Sol-Gel Derived Di-Ureasil Based Ormolytes for Electrochromic Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
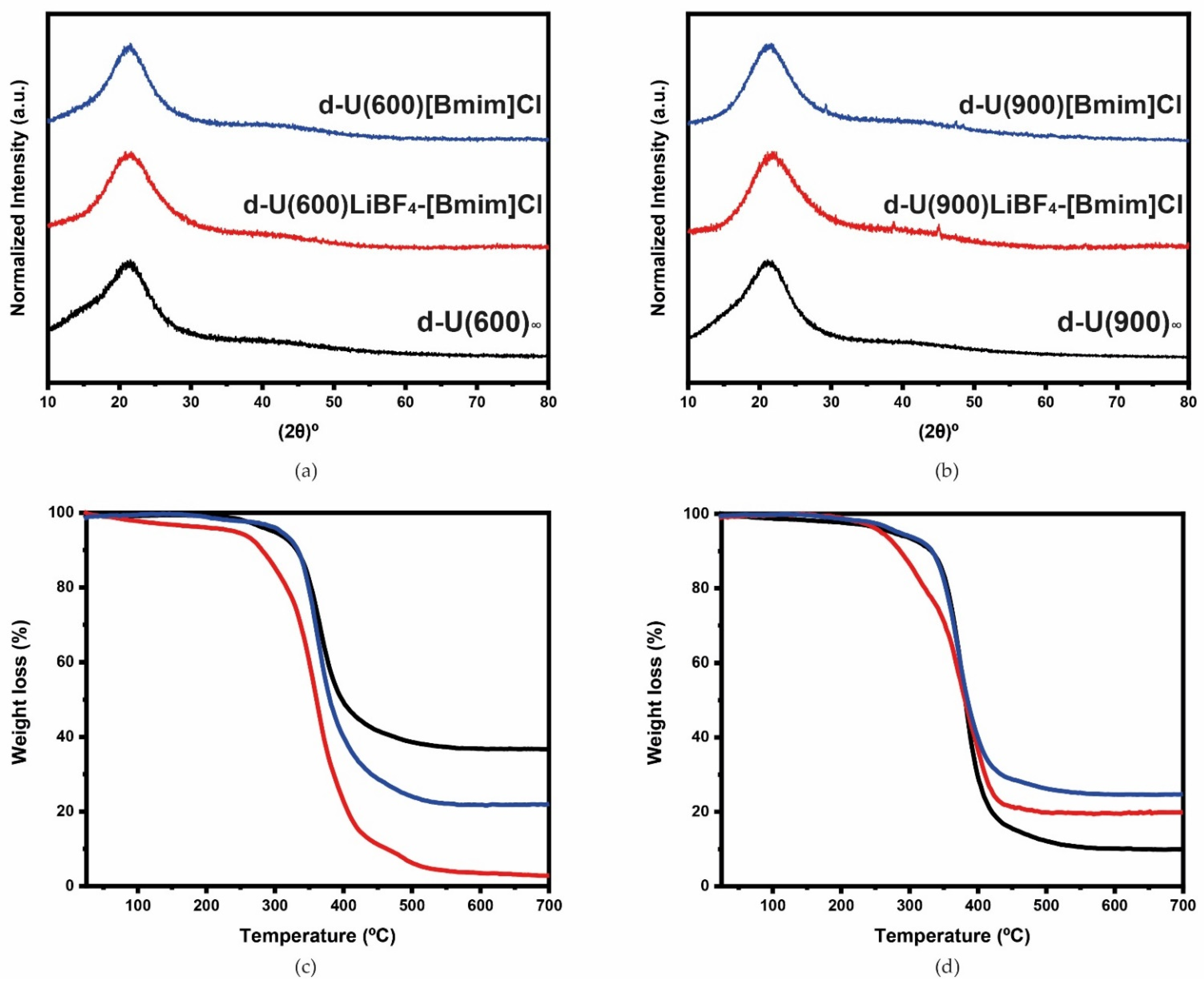
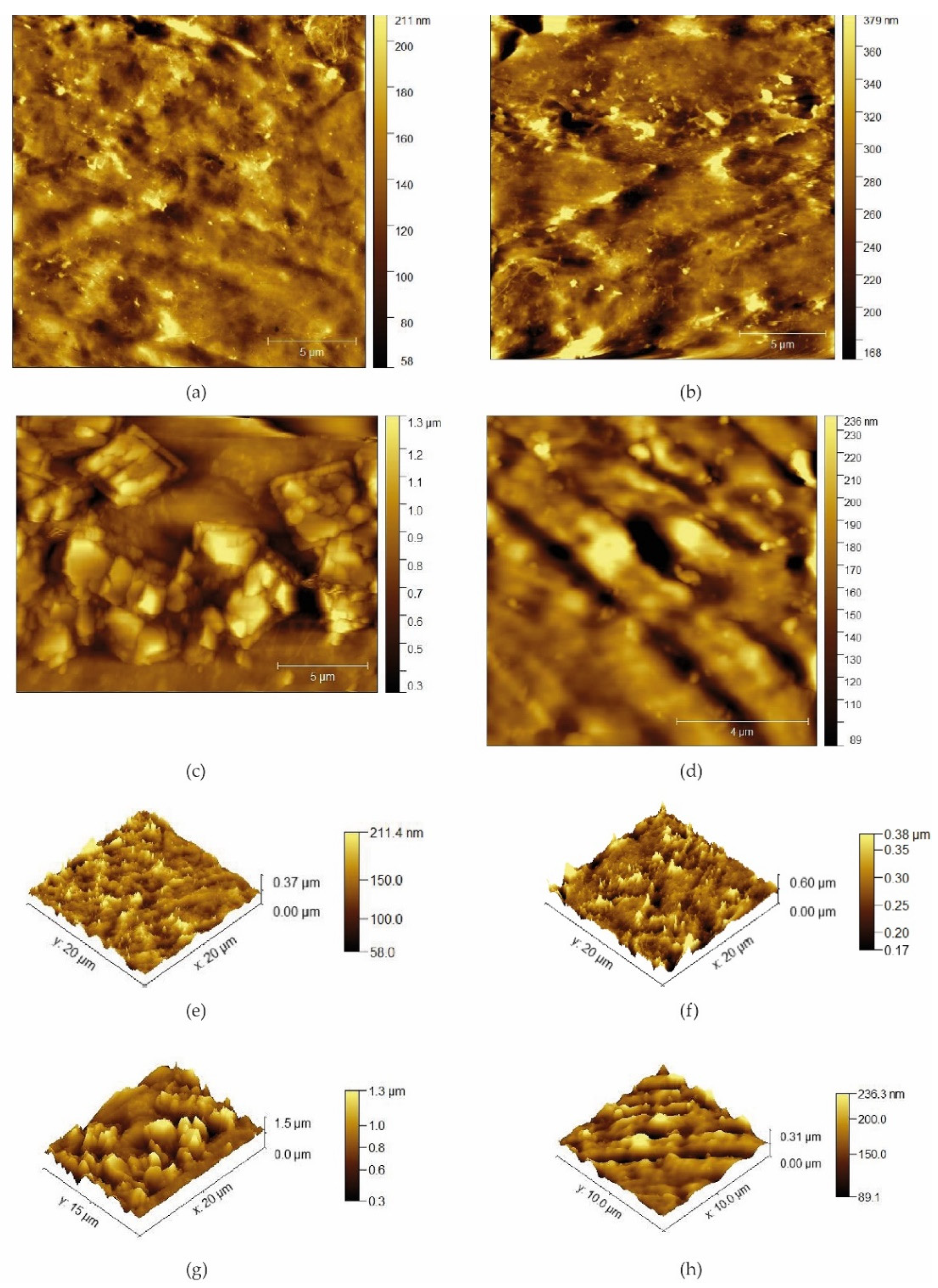
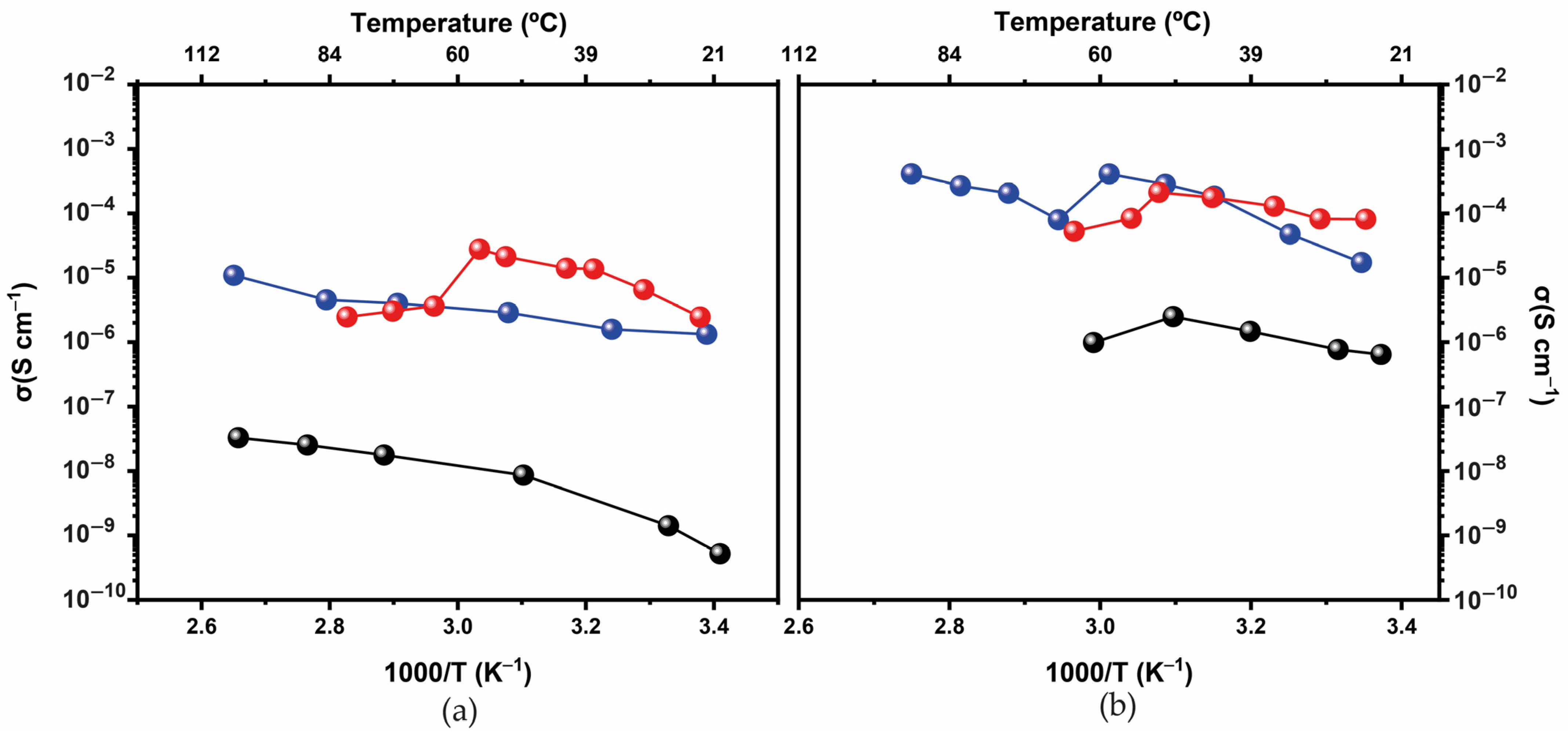
3.1. Physical-Chemical Characterization
d-U(600)LiBF4-[Bmim]Cl and d-U(900)LiBF4-[Bmim]Cl Electrolytes
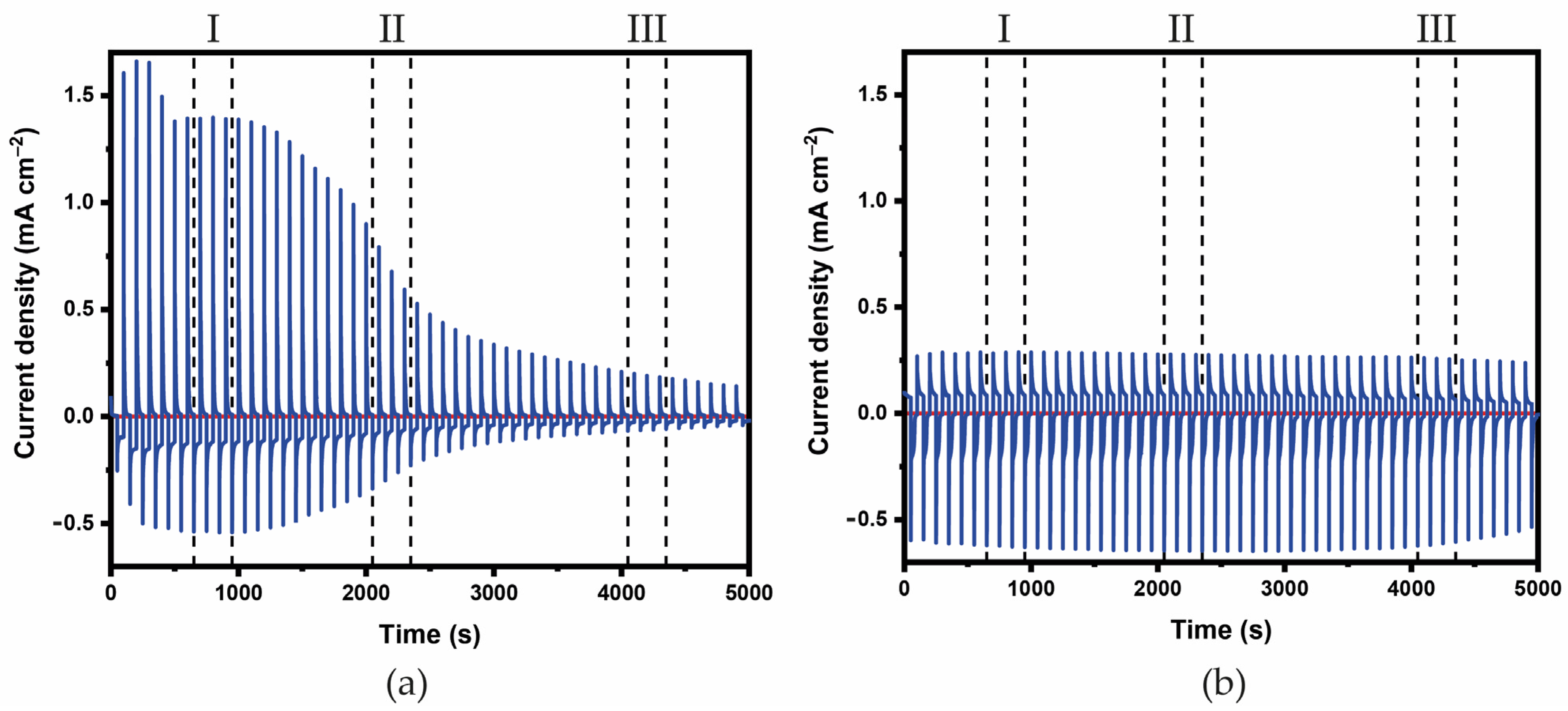
3.2. Characterization of the ECDs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goal 11: Make Cities Inclusive Resilient and Sustainable. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal11 (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Remarks to International Energy Agency Clean Energy Transition Summit. Available online: https://www.un.org/sg/en/content/sg/speeches/2020-07-09/remarks-international-energy-agency-clean-energy-transition-summit (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Granqvist, C.G.; Arvizu, M.A.; Bayrak Pehlivan, İ.; Qu, H.-Y.; Wen, R.-T.; Niklasson, G.A. Electrochromic Materials and Devices for Energy Efficiency and Human Comfort in Buildings: A Critical Review. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 259, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.C.; Silva, M.M.; Smith, M.J.; Gonçalves, A.; Fortunato, E.; Nunes, S.C.; de Zea Bermudez, V. Di-Ureasil Xerogels Containing Lithium Bis(Trifluoromethanesulfonyl)Imide for Application in Solid-State Electrochromic Devices. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rosseinsky, D.R.; Mortimer, R.J. Electrochromic Systems and the Prospects for Devices. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ong, G.K.; Wang, Y.; LeBlanc, G.; Williams, T.E.; Mattox, T.M.; Helms, B.A.; Milliron, D.J. Nanocomposite Architecture for Rapid, Spectrally-Selective Electrochromic Modulation of Solar Transmittance. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5574–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llordés, A.; Garcia, G.; Gazquez, J.; Milliron, D.J. Tunable Near-Infrared and Visible-Light Transmittance in Nanocrystal-in-Glass Composites. Nature 2013, 500, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeForest, N.; Shehabi, A.; O’Donnell, J.; Garcia, G.; Greenblatt, J.; Lee, E.S.; Selkowitz, S.; Milliron, D.J. United States Energy and CO2 Savings Potential from Deployment of Near-Infrared Electrochromic Window Glazings. Build. Environ. 2015, 89, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, M. Active Dynamic Windows for Buildings: A Review. Renew. Energy 2018, 119, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calnan, S.; Tiwari, A.N. High Mobility Transparent Conducting Oxides for Thin Film Solar Cells. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.C.; Pereira, R.F.P.; Alves, R.; Nunes, S.C.; Fernandes, M.; Gonçalves, H.M.R.; Pereira, S.; Silva, M.M.; Fortunato, E.; Rego, R.; et al. Electrochromic Device Composed of a Di-Urethanesil Electrolyte Incorporating Lithium Triflate and 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.A.; Pereira, R.F.P.; Pereira, S.; Gonçalves, H.; Silva, M.M.; Carlos, L.D.; Nunes, S.C.; Fortunato, E.; Ferreira, R.A.S.; Rego, R.; et al. Three-Mode Modulation Electrochromic Device with High Energy Efficiency for Windows of Buildings Located in Continental Climatic Regions. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2019, 3, 1800115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Freitas, V.; Pereira, S.; Leones, R.; Silva, M.M.; Carlos, L.D.; Fortunato, E.; Ferreira, R.A.S.; Rego, R.; Bermudez, V.D.Z. Luminescent Electrochromic Devices for Smart Windows of Energy-Efficient Buildings. Energies 2018, 11, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.C.; de Zea Bermudez, V.; Silva, M.M.; Smith, M.J.; Ostrovskii, D.; Sá Ferreira, R.A.; Carlos, L.D.; Rocha, J.; Gonçalves, A.; Fortunato, E. Sol–Gel-Derived Potassium-Based Di-Ureasils for “Smart Windows”. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Ferreira, R.A.S.; Gonçalves, A.; Fortunato, E.; Silva, M.M.; Smith, M.J.; Carlos, L.D.; de Zea Bermudez, V. K+-Doped Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Siloxane Biohybrid Electrolytes for Electrochromic Devices. Solid State Ionics 2011, 204–205, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Leones, R.; Pereira, S.; Costa, A.M.S.; Mano, J.F.; Silva, M.M.; Fortunato, E.; de Zea Bermudez, V.; Rego, R. Eco-Friendly Sol-Gel Derived Sodium-Based Ormolytes for Electrochromic Devices. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.F.P.; Sentanin, F.; Pawlicka, A.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Silva, M.M.; de Zea Bermudez, V. Smart Windows Prepared from Bombyx Mori Silk. ChemElectroChem 2016, 3, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.C.; Saraiva, S.M.; Pereira, R.F.P.; Pereira, S.; Silva, M.M.; Carlos, L.D.; Fortunato, E.; Ferreira, R.A.S.; Rego, R.; de Zea Bermudez, V. Sustainable Dual-Mode Smart Windows for Energy-Efficient Buildings. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.; Sentanin, F.; Sabadini, R.C.; Fernandes, M.; de Zea Bermudez, V.; Pawlicka, A.; Silva, M.M. Samarium (III) Triflate-Doped Chitosan Electrolyte for Solid State Electrochromic Devices. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 267, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.C.; Fernandes, M.; Silva, M.M.; Smith, M.J.; Vilela, S.M.F.; Gonçalves, A.; Olveira, M.C.; Fortunato, E.; Rego, R.; Zea Bermudez, V.d. Di-Ureasil Hybrids Doped with LiBF4: Attractive Candidates as Electrolytes for “Smart Windows”. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1822/13611 (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Fernandes, M.; Leones, R.; Costa, A.M.S.; Silva, M.M.; Pereira, S.; Mano, J.F.; Fortunato, E.; Rego, R.; de Zea Bermudez, V. Electrochromic Devices Incorporating Biohybrid Electrolytes Doped with a Lithium Salt, an Ionic Liquid or a Mixture of Both. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 161, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Thomas, M.L.; Zhang, S.; Ueno, K.; Yasuda, T.; Dokko, K. Application of Ionic Liquids to Energy Storage and Conversion Materials and Devices. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7190–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H. Electrochemical Aspects of Ionic Liquids; Ohno, H., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H. Functional Design of Ionic Liquids. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 79, 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Fadeev, A.G.; Qi, B.; Smela, E.; Mattes, B.R.; Ding, J.; Spinks, G.M.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Zhou, D.; Wallace, G.G.; et al. Use of Ionic Liquids for π-Conjugated Polymer Electrochemical Devices. Science 2002, 297, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bircan, H.; Seshadri, V.; Padilla, J.; Invernale, M.; Otero, T.F.; Sotzing, G.A. Use of Polymer/Ionic Liquid Plasticizers as Gel Electrolytes in Electrochromic Devices. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 127, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Gonzalo, C.; Mecerreyes, D.; Pomposo, J.A.; Salsamendi, M.; Marcilla, R.; Grande, H.; Vergaz, R.; Barrios, D.; Sánchez-Pena, J.M. All-Plastic Electrochromic Devices Based on PEDOT as Switchable Optical Attenuator in the near IR. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilla, R.; Alcaide, F.; Sardon, H.; Pomposo, J.A.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C.; Mecerreyes, D. Tailor-Made Polymer Electrolytes Based upon Ionic Liquids and Their Application in All-Plastic Electrochromic Devices. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiński, M.; Lewandowski, A.; Stępniak, I. Ionic Liquids as Electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5567–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, L.D.; de Zea Bermudez, V.; Sá Ferreira, R.A.; Marques, L.; Assunção, M. Sol−Gel Derived Urea Cross-Linked Organically Modified Silicates. 2. Blue-Light Emission. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zea Bermudez, V.; Carlos, L.; Duarte, M.; Silva, M.; Silva, C.J.; Smith, M.; Assunção, M.; Alcácer, L. A Novel Class of Luminescent Polymers Obtained by the Sol–Gel Approach. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 275–277, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.; Rodrigues, L.; Silva, M.; Smith, M.; Gonçalves, A.; Fortunato, E. Application of Di-Ureasil Ormolytes Based on Lithium Tetrafluoroborate in Solid-State Electrochromic Displays. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nakano, R.; Nakaba, R.; Nakamura, N.; Ohno, H. Hydrated Ionic Liquids Enable Both Solubilisation and Refolding of Aggregated Concanavalin A. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3578–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.M.; Nunes, S.C.; Barbosa, P.C.; Evans, A.; de Zea Bermudez, V.; Smith, M.J.; Ostrovskii, D. Sol–Gel Preparation of a Di-Ureasil Electrolyte Doped with Lithium Perchlorate. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.C.; de Zea Bermudez, V.; Ostrovskii, D.; Silva, M.M.; Barros, S.; Smith, M.J.; Carlos, L.D.; Rocha, J.; Morales, E. Diurea Cross-Linked Poly(Oxyethylene)/Siloxane Ormolytes for Lithium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, E.; Pimentel, A.; Gonçalves, A.; Marques, A.; Martins, R. High Mobility Amorphous/Nanocrystalline Indium Zinc Oxide Deposited at Room Temperature. Thin Solid Films 2006, 502, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.C.; Silva, M.M.; Smith, M.J.; Gonçalves, A.; Fortunato, E. Studies of Solid-State Electrochromic Devices Based on PEO/Siliceous Hybrids Doped with Lithium Perchlorate. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 2938–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.C.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Silva, M.M.; Smith, M.J. Preparation of Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Materials Based on a Di-Ureasil Matrix Doped with Lithium Bis(Trifluoromethanesulfonyl)Imide. J. Power Sources 2008, 180, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Monteiro, M.J.; Bazito, F.F.C.; Siqueira, L.J.A.; Ribeiro, M.C.C.; Torresi, R.M. Transport Coefficients, Raman Spectroscopy, and Computer Simulation of Lithium Salt Solutions in an Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Hybrid Di-Ureasil Host | Doping Agent | Voltage (V) | ∆T555 nm (%) | ∆(OD)555 nm | CA Interval 1 | CEin | CEout | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm2·C−1) | ||||||||
| d-U(600) | LiBF4-[Bmim]Cl | −2.0/+2.0 | 7.9 | 0.05 | ||||
