Polyhumous Dystrophic Pit Lakes: Hydrographic and Hydrochemical Characteristics on the Example of Reservoirs in the Włoszczowska Basin, Central Poland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Location of the Research Area
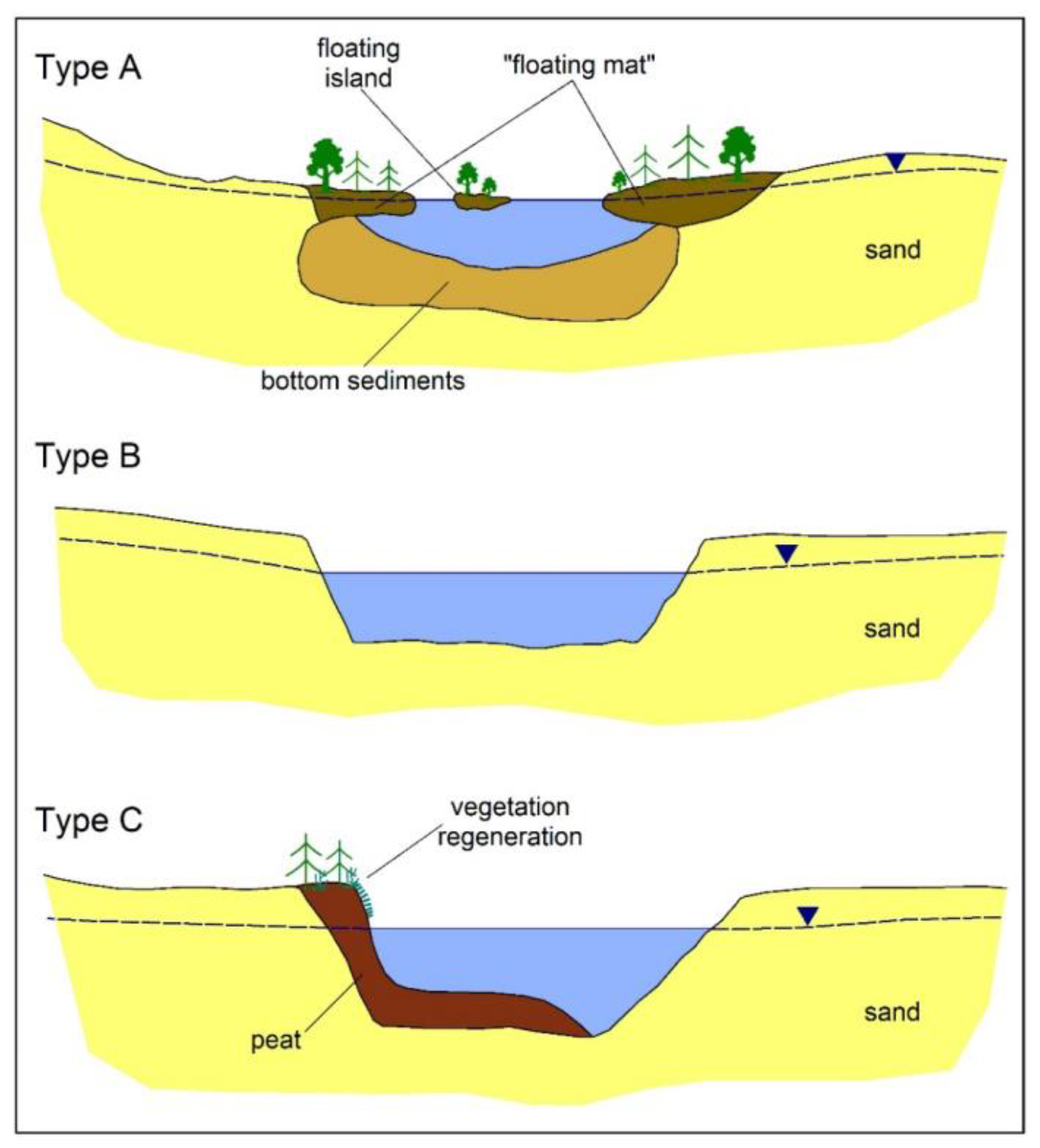
3. Research Methods
- -
- Determining the hydrological type of the reservoir (whether the reservoir is endorheic or flow-through).
- -
- Linking the location of the reservoir with the type of relief (the presence of dunes to confirm their aeolian origin).
- -
- Assessment of peat depletion in the shore zone of the reservoir.
