Effect of Fly Ash and Steel Fiber Content on Workability and Mechanical Properties of Roadway Side Backfilling Materials in Deep Mine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
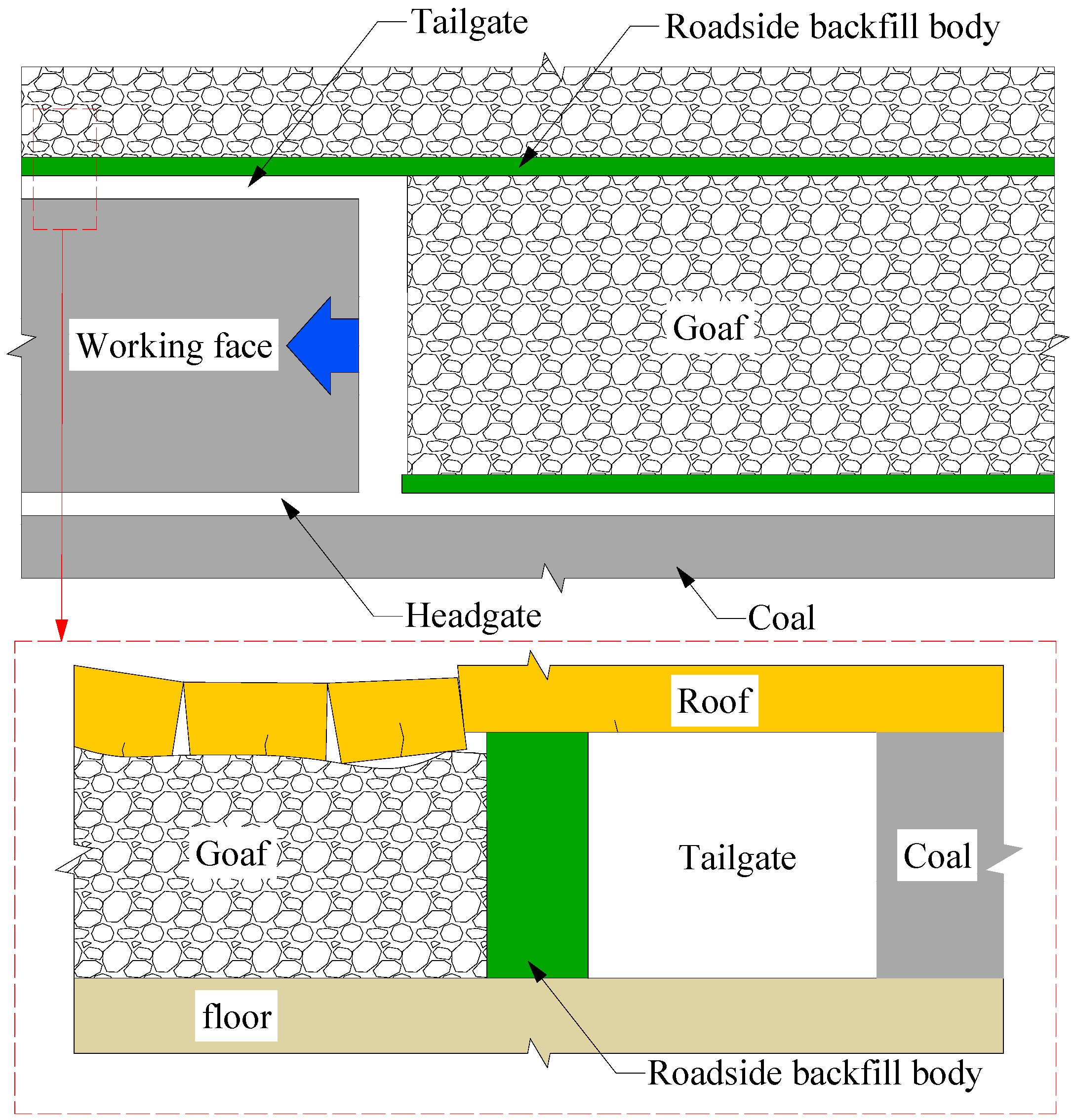
2. Gob-Side Entry Retaining Technology with Roadside Backfill Body
