Abstract
The rapid growth of the wind energy industry has resulted in a significant increase in Wind Turbine Blade (WTB) waste, posing challenges for recycling due to the composite materials used in their construction. Several proposed techniques, including mechanical, thermal, and chemical processes, have been considered for wind-blade recycling, but determining the most effective approach remains a critical issue. This study presents the first comprehensive systematic review of available wind-blade recycling processes, evaluating their economic, technical, and environmental performance. Additionally, we consider the physical and mechanical properties of the recycled materials, which can aid in identifying potential markets for these materials. Among the various recycling technologies, microwave pyrolysis emerges as the most promising technique for recycling large quantities of WTB, despite some challenges and uncertainties surrounding its effectiveness and feasibility at an industrial scale. However, the optimal recycling technique for WTB will depend on multiple factors, including the blade material, the desired environmental impact, and the economic feasibility of the process. Based on this review, mechanical recycling appears to be more energy-efficient, while the fluidised bed recycling process demonstrates a lower primary energy demand, global warming potential, and power consumption. These findings provide valuable guidance for decision-makers in the wind energy industry to develop effective waste management strategies and plans for sustainable wind energy development. Addressing WTB waste and implementing efficient recycling techniques will be critical in mitigating environmental impacts and promoting sustainability in the renewable energy sector as the wind energy industry grows.
1. Introduction
The wind energy sector is experiencing a rapid evolution due to the global demand for a clean energy supply to combat climate change and the energy crisis [1]. In 2021, wind energy supplied 744 GW (7% of global electricity demand), while in Europe, it provided 437 TWh of electricity (15% of EU-27 + UK electricity demand) [2,3,4].
By 2050, wind power is expected to supply more than one-third of the world’s electricity demand [5], while in Europe, it is projected to cover 50% [2,3]. The European Union’s goal of elevating the proportion of renewable energy to 27% by 2030 and achieving a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, ranging from 80% to 95% by 2050, underscores the pivotal significance of wind energy in the forthcoming energy landscape.
The wind industry faces a complex challenge as the number of wind turbines that need to be decommissioned continues to increase. The expected lifetime of a wind turbine is 20–25 years, and there are growing opportunities for repowering, which involves replacing the old models/components with newer and more efficient ones [1,6,7,8,9].
Several studies have estimated the amount of waste generated by Wind Turbine Blades (WTB) to find alternative waste management strategies [1,10,11,12]. Liu and Barlow (2017) estimate that the end-of-life waste stream will generate 2.9 million tonnes in 2050, with 43 million tonnes of cumulative blade waste [10]. The regional distribution shows that China will be responsible for most of the waste (40%), followed by Europe (25%), the rest of the world (19%), and the USA (16%). However, Lichtenegger et al. (2020) [11] forecast 325,000 tonnes of WTB waste, while Liu and Barlow’s estimate amounts to 495,000 tonnes [10,11]. In Germany, WTB waste is projected to reach 67,000 tonnes by 2050. Cooperman et al. (2021) [12] predict an estimated cumulative waste quantity of 2.2 million tonnes by 2050 in the United States. This projection of accumulated waste is lower than that of Liu and Barlow (3.8 million tonnes) [12]. The US states that may collect the highest amount of EOL blade waste by 2050 are Texas, with over 450,000 tonnes, followed by New York, with approximately 200,000 tonnes. California and Iowa are the following US states with almost 150,000 tonnes. In Canada, the accumulated waste will be 275,000 tonnes in 2050 [1].
The significant increase in decommissioned WTBs emphasises the necessity to develop and implement efficient waste processing systems for a more sustainable supply chain [3,4,5]. Recycling these blades lowers greenhouse gas emissions and reduces the energy costs associated with producing new fibres [1,2]. Nevertheless, recycling WTBs poses a formidable challenge due to their complex composite structure comprising multiple materials, resulting in a more intricate and demanding recycling process [2,4,5].
Wind turbine blades are composed of various materials, including reinforcement fibres (primarily glass and carbon fibres), a polymer matrix (consisting of thermosetting resins like epoxies and polyurethanes), a sandwich core (often made from materials like balsa wood or foams, including polyvinyl chloride), structural adhesives (such as epoxies and polyurethanes), coatings (like polyester and polyurethane), and specific metal components for lightning protection and structural support [4,5]. These blades typically consist of approximately 60–65% reinforcement fibres and 30–35% polymer matrices by weight, making up most of their weight, and reaching up to 90% of the total blade weight [7]. The core materials contribute around 4–5%, and the combined percentage of adhesives and additional materials typically remains under 5% [7].
The disposal of wind turbines offers various alternatives, which include landfilling, incineration, and recycling [1,4,5]. Landfilling is the most economically efficient option, although it does have significant environmental repercussions [1]. This is primarily due to the materials employed in their construction, which are non-biodegradable and, therefore, unable to degrade naturally [6,13]. As a result, incineration could be more environmentally friendly and economically viable for recycling. Consequently, current research is concentrated on developing innovative recycling technologies and processes specifically tailored to wind turbine blades to address the challenges associated with their disposal more sustainably [1,6,13]. At present, there exist three fundamental methodologies for the recycling of composite waste, namely mechanical recycling [14,15,16,17,18], thermal recycling involving pyrolysis [18,19,20], microwave pyrolysis [21,22], gasification fluidised beds [23,24,25,26,27], and chemical recycling utilising the solvolysis process [28,29,30,31,32,33]. The best recycling technique in terms of the physical and mechanical properties of the recycled compounds, operational costs, and energy consumption needs to be identified. These authors’ work presents the first systematic review of quantitative data on all available wind-blade recycling processes, evaluating the performance of the recycled material on an economic, technical, and environmental level. The outcome of this review can guide future research in this field and help decision-makers plan wind energy development and waste management strategies to make the most of the waste generated.
2. Methodology
A thorough examination of the existing literature was done by leveraging primary international interdisciplinary research support platforms such as Science Direct, Scopus, and Web of Science. The search was performed using a combination of the following keywords: “End-of-life”, “WTB”, “mechanical recycling”, “thermal recycling”, “chemical recycling”, and “experimental”. The review followed a “semi-systematic” approach, as proposed by [14,34].
While this review focuses on recycling EOL WTBs, other sectors, besides the energy sector, utilise thermosetting polymeric matrices and reinforced fibres to improve product performance. Due to similar conclusions, some studies on thermoset waste from these other sectors will be mentioned. These studies will add to the evaluation and discussion of recycled material properties, specifically the mechanical and physical properties, and help identify target markets for this material. An in-depth analysis of these studies will also identify potential solutions for the recycling process of EOL WTBs.
The review encompasses literature published in the past decade, containing a total of 77 research articles that were carefully examined, along with the inclusion of 35 case studies that met the criteria mentioned earlier. Figure 1 presents a detailed analysis based on the literature, focusing on the three fundamental methodologies for recycling composite waste and their applications for the recovered materials. The article is divided into six sections, which include (1) the methodology, (2) recycling technologies of EOL blades, (3) applications of recovered materials, (4) environmental and economic impact, and (5) the study’s main conclusions.
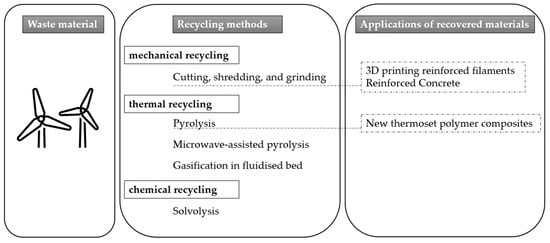
Figure 1.
Comprehensive analysis of recycling methodologies for composite waste and their applications for recovered materials.
3. Recycling of EOL Blades
The recycling of composite materials, particularly WTBs, poses significant challenges due to their intricate structure and diverse components. These materials comprise various fibres and polymer matrices and are used in multiple applications, making the recycling process complex and demanding. Consequently, developing effective recycling techniques for composite materials is an ongoing effort.
So far, three recycling techniques for thermosetting polymer composites are available, broadly categorised into thermal, chemical, and mechanical processes. Each method offers unique approaches for the EOL composites of WTBs.
Currently, three techniques are applied to recycle EOL WTBs. These techniques fall into mechanical, thermal, and chemical processes, each offering distinct approaches to the recycling challenge. Thermal recycling techniques encompass pyrolysis, microwave pyrolysis, and fluidised bed gasification. On the other hand, chemical recycling involves solvolysis. Mechanical recycling is the most extensively studied technique, employing cutting, crushing, and grinding methods to convert the material into a coarse mixture [13,15,19].
In the following subsections, we will delve into several case studies on WTB recycling, highlighting the available recycling techniques and their potential for sustainable waste management.
3.1. Cutting, Shredding, and Grinding
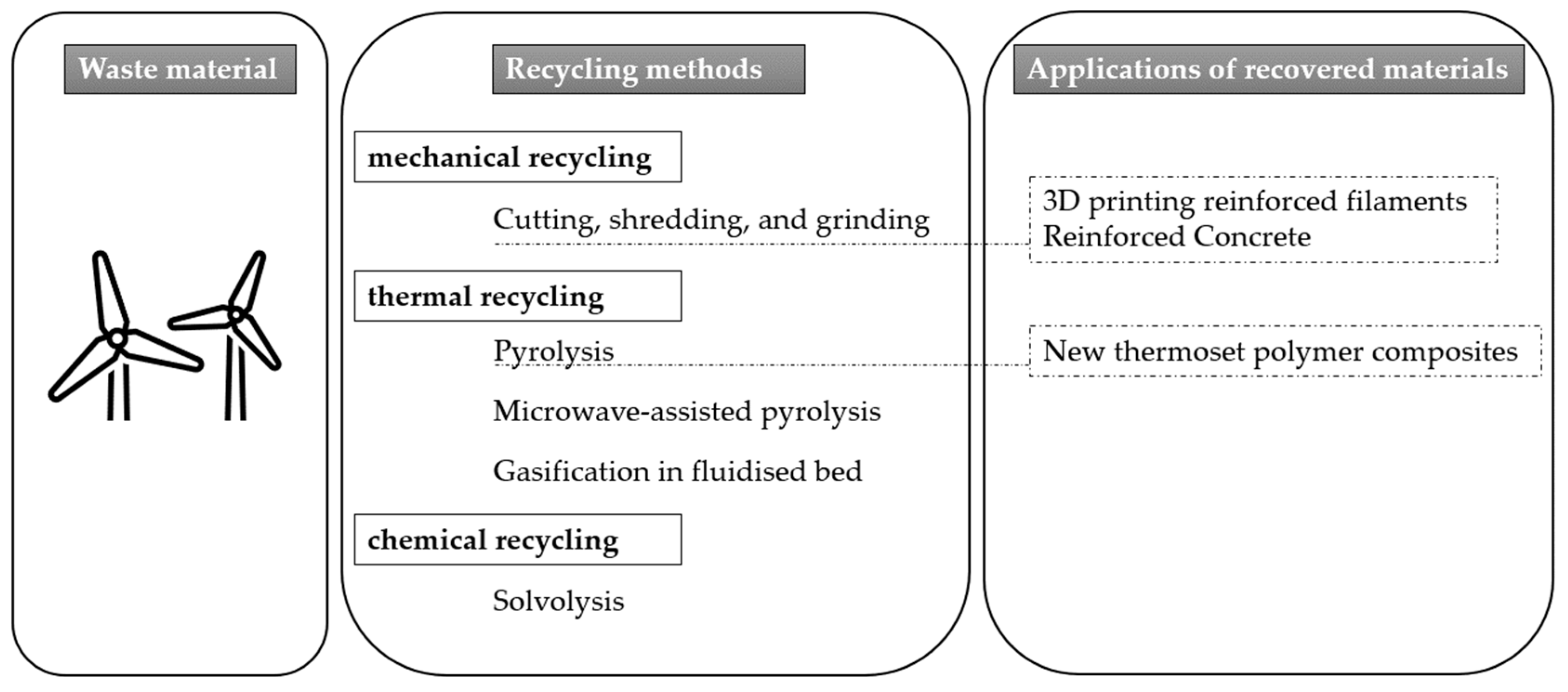
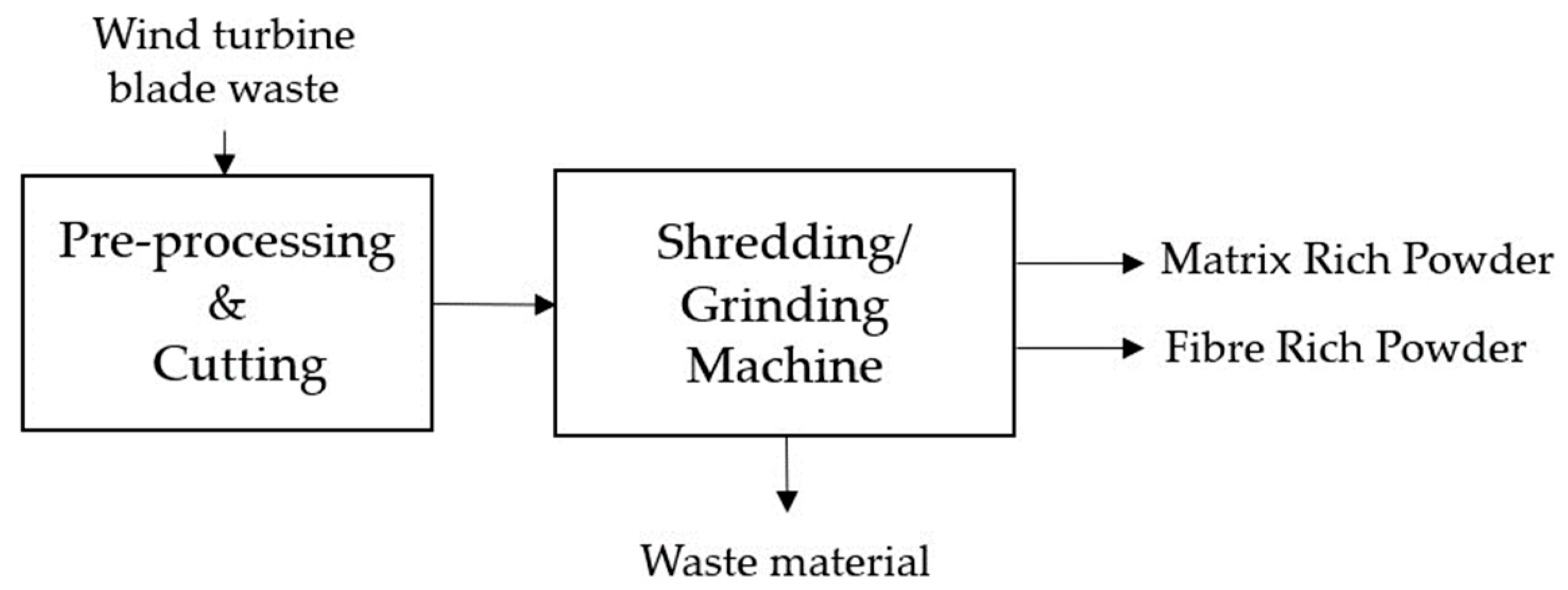
Mechanical recycling is a vital aspect of sustainable WTB management, involving size reduction to create granulate-like materials suitable for various applications [15]. This approach utilises cutting, shredding, and grinding techniques to break down the composite materials of the blades [19]. Cutting utilises sharp tools to divide the material into smaller pieces precisely. Shredding involves using mechanical equipment, like shredders, to tear the fabric into smaller fragments. Conversely, grinding reduces the materials into fine particles or powder through friction with abrasive surfaces. In Figure 2, a comprehensive diagram is presented, providing a detailed illustration of the mechanical pyrolysis-based recycling process designed for EOL WTBs.
