Geochemical Characteristics and Process of Hydrocarbon Generation Evolution of the Lucaogou Formation Shale, Jimsar Depression, Junggar Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
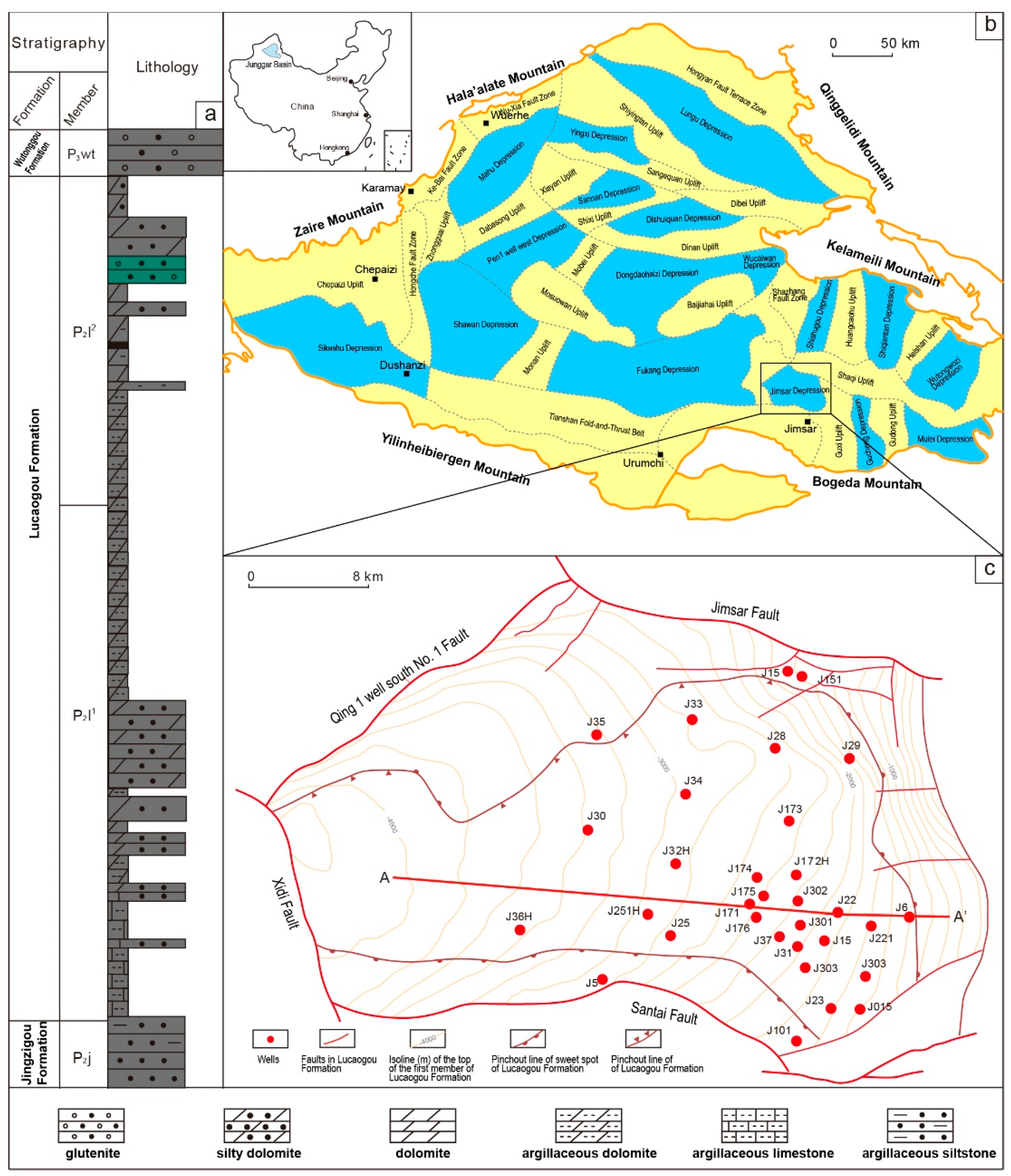
2. Geologic Background
3. Samples and Analytical Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Analytical Methods
3.2.1. Evaluation of Source Rocks
3.2.2. Simulation of Two-Dimensional Basin