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Raw Materials
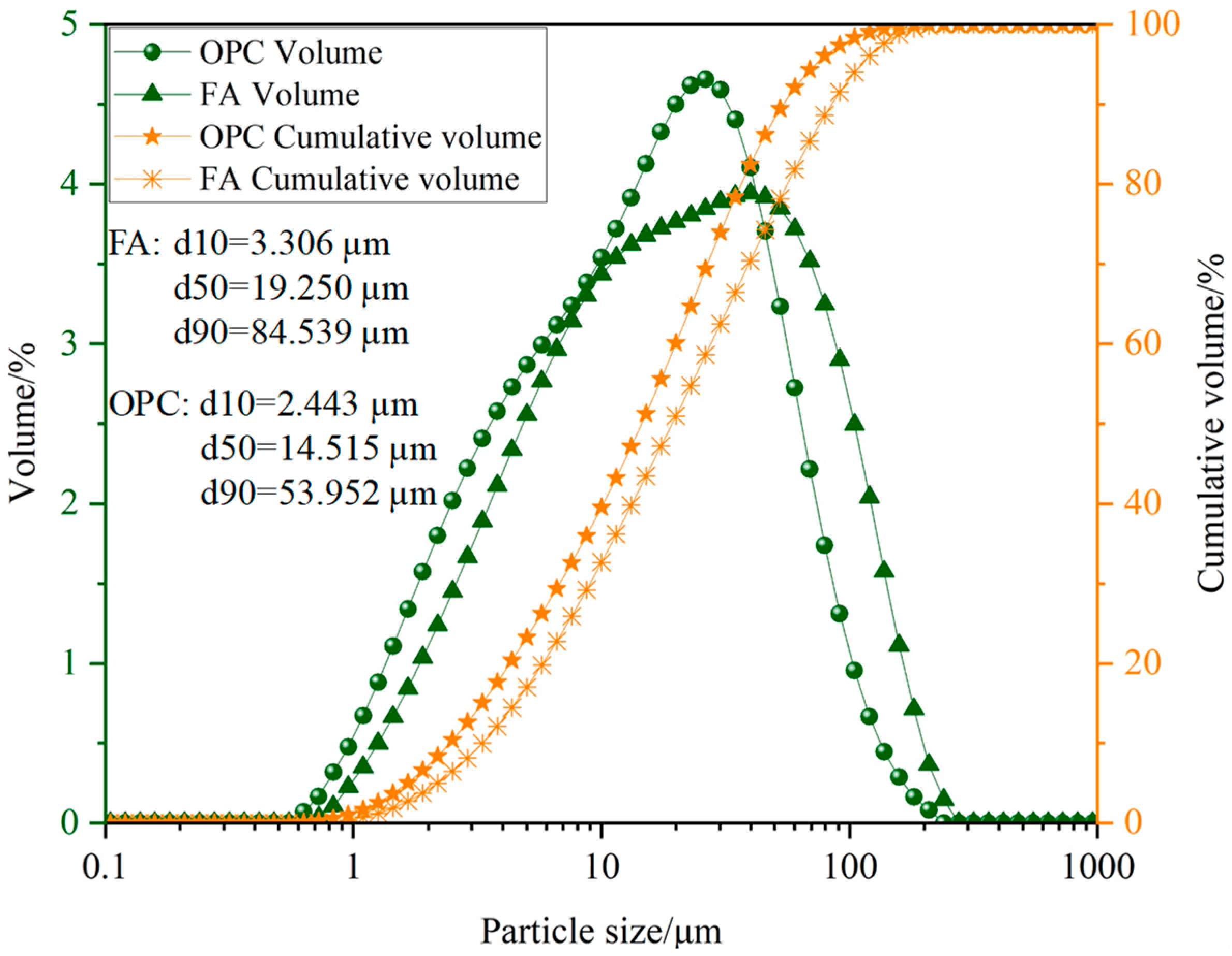
3.1.1. Cementitious Materials
3.1.2. Aggregate
3.1.3. Steel Fibers and Water
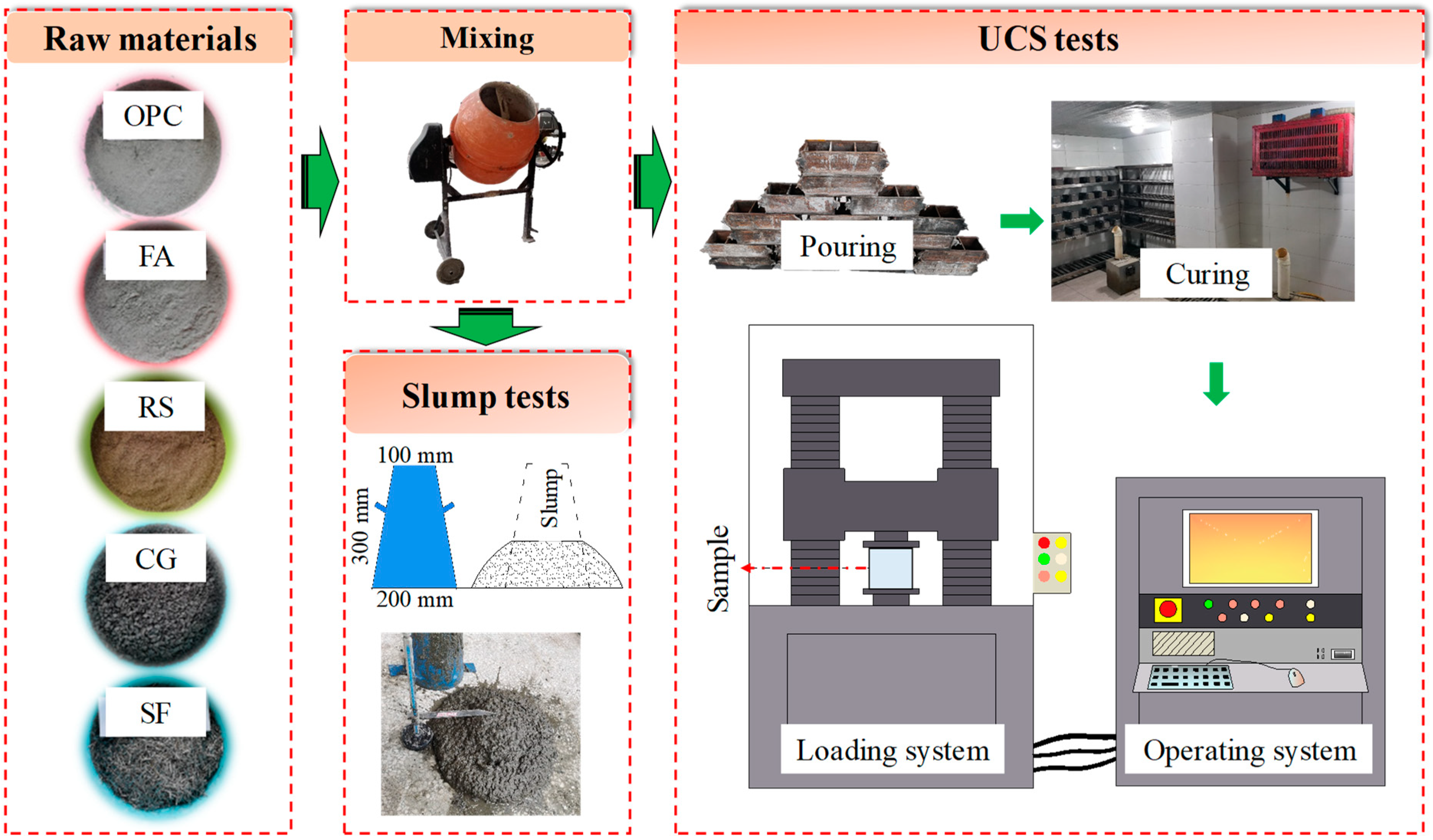
3.2. Experimental Design
