | 1.24 |
| Biopolymer | 46.3 | 46.3 | 41.0 | 1.98 | 1.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, C.; Wei, F.; Zhang, S.; Cai, C.; Lv, J.; Shao, L.; Wang, D. Experimental Investigation of a Mechanically Stable and Temperature/Salinity Tolerant Biopolymer toward Enhanced Oil Recovery Application in Harsh Condition Reservoirs. Energies 2022, 15, 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051601
Xiong C, Wei F, Zhang S, Cai C, Lv J, Shao L, Wang D. Experimental Investigation of a Mechanically Stable and Temperature/Salinity Tolerant Biopolymer toward Enhanced Oil Recovery Application in Harsh Condition Reservoirs. Energies. 2022; 15(5):1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051601
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Chunming, Falin Wei, Song Zhang, Cheng Cai, Jing Lv, Liming Shao, and Dianlin Wang. 2022. "Experimental Investigation of a Mechanically Stable and Temperature/Salinity Tolerant Biopolymer toward Enhanced Oil Recovery Application in Harsh Condition Reservoirs" Energies 15, no. 5: 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051601
APA StyleXiong, C., Wei, F., Zhang, S., Cai, C., Lv, J., Shao, L., & Wang, D. (2022). Experimental Investigation of a Mechanically Stable and Temperature/Salinity Tolerant Biopolymer toward Enhanced Oil Recovery Application in Harsh Condition Reservoirs. Energies, 15(5), 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051601