- -
- Measuring the maximum depth of the reservoir.
4. Results and Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jankowski, A.T. From Research on Anthropogenic Water Reservoirs in the Upper Silesian Area; Selected Geographical Issues; WNoZ UŚ: Sosnowiec, Poland, 1995. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Molenda, T. Impact of Saline Mine Water: Development of a Meromictic Reservoir in Poland. Mine Water Environ. 2014, 33, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenda, T. Conditions for development of anthropogenic meromictic reservoirs in the workings of crystalline rocks (based on the examples of the quarries of the Žulovská pahorkatina, NE Czech Republic). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubiak, J.; Machula, S.; Choiński, A. Particular Example of Meromixis in the Anthropogenic Reservoir. Carpath. J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 13, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenda, T.; Ciupa, T.; Suligowski, R. The properties of reservoir water in post mining excavations of Cambrian and Devoni-an quartzite sandstones (Holy Cross Mountains). Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castendyk, D.N.; Eary, L.E.; Balistrieri, L.S. Modeling and management of pit lake waterchemistry 1: Theory. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castendyk, D.; Balistrieri, L.; Gammons, C.; Tucci, N. Modeling and management of pit lake water chemistry 2: Case studies. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenda, T.; Kidawa, J. Natural and Anthropogenic Conditions of the Chemical Composition of Pit Lake Waters (Based on Example Pit Lakes from Central Europe). Mine Water Environ. 2020, 39, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czop, M.; Motyka, J.; Sracek, O.; Szuwarzyński, M. Geochemistry of the Hyperalkaline Gorka Pit Lake (pH > 13) in the Chrzanow Region, Southern Poland. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2010, 214, 423–434, ISSN 0049-6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motyka, J.; Postawa, A. Influence of contaminated Vistula River water on the groundwater entering the Zakrzówek limestone quarry, Cracow region, Poland. Environ. Earth Sci. 2000, 39, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierka, E.; Stalmachova, B.; Molenda, T.; Chmura, D.; Pierzchała, Ł. Environmental and Socio-Economic Importance of Mining Subsidence Reservoirs; Technicka Literatura BEN: Praha, Czech Republic, 2012; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Damnjanović, B.; Novković, M.; Vesić, A.; Živković, M.; Radulović, S.; Vukov, D.; Anđelković, A.; Cvijanović, D. Biodiversity-friendly designs for gravel pit lakes along the Drina River floodplain (the Middle Danube Basin, Serbia). Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 27, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaen, P.J.; Macdonald, M.A.; Bradbury, R. Ecosystem services provided by a former gravel extraction site in the uk under two contrasting restoration states. Conserv. Soc. 2016, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutry-Korycka, M.; Werner-Więckowska, H. Przewodnik do Hydrograficznych Badań Terenowych; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1996. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Macioszczyk, A.; Dobrzyński, D. Hydrogeochemia; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2002. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L.; Boulion, V.V. Regularities in primary production. Secchi depth and fish yield and a new system define trophic and humic state indices for lake ecosystems. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2001, 86, 23–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górniak, A. A new version of the Hydrochemical Dystrophy Index to evaluate dystrophy in lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 78, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team, R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczyk, C. Wioślarki (Cladocera) i Widłonogi (Copepoda) Dołów Potorfowych w Okolicach Parczewa; Sectio C, Biologia; Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Skłodowska: Lublin, Poland, 1969; Volume 24, pp. 323–339. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, S. Wrotki (Rotatoria) Torfianek Okolic Parczewa; Sectio C, Biologia; Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Skłodowska: Lublin, Poland, 1974; Volume 29, pp. 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Staniszewski, R.; Frankowski, P.; Kayzer, D.; Zbierska, J.; Achtenberg, K. Reconstruction of Ancient Lake after Peat Excavation—A Case Study about Water Quality. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mętrak, M.; Pawlikowski, P.; Suska-Malawska, M. Age and Land Use as Factors Differentiating Hydrochemistry and Plant Cover of Astatic Ponds in Post-Agricultural Landscape. J. Water Land Dev. 2014, 21, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobolski, K. Torfowiska na Przykładzie Ziemi Świeckiej; Towarzystwo Przyjaciół Dolnej Wisły: Świecie, Poland, 2003; p. 255. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Arvola, L.; Rask, M.; Forsius, M.; Ala-Opas, P.; Keskitalo, J.; Kulo, K.; Kurkilahti, M.; Lehtovaara, A.; Sairanen, S.; Salo, S.; et al. Food Web Responses to Artificial Mixing in a Small Boreal Lake. Water 2017, 9, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zieliński, A. Wstępne Badania Właściwości Fizyczno-Chemicznych Wód Jezior w Lasach Golejowskich koło Staszowa (Niecka Połaniecka). [w:] Ciupa T; Suligowski, R.C., Ed.; Woda w Badaniach Geograficznych: Kielce, Poland, 2010; pp. 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Gos, K.; Bociąg, K.; Banaś, K. Roślinność Podwodna w Kwaśnych Jeziorach Pomorza [w:]; Banaszak, J., Tobolski, K., Eds.; Park Narodowy Bory Tucholskie, WSP: Bydgoszcz, Poland, 1998; pp. 261–277. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Górniak, A.; Kajak, Z. Hydrobiologia-Limnologia; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2020; p. 452. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Ponziani, M.; Slob, E.C.; Ngan-Tillard, D.J.M.; Vanhala, H. Influence of water content on the electrical conductivity of peat. Int. Water Technol. J. 2011, 1, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, J.; Lück, E.; Bauriegel, A.; Richter, C.; Zeitz, J. Multi-scale analysis of electrical conductivity of peatlands for the assessment of peat properties. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugier, P. Ecological Processes and Properties of Excavated Peatlands of Eastern Poland; Towarzystwo Wydawnictw Nau-Kowych Libropolis: Lublin, Poland, 2014; p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- Sender, A.; Mysiak, G. Hydrobotanic Characteristic of Some Peat-Pits of the Polesie National Park with Special Emphasis on Charophytes; Sectio C, Biologia; Annales Universitatis Mariae Curie-Skłodowska: Lublin, Poland, 2010; Volume 65, pp. 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R.A.; Gherini, S.A.; Chen, C.W.; Mok, L.; Hudson, R.J.M. Integrated acidification study (ILWAS): A mechanistic ecosystem analysis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 1984, 305, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbury, C.E.; Vertucci, F.A.; Mattson, M.D.; Likens, G.E. Acidification of Adirondack lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choiński, A. Jeziora Kuli Ziemskiej; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2000. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard, W. Przewodnik-Flora i Fauna Wód Śródlądowych; Multico: Warszawa, Poland, 1998. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Górniak, A. Dystrophy level in the “suchars” of Wigry National Park. Rocz. Augustowsko-Suw. 2004, 4, 45–52. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
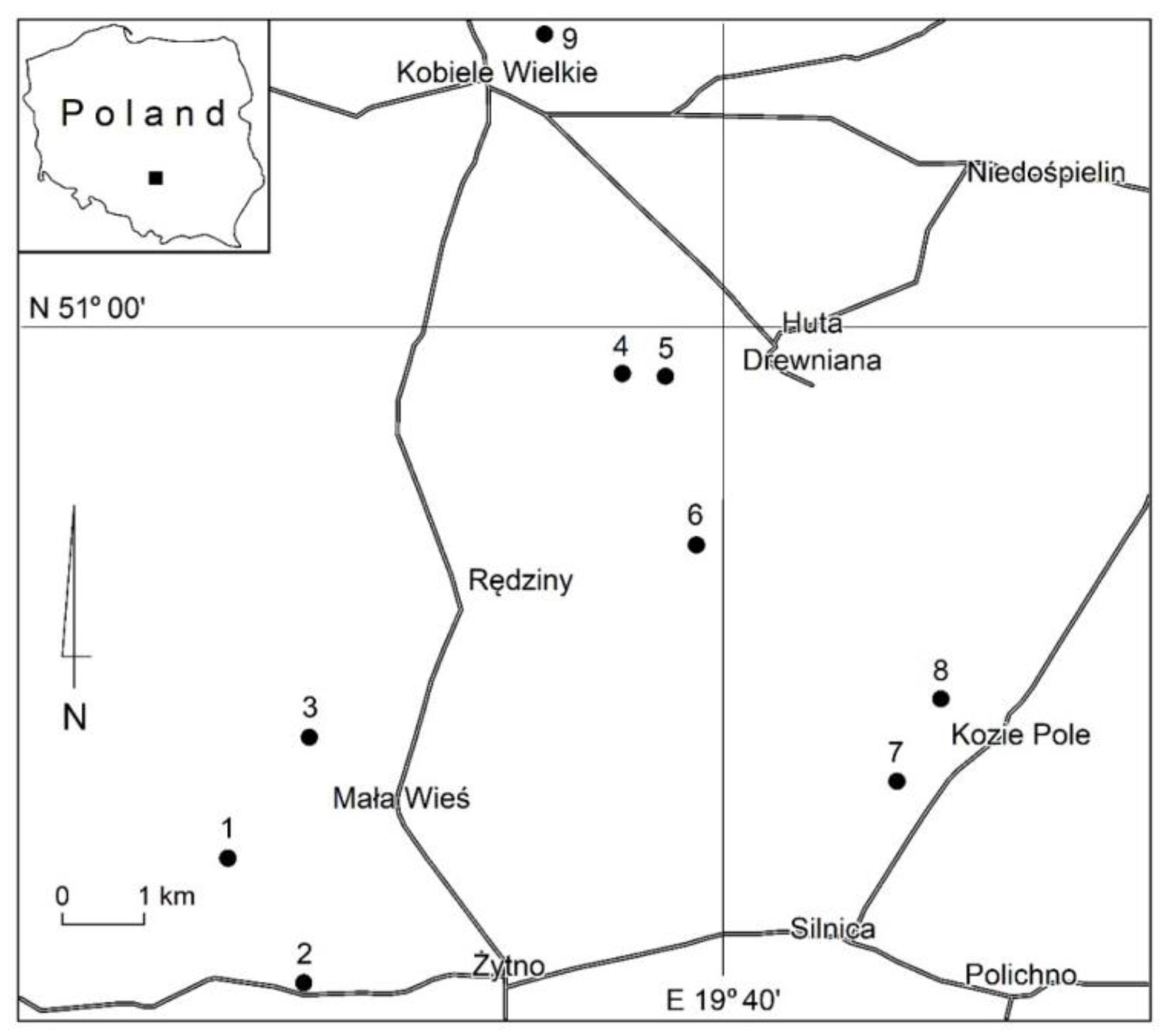







| Reservoir Number | Location | Area |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | N: 50°56′07.14″ E: 19°34′38.71″ | 1.90 ha |
| 2 | N: 50°55′34.80″ E: 19°35′38.31″ | 1.00 ha |
| 3 | N: 50°57′14.11″ E: 19°35′59.88″ | 7.30 ha |
| 4 | N: 50°59′42.89″ E: 19°38′36.21″ | 0.66 ha |
| 5 | N: 50°59′41.04″ E: 19°38′53.22″ | 1.70 ha |
| 6 | N: 50°58′36.13″ E: 19°39′27.12″ | 0.25 ha |
| 7 | N: 50°57′03.96″ E: 19°42′09.16″ | 0.47 ha |
| 8 | N: 50°57′31.96″ E: 19°43′08.22″ | 0.15 ha |
| 9 | N: 51°07′14.11″ E: 19°39′03.33″ | 9.80 ha |
| (a) | ||||||
| Reservoir Number | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | Hydrochemical Type | |
| 1 | 1.9 ± 0.61 | 0.42 ± 0.12 | 1.4 ± 0.81 | 0.7 ± 0.62 | Cl-Ca | |
| SO4-Cl-Ca | ||||||
| SO4-Cl-Ca-Na | ||||||
| 2 | 2.4 ± 0.62 | 0.55 ± 0.17 | 1.78 ± 0.59 | 1 ± 0.61 | Cl-Ca | |
| SO4-Cl-Ca | ||||||
| SO4-Ca-Na | ||||||
| Cl-SO4-Ca-Na | ||||||
| 3 | 18.9 ± 6.9 | 3.61 ± 1.66 | 3.86 ± 2.31 | 1.69 ± 1.84 | SO4-Ca | |
| 4 | 29.1 ± 21.3 | 5.48 ± 4.47 | 4.58 ± 3.39 | 2.85 ± 3.43 | SO4-Ca | |
| 5 | 10.1 ± 3.9 | 1.77 ± 0.66 | 1.53 ± 0.5 | 0.8 ± 0.08 | SO4-Ca | |
| 6 | 7.1 ± 2.9 | 0.73 ± 0.23 | 1.1 ± 0.55 | 1.41 ± 1.33 | SO4-Ca | |
| 7 | 7.5 ± 1.5 | 1.35 ± 0.23 | 1.45 ± 0.22 | 0.95 ± 0.32 | SO4-Ca | |