3.3. Sample Preparation and Curing Conditions
3.4. Methods
3.4.1. Slump Tests
3.4.2. UCS Tests
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Workability Analysis
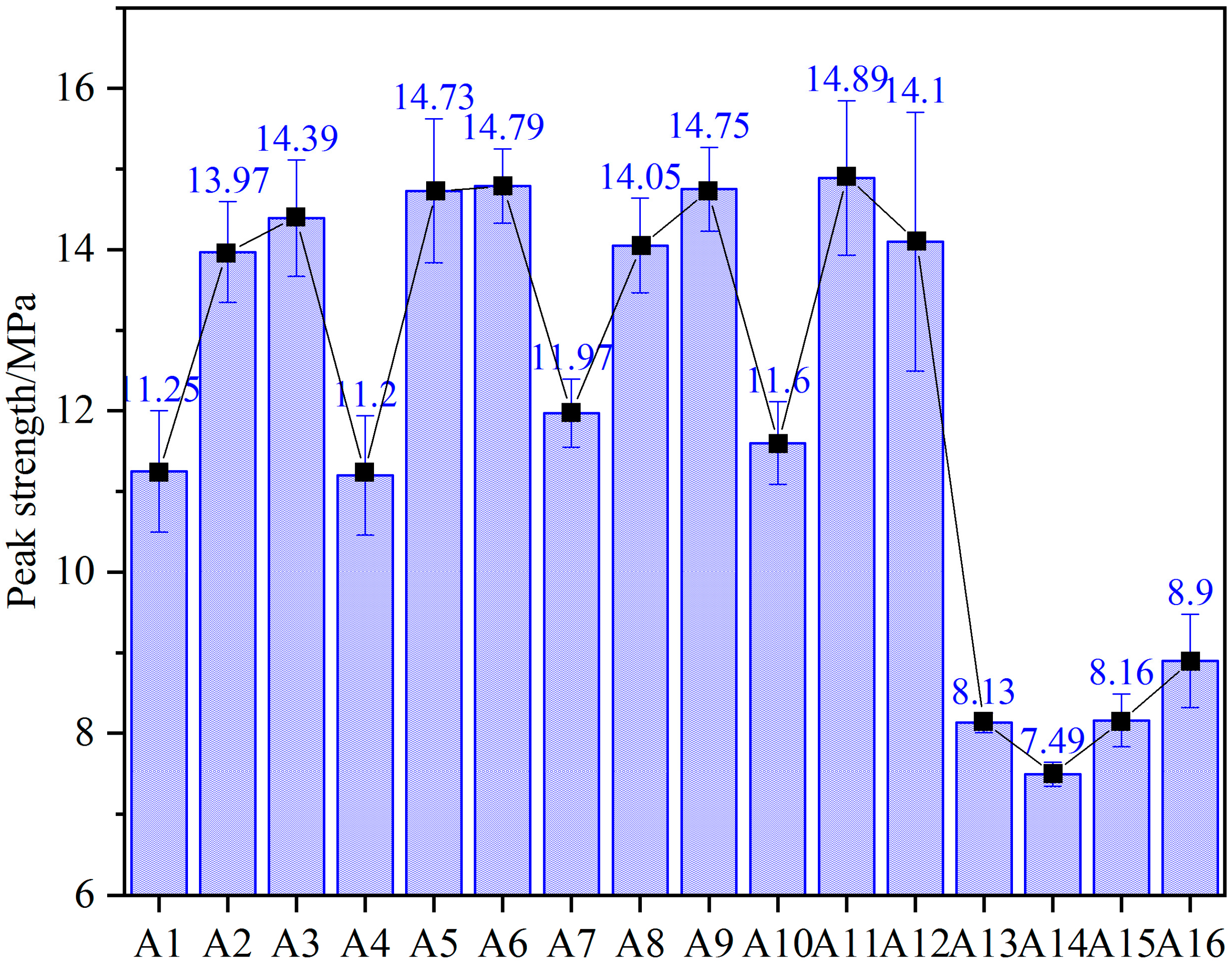
4.2. Peak Strength Analysis