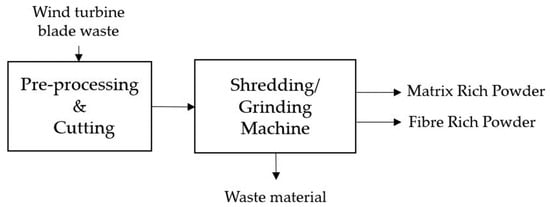
Figure 2.
Diagram illustrating mechanical pyrolysis-based recycling process for end-of-life wind turbine blades.
One of the critical advantages of mechanical recycling lies in the homogeneity of the granulate-like materials produced, making them suitable for reuse as fillers or reinforcements in new polymer composite materials or concrete applications [15]. However, the mechanical recycling of WTBs does face challenges, as the cut, shredded, and ground composite materials may not significantly enhance the mechanical properties of the resulting composites [13,16,20].
Despite its advantages, mechanical recycling also has some limitations. The process involves multiple steps, potentially leading to increased operational costs in transforming the EOL WTBs into granulates. Additionally, dust generation during mechanical recycling can pose health hazards to workers [17,19].
Mechanical recycling is crucial in various recycling techniques, including those used for recycling WTBs. In this initial phase, cutting and/or shredding the blades occurs before implementing thermal and chemical processes. Furthermore, researchers have explored the materials from cutting, shredding, and grinding to develop innovative materials.
For instance, recycling shredded composites can produce new polymer composites, utilising high-quality glass fibres and reducing reliance on virgin materials [13,18,35,36]. Moreover, the shredded composites can replace synthetic macro fibres in concrete, improving its tensile strength and crack resistance [37,38,39]. Additionally, the composites can produce fused filaments for 3D-printed parts, resulting in increased structural performance [40,41]. These studies on the reuse of WTBs at the end of their useful life through the development of innovative materials will be presented in detail in Section 4.
3.2. Pyrolysis
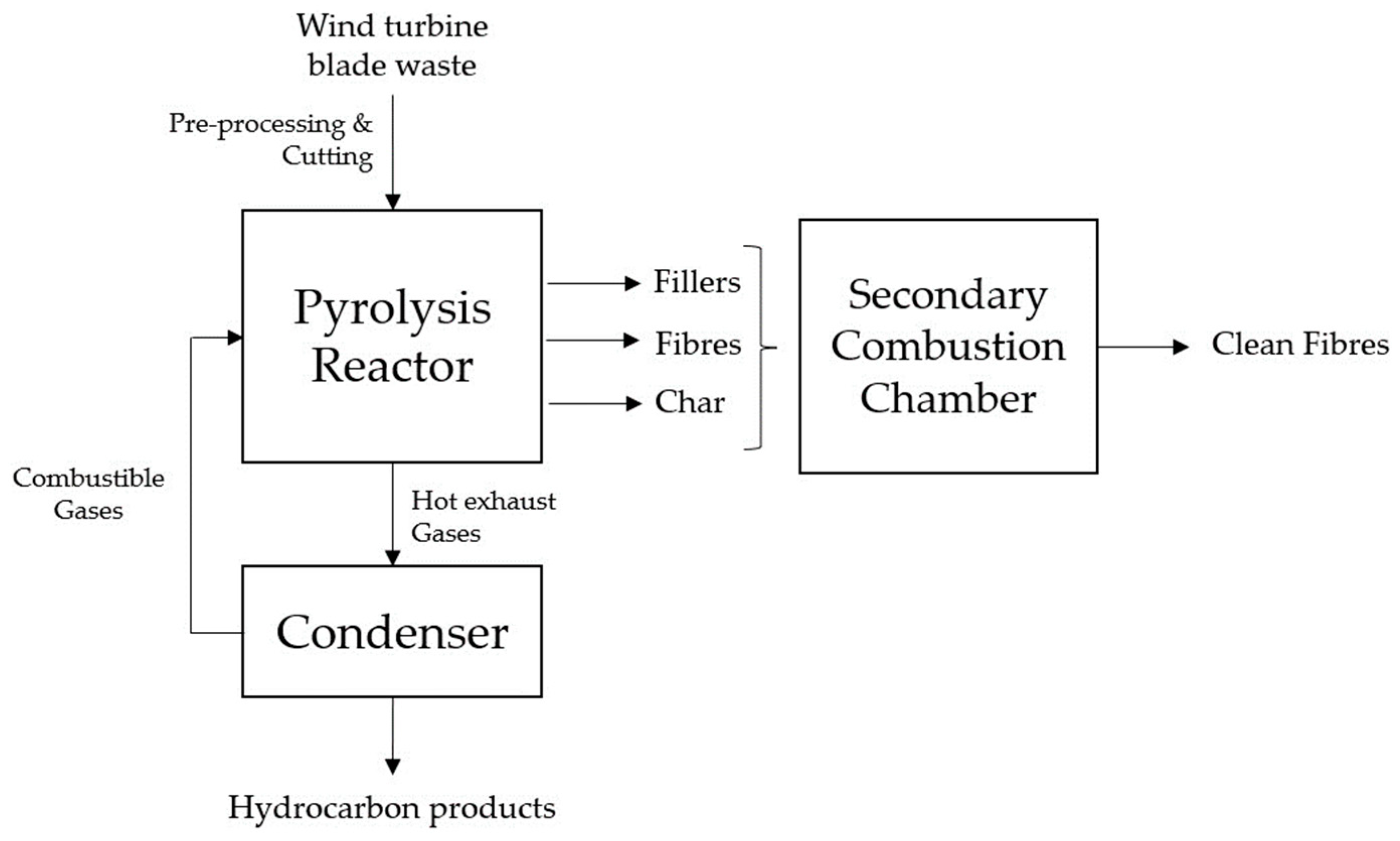
Pyrolysis is a recycling technique employed for wind turbine blade waste, involving the application of high temperatures in the absence of oxygen [18,19,21]. This thermal treatment induces the disintegration of the materials into gas, liquid, and solid forms. The blade constituents, such as epoxy resin, thermoplastic polyurethane, carbon fibre, and glass fibre, can be effectively broken down. Consequently, valuable substances like phenol and p-isopropenylphenol can be recovered from liquid products [42]. Furthermore, pyrolysis eliminates the resin matrix while maintaining the integrity of the fibre materials. Figure 3 presents a comprehensive diagram, providing a detailed illustration of the pyrolysis-based recycling process designed for EOL WTBs. Hence, recycling WTBs is a significant approach [22,42,43,44,45]. Furthermore, one of the advantages of pyrolysis is its potential for large-scale application in material recovery [42].
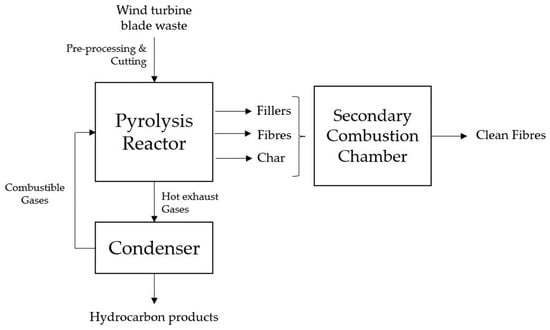
Figure 3.
Diagram illustrating the pyrolysis-based recycling process for end-of-life wind turbine blades.
However, the high temperatures involved in pyrolysis can damage the fibre surfaces and reduce its mechanical properties [43]. The operating temperature range for typical polymeric pyrolysis processes varies between 400 and 700 °C depending on the nature of the thermoset composite. This temperature range effectively breaks down the polymer matrix and recovers the fibre [42,43,44,45]. In some studies, the gases evolved during pyrolysis have been used as fuel to provide heat, thereby increasing energy efficiency [45,46].
Recent developments in pyrolysis processes have focused on using controlled atmospheric conditions to optimise the recovery of fibres. Nitrogen is chosen in the pyrolysis of wind turbine blades because it plays a crucial role in eliminating oxygen, which can cause thermal oxidation [43,47]. Oxygen dissolution in metallic matrices can lead to embrittlement, and nitrogen is a secondary oxidant that dissolves in and embrittles the alloy [34,40]. Nitrogen is pivotal in the forming of oxynitride and nitride interfacial layers, effectively serving as a robust diffusion barrier against oxygen infiltration. This exceptional barrier capability arises from nitrogen’s limited solubility [48].
Moreover, nitrogen fosters the development of a nitrogen-enriched solid solution, intensifying its efficacy in preventing oxygen diffusion [48]. By reducing the oxygen concentration, nitrogen helps prevent the cracking of epoxy resins and the accumulation of uncracked resins and pyrolysis char, which can degrade the mechanical properties of the recovered fibres [49]. Therefore, nitrogen is chosen to eliminate oxygen and mitigate thermal oxidation in pyrolysis [47]. Using such controlled atmospheric conditions aims to increase the yield of the desired products (hydrocarbons and ash) and improve the quality of the recovered fibres [44,45,50,51].
A fixed-bed reactor typically consists of a tubular reactor and an external heater. The processing temperature plays a critical role in the decomposition of the polymer matrix during the pyrolysis process for fibre recovery. Different temperature ranges impact polymer matrix decomposition and fibre recovery in pyrolysis for wind turbine blades. The pyrolysis process involves heating the blades from 300 to 600 °C [1,44,45] to decompose the matrix and recover high-quality fibres effectively [44,45].
The thermal degradation and pyrolysis kinetic behaviour of glass fibre-reinforced thermoplastic composites have been studied using TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS techniques, revealing the presence of volatile compounds and the activation energy for the pyrolysis process [47]. Yang et al. (2015) [51] observed that the impact of temperature on the mass loss rate in carbon fibre-reinforced polymer (CFRP) became less pronounced in an air environment, while the tensile strength exhibited a rapid decline. Furthermore, the tensile modulus showed minimal variations as the oxygen concentration increased from 5% to 10%. With an increase in temperature, the material’s tensile modulus experienced a slight reduction, but the reduction became significant as time progressed [45]. Ginder and Ozcan (2019) [50] employed a two-temperature step pyrolysis method for the reclamation of E-glass fibres, contrasting it with a single high-temperature step pyrolysis approach. Using a multistep process resulted in a noteworthy enhancement in the tensile strength of the recovered E-glass fibres, with improvements of up to 19%, and a significant increase in strain to failure, reaching as much as 43%. Nevertheless, initial measurements of the fibres before pyrolysis revealed that pre-existing damage might limit the quality of glass fibres obtained through pyrolysis unless further post-processing steps are applied [50].
Other variables significantly impacting the operation are the oxygen concentration in nitrogen and reaction time during thermal decomposition in fixed-bed reactors. Yang et al. (2015) [51] investigated the impact of oxygen concentration and reaction time during thermal decomposition in fixed-bed reactors on the operation and properties of recycled carbon fibres. Increasing the oxygen concentration up to 20% led to a levelling off tensile strength (at 2890 MPa) and a decrease in tensile modulus (at 191 GPa), with oxygen concentration being a significant factor in determining oxygen content on the surface of the carbon fibres [45]. As the oxygen concentration increased, there was a noticeable decrease in the weight residue, primarily attributed to the oxidation of pyrolytic carbon and carbon fibres. Furthermore, the mass loss of carbon fibres exhibited a linear correlation with extended oxidative durations, with a pronounced preference for the oxidation of carbon fibres characterised by low graphitisation degrees or surface imperfections. It is worth noting that the mass loss rate was more pronounced at elevated temperatures and higher oxygen concentrations. The dominant factor influencing the process changed from temperature to oxygen concentration when the composites were decomposed in air, with this transition occurring at an oxygen concentration between 10% and 20% [45]. The residue at 550 °C was close to the fibre content in the composites (47.4 wt%), and a higher mass loss rate was observed at 600 °C in the air compared to 650 °C with 5% or 10% oxygen concentration [45].
