Abstract
Integration of a grid with an under-developed remote hilly area faces various technical and geographical challenges. Thus, generation of power from renewable resources in off-grid conditions has become one of the most cost-effective and reliable solutions for such areas. The present research deals with the possible application of an integrated solar/hydro/biomass/battery-based system to generate power in autonomous mode for a remote hilly town of a northeastern Indian state. Four different cases of the integrated energy system (IES) were designed using the hybrid optimization model for electric renewable (HOMER Pro), examining the performance of each case. The best combination of the integrated system was chosen out of several cases depending upon the optimized solution that can meet the load demand of the proposed hilly town sustainably, reliably and continuously. The simulation results show that the integrated battery/biomass/hydro/solar-based system is the best optimized, cheapest and most suitable solution to generate renewable-based power for the specified location, having the lowest net present cost (NPC) of USD 644,183.70 with a levelized cost of energy (COE) of 0.1282 USD/kWh. Further, the result also indicates that the optimized configuration reduces the emission of CO2 gas in the environment compared to the battery/biomass/hydro system having the worst emission rate. A sensitivity study was also carried out with variation in load, hydro stream flow and solar irradiation, respectively that may largely affect the technical as well as economical aspect of an integrated energy system.
1. Introduction
The economical and social enhancement of any nation depends largely on electricity. At present, electricity plays a crucial part in various activities related to humankind. In general, the majority of the generation of electricity to date has depended on fossil fuel-based resources, viz., oil, gas and coal. Such conventional sources are estimated to be in limited quantity by 2050, creating a tremendous effect on the environment because of detrimental CO2 emissions []. Thus, there has been an increasing curiosity towards renewable-based sources of energy in the last twenty years because of their lack of emission of pollutants, accessibility all around the globe and reliability. A large number of developing / under-developed nations have low reserves of fossil-based fuels and therefore have to buy them from foreign nations at a very high price. Therefore, renewable-based integrated energy systems (IESs) can act as the best solution for providing a good quality, along with the most reliable supply, of power [] in comparison to single-source power generation such as a coal-based power plant []. Various geographical and technical challenges are the main reasons why integration of a grid in remote hilly regions has not become possible. Therefore, the cost-effective renewable-dependent IES offers the best solution to supply power to such areas. Solar, hydro, biomass, wind and fuel cells are now the most popular sources for generating renewable-based power, which helps to supply both environmentally friendly and sustainable electricity. Renewable resources, mainly wind and solar, are the most popular forms of renewable sources [], that depend largely on factors related to the geographical location of a particular area [,]. For an autonomous mode system, biomass-based power generation has gained huge publicity in recent times for fulfilling the energy requirement of remote regions [].
Generation of renewable power from fuel cells is also becoming popular as a next generation green energy resource because of their structural flexibility, higher efficacy and lack of carbon emission. Thus, the formation of a renewable-dependent IES is carried out by adding multiple sources and utilizing their best characteristics, overcoming the constraints in order to achieve the highest efficacy [,]. Moreover, due to the deficiency of primary facilities in remote locations and because of the lack of electricity supply, the migration of rural dwellers to urban areas is growing immensely. Therefore, in order to restrict this kind of immigration, which creates an imbalance in the demography of any nation, there is a high requirement for sustainable autonomous supply of electricity to hilly and rural areas []. Hence, the major challenge for engineers is to provide cost-competitive, sustainable and optimized electricity from an autonomous renewable-supplied IES to hilly and rural areas for improving their quality of life along with reducing the migration rate to urban areas.
In the last decade, a huge number of studies have been reported related to the generation of electricity from autonomous renewable-supplied IESs []. In [], an integrated energy system (IES) optimized through HOMER is developed for defining various cost-related factors such as NPC and COE. In [], an IES is developed by utilizing a genetic algorithm for fulfilling the demand of load to various parts of a remote village in the state of Karnataka of India. In [], IESs of various combinations were designed for six different regions of Nigeria using HOMER. The optimization outcome shows that, considering a sensitivity study of USD 1.1 per liter to USD 1.3 per liter of diesel depending upon COE and NPC, a battery/diesel-generator/solar-based IES is the best solution for all the specified rural locations. Here, the optimal price of the diesel is considered to be USD 1.1 in [] since the study was carried out as per the rate of diesel per liter available during the month of October in the year 2014 in Nigeria [,]. In [], an optimized autonomous solar/wind-based IES has been proposed for a rural location of Nigeria depending upon the statistical investigation of the renewable resources of that area by using HOMER as a software tool. In [], a comparison is carried out among two autonomous IESs comprising battery/diesel-generator/solar and battery/diesel-generator/solar/wind with the traditional coal-fed electricity generating system. The optimization result concludes that the battery/diesel/solar-based IES having NPC and COE of USD 69,811 and 0.409 USD/kWh is the most viable solution. In [], a novel optimization technique was proposed for optimum designing of an autonomous IES that uses three algorithms, simulated annealing and chaotic and harmony search. This newly developed algorithm is capable of reviewing the feasibility of the recommended system more reliably.
In [], two models are compared with each other, i.e., a diesel-generator/solar-based IES with autonomous solar PV for supplying the load. The result indicates that the integrated diesel-generator/solar-based system is the most effectual in comparison to the autonomous solar PV system. In [], an autonomous IES was designed to power up a tele-communication center of a remote location and was found much more effectual for fulfilling its electrical requirements. In [], an autonomous fuel cell/solar-based IES is designed to generate electrical energy for Egypt’s remote regions. A technical and economical viability study was also carried out for the proposed IES and the total annual cost (i.e., TAC) was found by the flower pollination algorithm (i.e., FPA). In [], an implementation of an autonomous battery/fuel cell/solar-based IES was carried out on a group of Indian villages. Through the simulation result, it is concluded that for instantaneous usage the batteries should be used while for continuous electricity supply the fuel cells should be utilized. In [], an autonomous diesel-generator/fuel cell/solar-based IES is designed to serve the rural region of Kerman located in the southern part of Iran under an operational reserve along with solar power and load ambiguity.
In [], an autonomous battery/biomass/hydro/solar-based IES has been designed for electricity supply to Kakkavayal, a remote forest located in the Indian state of Kerala. The simulation analysis indicates that the COE for the proposed integrated system is only 0.164 USD/kWh which is economical when compared to the existing diesel-generator/hydro system of the proposed area. In [], a non-grid battery/diesel-generator/solar/wind-based IES is designed considering the demand side management for the Chaghi area located in the province of Baluchistan of Pakistan. The proposed configuration shows a better result than the existing diesel-generator system of that area in terms of technological analysis and economical analysis. In [], a diesel-generator/gas-generator/wind-based IES in autonomous mode has been designed utilizing the HOMER Pro environment for the island of Masirah located in Oman, replacing the existing diesel-generator system. The simulation analysis shows that the designed optimum model has a COE of only 0.0724 USD/kWh when compared to the existing diesel-generator system which shows a COE of 0.302 USD/kWh. In [], a battery/solar-based integrated system is proposed for an isolated water supply facility center situated in the Indian city of Silchar. The simulated result shows that the COE for the system is only 0.307 USD/kWh with a 257,014 kWh yearly generation of energy. In [], a battery/solar-based system is designed considering four different loads for a remote region. The analysis presents that, when the system supplies variable loads, the COE is 0.74 USD/kWh, while, with fixed loads, the COE is 0.33 USD/kWh.
In [], an autonomous battery/biogas/diesel-generator/fuel cell/solar/wind-based IES has been modeled for the remotely located village of Thumkunta situated in the state of Telengana of India. The COE for the proposed model is found to be only 0.207 USD/kWh with non-intervention of policy and 0.14 USD/kWh with intervention of policy. The proposed IES also underwent a sensitivity study with the variation of solar irradiation, speed of the wind and load. A battery/diesel-generator/hydro/solar-based IES in off-grid mode is designed for the remote under-developed village of Mboke, located in the southern part of Nigeria []. The optimized model result indicates that the NPC of the proposed model is USD 963,431, while the COE is 0.112 USD/kWh only, with the rate of pollutant emission, i.e., CO2, being reduced to about 71% when compared to the worst combination (diesel-generator/solar). A sensitivity study with the model was also carried out in terms of state-of-charge (minimum) of the battery, capacity shortage, Sun’s radiation, discharge of the river water and rate related to interest. In [], a grid-free battery/solar/wind-based IES is designed for Makadi Bay, remotely located in Egypt. The proposed model has been optimized using linear-TORSCHE as a new technique. The result after running the simulation indicates that, for the specified location taken under consideration, the integrated battery/solar/wind system is a better solution than setting up a battery/solar system and battery/wind system individually. In [], an autonomous biomass/biogas/fuel cell/solar/wind-based IES containing a battery as a backup has been modeled for three un-electrified remotely located villages in the Chamarajanagar district of the Indian state of Karnataka. The proposed IES is found to be very reliable and cost effective from the optimization analysis, having 0.214 USD/kWh as the cheapest COE. In [], a battery/diesel-generator/solar/wind-based IES in autonomous mode is modeled for Bangladesh’s remote Kutubdia Island by utilizing both non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II (NSGA-II) and the HOMER environment. The comparative study between the two approaches indicates that the NPC achieved by using the NSGA-II method is almost 2.69% less when compared to the HOMER-optimized model. In [], a grid non-dependent battery/diesel-generator/solar/wind-based integrated system is designed for an isolated area located in Berenice, Egypt. The multi-objective multi-verse optimization (MOVO) algorithm is deployed for optimizing the modeled system in two cases: (i) only with renewables and (ii) with a battery/renewables. The result obtained from the optimization shows that the battery/diesel-generator/solar/wind system has COE of 0.272 USD/kWh.