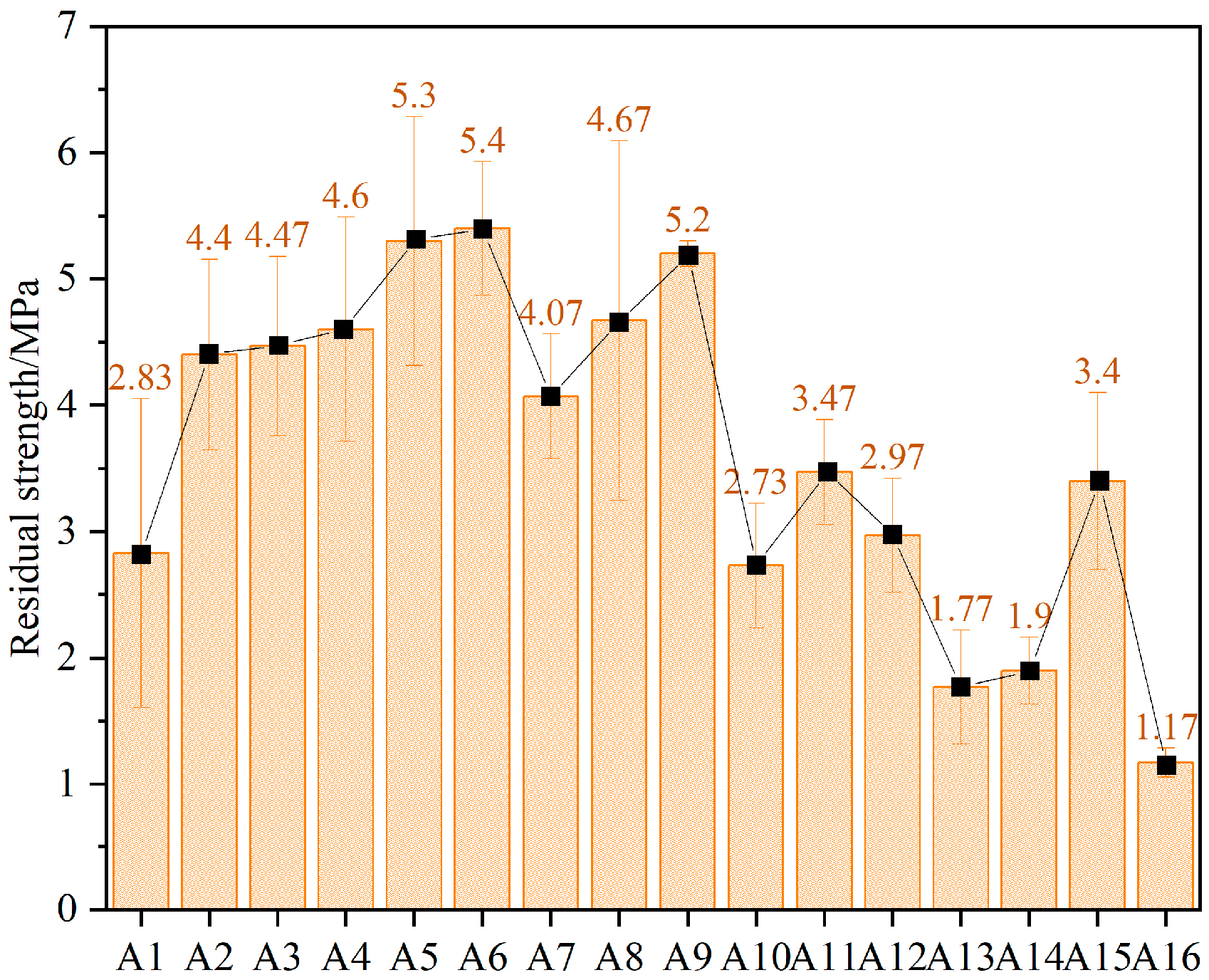
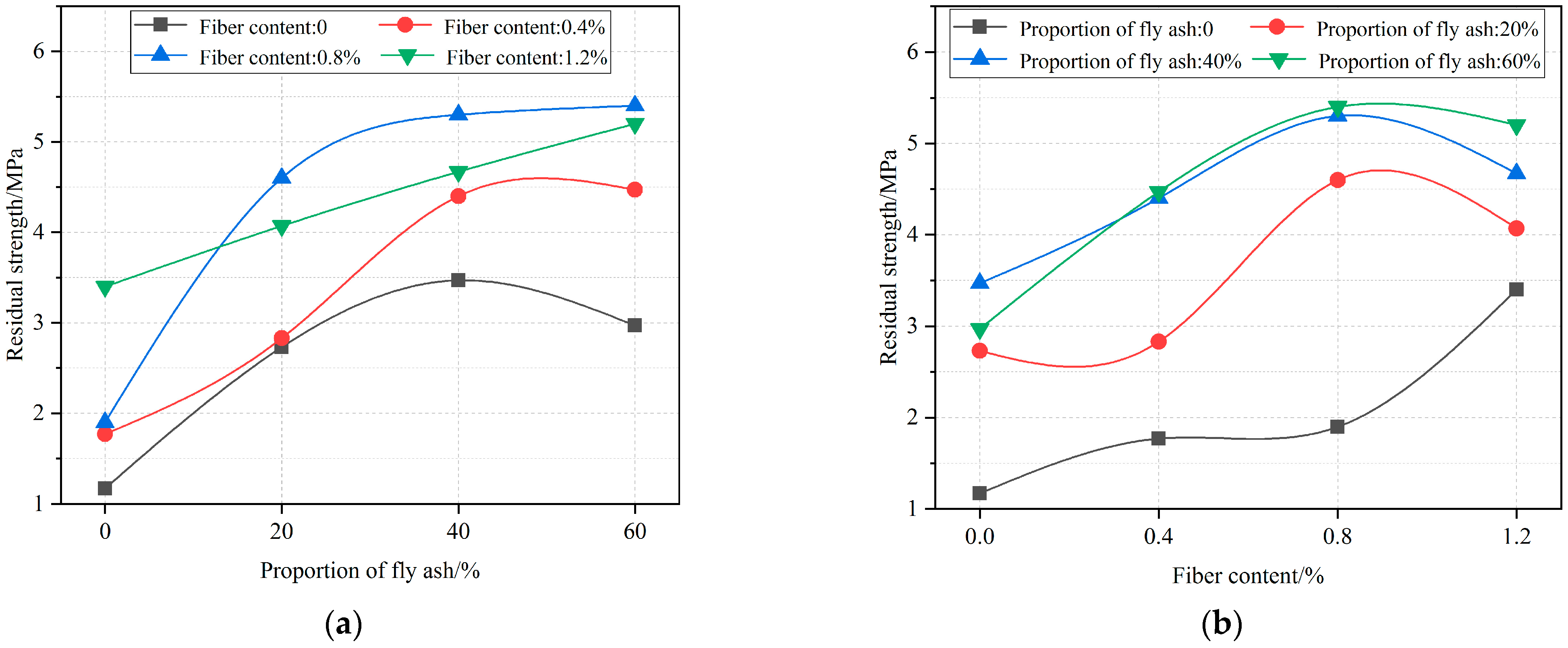
4.3. Residual Strength Analysis
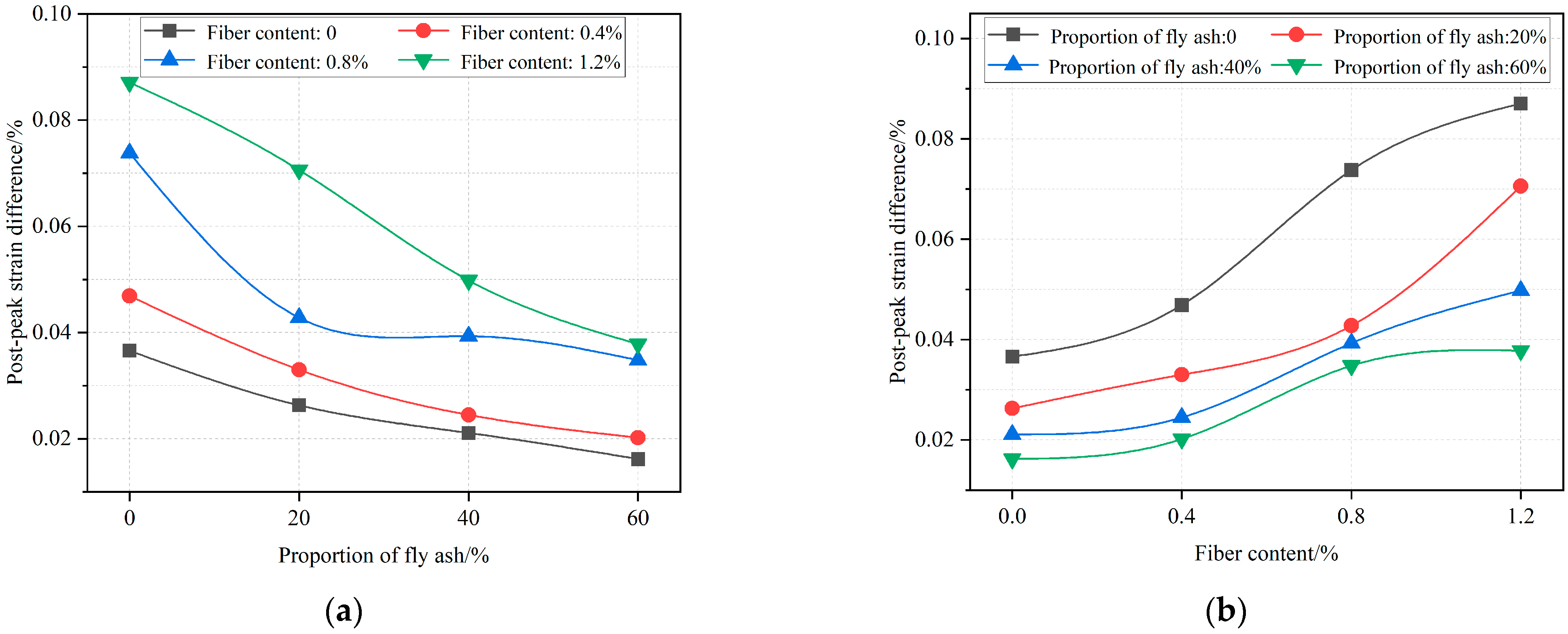
4.4. Analysis of the Deformation of RBB after Failure
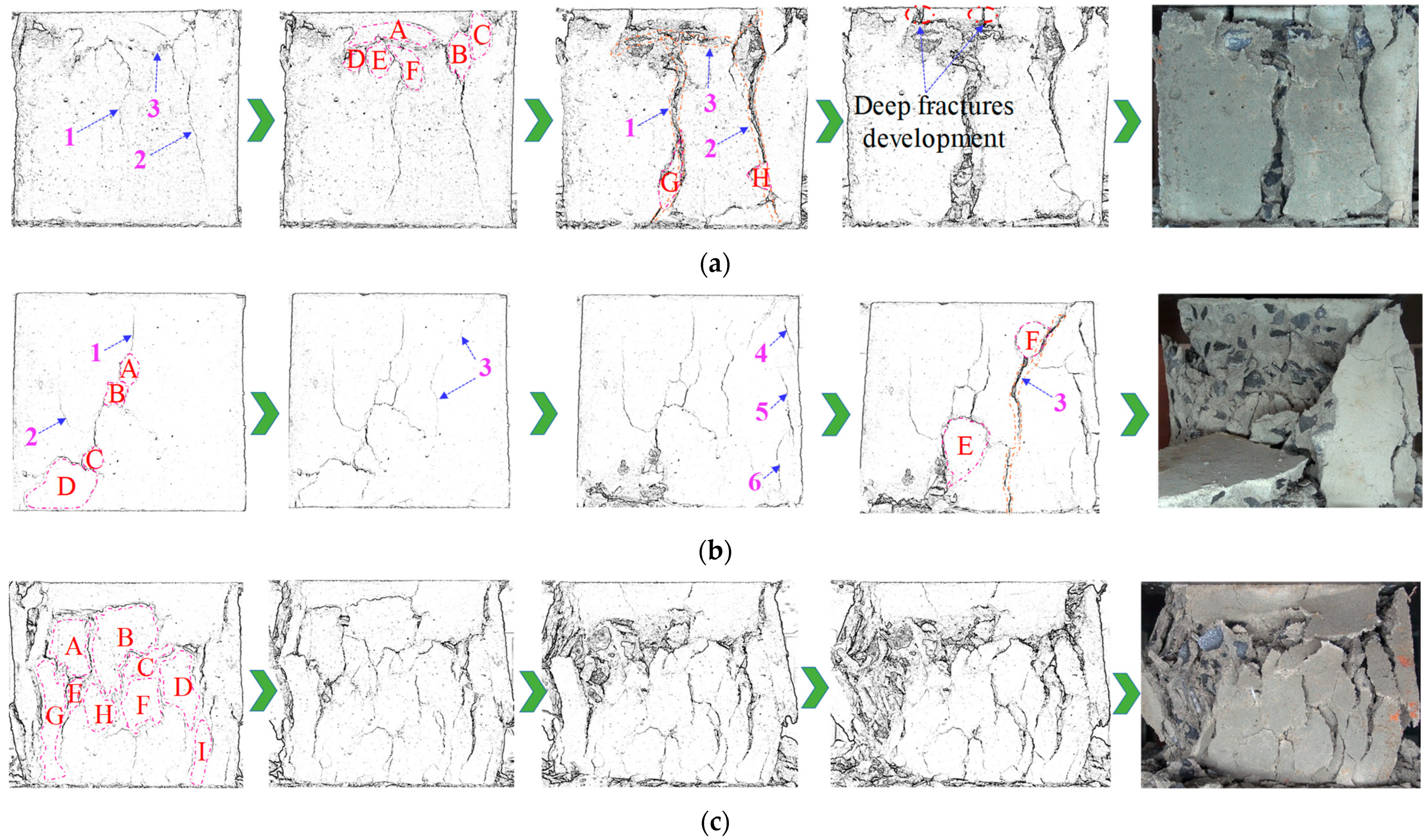
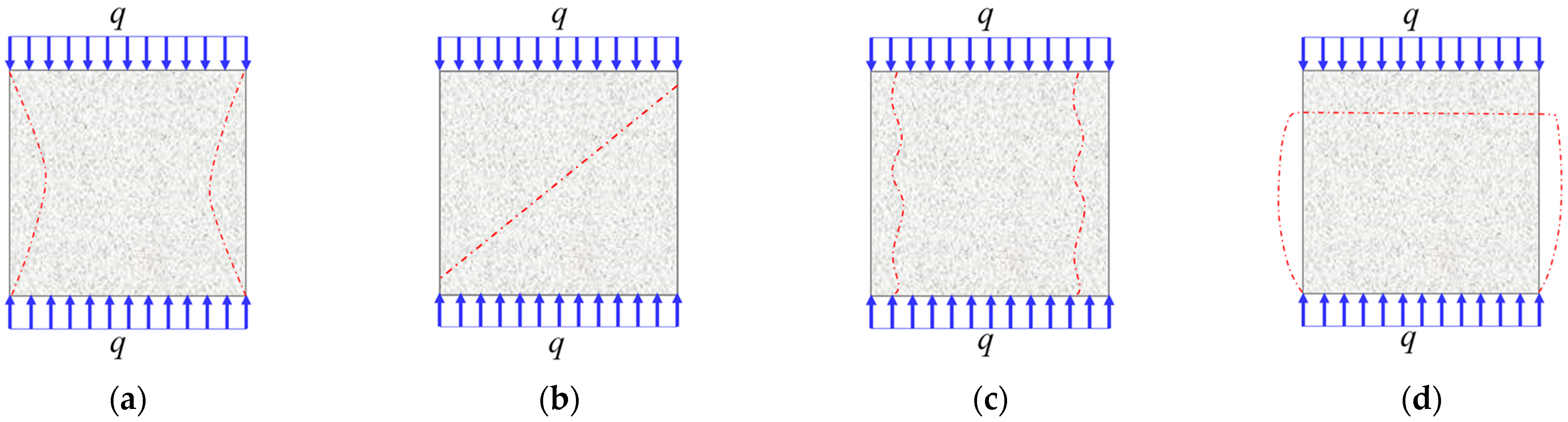