3.2.3. Thermal Simulation Experiment in a Closed System
4. Results and Discussion
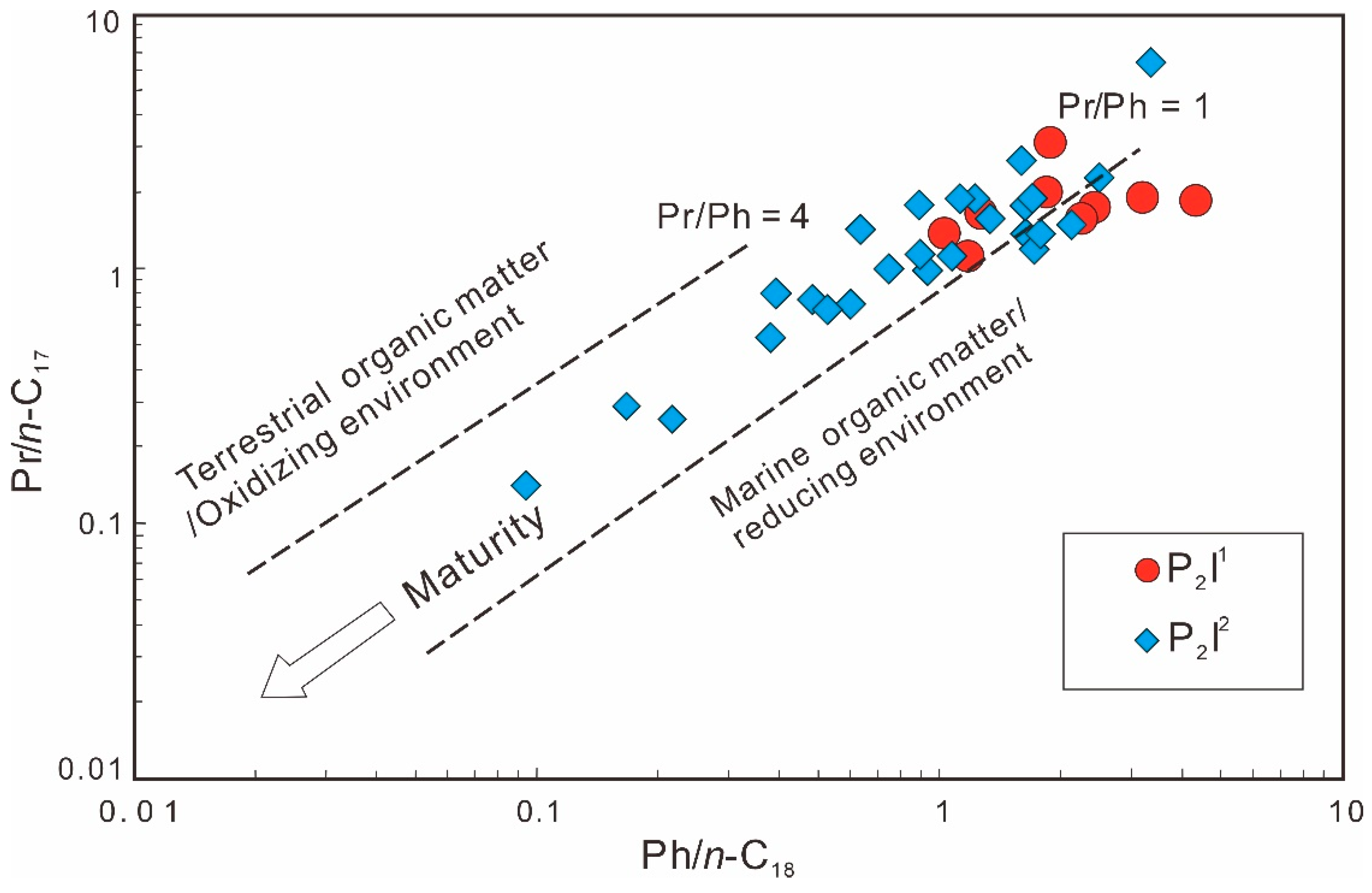
4.1. Depositional Environment of Source Rocks
4.1.1. Normal Alkanes and Isoprenoid Alkanes
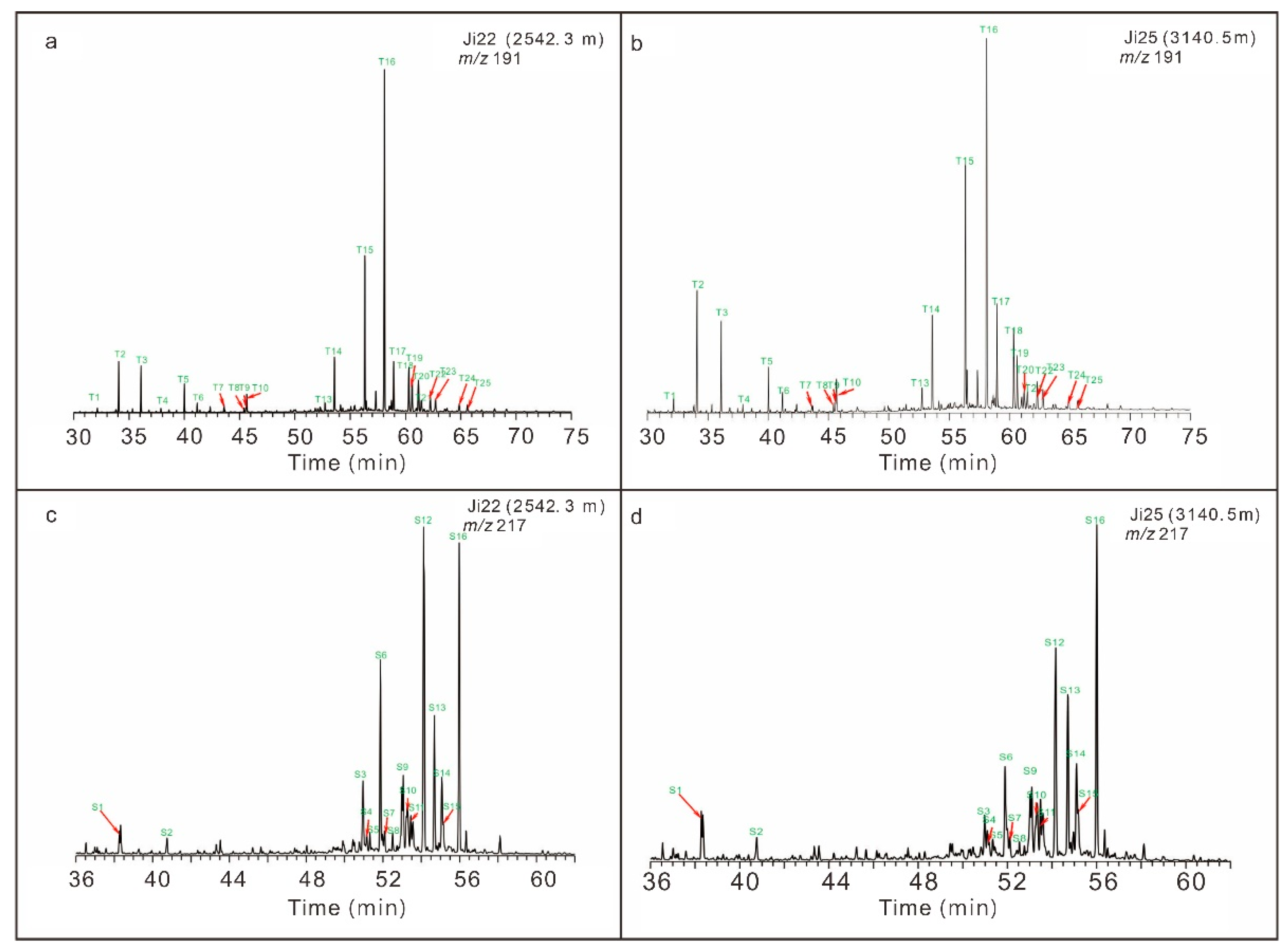
4.1.2. Terpanes
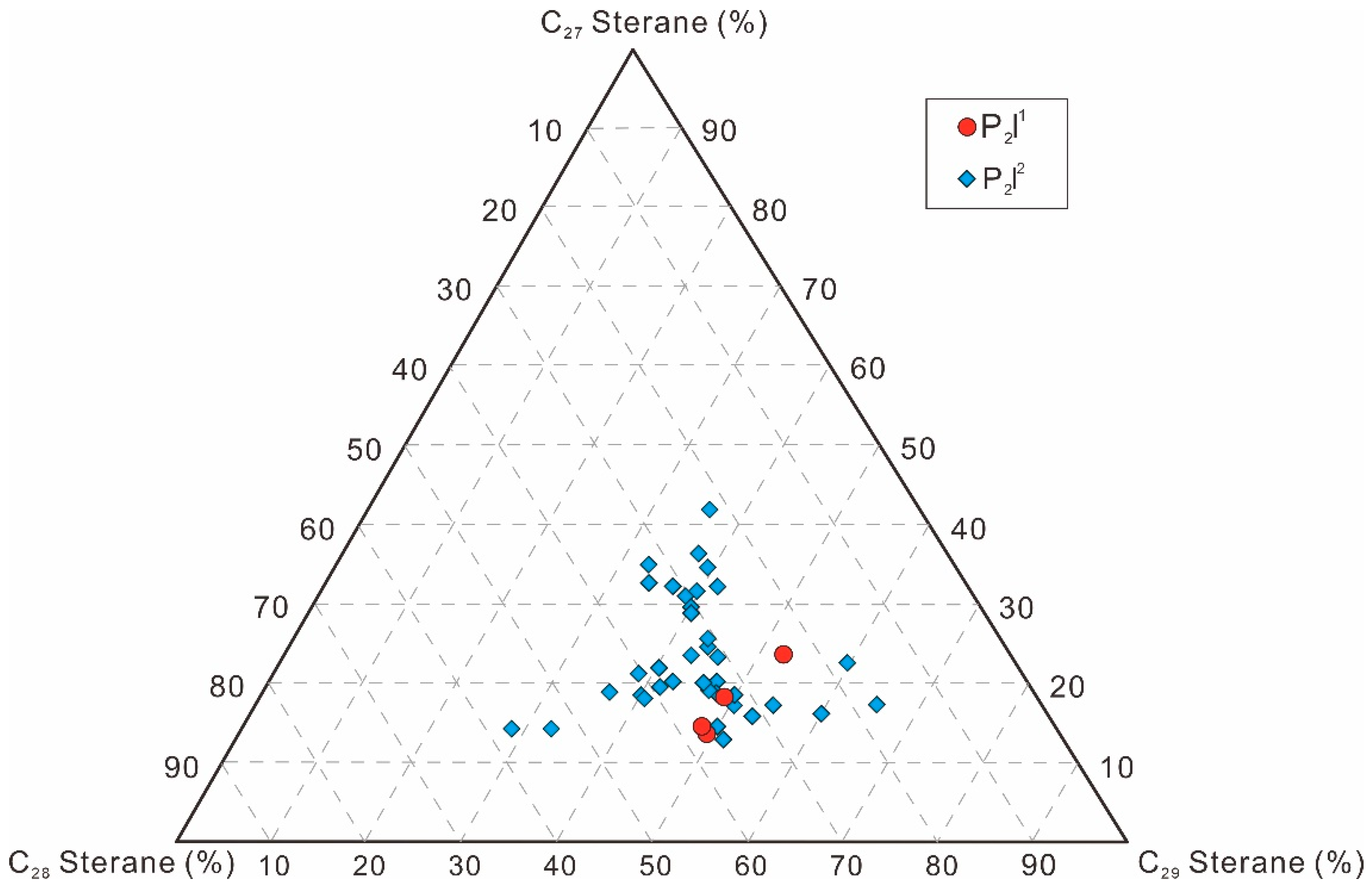
4.1.3. Sterane
4.2. Type and Abundance of Source Rocks
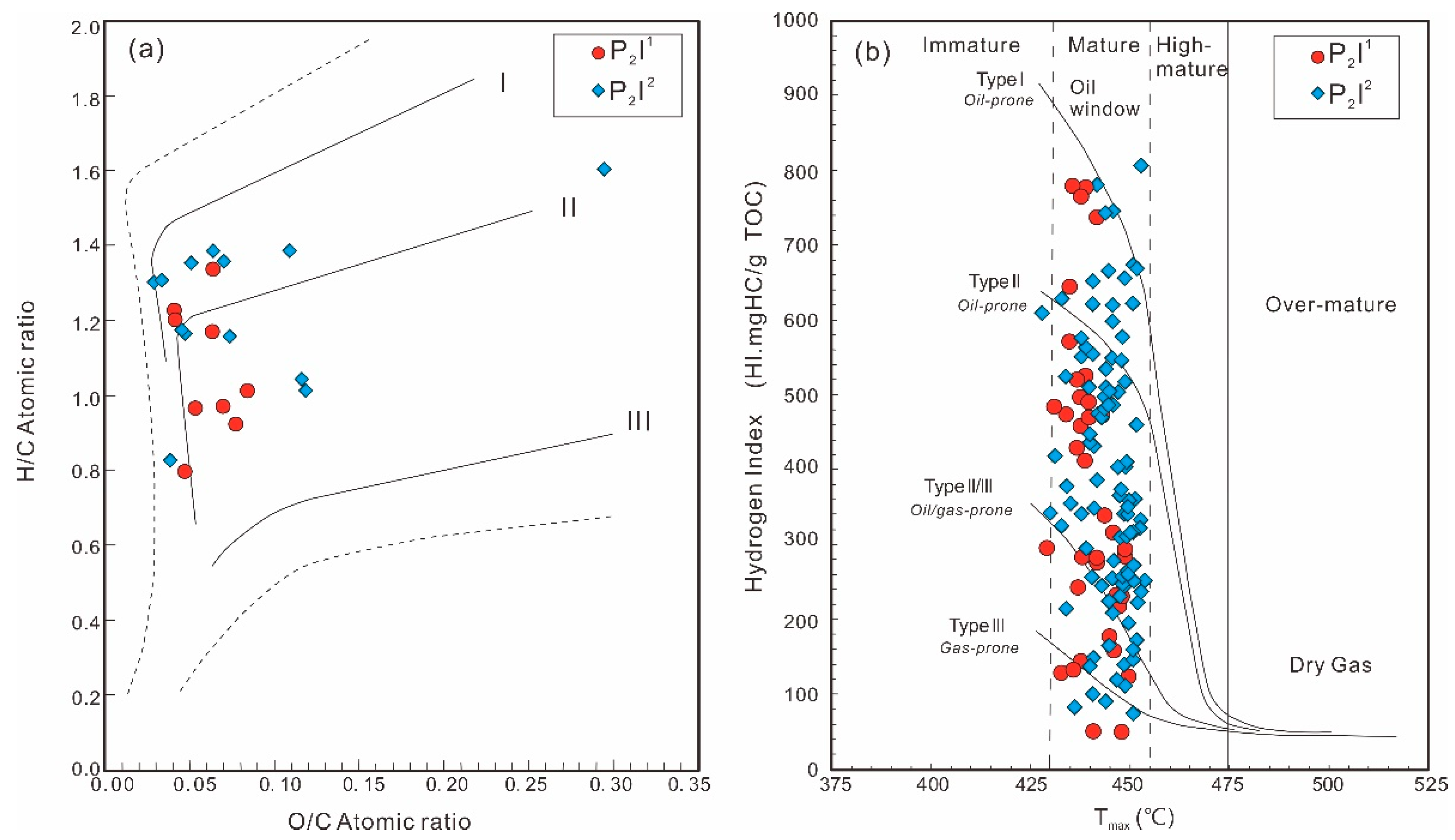
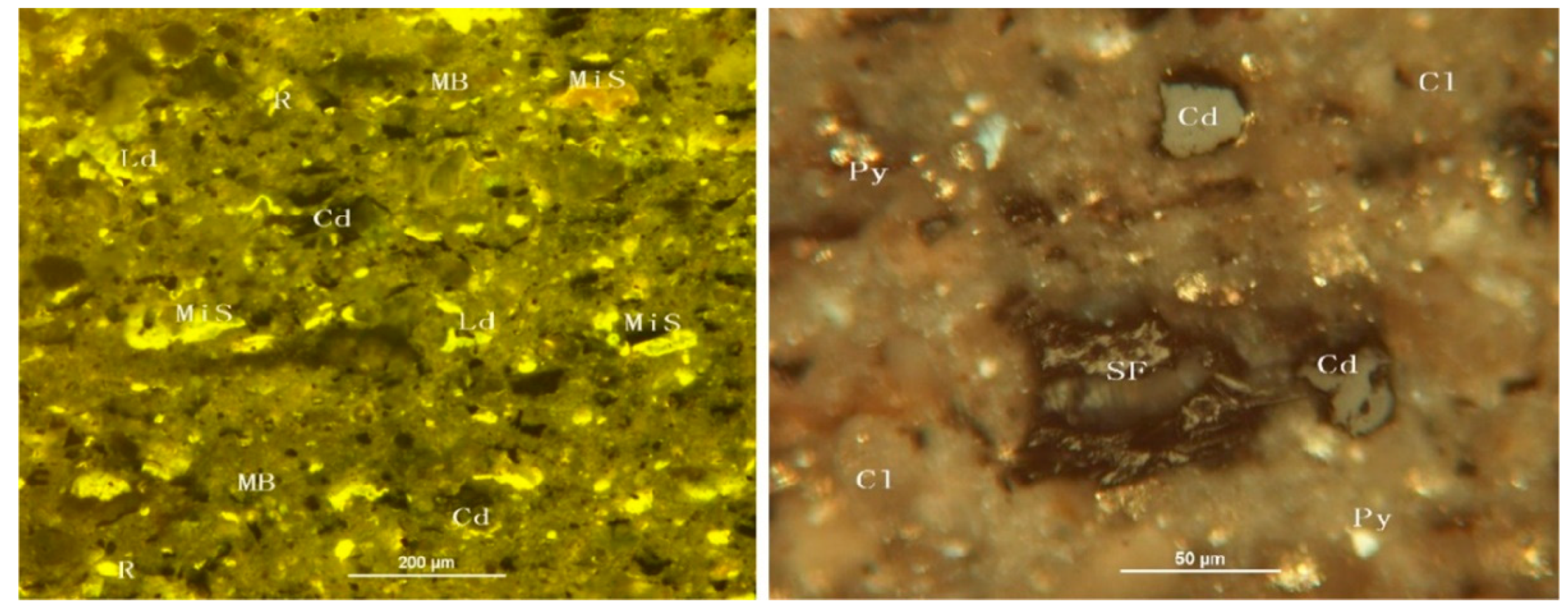
