Design and Control of a Three-Axis Motion Servo Control System Based on a CAN Bus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
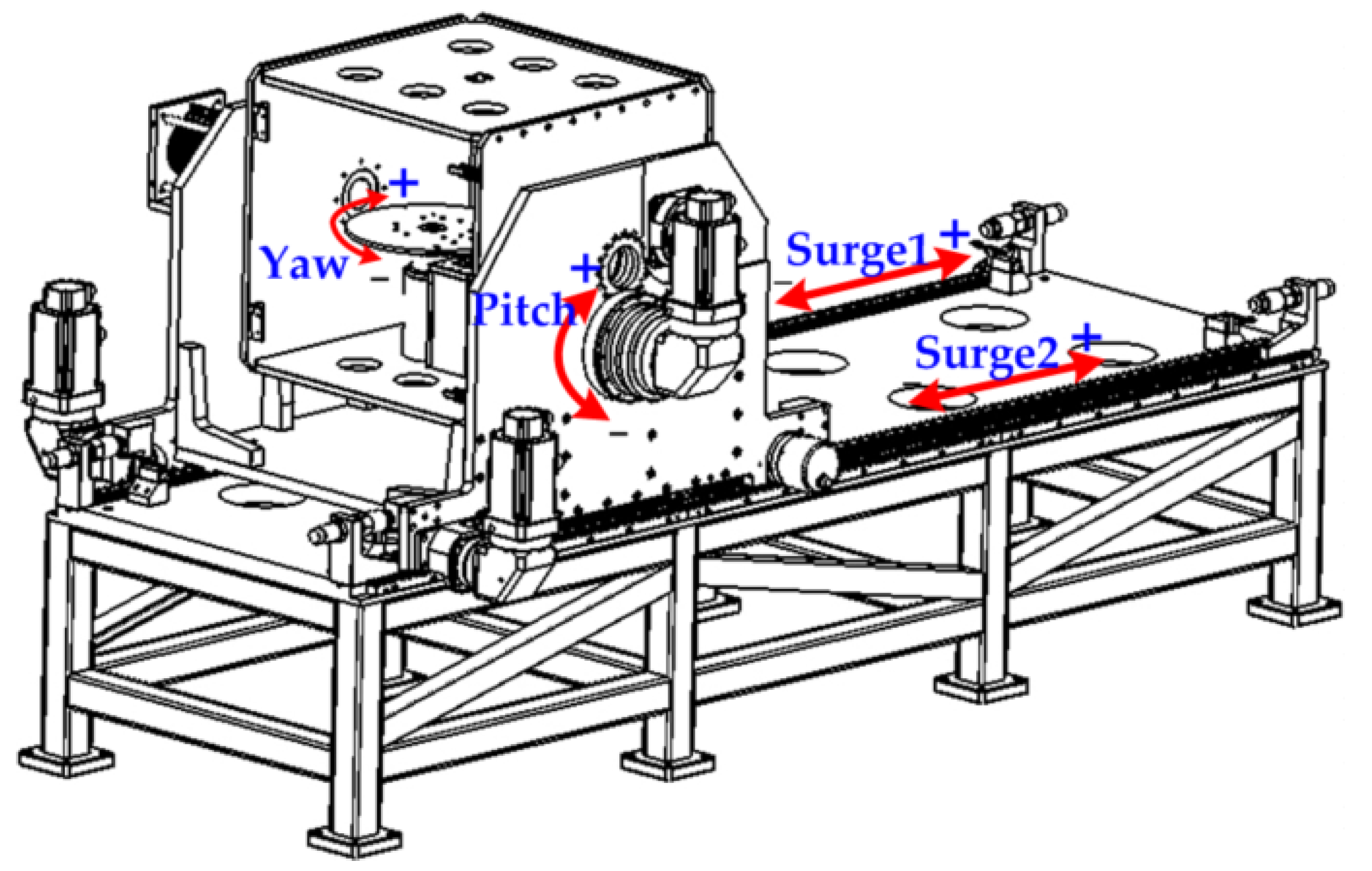
2. The Motion Platform Control
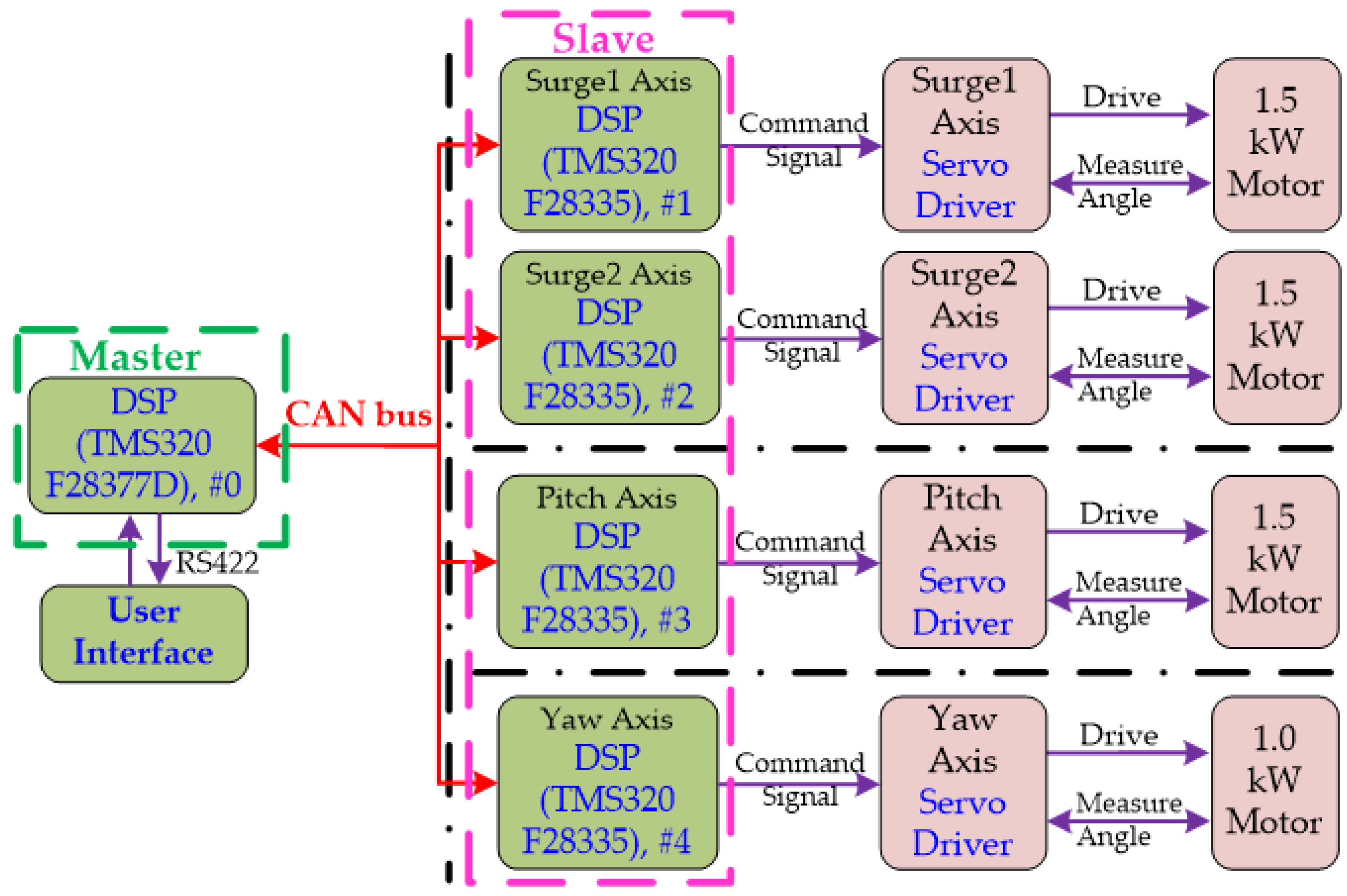
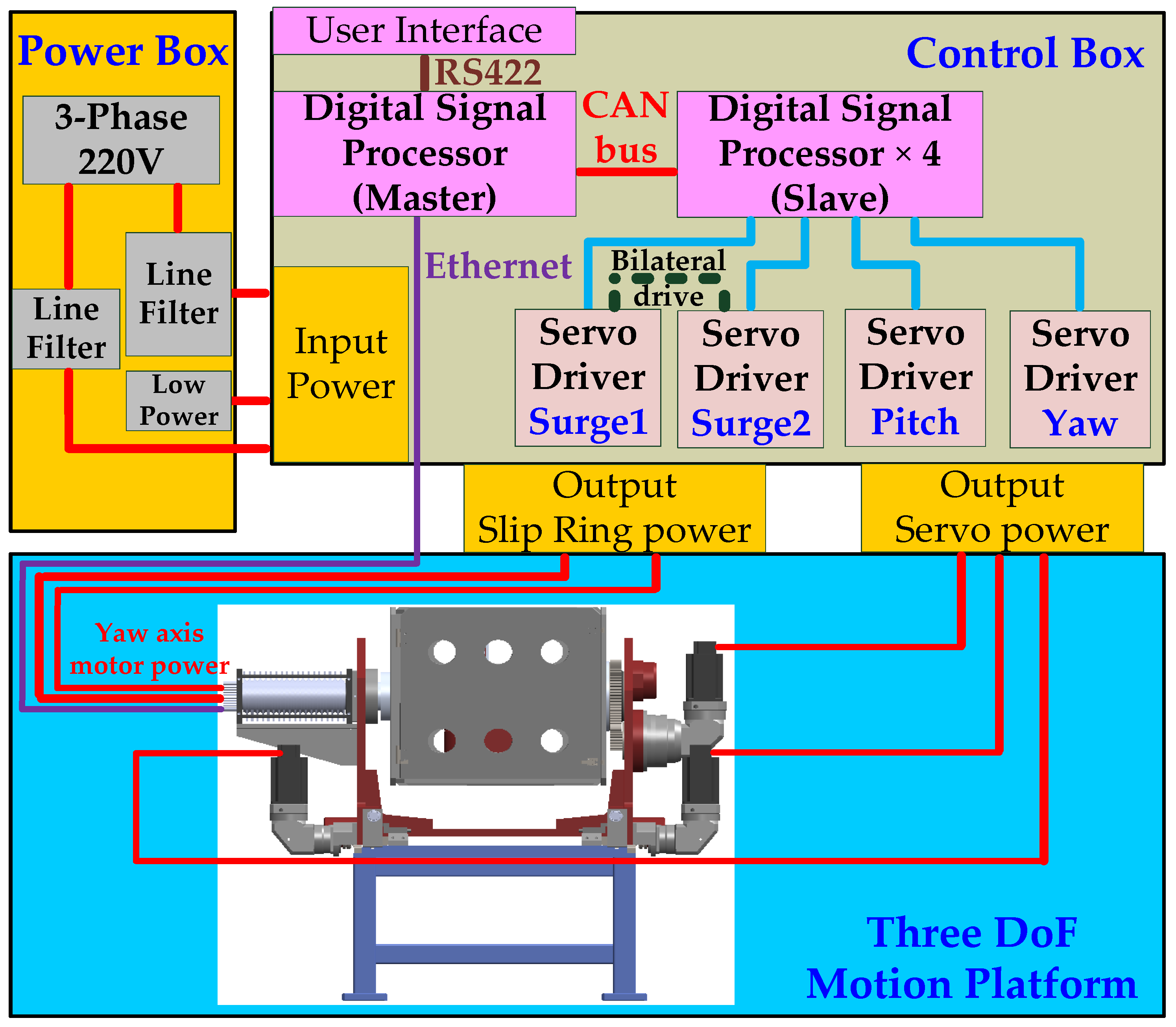
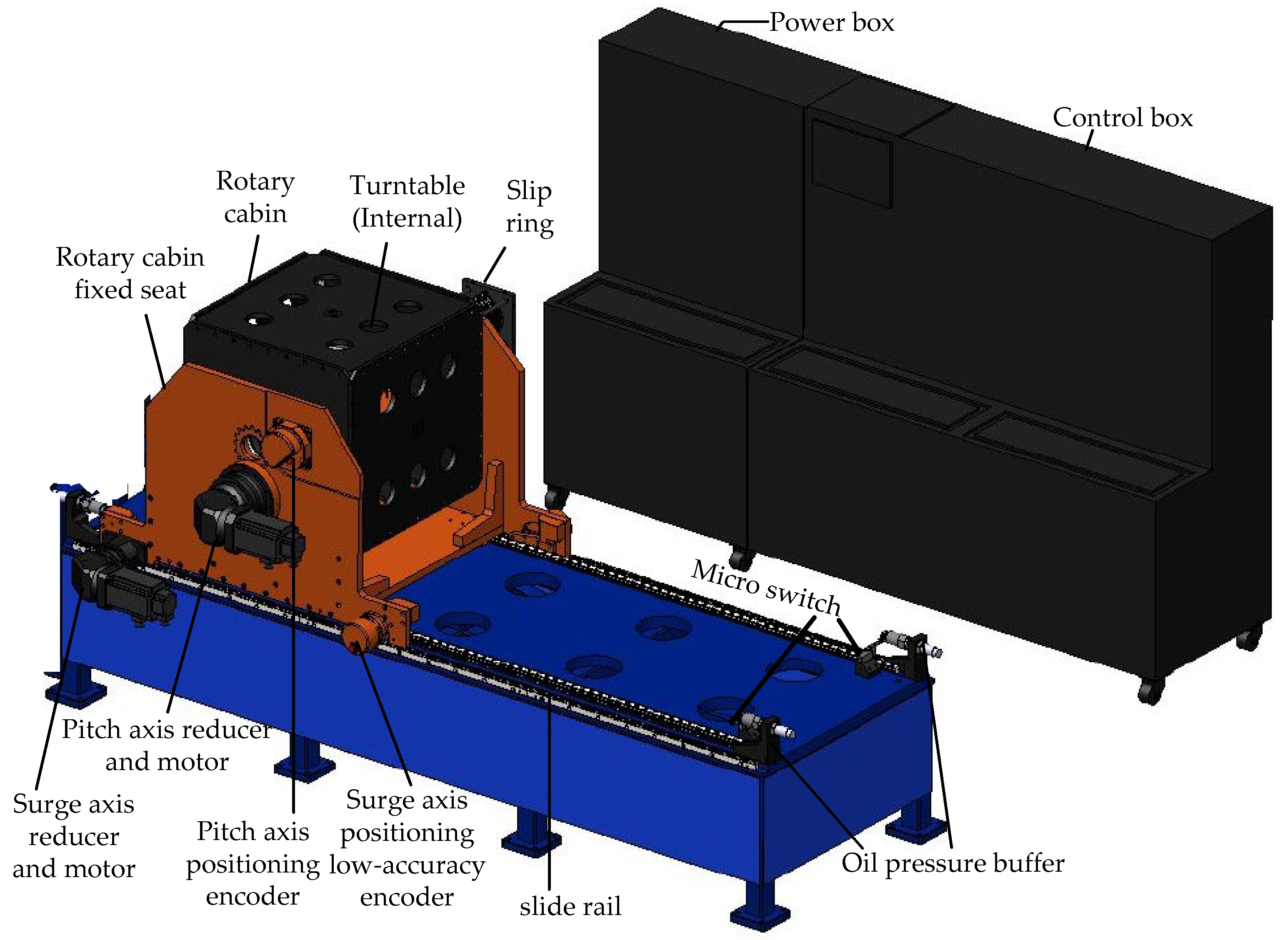
2.1. System Overview
2.2. Closed-Loop Control Strategy
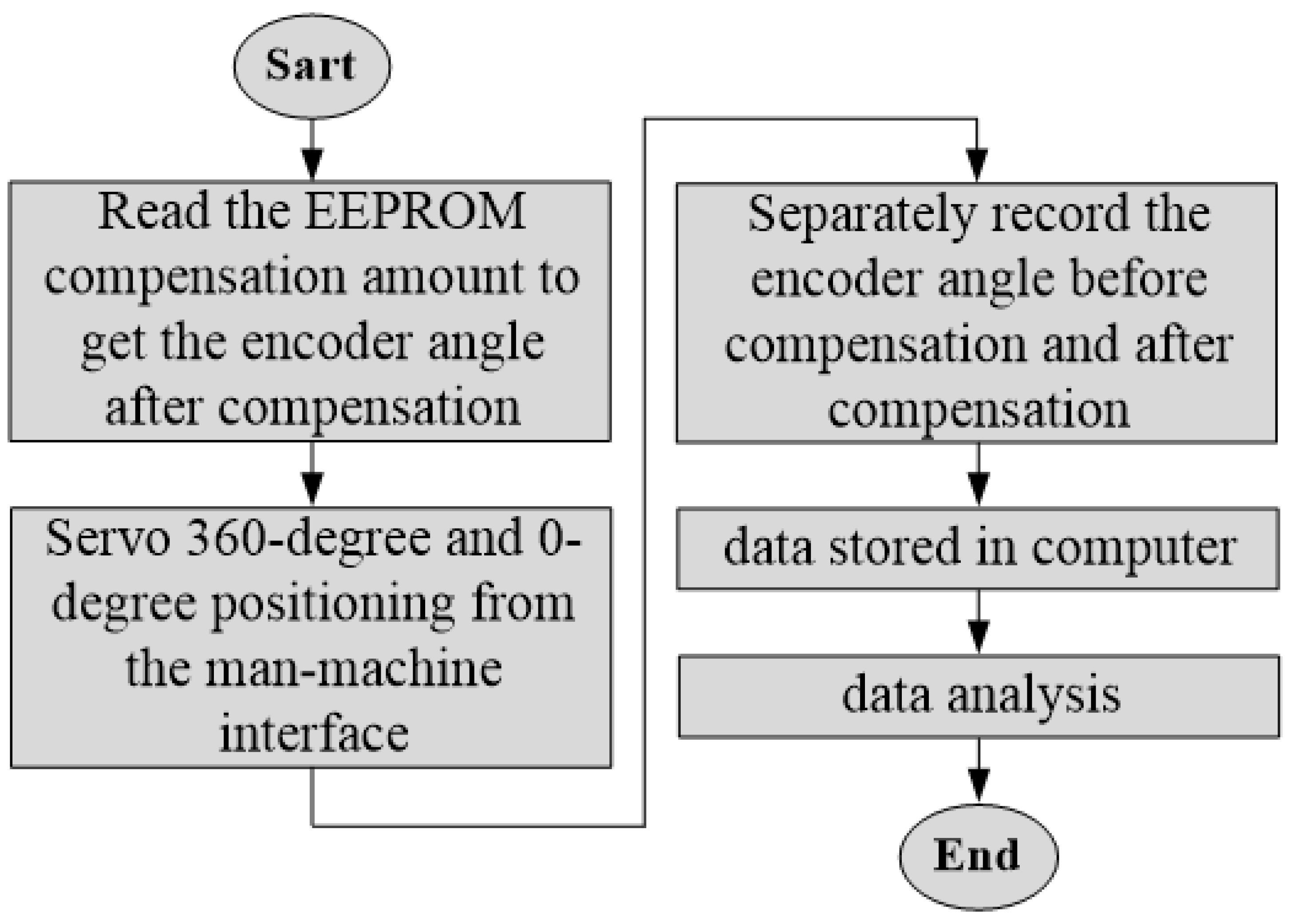
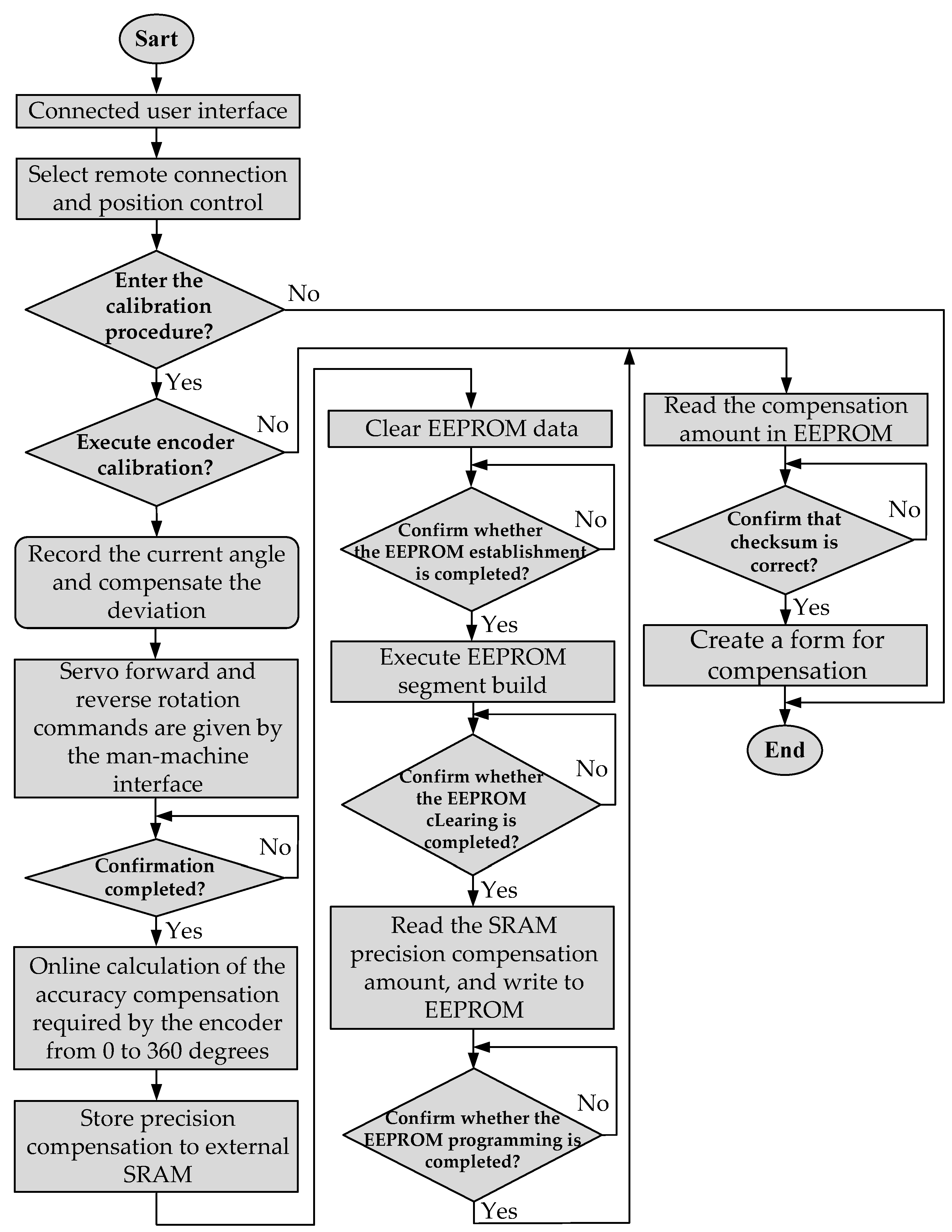
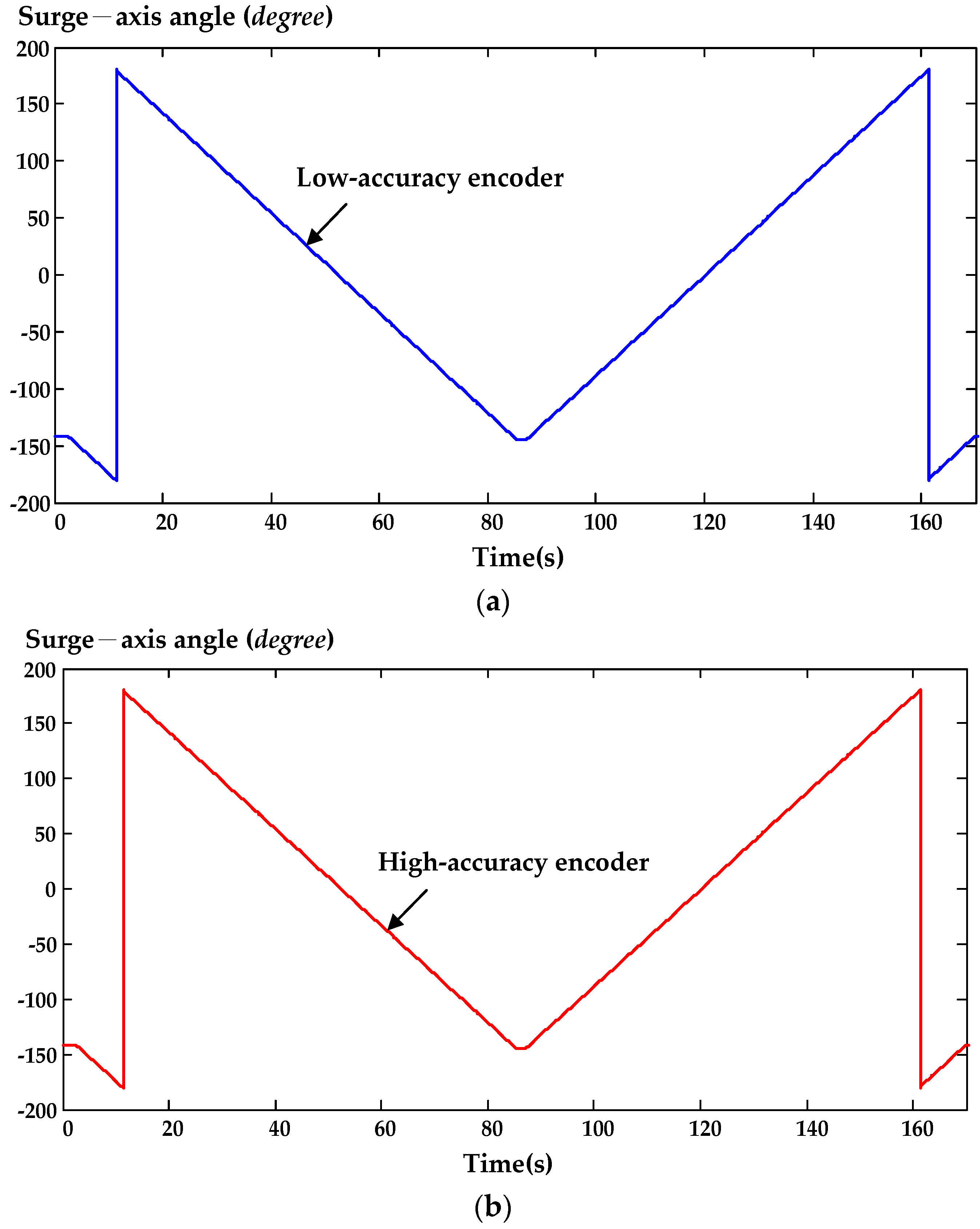
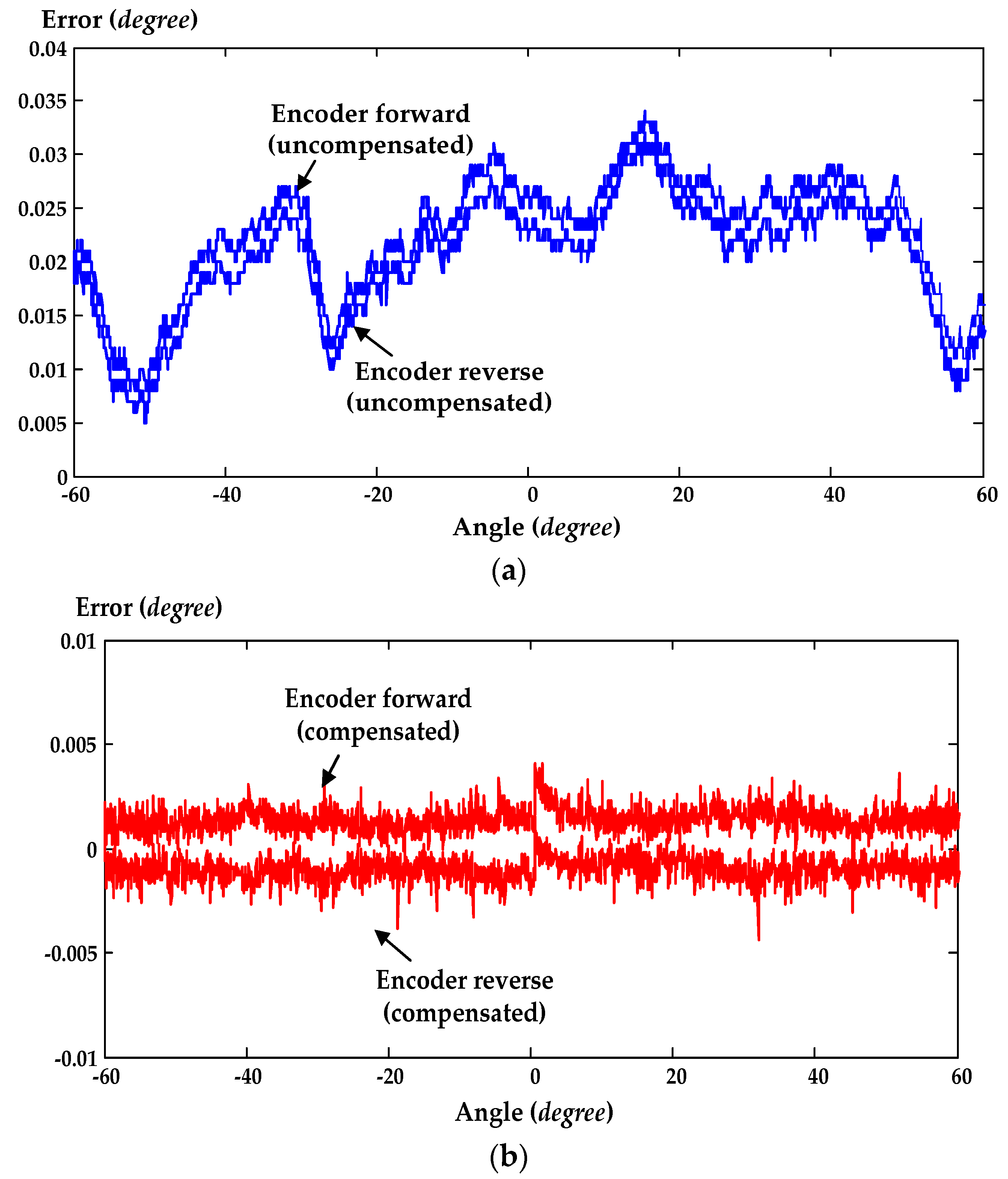
2.3. Encoder Error Compensation Embedded Executive
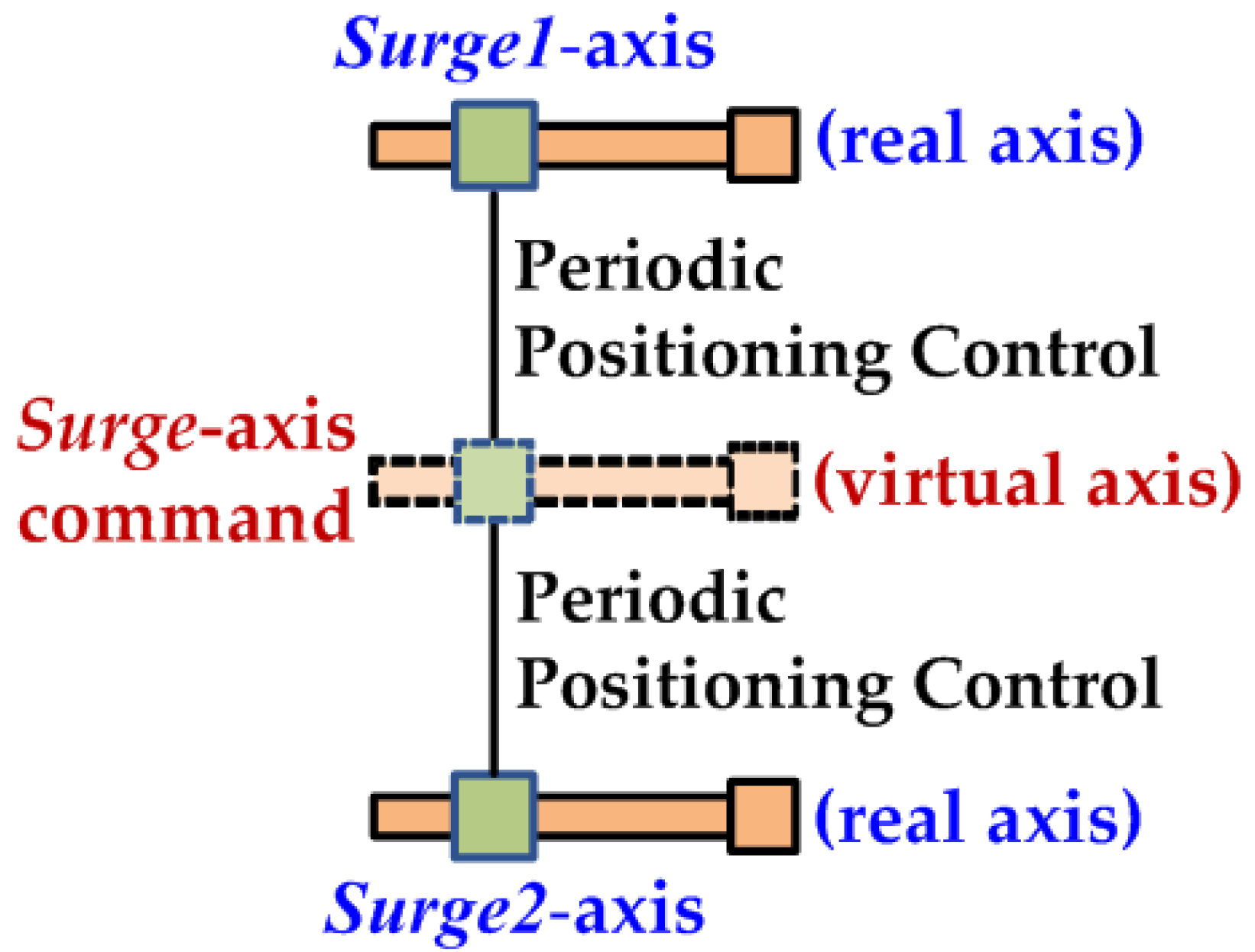
3. Kinematics Relations
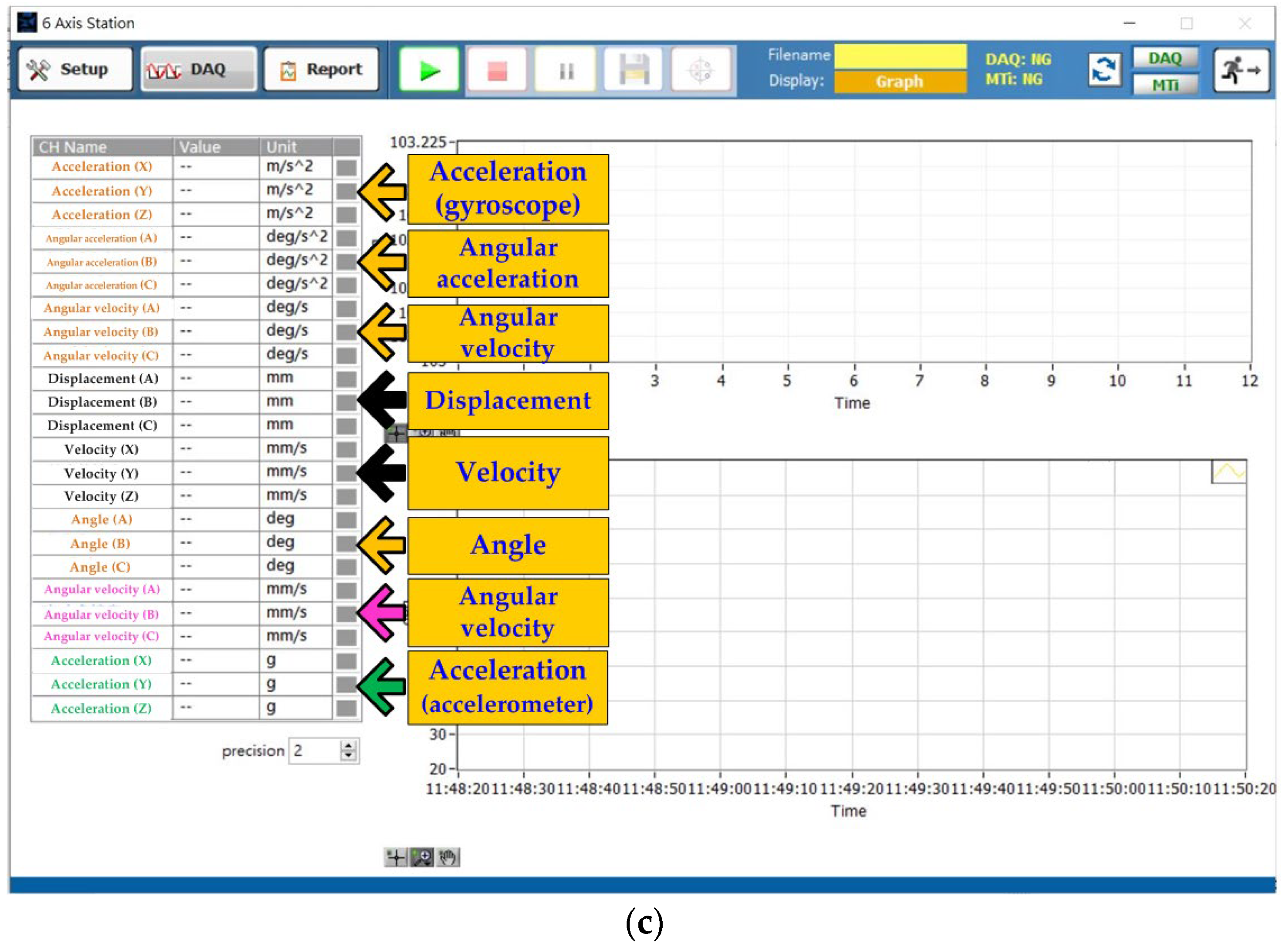
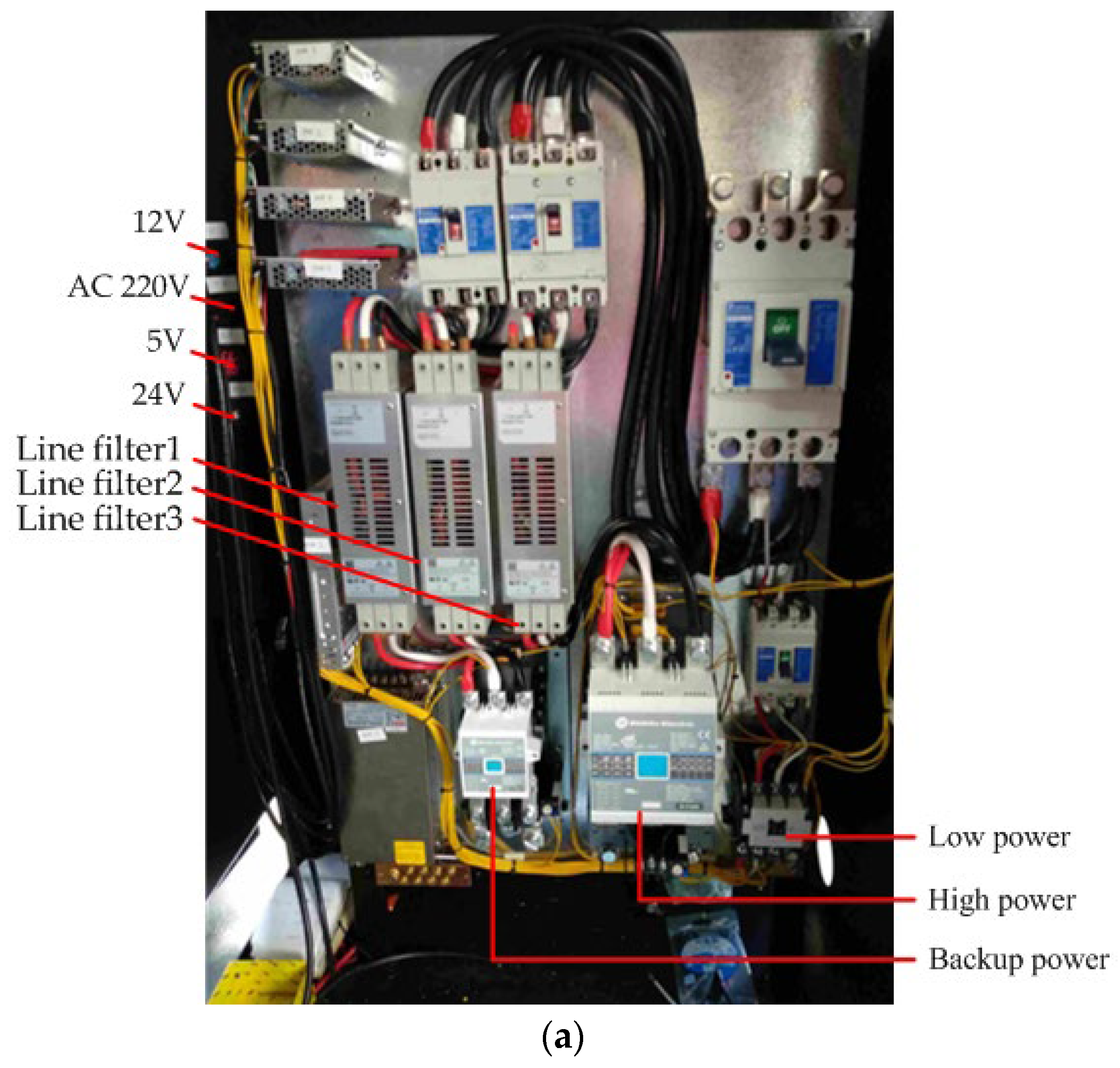
4. Monitoring System
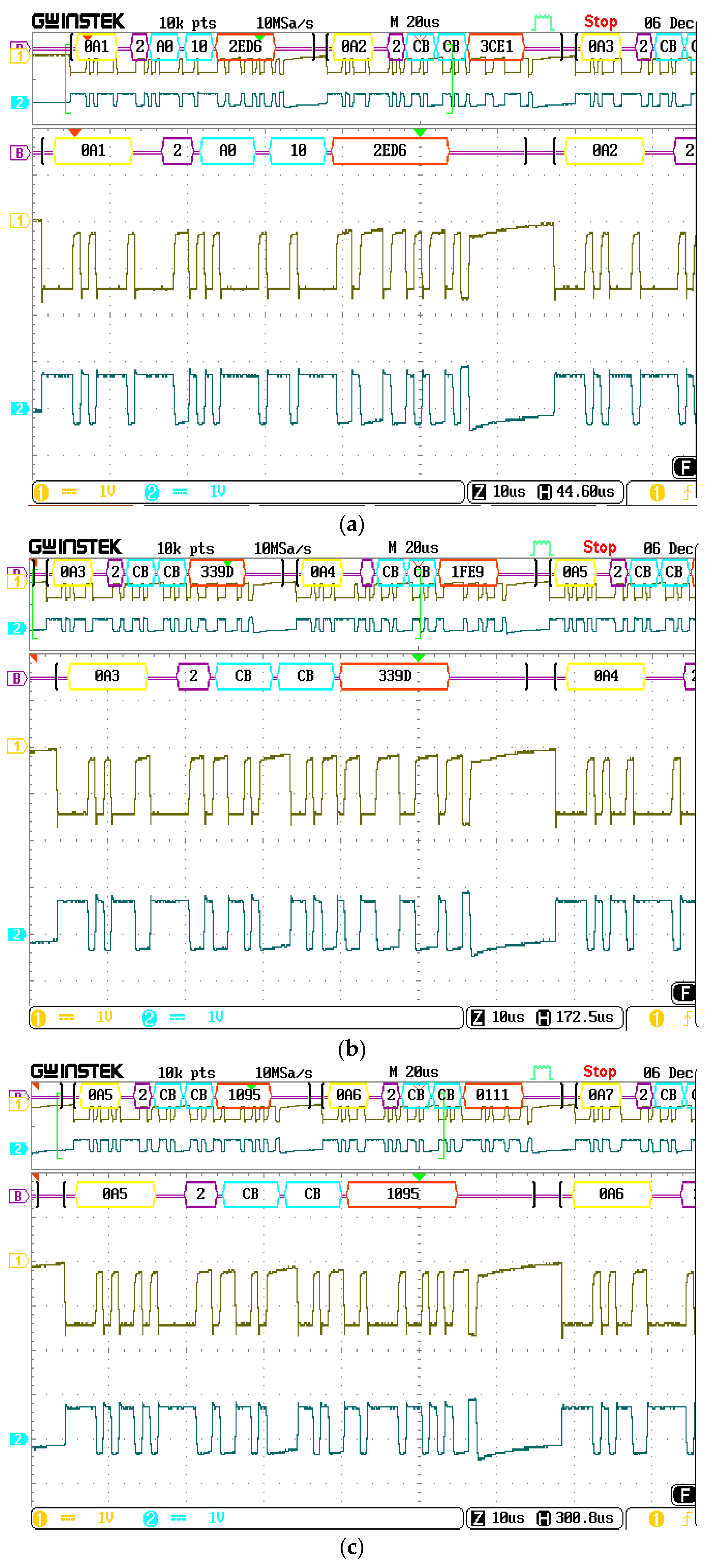
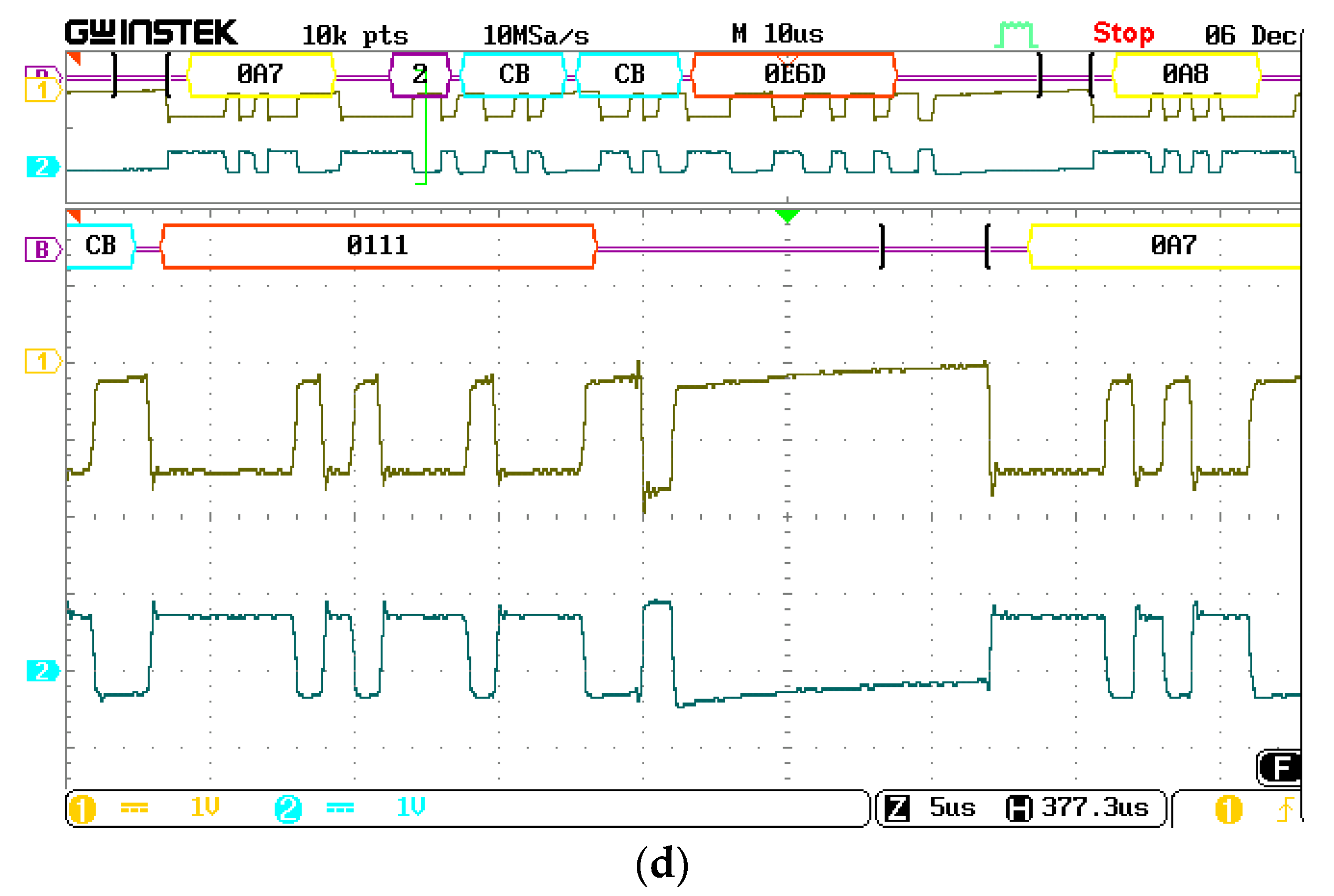
5. Implementation
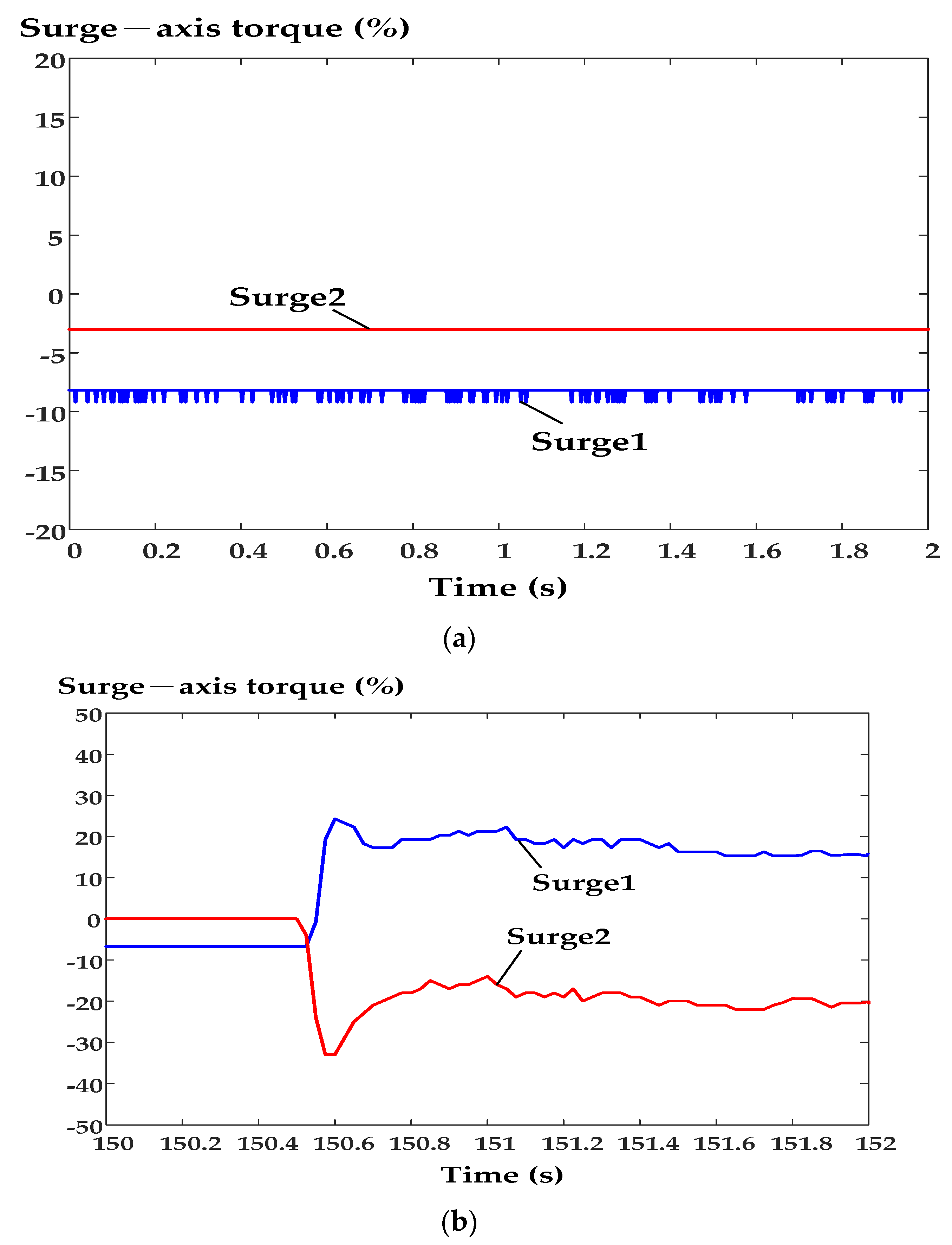
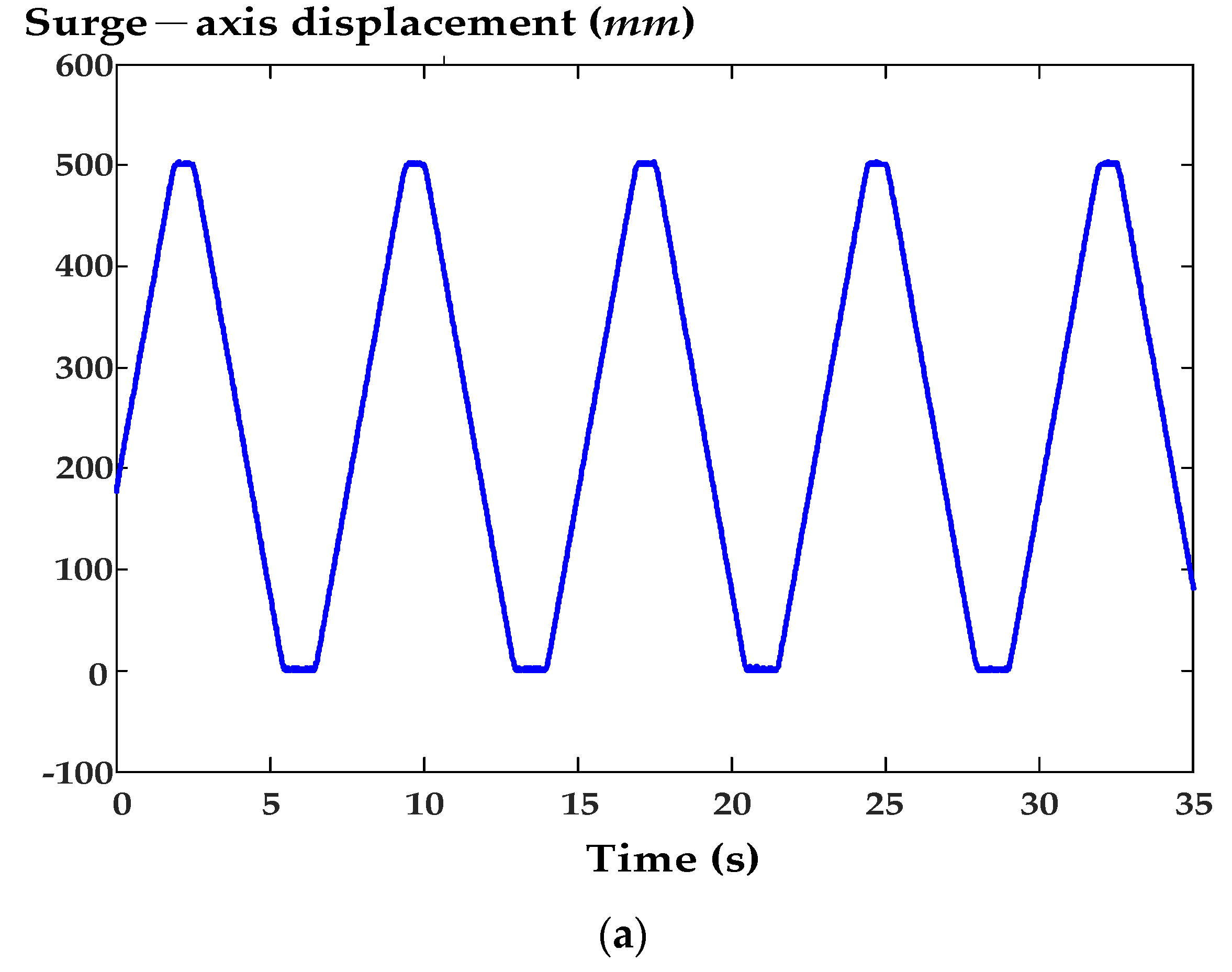
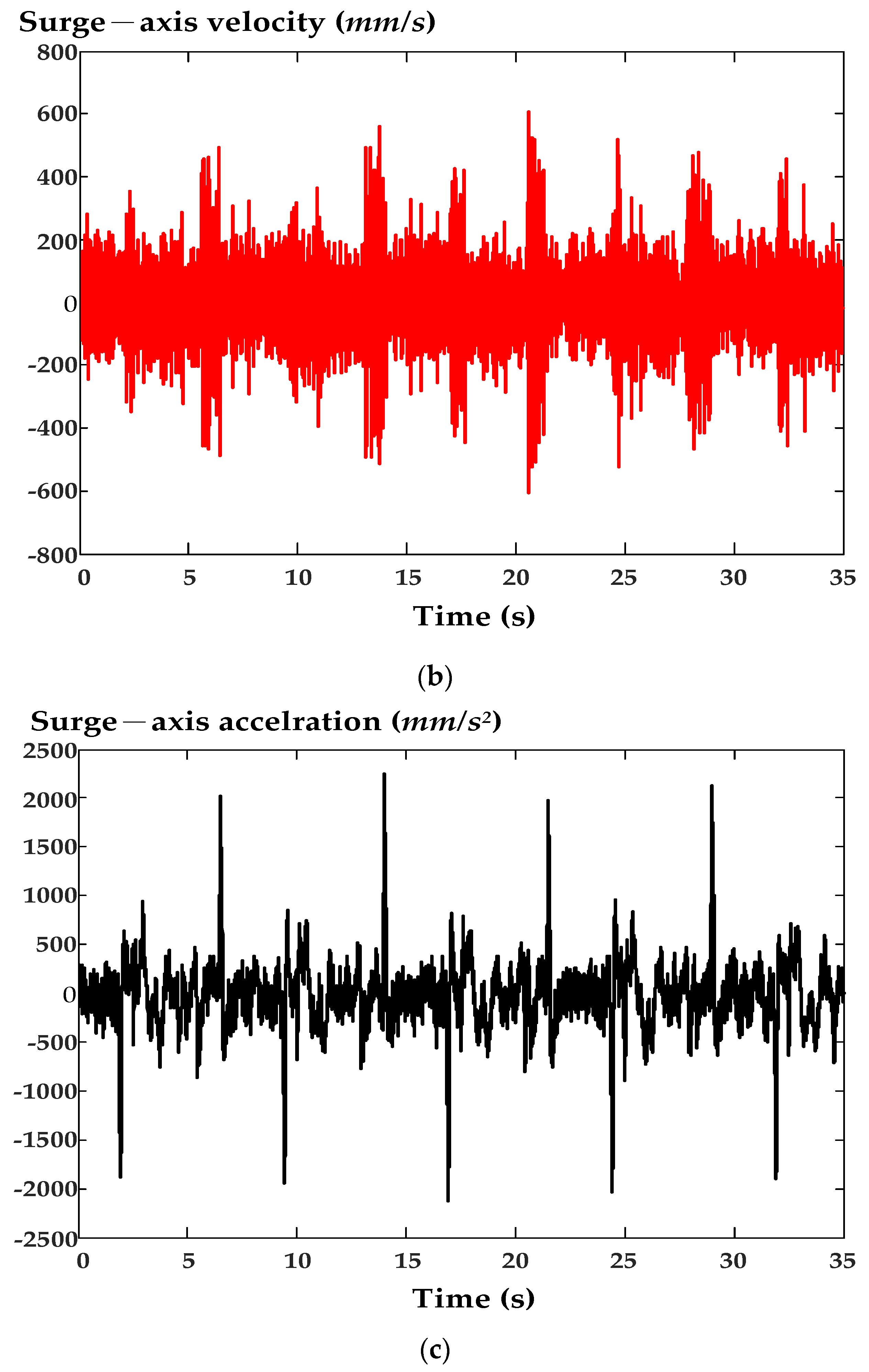
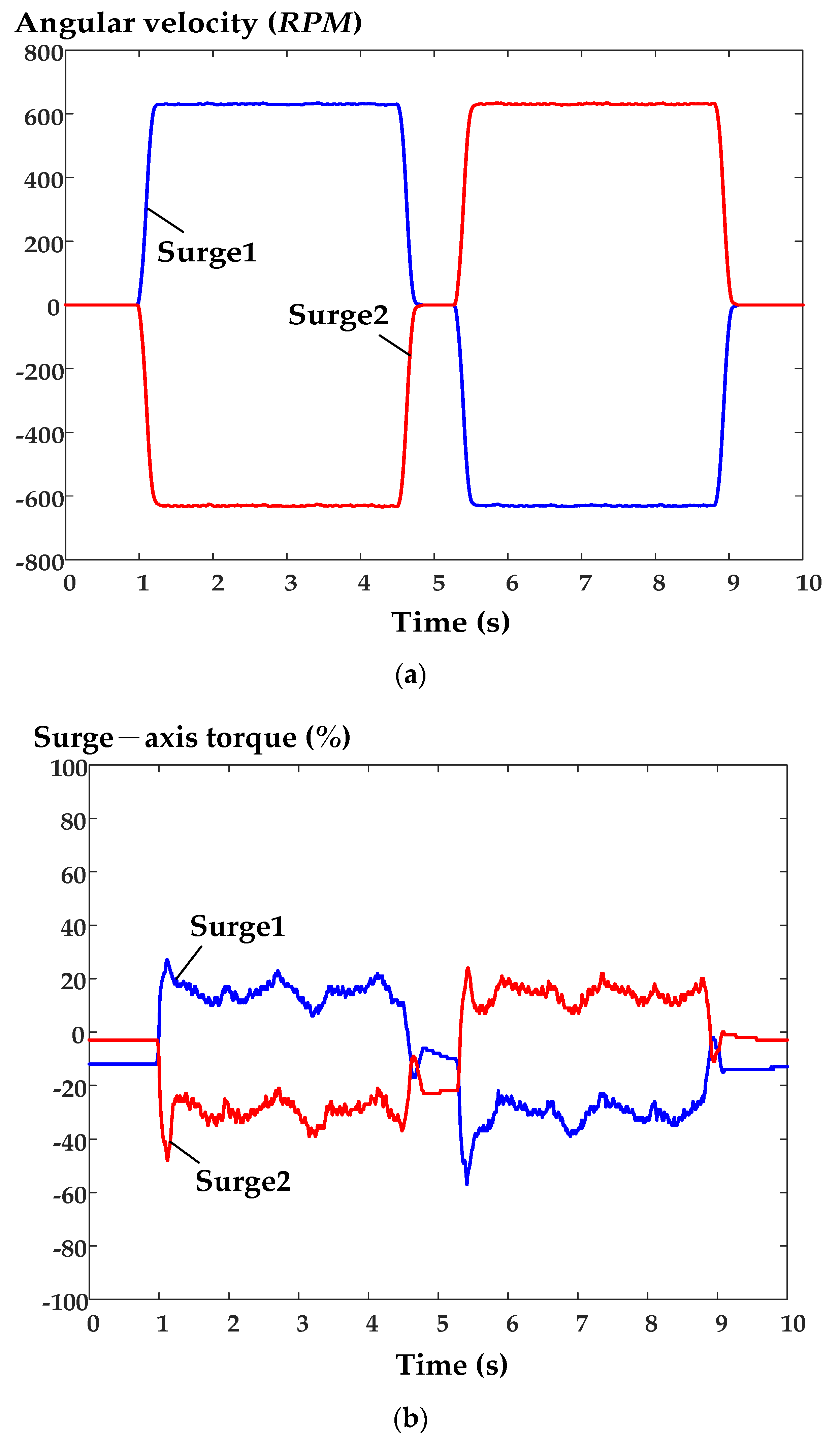
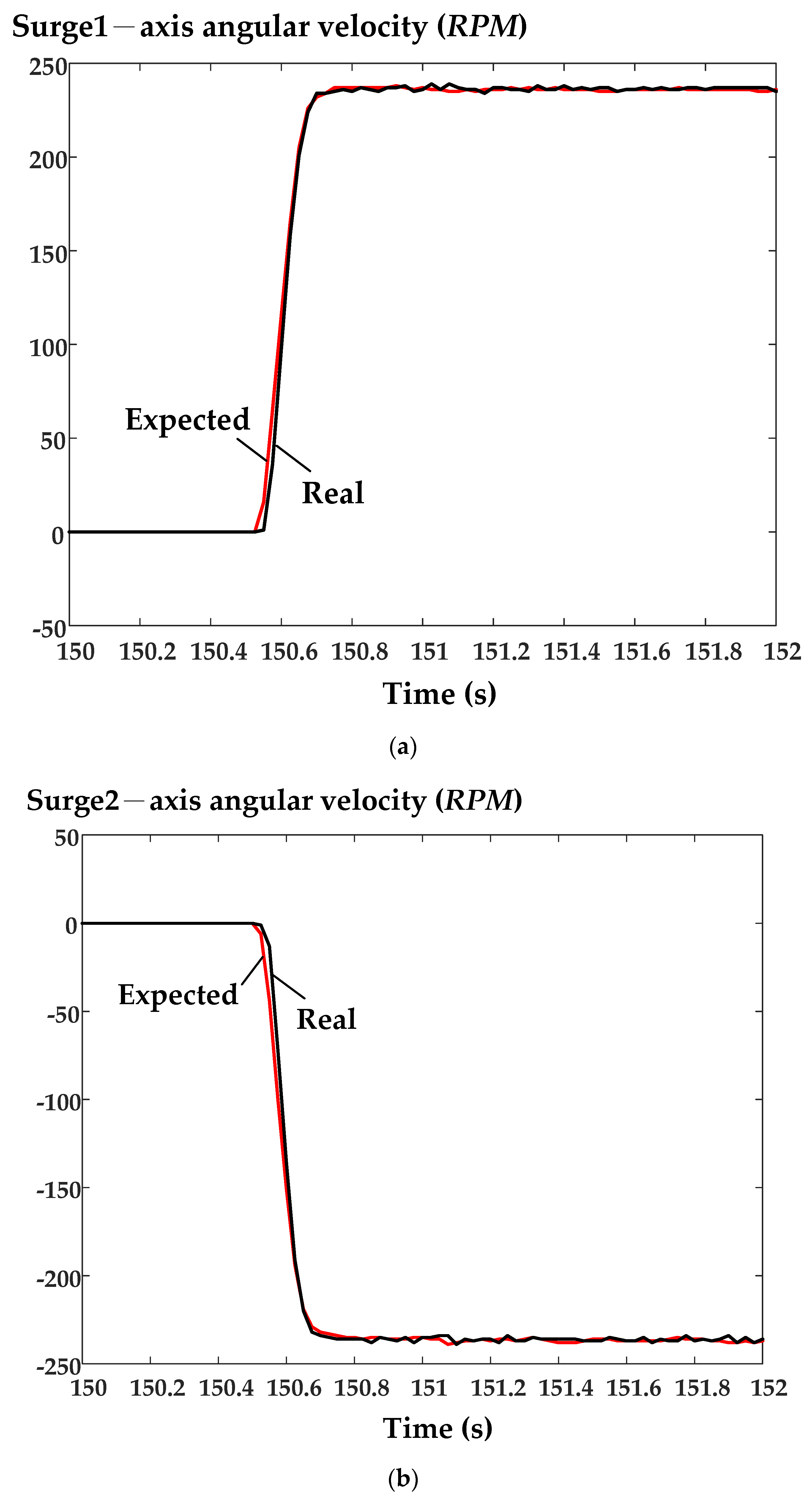
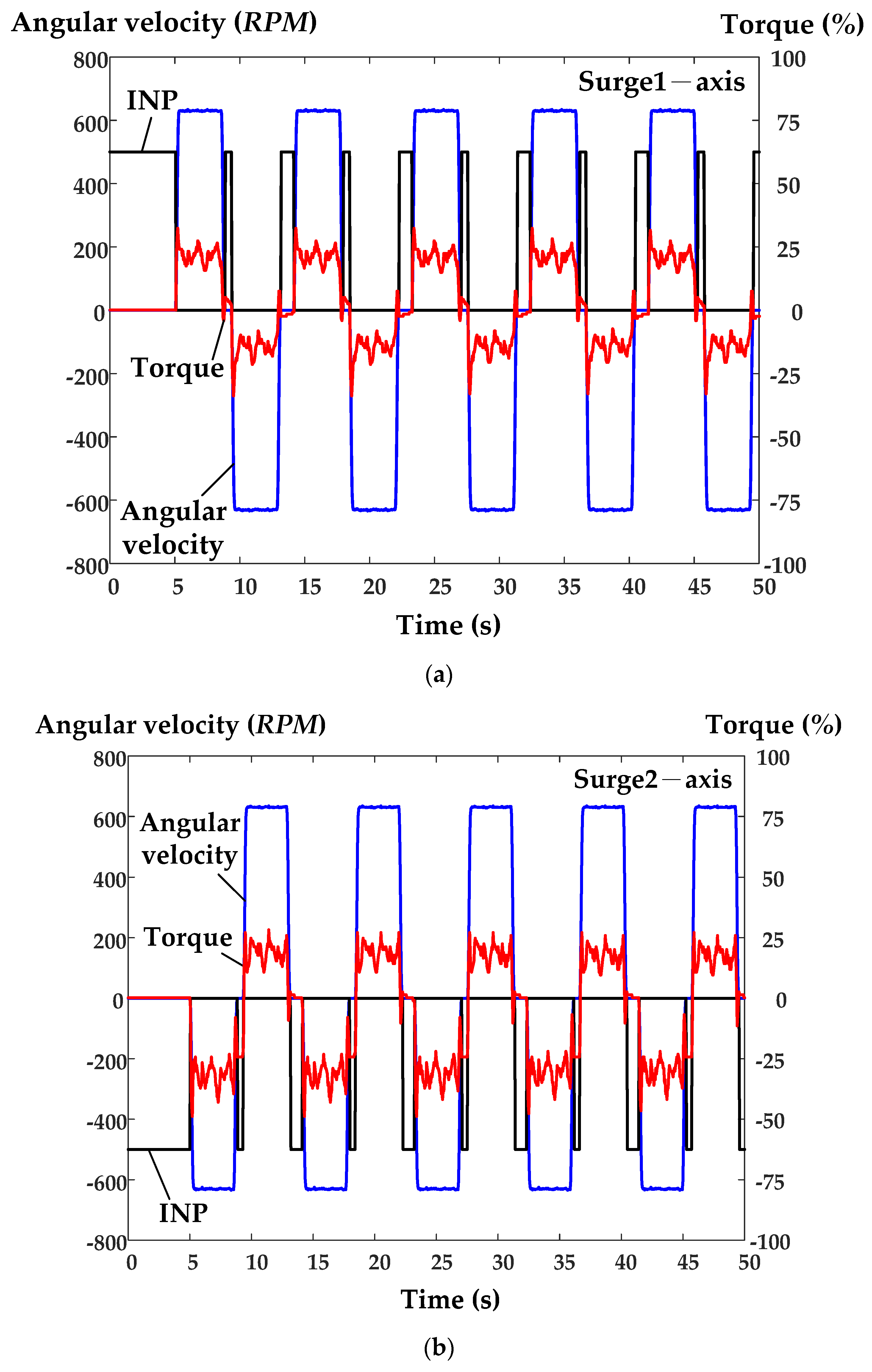
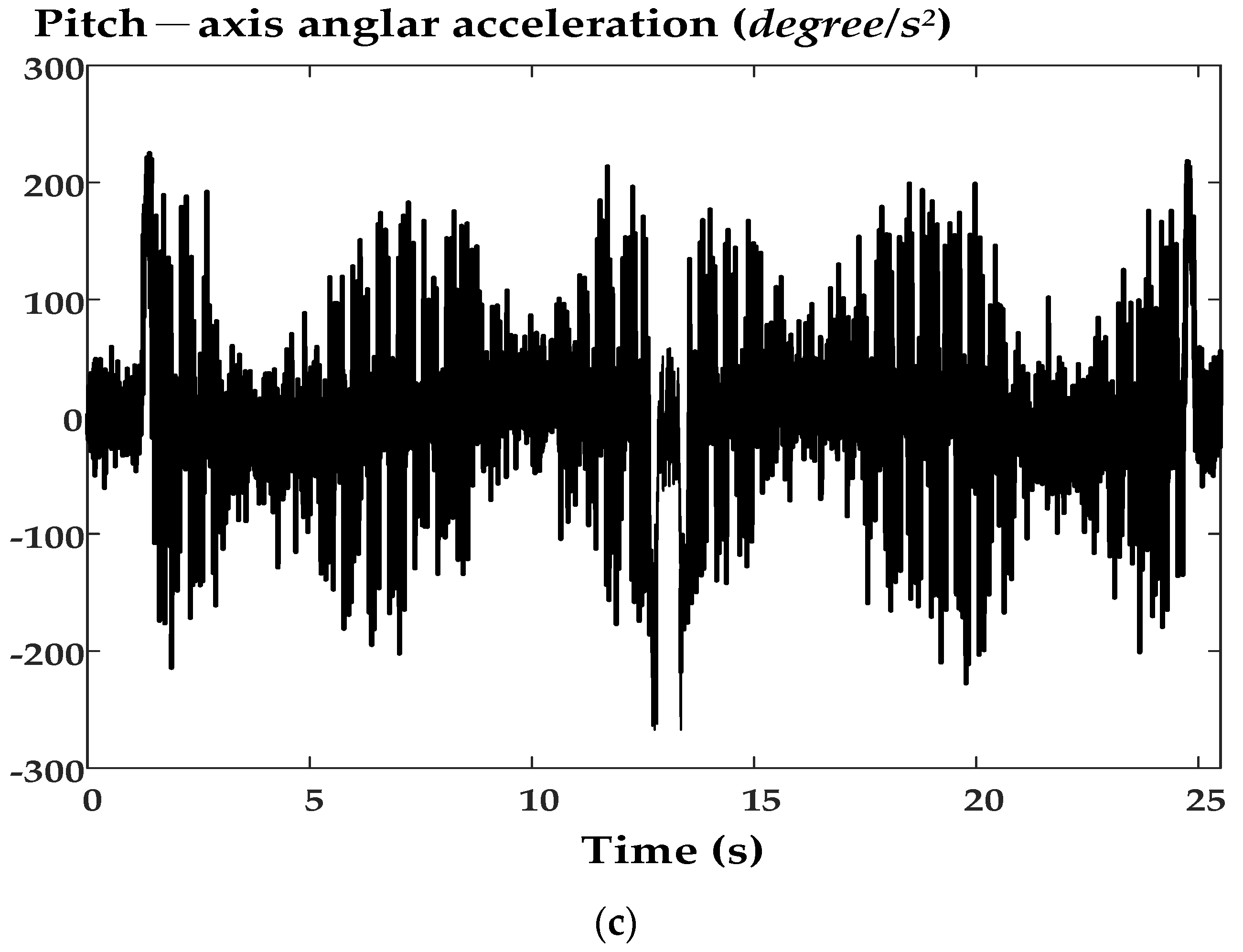
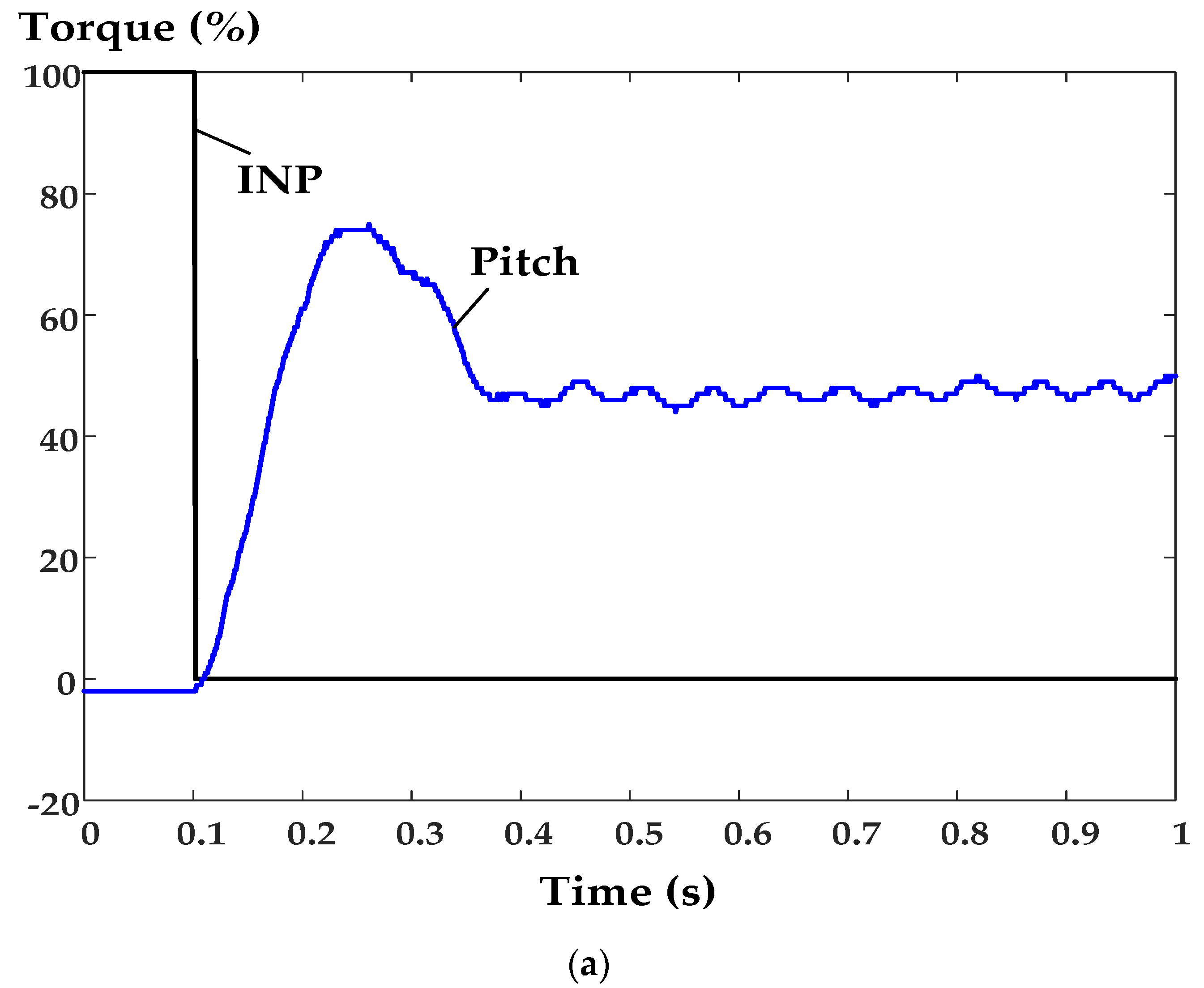
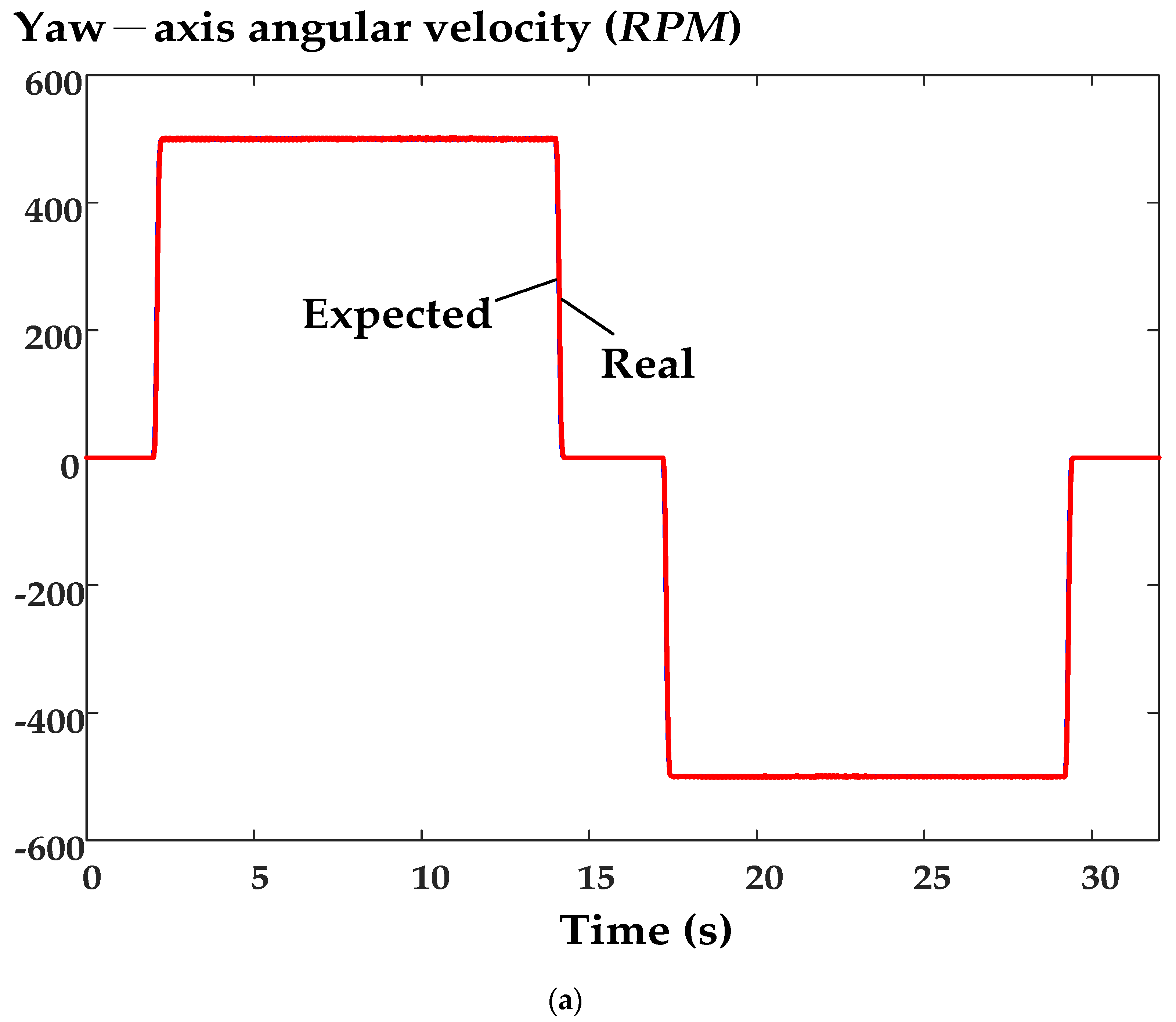
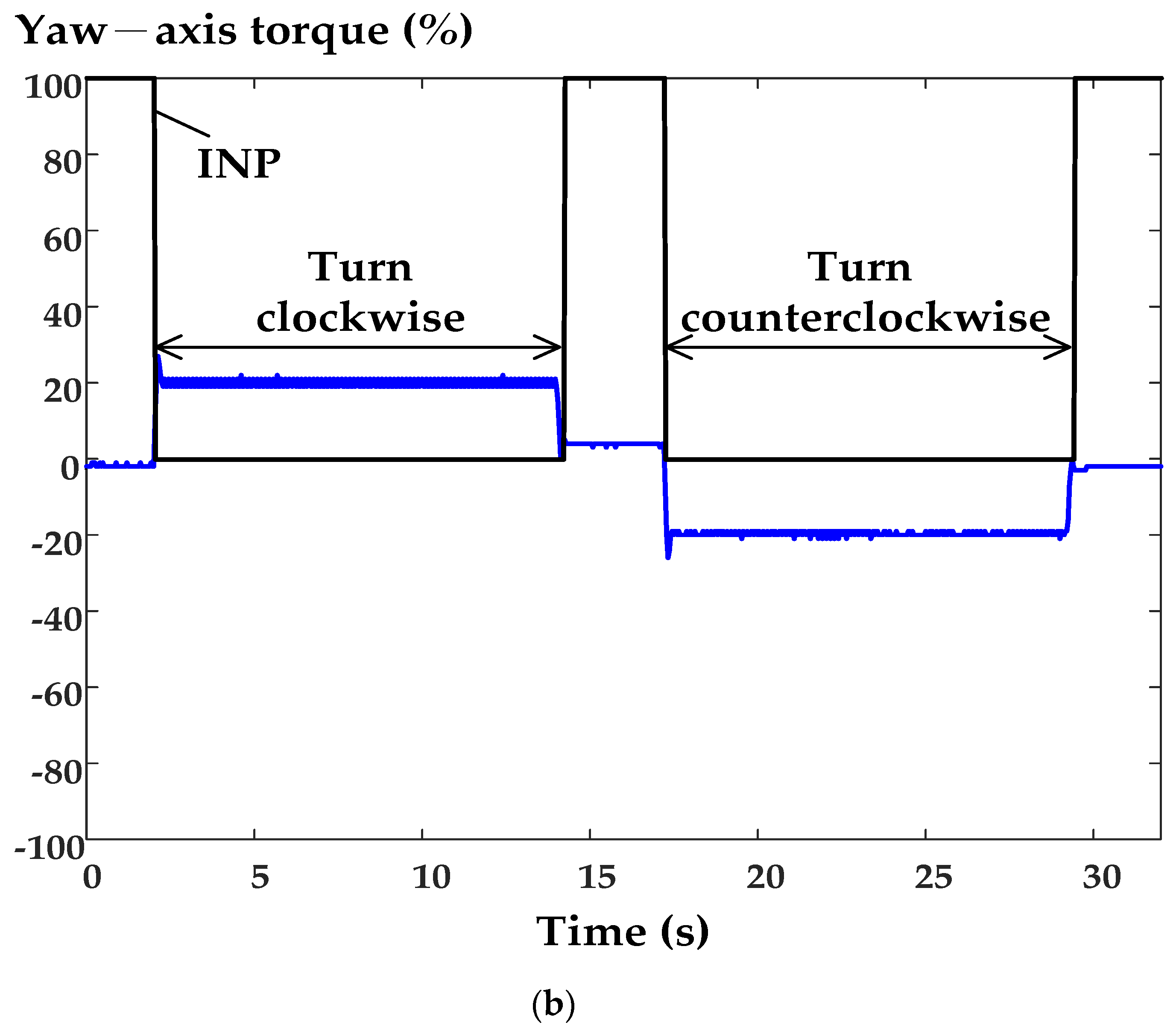
6. Experimental Results