A recent study by Smolen et al. [43] demonstrated the potential of using recycled carbon fibres from EOL WTBs in high-strength composite applications. The study found that pyrolysis was an effective technique for recovering carbon fibres from WTBs. The process was carried out at 500–600 °C in a non-oxidising atmosphere, preserving the shape and dimensions of the fibres [44]. The recycled carbon fibres obtained through pyrolysis had only 2% of the matrix material remaining on the fibre surface and a tensile strength approximately 20% lower than that of new carbon fibres. However, composite panels made using recycled carbon fibres showed no significant differences in mechanical properties compared to those made using new ones [44].
Composite panels using pyrolytic fibres demonstrated up to 35% higher flexural strength than those with new carbon fibres. Overall, the study highlights the potential of pyrolysis as an effective technique for recovering carbon fibres and demonstrates the practical use of these fibres in high-strength composite applications [44].
Table 1 presents a summary of the tensile properties of composites resulting from the pyrolysis of WTBs alongside virgin and original carbon fibres, utilizing fixed-bed reactors. The essential mechanical properties under consideration include the tensile strength, Young’s modulus, and the elongation at break. To enhance clarity, the data is organized in ascending order of tensile strength. Tensile strength is a critical indicator of the quality of fibres recovered through the recycling processes presented. It signifies how well the fibres retain their structural strength after recycling. High tensile strength is desirable as the recycled fibres can still be used in applications requiring substantial strength. Fibres with high tensile strength contribute significantly to the strength and durability of the final products. Moreover, fibres with good tensile strength can replace virgin fibres in many applications, conserving resources and reducing overall production costs.

Table 1.
Summary of tensile properties of virgin and fibres recovered using fixed-bed reactors for glass fibre-reinforced polymer (GFRP) and CFRP.
The data suggest that the tensile properties of composites obtained from the pyrolysis of WTBs are generally lower than those of virgin and original carbon fibres. Therefore, optimising the pyrolysis conditions could produce composites with improved mechanical properties. The tensile strength of virgin fibres after size removal was 2.71 GPa, and the tensile strength of original carbon fibres was 2.27 GPa and 1.84 GPa for pyrolyzed and carbon fibres, respectively. However, it is essential to recognise that the properties of fibres recovered were notably influenced by the diverse pyrolysis conditions applied across different studies. For instance, the tensile strength of pyrolyzed carbon fibres exhibited a range spanning from 1.80 GPa to 2.60 GPa. The outcome of this mechanical property hinged on variables such as the pyrolysis temperature, atmospheric conditions, and duration. Similarly, the Young’s modulus values for pyrolyzed carbon fibres displayed a wide spectrum, spanning from 154.8 GPa to 220.4 GPa, further emphasising the sensitivity of material properties to the intricacies of the pyrolysis process. The elongation at break ranged from 0.46% to 1.30%, emphasising the importance of precise control over pyrolysis parameters for achieving the desired mechanical characteristics in the fibres recovered.
3.3. Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis
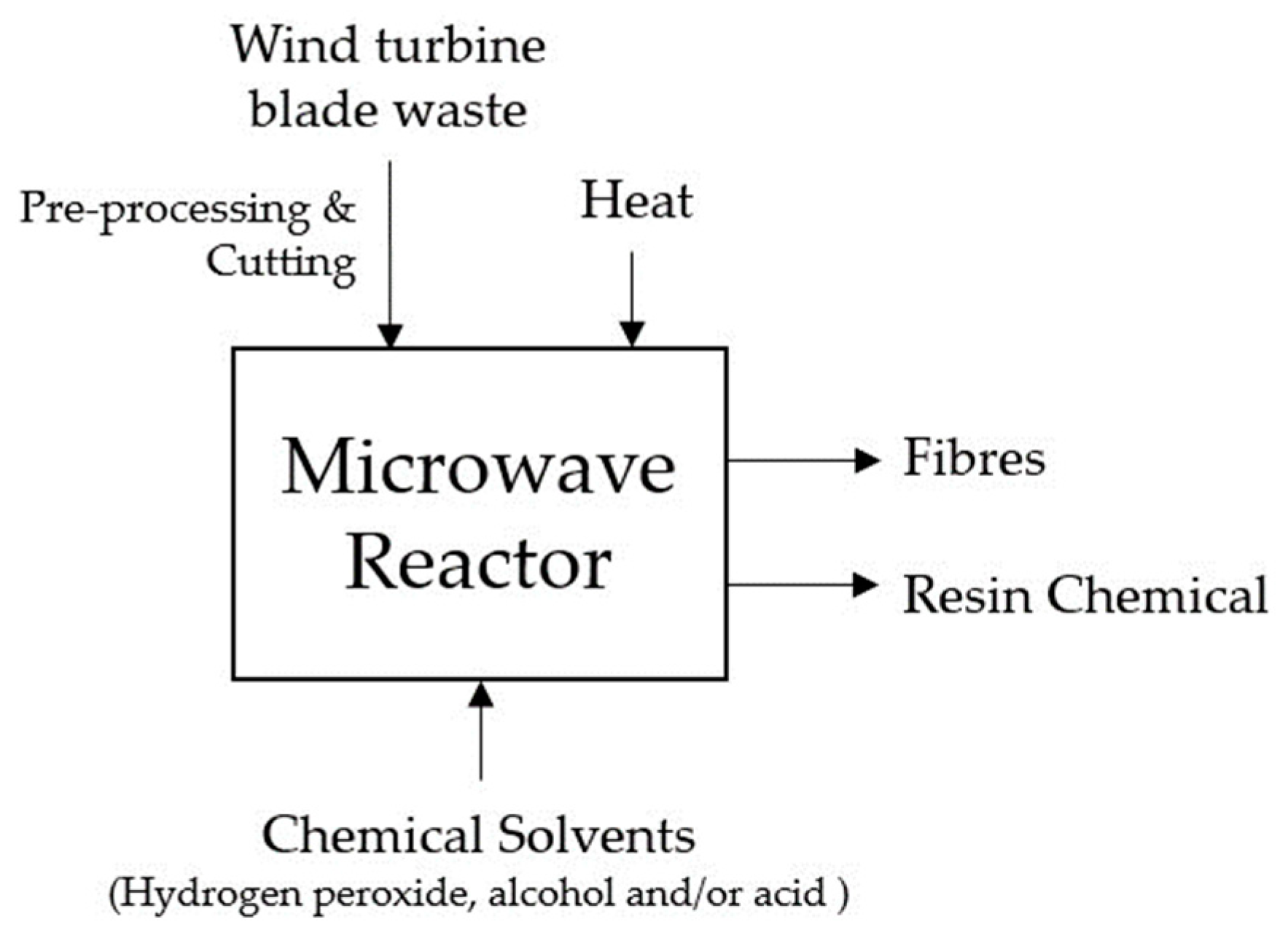
Microwave-assisted pyrolysis is an effective and promising technique for recycling composite materials. Studies have reported high recovery rates of reinforcing fibres with minimal damage to the fibres, indicating that this technique can retain the mechanical properties of the fibres recovered [21,52]. Microwave heating allows the bulk of the material to be heated evenly, which is particularly advantageous for polymers with low thermal conductivity. Furthermore, the resulting moderate temperatures are beneficial as glass fibres will not degrade thermally. Figure 4 presents a detailed diagram, offering a comprehensive illustration of the microwave-assisted pyrolysis recycling process designed explicitly for EOL WTBs.
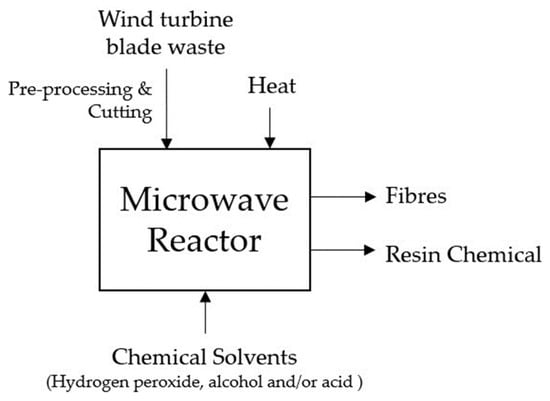
Figure 4.
Diagram illustrating the microwave-assisted pyrolysis recycling process for end-of-life wind turbine blades.
More recently, a new approach has been introduced using microwave-assisted chemical recycling with hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, and acetic acid, CH3COOH [52]. The method accomplished almost total epoxy disintegration, exhibiting a decomposition rate reaching 97.2%. The recovered glass fibres (RGF) retained 99.8% ultimate tensile strength, 93.3% Young’s modulus, and 95.7% strain-to-failure compared to virgin glass fibres (vGF) [52]. The investigation also put forward a conceivable process for the deterioration of the substance composing the matrix [52].
Ren et al. introduce a new approach for efficiently recovering carbon fibres from CFRP through microwave pyrolysis and oxidation [22]. This technique differs from the approach used by Rani et al., which utilised hydrogen peroxide and acetic acid to degrade GFRP composites for chemical recycling [52]. In the technique proposed by Ren et al. [22], the CFRPs are subjected to the rapid pyrolysis of the resin matrix using microwave radiation, followed by oxidation to remove the residual carbon and organic matter on the surface of carbon fibres. The authors achieved a high recovery rate of 96.5% for carbon fibres using microwave pyrolysis and oxidation, with a maximum tensile strength of the recycled carbon fibres at 99.42% compared to virgin carbon fibres with a tensile modulus of 239.39 GPa [22]. Additionally, the microstructure and chemical composition of the recycled carbon fibres were characterised, indicating that the technique effectively recovered high-quality carbon fibres from CFRPs.
Table 2 provides an overview of the tensile properties of both virgin and recycled fibres, which were obtained through microwave-assisted pyrolysis, along with the respective study that documented these findings. The properties under examination encompass the tensile strength, Young’s modulus, and the elongation at break. To enhance readability, the data is organized in ascending order of tensile strength.

Table 2.
Tensile properties of virgin and recycled carbon fibres using microwave-assisted pyrolysis. The data presented is organised in ascending order of tensile strength.
The study by Rani et al. (2022) reports the highest tensile strength of 3.03 GPa for virgin wool, but the elongation at break is relatively low compared to the other specimens [52]. The properties of the recycled carbon fibres from CFRP samples show variation depending on the temperature and duration of the microwave-assisted pyrolysis. The effect of H2O2 concentration on the properties of the fibres recovered is not straightforward and can be complex. Increasing the H2O2 concentration sometimes increases all three properties (tensile strength, Young’s Modulus, and elongation at break). In other cases, the properties start to decrease beyond a specific concentration. This suggests that the optimal H2O2 concentration may depend on the recycled carbon fibre and the processing conditions used.
Further research is needed to better understand the complex relationship between the H2O2 concentration and the mechanical properties of recycled carbon fibres. The study by Ren et al. reports a high Young’s Modulus of 240 GPa for virgin wool, but the elongation at break is not registered [22]. Overall, microwave-assisted pyrolysis can be a promising technique for recycling carbon fibres. However, further research is needed to optimise the process’s parameters and understand the effects of recycling on other mechanical properties, particularly for glass fibres.
3.4. Gasification in Fluidised Bed
Fluidised bed gasification is a promising solution for recycling EOL WTBs. This process offers many advantages, including scalability, operational continuity, and contaminant tolerance, making it an attractive option for various industries. These blades can be recycled using fluidised bed gasification, reducing waste sent to landfills and contributing to a circular economy.
In this process, shredded scrap composite is introduced into a bed of silica sand, which is then fluidised by hot air. The process involves thermally degrading the polymer matrix and liberating the reinforcement fibres, which can be collected for reuse.
The resulting gases produced from the thermal degradation of the polymer matrix are combusted with air to generate heat, which is then used to sustain the fluidised bed process. However, as the fluidised bed operates at a low temperature (450–500 °C), complete combustion of the organic constituents in the feed is not achieved [23,24,25,26]. Addressing this challenge mandates the deployment of a secondary combustion chamber capable of operating at an elevated temperature of 1000 °C, as stipulated in reference [25]. This chamber is a highly efficient means to oxidize residual organic compounds, guaranteeing comprehensive air purification.
