Design Enhancement of Eductor for Active Vapor Transport and Condensation during Two-Phase Single-Species Flow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
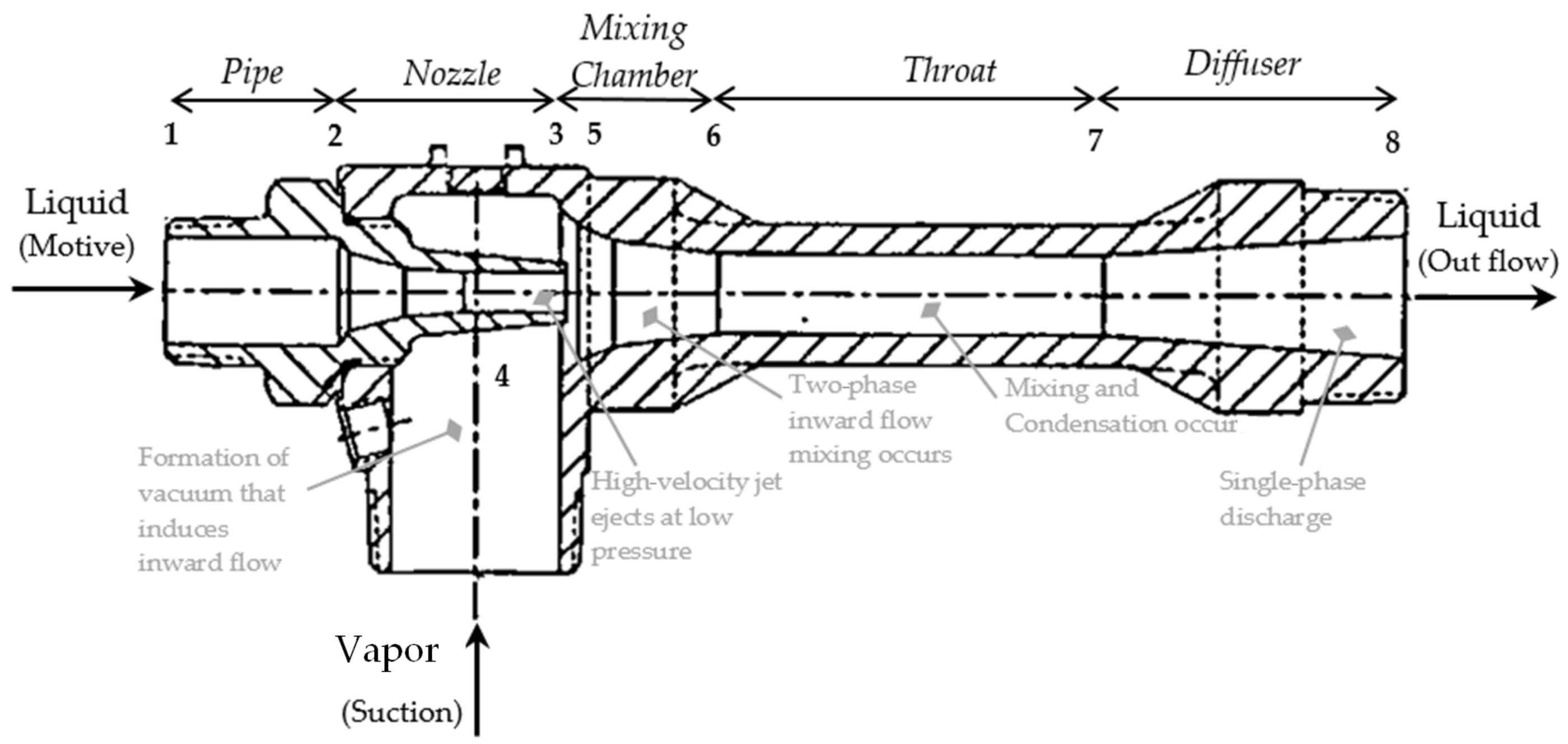
2. Methodology
2.1. Experimental Method
2.2. Computational Method
2.2.1. Solver Theory
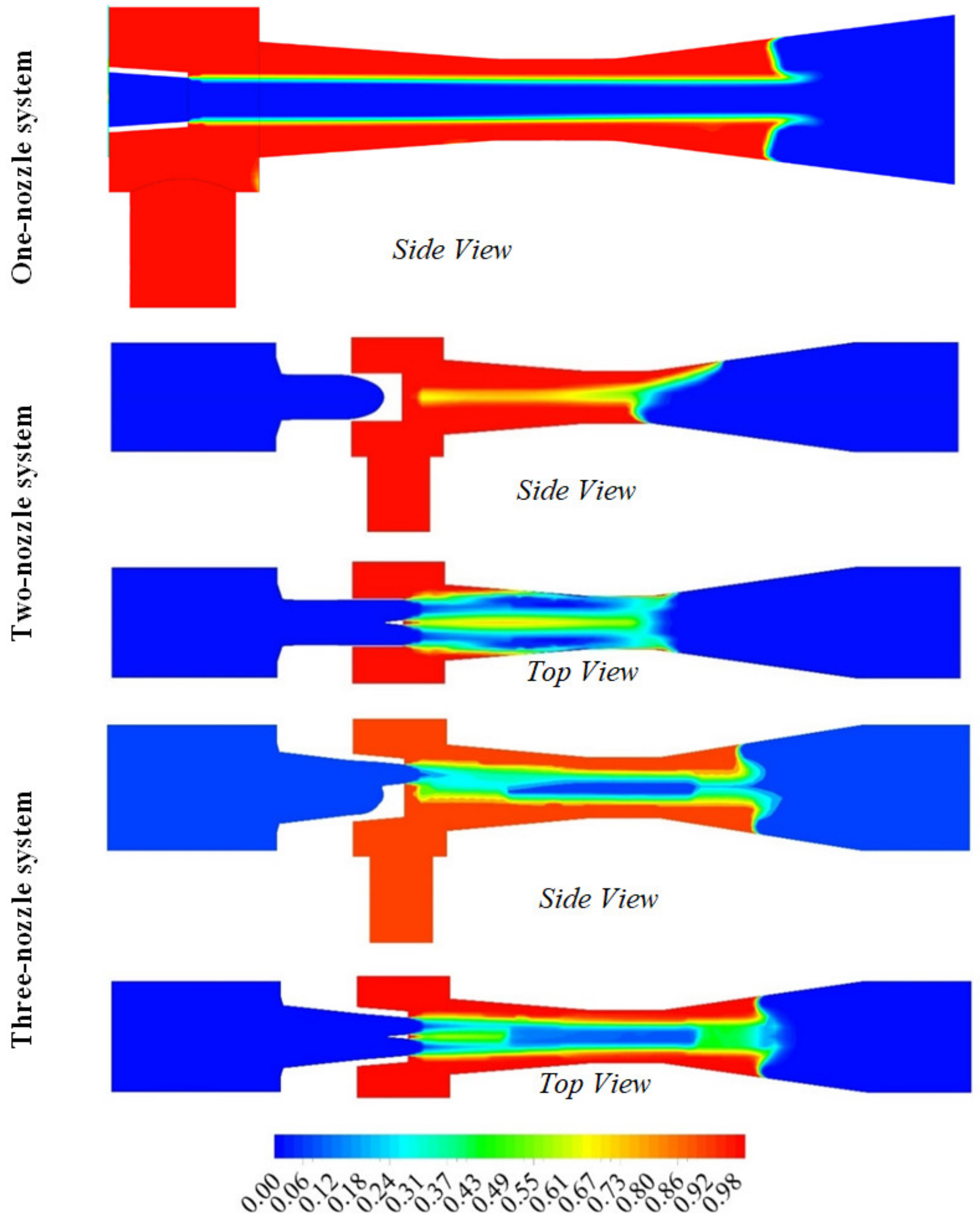
2.2.2. Computational Domain
2.2.3. Boundary Conditions
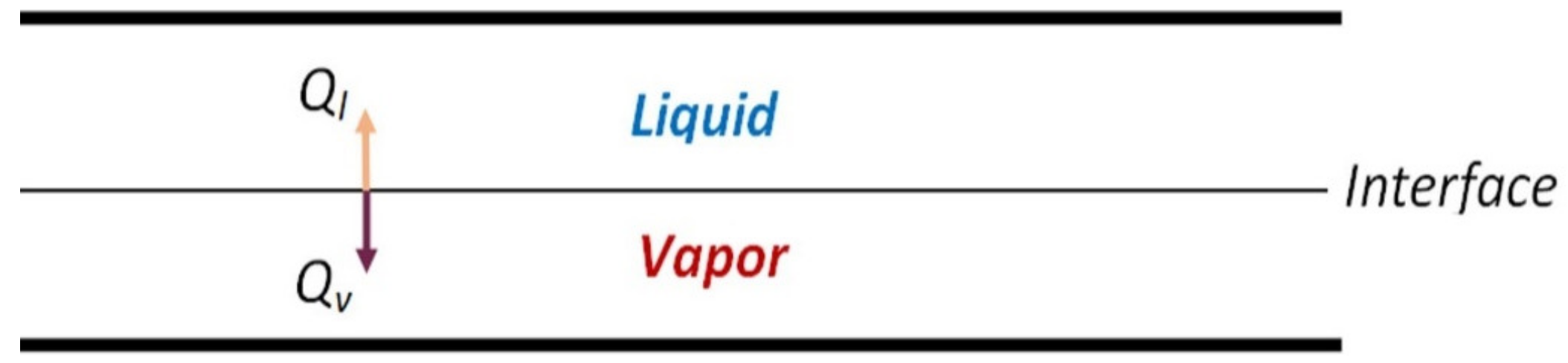
3. Anergy and Exergy in an Eductor
4. Performance Comparison
4.1. Relative Enhancement Study
4.1.1. Relative Enhancement in Mechanical Performance Coefficient ()
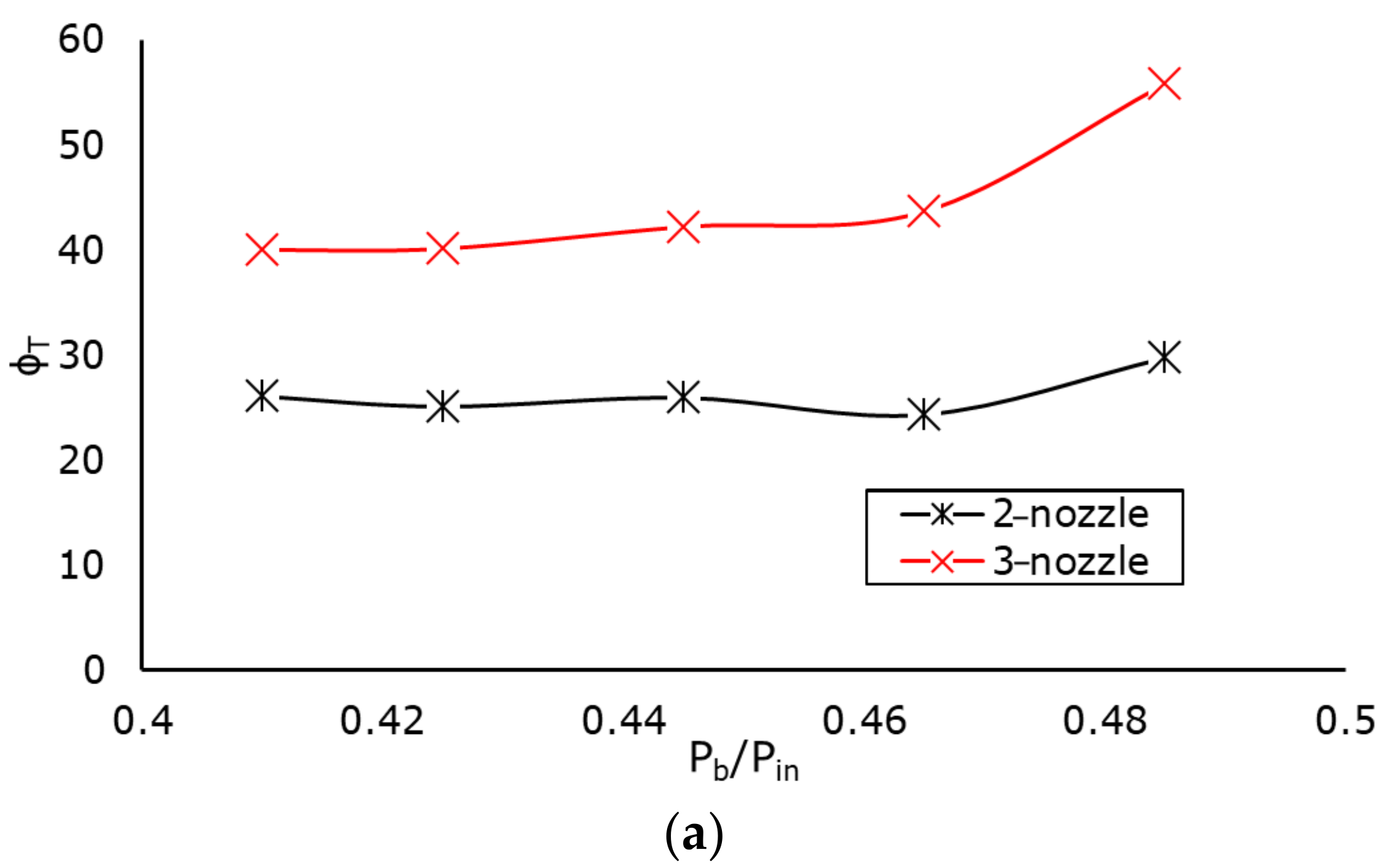
4.1.2. Relative Enhancement in Thermal Performance Coefficient ()
4.2. Heat Transfer Coefficient
5. Results and Discussion
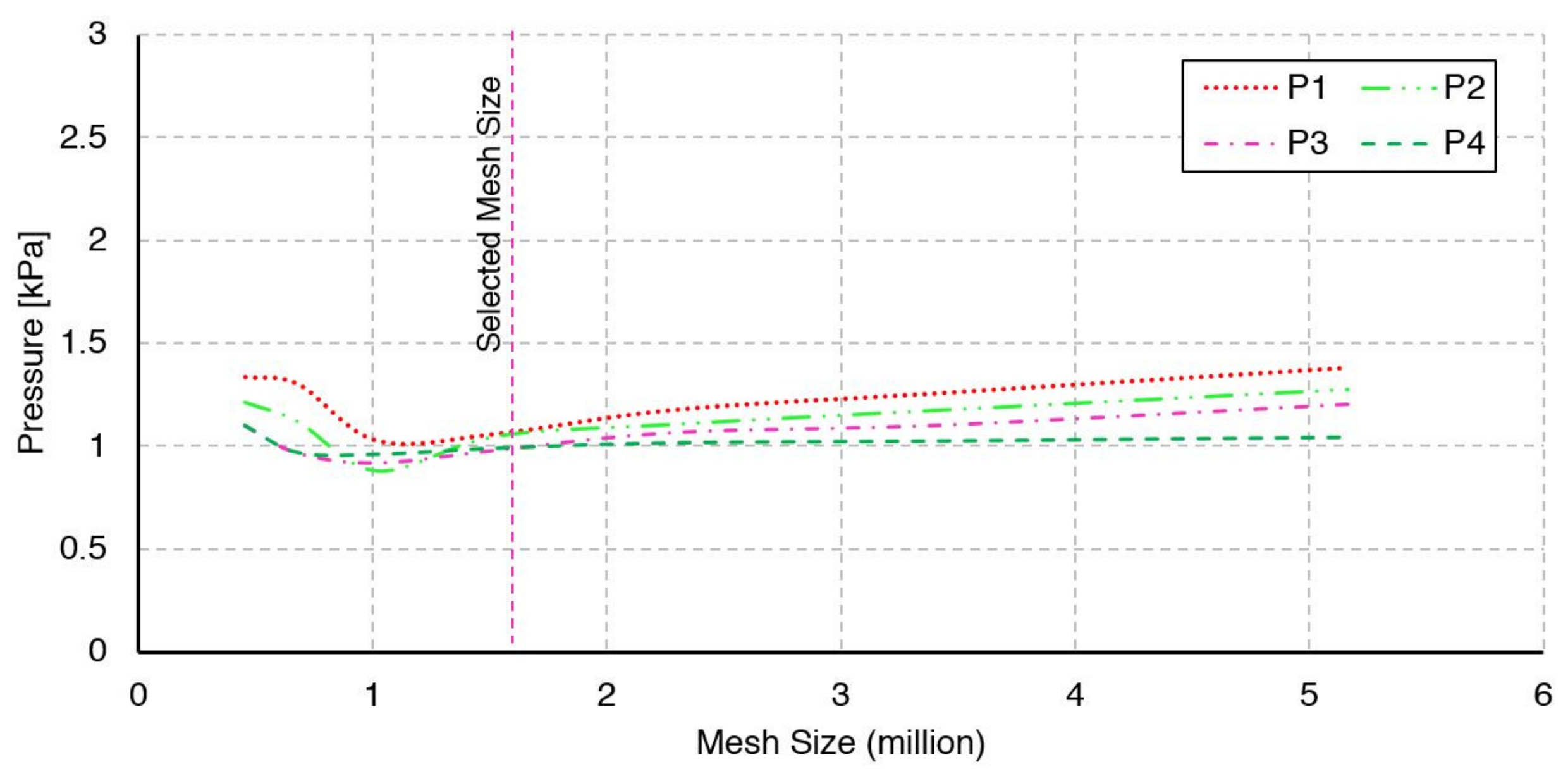
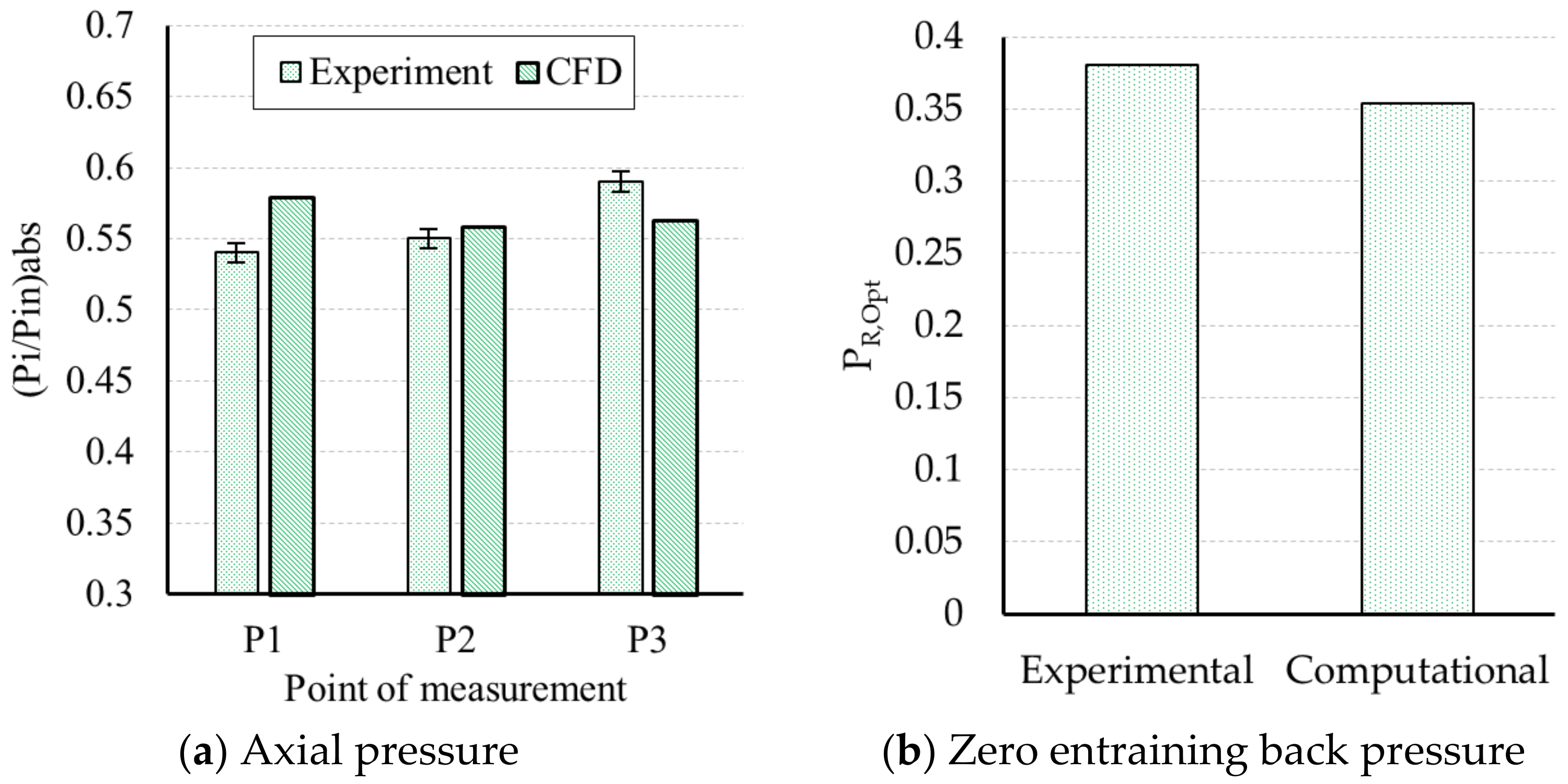
5.1. Verification of the Computational Process
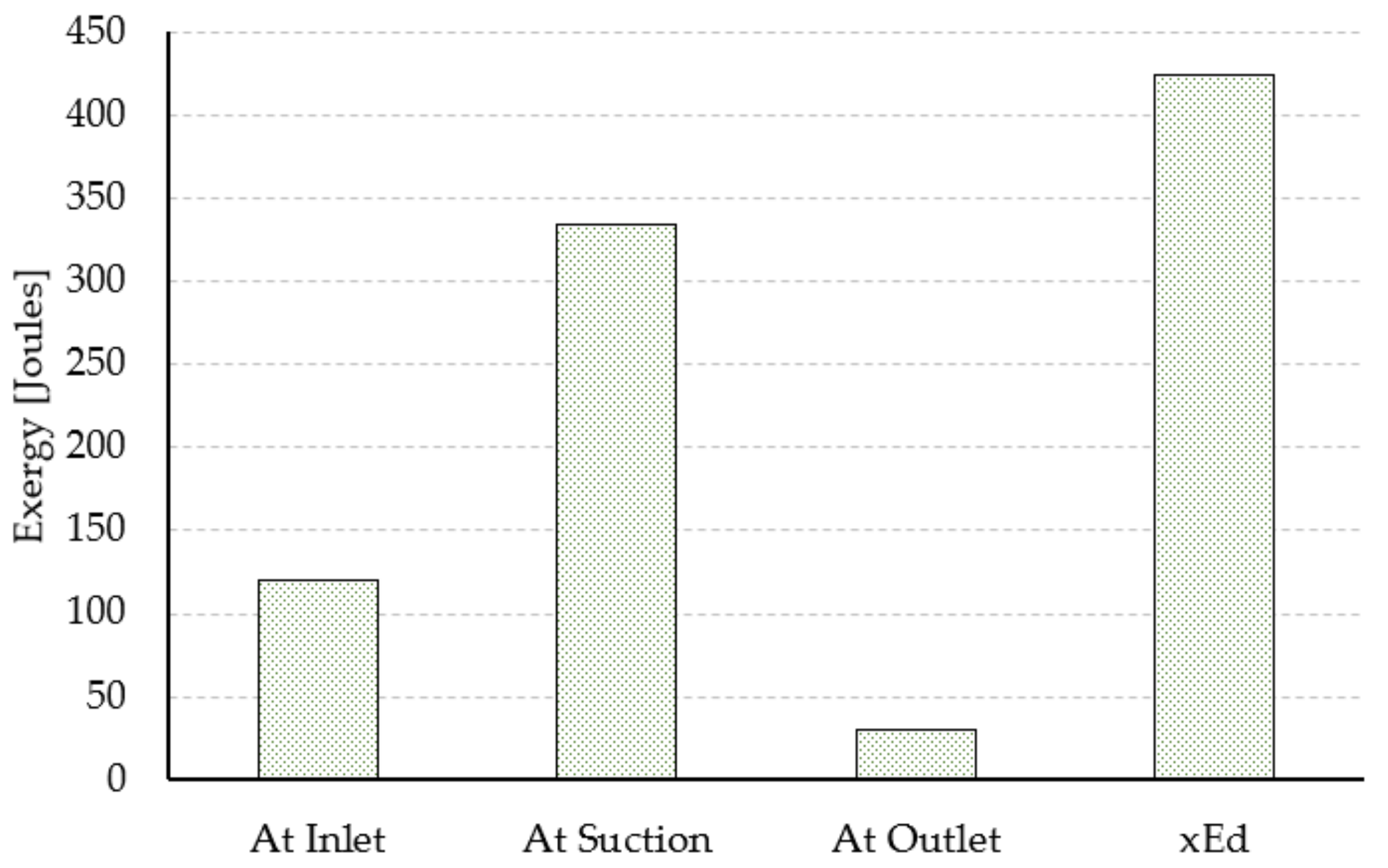
5.2. Exergy Analysis
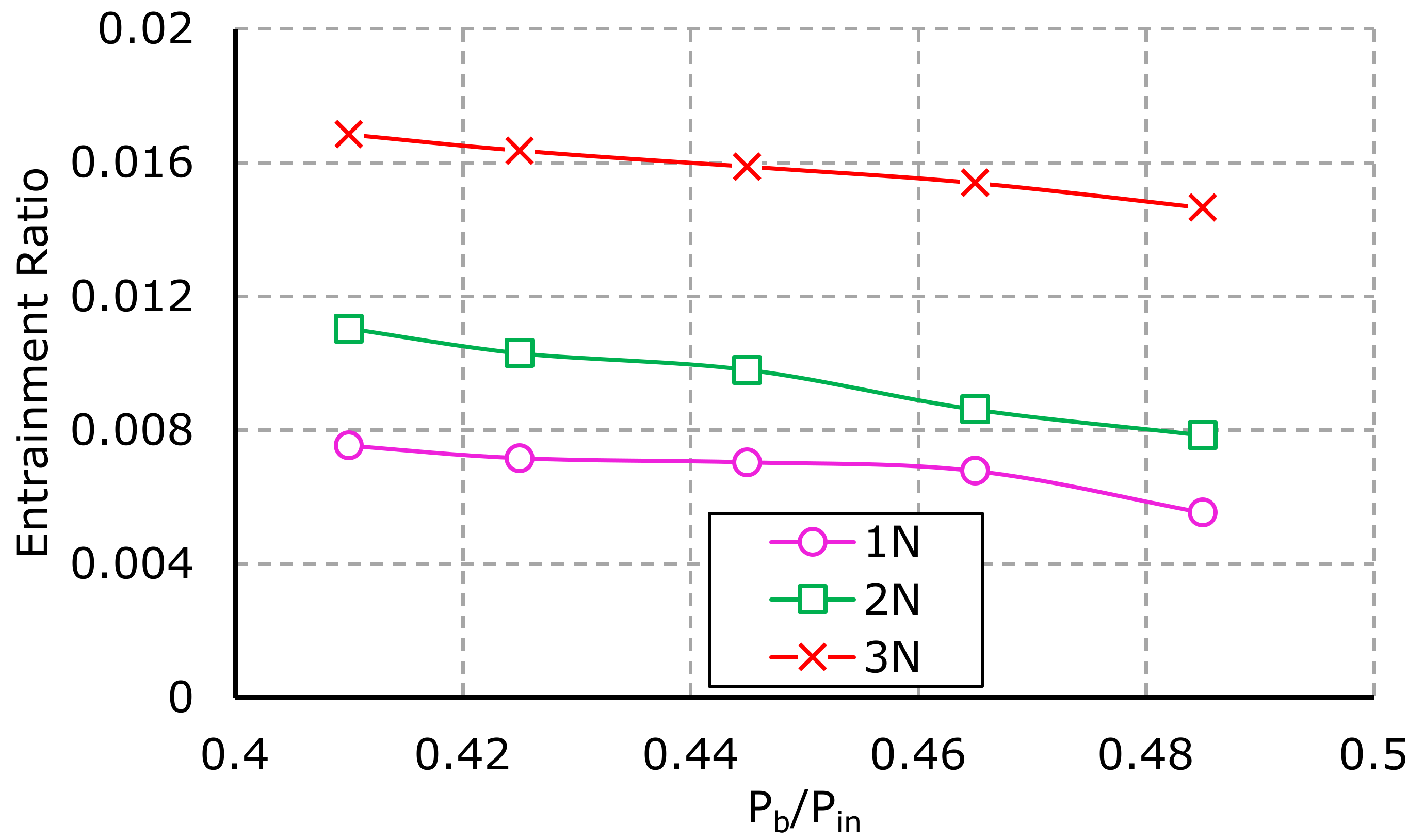
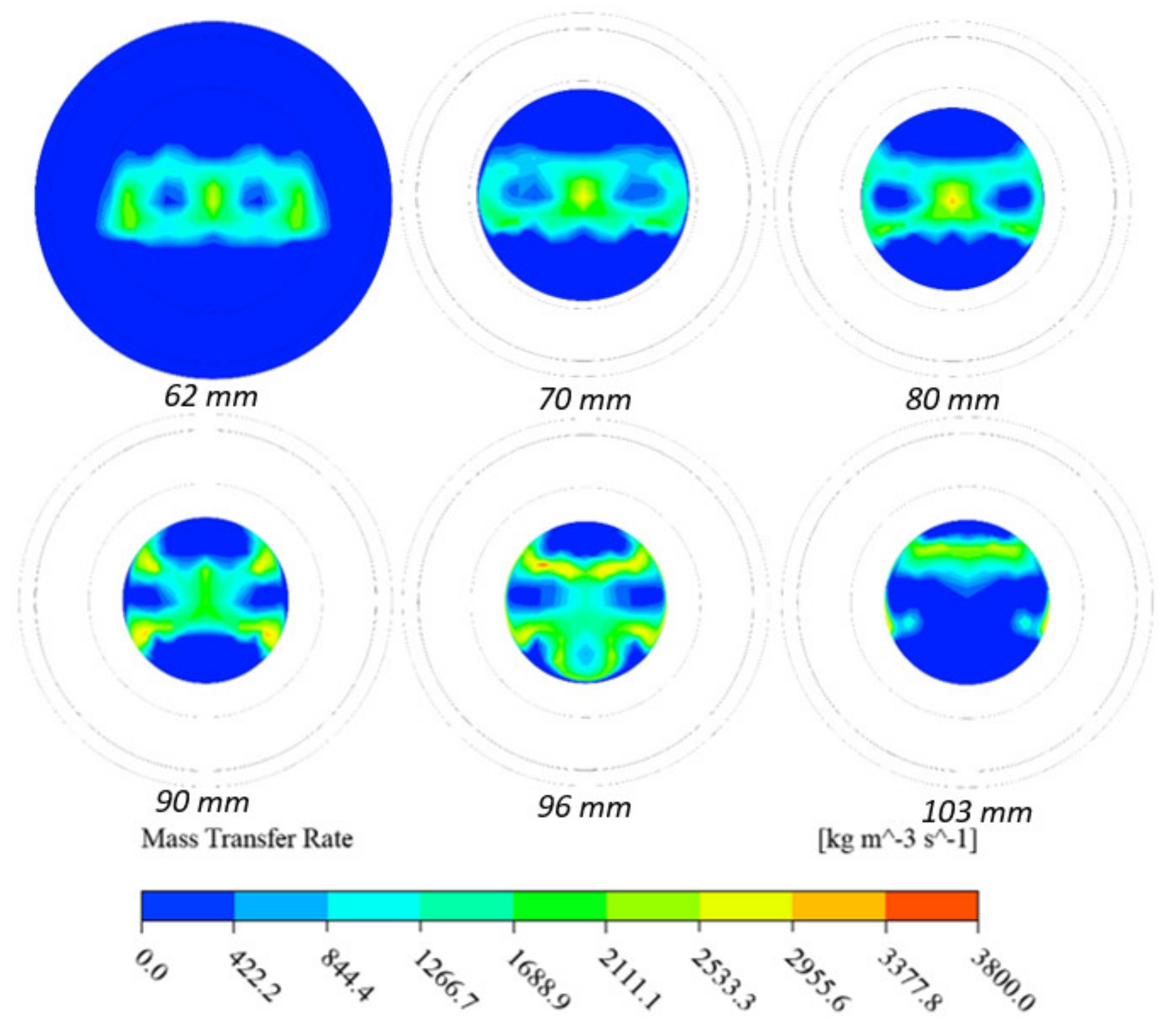
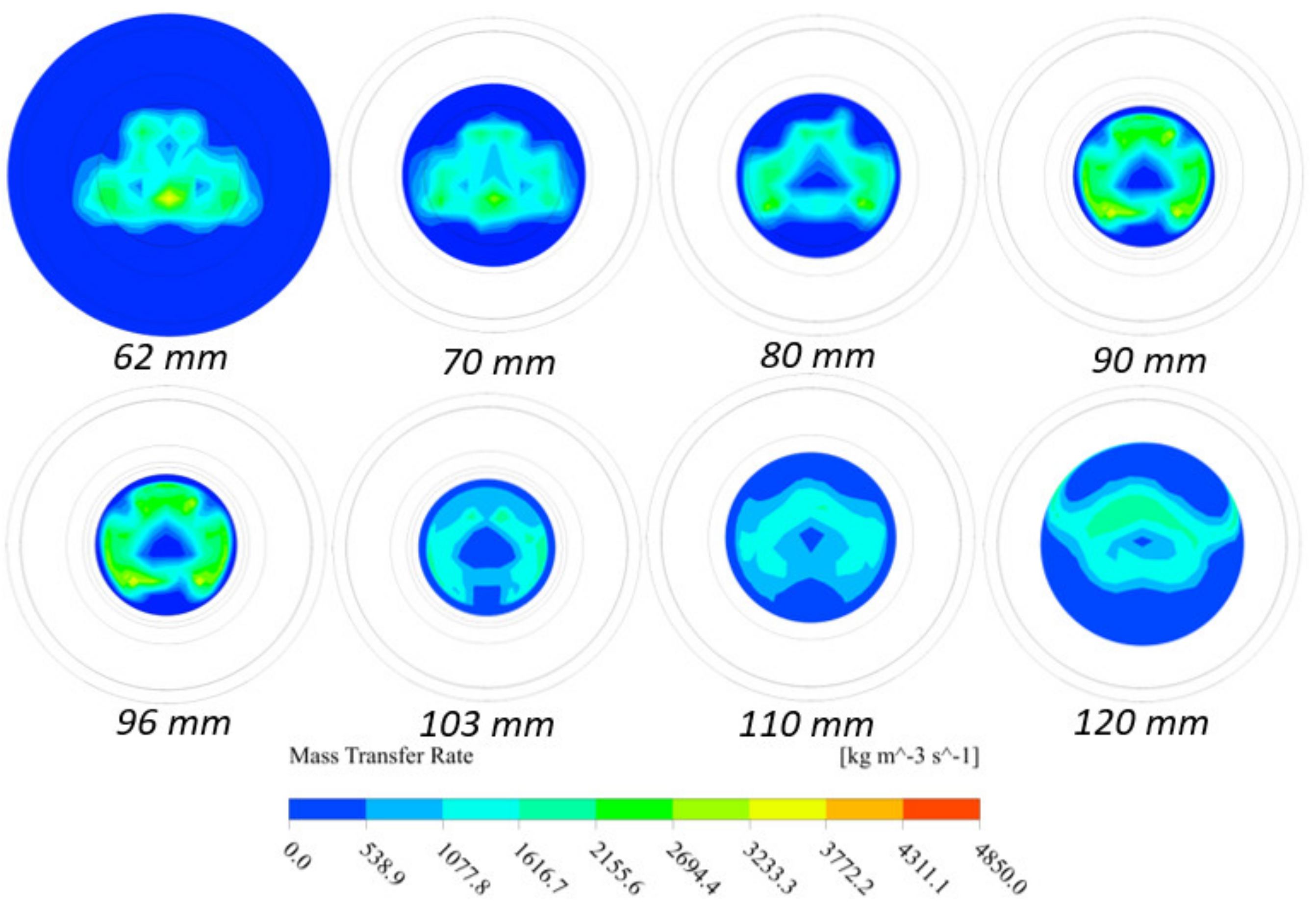
5.3. Computational Study
Performance Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics | p | Phase |
