Linear Model for Two-Layer Porous Bed Suspended with Nano Sized Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
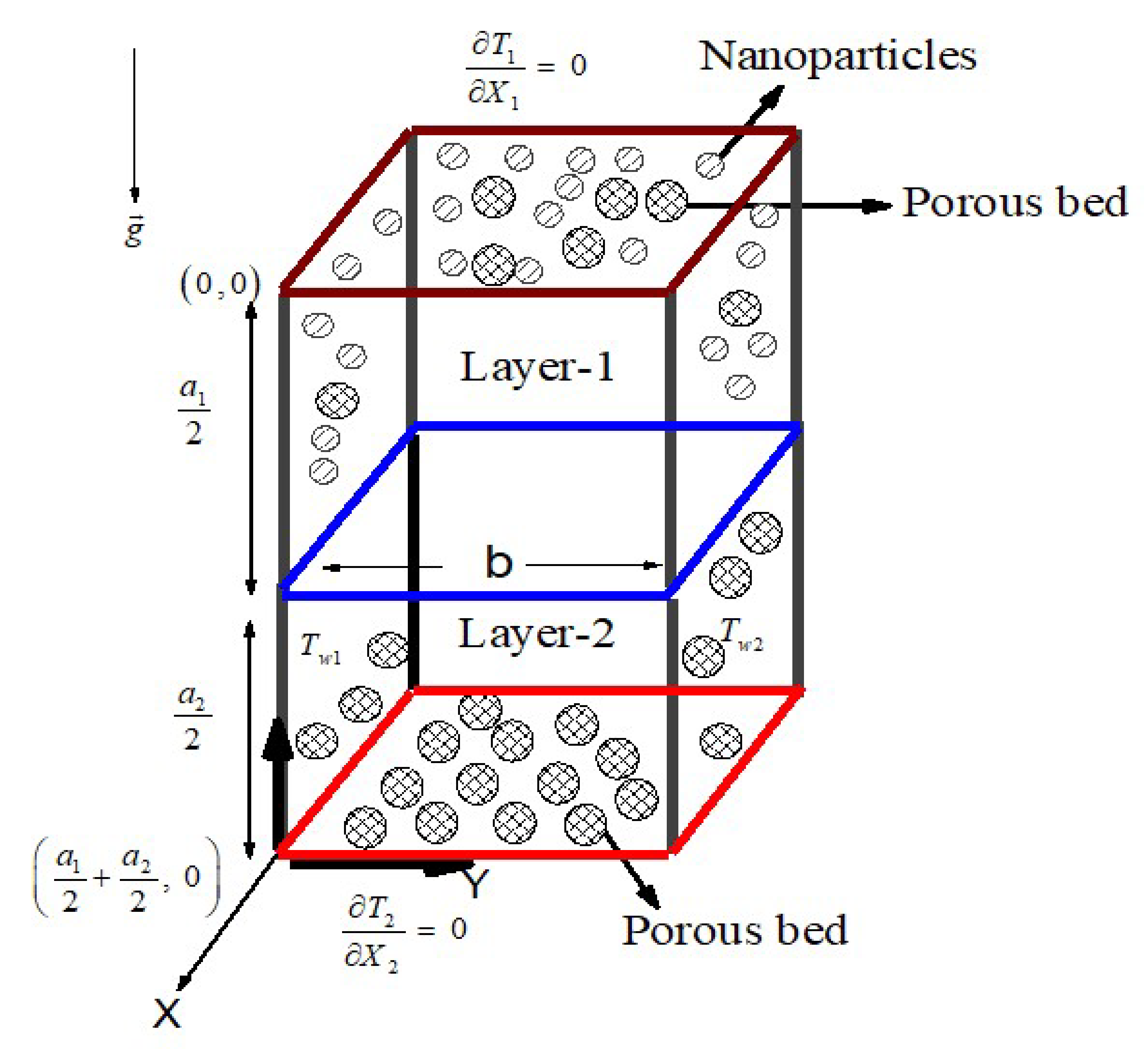
2. Mathematical Formulation
- -
- Layer-1 (Permeable nanofluid)
- -
- Layer-2 (Permeable fluid)
- -