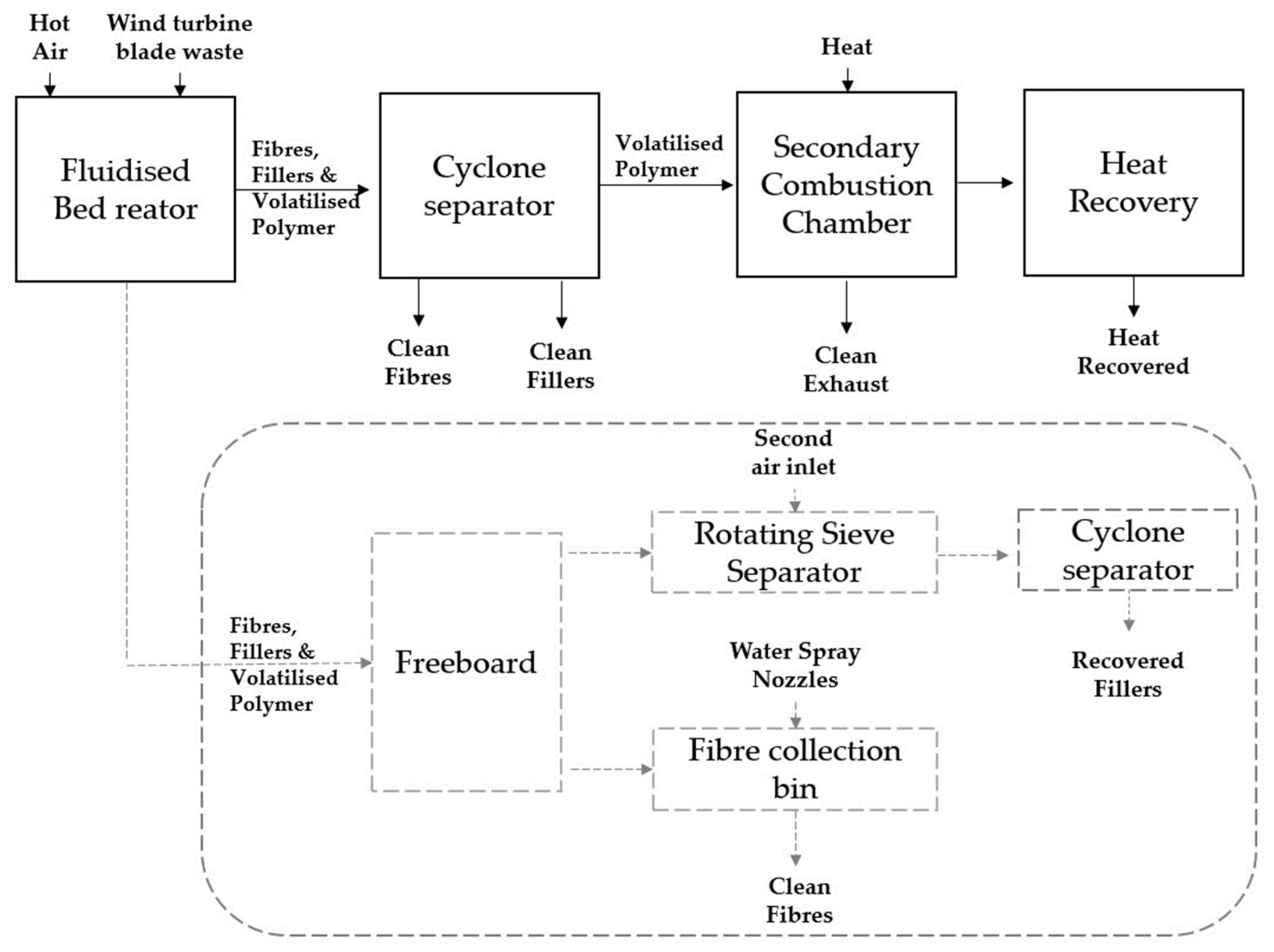
To separate the fibres and fillers from the fluidising air, a modified process proposed by Pickering et al. [27] incorporates a rotary sieve separator that removes long fibres from the fluidising air, allowing fillers and short fibres to pass through. These are then removed from the fluidising air using a cyclone. A counter-current cold air flow removes the trapped fibres from the sieve mesh. The fibres collected in the fibre collection bin are purified through a nylon mesh and continuously washed with a circulating aqueous spray [27]. In Figure 5, a comprehensive diagram is presented, providing a detailed illustration of the gasification process within the fluidized bed recycling method explicitly designed for end-of-life wind turbine blades.
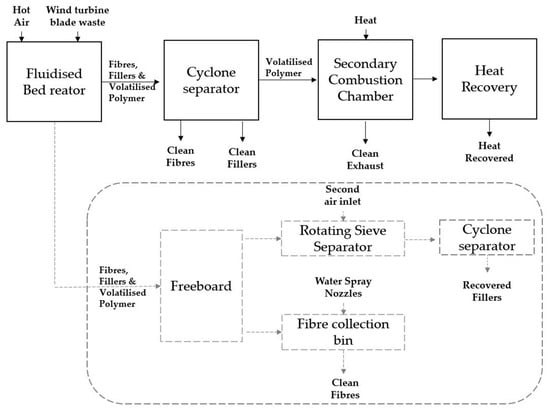
Figure 5.
Diagram illustrating the gasification in the fluidised bed recycling process for end-of-life wind turbine blades.
Various research inquiries have explored the fluidized bed procedure to restore the durability and surface efficacy of reused glass fibres extracted from decommissioned WTBs [24,53,54]. However, during the recycling process in the fluidised bed, the glass fibres are subjected to thermal degradation, which weakens their strength and reduces their quality. The extent of thermal degradation and the resulting loss in strength depend on the exposure time, temperature, and other process parameters. Therefore, it is essential to carefully control the exposure time to minimise the loss in fibre strength and quality.
Studies have demonstrated that fibres recovered within the fluidized bed experience a notable deterioration in strength, rendering them unsuitable for applications in high-strength constituents [24,25,26,54]. The reduction in fibre diameter intensifies as the treatment duration progresses, as Yang et al. observed in their investigation of the etching of glass fibres with hydrofluoric acid. Their findings revealed an inversely proportional correlation between the fibre reduction rate and treatment duration [45]. The extent of thermal degradation and the resulting loss in fibre strength and quality depends on the exposure time and recycling temperature. Higher temperatures can result in more significant thermal degradation and a greater loss of fibre strength, affecting the ability to regenerate the fibres to their original strength. For example, Pickering et al. (2000) [45] reported that the tensile strength of recycled glass fibres could range from 50% to 90% of the original fibre strength, depending on the temperature of the recycling process. However, the enhancement of the strength retention of the fibres in the fluidised bed is not observed with the decrease in the temperature required for epoxy decomposition (Thomason et al., 2016). Pender and Yang (2019) [23] recognise that the tensile strength of glass fibres obtained from fluidised bed recycling is significantly influenced by the recycling temperature, as reported in previous investigations [42,45,46,48]. Nevertheless, Pender and Yang (2019) [23] also propose that reducing the necessary recycling temperature does not augment the fibre strength retention in the fluidised bed process. Furthermore, the authors acknowledge that the loss of strength in the fibres recovered within fluidised bed systems is primarily attributed to mechanical damage during the recycling procedure rather than solely to the thermal deterioration caused by the elevated temperatures.
The restoration of strength in recycled glass fibres can be achieved through various treatments, including chemical techniques such as soaking in hot sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solutions (Pender and Yang (2020) [22]; Thomason et al. (2016) [54]). Some studies by Pender and Yang (2020) [22] and Thomason et al. (2016) [47] have shown that hot NaOH treatments can effectively restore the strength of recycled glass fibres. Pender and Yang (2020) [22] found that soaking the fibres for 120 min in 7 mol/L of NaOH increased their tensile strength by 130%. Similarly, Thomason et al. (2016) [47] reported that the hot NaOH treatment can increase the strength of thermally conditioned glass fibres by more than triple (up to 75%).
Pender and Yang (2020) [22] highlighted that, despite regeneration attempts, the fibres’ strength continues to be subpar compared to the original strength levels. Conversely, Thomason et al. (2016) [54] proposed that further enhancement of the chemical treatments could open the door for these fibres to replace the new, initial fibre products commonly employed in various applications involving glass fibre-reinforced composites that are not continuous. Moreover, Thomason et al. (2016) [54] also discovered that the average strength of fibres in chopped glass products available on the market can be as low as 1.5 GPa when measured at a 2 mm gauge length. This measurement notably falls below the regenerated strength of 1.4 GPa at a 20 mm gauge length, as reported by Pender and Yang (2020) [22]. Moreover, Thomason et al. (2016) [54] made a significant finding indicating that applying a silane coupling agent after the NaOH treatment considerably improved the restoration of strength in recycled glass fibres. As a result, polypropylene reinforced with glass fibres achieved an impressive 74% recuperation of tensile strength. This can be contrasted with the thermal fibres recovered that underwent no additional treatment. Pender and Yang (2020) [22] proposed that a product layer is formed on the surface during this reaction, comprising mainly sodium silicates, which are then rapidly diffused through the corrosive NaOH solution. It is noteworthy that treatments with higher concentrations of NaOH tended to eliminate the surface of the glass fibres more expeditiously, which can be attributed to the heightened density of hydroxide associated with higher concentrations of NaOH.
On the other hand, it is worth noting that including metal catalysts, such as CuO, within the epoxy matrix can significantly impact the mechanical characteristics of glass fibre-epoxy composites. This observation was made by Pender and Yang (2019) [23], who conducted a study and found that, unlike homogeneous alkali catalysts, metal catalysts have the potential to decrease the strain at which the epoxy ultimately fractures, thereby signalling an enhanced brittleness within the epoxy system. During their experiments, Pender and Yang (2019) [23] discovered that adding 5 wt% loadings of CuO did not result in any noticeable alterations in the tensile properties of glass fibre-reinforced epoxy. However, it is essential to highlight that the researchers were keen to stress that the complete impact of CuO on the brittleness of the epoxy is yet to be fully comprehended within the broader context of the overall tensile properties of glass fibre-reinforced epoxy. Furthermore, there remains a need to ascertain the influence of CuO on properties predominantly governed by the matrix, such as interlaminar shear strength.
Consequently, further investigations must be conducted to understand the potential ramifications of metal catalysts on the mechanical properties of glass fibre–epoxy composites [24]. The results indicate that fluidised bed technology can offer a feasible solution for recycling composite materials. However, it is crucial to exercise cautious control over the process’s parameters to minimise any potential loss in strength and maintain the quality of the recycled materials. Table 3 offers a succinct overview of the primary findings from the study, focusing on recycled glass fibres sourced from internally prepared composites (GFRE) and GFRPs. To enhance clarity, the data is systematically organized in ascending order of tensile strength.

Table 3.
Summarises the tensile strength, fibre diameter, and diameter reduction of fibres that were recycled using fluidised bed technology.
The data shows that the tensile strength of fibres recovered varies from 0.03 to 3.89 GPa, and the diameter reduction ranges from 0% to 35%. Moreover, some experiments involve treatments with NaOH and APS, which resulted in an increased tensile strength and a decreased diameter reduction. Overall, the study highlights the potential of fluidised bed technology for recycling composite materials, but further research is needed to optimise the process parameters and evaluate the mechanical properties of the recycled materials.
The most notable observation is the substantial variability of tensile strength across the examined specimens, ranging from a minimal 0.0 GPa to an impressive 3.9 GPa. This extensive range underscores the critical role of specific treatment conditions and variables in shaping the success of the recycling process. Parameters such as temperature, treatment duration, and the presence of additional agents are pivotal in determining the resulting tensile strength of the fibres recovered. This variability underscores the need for precision and meticulous control in recycling to attain the desired tensile strength outcomes.
Additionally, specific entries in the table provide valuable data on fibre diameter, spanning from 7.07 µm to 17 µm. The significance of this information lies in its potential to influence the mechanical properties and applications of the fibres recovered. The fibre diameter is a pivotal parameter affecting flexibility, tensile strength, and overall application performance. A comprehensive grasp of these diameter variations aids in assessing the suitability of the fibres recovered for specific intended uses.
Moreover, when available, diameter reduction percentages are meticulously documented, shedding light on changes in fibre diameter due to the recycling process. Reduction percentages fluctuate from 0% to as high as 35%, offering crucial insights into how the recycling process transforms the physical dimensions of the fibres. This data assumes paramount significance as it vividly illustrates how the recycling process reshapes the fibre structure, potentially influencing its mechanical properties and performance across diverse applications.
The discernible presence of varying NaOH (sodium hydroxide) concentrations within the treatment conditions showcased in the table implies that fluctuations in treatment chemistry can substantially impact both tensile strength and diameter reduction. The selection of a NaOH concentration, alongside other treatment parameters, emerges as a pivotal factor that can be fine-tuned to optimize the recycling process tailored explicitly to diverse materials and applications.
The studies underscore the promising potential of fluidized bed technology for recycling composite materials while emphasizing the need for further research and development efforts to refine the process parameters. These ongoing endeavours are poised to optimize the recycling process and facilitate a comprehensive assessment of the mechanical properties and overall quality of the recycled materials. Such achievements are instrumental in advancing the sustainability and efficacy of composite material recycling, contributing significantly to environmental conservation and resource utilization.