In [], five integrated energy systems are designed for a rural location of north Ghana to investigate their social, technical, economical, environmental and hydrogen productivity performance. The multi criteria decision making (MCDM) technique is deployed to choose the optimal model. A grid-independent battery/hydro-based IES was found to be the best one for the selected location, having a COE and OC of 0.06 USD/kWh and USD 18,318, respectively. In [], a novel battery/biomass/electrolyzer/fuel cell/hydrogen tank/solar/wind-based electric vehicle (EV) charging station in autonomous mode has been designed for four cities located in Qatar. The technical and economical study suggests that the novel IES for the proposed charging station has the NPC range of USD 2.53 to 2.92 M with the COE ranging from 0.285 to 0.329 USD/kWh. In [], an on-grid as well as an autonomous battery/diesel-generator/electrolyzer/hydrogen tank/solar/wind-based integrated energy system is designed for a coal mine located in the Chinese province of Shanxi in order to ease the process of mining. The technological, economical and environmental analysis shows that the proposed IES fulfills the load requirements of the coal mine and can also generate on-site hydrogen for 100% refueling of the hydrogen-run trucks which are used to transport coal, thereby replacing the diesel-run trucks. In [], an autonomous battery/electrolyzer/fuel-cell/hydrogen tank/solar-based integrated system is proposed for five cities of India in order to supply the electricity load, reduce the CO2 production and establish a hydrogen re-fueling station to supply fuel-cell-run vehicles by replacing the traditional diesel/petrol-run vehicles. The optimization outcome reflects that the city of Kolkata has the highest production capacity of hydrogen, amounting to 82,054 kg/year while Mumbai has the lowest. The COEs for all the cities were found to be in the range of 0.41 to 0.48 USD/kWh. In [], an autonomous battery/electrolyzer/hydrogen tank/wind-based hybrid system is proposed to set up refueling stations for hydrogen-run vehicles in seven different cities located in South Africa. The result achieved by simulating the recommended IES indicates that the cost of hydrogen (COH) production for the locations under study lies in the range of 6.34 to 8.97 USD/kg. Further, the proposed integrated system helps to diminish the toxic CO and CO2 gases yearly by 0.133 tons and 73.95 tons, respectively that are emitted from the traditional transportation system. In [], a grid-supported battery/diesel-generator/electrolyzer/hydrogen tank/solar/wind-based IES has been designed for a cultural-cum-sports complex in the Tehran region of Iran. The integrated system makes an attempt to utilize the diesel and hydrogen generators to act as a combined backup for the total system. The optimization outcome from the suggested system indicates that the emission of CO2 and the NPC are found to be at least 511,695 kg/year and USD 3.53 M, respectively, when compared to the integrated system where diesel and hydrogen generators are incorporated separately.
In [], a battery/hydro/solar/wind-based hybrid system is designed to supply renewable-generated power to the remote town of Maji located in Ethiopia. The optimization outcome shows that the NPC of the recommended IES is USD 4,377,731 which is much more profitable when compared to the same system connected to the central grid. In [], an autonomous battery/solar/wind-based renewable integrated system has been designed for twelve climatically diverse locations of Sudan for small-level irrigation and agricultural purposes. The technical and economical analysis of the proposed IES indicates that locations 10 and 12 are the most appropriate to produce power from wind while location 12 is the best location to hybridize two renewable sources. In [], four battery/diesel-generator/solar-based autonomous IESs were designed for an Ecuadorian island. The technical, economical and environmental study shows that the proposed system demonstrates excellent performance in terms of energy efficacy when compared with other combinational configurations having NPC and COE of USD 620,315 and 0.421 USD/kWh, respectively, with the lowest CO2 gas release rate of about 28,264 kg/year. In [], three different autonomous IESs: diesel-generator/solar, battery/diesel-generator/solar and diesel-generator/pumped hydro/solar, were designed for the Kerman region located in Iran. The technical, economical and environmental study of all the proposed IESs indicated that the lowest COE of 0.198 USD/kWh is achieved for the diesel-generator/pumped hydro/solar-based system while the lowest rate of emission is obtained for the battery/diesel-generator/solar-based system, amounting to 112,760 kg/year. In [], an off-grid battery/diesel-generator/solar-based IES has been designed to power an academic building of SRM-IST University located in the Delhi NCR region of India. The technical, economical and environmental analysis indicates that the proposed IES without any diesel-generator backup has a COE of 0.34 USD/kWh along with zero release of pollution. With the introduction of the diesel-generator in the system, the CO2 gas release rate is about 200,417 kg/year. In [], an autonomous battery/diesel-generator/wind/solar-based hybrid renewable system is designed for the remote village of Turtuk located in the Indian union territory of Ladakh. The economic, environmental and technical analysis reflects that the proposed IES has an NPC and COE of USD 278,176 and 0.29 USD/kWh, respectively. The recommended IES helps in the reduction of CO2 production of about 95.97% in comparison to the system that solely supplied power using a diesel-generator.
Table 1 shows a comparative analysis of the present research work with the selected existing studies which will be the key to validate and compare the current research.

Table 1.
Comparative analysis of the present research work with the selected existing studies.
Therefore, from the literature study on the research articles considered above, it is found that different researchers have designed renewable-based integrated energy systems of various combinations. Very few studies have conducted a reliability test of their proposed system alongside assessing the environmental impact of the system in detail in the Indian context. Hence, on the basis of the gaps found in the above studies, a renewable-based integrated energy system (IES) is designed, considering the environmental aspect, technical aspect, reliability aspect and economical aspect for autonomous (i.e., without grid) mode operation to electrify the households of the remote hilly town of Yupia, situated very near to the bank of the Dikrong River and located in the Papum Pare district of the mountainous northeastern Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh.
The proposed renewable-based IES comprises biomass/hydro/solar and is backed up by battery banks. The integrated model has been designed using HOMER Pro, which is a multi-objective oriented software employed for solving the economical and sizing-related problems of a renewable-based IES. Here, loss of power supply probability (LPSP) has been introduced as constraint in order to testify the reliability of the integrated system which is considered by HOMER Pro at the time of optimization. In this current research, four different configurations of the IES are considered for studying the performance of the proposed system along with finding the optimum configuration having minimal COE and NPC values. The COE and NPC of the system are calculated by taking into consideration the recent discount and inflation rates of India. The obtained optimum configuration showcases its economic reasonability, environmental friendliness and lower emission of pollutants. Here, the rate of emission in terms of kg-CO2/kWh is also considered for assessing the impact of the emission in the environment caused by the optimum IES. A sensitivity study is also carried out with the obtained optimum configuration having a variation in (i) load, (ii) solar irradiation/day and (iii) hydro stream flow/month.
Thus, the key contributions from this current research work are highlighted as bellow:
- An autonomous renewable-based integrated energy system (IES) is designed in the HOMER Pro environment for cost optimization- and size optimization-related problems in a remote hilly town, Yupia, located in the mountainous Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Out of the four different IES cases studied, i.e., (i) battery/biomass/hydro (Ba/Bi/H), (ii) battery/biomass/solar (Ba/Bi/S), (iii) battery/hydro/solar (Ba/H/S) and (iv) battery/biomass/hydro/solar (Ba/Bi/H/S), the best combination easily satisfies the remote hilly town’s requirement in terms of load with sustainability, reliability and continuity.
- The study showcases the minimal COE value and NPC value for the most optimized case of the IES as found from the simulation result, taking the latest inflation rate and discount rate of India as of December 2022.
- A combination of battery/biomass/hydro/solar (Ba/Bi/H/S) is found to be most effective for the proposed hilly area of study.
- The study also considers a sensitivity test having a variation in load, solar irradiation/day and hydro stream flow/month.
- The reliability test and a detailed environmental impact study are also carried out on all the proposed cases considering the Indian context.
- The result also indicates that the most optimized combination reduces the pollutant emission of CO2 gas in the environment when compared with the battery/biomass/hydro system having the worst emission rate.
The remaining sections of the research paper are as follows: Section 2 describes the methodology as adopted for the present study that comprises the description of the chosen hilly town, load-demand evaluation along with renewable resource evaluation for the chosen hilly town. Section 3 represents the mathematical formulation for the components that are used in the research. Section 4 highlights the formulation of the problems to be solved by HOMER Pro. Section 5 briefly illustrates the software (HOMER Pro) used for the research. Section 6 explains the results obtained by running the simulation, followed by the conclusion of the current research paper in Section 7.
2. Methodology Adopted for the Present Study
Designing any renewable-based integrated energy system (IES) in a software environment requires proper identification of the area in which the research is to be conducted. In order to optimize any IES in terms of technical and economical aspects under autonomous or on-grid mode, different types of parameter inputs are required, viz., requirements of loads, renewables available in that particular study area, components needed to setup an IES and market cost of those components []. Finally, the result requirements, viz., economic analysis, constraints, pollutant emission, etc., are to be specified before running the software. A detailed methodology related to the designing of any IES is shown as a flowchart in Figure 1.
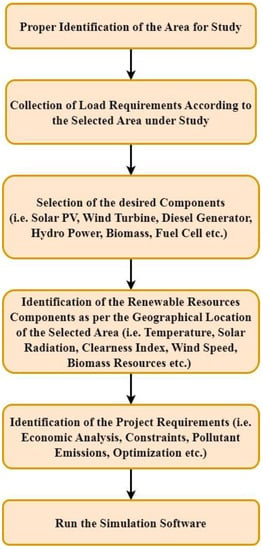
Figure 1.
Steps to design an integrated energy system.
2.1. Selection of Location
A recent report indicates that among all the un-electrified remote areas of India, the northeastern states, especially the state of Arunachal Pradesh, top the list []. Due to the difficult hilly terrain and various technical challenges, the small towns located in the state of Arunachal Pradesh very often face failure of the grid. Therefore, the current research aims to setup a renewable-based integrated energy system in the hilly town of Yupia (latitude: 27°8.8′ N and longitude: 99°43.8′ E) located very near to the Dikrong River. The proposed system will help to replace the traditional grid connectivity and can provide sustainable, reliable and continuous power to the hilly town. Yupia has a total population of 1261 with 253 households []. The proposed area has renewable potential of (i) biomass, because of its dense forest-cum-hilly location, (ii) hydro, because of its location near the Dikrong River, and (iii) solar, for setting up an autonomous IES. The map of Yupia is shown in Figure 2.
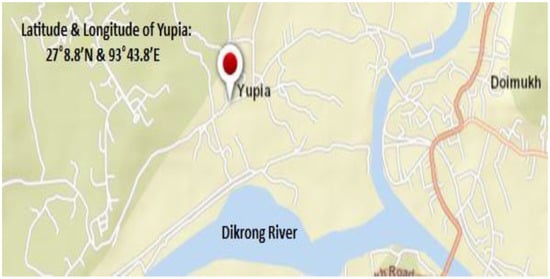
Figure 2.
Map for the remote hilly town of Yupia.