4.2.1. Types of Organic Matter
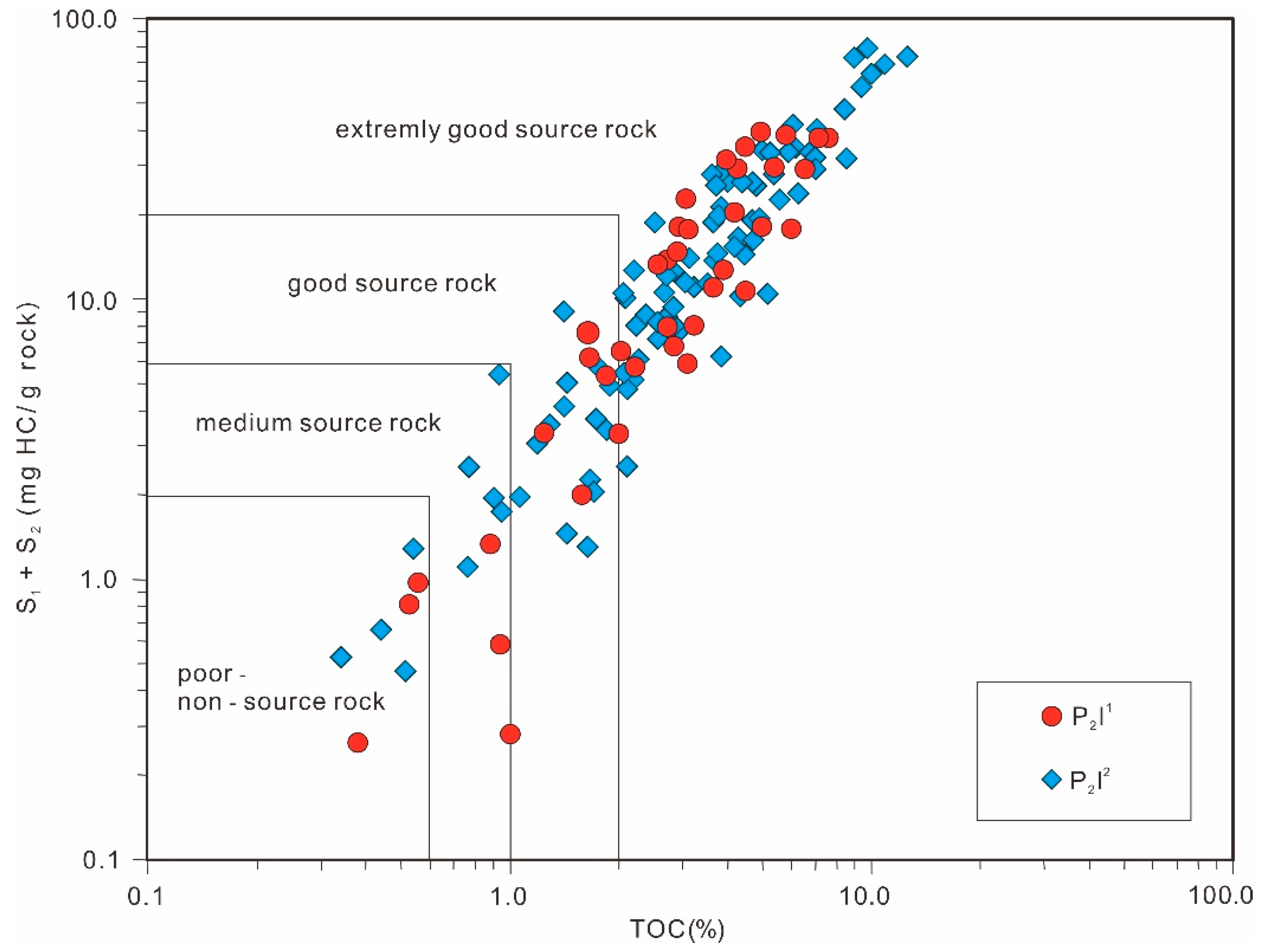
4.2.2. Abundance of Organic Matter
4.3. Thermal Evolution of the Source Rocks
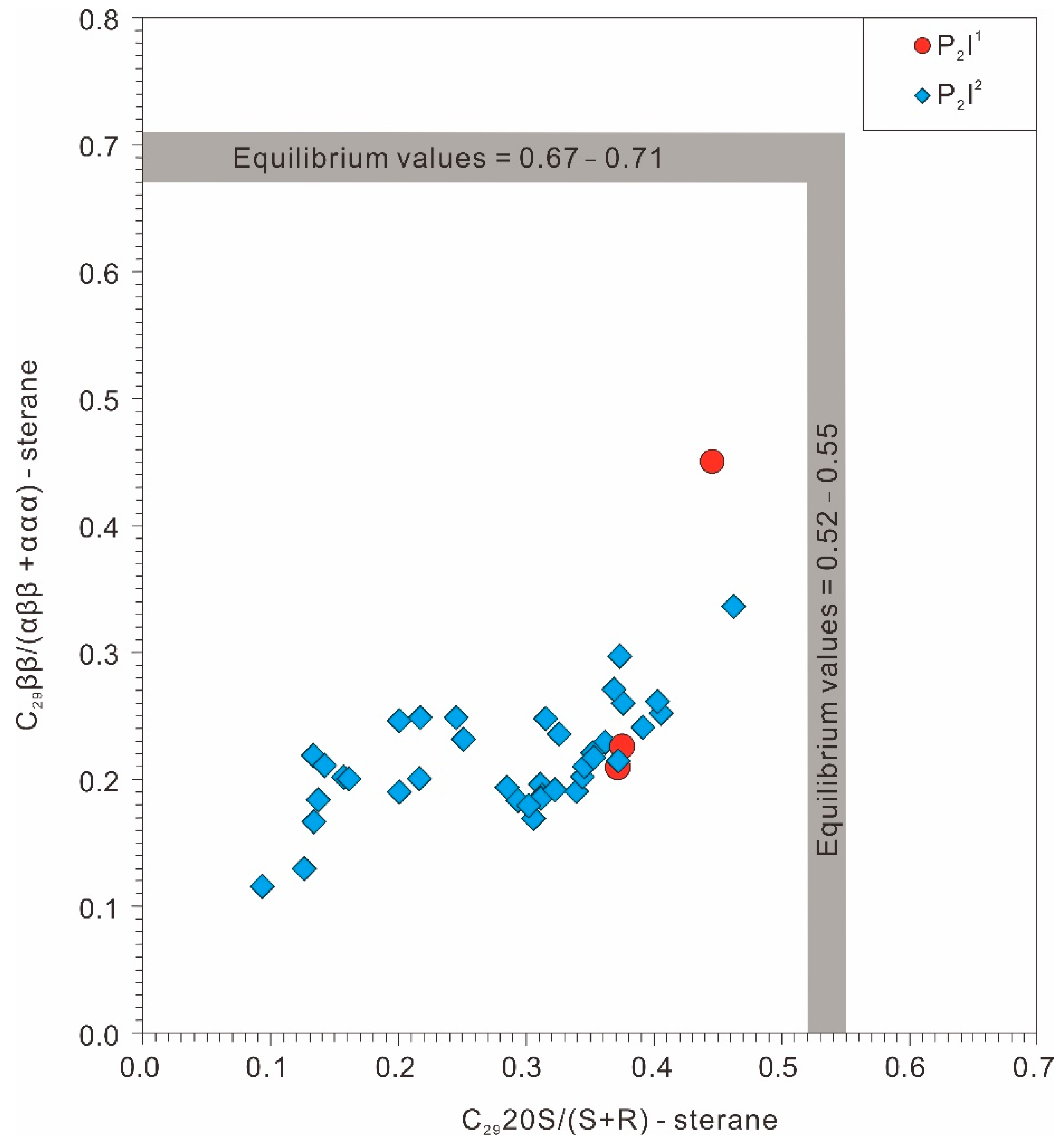
4.3.1. Maturity of the Source Rocks
4.3.2. Thermal Evolution of the Source Rocks
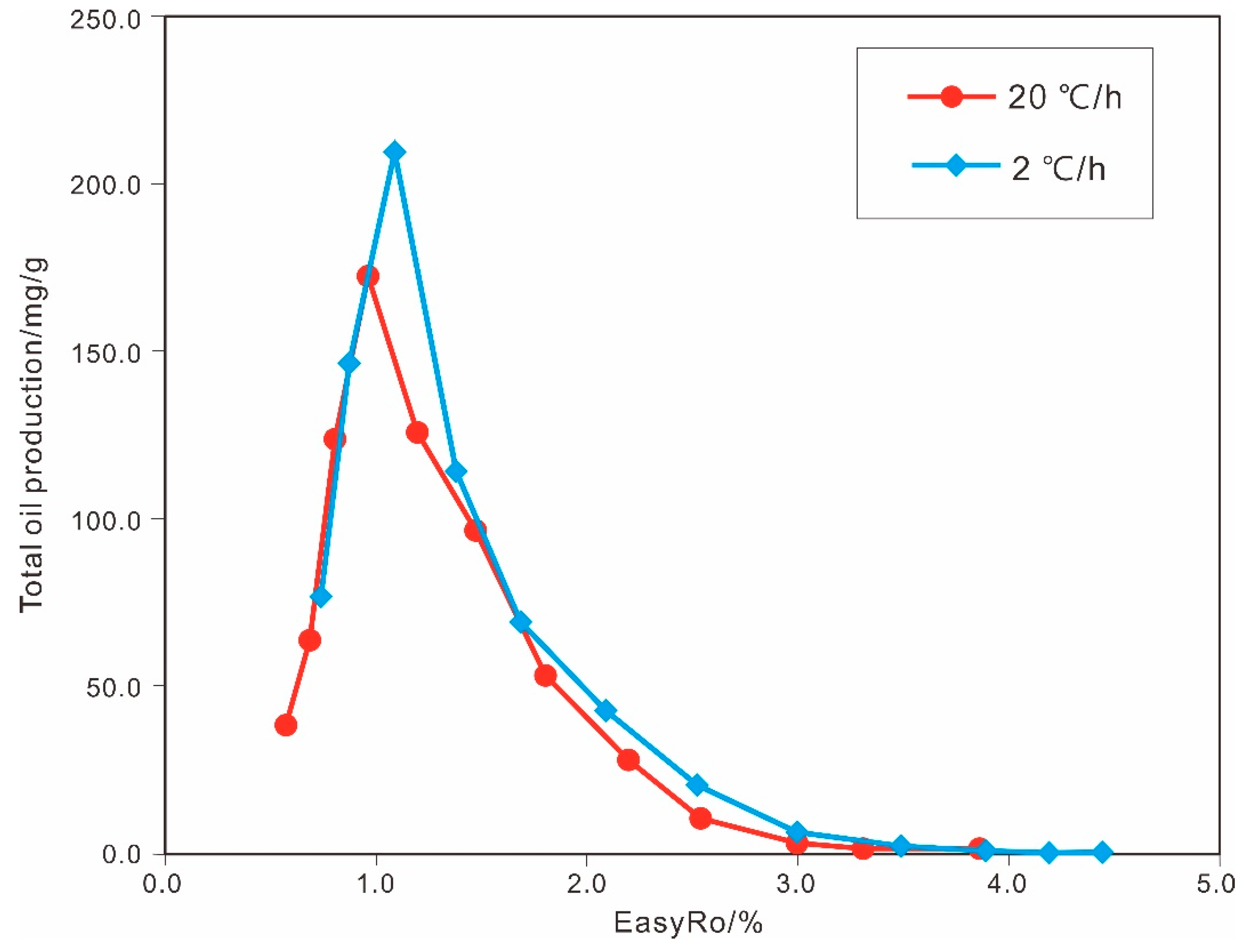
4.4. Thermal Simulation Experiment on Source Rocks in a Closed System
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The majority of the organic matter in the Lucaogou Formation came from algae, and the sedimentary water environment had high reducibility and salinity.
- (2)
- The organic microscopic components of the Lucaogou source rocks were dominated by the sapropelinite group and exinite group, and they were a set of oil-prone source rocks. Most of them were rated as good and extremely good, but their heterogeneity was strong.
- (3)
- At the end of the Cretaceous period, the Lucaogou Formation source rocks entered the main oil generation window and began to generate a large amount of normal crude oil. Currently, the deep part of the depression has generally reached the high-maturity stage and is generating a large amount of highly mature oil and condensate gas. The maturity of the shallow part is relatively low, and only a large amount of conventional crude oil can be generated.