- Layer-1
- -
- Interface
- -
- Layer-2
- -
- Layer-1
- -
- Layer-2
- -
- Layer-1
- -
- Interface
- -
- Layer-2
3. Numerical Solutions
- -
- Layer-1
- -
- Layer-2
- -
- Layer-1
- -
- Interface
- -
- Layer-2
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Velocity for Different Combinations of Base Fluid
4.2. Velocity Distributions for Different Nanoparticles Materials Using Water as the Base Fluid
4.3. Velocity Distributions for Different Values of Solid Volume Fraction
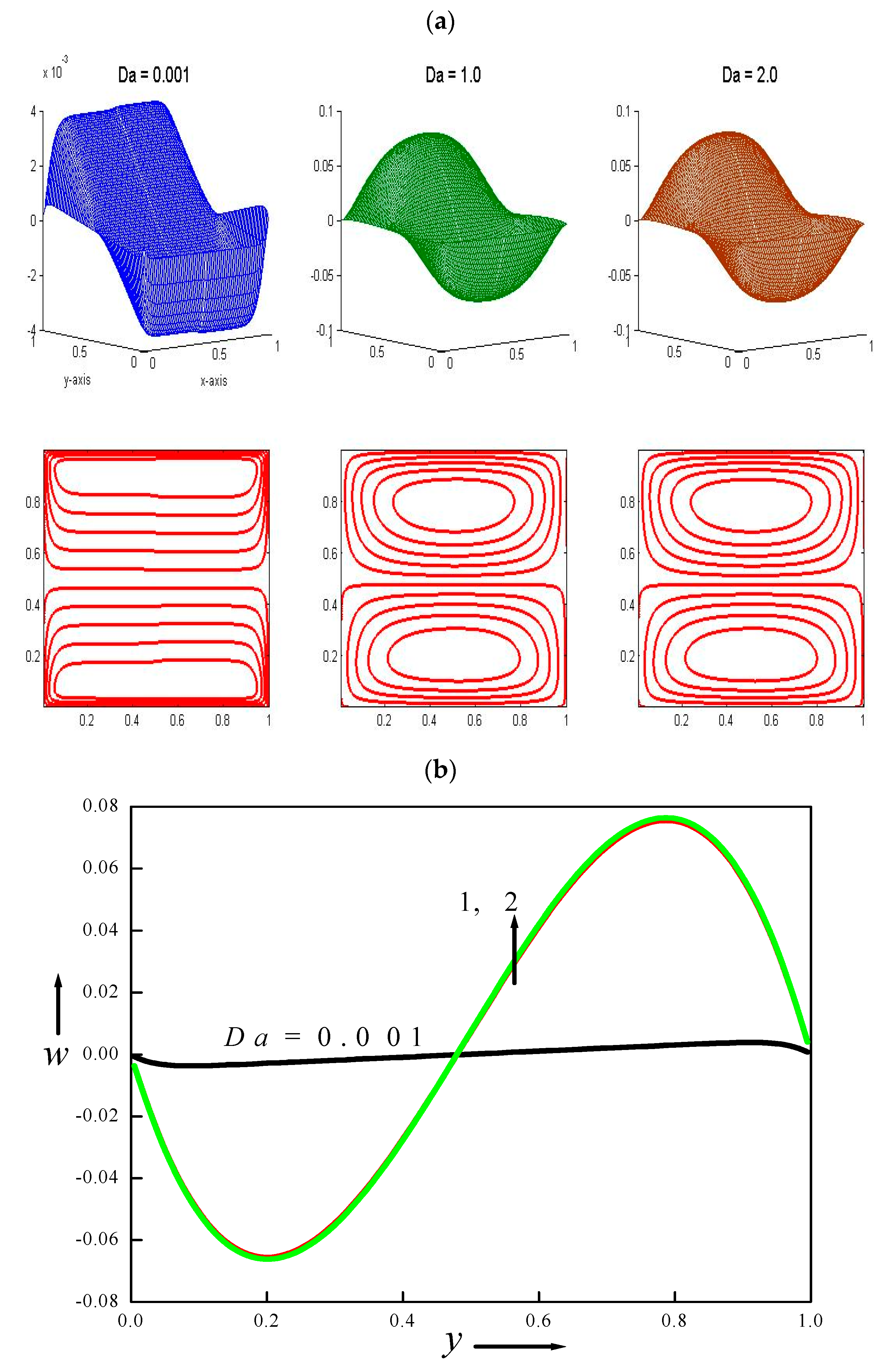