2.2. Assessment for Load Requirement
The presence of a very low population in Yupia makes the demand for domestic load very low. Since the generation of power will be carried out near the specified hilly town, it is supposed that, with time, there will be increment in load. Hence, the load takes into account the future necessities. The data related to the domestic load are taken from the local center office of the Department of Power, Government of Arunachal Pradesh []. The considered load comprises households, one health center, local shops, one degree college, one secondary school, a water-pumping station, one administrative office, street lights and one police check post. Figure 3 indicates the hourly distribution profile of the load consumption for the remote hilly town under study. The estimated overall load as consumed on a daily basis in the proposed location is 860.70 kWh/day with a peak value of 126.48 kW, while the yearly consumption of load calculated from HOMER [] is found to be 314,060 kWh/year. Figure 4 indicates the monthly distribution profile of the load consumption for Yupia. It is observed from Figure 4 that, from 10 p.m.to 11 p.m. and 12 a.m. to 5 a.m., the load demand is very low, and, from 6 a.m., the load demand gradually rises while at 1 p.m. it reaches the highest peak. Thereafter, from 3 p.m. to 5 p.m., the demand becomes approximately constant and then it rises again from 6 p.m. to 9 p.m.
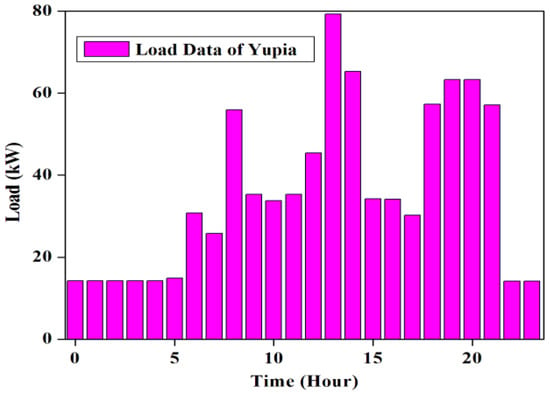
Figure 3.
Hourly distribution profile of the load consumption for Yupia.
Figure 4.
Monthly distribution profile of the load consumption for Yupia [].
2.3. Assessment for Renewable Sources
The remote hilly town of Yupia has a huge potential for available renewable-based resources, viz., (i) solar irradiance, (ii) sufficient stream flow of the Dikrong River and (iii) biomass resources available from bamboo and other forest vegetation. In this study, the availability data of stream flow for the Dikrong River and the solar irradiation of Yupia are from the year 2021. Depending upon the geographical locational data (i.e., latitude and longitude) provided, HOMER Pro computes the global horizontal index (GHI) of the solar radiation and the optimized size of the integrated energy system. The daily radiation in kWh/m2/day, clearness index and daily temperature data of the specified location are accessed by the HOMER Pro software from the database of NASA Surface Meteorology and Solar Energy [].
2.3.1. Solar Resource
The available monthly per day average solar irradiation in Yupia is indicated in Figure 5. Annually, the average per day solar irradiation is found to be 4.18 kWh/m2/day with the highest irradiance in May (5.22 kWh/m2/day) and the lowest irradiance in January (3.38 kWh/m2/day).
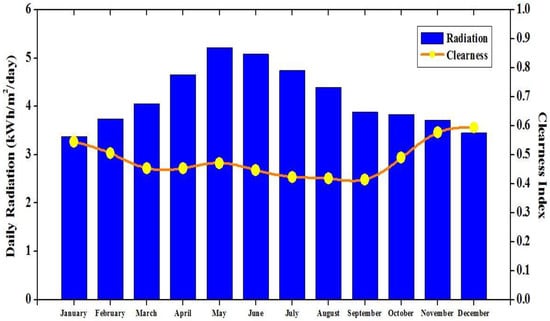
Figure 5.
Monthly per day average solar irradiation in Yupia [].
2.3.2. Hydro Resource
The Dikrong River is a distributary of the Brahmaputra River, which flows in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh as one of the major rivers. The available monthly average stream flow of the Dikrong River is indicated in Figure 6. The stream flow data of the Dikrong River is accessed from the local center office of Arunachal Pradesh Energy Development Agency (APEDA) []. Annually, the average stream flow is found to be 185 L/s, with the highest average stream flow for the months May, June and July (245 L/s) and the lowest stream flow for the months January and February (60 L/s).
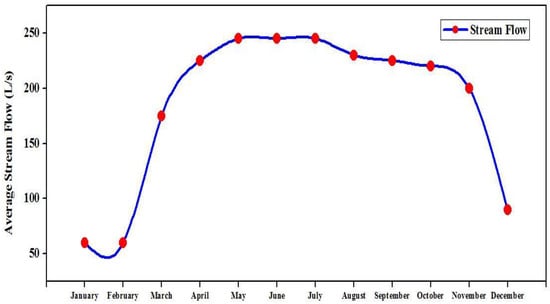
Figure 6.
Monthly average stream flow of Dikrong River [].
2.3.3. Biomass Resource
The hilly town of Yupia has a massive potential for biomass which generally comes from its huge bamboo reserves and other forest vegetation. Biomass resource availability data have been collected from []. Annually, the area has an average biomass reserve of 4.59 tons/day (t/d). The available monthly average biomass resources of Yupia are indicated in Figure 7.
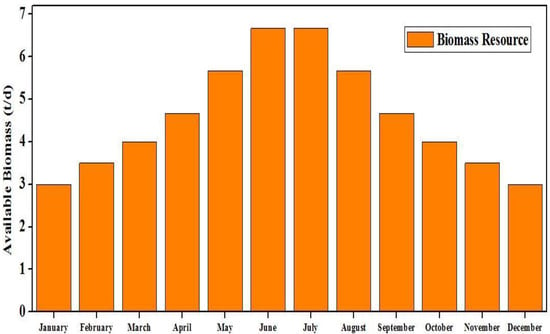
Figure 7.
Monthly average biomass resources of Yupia [].
3. Mathematical Formulation of the Components under Use
In order to find out the optimum sizing and combination of an integrated energy system (IES), mathematical formulation of the various components used is highly important. Therefore, mathematical formulation of the components used for the suggested IES are:
3.1. Solar Photovoltaic (PV)
In the current research, mathematical formulation of a single-diode PV system (PVS) is examined. Equation (1) expresses the voltage () generated by the PV module [].
Here, the maximum power-point (MPP) tracking voltage in volts is indicated by . The temperature’s coefficient is represented by , whereas the irradiation obtained by measurementin kW/m2 is denoted by . The standardized value for irradiation, i.e., , is measured in kW/m2 with a varying temperature of measured on the Kelvin scale. The PV module’s output current in amperes can be expressed by Equation (2), where represents the time in hours for a particular day.
In Equation (2), the photoelectric (phe) current in amperes is expressed as with the reverse saturation (rsat) current of in amperes. Here, three constants are considered: (ii) Boltzmann’s constant, (i) electron’s charge and (iii) ideal diode’s factor, which are represented as , and , respectively. The numbers of cells joined in series is indicated by . Therefore, the entire energy produced by the PV module in kWh can be indicated by Equation (3), where indicates the time-step in hours and the total number of PV modules is .
3.2. Hydro-Electric Turbine
Hydro-electric turbines (HETs) are generally used for the extraction of kinetic-based energy from the water flowing in rivers. These turbines are competent for ingenerating power in slow-flowing water, causing no emission in the environment. The hydro-electric-based turbine generates energy in kWh which is expressed by Equation (4) [], where represents the time in hours for a particular day.
The water stream flow (L/s) is indicated by whereas the cut-in stream flow (L/s) is indicated by . The flow of stream in rated speed (L/s) is indicated by . represents the rated HET power in kW, the density of water is represented by in kg/m3, the area of the turbine is represented by in m2, the HET’s performance coefficient is and represents the efficacy of the HET along with the generator. Here, indicates the time-step in hours.
3.3. Biomass Generator
Depending upon the massive potential for biomass which generally comes from Yupia’s huge bamboo reserves and other forest vegetation, the energy produced from a biomass-based generator (BGS) on an hourly basis can be indicated by Equation (6) [], where represents the time in hours for a particular day.
Here, is the energy produced from the biomass-based generator in kWh and the system’s conversion efficacy is denoted by . represents the calorific value (CV) of the biomass-gasifier whose numerical value is 4015 kcal/kg and is the operational hours/day of the BGS. Here, indicates the time-step in hours.
3.4. Battery Storage
The generation of energy and consuming it from the battery storage system (BSS) are associated within the time frame of to . Here, is the time for generation of the energy from the BSS in hours and is the time for consuming the energy from the BSS in hours. A battery starts charging when the production of energy surpasses the load’s demand. Thus, the energy which is stored inside a battery at any particular time can be expressed by Equation (7) [].
Here, represents the energy in kWh which is stored inside a battery, while the excess energy that is obtainable from the whole system in kWh is represented by . The efficacies of the charging battery and controller are denoted as and , respectively. The limitation of the state of charge () of the considered battery is expressed by Equation (8).
Here, represents the minimal state of charge value whereas the represents the maximal state of charge value which is presumed to be 1.
3.5. Bidirectional-Based System Converter
The bidirectional-based system converter is a major component in the renewable-based integrated energy system. A bidirectional-based system converter is used to manage the current’s flow in both directions at the time of an additional battery charging with power. This converter also helps in providing essential power to the load, coming from all the DC sources and batteries.
4. Formulation of the Problems Solved by HOMER Pro
The analysis of a renewable-based IES through the HOMER Pro environment requires the input of current financial-related parameters. The current study comprises COE, NPC, capital cost (initial), real interest rate (annually) and replacement cost of the several IES cases considered.
The net present cost (NPC) of a component represents the current price related to its installation and operation within the lifetime of the IES project subtracted from the current price related to the earned revenues within the lifetime of the IES project. An NPC generally comprises costs such as: capital, fuel, operation and management (O&M), replacement, etc. Therefore, the NPC of the total system as well as every component used in the IES is computed in HOMER environments and expressed by Equation (9) [].
The overall NPC in USD is represented by and the net yearly cost in USD per year is expressed as . The yearly rateofinterest in percentage is and the capital recovery factor is CRF with being the total project lifespan in years.
The levelized cost of energy (COE) is described as the average cost per kWh of the system-generated utilizable electric energy. The COE is expressed by Equation (10).