| 3D | Three-dimensional | D | Diameter |
| xe | Specific exergy | N | Number |
| xE | Exergy | Subscript | |
| h | Enthalpy | r | Region |
| s | Specific entropy | p | Phase |
| V | Velocity | o | Dead state |
| g | Acceleration due to gravity | d | Destruction |
| z | Elevation | v and l | Vapor and liquid |
| T | Temperature | nc | Non-condensing flow |
| ϕT | Relative enhancement in thermal performance coefficient | i | Number of nozzles |
| ϕm | Relative enhancement in mechanical performance coefficient | c | Condensing flow |
| Er | Entrainment ratio | b | Back |
| hDCC | Direct-contact heat transfer coefficient | in | In |
| hfg | Latent heat | TSA | Total surface area |
| AiA | Interface area | n | Nozzle |
| m˙ | Mass flow rate | ||
References
- Chang, Y.J.; Chen, Y.M. Enhancement of a steam-driven ejector using a novel application of the petal nozzle. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2000, 23, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garris, C.A.; Hong, W.J.; Mavriplis, C.M.; Shipman, J. The Pressure-Exchange Ejector Heat Pump. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Conference and Exposition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 15–20 November 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.J.; Alhussan, K.; Zhang, H.; Garris, C.A. A novel thermally driven rotor-vane/pressure-exchange ejector refrigeration system with environmental benefits and energy efficiency. Energy 2004, 29, 2331–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrowicz, S.; Kasperski, J. The numerical modeling of thermo-flow processes in high-speed rotation ejector used in refrigerating system. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Congress of Refrigeration, Beijing, China, 21–26 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.; Jagadeesh, G. Novel supersonic nozzles for mixing enhancement in supersonic ejectors. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 71, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, P.J.; Ramesh, V.; Meng, G.C.; Miller, D.N.; Domel, N. Air ejector pumping enhancement through pulsing primary flow. In Proceedings of the 2nd AIAA Flow Control Conference, Portland, Oregon, 28 June–1 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Riffat, S.B.; Omer, S.A. CFD modelling and experimental investigation of an ejector refrigeration