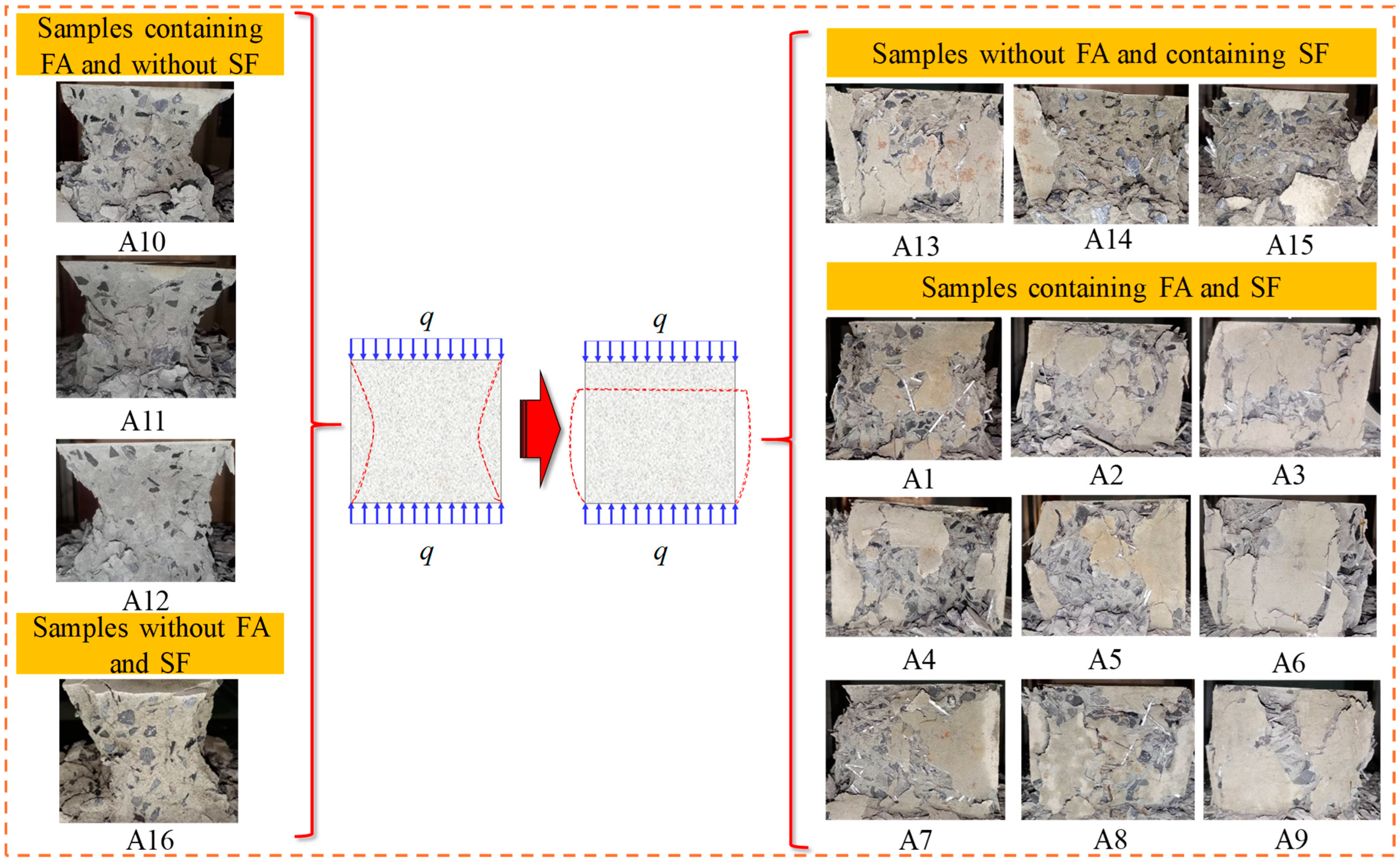
4.5. RBB Failure Modes Analysis
4.5.1. RBB Fracture Evolution Characteristics
4.5.2. Transformation of RBB Brittle-Ductile Failure Mode
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The slump first increases and then decreases with the increase of the FA proportion, and it reaches its maximum value when the FA proportion is 20%. SF has little influence on the slump. However, when the FA proportion is 60% and the SF content is 0.4%, the slump reaches a minimum value of 130 mm.