The primary supplied load in kWh per year is indicated by , the different supplied loads in kWh per year are indicated by and the energy sold in kWh per year to the central grid is indicated as . The CRF is expressed by Equation (11) [].
The current research considers the input of several necessary component parameters in the HOMER environment for designing an autonomous renewable-based IES, where the system’s net cost varies with regard to the components which have various specifications. The prices considered for different components as used in designing an IES, is shown in Table 2, and the detailed various specifications are described in the subsequent sub-sections.
4.1. SolarPV Panel Cost
In this work, 200 kW rated capacity flat-plate type solar-PV panels of Solar Square are considered, whose temperature-based coefficient, efficiency and operational temperature are −0.5, 13% and 47 °C, respectively. The de-rating factor of the considered solar-PV panel is taken as 80% with the lifespan of the panels as 25 years []. The capital, replacement and O&M prices of the panel are taken as 270 USD/kW, 270 USD/kW and 27 USD/kW/year, respectively []. The maximum power-point tracker (MPPT) converter capacity of the solar-PV panel is considered as 250 kW with a conversion efficacy of 95%. The solar MPPT converter capital, replacement and O&M prices are considered as 100 USD/kW, 100 USD/kW and 5 USD/kW/year, respectively [].

Table 2.
Price considered for different components as used in designing an IES.
Table 2.
Price considered for different components as used in designing an IES.
| Components | Manufacturer Name | Capital Cost | O&M Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 kW Solar-PV Panel | Solar Square | 270 USD/kW [] | 27 USD/kW/year [] |
| 250 kW PV Converter | Solar Square | 100 USD/kW [] | 5 USD/kW/year [] |
| 11 kW Hydro Turbine | Suneco | USD 36,000 [] | 2400 USD/year [] |
| 50 kW Biomass Genset | Prakash | USD 7500 [] | 1.5 USD/opr. h [] |
| Battery | DLECL | 220 USD/kWh [] | 10 USD/kWh/year [] |
| System Converter | Mouser | 250 USD/kW [] | 0 USD/kW/year [] |
4.2. Hydro-Electric Turbine Cost
In this work, a 11 kW rated capacity hydro-electric turbine of SUNECO is considered, whose capital, replacement and O&M prices are taken as USD 36,000, USD 18,000 and 2400 USD/year, respectively, having a lifespan of 25 years []. The head of the hydro-electric turbine is considered as 20 m with pipe-head loss and efficacy of 15% and 80%, respectively.
4.3. Biomass Generator Cost
In this work, a 50 kW rated capacity biomass generator of Prakash Genset is considered whose capital, replacement and O&M prices are taken as 150 USD/kW, 150 USD/kW and 0.030 USD/kW/operational hour, respectively, having a lifespan of 15,000 hours []. A minimum ratio for load as a percentage is considered to be 25%.
4.4. Battery Cost
In this work, lithium (Li)-ion battery manufactured by Dongguan-Liliang Electronic Co., Ltd. (DLECL, Guangdong, China) is considered. This type of battery is very cost effective and easily accessible. The considered battery has a nominal capacity and voltage of 1 kWh and 6 volts, respectively. The battery also has a round-trip efficacy of 90% along with maximum discharging and charging current of 500 A and 150 A, respectively []. The throughput of the battery is 3000 kWh and the lifespan is 15 years. The maximum SOC of the battery is 100% and its minimum SOC is 20%. The capital, replacement and O&M prices of the considered lithium-ion-based battery depending upon the present market price are USD 220, USD 220 and 10 USD/year, respectively [].
4.5. Bidirectional-Based System Converter Cost
The capacity of the MOUSER bidirectional-based system converter is considered as 250 kW in this work. The lifespan of the converter is considered to be 25 years with conversion efficacy of 95% []. The capital as well as the replacement price of the converter is taken as 250 USD/kW.
Therefore, the overall project span for establishing an integrated energy system in Yupia is taken as 25 years. The discount rate of the project is taken as 6.25% while the inflation rate in the context of India is taken as approximately 6% [].
5. About HOMER Pro Software
The HOMER software was first designed by P. Lilienthal in the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, USA for designing renewable-based integrated energy systems []. The software helps to simulate and design the systems in an optimized situation considering the required constraints. Using the HOMER software, both autonomous and grid-dependent IESs can be designed. Some recent versions of the HOMER software include HOMER Pro and HOMER Grid.
The software generally works in three steps: it simulates, optimizes and finally carried out the study of sensitivity for setting up an IES. In the simulation step, the software generally helps in modelling the IES and evaluates a specified IES combination’s performance for a particular hour for a given year in order to find its technological viability and cost. In the optimization step, the software searches for the optimum result after simulating various combinations of the IES which fulfils all the technological constraints having the lowest COE and NPC. In the sensitivity study step, the software computes a number of optimizations for different inputs in order to guess the ambiguity effect or variations in the system inputs. Therefore, in the optimization step, the optimum value is determined on the basis of designer-controlled variables such as: integration of various renewables, quantity of different components used and size of the components. The sensitivity study step includes an assessment on the basis of non-designer-controlled parameters such as: stream flow of the river, speed of the wind, solar radiation or cost of the fuel in the future.
The relation between the three steps of the analysis as carried out through the HOMER environment is illustrated in Figure 8. The red oval of optimization step surrounds the green oval of the simulation step which signifies the fact that various simulation results can be achieved from one optimization. The blue oval of the sensitivity study step surrounds the red oval of the optimization step, signifying the fact that one sensitivity study comprises many optimizations.
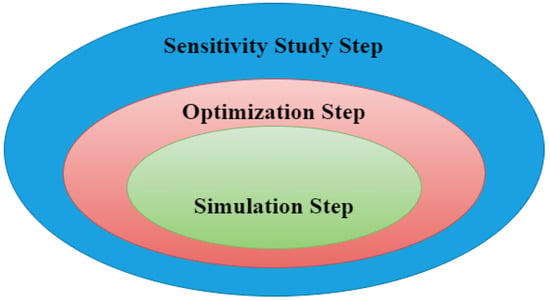
Figure 8.
Three-step analysis carried out through HOMER.
6. Results Obtained through Simulations
In the present research, four different IES cases are studied:
- (i)
- battery/biomass/hydro (Ba/Bi/H),
- (ii)
- battery/biomass/solar (Ba/Bi/S),
- (iii)
- battery/hydro/solar (Ba/H/S) and
- (iv)
- battery/biomass/hydro/solar (Ba/Bi/H/S),
which are depicted in Figure 9. The autonomous renewable-based IES supported by battery (Ba) banks comprises three renewable resources: biomass (Bi), hydro (H) and solar (S), which are easily available in the studied location.
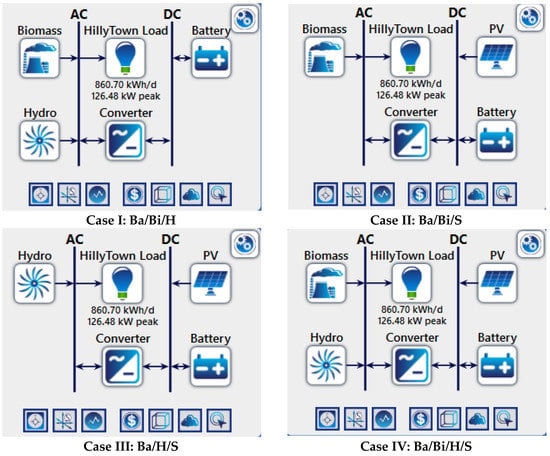
Figure 9.
Four different autonomous renewable-based IES cases considered for the studied location.
The designed IES consists of two different buses: DC load bus and AC load bus. The solar-PV and battery are connected to the DC bus whereas the biomass-based generator, hydro-electric turbine and load are connected to the AC bus. The converter helps to convert the energy generated from AC to DC and DC to AC. The simulation result obtained after running the HOMER software indicates various combinations of feasible IESs along with their cost analysis. Figure 10 indicates the feasible combinations available using different resources. The best combination is determined on the basis of the system having the lowest NPC and COE. Therefore, four optimized suitable cases are obtained from the simulation results, among which the autonomous Ba/Bi/H/S-based IES is the best combination that has an optimum NPC and COE value.
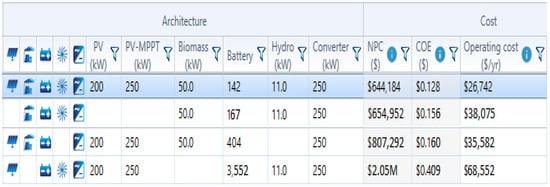
Figure 10.
Optimized feasible combinations obtained from simulation.
6.1. Case I: Ba/Bi/H
In case I, the renewable resources allocated for fulfilling the necessary load requirements are: biomass (Bi) and hydro (H) backed up by a battery (Ba). The simulation model for the proposed combination is shown as case I in Figure 9. In this case, the optimized NPC value was found to be USD 654,952, along with the COE being 0.1564 USD/kWh and cost of operation (OC) being 38,074.75 USD/year. The autonomous renewable-based IES sizes are: biomass-based generator—50 kW, hydro—11 kW and battery—167 kWh. The demand for satisfying the load is computed to be 314,034 kWh/year and the energy generated from the proposed configuration is 325,567 kWh/year among which the biomass-based generator generates 212,907 kWh/year (i.e., 65.4%) and the hydro-electric turbine generates 112,660 kWh/year (i.e., 34.6%). The percentage of energy generation from the renewables can be seen in Figure 11. Therefore, the proposed system generates excess energy of 417 kWh/year (i.e., 0.128%), which is stored in the battery after satisfying the demand for load. Figure 12 indicates the electrical energy generation on a monthly basis.
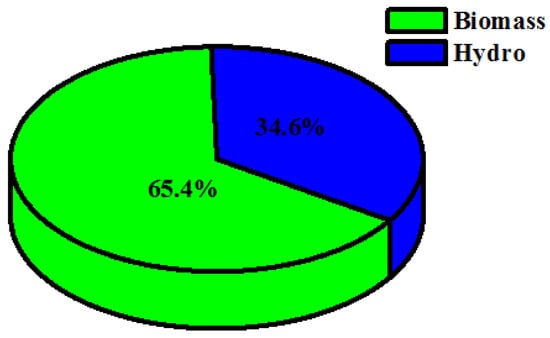
Figure 11.