system using methanol as the working fluid. Int. J. Energy Res. 2001, 25, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Hu, Y.; Giridharan, K. Numerical investigation of geometry parameters for pressure recovery of an adjustable ejector in multi-evaporator refrigeration system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 61, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariafar, K. Performance evaluation of a model thermos-compressor using computational fluid dynamics. Int. J. Mech. 2012, 6, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yapici, R.; Ersoy, H.K. Performance characteristics of the ejector refrigeration system based on the constant area ejector flow model. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 3117–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tao, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J. CFD analysis of ejector in an ejector cooling system. In Proceedings of the International Congress of Refrigeration, Beijing, China, 21–26 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S.; Chunnanond, K. Performance prediction of steam ejector using computational fluid dynamics: Part 1. Validation of the CFD results. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2007, 46, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Shatilla, Y.; Zhang, T. CFD-based design and simulation of hydrocarbon ejector for cooling. Energy 2019, 167, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianthong, K.; Seehanam, W.; Behnia, M.; Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S. Investigation and improvement of ejector refrigeration system using computational fluid dynamics technique. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE. Steam-Jet Refrigeration Equipment. In ASHRAE Equipment Handbook; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, M.; Utomo, T.; Woo, J.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, H.; Chung, H. CFD investigation on the flow structure inside thermo vapor compressor. Energy 2010, 35, 2694–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H. Design and numerical investigation of an adaptive nozzle exit position ejector in multi-effect distillation desalination system. Energy 2017, 140, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc. ANSYS Fluent Theory