- (4)
- The thermal simulation experiment conducted in a closed system suggests that the Lucaogou source rocks have great hydrocarbon generation capacity and expulsion efficiency, and the heating rate did not have a significant impact on the maximum amount of oil generated.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, H.; Pang, X.Q.; Kuang, L.C.; Pang, H.; Wang, X.L.; Jia, X.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Hu, T. Hydrocarbon expulsion potential of source rocks and its influence on the distribution of lacustrine tight oil reservoir, Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin, Northwest China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 149, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Cao, Y.C.; Ma, Z.J.; Zhen, Y.S. Geochemistry and origins of natural gases in the Zhongguai area of Junggar Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 119, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zha, M.; Liu, K.Y.; Ding, X.J.; Qu, J.X.; Jin, J.H. Characterization of Pore Structures and Implications for Flow Transport Property of Tight Reservoirs: A Case Study of the Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin, Northwestern China. Energies 2021, 14, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Hou, D.J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.M.; Guo, R.B. Impact of the Paleoclimate, Paleoenvironment, and Algae Bloom: Organic Matter Accumulation in the Lacustrine Lucaogou Formation of Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Energies 2020, 13, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Cao, J.; He, W.J.; Shan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, K.B. Development Tendency of Geological Theory of Total Petroleum System: Insights from the Discovery of Mahu Large Oil Province. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2021, 42, 1–9, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.Z.; Zou, C.N.; Li, J.Z.; Li, D.H.; Zheng, M. Assessment criteria, main types, basic features and resource prospects of the tight oil in China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 343–350, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.N.; Yang, Z.; Tao, S.Z.; Yuan, X.J.; Zhu, R.K.; Hou, L.H.; Wu, S.T.; Sun, L.; Zhang, G.S.; Bai, B.; et al. Continuous hydrocarbon accumulation over a large area as a distinguishing characteristic of unconventional petroleum; the Ordos Basin, north-central China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 126, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, C.N.; Zhu, R.K.; Bai, B.; Yang, Z.M.; Hou, L.H.; Zha, M.; Fu, J.H.; Shao, Y.; Liu, K.Y.; Cao, H.; et al. Significance, Geologic Characteristics, Resource Potential and Future Challenges of Tight Oil and Shale Oil. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2015, 34, 3–17, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Katz, B.; Lin, F. Lacustrine basin unconventional resource plays: Key differences. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 56, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R. Upper Permian lacustrine organic facies evolution, southern Junggar Basin, NW China. Org. Geochem. 1998, 28, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yang, Z.; Nan, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhou, P.; Yang, Y.J.; Kou, J.Y.; Zhou, N.C. Characteristics and origin of tuff-type tight oil in Jimusar Depression, Junggar Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 741–749, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Yang, Z.M.; Ma, W.C.; Pan, C.C.; Wang, F. Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Tight Oil in Lucaogou Formation of Jimsar Sag. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2017, 38, 379–384, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Pang, X.Q.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Q.F.; Zheng, X.W.; Ding, X.G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, C.X.; Li, H. Oil content evaluation of lacustrine organic-rich shale with strong heterogeneity: A case study of the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Fuel 2018, 221, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, L.C.; Wang, X.T.; Guo, X.G.; Chang, Q.S.; Jia, X.Y. Geological Characteristics and Exploration Practice of Tight Oil of Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2015, 36, 629–634, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Xiang, B.L.; Li, T.T.; Ren, J.L.; Kong, Y.H. Tight Oil System Particularity of Lucaogou Formation in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2017, 35, 824–833, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Zhi, D.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Chen, J.P.; Qin, Z.J.; Liu, D.G.; Xiang, Y.; Lan, W.F.; Li, N. Organic Geochemistry of Source Rocks and Hydrocarbons in the Junggar Basin; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 18–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.G.; Hu, W.X.; Tang, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Kang, X. The impact of organic fluids on the carbon isotopic compositions of carbonate-rich reservoirs: Case study of the Lucaogou Formation in the Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 85, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wan, M.; Qiu, L.W.; Cao, Y.C.; Yang, S.C. Sedimentary Characteristic and Facies Evolution of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2015, 36, 635–641, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.H.; Zou, C.N.; Liu, L.; Wen, B.H.; Wu, X.Z.; Wei, Y.Z.; Mao, Z.G. Geologic essential elements for hydrocarbon accumulation within Carboniferous volcanic weathered crusts in northern Xinjiang, China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 533–540, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, L.C.; Hu, W.X.; Wang, X.L.; Wu, H.G.; Wang, X.L. Research of the Tight Oil Reservoir in the Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar Sag: Analysis of Lithology and Porosity Characteristics. Geol. J. China Univ. 2013, 19, 529–535, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Liu, G.D.; Kong, Y.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Niu, Z.C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Geng, C.B.; Shan, X.; Wei, Z.P. Lacustrine tight oil accumulation characteristics: Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 153, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Hu, S.B.; Li, T.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhao, W.Z. Terrestrial heat flow in Junggar Basin, Northwest China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2000, 45, 1327–1332, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Hu, S.B.; Wang, J.Y. The Characteristics of heat flow and geothermal fields in Junggar Basin. Chin. J. Geophys. 2000, 43, 771–779, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, J.J.; Burnham, A.K. Evaluation of a Simple Model of Vitrinite Reflectance Based on Chemical Kinetics. AAPG Bull. 1990, 74, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, K.E.; Walters, C.C.; Moldowan, J.M. The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 1–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, T.G. Pristane/phytane ratio as environmental indicator. Nature 1988, 333, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugan, G. Significance of coniferous rain forests and related oil, Gippsland Basin, Australia. AAPG Bulletin 1985, 69, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, T.T.A.; Zink, K.G.; Mangelsdorf, K.; Sykes, R.; Wilkes, H.; Horsfield, B. Changes in bulk properties and molecular compositions within New Zealand Coal Band solvent extracts from early diagenetic to catagenetic maturity levels. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, D.A.; Aquino Neto, F.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T.; Pinto, A.C. Novel series of tricyclic aromatic terpanes characterized in Tasmanian tasmanite. Org. Geochem. 1992, 18, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ourisson, G.; Albrecht, P.; Rohmer, M. The hopanoids, paleochemistry and biochemistry of a group of natural products: Pure Applied Chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1979, 51, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsté, J.S.S.; Duin, A.; Hollander, D.; Kohnen, M.E.L.; Leeuw, J.W.D. Early diagenesis of bacteriohopanepolyol derivatives: Formation of fossil homohopanoids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 5141–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Haven, H.L.; De Leeuw, J.W.; Sinninghe, D.J.S.; Schenck, P.A.; Palmer, S.E.; Zumberge, J.E. Application of Biological Markers in the Recognition of Palaeohypersaline Environments. In Lacustrine Petroleum Source-Rocks; Fleet, A.J., Kelts, K., Talbot, M.R., Eds.; Geological Society Special Publication: Oxford, UK, 1988; Volume 40, pp. 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Schwark, L.; Empt, P. Sterane biomarkers as indicators of palaeozoic algal evolution and extinction events. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol 2006, 240, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldowan, J.M.; Seifert, W.K.; Gallegos, E.J. Relationship between Petroleum Composition and Depositional Environment of Petroleum Source Rocks1. AAPG Bull. 1985, 69, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.X. Large Coal-Formed Gas Fields and Gas Sources in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 1–454. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, D.Y.; Lan, W.F.; Xiang, H.; Ding, J.; Wu, W.A.; Hu, Z.L. Genetic types and origins of natural gases from the eastern Junggar basin. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2019, 48, 142–152, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J.M. Petroleum Geology and Geochemistry; Freeman Company: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Tissot, B.P.; Welte, D.H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 1–699. [Google Scholar]
- Bordenave, M.L. Applied Petroleum Geochemistry; Editions Technip: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 344–353. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.F.; Li, J.C. Continental Hydrocarbon Generation in China; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1982; pp. 1–355. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peters, K.E. Guidelines for Evaluating Petroleum Source Rock Using Programmed Pyrolysis1. AAPG Bulletin 1986, 70, 318–329. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, B.L.; Li, E.T.; Gao, X.W.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Huang, P.; Yu, S.; Liu, J.Z.; Zou, Y.R.; et al. Petroleum generation kinetics for Permian lacustrine source rocks in the Junggar Basin, NW China. Org. Geochem. 2016, 98, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, A.S. Estimating of Petroleum Expulsion Behavior of Source Rocks: A Novel Quantitative Approach. In Petroleum Migration; England, A.J., Fleet, A.J., Eds.; Geological Society Special Publication: London, UK, 1992; Volume 59, pp. 9–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sandvik, E.I.; Young, W.A.; Curry, D.J. Expulsion from hydrocarbon sources: The role of organic absorption. Org. Geochem. 1992, 19, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooles, G.P.; Mackenzie, A.S.; Quigley, T.M. Calculation of petroleum masses generated and expelled from source rocks. Org. Geochem. 1986, 10, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Well | Depth(m) | Strata | Lithology | C19/C21-Tricyclic Terpane | Tricyclic Terpane/Pentacyclic Terpane | C24-Tetracyclic Terpane/C26-Tricyclic Terpane | C35/(C31–C35)Homohopane % | C30αβ-Hopane/C29ααα,(R + S)-Sterane | Gammacerane Index | C31R/C30-Hopane | Ts/(Ts + Tm) | C27-Sterane (%) | C28-Sterane (%) | C29-Sterane (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ji15 | 2280.63 | P2l1 | Dark gray fluorescent mudstone | 0.41 | 0.29 | 1.12 | 7.07 | 6.79 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.43 | 23.78 | 23.77 | 52.46 |
| Ji174 | 3218.97 | P2l1 | Dark gray calcareous mudstone | 0.12 | 0.12 | 1.95 | 2.72 | 4.85 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 13.80 | 37.24 | 48.96 |
| Ji174 | 3227.14 | P2l1 | Dark gray dolomitic mudstone | 0.13 | 0.13 | 1.55 | 2.66 | 6.59 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 14.81 | 37.11 | 48.09 |
| Ji24 | 1691.75 | P2l1 | Gray black mudstone | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.62 | 2.87 | 5.58 | 0.31 | n.d. | 0.27 | 18.41 | 32.77 | 48.83 |
| Ji17 | 3138.01 | P2l2 | Black gray mudstone | 0.10 | 0.14 | 1.06 | 4.16 | 8.20 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 14.99 | 35.39 | 49.62 |
| Ji17 | 3138.01 | P2l2 | Black gray mudstone | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.82 | 4.01 | 12.73 | 0.36 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 34.81 | 26.13 | 39.06 |
| Ji17 | 3135.33 | P2l2 | Gray black mudstone | 0.13 | 0.06 | 1.40 | 3.79 | 9.88 | 0.39 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 36.51 | 26.17 | 37.33 |
| Ji17 | 3135.33 | P2l2 | Gray black mudstone | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.71 | 4.05 | 19.28 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 42.15 | 22.16 | 35.70 |
| Ji174 | 3135.31 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.12 | 0.15 | 1.28 | 2.40 | 4.62 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 20.25 | 34.09 | 45.66 |
| Ji174 | 3113.3 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.10 | 0.16 | 1.46 | 2.57 | 4.08 | 0.42 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 18.88 | 33.39 | 47.73 |
| Ji174 | 3134.05 | P2l2 | Black gray mudstone | 0.08 | 0.10 | 1.38 | 2.70 | 5.44 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 22.94 | 31.56 | 45.50 |
| Ji174 | 3146.16 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.12 | 0.18 | 1.65 | 2.90 | 3.39 | 0.19 | n.d. | 0.12 | 18.53 | 41.45 | 40.01 |
| Ji174 | 3158.88 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.32 | 0.04 | 8.93 | 2.56 | 6.01 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 19.84 | 39.07 | 41.10 |
| Ji174 | 3166.74 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.11 | 0.21 | 2.42 | 2.23 | 3.02 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 21.47 | 40.29 | 38.24 |
| Ji174 | 3177.55 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.16 | 0.09 | 3.62 | 2.13 | 6.44 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 22.08 | 37.87 | 40.05 |
| Ji174 | 3217.51 | P2l2 | Dark gray calcareous mudstone | 0.12 | 0.17 | 1.30 | 2.80 | 4.89 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 13.10 | 35.79 | 51.11 |