Renewable energy generation percentage for case I (Ba/Bi/H).
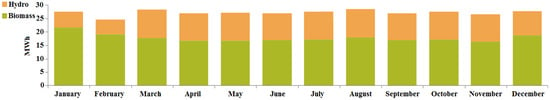
Figure 12.
Electrical energy generation on a monthly basis for case I (Ba/Bi/H).
The maximum component cost is that incurred by the biomass-based generator of USD 394,380.79 and the lowest component cost is that incurred by the hydro-electric turbine of USD 67,026.04. The total component cost breakdown for case I is shown in Figure 13. A cash-flow study is shown in Figure 14. The overall replacement and capital prices for the total system are computed as USD 86,210.25 and USD 142,740, respectively.
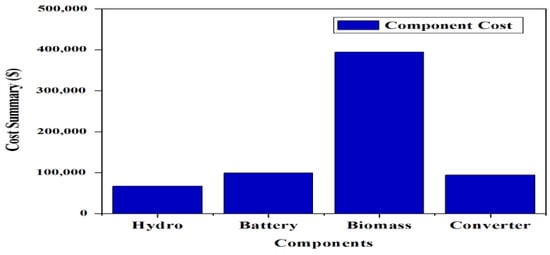
Figure 13.
Total component cost breakdown for case I (Ba/Bi/H).
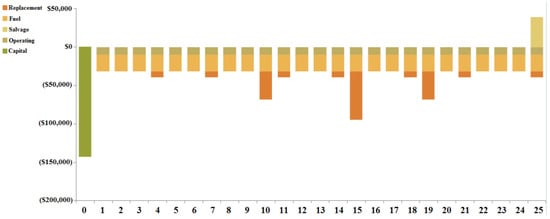
Figure 14.
Total cash-flow study for case I (Ba/Bi/H).
6.2. Case II: Ba/Bi/S
In case II, the renewable resources allocated for fulfilling the necessary load requirements are: biomass (Bi) and solar-PV (S) backed up by a battery (Ba). The simulation model for the proposed combination is shown as case II in Figure 9. In this case, the optimized NPC value was found to be USD 807,292.10, along with the COE being 0.1607 USD/kWh and cost of operation (OC) being 35,582.13 USD/year. The autonomous renewable-based IES sizes are: solar-PV—200 kW, biomass-based generator—50 kW and battery—404 kWh. The demand for satisfying the load is computed to be 314,013 kWh/year and the energy generated from the proposed configuration is 393,071 kWh/year, among which the solar-PV generates 250,497 kWh/year (i.e., 63.7%) and the biomass-based generator generates 142,573 kWh/year (i.e., 36.3%). The percentage of energy generation from the renewables can be seen in Figure 15. Therefore, the proposed system generates excess energy of 58,214 kWh/year (i.e., 14.8%), which is stored in the battery after satisfying the demand for load. Figure 16 indicates the electrical energy generation on a monthly basis.
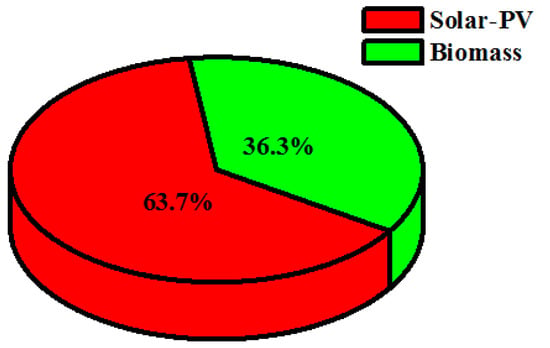
Figure 15.
Renewable energy generation percentage for case II (Ba/Bi/S).
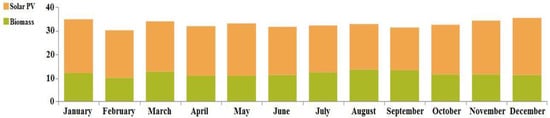
Figure 16.
Electrical energy generation on a monthly basis for case II (Ba/Bi/S).
The maximum component cost for case II is that incurred by the biomass-based generator of USD 327,939.96 and the lowest component cost is that incurred by the solar-PV converter of USD 56,045.35. The total component cost breakdown for case II is shown in Figure 17. A cash-flow study for case II is shown in Figure 18. The overall replacement and capital prices for the total system are computed as USD 120,080.19 and USD 237,880, respectively.
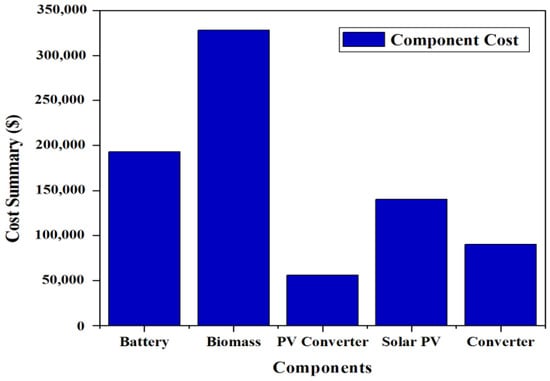
Figure 17.
Total component cost breakdown for case II (Ba/Bi/S).
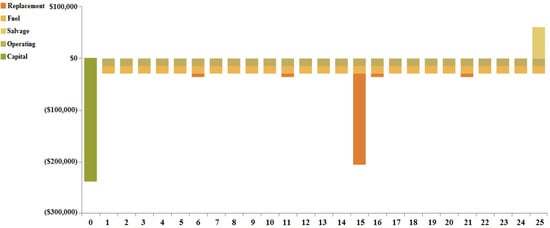
Figure 18.
Total cash-flow study for case II (Ba/Bi/S).
6.3. Case III: Ba/H/S
In case III, the renewable resources allocated for fulfilling the necessary load requirements are: solar-PV (S), hydro (H) and backed up by a battery (Ba). The simulation model for the proposed combination is shown as case III in Figure 9. In this case, the optimized NPC value was found to be USD 20,55,973, along with the COE being 0.4091 USD/kWh and cost of operation (OC) being 68,552.75 USD/year. The autonomous renewable-based IES sizes are: solar-PV—200 kW, hydro-electric generator—11 kW and battery—3552 kWh. The demand for satisfying the load is computed to be 314,060 kWh/year and the energy generated from the proposed configuration is 363,157 kWh/year, among which the solar-PV generates 250,497 kWh/year (i.e., 69%) and the hydro-electric generator generates 112,660 kWh/year (i.e., 31%). The percentage of energy generation from the renewables can be seen in Figure 19. Therefore, the proposed system generates excess energy of 27,448 kWh/year (7.56%), which is stored in the battery after satisfying the demand for load. Figure 20 indicates the electrical energy generation on a monthly basis.
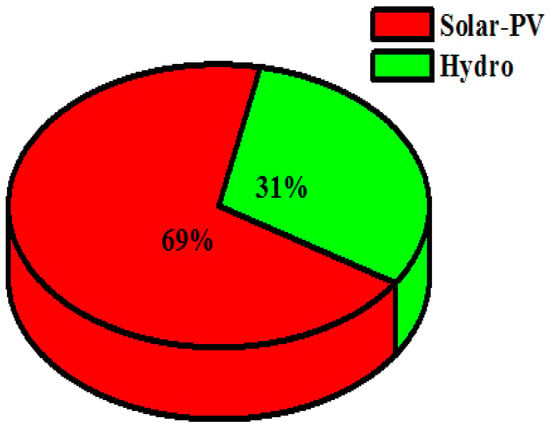
Figure 19.
Renewable energy generation percentage for case III (Ba/H/S).
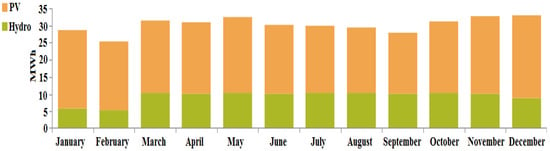
Figure 20.
Electrical energy generation on a monthly basis for case III (Ba/H/S).
The maximum component cost for case III is that incurred by the battery of USD 1,695,001.23 and the lowest component cost that is incurred by the solar-PV converter of USD 56,045.35. The total component cost breakdown for case III is shown in Figure 21. A cash-flow study for case III is shown in Figure 22. The overall replacement and capital prices for the total system are computed as USD 498,525.63 and USD 958,940, respectively.
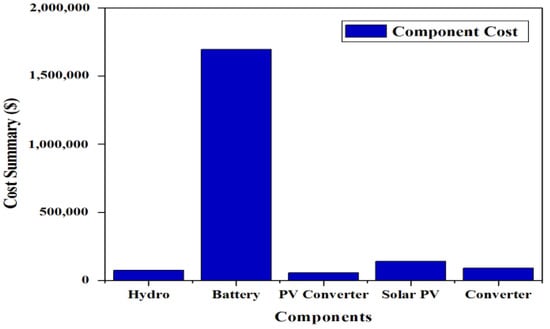
Figure 21.
Total component cost breakdown for case III (Ba/H/S).
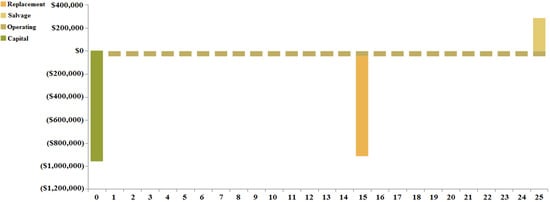
Figure 22.
Total cash-flow study for case III (Ba/H/S).
6.4. Case IV: Ba/Bi/H/S
In the current configuration i.e., in case IV, an autonomous renewable-based integrated system consisting of solar-PV (S), hydro (H), biomass (Bi) and a battery (Ba) for backup purposes is considered. The simulation model for the proposed combination is shown as case IV in Figure 9. After running 2140 simulations, 1990 cases were feasible enough to have solutions. Among them, the optimized NPC value was found to be USD 644,183.70, along with the COE being 0.1282 USD/kWh and cost of operation (OC) being 26,741.88 USD/year, which are observed to be the lowest when compared to other cases, i.e., case I, case II and case III, with the capacity shortage being only 0.0823%. Figure 23 indicates the simulated results for the current configuration. Therefore, the optimized proposed autonomous renewable-based IES has the following size: solar-PV of 200 kW, hydro-electric generator of 11 kW, biomass-based generator of 50 kW and battery of 142 kWh.
