Synthesis of (Cu,Mn,Co)3O4 Spinel: Effects of Citrate-to-Nitrate Ratio on Its Homogeneity and Electrical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
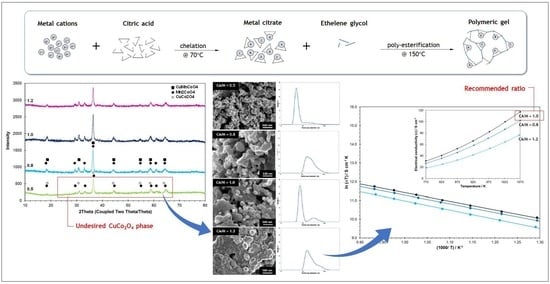
3.1. CMC Spinel Powders
3.2. CMC Spinel Sintered at 1200 °C
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahmud, L.S.; Muchtar, A.; Somalu, M.R. Challenges in Fabricating Planar Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: A Review. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.S.; de Souza, T.M. Novel Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Technologies: A Literature Review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 26020–26036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, X. Chromium Deposition and Poisoning of Cathodes of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells—A Review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk-Windisch, H.; Svensson, J.E.; Froitzheim, J. The Effect of Temperature on Chromium Vaporization and Oxide Scale Growth on Interconnect Steels for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. J. Power Source 2015, 287, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Mason, J.H.; Li, W.; Liu, X. Comprehensive Review of Chromium Deposition and Poisoning of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) Cathode Materials. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, J.C.W.; Muchtar, A.; Somalu, M.R.; Ghazali, M.J. Metallic Interconnects for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell: A Review on Protective Coating and Deposition Techniques. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 9219–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of CuFeMnO4 Prepared by Co-Precipitation Method. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 3581–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; You, P.F.; Zhang, H.L.; Yang, X.G.; Luo, M.Q.; Zeng, C. Preparation and Performances of Cu–Co Spinel Coating on Ferritic Stainless Steel for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Interconnect. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 3273–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, I.; Agarwal, B.; Goyal, P.; Singh, S.A. Recent Advances in Material and Performance Aspects of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 848, 113315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, A.; Bellusci, M.; McPhail, S.J.; Padella, F.; Reale, P.; Hong, J.E.; Steinberger-Wilckens, R.; Carlini, M. Cu-Mn-Co Oxides as Protective Materials in SOFC Technology: The Effect of Chemical Composition on Mechanochemical Synthesis, Sintering Behaviour, Thermal Expansion and Electrical Conductivity. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 37, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talic, B.; Falk-Windisch, H.; Venkatachalam, V.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Wiik, K.; Lein, H.L. Effect of Coating Density on Oxidation Resistance and Cr Vaporization from Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Interconnects. J. Power Source 2017, 354, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Geng, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, F. Effect of NiFe2 Coating Thickness on High Temperature Oxidation and Electrical Behavior of Coated Steel Interconnect. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 858, 157746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufner, J.F.; Castro, R.H.R.; Holland, T.B.; Benthem, K. Van Mechanical Properties of Individual MgAl2O4 Agglomerates and Their Effects on Densification. Acta Mater. 2014, 69, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molin, S. Evaluation of Electrodeposited Mn-Co Protective Coatings on Crofer 22 APU Steel. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2018, 15, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, Y. Sol–Gel Research in China: A Brief History and Recent Research Trends in Synthesis of Sol–Gel Derived Materials and Their Applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–16, In press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Wei, Y.S.; Wu, S.H. Preparation and Characterization of Cr-Doped LiMnO2 Cathode Materials by Pechini’s Method for Lithium Ion Batteries. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samat, A.A.; Somalu, M.R.; Muchtar, A.; Hassan, O.H.; Osman, N. LSC Cathode Prepared by Polymeric Complexation Method for Proton-Conducting SOFC Application. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, A.E.; Hall, S.R.; Schnepp, Z. The Evolution of ‘Sol–Gel’ Chemistry as a Technique for Materials Synthesis. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, V.R.; Humbe, A.V.; More, S.D.; Jadhav, K.M. Sol-Gel Auto Combustion Synthesis and Characterizations of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles: Different Fuels Approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2019, 248, 114388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanasiriwech, D.; Wattanasiriwech, S. Effects of Fuel Contents and Surface Modification on the Sol-Gel Combustion Ce0.9 Gd0.1O1.95 Nanopowder. Energy Procedia 2013, 34, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihaib, Z.; Puleo, F.; Pantaleo, G.; La Parola, V.; Valverde, J.L.; Gil, S.; Liotta, L.F.; Fendler, A.G. The Effect of Citric Acid Concentration on the Properties of LaMnO3 as a Catalyst for Hydrocarbon Oxidation. Catalysts 2019, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadabadi, H.; Allahkaram, S.R.; Kordijazi, A.; Akbarzadeh, O.; Rohatgi, P.K. Structural Characterization of LaCoO3 Perovskite Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol–Gel Autocombustion Method. Eng. Rep. 2021, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjeh, M.; Amiri, O.