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, H.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y. A novel geometric error compensation method for gantry-moving CNC machine regarding dominant errors. Processes 2020, 8, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinov, G.M.; Al Khoury, A.; Issa, A. An approach of developing low cost ARM based CNC systems by controlling CAN drive. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Modern Trends in Manufacturing Technologies and Equipment (ICMTMTE 2018), Sevastopol, Russia, 10–14 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Babici, L.M.; Tudor, A.; Romeu, J. Stick-Slip Phenomena and Acoustic Emission in the Hertzian Linear Contact. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimura, Y.; Yakoh, T. Bilateral robot system on the real-time network structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrel, W.R. Remote manipulation with transmission delay. IEEE Trans. Human Factors Electron. 1965, 6, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, O.J. A controller to overcome dead time. ISA J. 1959, 6, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.J.; Spong, M.W. Bilateral control of teleoperators with time delay. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 1989, 34, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, G.; Francis, B.; Apkarian, J. Bilateral controller for teleoperators with time delay via –synthesis. IEEE Trans. Robot. Automat. 1997, 11, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. Control and communication of a multi-motor system based on LAN. J. Inf. Commun. Eng. 2016, 2, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAN_bus (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Deng, R.; Wang, Y. Design and preliminary implementation of distributed control system for pipeline detection serpentine robot based on CAN bus. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Chinese Automation Congress (CAC 2019), Hangzhou, China, 22–24 November 2019; pp. 3124–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, G.; Velasco, M.; Marti, P.; Fuertes, J.M. An alternative discrete time model for networked control systems with time delay less than the sampling period. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2013), Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 5626–5631. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Liu, G.P.; Shi, P.; Thomas, C.; Basin, M.V. Predictive output feedback control for networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpel, T.; Hielscher, K.S.; Klehmet, U.; German, R. Stochastic and deterministic performance evaluation of automotive CAN communication. Comput. Netw. 2009, 53, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y. Design and Implementation of Inverse Kinematics and Motion Monitoring System for 6DoF Platform. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y. Design of a DSP-based motion-cueing algorithm using the kinematic solution for the 6-DoF motion platform. Aerospace 2022, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, V.E. Practical tire research. SAE Trans. 1956, 64, 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, D. A platform with six degrees of freedom. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1965, 180, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Molina, F.A.; Rosario, J.M.; Dumur, D. Architecture of predictive control for a Stewart platform manipulator. In Proceedings of the International Conference on World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA 2010), Jinan, China, 7–9 July 2010; pp. 6584–6589. [Google Scholar]
- Bruschetta, M.; Maran, F.; Beghi, A. A Nonlinear, MPC-based motion cueing algorithm for a high-performance, nine-DoF dynamic simulator platform. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2017, 25, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Mohamed, S.; Qazani, M.R.C.; Lim, C.P.; Khosravi, A.; Nahavandi, S. A model predictive control-based motion cueing algorithm using an optimized nonlinear scaling for driving simulators. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 1245–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.M.; Li, S. Dynamic neural networks for kinematic redundancy resolution of parallel Stewart platforms. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2016, 46, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Hu, M.; Pei, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J. A new numerical method for Stewart platform forward kinematics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Chengdu, China, 27–29 July 2016; pp. 6311–6316. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, J.H.; Tseng, S.P. Developing a real-time serial servo motion control system for electric Stewart platform. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Intelligent Systems (ARIS), Taipei, Taiwan, 6–8 June 2014; pp. 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Qazani, M.R.C.; Asadi, H.; Khoo, S.; Nahavandi, S. A linear time-varying model predictive control-based motion cueing algorithm for hexapod simulation-based motion platform. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. 2021, 51, 6096–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Lim, C.P.; Mohamed, S.; Nahavandi, D.; Nahavandi, S. Increasing motion fidelity in driving simulators using a fuzzy-based washout filter. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2019, 4, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y.; Yeh, Y.L.; Liu, J.W.; Wu, H.M. Design and control of a multi-axis servo motion chair system based on a microcontroller. Energies 2022, 15, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, H.; Roy, S.; Gupta, S. Robust adaptive control of steer-by-wire systems under unknown state-dependent uncertainties. Int. J. Adapt. Control. Signal Process. 2022, 36, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.D.; Sankaranarayanan, V.N.; Roy, S. Adaptive sliding mode control for autonomous vehicle platoon under unknown friction forces. In Proceeding of the International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR 2021), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 6–10 December 2021; pp. 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Rayguru, M.M.; Mohan, R.E.; Parween, R.; Yi, L.; Le, A.V.; Roy, S. An Output Feedback Based Robust Saturated Controller Design for Pavement Sweeping Self-Reconfigurable Robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.H.; Lu, W.R.; Cheng, S.H. Design and implementation of predictive controllers for a 36-slot 12-pole outer-rotor SPMSM/SPMSG system with energy recovery. Energies 2023, 16, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AI-Mualla, M.E.; Canagarajah, N.; Bull, D.R. Error concealment using motion field interpolation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 98), Chicago, Il, USA, 7 October 1998; pp. 512–516. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorineschi, L.; Pugi, L.; Rotini, F. New mechanism for press-fit processes: Preliminary analysis. World J. Eng. 2023, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducci, M.; Peruzzi, A.; Pugi, L. Impact of combined roto-linear drives on the design of packaging systems: Some applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applications in Electronics Pervading Industry, Environment and Society; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 738, pp. 235–240. [Google Scholar]













| DOF | Surge1 | Surge2 | Pitch | Yaw | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | |||||
| Power dissipation (kW) | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.0 | |
| Rated Voltage (V) | 220 | 220 | 220 | 220 | |
| Rated Current (A) | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 5.1 | |
| Rotor inertia (kg-cm2) | 9.58 | 9.58 | 9.58 | 6.96 | |
| Rated speed | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | |
| Maximum Speed (r/min) | 2500 | 2500 | 2500 | 2500 | |
| Rated Torque (N.m) | 7.16 | 7.16 | 7.16 | 4.77 | |
| Maximum Torque (N.m) | 21.48 | 21.48 | 21.48 | 14.31 | |
| Reduction ratio of direct link reducer | 1:14 | 1:14 | 1:50 | 1:20 | |
| DOF | Surge1 | Surge2 | Pitch | Yaw | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | |||||
| Stroke | 500 mm | 500 mm | 360° | 360° | |
| Velocity | >500 mm/s | >500 mm/s | >30°/s | >60°/s | |
| Acceleration | >2000 mm/s2 | >2000 mm/s2 | >30°/s2 | >60°/s2 | |
| Actual motor torque | >25% | >25% | >40% | >20% | |
| Axis load weights | 190 Kg | 190 Kg | 100 Kg | 15.4 Kg | |
| Communication | CAN bus and RS485 | CAN bus and RS485 | CAN bus and RS485 | CAN bus and RS485 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, M.-Y. Design and Control of a Three-Axis Motion Servo Control System Based on a CAN Bus. Energies 2023, 16, 4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16104208
Wei M-Y. Design and Control of a Three-Axis Motion Servo Control System Based on a CAN Bus. Energies. 2023; 16(10):4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16104208
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Ming-Yen. 2023. "Design and Control of a Three-Axis Motion Servo Control System Based on a CAN Bus" Energies 16, no. 10: 4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16104208
APA StyleWei, M.-Y. (2023). Design and Control of a Three-Axis Motion Servo Control System Based on a CAN Bus. Energies, 16(10), 4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16104208