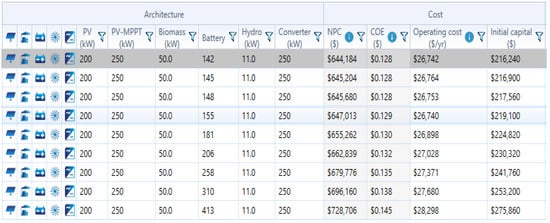
Figure 23.
Simulation results for case IV (Ba/Bi/H/S).
From the simulation result, it is found that the demand for satisfying the load is 314,060 kWh/year, for which the overall energy generated from the proposed configuration is 457,651 kWh/year. In this case, the solar-PV generates 252,890 kWh/year (i.e., 55%), the biomass-based generator generates 92,272 kWh/year (i.e., 20.3%) and the hydro-electric generator generates 112,489 kWh/year (i.e., 24.7%). Figure 24 indicates the electrical energy generation on a monthly basis and the renewable energy generation percentage for the current case is shown in Figure 25. It is computed that the proposed optimized system generates excess energy of 143,496 kWh/year (28.6%), which is stored in the battery after satisfying the demand for load. The state-of-charge (SOC) of the battery is shown in Figure 26. It can be observed that the battery remains charged for most of the hours of a particular day. The proposed optimized system utilizes an average biomass-based fuel rate of about 61 kg/hour each month. The average utilization of biomass-based fuel resources in a month is shown in Figure 27. An enviro-economic comparative analysis among all the simulated cases is carried out in the subsequent sub-section, where it is observed that the current battery/biomass/hydro/solar-based system (i.e., case IV) is the most optimized system for Yupia.
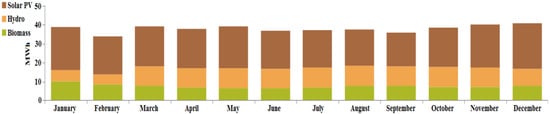
Figure 24.
Electrical energy generation on a monthly basis for case IV (Ba/Bi/H/S).
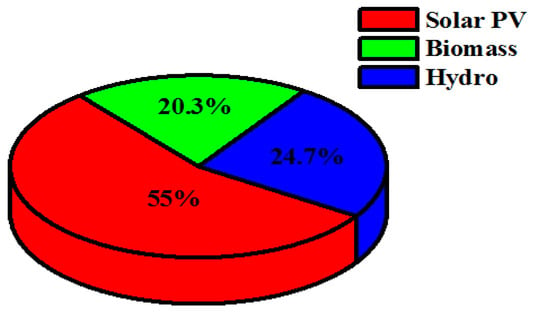
Figure 25.
Renewable energy generation percentage for case IV (Ba/Bi/H/S).
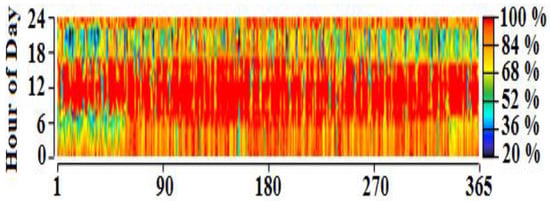
Figure 26.
SOC of battery for case IV (Ba/Bi/H/S).
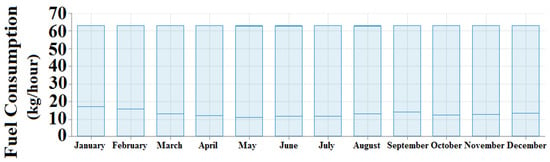
Figure 27.
Average monthly utilization of biomass-based fuel resource for case IV (Ba/Bi/H/S).
From the simulation, it is found that the maximum component cost for the optimized battery/biomass/hydro/solar-based system is that incurred by the biomass-based generator of USD 211,650.53 while the lowest component cost is that incurred by solar-PV converter of about USD 56,045.35. The total component cost breakdown for this case is shown in Figure 28. A cash-flow analysis for the optimized system is shown in Figure 29. The overall replacement and capital prices for the total system are observed to be USD 82,108.23 and USD 216,240, respectively.
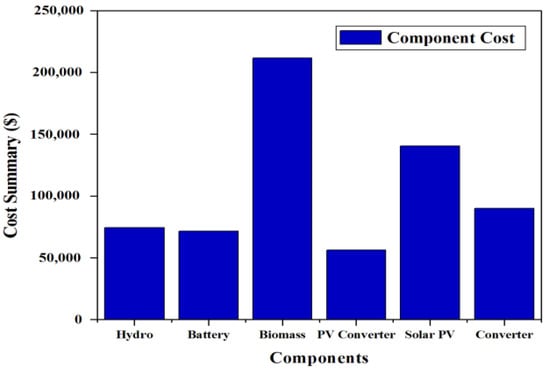
Figure 28.
Total component cost breakdown for case IV (Ba/Bi/H/S).
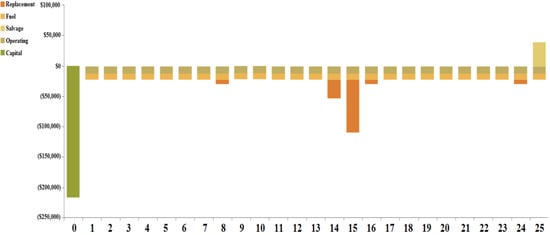
Figure 29.
Totalcash-flow study for case IV (Ba/Bi/H/S).
A comparative study in terms of economics for the base as well as the current system for case IV comprising various considered parameters is illustrated in Figure 30.
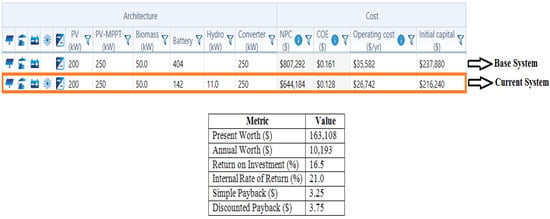
Figure 30.
Comparative economical study for case IV (Ba/Bi/H/S).
6.5. Comparison Study among Considered Cases I to IV
The present study includes two major indicating criteria i.e., economics and emissions, in order to select the optimum autonomous renewable-based IES. Amongst the four cases, case IV is found to be the most price-competitive IES since it has the lowest COE of 0.1282 USD/kWh while the NPC is USD 644,183.70. Table 3 indicates the economical indicators for all the cases, while Figure 31 gives a comparative bar-plot representation. Thus, in comparison to all other IES combinations, case IV, consisting of an autonomous battery/biomass/hydro/solar (i.e., Ba/Bi/H/S)-based integrated energy system (IES), was found to be the best combination for Yupia, since it has the lowest and most optimized economic prices, i.e., COE—0.1282 USD/kWh and NPC—USD 644,183.70 when the capacity shortage is only 0.0823%.

Table 3.
Comparative economical indicators for cases I to IV.
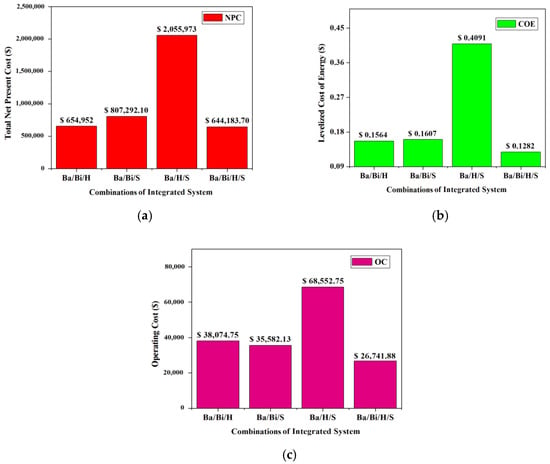
Figure 31.
Comparative bar-plot representation of economical indicators (a) NPC, (b) COE and (c) OC for cases I to IV.
The recommended autonomous renewable-based IES emits an approximate amount of CO2 of 5084 kg/year. Therefore, the release of CO2 gas from the recommended optimized IES is very low when compared to the emission from traditional energy generators. Table 4 indicates the comparative representation for emissions from all the cases along with a case when the load is totally supplied by a diesel-based generator. It is observed that the recommended IES has the lowest emission rate when compared to other cases whereas the Ba/Bi/H-based IES has the worst emission rate, having CO2 emission of 18,057 kg/year.

Table 4.
Comparative representation of emissions from all the cases along with diesel-based generator supply case.
At the time of conversion of energy from fossil fuel-based resources, various poisonous gases are released that cause an impact on the environment as well as on humans. These gases are carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (UHCs), sulfur dioxide (SO2), etc. In this research, none of the considered cases have a diesel-based generator to generate energy as they are fully dependent on renewable-based resources. For cases I, II and IV, very minimal emissions can be noticed, while case III has zero emissions. Nevertheless, for a condition when the load demand of Yupia is totally supplied by a diesel-based generator, the release of all poisonous gases due to the use of the diesel-based generator are shown in Table 4.
Now, for estimating the equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emission for cases I, II and IV, 0.93 kg-CO2/KWh has been considered which lies inside the range computed by [] for India. The electricity generated in case I is 212,907 kWh/year and its equivalent annual GHG emission is computed to be 198 tons of equivalent CO2. Then, 393,071 kWh/year of electricity is generated in case II which signifies an annual GHG emission of 365 tons of equivalent CO2. Similarly, in case IV, the annual GHG emission is found to be 425 tons of equivalent CO2 for electricity generation of 457,651 kWh/year. Therefore, with the deploying of any of the renewable-based IESs designed for Yupia by the Govt. of Arunachal Pradesh as well as by the Govt. of India, there will be a massive reduction of poisonous emissions. It is recommended to deploy the autonomous battery/biomass/hydro/solar-based IES in the proposed hilly town since the NPC and COE are the lowest along with an emission rate of only 8 tons of CO2/year.
Thus, the recommended renewable-based integrated energy system can help the remote hilly town to have better way of living, sustainability in various types of infrastructural growth, etc. The autonomous Ba/Bi/H/S-based IES also helps to support green and emission less surroundings. The energy which is generated excessively is consumed by the loads and some remaining energy can also be sold to the central power grid. With the joint venture of private and government players, an autonomous renewable-based IES can be established in this kind of remote hilly region. Therefore, an integrated energy system reduces the release of toxic emissions along with an enhancement in the reliable energy supply for fulfilling the load’s requirement.
