Long-Term Pore-Scale Experiments on MEOR by Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms Reveal the Altering Dominant Mechanisms of Oil Recovery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microorganisms Cultivation
2.3. Micro-Flooding Device
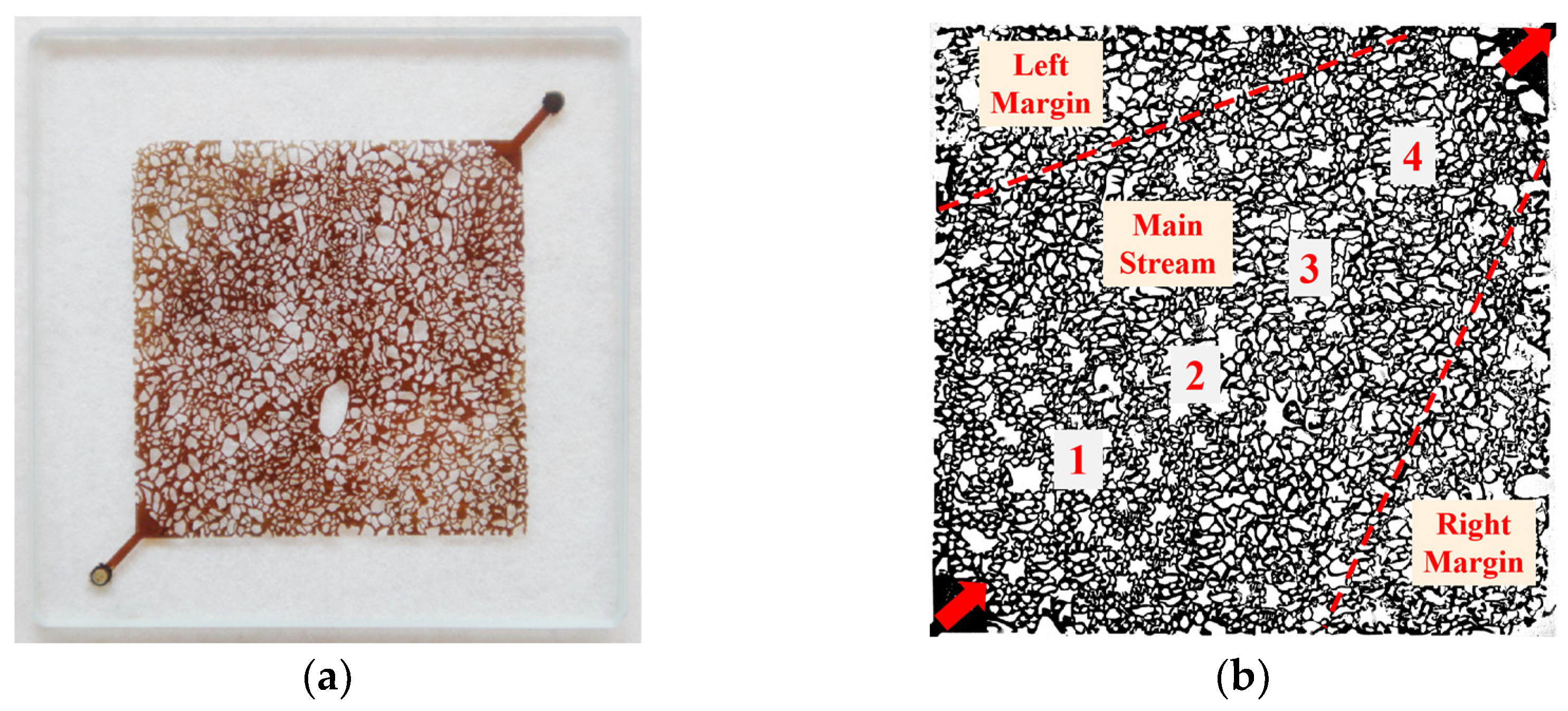
2.4. Micro-Model
2.5. Micro-Flooding Experiment
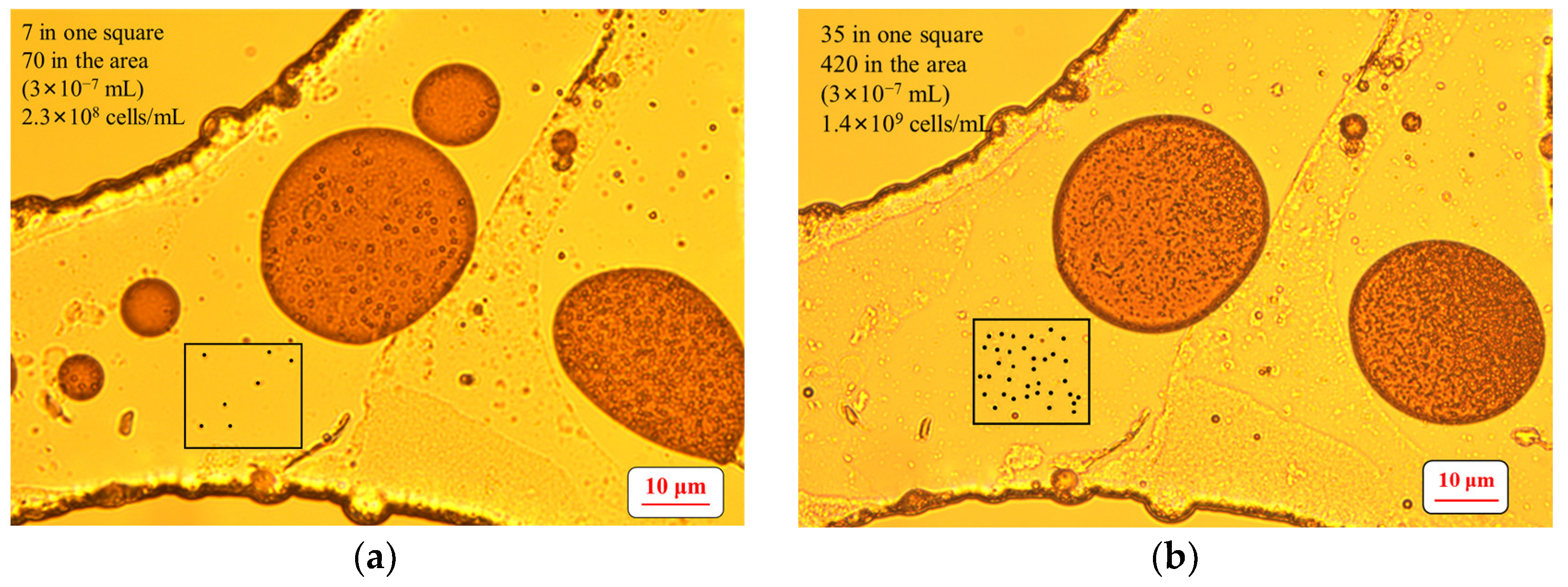
2.6. Determination of the Number of Microbial Cells
2.7. Determination of Oil Saturation in the Micro-Model
2.8. Measurement of the Contact Angle
3. Results
3.1. Growth of the Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms
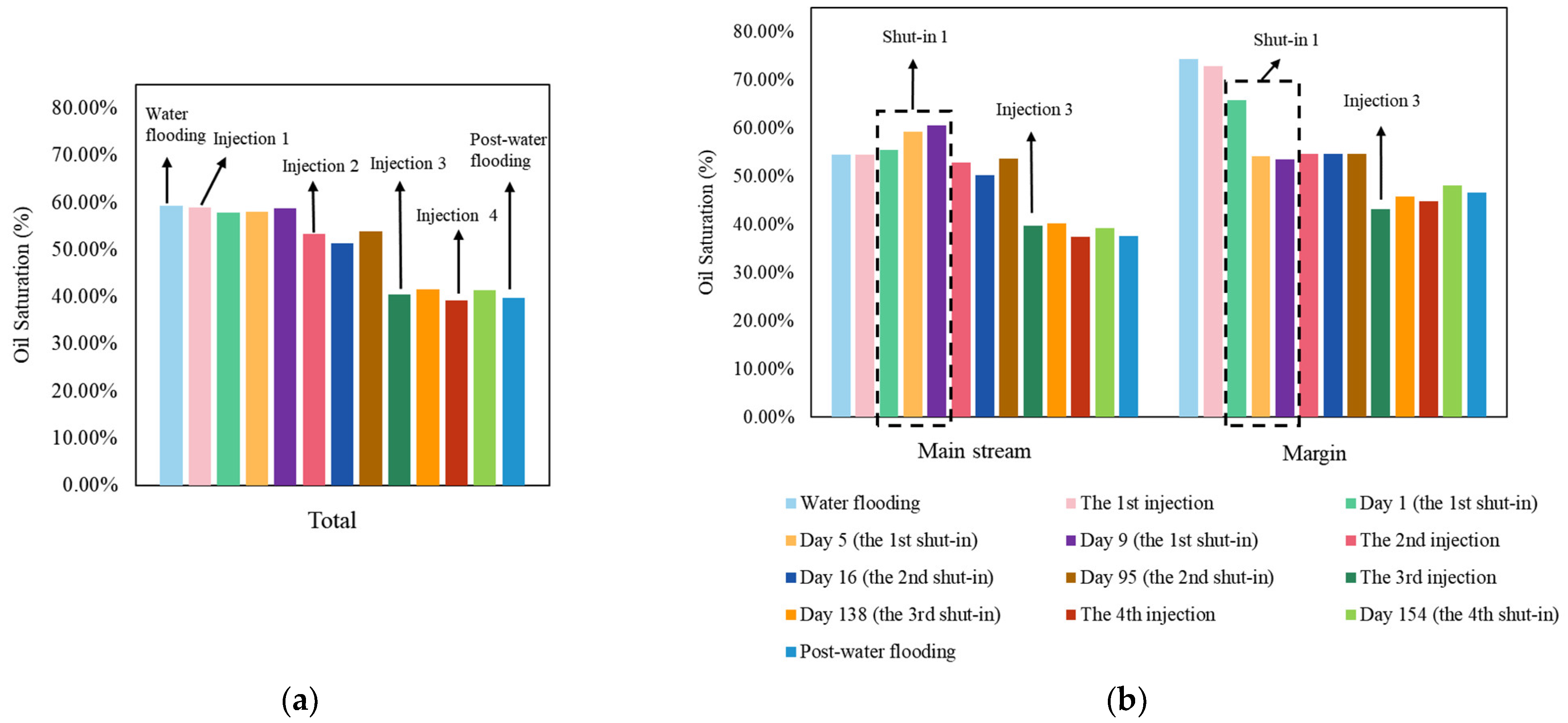
3.2. The Total and Divisional Oil Saturation after Each Stage by Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms
3.3. Wettability Alteration on Pore Surface
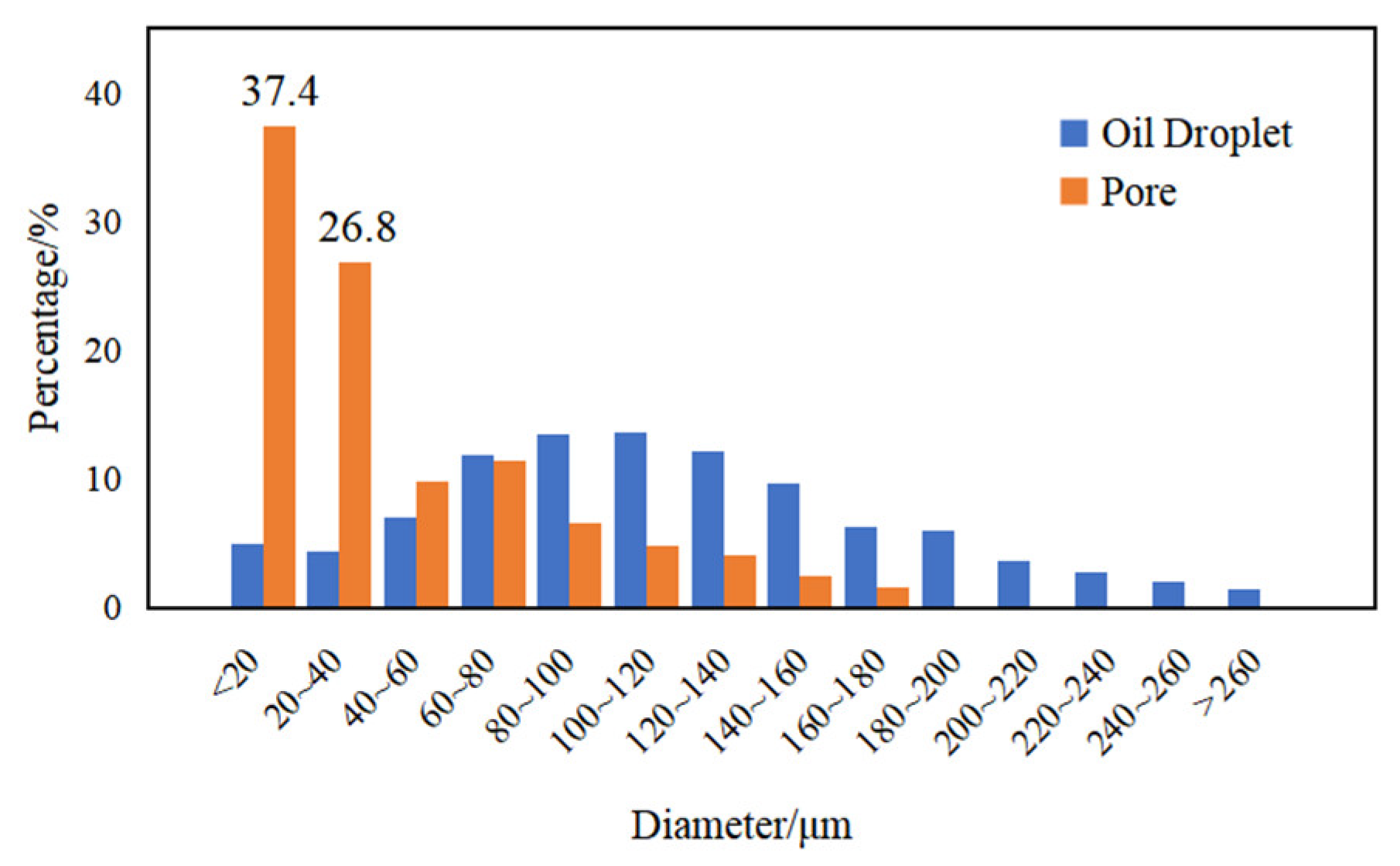
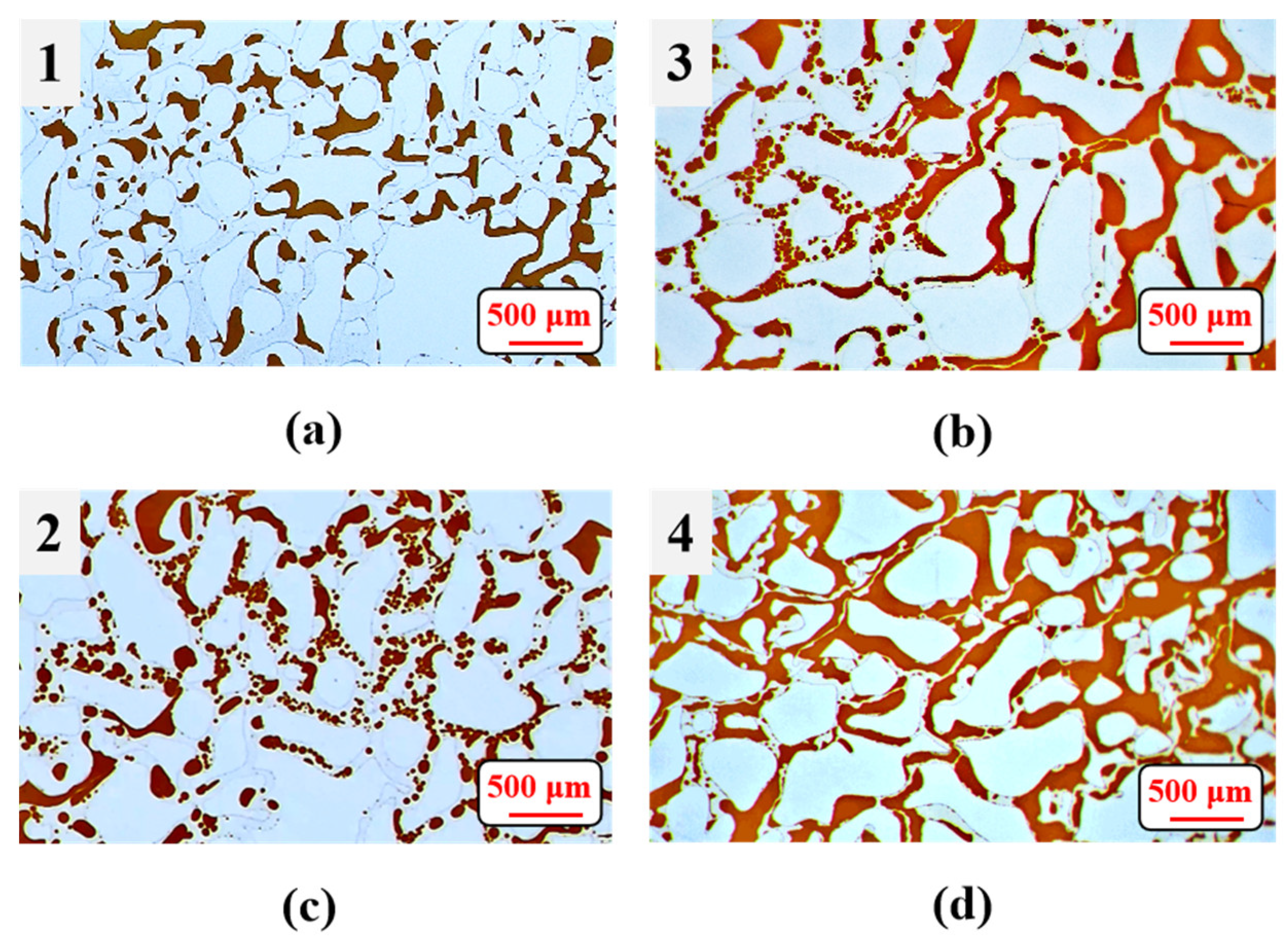
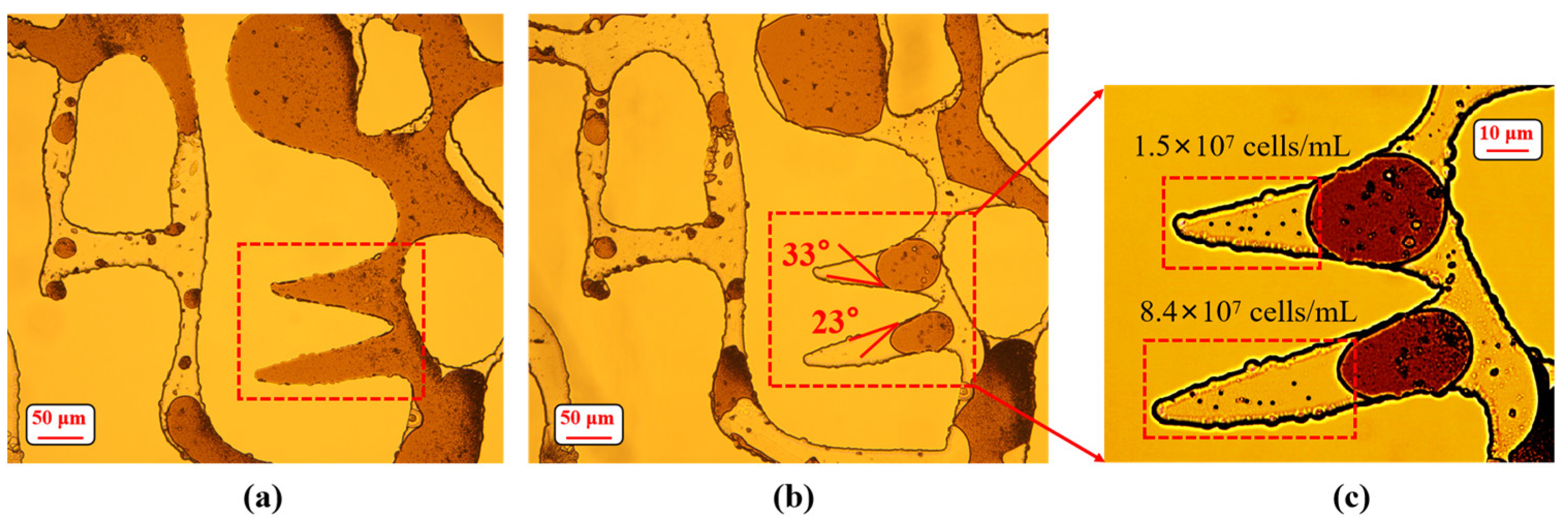
3.4. Emulsification of Residual Oil
3.5. Effects of Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms on Residual Oil Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms Can Improve Not Only Displacement Efficiency but Also Sweep Efficiency
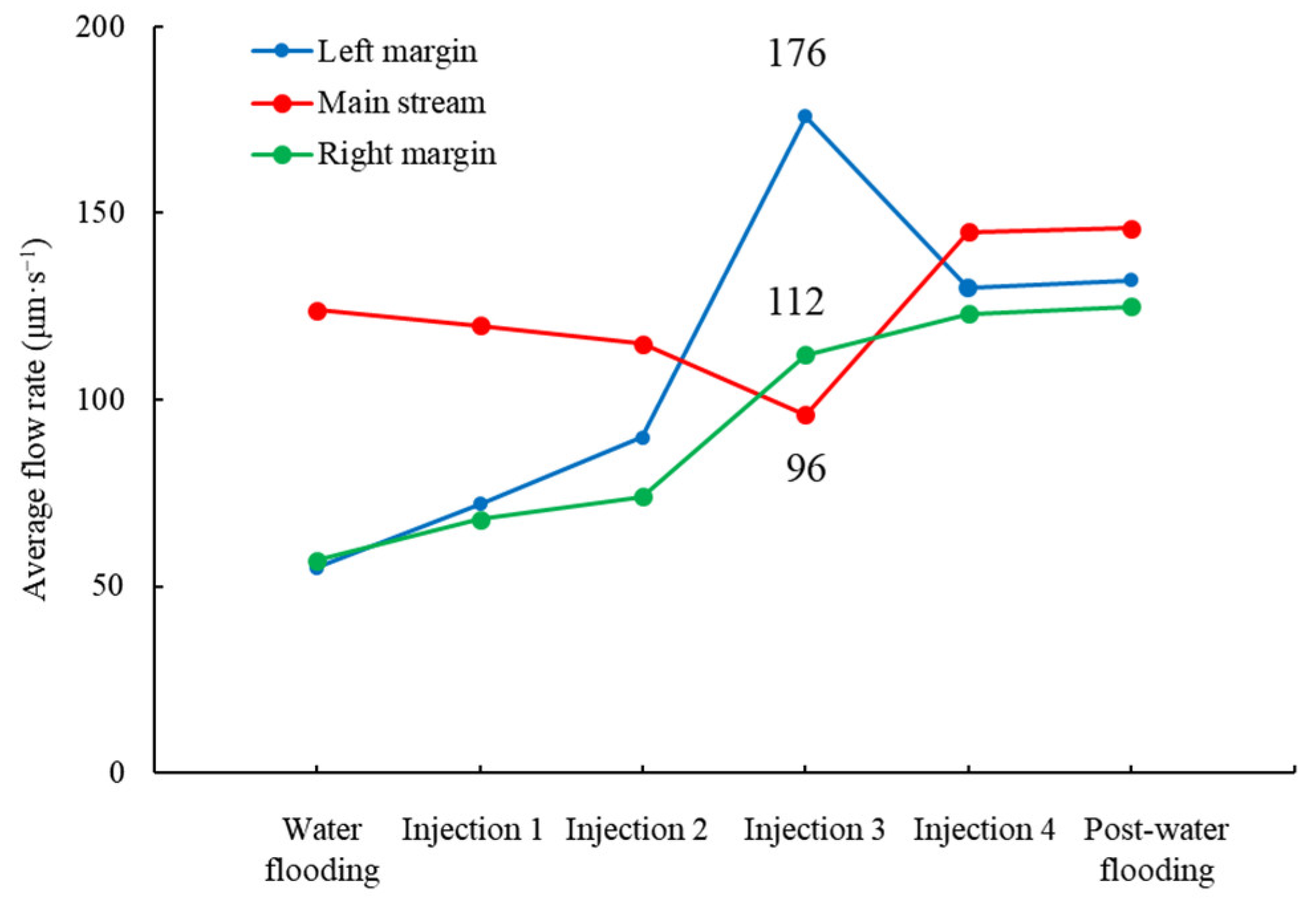
4.2. Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms Improve Sweep Efficiency during Not Only Flooding Period but Also Shut-in Period
4.3. Mechanism of the Improvement of Sweep Efficiency in Shut-in Period