3.5. Solvolysis
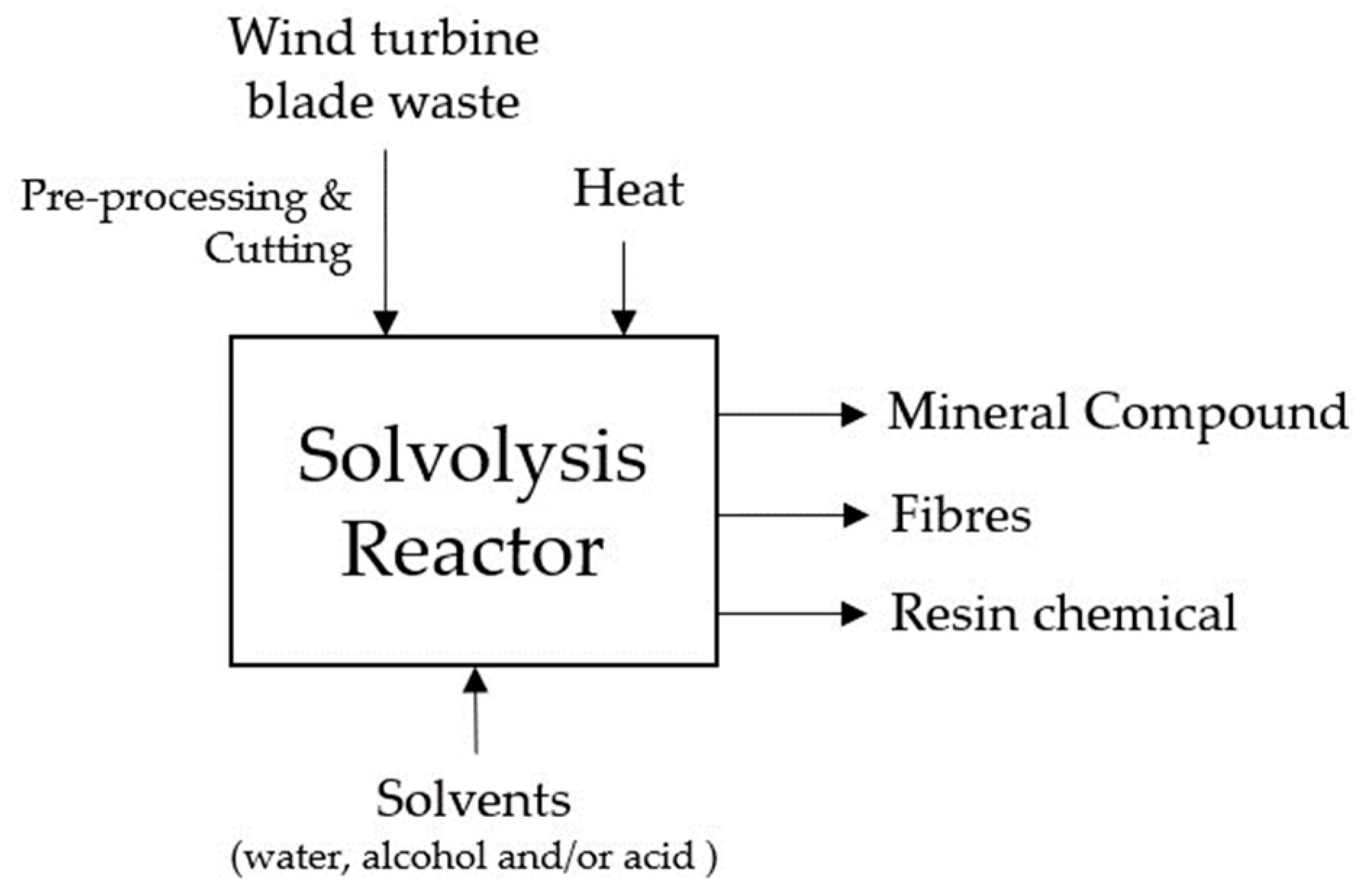
Solvolysis, an intriguing chemical treatment process, utilises a combination of water, alcohol, and acid to dismantle the matrix bonds meticulously, all within a specific temperature and pressure regime [28,30]. The beauty of solvolysis lies in its many possibilities, owing to the vast array of solvent, temperature, and pressure options available [29,31]. In stark contrast to thermal technologies, solvolysis boasts the advantage of operating at lower temperatures, thereby minimising the degradation of fibres [28,29,30]. Of all the solvolysis techniques, the one that stands out as the most promising is solvolysis with supercritical water, wherein the fibres and resins can be extracted without causing any significant harm to their mechanical properties, which is a truly remarkable feat indeed [29,30,31]. In Figure 6, a comprehensive diagram is presented, providing a detailed illustration of the solvolysis recycling process tailored for EOL WTBs.
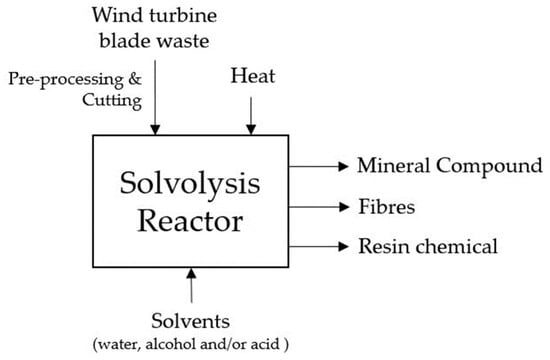
Figure 6.
Diagram illustrating the solvolysis recycling process for end-of-life wind turbine blades.
In recent years, solvolysis has garnered considerable attention, primarily due to its unique ability to recover matrix materials in an alternative form, an achievement that needs to be more attainable with processes such as pyrolysis [32,33,53]. The temperature range within which solvolysis is typically carried out, ranging from 350 °C to 500 °C, is notably lower than the corresponding range for pyrolysis, making it an appealing choice for various applications [32,33,53]. It is worth noting that the success of solvolysis hinges on the nature of the resin itself, as it determines the specific temperatures and solvents required to effectuate effective degradation [32,33].
Several studies have also recovered glass and carbon fibres with retained mechanical properties. In general, organic solvents such as acetone have been found to preserve the mechanical properties of glass fibres, whereas carbon fibres are recovered with maintained mechanical properties using water or organic solvents at temperatures ranging from 260 to 280 °C [53,54].
Most of the chemical recycling research has focused on determining the optimal temperature, composite/solvent ratio, reaction time, and solvent type that will result in the highest resin degradation efficiencies. All studies have one thing in common: temperature and reaction time significantly influence resin degradation efficiency. According to Morin et al., the optimal process parameters for solvolysis differ depending on the solvent used [55]. For instance, the optimal temperature for water-based solvolysis is typically between 250 and 350 °C, while that for methanol-based solvolysis generally is between 200 and 300 °C. The composite-to-solvent ratio is also a critical parameter affecting the process’s efficiency. The higher the composite-to-solvent percentage, the longer the reaction time required for complete resin degradation. Additionally, catalysts can significantly enhance solvolysis, especially when degrading resistant resins such as PEEK or epoxy at lower temperatures [55]. The authors suggest that the optimisation of process parameters is necessary for successfully scaling up solvolysis technology [55].
Several studies have focused on finding more sustainable and resource-efficient techniques for recycling WTBs. Specifically, the studies by Sokoli et al. (2017) [53] and Mattsson et al. (2020) [56] have explored the chemical recycling of fibre-reinforced thermoset composites, each with its specific approach [56].
Sokoli et al. (2017) [53] conducted a study specifically focused on using acetone as the organic solvent for solvolysis. Their research aimed to showcase the potential of recycled acetone in generating valuable bulk chemicals, such as mesityl oxide. The authors successfully recycled the solvent, acetone, for eight consecutive batches, resulting in a remarkable reduction of solvent consumption by 88%. Moreover, with each recycling iteration, they observed an enhanced efficiency in the resin degradation [53]. This observation was attributed to the presence of degradation products from the epoxy resin and compounds formed through acetone aldol reactions, such as mesityl oxide, isophorone, and phorone. Notably, the concentration of these degradation products and acetone aldol reaction compounds increased progressively as the solvent was recycled [53]. These degradation products played a crucial role in promoting and augmenting the degradation process of the composite material. Among the compounds generated through the acetone aldol reactions, mesityl oxide, a bulk chemical of significant industrial importance, accounted for a substantial proportion, ranging from 68% to 79% of the total chromatographic peak area.
Consequently, by optimising the process of converting composite waste into its constituent components, namely fibres and resin, it becomes possible to produce valuable bulk chemicals and thereby enhance the overall commercial viability of the recycling process [53]. Mattsson et al. (2020) [55] undertook a study exploring the application of a proprietary epoxy curing agent in developing recyclable resins. Their research centred around creating a closed-loop recycling technique specifically tailored for FRP. To achieve this, the authors employed solvolysis and hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) techniques utilising subcritical water as the solvent for GFRP waste derived from WTBs [55]. The most favourable reaction conditions were obtained through a two-step process. Firstly, the GFRP material was heated to a temperature of 270 °C in ethylene glycol for 16 h. Subsequently, the material was subjected to further heating, this time to a temperature of 330 °C, in a mixture of water, 1-propanol, and KOH for 3 h [55]. The resulting oil phase products obtained from the GFRP waste and foam cores indicated the successful removal of nitrogen-containing hardeners present in the epoxy and a reduction in the chlorine content originating from the PVC-based foam cores [55]. The findings of this study highlight the potential of solvolysis as a recycling technique for effectively treating and purifying mixed plastic waste streams, such as GFRPs derived from WTBs, before their subsequent processing and upgrading in a refinery. However, it is essential to acknowledge that the study also identified specific challenges associated with the solvolysis process, particularly the extended reaction times necessitated by the presence of thick and dense materials and the consumption of energy and chemicals. These challenges emphasise the need for ongoing development and refinement of the solvolysis technique [55]. Despite the considerable amount of research conducted in this field, it is essential to note that chemical solvolysis technology is still in its nascent stages of development. One of the primary drawbacks of the chemical recycling process is its high energy and solvent consumption, which contribute significantly to the overall costs involved in the process. Consequently, these disadvantages render recovered fibres and monomers less competitive when compared to their virgin counterparts [19,53,55].
4. Applications of Recovered Materials
The diverse recycling technique for EOL WTBs was explored in Section 3. This section focuses on the crucial aspect of processing the resulting waste materials from pyrolysis and mechanical recycling. Each recycling technique employs distinct approaches, all to reclaim the valuable fibres in these blades. Mechanical recycling yields resin-rich, fibre-rich, and other qualities of byproducts [46,57], while pyrolysis generates fibres, fillers, gas, and oil [57,58]. This section aims to showcase the exceptional materials from these recycling processes. The intent is to highlight significant advancements in applications and material development that stem from the innovative repurposing of EOL WTBs. By embracing sustainable practices, this section contributes to driving progress and advancing the principles of the circular economy.
4.1. 3D Printing Reinforced Filaments
Some authors have developed new fused filament fabrication (FFF) filaments that utilize glass fibres from old blades to create structurally rigid parts using 3D printing [40,59]. This innovative process requires a mechanical recycling technique that combines grinding and double sieving to develop value-added FFF from scrap blades. However, FFF parts typically lack strength and stiffness due to their pure thermoplastic material composition, significantly limiting their structural performance [40].
Various factors, including the filament material (e.g., polylactic Acid (PLA)), extrusion and manufacturing processes, and design parameters, influence the mechanical properties of FFF-manufactured parts [40,59,60]. A 3D printer nozzle diameter of 0.4 mm is used in all studies. Simultaneously, the double-sieving process guarantees the availability of fibres shorter than 0.4 mm, a critical requirement for highly processable filaments [20,59,61].
However, using fibres recovered from mechanical recycling presents challenges, such as traces of old resin that may weaken the interface between fibres and matrices (scrap blades are generally reinforced epoxy composites). The fibre’s surface still contains remnants of epoxy, which possess multiple 1,2-epoxy groups per molecule and are highly reactive to various substances such as PLA [59]. However, these difficulties can be overcome by leveraging the beneficial interactions between the functional groups of PLA and epoxy through hydrogen bonding. These reactions elongate molecular chains, enhancing the interfacial strength between PLA and fibres recovered without necessitating costly thermal or chemical treatment processes to eliminate the previous resin. Additionally, the matrix residue on the fibre’s surface augments its unevenness, thereby contributing to the mechanical interactions between the fibres and PLA molecules [59].
In contrast, Moslehi et al. (2022) [61] treated the fibres with a silane-coupling agent to improve the interface between the matrix and the fibre (15 wt% Recycled Glass Fibre Reinforced Filament (RGFRF)). The incorporation of 1,2,3,4-butane tetracarboxylic acid (0.425 wt% BTCA) and the application of a silane treatment (0.6 wt% silane) onto the fibres recovered resulted in a significant improvement in strength, with a 30% increase in the elongation at break and impact strength of the composite being observed, as noted in a previous study [61]. A comparison between PLA/S RGFRF and neat PLA revealed a considerable enhancement in both tensile strength and tensile modulus, with an increase of 36% and 45%, respectively. This indicates the potential of modified glass fibres to enhance the strength and rigidity of PLA [62]. Furthermore, when comparing PLA/S RGFRF, which consists of fibres modified with organic silane, to PLA/RGFRF, it was found that the tensile strength and modulus were improved by 20% and 10%, respectively. It is worth mentioning that although the addition of modified fibres led to a reduction in the elongation at the break of PLA, this reduction was less pronounced compared to the composite with non-modified fibres. This can be attributed to the improved compatibility between SR-GFs and PLA achieved through silane modification. The decreased elongation at break in the composite can be attributed to the higher rigidity of glass fibres, which exhibit less flexibility than the polymeric matrix and consequently limit the deformation of the polymer [61]. Table 4 summarises the crucial findings from the study involving various PLA variants. The data is methodically arranged in ascending tensile strength order for improved clarity.

Table 4.
Summary of tensile characteristics: modulus, elongation at break, and strength of different PLA variants.
Rahimizadeh et al. (2019) [58] demonstrated that reinforced filaments with 25% fibre content could increase the specific stiffness of PLA samples by up to 74%. However, this increase comes at the cost of a reduced specific tensile strength and failure strain by 42% and 65%, respectively. The study explored the use of virgin and recycled glass fibres and found that fibres recovered partially covered with epoxy particles led to an 18% increase in specific modulus and a 19% increase in tensile strength compared to virgin fibres [58]. However, adding fibres harmed the ductility and ultimate strength of the samples due to the development of excessive stress concentration regions caused by fibre aggregation and resin particles with sharp corners on the surfaces of the fibres recovered.