6.6. Sensitivity Study for the Optimized Autonomous Ba/Bi/H/S Integrated System
In this current research, a sensitivity study is carried out for the proposed optimized autonomous battery/biomass/hydro/solar-based IES. The study investigates the outcome achieved because of the deviation of 10% in the electrical-based load, hydro stream flow and irradiance on solar-PV from their mean value. Figure 32 presents a sensitivity study for variation in irradiance on solar-PV and hydro stream flow. It can be observed that with the increase in the hydro stream flow above 173.90 L/s, the COE value decreases while generating more energy and, with the decrease in the hydro stream flow, the COE value increases. Further, it can also be deduced from Figure 32 that with the increase in the irradiance on solar-PV above 4.08 kWh/m2/day, the COE value also decreases and, similarly, with the decrement in the irradiance on solar-PV, the COE increases.
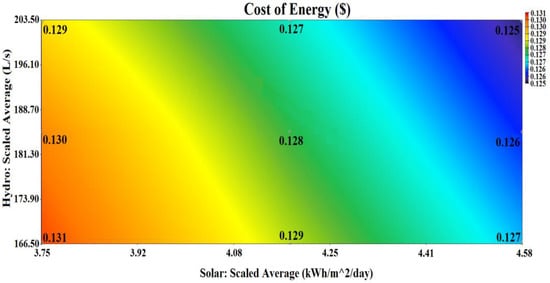
Figure 32.
Surface-type plot showing scaled stream flow against scaled irradiance.
A sensitivity study for variation in electrical-based load, irradiance on solar-PV and hydro stream flow is showcased in Figure 30. The plot represents the deviation in NPC with contrast to electrical-based load, irradiance on solar-PV and hydro stream flow. In this case, a deviation from the mean value of irradiance on solar-PV and hydro stream flow of 12% respectively is considered, whereas a 10% deviation is considered for electrical-based load. It can be concluded from Figure 33 that the sensitivity with regard to NPC due to electrical-based load is the highest, whereas the NPC due to irradiance on solar-PV is the lowest. Hence, if there is a small deviation in the electrical-based load, then the NPC varies largely because of its elevated slope. Further, it can be seen from Figure 33 that the effect of the hydro stream flow on the integrated system’s NPC tends to contrast the irradiance on solar-PV as, with the slight alteration in the mean value of the irradiance on solar-PV, its effect over the system’s NPC remains unaltered.
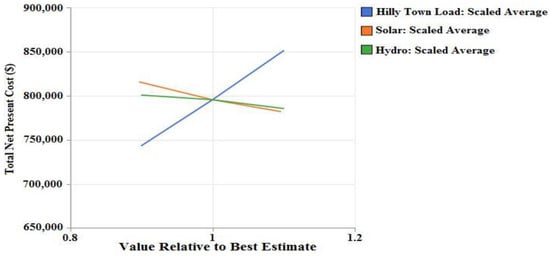
Figure 33.
Spider-type plot showing scaled sensitive variables of hydro, load and solar.
6.7. Estimation of System Reliability
In order to verify the capability regarding the power generation of a renewable-based IES, estimation of system reliability is highly important. Among several techniques available to estimate system reliability, loss of power supply probability (LPSP) is one of the most prominent approaches. The LPSP is a probability-based function, and it varies from 0 to 1. When the LPSP becomes equal to 1, it implies that there is 100% loss in supplying the power. However, when the LPSP becomes equal to 0, it implies that there is no loss in supplying the power, indicating that the demand for load will always be served. Thus, LPSP can be defined as the ratio of unmet electrical loads (UELs) in total to the demand for loads in total (TLD) which can be expressed by Equation (12) [].
Here, represents the unmet demand for electrical loads in kWh, where is the time in hours for a particular year. represents the total yearly demand for electrical loads in kWh. Now, in order to realize perfect reliability in a renewable-based IES, the constraints as shown in Equation (13) must be fulfilled.
Here, indicates the user-described value of LPSP. In the current research, is taken as 1% (i.e., 0.01) []. Table 4 shows the estimation of system reliability for all considered cases. It can be observed from Table 5 that, among all the considered cases, case IV has the lowest LPSP, i.e., 0.01%, and hence can be considered as a reliable autonomous renewable-based integrated system.

Table 5.
Estimation of system reliability for cases I to IV.
6.8. Limitations of the Current Research
In this current research, some real-world problems such as malfunctioning of certain machine parts, losses during power generation, etc. are not considered and therefore accurate results are not achieved. Thus, the results obtained from the simulation of the proposed IES must be considered to be approximate. Despite the fact that the results obtained from the current research are not exact, it is anticipated that the theoretically obtained results from the HOMER Pro platform are very close to the real value.
7. Conclusions
In this research, four distinct renewable-based IES configurations are examined which comprises: battery/biomass/hydro; battery/biomass/solar; battery/hydro/solar and battery/biomass/hydro/solar for the remote hilly Arunachali town of Yupia. A variety of parameters are taken into account to develop the functioning scheme of the IES, which include: evaluation of energy requirements, allocating renewable resources depending on the location, energy production per month, price breakdown study, system-produced emissions and sensitivity study. All these four distinct renewable-based IES configurations are designed and simulated in the HOMER Pro environment.
In comparison with all the cases considered, the simulation result for case I was found to include the lowest COE of 0.1282 USD/kWh and NPC of USD 644,183.70 with shortage of capacity being 0.0823% (i.e., 0%) under the current discount and inflation rate in India. The recommended renewable-based IES thus has the lowest economical price parameters while satisfying the load requirements for Yupia. In this case, the generation of total electricity by the optimum system is 457,651 kWh/year. The annual equivalent GHG emission is found to be 425 tons of equivalent CO2 for case I, if the same electricity as generated by the recommended system is supplied by the diesel-based generator alone. Therefore, the battery/biomass/hydro/solar-based IES is selected as the best option since such huge emission of CO2 in the environment could be reduced. Moreover, the proposed IES has the lowest CO2 and other poisonous gas emission with an annual equivalent GHG emission of only 8 tons of equivalent CO2. The optimized autonomous renewable-based IES has a size of: solar-PV—200 kW, solar-PV MPPT converter—250 kW, hydro-electric generator—11 kW, biomass-based generator—50 kW, total system converter—250 kW and battery—142 kWh. Further, the proposed case has LPSP of only 0.01% which is under the limit of the constraint . This indicates that the system is perfectly reliable, that there is a negligible loss in supplying the power and the demand for load will always be served.
The sensitivity study of the optimized battery/biomass/hydro/solar-based IES showcases the highest sensitivity with regard to NPC due to electrical-based load whereas the NPC due to irradiance on solar-PV is the lowest. Further, it can also be concluded from the sensitivity study that the variational effect of irradiance on solar-PV and hydro stream flow on NPC remains unaltered even when they increase with respect to their mean value.
The proposed renewable-based integrated system shows a promising emission level by reducing annual GHG emission significantly. The hilly Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh has a huge potential for hydro alongside biomass and solar and this kind of study is a first for the state. Therefore, it is recommended that the local government should conduct feasibility-based studies for other parts of the state as well as setting up a renewable-based integrated system. This will enable generation of more power to serve the remote areas of Arunachal Pradesh which are yet to be electrified. Finally, it is recommended that a strict framework is formed by government agencies so that private players can invest insetting up this kind of viable renewable-based integrated energy system.
Further studies would include the hybridization of the present system with other possible renewables such as wind and also its connection to the central grid. Such a developed system would help to increase the generation capacity of the IES, can fulfil the load requirements of nearby hilly towns and can make profits by selling the excessively generated power to the central grid.