Guide; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Koirala, R.; Inthavong, K.; Date, A. Numerical study of flow and direct contact condensation of entrained vapor in water jet eductor. Exp. Comput. Multiph. Flow 2021, 4, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, R.; Ve, Q.L.; Rupakheti, E.; Inthavong, K.; Date, A. Performance Analysis of an Eductor-based Membrane Distillation Unit. Water 2022, 14, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, R.; Zhang, X.; Rupakheti, E.; Inthavong, K.; Date, A. Performance study of Eductor with Finite secondary source for Membrane Distillation. Energies 2022, 15, 8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chong, D.; Yan, J. Modeling and experimental investigation on water-driven steam injector for waste heat recovery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 40, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Chughtai, I.R.; Inayat, M.H. Experimental and numerical analysis of steam jet pump. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2011, 37, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
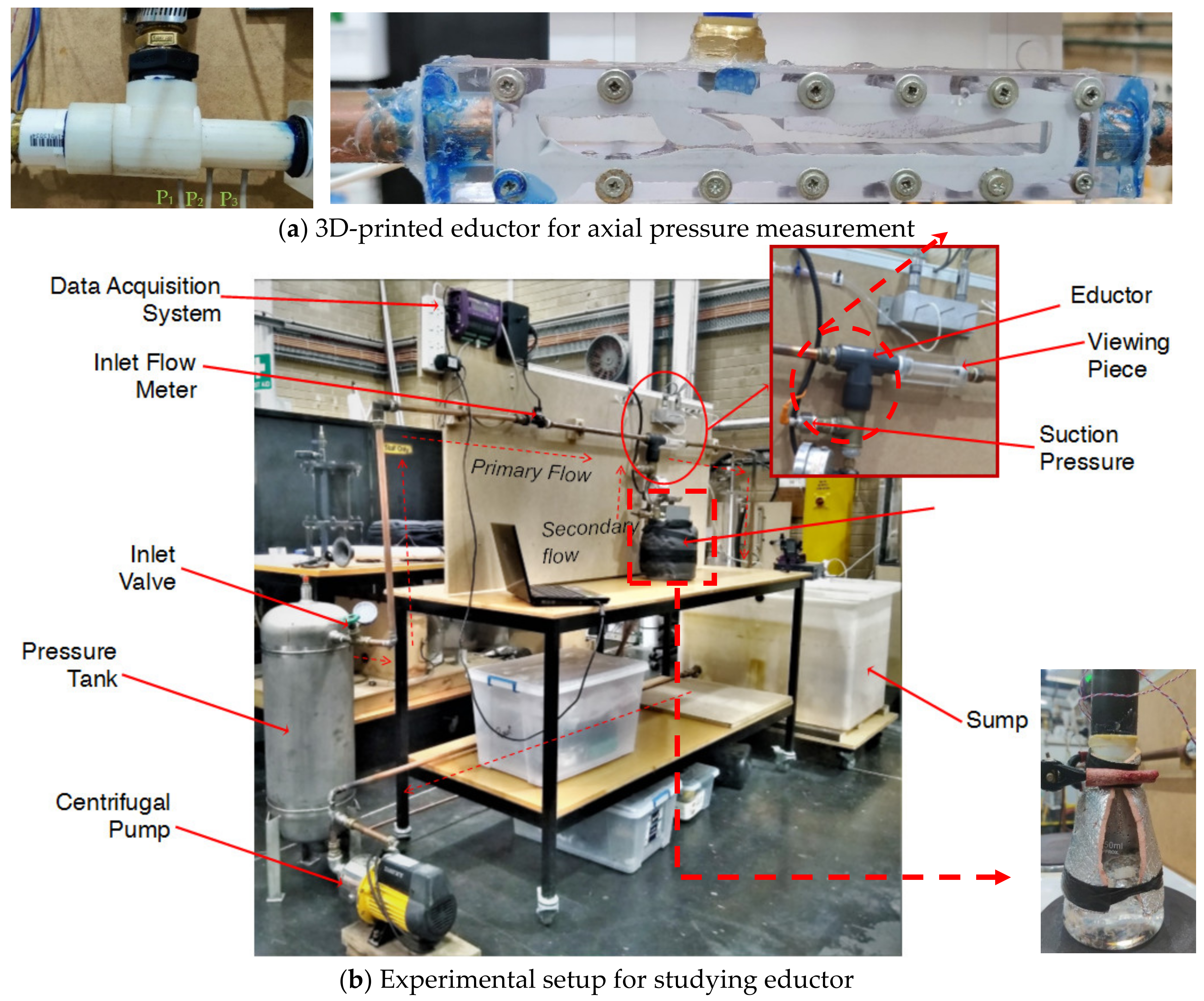










| Inlet Pressure | 250 kPa (absolute) |