Recent studies have shown that the recycled feedstock filament for FFF has superior tensile properties compared to that of pure polymer filaments, according to research by Rahimizadeh et al. (2020) [59] and Tahir et al. (2021) [63]. Rahimizadeh et al. (2020) [59] revealed that ground fibres with a 20 mm gauge length had strength like virgin fibres. However, increasing the gauge length to 40 mm and 60 mm resulted in a brittle failure mode and lower average strength. The primary determinant of the mechanical properties of fibres is the distribution of surface imperfections. Generally, shorter fibres exhibit fewer flaws, while longer fibres are more prone to external surface defects, which can increase the likelihood of microcrack formation [59].
Interestingly, the stiffness of the fibres after undergoing mechanical recycling was comparable to that of pristine threads when measured at various gauge lengths, indicating no deterioration in stiffness. In contrast to strength, longer gauge lengths are suggested to result in a higher modulus, as per research findings [64]. This is attributed to a more substantial decrease in ductility than ultimate strength. While the stiffness of the processed fibres displayed some variability, it is noteworthy that the average stiffness values remained remarkably consistent across various gauge lengths, as indicated in reference [60].
Tahir et al. (2021) [63] compared three different fibre categories: virgin, ground, and pyrolyzed, using experimental and analytical micromechanical models. The results showed that both fibres recovered (ground and pyrolyzed) had higher strength and stiffness values than virgin fibres. The specific stiffness of 3D-printed reinforced specimens improved by 39.5%, 43.1%, and 69.6% for 10% fibre content using virgin, ground, and pyrolyzed fibres, respectively [65]. However, adding fibres harmed the sample ductility and ultimate strength, resulting in a significant average drop of 29.3%, 13.4%, and 17.9% for 10% fibre content using virgin, ground, and pyrolyzed fibres, respectively [65]. Nevertheless, the tensile strength of 3D-printed samples reinforced with the three distinct fibre categories was observed to be lower when compared to the strength of pure PLA samples. This decrease in strength can be attributed to the relatively shorter fibre lengths, with an average measurement of 0.226 mm, falling below the critical threshold of 0.87 mm for ground fibres. As a result, the study recommends repeating the experiment employing fibre categories characterised by lengths closer to the essential point. This adjustment is necessary to precisely ascertain the tensile properties of reinforced 3D-printed samples [65].
Rahimizadeh et al. (2021) [60] investigated the effect of ground fibres above the critical length on the strength of 3D-printed parts, with 3, 5, and 10 wt% of recycled content. The study found that 3D-printed parts with 5 wt% of recycled content had a 20% increase in specific strength compared to pure PLA specimens. However, increasing the recycled content to 10 wt% resulted in a slight reduction in tensile strength, likely due to low surface quality. Samples with up to 5 wt% of recycled content exhibited higher ductility than pure PLA parts due to the low fibre volume fraction of the recycled and the favourable interactions between the fibres and PLA.
Furthermore, Rahimizadeh et al. (2021) [60] compared the properties of 3D-printed samples reinforced with long glass fibres and short recycled glass fibres. The results showed that samples reinforced with long fibres had higher tensile properties, which could be attributed to two factors [60]. In the first step, the researchers employed micromechanical characterisation to determine the appropriate parameters for manufacturing and recycling, resulting in longer fibres in the final product. Subsequently, multiple classification operations were conducted post-grinding to minimize the presence of epoxy powder particles and preserve the epoxy residues on the surface of the reclaimed extended glass fibres. The preservation of these surface epoxy residues proves crucial in enhancing the mechanical performance of the fibres, as it establishes an interface that is 26% stronger compared to that formed between fibres with a smooth surface (Rahimizadeh et al. (2021) [60]). This finding suggests that surface epoxy residues significantly contribute to the overall strength improvement of the recycled composites. By ensuring the preservation of these residues during the manufacturing process, the composites can be produced with enhanced mechanical properties, making them suitable for various industrial applications. The study highlights the importance of proper manufacturing and recycling parameters and the preservation of surface epoxy residues in producing recycled composites with improved mechanical properties.
Table 5 presents a summary of the mechanical properties and their corresponding standard deviations for FFF 3D printing filaments with varying fibre contents, as explored in previous research. To enhance clarity, the data has been meticulously organized in ascending order of specific strength.

Table 5.
Summary of the mechanical properties of FFF 3D printing filament composed of polylactic acid with varying weight percentages of recycled glass fibre-reinforced filament.
Adding recycled glass fibre-reinforced filament to PLA can increase the filament’s specific stiffness but decrease the failure strain and specific strength. The strength of the filament decreases with the increasing weight percentage of the reinforced filament while the specific stiffness increases. This trend can be seen in both studies in the table that were conducted by Rahimizadeh et al. in 2019 [58] and 2021 [59]. The decrease in particular strength can be attributed to the addition of the reinforced filament, leading to the dilution of the polymer matrix, which decreases the filament’s strength. However, the increase in specific stiffness can be attributed to the fact that the reinforced filament provides a reinforcement effect, which improves the stiffness of the filament. Another important observation is that the failure strain of the filament decreases with the increasing weight percentage of the reinforced filament. This means that the filament becomes more brittle and less ductile with the addition of the reinforced filament. This trend can be seen in both studies presented in the table. Lastly, it is important to note that the length of the fibres used can also affect the mechanical properties of the filament. It can be observed that longer fibres lead to a higher specific stiffness, as seen in the study conducted by Rahimizadeh et al. in 2021 [60].
In conclusion, optimising the weight percentage and length of the reinforced fibres can improve the mechanical properties of FFF 3D printing filaments. However, it is important to note that adding the reinforced filament can decrease specific strength and failure strain, making the filament more brittle.
4.2. Reinforced Concrete
The use of GFRP waste from EOL wind turbines for fibre extraction as a replacement for synthetic macro fibres in concrete is supported by several studies, including those by Fu et al. (2021) [64], Yazdanbakhsh et al. (2018) [66], and Rodin et al. (2018) [67]. These studies have consistently shown that adding GFRP fibres can significantly enhance the mechanical properties of concrete, resulting in more resilient and longer-lasting structures that can withstand the demands of infrastructure and construction projects.
Specifically, GFRP fibres have been shown to enhance the tensile and flexural strength, durability, and resistance to cracking of concrete in studies such as Fu et al. (2021) [64], Yazdanbakhsh et al. (2018) [66], and Rodin et al. (2018) [67]. Baturkin et al. (2021) [68] found that using it as fibre reinforcement improved the flexural capacity without sacrificing compressive strength. Haider et al. (2021) [69] found that recycled GFRP used as mortar also exhibited improved toughness. At the same time, Fu et al. (2021) [64] and Xu et al. (2022) [70] found that macro fibres with hybrid lengths improved flexural performance, including flexural strength, deformation capacity, and toughness. However, Fu et al. [64] did not report the negative impact on compression behaviour that Xu et al. [70] observed. Table 6 summarises the mechanical properties of the concrete samples tested in the laboratory, including the compressive strength and modulus of elasticity. Overall, these studies demonstrate the potential of recycled and waste GFRP materials as a substitute for traditional reinforcement materials in concrete. However, a careful selection of the specific form and recycling technique is necessary to achieve the desired mechanical properties. For instance, the size and shape of the recycled GFRP can vary depending on the mechanical process used, which can affect the properties of GFRP. Therefore, carefully selecting the recycling technique used to extract GFRP fibres from waste materials is crucial to achieving the desired mechanical properties for concrete reinforcement. Yazdanbakhsh et al. (2018) [66] found that the size and shape of the recycled GFRP varied depending on the mechanical technique used. A recycling technique that preserves the composite nature of GFRP by creating large needles with cross-sections of 6 mm by 6 mm and a length of 100 mm, both in the plain and grooved varieties produced, has yielded superior mechanical properties when compared to alternative recycling techniques. To be more specific, the study by Yazdanbakhsh et al. (2018) [66] found that the replacement of 5% and 10% of the coarse aggregate by volume with plain needles led to a significant increase in the average equivalent flexural strength of concrete, from 1.1 MPa to 14.0 MPa and 32.3 MPa, respectively. When grooved needles were used, the average comparable flexural strength for 5% and 10% replacements was 12.6 and 24.7, respectively [66].

Table 6.
Mechanical properties of concrete with varying weight percentages of glass fibre-reinforced polymer. “PLN” and “GRV” represent plain and grooved needles.
Fu et al. (2021) [64] demonstrated that including macro fibres significantly enhanced the flexural performance of concrete beams. This improvement encompassed flexural strength, deformation capacity, and toughness. These macro fibres possess a typical thickness like that of a lamina (e.g., 0.4–1.0 mm), a width of several millimetres, and a length ranging from 30 to 100 mm. Consequently, their aspect ratio (i.e., length-to-thickness ratio) falls within the range of 30–120, which resembles that of standard steel fibres employed in concrete [64]. The flexural strength experienced a substantial increase of 135% compared to the reference beams when 1.5% macro fibres were incorporated into the concrete specimens.
Furthermore, the residual flexural strengths at deflections of 1/600 and 1/150 of the span (i.e., f600 and f150) also displayed an augmentation with adding fibres. Similarly, the average toughness of the control group specimens was a mere 0.97 J, whereas samples with 1.0% and 1.5% macro fibres exhibited toughness values of 151.3 J and 182.4 J, respectively [64].
The examination outcomes indicate that, like discoveries about macro fibres of predetermined lengths [71], including hybrid-length macro fibres can enhance concrete beams’ flexural strength and toughness. Additionally, this enhancement becomes more pronounced as the fibre volume ratio increases [64,70]. Similarly, Xu et al. (2022) [70] reported that using macro fibres with hybrid lengths in a concrete mix can improve concrete performance, including flexural strength and toughness. The investigation revealed a notable increase in flexural strength for the various groups with fibre volume ratios of 0.5%, 1.5%, and 2.5%. Specifically, the flexural strength exhibited an augmentation of 4.34%, 13.30%, and 37.85%, respectively, compared to the control group. Furthermore, as the fibre volume ratio increased, the enhancement in flexural strength became more pronounced. In addition, the flexural toughness for the groups with fibre volume ratios of 0.5%, 1.5%, and 2.5% experienced a significant improvement, with a respective increase of 15.5, 22.7, and 36.8 times compared to that of the control group. Remarkably, the flexural toughness of the groups with fibre volume ratios of 0.5%, 1.5%, and 2.5% demonstrated a substantial enhancement of 15.5, 22.7, and 36.8 times, respectively, compared to the control group. However, incorporating macro fibres negatively impacted the concrete’s compression behaviour, resulting in a significant loss of 54% [70].
Haider et al. (2021) [69] conducted a study on producing recycled GFRP in three different sizes through hammer milling of 12.7 mm and screening. The researchers found no significant trend in the size or quantity of GFRP on the compressive strength of the mortar. However, almost all GFRP mortars exhibited significantly improved flexural strength due to their high modulus [69]. In addition, it is observed that the fracture toughness of GFRP mortars shows a progressive increase as the proportion of GFRP in all size categories rises. Notably, large GFRP proportions, specifically 5% and 7% by volume, manifest exceptional toughness indices characterised by strain-hardening behaviour after the peak and an approximate equivalent flexural ratio of 60% and 70%. A comprehensive examination of the micrographs depicting the GFRP–mortar interfaces reveals the successful integration and anchoring of GFRP shreds within the mortar matrix. Furthermore, the failure modes observed in the experiments encompassed both pullout and fracture phenomena, indicating the successful incorporation and bond formation between the GFRP and mortar components [69].
Baturkin et al. (2021) [68] evaluated the impacts of incorporating GFRP in concrete as a powder, aggregate, or fibre on its performance. They attempted 10–30% cement replacement rates, coarse aggregate replacement levels of 33–100%, and fibre addition rates of 1–1.75 vol.% [68]. When introduced in powder form, adding GFRP led to a notable extension in the time taken for the concrete to set. Furthermore, it caused a significant decline in both compressive and flexural strengths. This reduction can be attributed to wood-based polysaccharides interfering with the kinetics of cement hydration. However, when the wooden components were eliminated, mixtures containing 10% GFRP powder as a replacement for cement demonstrated comparable compressive strength to that of the control mixture (without GFRP) after 90 days [68]. In the case of GFRP incorporated as a fibre reinforcement in concrete, an improvement in the flexural capacity of up to 15% was achieved without any noticeable decrease in the compressive strength. Conversely, when GFRP was added as aggregates, lower compressive and flexural strengths were observed. This is due to the smooth surface of GFRP, which leads to reduced adhesion with the matrix and the creation of a weak interfacial transition zone [68].
Table 6 provides a concise summary of the mechanical properties of concrete samples containing varying weight percentages of GFRP, encompassing compressive strength and modulus of elasticity. To improve clarity, the data has been systematically arranged in ascending order based on compressive strength (28 days strength).
Based on the studies summarised, incorporating GFRP materials in concrete can reduce the compressive strength and modulus of elasticity, especially at higher weight percentages. However, the reduction can be limited by carefully selecting the form and recycling technique of GFRP and other supplementary materials such as fly ash. Using grooved needles instead of plain needles can also improve the properties of the GFRP-reinforced concrete. Overall, the results suggest that GFRP materials have the potential to be a viable alternative to traditional reinforcement materials in concrete, but further research is needed to optimise their properties and ensure their long-term durability.