Author Contributions
S.C., D.M., P.K.G. and S.B.: conceptualization, methodology, software and writing—original draft; A.Y.A.: investigation, supervision, validation and writing—review and editing; A.E.-S.: supervision and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Das, R.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Das, U. Importance of Hybrid Energy System in Reducing Greenhouse Emissions. In Renewable Energy Systems: Modeling, Optimization and Applications, 1st ed.; Kumar, S., Gupta, N., Kumar, S., Upadhyay, S., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Guchhait, P.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Banerjee, R. Intelligent reactive power control of renewable integrated hybrid energy system model using static synchronous compensators and soft computing techniques. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.; Mandal, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Nandi, C. A review of different configuration of hybrid energy systems with case study analysis. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 21, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, P.; Ashok, S.; Jose, T.L. Optimal operation of biomass/wind/PV hybrid energy system for rural areas. Int. J. Green Energy 2009, 6, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. Deep learning assisted prediction for generation of power from solar PV. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 10th Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference (R10-HTC), Hyderabad, India, 16–18 September 2022; pp. 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Guchhait, P.K.; Bhunia, J. Machine learning based solar power generation forecasting with and without MPPT controller. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 1st International Conference for Convergence in Engineering (ICCE), Kolkata, India, 5–6 September 2020; pp. 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Nandi, C. Technical feasibility study and optimisation analysis on solar biomass-based pumped storage hydropower plant. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 20, 404–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendoti, S.; Muralidhar, M.; Kiranmayi, R. HOMER based optimization of solar-wind-diesel hybrid system for electrification in a rural village. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), Coimbatore, India, 4–6 January 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rajanna, S.; Saini, R.P. Employing demand side management for selection of suitable scenario-wise isolated integrated renewal energy models in an Indian remote rural area. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 1161–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Olatomiwa, L. Performance evaluation of a stand-alone PV-wind-diesel-battery hybrid system feasible for a large resort center in South China Sea, Malaysia. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabode, O.E.; Ajewole, T.O.; Okakwu, I.K.; Alayande, A.S.; Akinyele, D.O. Hybrid power systems for off-grid locations: A comprehensive review of design technologies, applications and future trends. Sci. Afr. 2021, 13, e00884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanna, S.; Saini, R.P. Optimal modeling of solar/biogas/biomass based IRE system for a remote area electrification. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th IEEE Power India International Conference (PIICON), Delhi, India, 5–7 December 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rajanna, S.; Saini, R.P. Modeling of integrated renewable energy system for electrification of a remote area in India. Renew. Energy 2016, 90, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatomiwa, L.; Mekhilef, S.; Huda, A.S.N.; Ohunakin, O.S. Economic evaluation of hybrid energy systems for rural electrification in six geo-political zones of Nigeria. Renew. Energy 2015, 83, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trading-Economies. 2014. Available online: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/nigeria/pump-price-for-diesel-fuel-us-dollar-per-liter-wb-data.html (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Worldbank. 2014. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/ (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Olatomiwa, L.; Blanchard, R.; Mekhilef, S.; Akinyele, D. Hybrid renewable energy supply for rural healthcare facilities: An approach to quality healthcare delivery. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2018, 30, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatomiwa, L.; Mekhilef, S.; Huda, A.N.; Sanusi, K. Techno-economic analysis of hybrid PV–diesel–battery and PV–wind–diesel–battery power systems for mobile BTS: The way forward for rural development. Energy Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Maleki, A.; Rosen, M.A.; Liu, J. Sizing a stand-alone solar-wind-hydrogen energy system using weather forecasting and a hybrid search optimization algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 180, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givler, T.; Lilienthal, P. Using HOMER Software, NREL’s Micropower Optimization Model, to Explore the Role of Gen-Sets in Small Solar Power Systems. In Case Study: Sri Lanka; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.O.; Yung, V.C.; Anyi, M.; Othman, A.K.; Hamid, K.A.; Tarawe, J. Review and comparison study of hybrid diesel/solar/hydro/fuel cell energy schemes for a rural ICT Telecenter. Energy 2010, 35, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, M.M.; Barakat, S.; Ramadan, H.S. A flower pollination optimization algorithm for an off-grid PV-Fuel cell hybrid renewable system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 2141–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendoti, S.; Muralidhar, M.; Kiranmayi, R. Design and analysis of solar PV-fuel cell-battery based hybrid renewable energy system (HRES) for off-grid electrification in rural areas. i-Manag. J. Instrum. Control. Eng. 2018, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi, M.; Askarzadeh, A. Techno-economic analysis and size optimization of an off-grid hybrid photovoltaic, fuel cell and diesel generator system. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 44, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaravel, S.; Ashok, S. An optimal stand-alone biomass/solar-PV/pico-hydel hybrid energy system for remote rural area electrification of isolated village in Western-Ghats region of India. Int. J. Green Energy 2012, 9, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, F.; Asghar, F.; Majeed, M.A.; Amjad, W.; Manzoor, M.O.; Munir, A. Techno-economic optimization analysis of stand-alone renewable energy system for remote areas. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 38, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Charabi, Y.; Al-Mahruqi, A.M.; Osman, I. Design and evaluation of a hybrid energy system for Masirah Island in Oman. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2020, 13, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisanam, A.K.S.; Podder, B.; Biswas, A.; Sharma, K.K. Site-specific tailoring of an optimal design of renewable energy system for remote water supply station in Silchar, India. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 36, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurasz, J.; Ceran, B.; Orłowska, A. Component degradation in small-scale off-grid PV-battery systems operation in terms of reliability, environmental impact and economic performance. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 38, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, K.; Deshmukh, S.; Mustafa, R.S. Feasibility and sensitivity analysis of a hybrid photovoltaic/wind/biogas/fuel-cell/diesel/battery system for off-grid rural electrification using HOMER. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2020, 142, 61307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladigbolu, J.O.; Ramli, M.A.; Al-Turki, Y.A. Optimal design of a hybrid PV solar/micro-hydro/diesel/battery energy system for a remote rural village under tropical climate conditions. Electronics 2020, 9, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeida, A.M.; El-Ahmar, M.H.; El-Sayed, A.M.; Hasanien, H.M.; Alkhalaf, S.; Esmail, M.F.C.; Senjyu, T. Optimum design of hybrid wind/PV energy system for remote area. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020, 11, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendoti, S.; Muralidhar, M.; Kiranmayi, R. Techno-economic analysis of off-grid solar/wind/biogas/biomass/fuel cell/battery system for electrification in a cluster of villages by HOMER software. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Akter, H.; Howlader, H.O.R.; Senjyu, T. Optimal sizing and techno-economic analysis of grid-independent hybrid energy system for sustained rural electrification in developing countries: A case study in Bangladesh. Energies 2022, 15, 6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeida, A.M.; Omer, A.S.; Bahaa-Eldin, A.M.; Alkhalaf, S.; Ahmed, M.; Senjyu, T.; El-Saady, G. Multi-objective multi-verse optimization of renewable energy sources-based micro-grid system: Real case. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyekum, E.B.; Ampah, J.D.; Afrane, S.; Adebayo, T.S.; Agbozo, E. A 3E, hydrogen production, irrigation, and employment potential assessment of a hybrid energy system for tropical weather conditions—Combination of HOMER software, shannon entropy, and TOPSIS. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 31073–31097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahedi, A.A.; Bicer, Y. Techno-economic optimization of novel stand-alone renewables-based electric vehicle charging stations in Qatar. Energy 2022, 243, 123008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampah, J.D.; Jin, C.; Agyekum, E.B.; Afrane, S.; Geng, Z.; Adun, H.; Yusuf, A.A.; Liu, H.; Bamisile, O. Performance analysis and socio-enviro-economic feasibility study of a new hybrid energy system-based decarbonization approach for coal mine sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveenkumar, S.; Agyekum, E.B.; Ampah, J.D.; Afrane, S.; Velkin, V.I.; Mehmood, U.; Awosusi, A.A. Techno-economic optimization of PV system for hydrogen production and electric vehicle charging stations under five different climatic conditions in India. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 38087–38105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodele, T.R.; Mosetlhe, T.C.; Yusuff, A.A.; Ntombela, M. Optimal design of wind-powered hydrogen refuelling station for some selected cities of South Africa. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 24919–24930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangir, M.H.; Javanshir, F.; Kargarzadeh, A. Economic analysis and optimal design of hydrogen/diesel backup system to improve energy hubs providing the demands of sport complexes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 14109–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayu, E.S.; Khan, B.; Hagos, I.G.; Mahela, O.P.; Guerrero, J.M. Feasibility analysis and development of stand-alone hybrid power generation system for remote areas: A case study of Ethiopian rural area. Wind 2022, 2, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Imran, M.; Altamimi, A.; Diemuodeke, O.E.; Abdelatif, A.O. Assessment of wind and solar hybrid energy for agricultural applications in Sudan. Energies 2022, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Leon, R.; Amoroso, F.; Urquizo, J.; Villavicencio, V.; Torres, M.; Singh, P.; Soriano, G. Feasibility study for off-grid hybrid power systems considering an energy efficiency initiative for an island in Ecuador. Energies 2022, 15, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhdoomi, S.; Askarzadeh, A. Techno-enviro-economic feasibility assessment of an off-grid hybrid energy system with/without solar tracker considering pumped hydro storage and battery. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambhi, S.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, P.; Fotis, G.; Vita, V.; Ekonomou, L. Techno-economic optimization of an off-grid hybrid power generation for SRM IST, Delhi-NCR campus. Energies 2022, 15, 7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambhi, S.; Sharma, H.; Bhadoria, V.; Kumar, P.; Chaurasia, R.; Chaurasia, G.S.; Fotis, G.; Vita, V.; Ekonomou, L.; Pavlatos, C. Economic feasibility of a renewable integrated hybrid power generation system for a rural village of Ladakh. Energies 2022, 15, 9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaithi, H.M.A.; Fotis, G.P.; Vita, V. Techno-economic assessment of hybrid energy off-grid system—A case study for Masirah island in Oman. Int. J. Power Energy Res. 2017, 1, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rural Electrification: Arunachal a Major Hurdle in Achieving May 1 Deadline. Available online: https://indianexpress.com/article/business/budget/union-budget-rural-electrification-arunachal-a-major-hurdle-in-achieving-may-1-deadline-5042809/ (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Census of India 2011: Arunachal Pradesh. Series 13, Para XII–B. Available online: https://censusindia.gov.in/nada/index.php/catalog/181 (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Department of Power—Government of Arunachal Pradesh. Available online: http://power.arunachal.gov.in/ (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- HOMER Software. Available online: https://www.homerenergy.com/ (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- POWER|Data Access Viewer. Available online: https://power.larc.nasa.gov/data-access-viewer/ (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Arunachal Pradesh Energy Development Agency (APEDA). Available online: https://apeda.nic.in/ (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Chauhan, A.; Saini, R.P. Size optimization and demand response of a stand-alone integrated renewable energy system. Energy 2017, 124, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.; Alanazi, M.; Nowdeh, S.A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y.; El-Shahat, A. An optimal sizing framework for autonomous photovoltaic/hydrokinetic/hydrogen energy system considering cost, reliability and forced outage rate using horse herd optimization. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 7154–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanase-Patil, A.B.; Saini, R.P.; Sharma, M.P. Development of IREOM model based on seasonally varying load profile for hilly remote areas of Uttarakhand state in India. Energy 2011, 36, 5690–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishan, O.; Sathans. Design and techno-economic analysis of a HRES in a rural village. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 125, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Nandi, C. An Optimization Case Study of Hybrid Energy System in Four Different Regions of India. In Advances in Greener Energy Technologies, 1st ed.; Bhoi, A.K., Sherpa, K.S., Kalam, A., Chae, G.S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 399–437. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos, J.G.; Walker, M.; Poggio, D.; Pourkashanian, M.; Nimmo, W. Modelling an off-grid integrated renewable energy system for rural electrification in India using photovoltaics and anaerobic digestion. Renew. Energy 2015, 74, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solar Square. Available online: https://www.solarsquare.in/ (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Suneco Hydro Available online: Turbines. Available online: https://www.micro-hydro-power.com/ (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Prakash Genset. Available online: https://www.prakashgenset.in/ (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Dongguan Liliang Electronics Co., Ltd. Available online: https://www.liliangbattery.com/ (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Mouser Electronics. Available online: https://www.mouser.in/ (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Trading Economics. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/ (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Lambert, T.; Gilman, P.; Lilienthal, P. Micropower system modeling with HOMER. Integr. Altern. Sources Energy 2006, 1, 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, M.L.; Sharma, C.; Singh, R. Estimates of emissions from coal fired thermal power plants in India. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Emission Inventory Conference, Tampa, FL, USA, 13–16 August 2012; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumar, R.K.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Yong, B.L.; Chia, D.B. Techno-economical optimization of hybrid pv/wind/battery system using Neuro-Fuzzy. Energy 2011, 36, 5148–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).