| Ji174 | 3130.76 | P2l2 | Black gray mudstone | 0.12 | 0.12 | 2.29 | 2.32 | 8.37 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 25.81 | 30.83 | 43.36 |
| Ji174 | 3114.73 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.11 | 0.16 | 1.37 | 2.39 | 7.26 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 31.83 | 28.72 | 39.45 |
| Ji174 | 3117.75 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.13 | 0.15 | 1.96 | 2.45 | 11.13 | 0.41 | n.d. | 0.10 | 20.59 | 32.54 | 46.88 |
| Ji174 | 3118.78 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.14 | 0.19 | 2.15 | 2.04 | 7.08 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 17.65 | 34.22 | 48.13 |
| Ji174 | 3122.14 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.18 | 0.09 | 5.37 | 3.39 | 4.14 | 0.31 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 15.76 | 31.31 | 52.93 |
| Ji174 | 3146.19 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.12 | 0.16 | 1.11 | 3.66 | 2.80 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 19.22 | 44.60 | 36.19 |
| Ji174 | 3152.98 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.18 | 0.21 | 4.31 | 2.94 | 6.27 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 14.69 | 52.95 | 32.36 |
| Ji174 | 3155.32 | P2l2 | Dark gray dolomitic mudstone | 0.22 | 0.10 | 8.54 | 1.46 | 5.91 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 14.69 | 57.26 | 28.05 |
| Ji174 | 3162.02 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.22 | 0.03 | 7.27 | 2.34 | 7.27 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 18.76 | 41.56 | 39.68 |
| Ji174 | 3196.3 | P2l2 | Dark gray dolomitic mudstone | 0.09 | 0.16 | 1.55 | 2.44 | 7.47 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 20.70 | 37.28 | 42.02 |
| Ji22 | 2543.06 | P2l2 | Dark gray mudstone | 0.10 | 0.15 | 1.69 | 1.75 | 5.25 | 0.35 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 23.97 | 33.63 | 42.40 |
| Ji22 | 2554.54 | P2l2 | Dark gray dolomitic mudstone | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.87 | 2.44 | 6.56 | 0.40 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 23.69 | 30.96 | 45.35 |
| Ji22 | 2552.67 | P2l2 | Dark gray dolomitic mudstone | 0.09 | 0.09 | 2.39 | 1.51 | 5.97 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 35.35 | 32.11 | 32.54 |
| Ji22 | 2554.8 | P2l2 | Dark gray dolomitic mudstone | 0.08 | 0.07 | 1.76 | 2.35 | 10.36 | 0.55 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 33.07 | 33.13 | 33.80 |
| Ji23 | 2296.12 | P2l2 | Gray black calico mudstone | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.81 | 2.59 | 8.57 | 0.51 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 31.11 | 30.44 | 38.46 |
| Ji23 | 2296.04 | P2l2 | Gray black mudstone | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.61 | 2.48 | 8.32 | 0.50 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 30.02 | 30.41 | 39.57 |
| Ji5 | 3535.56 | P2l2 | Gray black mudstone | 1.43 | 0.08 | n.d. | n.d. | 4.73 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 0.52 | 17.43 | 32.51 | 50.06 |
| Ji7 | 2059 | P2l2 | Gray black mudstone | 0.16 | 0.05 | 1.26 | 4.76 | 1.72 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 17.42 | 17.36 | 65.22 |
| Ji7 | 1949.61 | P2l2 | Gray black mudstone | 0.05 | 0.08 | 1.19 | 6.70 | 1.26 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 18.73 | 31.91 | 49.36 |
| Ji7 | 2069.99 | P2l2 | Dolomitic mudstone | 0.29 | 0.19 | n.d. | n.d. | 2.10 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 32.46 | 31.15 | 36.39 |
| Ji7 | 2160.2 | P2l2 | Dolomitic mudstone | 0.13 | 0.12 | 3.62 | 3.62 | 2.50 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 24.89 | 31.31 | 43.79 |
| Ji7 | 2287.45 | P2l2 | Dolomitic mudstone | 0.09 | 0.17 | 1.06 | 2.75 | 1.29 | 0.14 | n.d. | 0.35 | 22.83 | 17.69 | 59.47 |
| Ji7 | 1949.61 | P2l2 | Dark gray dolomitic mudstone | 0.00 | 0.08 | 1.17 | 7.19 | 2.16 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 19.69 | 33.79 | 46.52 |
| Ji7 | 2160.2 | P2l2 | Dark gray dolomitic mudstone | 0.24 | 0.05 | 10.90 | n.d. | 8.14 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.37 | 29.38 | 30.63 | 39.99 |
| Ji7 | 2287.45 | P2l2 | Dark gray dolomitic mudstone | 0.33 | 0.06 | 2.80 | 3.06 | 9.21 | 0.20 | n.d. | 0.10 | 32.70 | 26.05 | 41.25 |
| Ji7 | 2069 | P2l2 | Black mudstone | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.86 | n.d. | 1.51 | 0.27 | n.d. | 0.21 | 17.61 | 28.06 | 54.33 |
| Ji7 | 2160 | P2l2 | Black dolomitic mudstone | 0.15 | 0.06 | 1.86 | 5.31 | 4.14 | 0.61 | n.d. | 0.28 | 16.64 | 23.63 | 59.73 |
| Code | Name | Code | Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 5α(H),14β(H)-pregnane | T6 | C24,13β(H),14α(H)-tricyclic terpane |
| S2 | C22-homopregnane | T7 | C25,13β(H),14α(H)-tricyclic terpane |
| S3 | 20S-ααα-sterane | T8 | C26-tricyclic terpane |
| S4 | 20R-αββsterane | T9 | C26-tricyclic terpane |
| S5 | 20S-αββ-sterane | T10 | C24-tetracyclic terpane |
| S6 | 20R-ααα-sterane | T11 | C28-tricyclic terpane |
| S7 | 20R-24-ethyl-10α13β17α-rearranged sterane | T12 | C28-tricyclic terpane |
| S8 | 20S-24-ethyl-10α13α17β-rearranged sterane | T13 | 18α,-22,29,30-trisnorhopane(Ts) |
| S9 | 20S-24-methyl-ααα-sterane | T14 | 17α,-22,29,30-trisnorhopane(Tm) |
| S10 | 20R-24-methyl-αββ-sterane | T15 | 17α,21β-30-norhopane |
| S11 | 20S-24-methyl-αββ-sterane | T16 | 17α(H),21β(H)-hopane |
| S12 | 20R-24-methyl-ααα-sterane | T17 | 17β(H),21α(H)-moretane |
| S13 | 20S-24-ethyl-ααα-sterane | T18 | 22S-17α(H),21β(H)-homohopane |
| S14 | 20R-24-ethyl-αββ-sterane | T19 | 22R-17α(H),21β(H)-homohopane |
| S15 | 20S-24-ethyl-αββ-sterane | T20 | Gammacerane |
| S16 | 20R-24-ethyl-ααα-sterane | T21 | 22R-17β(H),21α(H)-homohopane |
| T1 | C19,14β(methyl)-tricyclic terpane | T22 | 22S-17α(H),21β(H)-double homohopane |
| T2 | C20,13β(H),14α(H)-tricyclic terpane | T23 | 22R-17α(H),21β(H)-double homohopane |
| T3 | C21,13β(H),14α(H)-tricyclic terpane | T24 | 22S-17α(H),21β(H)-trishomohopane |
| T4 | C22,13β(H),14α(H)-tricyclic terpane | T25 | 22R-17α(H),21β(H)-trishomohopane |
| T5 | C23,13β(H),14α(H)-tricyclic terpane |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Lei, D.; Liu, G.; Gao, G.; Huang, L.; Qi, Y. Geochemical Characteristics and Process of Hydrocarbon Generation Evolution of the Lucaogou Formation Shale, Jimsar Depression, Junggar Basin. Energies 2022, 15, 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072331
He W, Liu Y, Wang D, Lei D, Liu G, Gao G, Huang L, Qi Y. Geochemical Characteristics and Process of Hydrocarbon Generation Evolution of the Lucaogou Formation Shale, Jimsar Depression, Junggar Basin. Energies. 2022; 15(7):2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072331
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Wenjun, Yin Liu, Dongxue Wang, Dewen Lei, Guangdi Liu, Gang Gao, Liliang Huang, and Yanping Qi. 2022. "Geochemical Characteristics and Process of Hydrocarbon Generation Evolution of the Lucaogou Formation Shale, Jimsar Depression, Junggar Basin" Energies 15, no. 7: 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072331
APA StyleHe, W., Liu, Y., Wang, D., Lei, D., Liu, G., Gao, G., Huang, L., & Qi, Y. (2022). Geochemical Characteristics and Process of Hydrocarbon Generation Evolution of the Lucaogou Formation Shale, Jimsar Depression, Junggar Basin. Energies, 15(7), 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072331