4.3. New Thermoset Polymer Composites from Fibres Pyrolyzed
Some studies provide valuable insights into the potential of using recycled glass fibres in new composite materials and demonstrate the feasibility of using microwave pyrolysis as a recycling technique for composites. The research conducted by Åkesson et al. [72] investigated the feasibility of extracting glass fibres from previously utilized reinforced composites through microwave pyrolysis and assessing their potential for incorporation into fresh composites. In the first study, Åkesson et al. (2012) [72] conducted a study to assess the mechanical properties of composites made with recovered glass fibres and polypropylene (PP) to enhance the adhesion between the recovered glass fibres and the polymer matrix in composite materials produced through microwave pyrolysis. Examining SEM micrographs demonstrated a diminished level of adhesion between the recuperated fibres and the polymer matrix. The incorporation of maleic anhydride-grafted PP (MA-PP) exhibited a notably influential impact on the mechanical characteristics, resulting in an elevation of flexural strength from 46 MPa to 62 MPa and a rise in flexural modulus from 2.4 GPa to 3.4 GPa. Nevertheless, the augmentation of the weight percentage of MA-PP led to a decline in the strength and modulus of the composites. The mechanical properties of the composites experienced an enhancement up to a specific threshold with the escalation in MA-PP concentration and subsequently deteriorated at higher concentrations. The lower molecular weight of MA-PP compared to polypropylene may explain the reduced bending properties at high weight percentages of MA-PP. Including coupling agents in the formulation resulted in an augmentation of the tensile strength and modulus of the composites. However, this enhancement came at the expense of a decrease in maximum elongation. The recovered fibres were weaker than virgin fibres, even with coupling agents. Using chalk as a filler resulted in a tensile strength of 26 MPa and a modulus of 2.6 GPa [38].
In the second study [45], the researchers aimed to evaluate the potential of the recovered glass fibres from a WTB obtained through microwave pyrolysis as a reinforcement for thermoset composites. Non-woven fibre mats were fabricated by manually blending recycled glass fibres with bicomponent fibres, followed by a heat treatment to facilitate fibre bonding. The polyester resin was then applied to the mats via hand lay-up and cured using compression moulding, resulting in composites with varying proportions of recycled and virgin glass fibres. The decline in tensile strength can be remedied by employing a hybrid composite that combines recycled glass fibres with virgin fibres. Experimental analysis has demonstrated that composites containing 25 wt% of fibres recovered exhibited favourable mechanical properties, characterised by a flexural strength of 157 MPa and a flexural modulus of 12 GPa.
Nonetheless, compared to composites consisting solely of 100 wt% virgin fibres, the flexural strength experienced a decrease from approximately 189 MPa to 157 MPa, while the flexural modulus decreased from roughly 16 MPa to 12 MPa. This observation implies that the reinforcing influence of mats derived from reclaimed fibres was relatively modest, potentially due to alterations in the surface characteristics of the fibres after pyrolysis. The adhesion between the fibres and matrix could have been higher due to the degraded glass fibre sizing. One potential solution is to improve adhesion by heating the fibres with oxygen to remove the char and adding a new sizing, which could lower tensile strength [45].
Table 7 offers a succinct summary of the flexural strength and flexural modulus values for the different composites prepared using recovered fibres obtained through microwave pyrolysis, as reported in Akesson’s studies. To enhance clarity, the data has been meticulously organized in ascending order according to flexural strength.

Table 7.
Flexural strength and flexural modulus of composites prepared using the recovered fibres.
The composites with glass fibres and MA-PP had higher flexural strength and flexural modulus values compared to a PP composite. The 100% virgin glass fibre composite had the highest flexural strength value. The studies suggest that using recovered fibres obtained through microwave pyrolysis in composites can improve their mechanical properties and be a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional composites made of virgin materials. The studies suggest that using recovered fibres obtained through microwave pyrolysis in composites can improve their mechanical properties, particularly when combined with glass fibres and MA-PP. These findings could have important implications for developing sustainable and eco-friendly composites with comparable or better mechanical properties than traditional composites made of virgin materials.
5. Environmental and Economic Impact
The environmental and economic impact of recycling WTBs at their EOL must be carefully evaluated. The energy consumed in the recycling process must be balanced against the quality and value of the recycled material to ensure sustainability. Recycling techniques should aim to produce a lower overall environmental impact than producing virgin material or other waste management techniques.
Industrial-scale studies indicate that the energy required to recycle carbon fibre (CF) by mechanical recycling is lower than that required to manufacture virgin CF [25,73,74]. Under optimal conditions, the fluidised bed process has an energy demand of around 10 MJ/kg of recycled CF, which can reduce global warming potential and primary energy demand [75]. Recycling CF through a fluidised bed process was 15% of the manufacturing cost of virgin CF, indicating environmental and economic benefits [76].
Pyrolysis is a potentially profitable recycling technique for WTB materials, offering valuable products. However, fibres recovered produced by pyrolysis often need to meet the property requirements of manufacturers. Pyrolyzed fibres derived from WTB materials are suitable for use as thermal and acoustic insulation materials, offering similar properties at lower sale prices than virgin fibres [77]. Pyrolytic oil derived from glass fibre-reinforced polymers is also valuable, with high heating values comparable to diesel and heating oil [78]. The process of pyrolysis, which utilises microwave heating to internally heat the material, offers a means of conserving energy compared to traditional pyrolysis methods. The energy consumption associated with this process has been documented as 10 MJ/kg [79,80]. The fluidised bed process for recycling EOL WTBs can offer substantial environmental and cost benefits [76]. Pyrolysis is also a viable option for recycling WTB materials, especially carbon fibre, but the quality of the recycled materials must meet manufacturers’ specifications [44,50,81]. Table 8 summarises the unit processing energy for all available WTB options.

Table 8.
The energy requirements for each EOL process of WTB materials.
The recycling benefits are essential in evaluating the environmental impact of each EOL option for WTBs. This includes the energy consumption required for EOL processing, the recycling benefits obtained from the specific recycling technology used, and the effect of blade technology development trends on the recycling process.
Liu et al. conducted two studies, one in 2019 [85] and another in 2022 [86], to investigate WTBs’ environmental and economic impacts throughout their lifecycle, including the EOL stage. Both studies highlight the importance of considering benefits from EOL waste management and recycled value per tonne in evaluating the environmental and economic impacts of WTB recycling [82,85].
According to Liu et al. (2019) [85], the benefits from EOL [GJ] refer to the positive environmental impact achieved through proper EOL waste management and recycling. The study calculates the EOL impact of unit recycling processing energy (MJ/kg) multiplied by the amount of waste processed (kg), with recycling benefits proportional to the recycler’s tensile strength compared to the strength of virgin material. Negative values indicate a negative environmental impact, while positive values indicate a positive one. Low-energy processing technologies, such as mechanical recycling, are more favourable than high-energy processes, such as fluidised beds and pyrolysis, which have high environmental impacts.
The recycling potential of CF blades is high, with minor energy consumption during recycling. In contrast, the variation in EOL processing energy significantly impacts GF blades’ viability for recycling. Hybrid blades fall somewhere in the middle, and reliable data on recycling benefits is crucial for determining the optimal EOL option.
According to Liu et al. 2022 [86], recycle value per tonne refers to the value obtained from the recycled materials produced by recycling WTBs. The study uses a financial performance model to evaluate and compare the economic feasibility of different recycling technology options for blade waste management. The mechanical recycling process recycle value for CF is higher than that of GF, while the fluidised bed process recycle value for CF is much higher than that of GF. The cost of recycling CFRP waste through pyrolysis is much higher than that of recycling GFRP waste. The recycle value for CF through the MAP process is significantly higher than that for GF [86].
Table 9 summarises the values for the benefits from EOL [GJ] and recycle value per tonne of WTBs, which are discussed in both studies. The table presents results for three types of WT blades: glass fibre-reinforced plastic (GF), carbon fibre-reinforced plastic (CF), and a hybrid blade made of GF and CF. The different EOL treatments evaluated are mechanical recycling, fluidised bed recycling, pyrolysis, microwave pyrolysis, and chemical recycling.

Table 9.
Summarising the benefits from EOL and recycle value per tonne of WTBs were evaluated, providing insights into the environmental and economic impacts of EOL management by Liu et al. (2019) [85] and Liu et al. (2022) [86].
According to the table, the optimal EOL treatments for the GF blade and the hybrid blade are mechanical recycling, and for the CF blade, fluidised bed recycling is the optimal treatment. The GF and hybrid blades show positive values for benefits from EOL for all the treatments, indicating that they can provide energy recovery and recyclable material. In contrast, the CF blade has negative values for the benefits from EOL for all treatments, indicating that the EOL treatments can result in energy consumption instead of energy recovery.
The recycle values vary depending on the EOL treatment and blade type. The highest recycle values for the chemical recycling of the GF and hybrid blades are $1488.3 and $13,992.3 per tonne, respectively. The lowest recycle values are obtained for the GF blade treated with mechanical recycling, $410.6 per tonne, and the CF blade treated with fluidised bed recycling, $176.4 per tonne.
6. Conclusions
The wind energy industry has grown significantly, increasing WTB waste. WTBs can be recycled through mechanical, thermal, and chemical processes. However, identifying the best recycling technique requires considering multiple factors, including the physical and mechanical properties of the recycled compounds, operational costs, and energy consumption. This study presents a comprehensive systematic review of available wind-blade recycling processes, evaluating their economic, technical, and environmental performance. The findings of this review can guide future research and help decision-makers in planning sustainable wind energy development and waste management strategies.
Different recycling techniques have shown promise regarding recycled materials’ physical and mechanical properties. For example, shredding composites can maintain their mechanical properties, and recycled glass fibres have demonstrated the potential to enhance the properties of 3D-printed parts. GFRP waste in concrete has consistently shown significant enhancements in mechanical properties. Pyrolysis has the potential for recovering valuable materials, while the fluidised bed gasification process shows promise for recycling WTBs. However, challenges and limitations exist, such as those of strength loss in recycled glass fibres and the need to optimise process parameters in solvolysis.
Microwave pyrolysis is identified as the most promising technology for recycling large quantities of WTBs. However, challenges and uncertainties still need to be addressed regarding its effectiveness and feasibility at an industrial scale. Operational costs and energy consumption are crucial in determining the best recycling technique. For instance, fluidised bed and mechanical recycling processes are more environmentally sustainable due to their lower energy consumption requirements. Economic feasibility also depends on the type of blade material being recycled, with carbon fibre recycling through microwave-assisted pyrolysis and fluidised bed recycling potentially being more economically feasible than that of glass fibre.
The quality of fibres recovered is closely linked to their tensile strength, a crucial indicator in assessing post-recycling structural integrity. In essence, tensile strength reflects how effectively fibres maintain their strength after recycling. In practical terms, higher tensile strength is desirable, particularly for applications with paramount robustness and durability.
The results from various recycling methods shed light on this aspect. Notably, fluidized bed technology emerged as a standout performer, delivering some of the highest tensile strengths observed, especially in the case of GFRE (glass fibres recycled from in-house prepared composites). However, it is important to note that the outcomes varied significantly due to the differing conditions, including NaOH concentrations, temperatures, and treatment durations.
On the other hand, microwave-assisted pyrolysis also showed promise, though it generally yielded slightly lower tensile strengths compared to those of fluidized bed pyrolysis. Meanwhile, while effective in recycling, conventional pyrolysis tended to produce fibres with lower tensile strengths compared to those of these other methods.
Overall, the best recycling technique for WTBs should balance the physical and mechanical properties of the recycled compounds with operational costs and energy consumption requirements. Further research and development are needed to improve the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability of recycling techniques for WTBs. The findings of this study provide valuable guidance for decision-makers in the wind energy industry to develop waste management strategies and plan sustainable wind energy development.
Based on this review, mechanical recycling appears to be more energy-efficient, while the fluidised bed recycling process demonstrates a lower primary energy demand, global warming potential, and power consumption. These findings provide valuable guidance for decision-makers in the wind energy industry to develop effective waste management strategies and plans for sustainable wind energy development. As the wind energy industry continues to grow, addressing the issue of WTB waste and implementing efficient recycling techniques will be critical in mitigating its environmental impacts and promoting sustainability in the renewable energy sector.