- (2)
- The peak strength and residual strength increase with the increase of the FA proportion. However, the strength gain starts to decrease when the FA proportion exceeds 40%. SF only has a small effect on the peak strength when the dosage is 0.8%. When the proportion of FA is 0, the residual strength increases with the increase of the SF content. When the proportion of FA is in the range of 20–60%, the residual strength first increases and then decreases with the increase of the SF content, while the 0.8% SF content is the critical point.
- (3)
- The post-peak strain difference decreases with the increase of the FA proportion and increases with the increase of the SF content. The addition of SF makes up for the problem of reduced post-peak capacity to deformation caused by the addition of FA to some extent.
- (4)
- The RBB samples with and without FA have fewer cracks and they connected the upper and lower ends of the samples, showing the brittle failure mode of X-shaped conjugate inclined plane shear. After SF incorporation, the fracture of the backfill body has variable direction and short length, and the backfill body changes from brittle failure mode to ductile failure mode.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Q.; Yang, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; He, X.; Lyu, X. Optimization of Barrier Pillar Design in Longwall Mining with Top Coal Caving in Spontaneous Combustion Coal Seam. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 2749373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.C.; Xie, H.P.; Peng, S.P.; Jiang, Y.D. Study on rock mechanics in deep mining engineering. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2005, 24, 2803–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Li, L.Y.; Wang, L.; Qi, L.L. The current situation and prevention and control countermeasures for typical dynamic disasters in kilometer-deep mines in China. Saf. Sci. 2019, 115, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Zhou, N.; Qi, W.Y.; Li, A.L.; Cui, Z.Z. Surface subsidence control during deep backfill coal mining: A case study. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6876453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.P. Research Framework and Anticipated Results of Deep Rock Mechanics and Mining Theory. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2017, 49, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.R.; Ma, Z.G.; Yang, D.W.; Qi, F.Z.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.H. Study on key parameters of filling gob-side roadway in the thick layer soft rock fault top. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2019, 36, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.J.; Dong, C.W.; Yuan, Z.X.; Zhou, N.; Yin, W. Deformation behavior of gob-side filling body of gob-side retaining entry in the deep backfilling workface. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2020, 37, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.W.; Wang, X.Y.; Bai, J.B.; Wu, W.D.; Zhu, X.X.; Li, G.D. Study on crack evolution mechanism of roadside backfill body in gob-side entry retaining based on UDEC trigon model. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 3385–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.P. Research review of the state key research development program of China: Deep rock mechanics and mining theory. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 1283–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.K.; Bai, J.B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Wu, W.D.; Wu, B.W. Stability analysis of roadside backfill body at gob-side entry retaining under combined static and dynamic loading. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 127, 105531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Li, X.W.; Yang, K.; Wei, Z.; Fu, Q. The segmental subsidence structure with immediate roof of gob side entry retaining in backfill mining. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2021, 39, 1262–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.G.; Wang, J.; Bu, T.T.; Hu, S.C.; Liu, X.S. An innovative support structure for gob-side entry retention in steep coal seam mining. Minerals 2017, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Ma, Z.G.; Zhang, R.R.; Ning, X.Y.; Liu, F.; Huang, Z.M. Surrounding rock deformation mechanism and control technology for gob-side entry retaining with fully mechanized gangue backfilling mining: A case study. Shock Vib. 2017, 2017, 6085941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.L.; Yilmaz, E.; Song, W.D.; Yilmaz, E. Influence of fiber reinforcement on mechanical behavior and microstructural properties of cemented tailings backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 213, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Song, W.D. Fiber type effect on strength, toughness and microstructure of early age cemented tailings backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.J.; Zhou, X.L.; Yi, X.F.; Xiao, Y.G.; Wei, X.M. In Situ X-ray CT Investigations of Meso-Damage Evolution of Cemented Waste Rock-Tailings Backfill (CWRTB) during Triaxial Deformation. Minerals 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Li, J.C. Experimental investigation on strength and failure characteristics of cemented tailing backfill. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Huang, Y.L.; Wu, L.W.; Yin, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.Q.; Wang, G.Y.; Li, J.M.; Lei, Y.C. Effects of chlorides on setting time, hydration heat and hydration products of fresh slurry of cemented paste backfill. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavusoglu, I.; Yilmaz, E.; Yilmaz, A.O. Additivity effect on properties of cemented coal fly ash backfill containing water-reducing admixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 121021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.M.; Du, C.F.; Chu, X.F.; Zhang, L. Study on the Optimization of Filling Ratio and Strength Variation Characteristics Containing Fly Ash. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzeniowski, W.; Poborska-Młynarska, K.; Skrzypkowski, K. The idea of the recovery of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) residues in Kłodawa Salt Mine SA by filling the excavations with self-solidifying mixtures. Arch. Min. Sci. 2018, 63, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypkowski, K.; Korzeniowski, W.; Poborska-Młynarska, K. Binding capability of ashes and dusts from municipal solid waste incineration with salt brine and geotechnical parameters of the cemented samples. Arch. Min. Sci. 2018, 63, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Feng, M.M.; Xu, J.M.; Qiu, P.T.; Wang, Y.M.; Han, G.S. Particle size distribution of cemented rockfill effects on strata stability in filling mining. Minerals 2018, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petlovanyi, M.; Mamaikin, O. Assessment of an expediency of binder material mechanical activation in cemented rockfill. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2019, 14, 3492–3503. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/288815705.