Technical Scheme and Application Prospects of Oil Shale In Situ Conversion: A Review of Current Status
Abstract
:1. Introduction
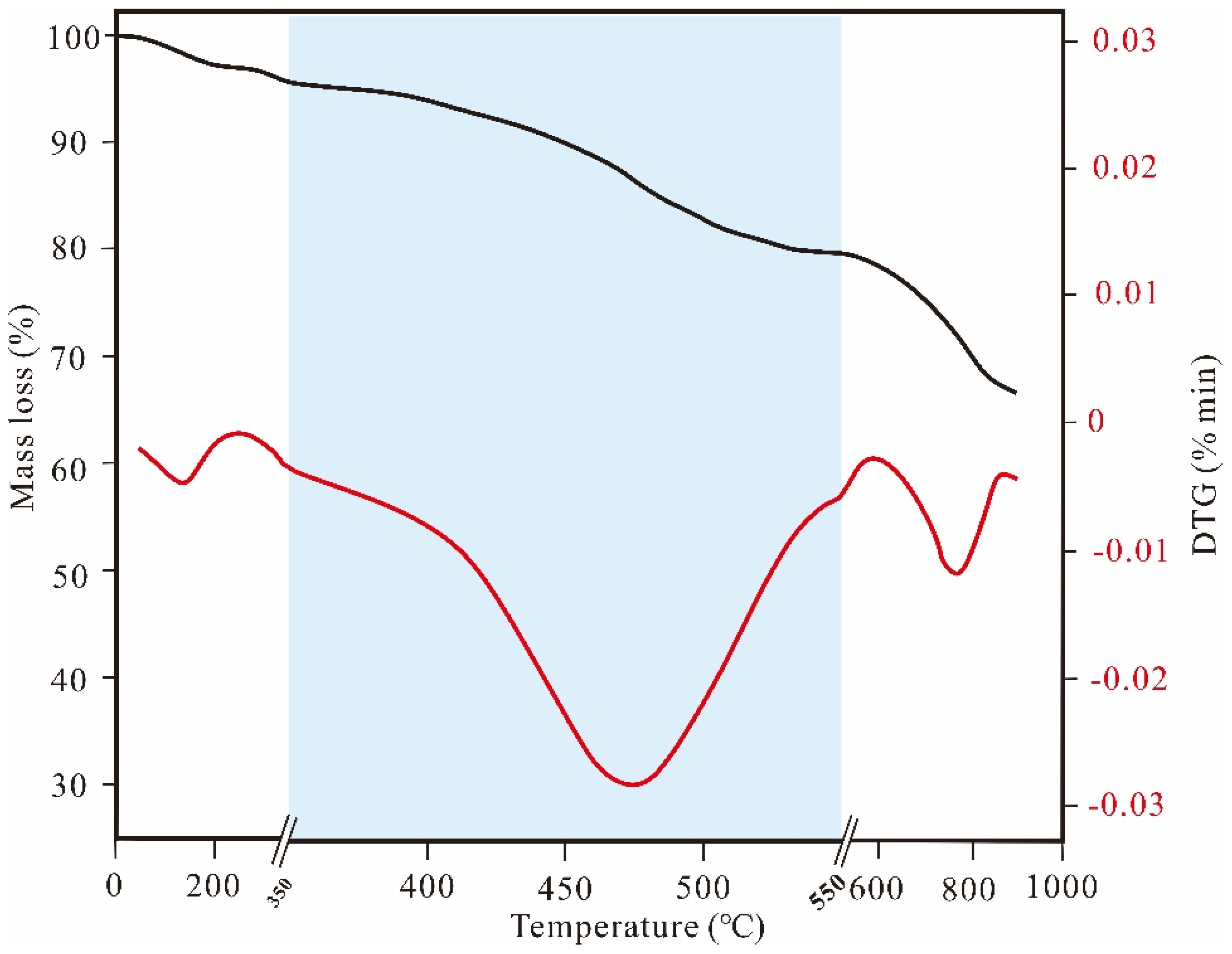
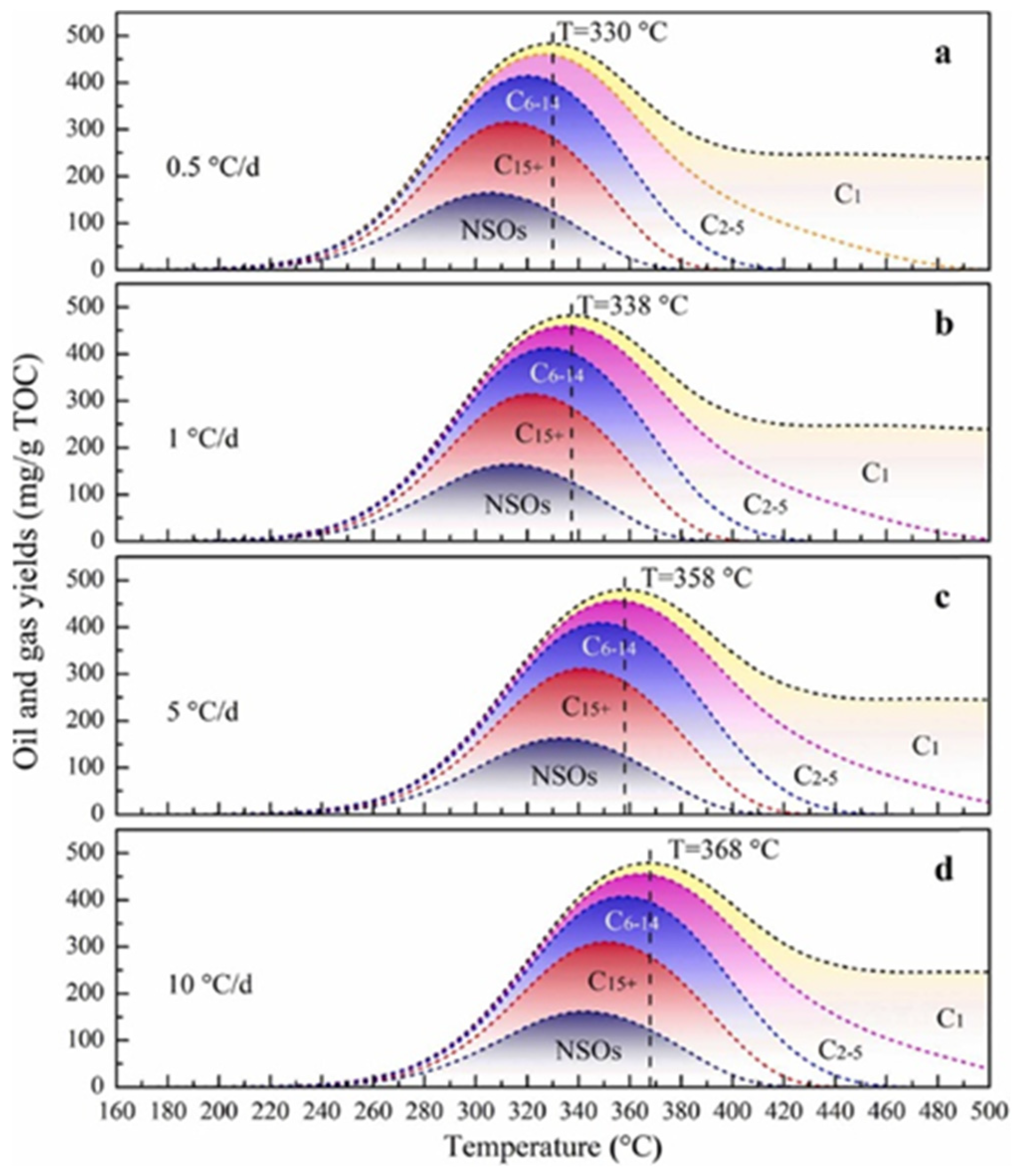
2. Pyrolytic Process of Organic-Rich Shale
2.1. Low-Temperature Stage
2.2. Medium-Temperature Stage
2.3. High-Temperature Stage
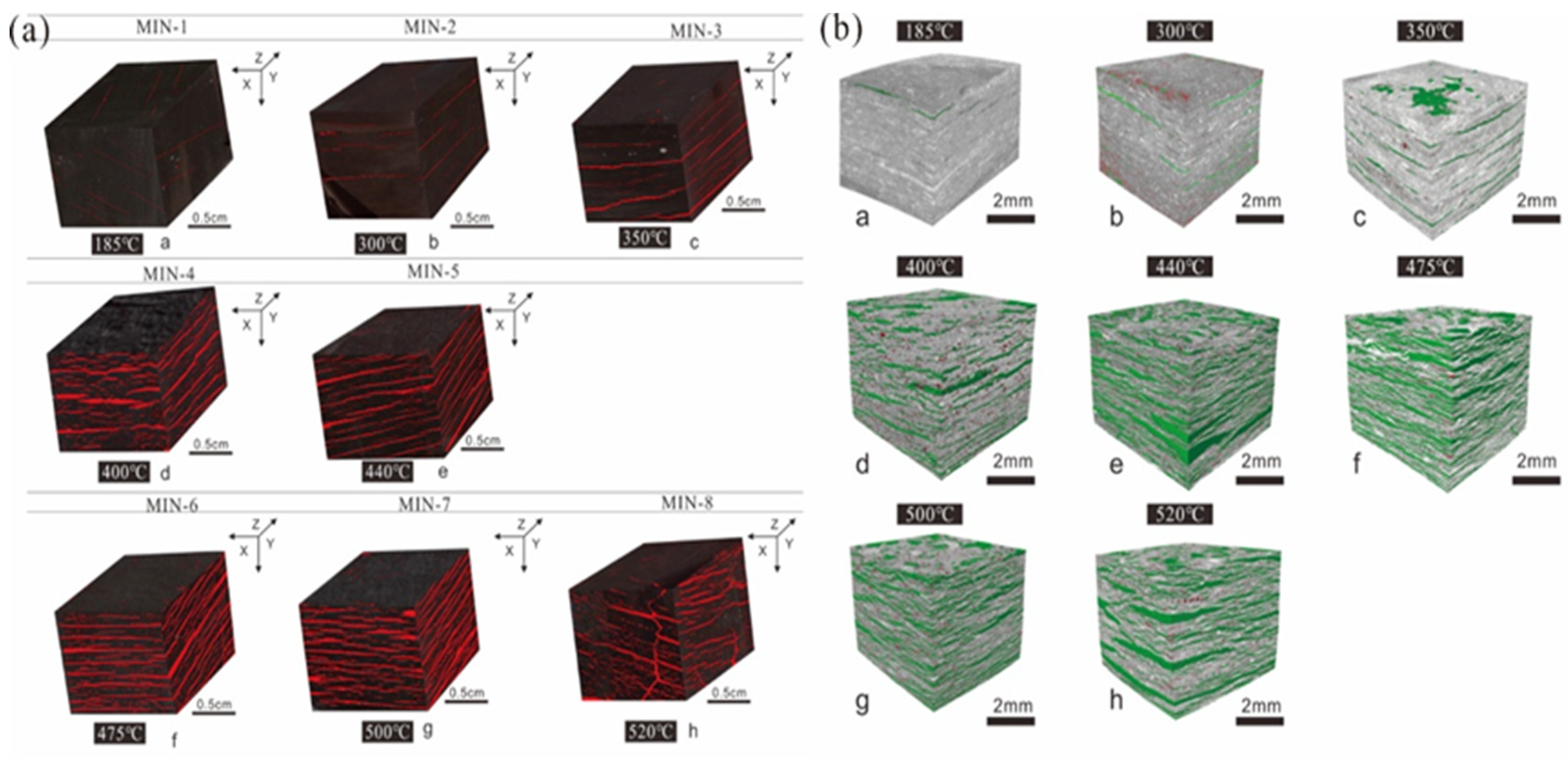
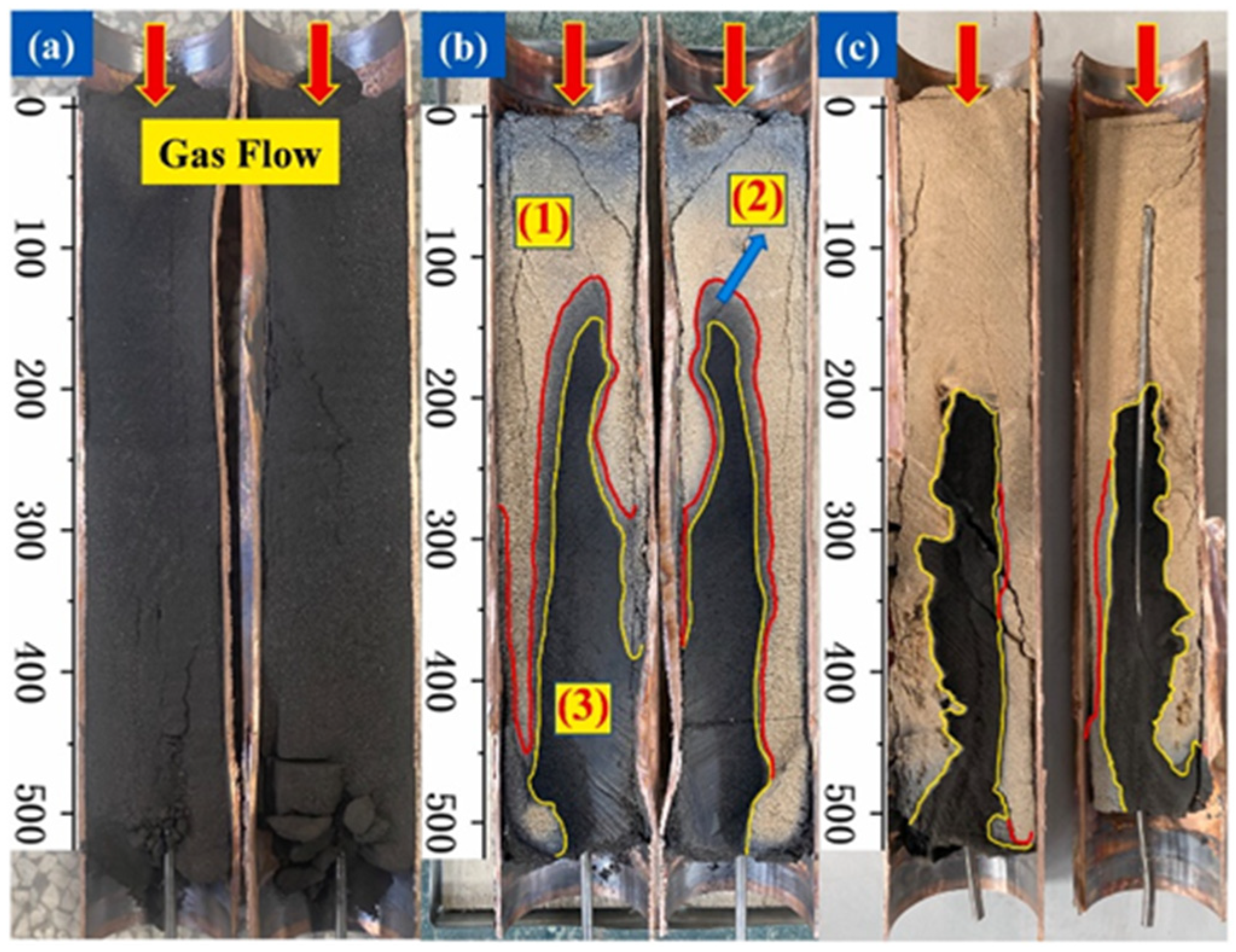
3. Evolution of Pore Structure and Fractures during Organic-Rich Shale Pyrolysis
4. Present Situation of In Situ Conversion Technology
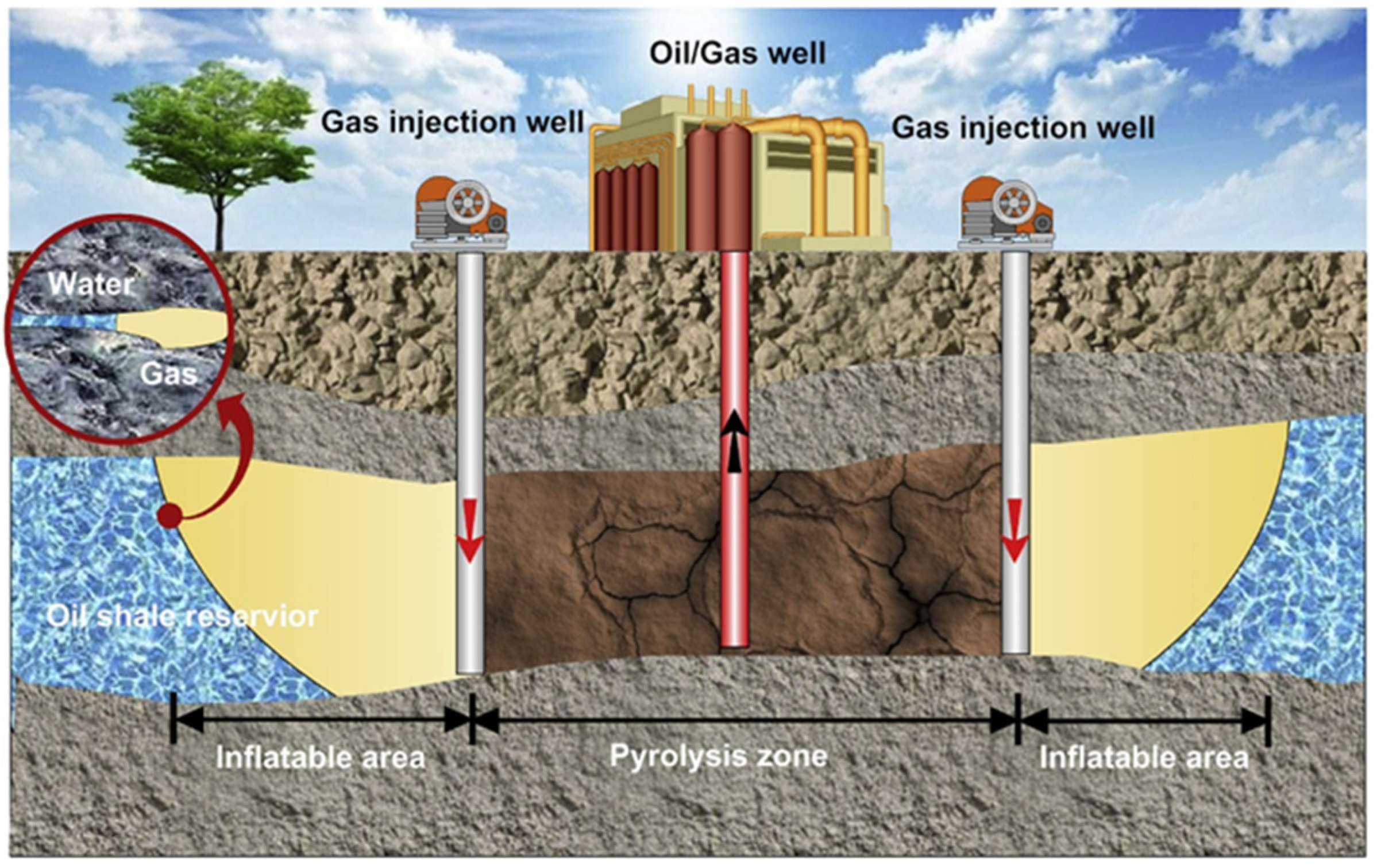
4.1. In Situ Conductive Heating Technology
4.2. In Situ Convection Heating Technology
4.3. In Situ Reaction-Heat Heating Technology
4.4. In Situ Radiant Heating Technology
5. Factors Affecting the Economic Benefits of In Situ Organic-Rich Shale Conversion
5.1. Influence of Heating Mode
5.2. Influence of Formation Conditions
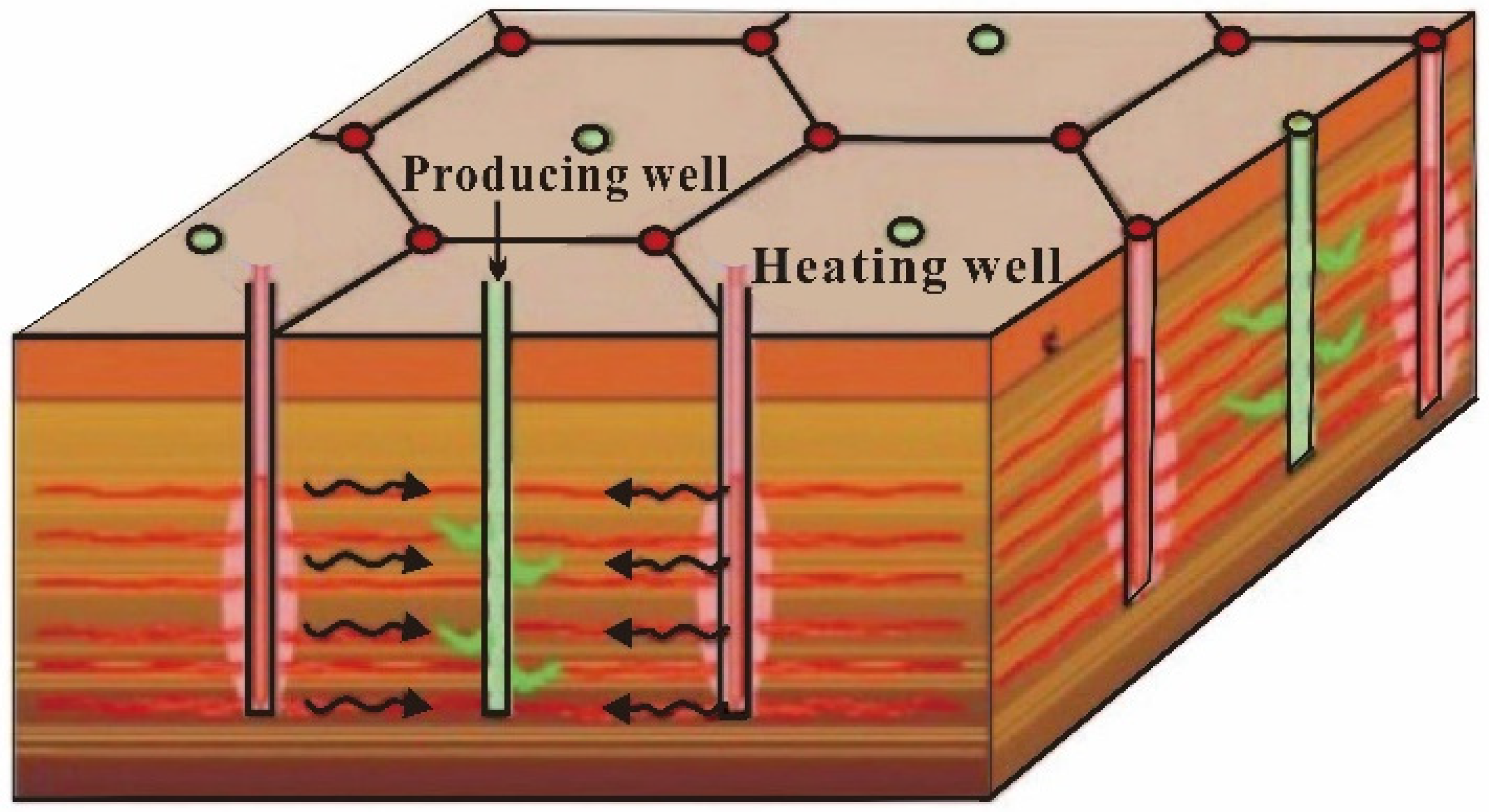
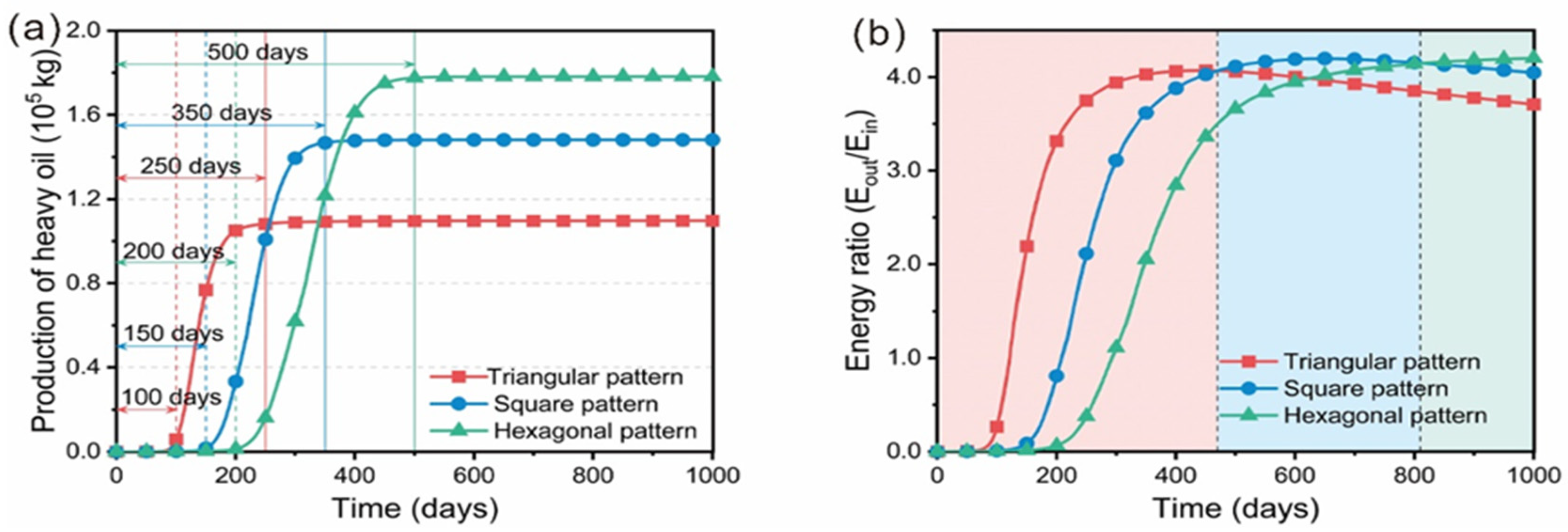
5.3. Distribution Pattern of Wells
5.4. Catalytic Agent
6. Influence of oil Shale In Situ Conversion on a Groundwater Environment
7. Prospects
7.1. Description of the Hydrocarbon Generation Process of Target Formation
7.2. Developed New and Efficient Catalyst
7.3. Supporting Carbon Storage Technology
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, W.; Hu, S.; Hou, L. Connotation and strategic role of in-situ conversion processing of shale oil underground in the onshore China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhao, W.; Hou, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, R.; Wu, S.; Bai, B.; Jin, X. Development potential and technical strategy of continental shale oil in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhu, R.; Dong, D.; Wu, S. Scientific and technological progress, development strategy and policy suggestion regarding shale oil and gas. Acta Pet. Sin. 2020, 43, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.N.; Zhai, G.M.; Zhang, G.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, G.S.; Li, J.Z.; Wang, Z.M.; Wen, Z.X.; Ma, F.; Liang, Y.B.; et al. Formation, distribution, potential and prediction of global conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon resources. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.J.; Zhu, R.K.; Liang, X.P.; Shen, Y.Q. Several issues worthy of attention in current lacustrine shale oil exploration and development. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, D.; Xue, H.; Zheng, D.; Du, D. Discission of Oil Shale In-situ Conversion Process in China. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. 2014, 36, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.; He, K.; Zhai, J.; Mi, J.; Weng, N. Compositional kinetics for hydrocarbon evolution in the pyrolysis of the Chang 7 organic matter: Implications for in-situ conversion of oil shale. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 162, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waples, D.W. The kinetics of in-reservoir oil destruction and gas formation: Constraints from experimental and empirical data, and from thermodynamics. Org. Geochem. 