Author Contributions
S.S.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review & editing, Visualization. N.M.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing–review & editing, Supervision. M.S.A.O.: Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation. G.L.V.: Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation. C.R.: Writing–review & editing, Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work received support from the Center for Mechanical Technology and Automation (TEMA) under project codes UIDB/00481/2020 and UIDP/00481/2020. We also extend our gratitude for the support received from the Center for Risks and Sustainability in Construction (RISCO) under project code UIDB/04450/2020. Additionally, this work was financially supported by the project RE-LIVE BLADES (CENTRO-01-0247-FEDER-069820) funded by FEDER, through Portugal 2020.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Heng, H.; Meng, F.; McKechnie, J. Wind turbine blade wastes and the environmental impacts in Canada. Waste Manag. 2021, 133, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Wind Energy Association (EWEA). Working Group on Grid Code Requirements, Position Paper, European Grid Code Requirements for Wind Power Generation; EWEA: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- WindEurope. Accelerating Wind Turbine Blade Circularity; WindEurope: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- WindEurope. Wind Energy in Europe—2021 Statistics and the Outlook for 2022–2026; WindEurope: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Future of Wind: Deployment, Investment, Technology, Grid Integration and Socio-Economic Aspects (A Global Energy Transformation Paper); IRENA: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Majewski, P.; Florin, N.; Jit, J.; Stewart, R.A. End-of-life policy considerations for wind turbine blades. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 164, 112538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.; Skelton, K. Wind turbine blade recycling: Experiences, challenges and possibilities in a circular economy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, V.; Stockschläder, J.; Walther, G. Estimation of glass and carbon fiber reinforced plastic waste from end-of-life rotor blades of wind power plants within the European Union. Waste Manag. 2020, 115, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefeuvre, A.; Garnier, S.; Jacquemin, L.; Pillain, B.; Sonnemann, G. Anticipating in-use stocks of carbon fibre reinforced polymers and related waste generated by the wind power sector until 2050. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Barlow, C.Y. Wind turbine blade waste in 2050. Waste Manag. 2017, 62, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenegger, G.; Rentizelas, A.A.; Trivyza, N.; Siegl, S. Offshore and onshore wind turbine blade waste material forecast at a regional level in Europe until 2050. Waste Manag. 2020, 106, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperman, A.; Eberle, A.; Lantz, E. Wind turbine blade material in the United States: Quantities, costs, and end-of-life options. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauson, J.; Laurent, A.; Rudolph, D.; Jensen, J.P. The complex end-of-life of wind turbine blades: A review of the European context. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 155, 111847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauson, J.; Madsen, B.; Toncelli, C.; Brøndsted, P.; Bech, J.I. Recycling of shredded composites from wind turbine blades in new thermoset polymer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 90, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamanpush, S.H.; Tabatabaei, A.T.; Li, H.; Englund, K. Physical properties data of extruded composites from recycled wind turbine blade material. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, R.; Xydis, G. Wind turbine blade recycling: An evaluation of the European market potential for recycled composite materials. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauson, J.; Lilholt, H.; Brøndsted, P. Recycling solid residues recovered from glass fibre-reinforced composites—A review applied to wind turbine blade materials. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, D.S.; Suzuki, Y.; Murray, R.E.; Samaniuk, J.R.; Stebner, A.P. Recycling glass fiber thermoplastic composites from wind turbine blades. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.; Ghita, O.; Savage, L.; Evans, K. Successful closed-loop recycling of thermoset composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.; Choudhary, P.; Krishnan, V.; Zafar, S. A review on recycling and reuse methods for carbon fiber/glass fiber composites waste from wind turbine blades. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 215, 108768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.; Choudhary, P.; Krishnan, V.; Zafar, S. Development of sustainable microwave-based approach to recover glass fibers for wind turbine blades composite waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 179, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pender, K.; Yang, L. Regenerating performance of glass fibre recycled from wind turbine blade. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 198, 108230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pender, K.; Yang, L. Investigation of catalyzed thermal recycling for glass fiber-reinforced epoxy using fluidized bed process. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 3510–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.J.; Turner, T.A.; Meng, F.; Morris, C.N.; Heil, J.P.; Wong, K.H.; Melendi-Espina, S. Developments in the fluidised bed process for fibre recovery from thermoset composites. In Proceedings of the 2nd Annual Composites and Advanced Materials Expo, CAMX 2015, Dallas, TX, USA, 26–29 November 2015; pp. 2384–2394. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, H.L.H.; Pickering, S.J.; Rudd, C.D. Characterisation of carbon fibres recycled from scrap composites using fluidised bed process. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2002, 31, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.; Kelly, R.; Kennerley, J.; Rudd, C.; Fenwick, N. A fluidised-bed process for the recovery of glass fibres from scrap thermoset composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Yang, L.; Anderson, R.; Tang, P.; Liggat, J.; Thomason, J. A simple chemical approach to regenerating the strength of thermally damaged glass fibre. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 102, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, L.; Schneller, A.; Doerfler, J.; Mueller, W.M.; Aymonier, C.; Horn, S. Semi-continuous flow recycling method for carbon fibre reinforced thermoset polymers by near- and supercritical solvolysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 133, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, Y. Sustainability assessment of solvolysis using supercritical fluids for carbon fiber reinforced polymers waste management. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2019, 17, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinçaud, M.; Aymonier, C.; Loppinet-Serani, A.; Perry, N.; Sonnemann, G. Environmental Feasibility of the Recycling of Carbon Fibers from CFRPs by Solvolysis Using Supercritical Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1498–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-S.; Jin, B.C.; Li, X.; Nutt, S. A recyclable epoxy for composite wind turbine blades. Adv. Manuf. Polym. Compos. Sci. 2019, 5, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.E.; Penumadu, D.; Cousins, D.; Beach, R.; Snowberg, D.; Berry, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Stebner, A. Manufacturing and Flexural Characterization of Infusion-Reacted Thermoplastic Wind Turbine Blade Subcomponents. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2019, 26, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoli, H.U.; Simonsen, M.E.; Søgaard, E.G. Investigation of degradation products produced by recycling the solvent during chemical degradation of fiber-reinforced composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2017, 36, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Nunes, M.I. Recent trends and developments in Fenton processes for industrial wastewater treatment—A critical review. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, K.; Skórczewska, K.; Piszczek, K.; Urbaniak, W. Recycled Glass Fibres from Wind Turbines as a Filler for Poly(Vinyl Chloride). Adv. Polym. Technol. 2019, 2019, 8960503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, N.; Mazzotti, C.; Savoia, M. Post-cracking behaviour of steel and macro-synthetic fibre-reinforced concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, P.A.; Galvín, A.P.; Ayuso, J.; Barbudo, A.; López-Uceda, A. Mechanical Performance of Concrete Made with the Addition of Recycled Macro Plastic Fibres. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariak, A.; Kurpińska, M. The effect of macro polymer fibres length and content on the fibre reinforced concrete. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 219, 03004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rahimizadeh, A.; Kalman, J.; Henri, R.; Fayazbakhsh, K.; Lessard, L. Recycled Glass Fiber Composites from Wind Turbine Waste for 3D Printing Feedstock: Effects of Fiber Content and Interface on Mechanical Performance. Materials 2019, 12, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, A.N.; Abourayana, H.M.; Dowling, D.P. 3D Printing of Fibre-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites Using Fused Filament Fabrication—A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveux, G.; Dandy, L.O.; Leeke, G.A. Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: Review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Tang, T. Recycling of carbon fibre reinforced epoxy resin composites under various oxygen concentrations in nitrogen–oxygen atmosphere. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 112, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoleń, J.; Olesik, P.; Jała, J.; Adamcio, A.; Kurtyka, K.; Godzierz, M.; Kozera, R.; Kozioł, M.; Boczkowska, A. The Use of Carbon Fibers Recovered by Pyrolysis from End-of-Life Wind Turbine Blades in Epoxy-Based Composite Panels. Polymers 2022, 14, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginder, R.S.; Ozcan, S. Recycling of Commercial E-glass Reinforced Thermoset Composites via Two Temperature Step Pyrolysis to Improve Recovered Fiber Tensile Strength and Failure Strain. Recycling 2019, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, D.; Krishnamoorthi, R.; Foltynowicz, Z.; Christέen, J.; Kalantar, A.; Skrifvars, M. Glass Fibres Recovered by Microwave Pyrolysis as a Reinforcement for Polypropylene. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2013, 21, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, E.; Twomey, J.; Overcash, M. Recycling of fiber-reinforced composites and direct structural composite recycling concept. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ye, M.; Li, M.; Xi, B.; Hou, J.; Qi, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Meng, F. Characteristics, kinetics and product distribution on pyrolysis process for waste wind turbine blades. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 169, 105859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, H.; Sobek, S.; Sajdak, M.; Muzyka, R.; Drewniak, S.; Werle, S. Oxidative liquefaction as an alternative method of recycling and the pyrolysis kinetics of wind turbine blades. Energy 2023, 278 Pt B, 127950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-X.; Ji, H.-W.; Wu, Y.-C.; Di, J.-Y.; Meng, X.-X.; Jiang, H.; Lu, Q. The pyrolysis of end-of-life wind turbine blades under different atmospheres and their effects on the recovered glass fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 251, 110493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; Schulte, K.; Grove-Nielsen, E. CFRP-Recycling Following a Pyrolysis Route: Process Optimization and Potentials. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sáez, E.; Nagel, U.; Thomason, J. Can thermally degraded glass fibre be regenerated for closed-loop recycling of thermosetting composites? Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 72, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Xu, L.; Shang, X.; Shen, Z.; Fu, R.; Li, W.; Guo, L. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Pyrolysis Products of Carbon Fibers Recycled by Microwave Pyrolysis. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 13529–13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoli, H.U.; Beauson, J.; Simonsen, M.E.; Fraisse, A.; Brøndsted, P.; Søgaard, E.G. Optimized process for recovery of glass- and carbon fibers with retained mechanical properties by means of near- and supercritical fluids. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 124, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Loppinet-Serani, A.; Cansell, F.; Aymonier, C. Near- and supercritical solvolysis of carbon fibre reinforced polymers (CFRPs) for recycling carbon fibers as a valuable resource: State of the art. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 66, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, C.; André, A.; Juntikka, M.; Tränkle, T.; Sott, R. Chemical recycling of End-of-Life wind turbine blades by solvolysis/HTL. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 942, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, H.K.; Kachhwaha, S.S.; Nagababu, G.; Das, A. A brief review on recycling and reuse of wind turbine blade materials. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 7124–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; De Marco, I.; Caballero, B.M.; Laresgoiti, M.F.; Chomón, M.J.; Kondra, G. Recycling of the solid residue obtained from the pyrolysis of fiberglass polyester sheet molding compound. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2009, 28, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimizadeh, A.; Kalman, J.; Fayazbakhsh, K.; Lessard, L. Recycling of fiberglass wind turbine blades into reinforced filaments for use in Additive Manufacturing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimizadeh, A.; Tahir, M.; Fayazbakhsh, K.; Lessard, L. Tensile properties and interfacial shear strength of recycled fibers from wind turbine waste. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 131, 105786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimizadeh, A.; Kalman, J.; Fayazbakhsh, K.; Lessard, L. Mechanical and thermal study of 3D printing composite filaments from wind turbine waste. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslehi, A.; Ajji, A.; Heuzey, M.; Rahimizadeh, A.; Lessard, L. Polylactic acid/recycled wind turbine glass fiber composites with enhanced mechanical properties and toughness. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, D.; Wan, G.; Li, B.; Zhao, G. Glass fiber reinforced PLA composite with enhanced mechanical properties, thermal behavior, and foaming ability. Polymer 2019, 181, 121803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Rahimizadeh, A.; Kalman, J.; Fayazbakhsh, K.; Lessard, L. Experimental and analytical investigation of 3D printed specimens reinforced by different forms of recyclates from wind turbine waste. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 4533–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, K.; Chen, J.; Teng, J. Concrete reinforced with macro fibres recycled from waste GFRP. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, D.L.; Fronk, T.H. Weibull distribution analysis of the tensile strength of the kenaf bast fiber. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Bank, L.C.; Rieder, K.-A.; Tian, Y.; Chen, C. Concrete with discrete slender elements from mechanically recycled wind turbine blades. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 128, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodin, H.; Nassiri, S.; Englund, K.; Fakron, O.; Li, H. Recycled glass fiber reinforced polymer composites incorporated in mortar for improved mechanical performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baturkin, D.; Hisseine, O.A.; Masmoudi, R.; Tagnit-Hamou, A.; Massicotte, L. Valorization of recycled FRP materials from wind turbine blades in concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.; Nassiri, S.; Englund, K.; Li, H.; Chen, Z. Exploratory Study of Flexural Performance of Mechanically Recycled Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Shreds as Reinforcement in Cement Mortar. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2021, 2675, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-T.; Liu, M.-J.; Xiang, Y.; Fu, B. Valorization of macro fibers recycled from decommissioned turbine blades as discrete reinforcement in concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-D.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.-J.; Wang, L.; Yao, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-L. Indoor air quality in the primary school of China—Results from CIEHS 2018 study. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, D.; Foltynowicz, Z.; Christéen, J.; Skrifvars, M. Microwave pyrolysis as a method of recycling glass fibre from used blades of wind turbines. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chevali, V.S.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.-H. Current status of carbon fibre and carbon fibre composites recycling. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 193, 108053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, J.; Mareddy, S.S.; Mativenga, P.T. Energy intensity and environmental analysis of mechanical recycling of carbon fibre composite. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 81, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; McKechnie, J.; Turner, T.A.; Pickering, S.J. Energy and environmental assessment and reuse of fluidised bed recycled carbon fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 100, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; McKechnie, J.; Pickering, S.J. An assessment of financial viability of recycled carbon fibre in automotive applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 109, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Guo, G.; Memon, S.A.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.-H.; Xing, F. Recycling of carbon fibers from carbon fiber reinforced polymer using electrochemical method. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 78, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmay, P.; Haro, C.; Huacho, I.; Barzallo, D.; Bruno, J.C. Production and Analysis of the Physicochemical Properties of the Pyrolytic Oil Obtained from Pyrolysis of Different Thermoplastics and Plastic Mixtures. Molecules 2022, 27, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Karl, C.W.; Gagani, A.I.; Jørgensen, J.K. Composite Material Recycling Technology—State-of-the-Art and Sustainable Development for the 2020s. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Youn, J.R.; Gutowski, T.G. Life cycle energy analysis of fiber-reinforced composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalraj, S.K.; Kärki, T. A review on the recycling of waste carbon fibre/glass fibre-reinforced composites: Fibre recovery, properties and life-cycle analysis. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S. Recycling technologies for thermoset composite materials—Current status. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Pickering, S.; Walker, G.; Wong, K.; Rudd, C. Surface characterisation of carbon fibre recycled using fluidised bed. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2588–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, S.; Pinho, S.T. Recycling carbon fibre reinforced polymers for structural applications: Technology review and market outlook. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Meng, F.; Barlow, C.Y. Wind turbine blade end-of-life options: An eco-audit comparison. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Meng, F.; Barlow, C.Y. Wind turbine blade end-of-life options: An economic comparison. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).