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Shabani-Nooshabadi, M. Preparation and Study of Characteristics of LiCoO2/Fe3O4/Li2B2O4 nanocomposites as Ideal Active Materials for Electrochemical Hydrogen Storage. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 23430–23436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijo, A.K. Influence of Fuel-Nitrate Ratio on the Structural and Magnetic Properties of Fe and Cr Based Spinels Prepared by Solution Self Combustion Method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.; Faccio, R.; Martínez, J.; Pardo, H.; Montenegro, B.; Plá Cid, C.C.; Pasa, A.A.; Mombrú, Á.W. Effect of Lanthanide on the Microstructure and Structure of LnMn0.5Fe0.5O3 Nanoparticles with Ln=La, Pr, Nd, Sm and Gd Prepared by the Polymer Precursor Method. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 221, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, D.S.; Rosenhaim, R.; Lima, S.J.G.; Longo, E.; De Souza, A.G.; Dos Santos, I.M.G. The Characterization of CoxZn7-XSb2O12 Spinel Obtained by the Pechini Method. Mater. Res. 2005, 8, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, J.C.W.; Muchtar, A.; Somalu, M.R.; Ghazali, M.J.; Raharjo, J. Formation of Sol–Gel Derived (Cu,Mn,Co)3O4 Spinel and Its Electrical Properties. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 7641–7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Peng, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, F. hui Effect of a Small Increase in the Ni Content on the Properties of a Laser Surface Clad Fe-Based Alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 4420–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharuddin, N.A.; Muchtar, A.; Somalu, M.R.; Kalib, N.S.; Raduwan, N.F. Synthesis and Characterization of Cobalt-Free SrFe0·8Ti0·2O3-δ Cathode Powders Synthesized through Combustion Method for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 44, 30682–30691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Yin, W.; Cao, L.; Zeng, Y. Synthesis of Manganese-Zinc Ferrite Nanopowders Prepared by a Microwave-Assisted Auto-Combustion Method: Influence of Sol-Gel Chemistry on Microstructure. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 23, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brylewski, T.; Kucza, W.; Adamczyk, A.; Kruk, A.; Stygar, M.; Bobruk, M.; Dąbrowa, J. Microstructure and Electrical Properties of Mn1+xCo2−xO4 (0≤x≤1.5) Spinels Synthesized Using EDTA-Gel Processes. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 13873–13882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobler, A.; Lohmiller, J.; Schäfer, J.; Kerber, M.; Castrup, A.; Kashiwar, A.; Gruber, P.A.; Albe, K.; Hahn, H.; Kübel, C. Deformation-Induced Grain Growth and Twinning in Nanocrystalline Palladium Thin Films. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Agli, G.; Mascolo, G.; Mascolo, M.C.; Pagliuca, C. Weakly-Agglomerated Nanocrystalline (ZrO2)0.9(Yb2O3) 0.1 Powders Hydrothermally Synthesized at Low Temperature. Solid State Sci. 2006, 8, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridigliozzi, L.; Dell’agli, G.; Biesuz, M.; Sglavo, V.M.; Pansini, M. Effect of the Precipitating Agent on the Synthesis and Sintering Behavior of 20 Mol% Sm-Doped Ceria. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.D.; Mukhopadhyay, J.; Basu, R.N. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline MnCo2O4-d Spinel for Protective Coating Application in SOFC. ECS Trans. 2011, 35, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Basu, A.; Brinkman, A.W. Small Polaron Hopping in Spinel Manganates. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2005, 72, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majedi, A.; Abbasi, A.; Davar, F. Green Synthesis of Zirconia Nanoparticles Using the Modified Pechini Method and Characterization of Its Optical and Electrical Properties. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 77, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| CA/MN | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystallinity | 59.0% | 90.3% | 88.5% | 77.8% |
| CuCo2O4 Cubic (a = 0.8140 nm) | 22.6% | - | - | - |
| Mn2CoO4 Tetragonal (a = 0.8090 nm, c = 0.9270 nm) | 77.4% | 41.8% | 44.3% | 45.7% |
| CuMnCoO4 Cubic (a = 0.8189 nm) | - | 58.2% | 55.7% | 54.3% |
| Crystallite size | 21 nm | 19 nm | 21 nm | 26 nm |
| CA/MN | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystallinity | 62.1% | 70.0% | 60.4% |
| MnCo2O4 Cubic (a = 0.8269 nm) | 49.0% | 46.4 | 46.1 |
| Cu1.5Mn1.5O4 Cubic (a = 0.8300 nm) | 51% | 53.6 | 53.9 |
| Grain size | 15.14 μm | 15.85 μm | 13.97 μm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mah, J.C.W.; Aznam, I.; Muchtar, A.; Somalu, M.R.; Raharjo, J. Synthesis of (Cu,Mn,Co)3O4 Spinel: Effects of Citrate-to-Nitrate Ratio on Its Homogeneity and Electrical Properties. Energies 2023, 16, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031382
Mah JCW, Aznam I, Muchtar A, Somalu MR, Raharjo J. Synthesis of (Cu,Mn,Co)3O4 Spinel: Effects of Citrate-to-Nitrate Ratio on Its Homogeneity and Electrical Properties. Energies. 2023; 16(3):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031382
Chicago/Turabian StyleMah, Joelle C. W., Isyraf Aznam, Andanastuti Muchtar, Mahendra Rao Somalu, and Jarot Raharjo. 2023. "Synthesis of (Cu,Mn,Co)3O4 Spinel: Effects of Citrate-to-Nitrate Ratio on Its Homogeneity and Electrical Properties" Energies 16, no. 3: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031382
APA StyleMah, J. C. W., Aznam, I., Muchtar, A., Somalu, M. R., & Raharjo, J. (2023). Synthesis of (Cu,Mn,Co)3O4 Spinel: Effects of Citrate-to-Nitrate Ratio on Its Homogeneity and Electrical Properties. Energies, 16(3), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031382