Real-Time Solution of Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Problem Based on Parameter-Adaptive PID with Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
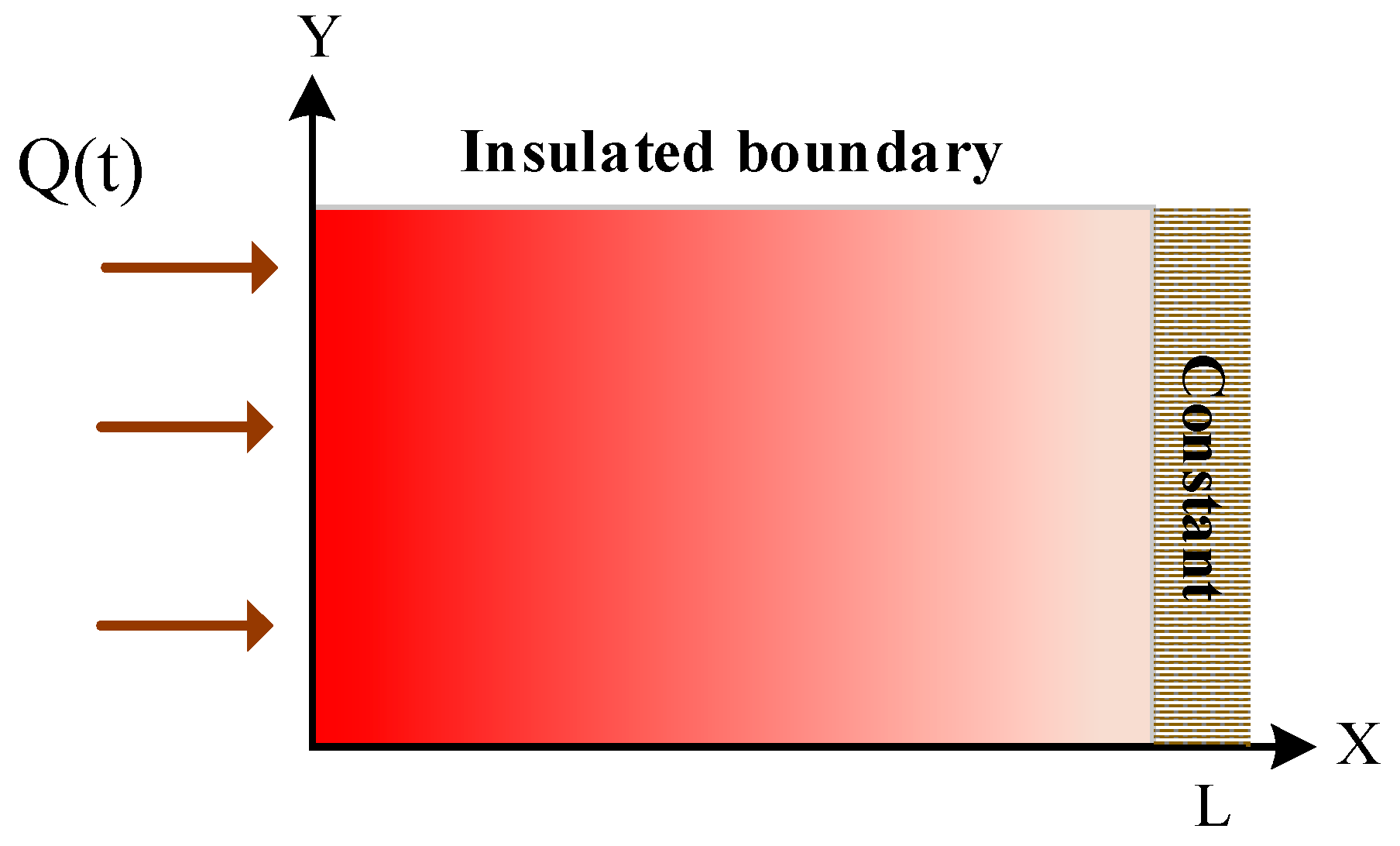
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Thermal System Model
2.2. Finite Difference Method
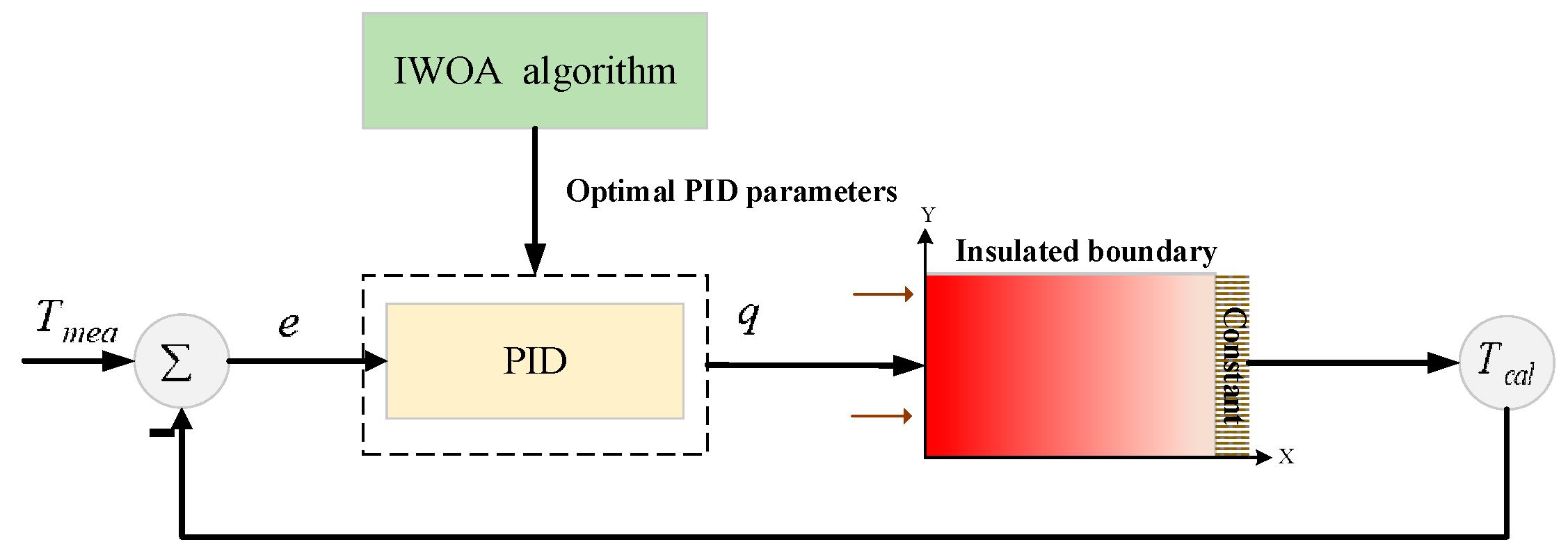
3. Parametric Adaptive PID Algorithm to Estimate Heat Flux
3.1. Whale Optimization Algorithm
3.2. Improving the Whale Optimization Algorithm
3.2.1. Optimizing the Initial Solution Space
3.2.2. Segment Control Parameters and Adaptive Weights
3.2.3. Adaptive Learning Factor
3.2.4. Cauchy Perturbation Strategy
3.3. IWOA-PID Estimated Heat Flux
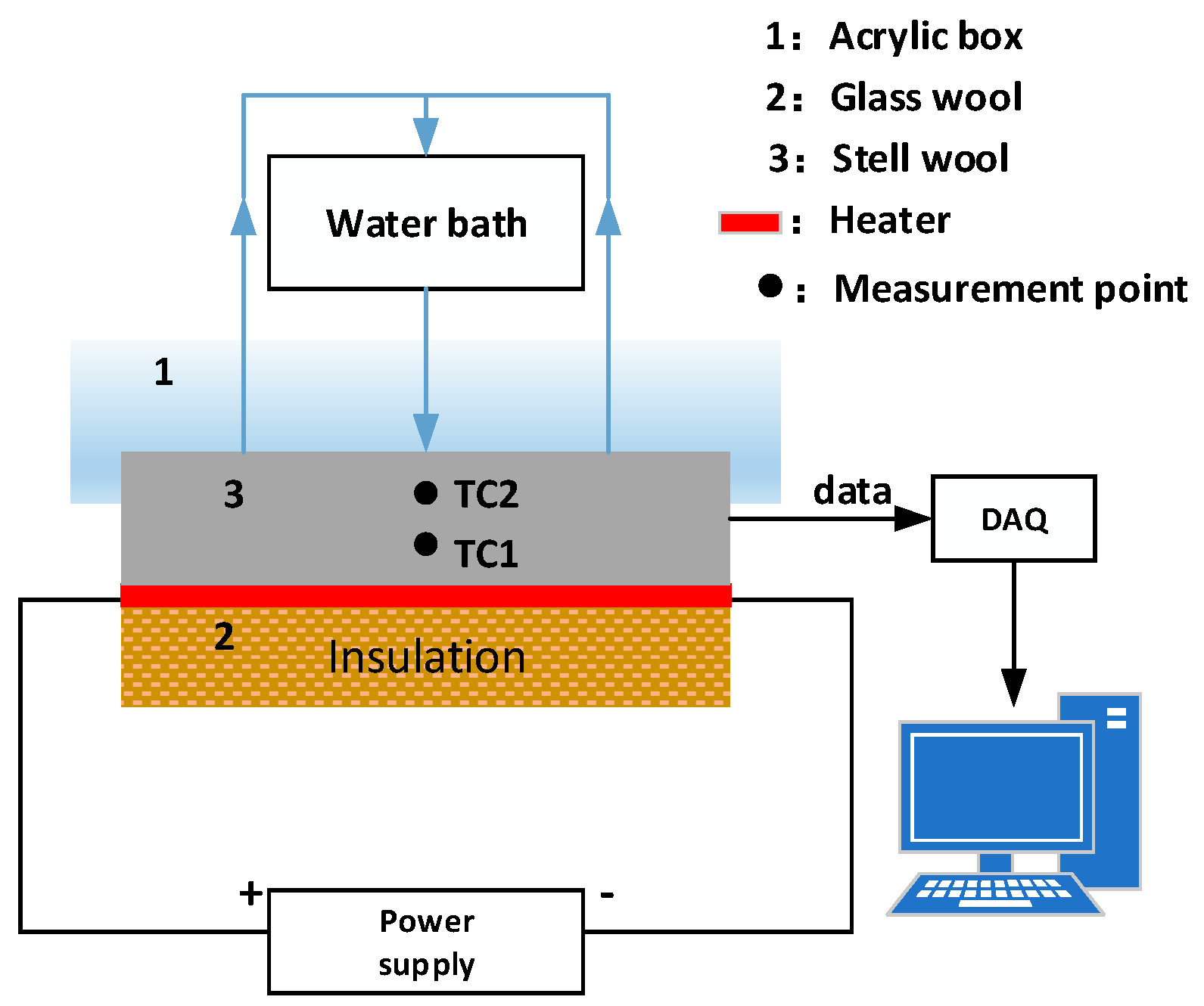
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Model Validation
4.2. Influence of Measurement Point Location on Inversion Results
4.3. Influence of Measurement Error on Inversion Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forooza, S.; Keith, W.; Farshad, K. Optimal combinations of Tikhonov regularization orders for IHCPs. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 161, 106697. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Heng, Y.; Mhamdi, A. A robust and fast algorithm for three-dimensional transient inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 7865–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangian-Tabrizi, A.; Jaluria, Y. An optimization strategy for the inverse solution of a convection heat transfer problem. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 124, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; He, L. Evaluation of multi-objective inverse heat conduction problem based on particle swarm optimization algorithm, normal distribution and finite element method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 127, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.C.; Maurya, S.N.; Luo, W.J. Coolant Volume Prediction for Spindle Cooler with Adaptive Neuro-fuzzy Inference System Control Method. Sens. Mater. Int. J. Sens. Technol. 2022, 34, 2447–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.; Qiu, Z.; Lu, Q. Simultaneous estimation of fluid temperature and convective heat transfer coefficient by sequential function specification method. Progress. Nucl. Energy 2020, 131, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Wen, S.; Wang, Y. Real-time reconstruction of the time-dependent heat flux and temperature distribution in participating media by using the Kalman filtering technique. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 157, 113667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, H. Application of unscented Rauch-Tung-Striebel smootherto nonlinear inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 112, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tao, B.; Li, J. On-line heat flux estimation of a nonlinear heat conduction system with complex geometry using a sequential inverse method and artificial neural network. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 143, 118491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, H.; Woodbury, K.A. Online heat flux estimation using artificial neural network as a digital filter approach. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 91, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cai, L.; Hong, C. A multiple model adaptive inverse method for nonlinear heat transfer system with temperature-dependent thermophysical properties. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 118, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S. Simultaneous reconstruction of thermal boundary condition and physical properties of participating medium. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 163, 106853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Xu, P.; Wang, K. Real-time estimation of thermal boundary of unsteady heat conduction system using PID algorithm. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 153, 106395S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Wang, K.; Xu, P.; Huang, Y. Numerical and experimental verification of the single neural adaptive PID real-time inverse method for solving inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 189, 122657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjun, B. The Method of Finite Difference Regression. Open J. Stat. 2018, 8, 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ming-Chih, L.; Sangbeom, P.; Yunchang, S. An energy stable finite difference method for anisotropic surface diffusion on closed curves. Appl. Math. Lett. 2022, 127, 107848. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Li, S. Numerical Computation Method for Solving Flow Model of ASP Flooding Based on Full Implicit Finite Difference. Adv. Appl. Math. 2018, 7, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A.D. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeid, S. An effective fake news detection method using WOA-xgbTree algorithm and content-based features. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 109, 107559. [Google Scholar]
- Anitha, J.; Immanuel, A.; Akila, A. An efficient multilevel color image thresholding based on modified whale optimization algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 178, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, C.; Chai, T.; Lu, S.; Cui, D. Un-modeled Dynamics Increment Compensation Driven Nonlinear PID Control and Its Application. Acta Autom. Sin. 2020, 46, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Yadav, M.K.; Sonawane, R. Estimation of time-dependent wall heat flux from single thermocouple data. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 115, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkowski, A.; Krane, M.J.M. The Use of Inverse Heat Conduction Models for Estimation of Transient Surface Heat Flux in Electroslag Remelting. J. Heat Transf. 2015, 137, 031301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

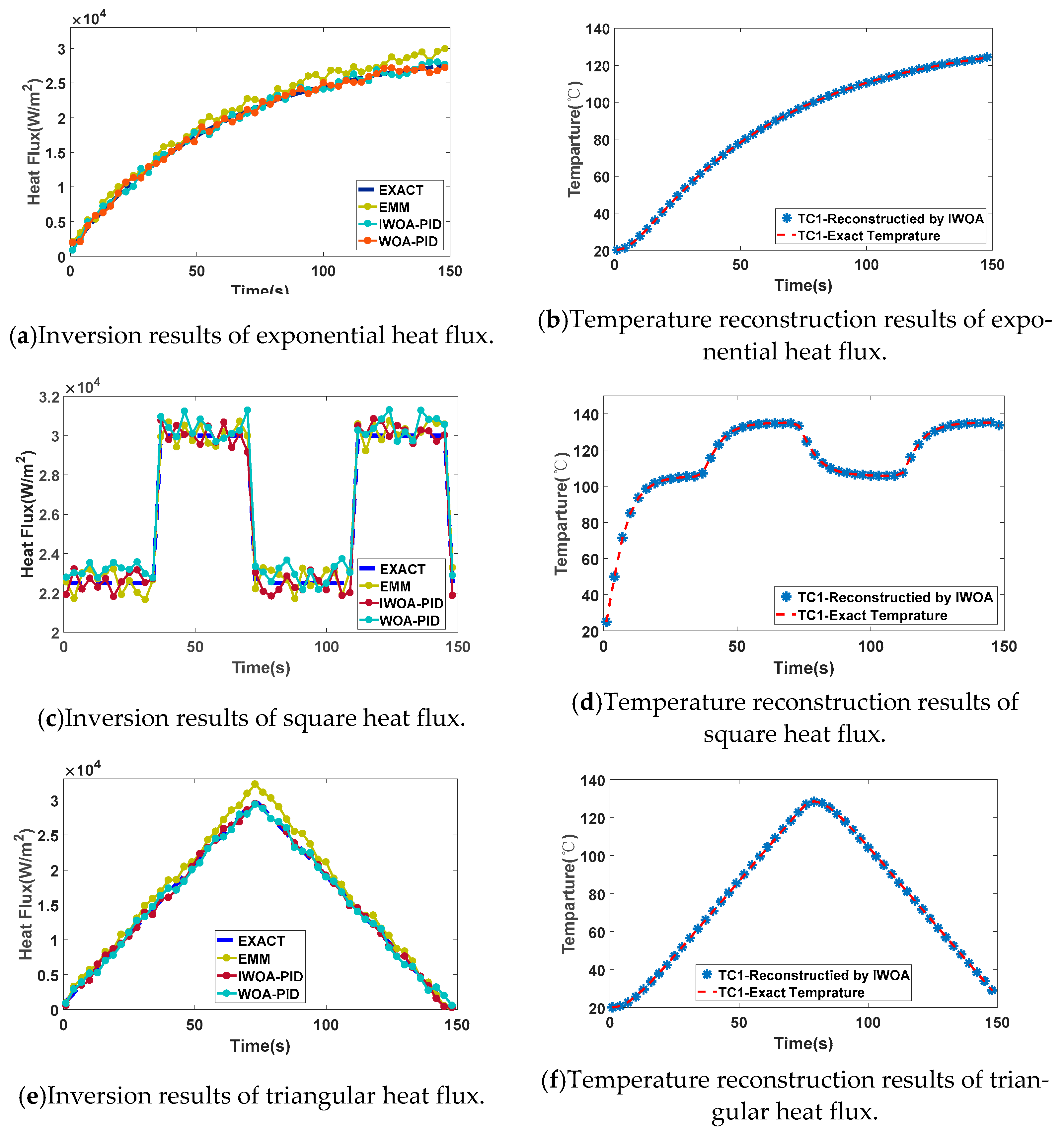
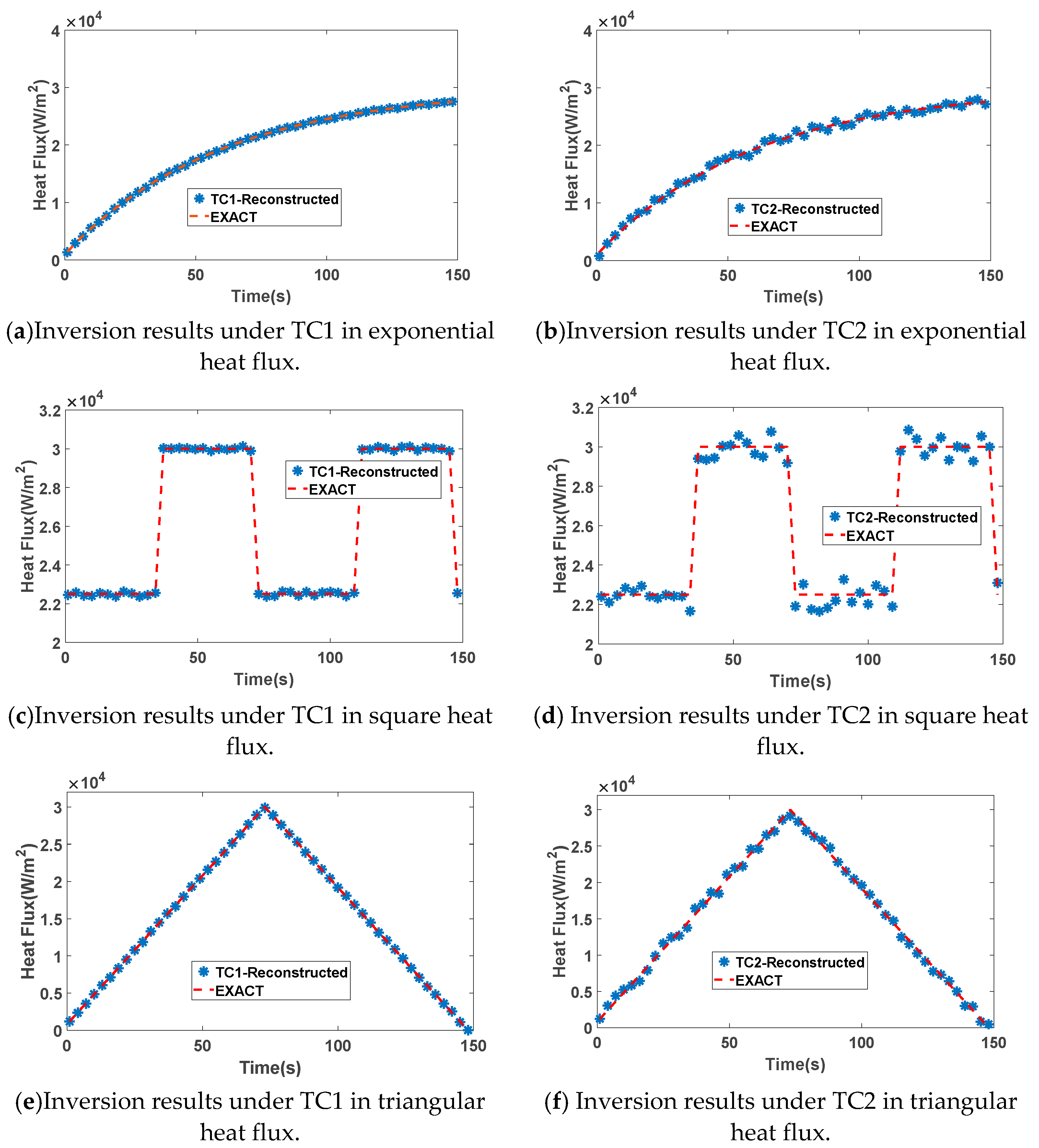
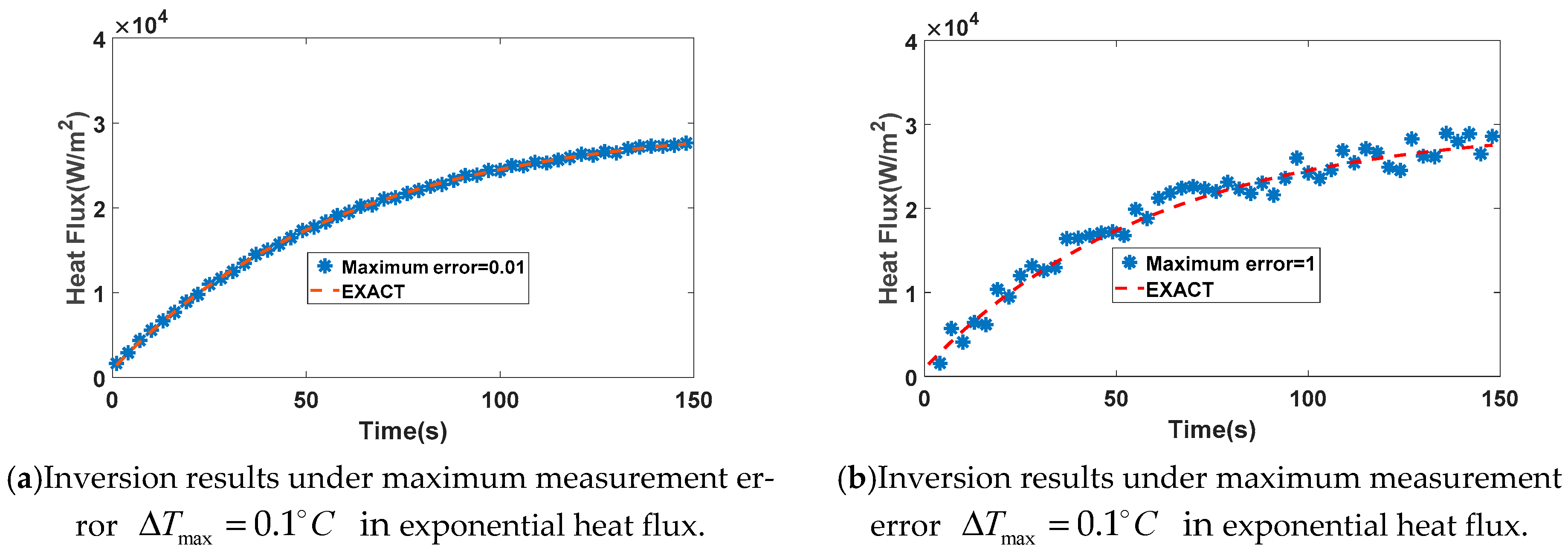
| Heat Flux | IWOA-PID | WOA-PID | EMM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triangle type | 458.2762 | 0.7573 | 553.5310 | 0.9321 | 1.3706 × 103 | 5.0911 |
| Exponential type | 450.9074 | 0.6309 | 492.0142 | 0.7054 | 1.3348 × 103 | 4.5969 |
| Square type | 471.3375 | 0.7319 | 530.9213 | 0.8770 | 686.9112 | 2.044 |
| Heat Flux | IWOA-PID and WOA-PID | IWOA-PID and EMM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triangle type | 20.78% | 23.08% | 189% | 572.53% |
| Exponential type | 9.33% | 10.56% | 196% | 628.62% |
| Square type | 12.52% | 16.54% | 45.84% | 179.27% |
| Heat Flux | TC1 | TC2 |
|---|---|---|
| Triangle type | 72.641 | 500.2478 |
| Exponential type | 73.4419 | 571.5412 |
| Square type | 78.8352 | 438.1187 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Li, J.; Liu, D. Real-Time Solution of Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Problem Based on Parameter-Adaptive PID with Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm. Energies 2023, 16, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010225
Huang W, Li J, Liu D. Real-Time Solution of Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Problem Based on Parameter-Adaptive PID with Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm. Energies. 2023; 16(1):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010225
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Weichao, Jiahao Li, and Ding Liu. 2023. "Real-Time Solution of Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Problem Based on Parameter-Adaptive PID with Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm" Energies 16, no. 1: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010225
APA StyleHuang, W., Li, J., & Liu, D. (2023). Real-Time Solution of Unsteady Inverse Heat Conduction Problem Based on Parameter-Adaptive PID with Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm. Energies, 16(1), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010225