2000, 31, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waples, D.W. Time and Temperature in Petroleum Formation—Application of Lopatins Method to Petroleum-Exploration. AAPG Bull. 1980, 64, 916–926. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, H.; Tian, H.; Cheng, P.; Zhou, Q.; Li, T.; Wang, X.; Xiao, X. Influence of retained bitumen in oil-prone shales on the chemical and carbon isotopic compositions of natural gases: Implications from pyrolysis experiments. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 101, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yu, H.; Xu, W.; Lyu, C.; Micheal, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, H. A coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical model for production performance of oil shale reservoirs during in-situ conversion process. Energy 2023, 268, 126700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, F.; Lorant, F.; Lewan, M. Role of NSO compounds during primary cracking of a Type II kerogen and a Type III lignite. Org. Geochem. 2008, 39, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Finsterle, S.; Moridis, G.J. Analyzing the impact of reaction models on the production of hydrocarbons from thermally upgraded oil shales. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 168, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, L.; Cui, G.; Zhang, P.; Ren, S. An innovative nitrogen injection assisted in-situ conversion process for oil shale recovery: Mechanism and reservoir simulation study. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 171, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Yue, C.T. Study of pyrolysis kinetics of oil shale. Fuel 2003, 82, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, C.; Cui, J.; Mi, J.; Li, H.; He, F. Kinetic simulation of hydrocarbon generation and its application to in-situ conversion of shale oil. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Sun, P.; Ma, L.; Zhao, K.A.; Ding, C. Porosity evolution of Minhe oil shale under an open rapid heating system and the carbon storage potentials. Renew. Energy 2023, 205, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, M. Evaluation of the porous structure of Huadian oil shale during pyrolysis using multiple approaches. Fuel 2017, 187, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Jack, E.; Tom, F. In-Situ Oil Shale Development in Jordan through ICP Technology. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 10–14 November 2014; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, D. Review of oil shale in-situ conversion technology. Appl. Energy 2020, 269, 115121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, L.; Xie, T.; Bawaa, B.; Jin, H.; Guo, L. Sub- and supercritical water conversion of organic-rich shale with low-maturity for oil and gas generation: Using Chang 7 shale as an example. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2022, 7, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Zhang, S. Sequence Stratigraphy and Geochemistry of Oil Shale Deposits in the Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation of the Songliao Basin, NE China: Implications for the Geological Optimization of In Situ Oil Shale Conversion Processing. Energies 2020, 13, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Liu, S.W.; Yang, D.; Fu, M.X. Numerical study on the in-situ pyrolysis process of steeply dipping oil shale deposits by injecting superheated water steam: A case study on Jimsar oil shale in Xinjiang, China. Energy 2022, 239, 122182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Fu, X. Prediction of low-maturity shale oil produced by in situ conversion: A case study of the first and second members of Nenjiang Formation in the Central Depression, southern Songliao Basin, Northeast China. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2020, 42, 533–544. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Shan, X.L.; Song, X.; He, W.T. Evaluation of the organic matter product of Huadian oil shale during pyrolysis using multiple approaches: Guidance for the in situ conversion of oil shale. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 167, 105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Ma, W.; Luo, X.; Liu, J. Characteristics and quantitative models for hydrocarbon generation-retention-production of shale under ICP conditions: Example from the Chang 7 member in the Ordos Basin. Fuel 2020, 279, 118497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Meng, Q.A.; Lin, T.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Ma, S.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Sun, G. Evolution of in-situ permeability of low-maturity shale with the increasing temperature, Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation, northern Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 49, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Doan, T.V.; Bostrom, N.W.; Burnham, A.K.; Kleinberg, R.L.; Pomerantz, A.E.; Allix, P. Green River Oil Shale Pyrolysis: Semi-Open Conditions. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 6447–6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, P.; Yeakel, J.; Symington, W. Plan to Test ExxonMobil’s In Situ Oil Shale Technology on a Proposed RD & D Lease. In Proceedings of the 31st Oil Shale Symposium, Golden, CO, USA, 7–21 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, N.; Anyenya, G.; Haun, B.; Daubenspeck, M.; Bonadies, J.; Kerr, R.; Fischer, B.; Wright, A.; Jones, G.; Li, R.; et al. In-ground operation of Geothermic Fuel Cells for unconventional oil and gas recovery. J. Power Sources 2016, 302, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyenya, G.A.; Braun, R.J.; Lee, K.J.; Sullivan, N.P.; Newman, A.M. Design and dispatch optimization of a solid-oxide fuel cell assembly for unconventional oil and gas production. Optim. Eng. 2018, 19, 1037–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Rapakin, F.; Han, W.; Maljim, Y.S.; Li, Q.; Bukharkin, A.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, B.; Guo, W.; et al. A Method of Underground In-Situ Heating of Oil Shale. CN103174406B, 12 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Theoretical and Experimental Study on In-Situ Pyrolysis of Oil Shale by High Pressure-Power Frequency Electric Heating. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, W.; Deng, S. The status and development trend of in-situ conversion and drilling exploitation technology for oil shale. Drill. Eng. 2021, 48, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Han, Y.; Chen, W.; Kon, K. Development Status and Prospects of In-situ Conversion Technology in Oil Shale. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2022, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L. Pilot test of in-situ steam injection for oil and gas production from oil shale and applicability of and multi-mode in-situ thermal recovery technology. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 1458–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.Q.; Zhao, Y.S.; Yang, D.; Tian, L.J.; Li, X. A pilot investigation of pyrolysis from oil and gas extraction from oil shale by in-situ superheated steam injection. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 186, 106785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.Q.; Xie, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.S.; Zhao, J. The feasibility of in-situ steam injection technology for oil shale underground retorting. Oil Shale 2020, 37, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Li, B.; Che, D.; Liu, S. The mechanism of H2O in the superheated steam affecting the quality of in-situ pyrolysates of oil shale kerogen: Part B-favorable conversion of residues. Fuel 2023, 337, 127146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, S.J.; Lu, J.G.; Ma, J.; He, J.B. The influence of water on the thermal simulation experiment of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, J. Laboratory Experiment of In-situ Conversion Process in Near-critical Water of Huadian Oil Shale of Jilin. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2016, 16, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, T.; Hascakir, B. In-situ kerogen extraction via combustion and pyrolysis. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 154, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, J.H.; Deo, M. Simulation of a Conceptualized Combined Pyrolysis, In Situ Combustion, and CO2 Storage Strategy for Fuel Production from Green River Oil Shale. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yang, Q.; Deng, S.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Su, J.; Zhu, C. Experimental study of the autothermic pyrolysis in-situ conversion process (ATS) for oil shale recovery. Energy 2022, 258, 124878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, Q.; Deng, S.-H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.-F. Mechanism and reservoir simulation study of the autothermic pyrolysis in-situ conversion process for oil shale recovery. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, S.; Sun, Y. Theory and method of in-situ conversion of shale oil by chemical thermal. J. Eng. Geol. 2022, 30, 127–143. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri-Shakib, J.; Kantzas, A. A comprehensive review of microwave application on the oil shale: Prospects for shale oil production. Fuel 2021, 305, 121519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, R.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Shao, H.; Zhang, J.; Fei, J.; Deng, Z.; et al. Thermal and nonthermal effect of microwave irradiation on the pore microstructure and hydrocarbon generation of organic matter in shale. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 150, 106151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Sun, Y.; Guo, W.; Shan, X. Controlling the in-situ conversion process of oil shale via geochemical methods: A case study on the Fuyu oil shale, China. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 219, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Sun, Y.; Shan, X. Organic matter evolution in pyrolysis experiments of oil shale under high pressure: Guidance for in situ conversion of oil shale in the Songliao Basin. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eseme, E.; Littke, R.; Krooss, B.M. Factors controlling the thermo-mechanical deformation of oil shales: Implications for compaction of mudstones and exploitation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2006, 23, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.A.; Sun, P.; Yu, F.; Liu, R.; Zhang, D. Study on Reservoir Physical Properties of Oil Shale During Heating in Minhe Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2020, 41, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, D.; Nie, W.; Li, R. Review on the Characteristics of Pyrolysis During In-situ Conversion of Oil Shale. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. 2021, 43, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, P.; Wang, M.; Tian, H. The relationship between oil generation, expulsion and retention of lacustrine shales: Based on pyrolysis simulation experiments. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lü, X.; Sun, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Kang, S.; Deng, S. Optimization of temperature parameters for the autothermic pyrolysis in-situ conversion process of oil shale. Energy 2023, 264, 126309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xiao, C.; Liang, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, M. The influence of oil shale in situ mining on groundwater environment: A water-rock interaction study. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; He, W.; Yang, L.; Su, J.; Meng, X.; Cen, X.; Guo, W. Evolution of Biomarker Maturity Parameters and Feedback to the Pyrolysis Process for In Situ Conversion of Nongan Oil Shale in Songliao Basin. Energies 2022, 15, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, D.; Kang, Z.; Zhao, J. Anisotropy in Thermal Recovery of Oil Shale Part 1: Thermal Conductivity, Wave Velocity and Crack Propagation. Energies 2018, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Liang, W.; Liu, J.; Cao, M.; Kang, Z. Evolution of Pore and Fracture Structure of Oil Shale under High Temperature and High Pressure. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 10404–10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, H.; Fan, J.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, H. Formation mechanism and structural characteristic of pore-networks in shale kerogen during in-situ conversion process. Energy 2022, 242, 122992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Yang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y. Thermal cracking and corresponding permeability of Fushun oil shale. Oil Shale 2011, 28, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibodeaux, K.R. Evolution of Porosity, Permeability, and Fluid Saturations during Thermal Conversion of Oil Shale. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 27–29 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Bian, J.; Li, J.; Ma, Z.; Long, Q.; Su, J. Porous aluminosilicates catalysts for low and medium matured shale oil in situ upgrading. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 2859–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.R. Converting oil shale to liquid fuels: Energy inputs and greenhouse gas emissions of the Shell in situ conversion process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7489–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, B.; Durand, B.; Espitali, J.; Combaz, A. Influence of Nature and Diagenesis of Organic-Matter in Formation of Petroleum. AAPG Bull. 1974, 58, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; Feng, Z. Oil and Gas Geochemistry; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alhesan JS, A.; Fei, Y.; Marshall, M.; Jackson, W.R.; Qi, Y.; Chaffee, A.L.; Cassidy, P.J. Long time, low temperature pyrolysis of El-Lajjun oil shale. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 130, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Durlofsky, L.J.; Tchelepi, H.A. Numerical Simulation of the In-Situ Upgrading of Oil Shale. SPE J. 2010, 15, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, C. Identification method and application of temperature-time-conversion ratio for in-situ production of oil shale. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2019, 49, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Meng, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Jiao, H.; Liu, X.; Jin, X.; Tuo, J. Petroleum Generation, Retention, and Expulsion in Lacustrine Shales Using an Artificial Thermal Maturation Approach: Implications for the In-Situ Conversion of Shale Oil. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, Z. Influence and its Revelation of oil shale in-situ Mining Simulation in different boundary conditions. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2017, 47, 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, L.; Bao, F. Change of physical properties at different heating rates, time and water content for oil shale. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2018, 40, 545–550. [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann, V.; Schenk, H.J.; Horsfield, B.; Welte, D.H. Kinetics of petroleum generation and cracking by programmed-temperature closed-system pyrolysis of Toarcian Shales. Fuel 1998, 77, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhin, A.V. Rock Mineral Components’ Effects on Heavy and Shale Oil Transformation during Aquathermolysis. Energies 2022, 15, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewan, M.D. Sulphur-radical control on petroleum formation rates. Nature 1998, 391, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewan, M.D. Experiments on the role of water in petroleum formation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 3691–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Cao, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Xue, H.; Wang, M. In-situ upgrading and transformation of low-maturity shale: Economic feasibility and efficiency enhancement approaches from the perspective of energy consumption ratio. Earth Sci. Front. 2023, 30, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Song, R.; Meng, X.; Yu, C.; Bian, J.; Su, J. Oil shale in-situ upgrading with natural clay-based catalysts: Enhancement of oil yield and quality. Fuel 2022, 314, 123076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Fishwick, R.; Wood, J.; Leeke, G.; Rigby, S.; Greaves, M. A review of novel techniques for heavy oil and bitumen extraction and upgrading. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Qi, Z.; Yu, C.; Bian, J.; Ma, Z.; Long, Q.; Su, J. Solid-Acid Catalytic Conversion of Oil Shale: Effects of Sulfonic Acid Grafting on Oil Yield Enhancing and Quality Improvement. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, X.; Wu, D.; Zhai, S.; Yang, S.; Toktonaliev, A.; Pan, Y. Application of Oil Shale Molecular Sieve Catalyst: A Review. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2022, 58, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.B.; Chu, M.; Zhang, C.; Bai, S.X.; Lin, H.; Ma, L.B. Investigation of the Effect of Selected Transition Metal Salts on the Pyrolysis of Huadian Oil Shale, China. Oil Shale 2017, 34, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Qi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Bian, J.; Meng, X.; Long, Q. Oil shale in situ catalytic conversion over clin/SBA-15 composites under subcritical water. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 152, 104942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hou, Q.; Lu, K.; Jin, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Liao, B. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Oil Shale by CrCl3 and Its Molecular Simulation Mechanism. J. China Univ. Pet. Ed. Nat. Sci. 2023, 47, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.Y.; Wu, H.; Liang, X.J.; Xiao, C.L.; Zhao, Q.S.; Cao, Y.Q.; Han, X.R. A preliminary study on the eco-environmental geological issue of in-situ oil shale mining by a physical model. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, T.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.; Al-Khulaifi, Y.; Marone, F.; Hollis, D.; Blunt, M.J.; Bijeljic, B. 4D in situ synchrotron X-ray tomographic microscopy and laser-based heating study of oil shale pyrolysis. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, F. Experiments and simulations of underground artificial freezing with the use of natural cold resources in cold regions. Build. Environ. 2015, 87, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canoglu, M.C. Selection of Suitable Dam Axis Location Considering Permeability and Grout Curtain Optimization. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2019, 25, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Deng, S.; Guo, W. Controlling groundwater infiltration by gas flooding for oil shale in situ pyrolysis exploitation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 179, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, S.; Deng, S. Numerical simulation and field test of grouting in Nong’an pilot project of in-situ conversion of oil shale. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 184, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, R.; Nassar, N.N.; Pereira Almao, P. Nanoparticle technology for heavy oil in-situ upgrading and recovery enhancement: Opportunities and challenges. Appl. Energy 2014, 133, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Heating Method | Process | Last Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conduction | In situ conversion process (ICP) | Demonstration | [19,20,28] |
| ElectrofracTM | Planned field experiment | [20,29] | |
| Geothermic fuel cell (GFC) | Laboratory simulation | [20,30,31] | |
| High voltage—power frequency electric heating (HVF) | Laboratory simulation | [32,33] | |
| Convection | CRUSH | Abandon | [20,34] |
| CCR | Abandon | [34] | |
| In situ vapor extraction (IVE) | Field experiment | [20,35] | |
| MTI | Planned field experiment | [20,36,37,38,39,40] | |
| Near-critical water (NCW) | Field experiment | [34,35,41] | |
| Reaction | Ture in situ (TIS) | Abandon | [20,42,43] |
| Modified in situ (MIS) | Abandon | [20,42,43] | |
| Autothermic pyrolysis in situ conversion (ATS) | Field experiment | [18,44,45] | |
| Reaction heat of calcium oxide and water | Thesis | [46] | |
| Radiant | Radio frequency and supercritical fluid (RF/CF) | Laboratory simulation | [20,47] |
| Microwave | Planned field experiment | [20,47,48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Gai, H.; Cheng, P. Technical Scheme and Application Prospects of Oil Shale In Situ Conversion: A Review of Current Status. Energies 2023, 16, 4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114386
Liu S, Gai H, Cheng P. Technical Scheme and Application Prospects of Oil Shale In Situ Conversion: A Review of Current Status. Energies. 2023; 16(11):4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114386
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shangli, Haifeng Gai, and Peng Cheng. 2023. "Technical Scheme and Application Prospects of Oil Shale In Situ Conversion: A Review of Current Status" Energies 16, no. 11: 4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114386
APA StyleLiu, S., Gai, H., & Cheng, P. (2023). Technical Scheme and Application Prospects of Oil Shale In Situ Conversion: A Review of Current Status. Energies, 16(11), 4386. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114386