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Jiang, H.Q.; Fall, M.; Li, Y.H.; Han, J. An experimental study on compressive behaviour of cemented rockfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 213, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.; Yilmaz, E.; Kasap, T.; Guner, N. Strength and microstructure evolution in cemented mine backfill with low and high pH pyritic tailings: Effect of mineral admixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuylu, S. Investigation of the Effect of Using Different Fly Ash on the Mechanical Properties in Cemented Paste Backfill. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2022, 37, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Ali, I.; Room, S.; Khan, S.; Ali, A. Enhanced mechanical properties of fiber reinforced concrete using closed steel fibers. Mater. Struct. 2019, 52, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Bagherieh, A.R.; Esfahani, M.R. Constitutive modeling of steel fiber-reinforced concrete. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2020, 29, 388–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.T.; Li, C.C.; Gao, D.Y.; Yang, L.; Cheng, S.Z. Study on mechanical properties and strength relation between cube and cylinder specimens of steel fiber reinforced concrete. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814019842423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Huang, Y.L.; Zhou, N.; Li, J.M.; Gao, H.D.; Guo, Y.C. Experiment on hydration exothermic characteristics and hydration mechanism of sand-based cemented paste backfill materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 125870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Research and Application of Bearing Characteristics of Strong-Toughness Cemented Backfilling Materials. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C 143; Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Hu, Z.J.; Feng, H.; Wang, X.F. Preparation for retarding and high early strength concrete. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2015, 30, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, X.Y. Assumption and Suggestions for Constructing the New Scientific & Smart System of Concrete Proportioning(2). China Concr. 2019, 11, 48–61. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2019&filename=JZSJ201911009&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=o8pfhiJGn2W-qv53aTvHje8are2757PsicRXvGMAVDCMpg_SF9H3cFtoFxqUrIvG (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Figueiredo, A.D.; Ceccato, M.R. Workability analysis of steel fiber reinforced concrete using slump and Ve-Be test. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, M.A.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Muniandy, R.; Abu Hashim, M.F.; Błoch, K.; Jeż, B.; Garus, S.; Palutkiewicz, P.; Mohd Mortar, N.A.; Ghazali, M.F. Comparison of hook and straight steel fibers addition on malaysian fly ash-based geopolymer concrete on the slump, density, water absorption and mechanical properties. Materials 2021, 14, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belem, T.; Benzaazoua, M. Design and application of underground mine paste backfill technology. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2008, 26, 147–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Ding, Q.J. Study on properties of steel fiber reinforced concrete. Concrete 2017, 7, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.K.; Feng, Y.L.; Sun, C.D.; Li, M. Test of high-water material width and strength for roadway-side stowing and its application. Coal Min. Technol. 2014, 19, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, H.W.; Zhao, R.S. Experimental research on filling material in deep gob-side entry retaining. Coal Sci. Technol. Mag. 2020, 41, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Raw Material | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | K2O | TiO2 | MgO | Na2O | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPC | 23.49 | 7.81 | 4.40 | 53.91 | 1.04 | 0.66 | 3.14 | 0.36 | 5.19 |
| FA | 53.08 | 27.70 | 7.17 | 3.58 | 3.08 | 1.47 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 2.31 |
| CG | 33.51 | 18.83 | 19.12 | 21.43 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.80 | 0.24 | 4.23 |
| Particle size/mm | 2–4.75 | 1.5–2 | 1–1.5 | <1 |
| Percentage by mass | 3% | 4% | 9% | 84% |
| Factor of Variables | FA Proportion/% | SF Content/% |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Level 2 | 20 | 0.4 |
| Level 3 | 40 | 0.8 |
| Level 4 | 60 | 1.2 |
| Mixing Ratio | OPC | RS | FA | CG | SF | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 1 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.206 | 1.272 |
| A2 | 1 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 2 | 0.211 | 1.272 |
| A3 | 1 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2 | 0.215 | 1.273 |
| A4 | 1 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.416 | 1.308 |
| A5 | 1 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 2 | 0.425 | 1.310 |
| A6 | 1 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2 | 0.435 | 1.312 |
| A7 | 1 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.630 | 1.346 |
| A8 | 1 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 2 | 0.644 | 1.352 |
| A9 | 1 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2 | 0.659 | 1.352 |
| A10 | 1 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 1.235 |
| A11 | 1 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 2 | 0 | 1.235 |
| A12 | 1 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2 | 0 | 1.235 |
| A13 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0.201 | 1.283 |
| A14 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0.407 | 1.307 |
| A15 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0.620 | 1.345 |
| A16 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1.235 |
| Mixing Ratio | Slump Value/mm | Mixing Ratio | Slump Value/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 255 | A9 | 220 |
| A2 | 220 | A10 | 260 |
| A3 | 130 | A11 | 260 |
| A4 | 270 | A12 | 170 |
| A5 | 255 | A13 | 205 |
| A6 | 185 | A14 | 225 |
| A7 | 250 | A15 | 210 |
| A8 | 240 | A16 | 205 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Che, C.; Zhao, C.; Du, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, S. Effect of Fly Ash and Steel Fiber Content on Workability and Mechanical Properties of Roadway Side Backfilling Materials in Deep Mine. Energies 2023, 16, 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031505
Zhang S, Che C, Zhao C, Du S, Liu Y, Li J, Yang S. Effect of Fly Ash and Steel Fiber Content on Workability and Mechanical Properties of Roadway Side Backfilling Materials in Deep Mine. Energies. 2023; 16(3):1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031505
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shujuan, Chiyuan Che, Changzheng Zhao, Shuyu Du, Yang Liu, Jiang Li, and Shengqiang Yang. 2023. "Effect of Fly Ash and Steel Fiber Content on Workability and Mechanical Properties of Roadway Side Backfilling Materials in Deep Mine" Energies 16, no. 3: 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031505
APA StyleZhang, S., Che, C., Zhao, C., Du, S., Liu, Y., Li, J., & Yang, S. (2023). Effect of Fly Ash and Steel Fiber Content on Workability and Mechanical Properties of Roadway Side Backfilling Materials in Deep Mine. Energies, 16(3), 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031505