4.4. Velocity and Temperature Distributions for Different Values of Darcy Number
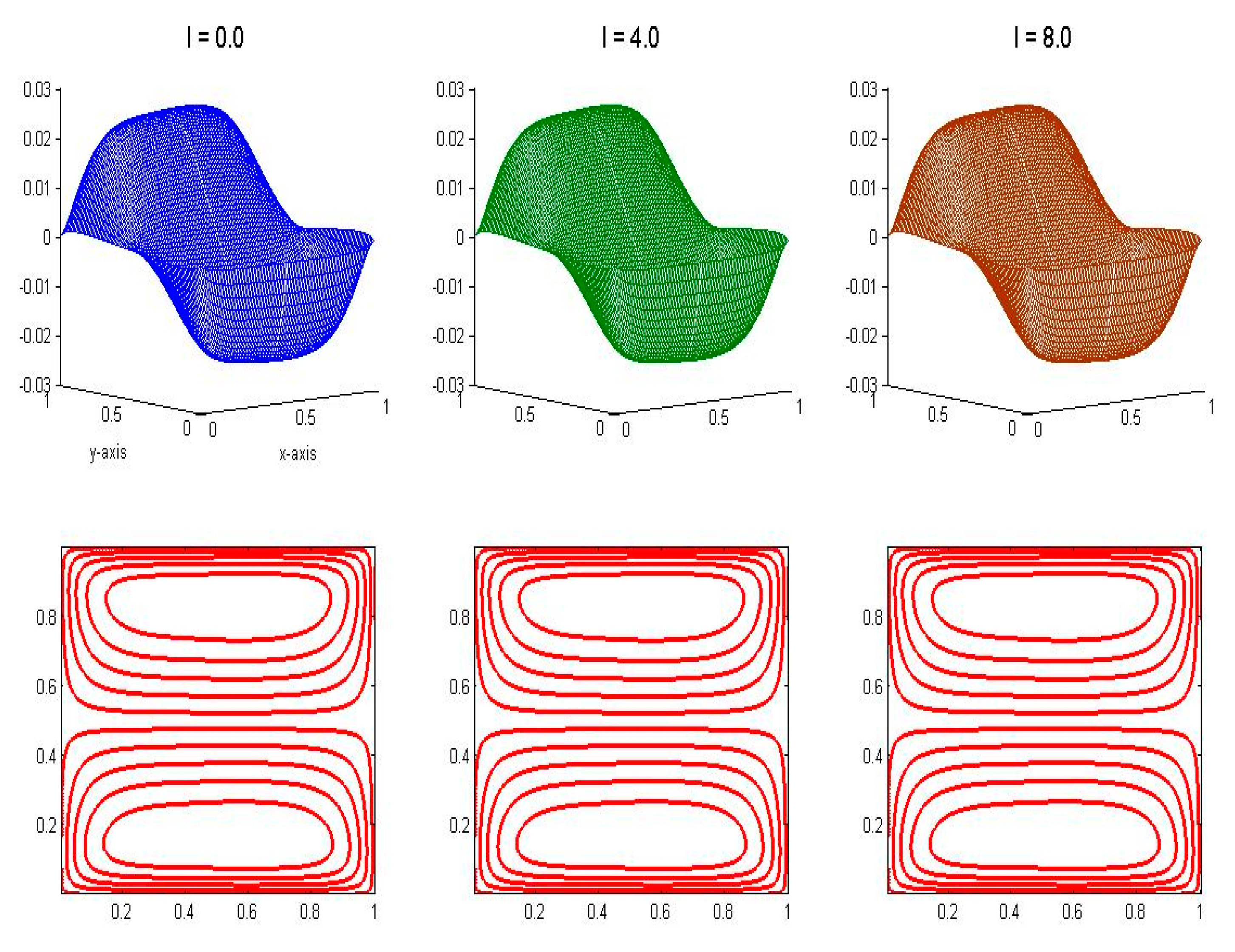
4.5. Velocity and Temperature Distributions for Different Values of Inertial Parameter
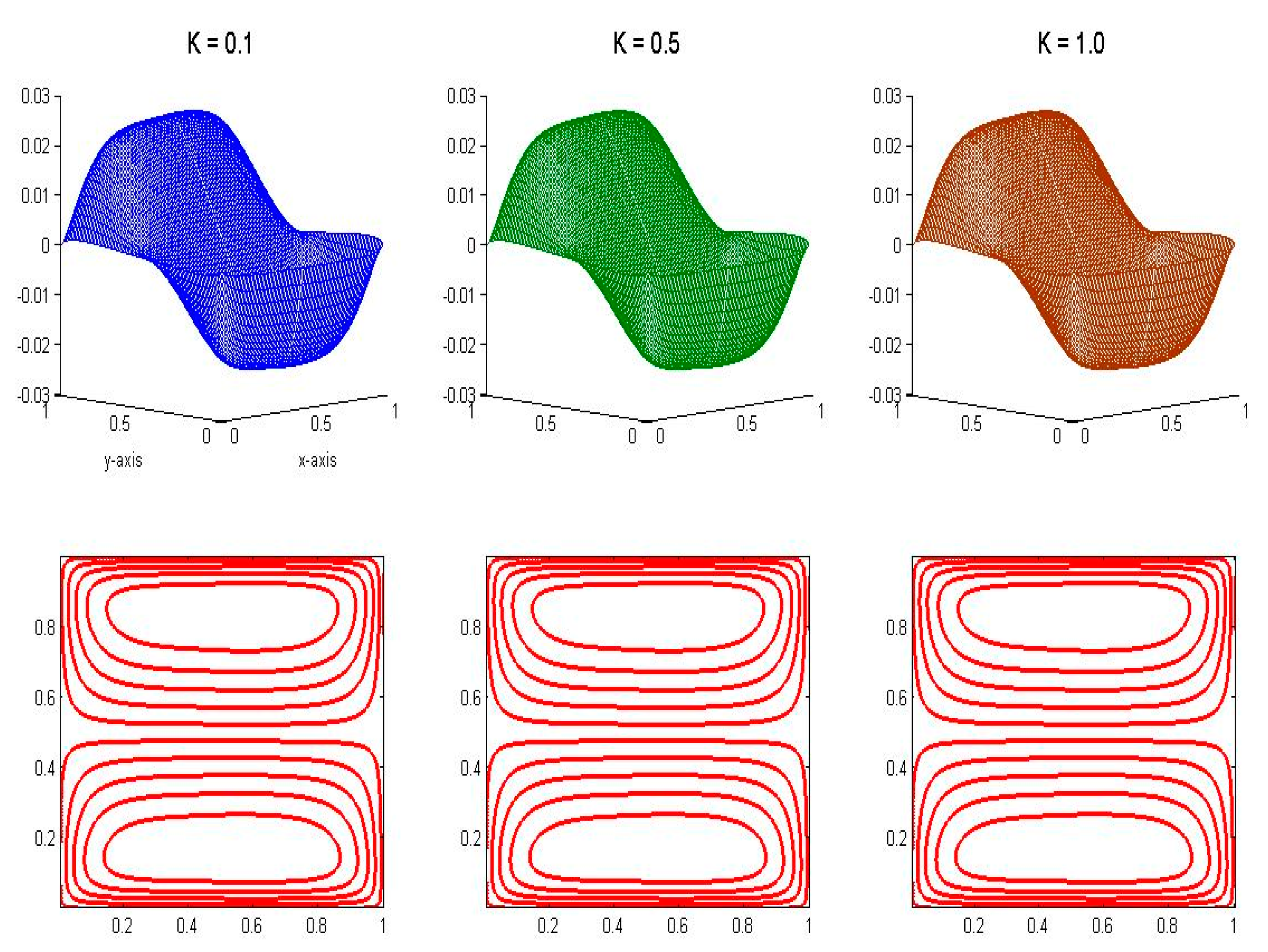