| −2.5/+2.5 | 14.6 | 0.10 | ECD1 | |||||
| −3.0/+3.0 | 16.5 | 0.13 | I | −88.02 | +25.66 | This work | ||
| II | −110.469 | +43.98 | ||||||
| III | −420.621 | +111.40 | ||||||
| d-U(900) | LiBF4-[Bmim]Cl | −2.0/+2.0 −2.5/+2.5 | 7.8 16.3 | 0.05 0.12 | ||||
| ECD2 | ||||||||
| I | −26.609 | +91.90 | This work | |||||
| −3.0/+3.0 | 19.1 | 0.15 | II | −27.272 | +115.13 | |||
| III | −39.236 | +90.35 | ||||||
| d-U(900) | LiBF4 | −1.5/+6.5 | 18.8 | 0.11 | [32] | |||
| d-U(2000) | LiBF4 | −4.0/+4.0 | 18 | 0.13 | [20] | |||
| d-U(2000) | [BIm][TfO] 2 | −2.0/+3.0 | 33 | 0.28 | [12] | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nunes, P.J.; Pereira, R.F.P.; Pereira, S.; Silva, M.M.; Fortunato, E.; Bermudez, V.d.Z.; Fernandes, M. Sol-Gel Derived Di-Ureasil Based Ormolytes for Electrochromic Devices. Energies 2023, 16, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010426
Nunes PJ, Pereira RFP, Pereira S, Silva MM, Fortunato E, Bermudez VdZ, Fernandes M. Sol-Gel Derived Di-Ureasil Based Ormolytes for Electrochromic Devices. Energies. 2023; 16(1):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010426
Chicago/Turabian StyleNunes, Paulo Joaquim, Rui Francisco Pinto Pereira, Sónia Pereira, Maria Manuela Silva, Elvira Fortunato, Verónica de Zea Bermudez, and Mariana Fernandes. 2023. "Sol-Gel Derived Di-Ureasil Based Ormolytes for Electrochromic Devices" Energies 16, no. 1: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010426
APA StyleNunes, P. J., Pereira, R. F. P., Pereira, S., Silva, M. M., Fortunato, E., Bermudez, V. d. Z., & Fernandes, M. (2023). Sol-Gel Derived Di-Ureasil Based Ormolytes for Electrochromic Devices. Energies, 16(1), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010426