4.4. The Long-Term Experiment Reveals the Dominant EOR Mechanisms Altering with Residual Oil Saturation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Adasani, A.; Bai, B.J. Analysis of EOR projects and updated screening criteria. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2011, 79, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R. Biotechnology in petroleum recovery: The microbial EOR. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.J.; Liu, Q.; Lv, J.; Peng, B. Review on microbial enhanced oil recovery: Mechanisms, modeling and field trials. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020192, 107350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, R.; Bodratti, A.M.; Tsianou, M.; Alexandridis, P. Biosurfactants, natural alternatives to synthetic surfactants: Physicochemical properties and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, H.; Sarrafzadeh, M.H.; Haghighi, M.; Mehrnia, M.R. Comparative study of biosurfactant producing bacteria in MEOR applications. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 75, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansah, E.O.; Sugai, Y.; Nguele, R.; Sasaki, K. Integrated microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR) simulation: Main influencing parameters and uncertainty assessment. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 171, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.Y.; Lu, G.M.; Li, Y.B.; Sun, W.J.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Zhang, X.L. A pilot study on large-scale microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR) in Baolige Oilfield. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 127, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Lu, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.J.; Yuan, W.B. Mechanism and community distribution of microbially activated water flooding in Sai 169 low-permeability reservoir. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2022, 29, 47–153. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, R.T.; Wildenschild, D. Investigating the pore-scale mechanisms of microbial enhanced oil recovery. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 94–95, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.J.; Meng, X.X.; Qv, X.H.; Zhan, G.X.; Li, L.; Lei, G.L. Reaction kinetics model and numerical simulation method of microbial flooding in oil reservoirs. J. China Univ. Petrol. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2021, 45, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Y.; Guo, S.X.; Lei, G.L.; Wang, W.D. Microscopic mechanism studies on microbial enhanced oil recovery under high temperature high pressure reservoir conditions. Oilfield Chem. 2008, 25, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Tian, Y.A.; Wang, W.D.; Song, Z.Y.; Han, H.Y.; Song, Y.T.; Li, C.F. Mechanisms of oil displacement by indigenous microorganism producing bio-emulsifier using microscopic modeling. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Tech.) 2016, 47, 3280–3288. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.D. Research advance and development trend in microbial enhanced oil recovery technology. Petrol. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2021, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhu, W.Y.; Song, Z.Y. 2-D pore-scale oil recovery mechanisms of the anionic and nonionic surfactants. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 655, 130245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Song, Z.Y. Pore-scale experiments reveal distinct flow field of polymer flooding with viscoelasticity loss by high salinity. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 668, 131473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Cao, Y.B.; Wang, W.D.; Bao, M.T. Study on the activation Geobacillus species in Zhan 3 blocks of Shengli Oilfield. J. Univ. Petrol. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2016, 40, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Y.; Ding, M.S.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.J.; Ren, S.L. Physical simulation experiment of oil displacement by bacillus subtilis for enhanced oil recovery. Chem. Eng. Oil Gas 2016, 45, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lin, J.Z.; Song, X.; Tan, X.M.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.B. A strain of lipopeptide producing bacteria identification and its metabolic product performance evaluation. J. Northeast Petrol. Uni. 2016, 40, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, B.; Shi, J.W.; Feng, J.; Yang, Z.Y.; Peng, B.L.; Zhao, S.L. Research progress of surfactant enhanced oil recovery based on microfluidics technology. Acta Petrolei Sin. 2022, 43, 432–442,452. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.Q.; Gao, Y.T.; Wang, C.Y.; Xiu, J.L.; Yi, L.N. Effect of permeability on profile control and oil displacement by bacteria. Fault-block Oil Gas Field 2020, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, L.S.; Jin, Y.X.; Wang, T.; Li, W.Z. Effect of shear action on enhanced oil recovery of spontaneous emulsification flooding. Oilfield Chem. 2016, 33, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhu, W.Y.; Niu, H.; Gao, Y.B.; Chen, Z.; Song, Z.Y.; Kong, D.B. 2-D porous flow field reveals different EOR mechanisms between the biopolymer and chemical polymer. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 210, 110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Z.; Yin, D.Y.; Cao, R. Research on profile control and displacement mechanism of discontinuous emulsion in late high water-cut stage. Oilfield Chem. 2016, 33, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Khajepour, H.; Mahmoodi, M.; Biria, D.; Ayatollahi, S. Investigation of wettability alteration through relative permeability measurement during MEOR process: A micromodel study. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 120, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Borgohain, S.; Kumar, M.; Rangarajan, V.; Somasundaran, P.; Sen, R. Recent developments in microbial enhanced oil recovery. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Niazi, A.