| Outlet Pressure | 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150 kPa |
| Suction pressure | 82 kPa |
| Primary mass flow rate | 6.2 LPM |
| Nozzle Reynold’s number | 100,820.2 |
| Outlet Reynold’s number | 62,732.58 |
| Point | Eductor Region | Exergy Equation | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Primary inlet | J/kg | (18) | |
| 2 | Primary outlet | J/kg | (19) | |
| 3 | Secondary inlet | J/kg | (20) | |
| 4 | Secondary outlet | J/kg | (21) | |
| 5 | Mixing chamber inlet | J/kg | (22) | |
| (23) | ||||
| 6 | Mixing chamber outlet | J/kg | (24) | |
| (25) | ||||
| 7 | Throat outlet | J/kg | (26) | |
| (27) | ||||
| 8 | Outlet | J/kg | (28) |
| Zone | Exergy Destruction | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary nozzle | J | (30) | |
| Secondary nozzle | J | (31) | |
| Suction chamber | J | (32) | |
| Mixing chamber | J | (33) | |
| Throat | J | (34) | |
| Diffuser | J | (35) | |
| Overall | J | (36) |
| Design | Dn | Nn | m˙s | ATSA | hDCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | kg/s | m2 | kW/K·m2 | ||
| Design 01 | 0.0028 | 1 | 0.00300 | 0.00048 | 210.53 |
| Design 02 | 0.0019 | 2 | 0.00439 | 0.00027 | 532.50 |
| Design 03 | 0.0016 | 3 | 0.00671 | 0.00031 | 711.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koirala, R.; Ve, Q.L.; Rupakheti, E.; Inthavong, K.; Date, A. Design Enhancement of Eductor for Active Vapor Transport and Condensation during Two-Phase Single-Species Flow. Energies 2023, 16, 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031265
Koirala R, Ve QL, Rupakheti E, Inthavong K, Date A. Design Enhancement of Eductor for Active Vapor Transport and Condensation during Two-Phase Single-Species Flow. Energies. 2023; 16(3):1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031265
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoirala, Ravi, Quoc Linh Ve, Eliza Rupakheti, Kiao Inthavong, and Abhijit Date. 2023. "Design Enhancement of Eductor for Active Vapor Transport and Condensation during Two-Phase Single-Species Flow" Energies 16, no. 3: 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031265
APA StyleKoirala, R., Ve, Q. L., Rupakheti, E., Inthavong, K., & Date, A. (2023). Design Enhancement of Eductor for Active Vapor Transport and Condensation during Two-Phase Single-Species Flow. Energies, 16(3), 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031265