| 8 | 10.6 ± 4.4 | 1.02 ± 0.32 | 1.43 ± 0.22 | 0.62 ± 0.16 | SO4-Ca | |
| 9 | 4 ± 0.45 | 1.05 ± 0.17 | 1.6 ± 0.38 | 5 ± 0.8 | SO4-Ca | |
| (b) | ||||||
| Reservoir Number | HCO3− | Cl− | SO42− | NO3− | DOC | COLOUR |
| 1 | 7 ± 1 | 2.67 ± 1.2 | 3.6 ± 4.3 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 2.4 ± 3.5 | 196 ± 6 |
| 2 | 4.8 ± 1 | 2.66 ± 0.15 | 5.1 ± 2.7 | 0.3 ± 0.05 | 30 ± 9 | 243 ± 98 |
| 3 | 2.5 ± 2 | 5.17 ± 2.62 | 71.5 ± 32.4 | 0.76 ± 1.22 | 15 ± 6 | 58 ± 12 |
| 4 | 0 | 6.32 ± 3.17 | 99 ± 77 | 2.67 ± 3.91 | 14 ± 7 | 44 ± 9 |
| 5 | 2.5 ± 2.5 | 1.72 ± 0.22 | 27.7 ± 14.8 | 1.04 ± 0.96 | 15 ± 4.7 | 50 ± 10 |
| 6 | 6.5 ± 2 | 1.97 ± 0.78 | 22.1 ± 19 | 1.11 ± 1.06 | 16 ± 2.2 | 72 ± 38 |
| 7 | 4.5 ± 3 | 2.25 ± 0.42 | 15.5 ± 3.4 | 0.7 ± 0.53 | 30 ± 9.3 | 267 ± 80 |
| 8 | 5 ± 3.5 | 2.52 ± 0.55 | 23 ± 8.6 | 0.28 ± 0.06 | 36.5 ± 6.4 | 436 ± 90 |
| 9 | 5 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.58 | 12.2 ± 2.3 | 0.7 ± 0.23 | 18 ± 2 | 171 ± 9 |
| Water Resrvoir Number | HSI | Classification | HDI | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (natural lake) | 72–80 76 | polyhumic | 81–95 73 | moderate dystrophy |
| 2 (natural lake) | 73–85 79 | polyhumic | 71–96 86 | high dystrophy |
| 3 (pit lake) | 51–58 54 | mesohumic | 87–93 89 | high dystrophy |
| 4 (pit lake) | 52–59 55 | mesohumic | 87–90 88 | high dystrophy |
| 5 (pit lake) | 55–70 63 | mesohumic | 73–92 86 | high dystrophy |
| 6 (pit lake) | 58–92 76 | polyhumic | 66–78 74 | moderate dystrophy |
| 7 (pit lake) | 73–89 81 | polyhumic | 72–95 88 | high dystrophy |
| 8 (pit lake) | 79–86 84 | hyperhumic | 79–87 83 | high dystrophy |
| 9 (pit lake) | 74–79 76 | polyhumic | 83–93 90 | high dystrophy |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molenda, T.; Kostka, B.; Malik, I.; Lejwoda, P.; Radziejowski, W.; Kidawa, J. Polyhumous Dystrophic Pit Lakes: Hydrographic and Hydrochemical Characteristics on the Example of Reservoirs in the Włoszczowska Basin, Central Poland. Energies 2022, 15, 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072681
Molenda T, Kostka B, Malik I, Lejwoda P, Radziejowski W, Kidawa J. Polyhumous Dystrophic Pit Lakes: Hydrographic and Hydrochemical Characteristics on the Example of Reservoirs in the Włoszczowska Basin, Central Poland. Energies. 2022; 15(7):2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072681
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolenda, Tadeusz, Beata Kostka, Ireneusz Malik, Paweł Lejwoda, Wiktor Radziejowski, and Joanna Kidawa. 2022. "Polyhumous Dystrophic Pit Lakes: Hydrographic and Hydrochemical Characteristics on the Example of Reservoirs in the Włoszczowska Basin, Central Poland" Energies 15, no. 7: 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072681
APA StyleMolenda, T., Kostka, B., Malik, I., Lejwoda, P., Radziejowski, W., & Kidawa, J. (2022). Polyhumous Dystrophic Pit Lakes: Hydrographic and Hydrochemical Characteristics on the Example of Reservoirs in the Włoszczowska Basin, Central Poland. Energies, 15(7), 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15072681