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.; Ayatollahi, S. Investigating wettability alteration during MEOR process, a micro/macro scale analysis. Coll. Colloids Surf. B 2012, 95, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falode, O.; Manuel, E. Wettability effects on capillary pressure, relative permeability, and irredcucible saturation using porous plate. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, K.V.; Keharia, H. Application of extracellular lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by endophytic Bacillus subtilis K1 isolated from aerial roots of banyan (Ficus benghalensis) in microbially enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). 3 Biotech 2014, 4, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameotra, S.S.; Makkar, R.S.; Kaur, J.; Mehta, S.K. Synthesis of biosurfactants and their advantages to microorganisms and mankind. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 672, 261–280. [Google Scholar]
- Jacques, P.; Hbid, C.; Destain, J.; Razafindralambo, H.; Paquot, M.; Pauw, E.D.; Jacques, P.T. Optimization of biosurfactant lipopeptide production from Bacillus subtilis S499 by Plackett-Burman design. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1999, 77, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Dieckmann, U.; Franklin, O.; Kaiser, C. Synergistic effects of diffusion and microbial physiology reproduce the Birch effect in a micro-scale model. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mou, B.Z. The diffusion coefficient of Bacillus subtilis HSO. Oilfield Chem. 2005, 22, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, A.; Ranjbar, B.; Kazemzadeh, Y.; Niazi, A.; Riazi, M. Effect of bacteria on oil/water interfacial tension in asphaltenic oil reservoirs. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 639, 128263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jiang, L.; Ren, N.Q.; Sun, K. Advance in bacteria chemotaxis on microfluidic devices. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Yu, L.; Xiu, J.L.; Ma, Y.D.; Lin, W.; Ma, T.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, L. A mathematical model for microbial enhanced oil recovery using biopolymer-producing microorganism. Fuel 2018, 216, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.F.; Shen, C.; Wei, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.B. A comprehensive review of polysaccharide biopolymers for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) from flask to field. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Y.; Zhu, P.R.; Wu, X.L.; Xu, P.; Li, H.; Du, C.A.; He, X.; Yang, L.Z.; Zhu, W.Y. Vertical distribution of biofilm communities along an injection wellbore in a deep petroleum reservoir. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 206, 109024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.J.; Meng, X.X.; Qu, X.H.; Cheng, T.X.; Da, Q.A.; Zhang, K.; Lei, G.L. Kinetic model and numerical simulation of microbial growth, migration, and oil displacement in reservoir porous media. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 32549–32561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.B.; Shan, W.W.; Yu, L. Simulation and application of mathematical model of enhanced oil recovery by indigenous microbes. J. Liaoning Tech. Uni. (Nat. Sci.) 2008, 27, 709–712. [Google Scholar]



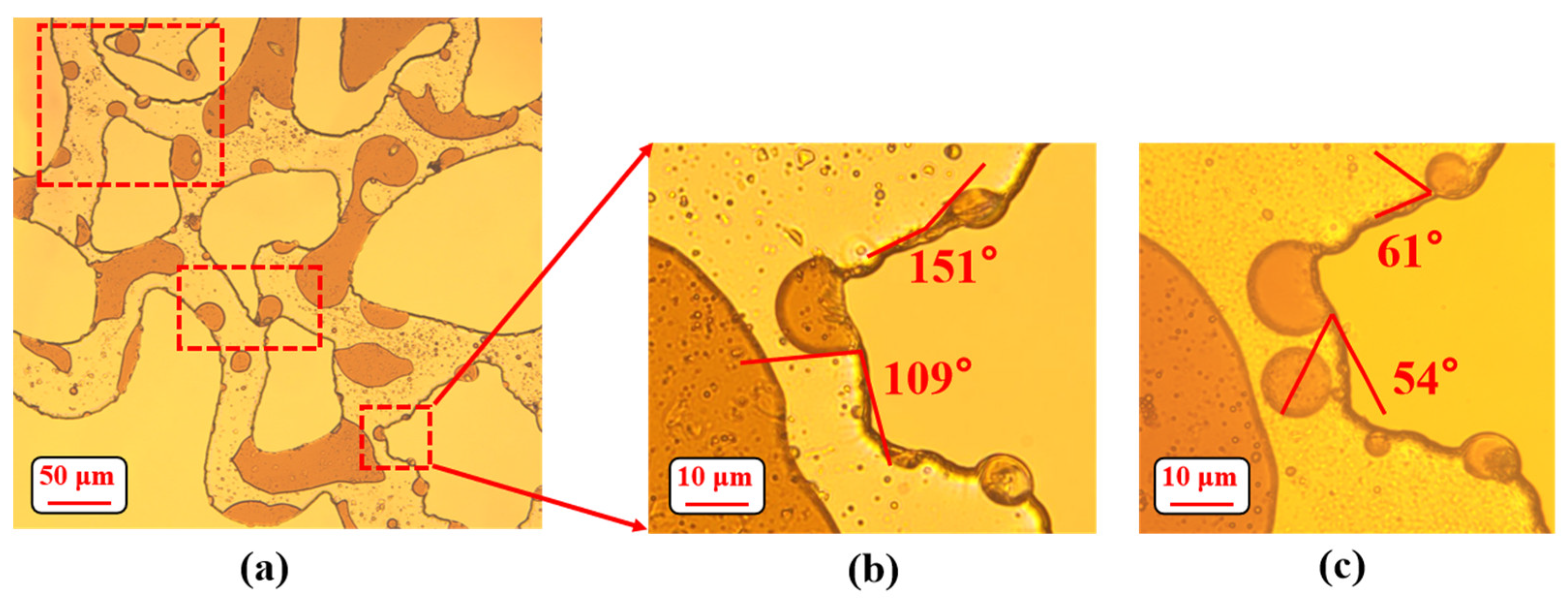



| Position | Proportion of Contact Angles Smaller than 90°/% | Increase/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 9 | ||
| Inlet | 8 | 98 | 90 |
| Center | 5 | 88 | 83 |
| Outlet | 3 | 80 | 77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Li, H.; Song, Z.; Zhu, W. Long-Term Pore-Scale Experiments on MEOR by Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms Reveal the Altering Dominant Mechanisms of Oil Recovery. Energies 2023, 16, 6854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196854
Yu X, Li H, Song Z, Zhu W. Long-Term Pore-Scale Experiments on MEOR by Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms Reveal the Altering Dominant Mechanisms of Oil Recovery. Energies. 2023; 16(19):6854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196854
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xiaoluan, Hua Li, Zhiyong Song, and Weiyao Zhu. 2023. "Long-Term Pore-Scale Experiments on MEOR by Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms Reveal the Altering Dominant Mechanisms of Oil Recovery" Energies 16, no. 19: 6854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196854
APA StyleYu, X., Li, H., Song, Z., & Zhu, W. (2023). Long-Term Pore-Scale Experiments on MEOR by Surfactant-Producing Microorganisms Reveal the Altering Dominant Mechanisms of Oil Recovery. Energies, 16(19), 6854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196854