4.6. Velocity Distributions for Different Values of Permeability Ratio
4.7. Velocity Distributions for Different Values of Viscosity Ratios
4.8. Velocity Distributions for Different Values of Thermal Conductivity Ratio
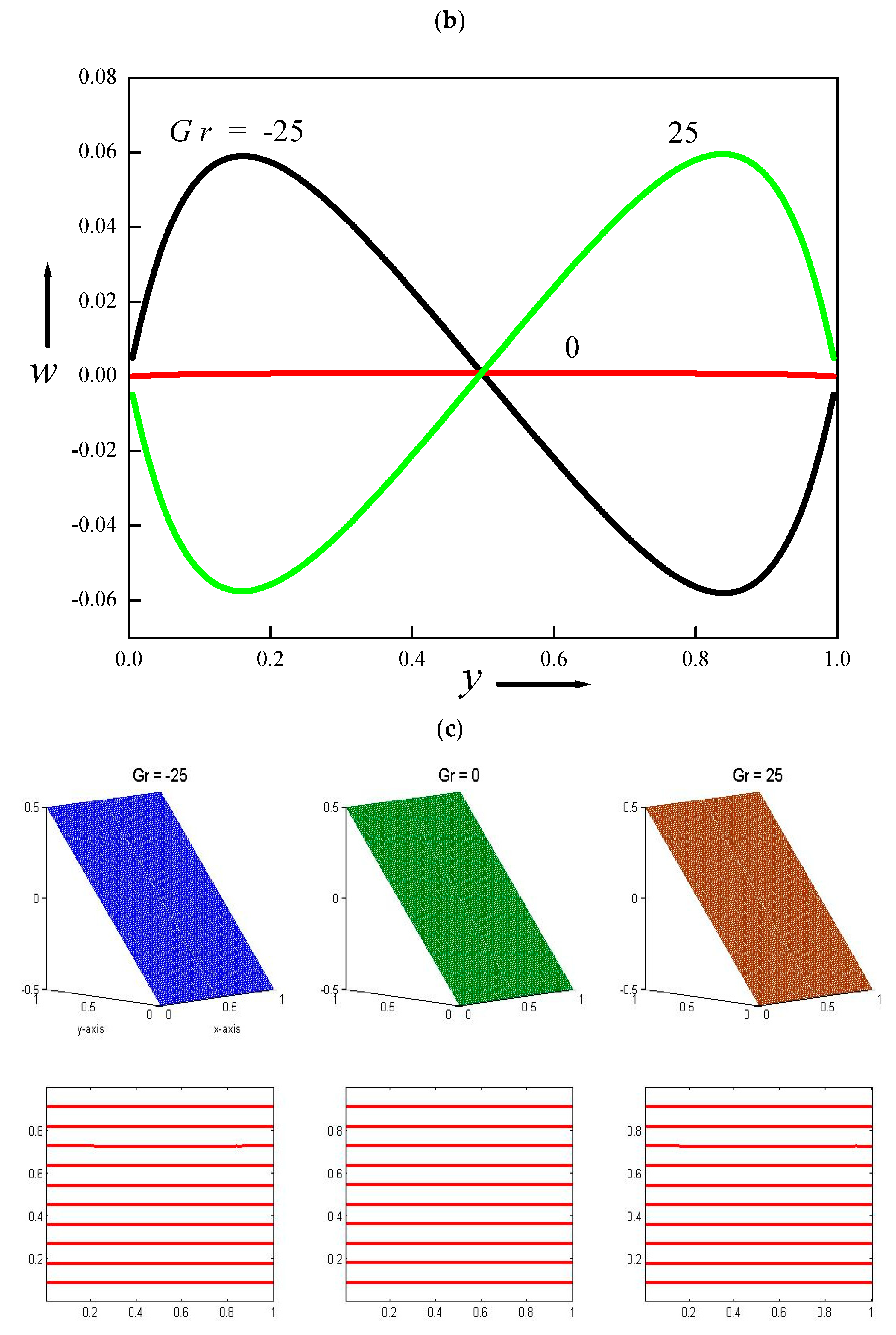
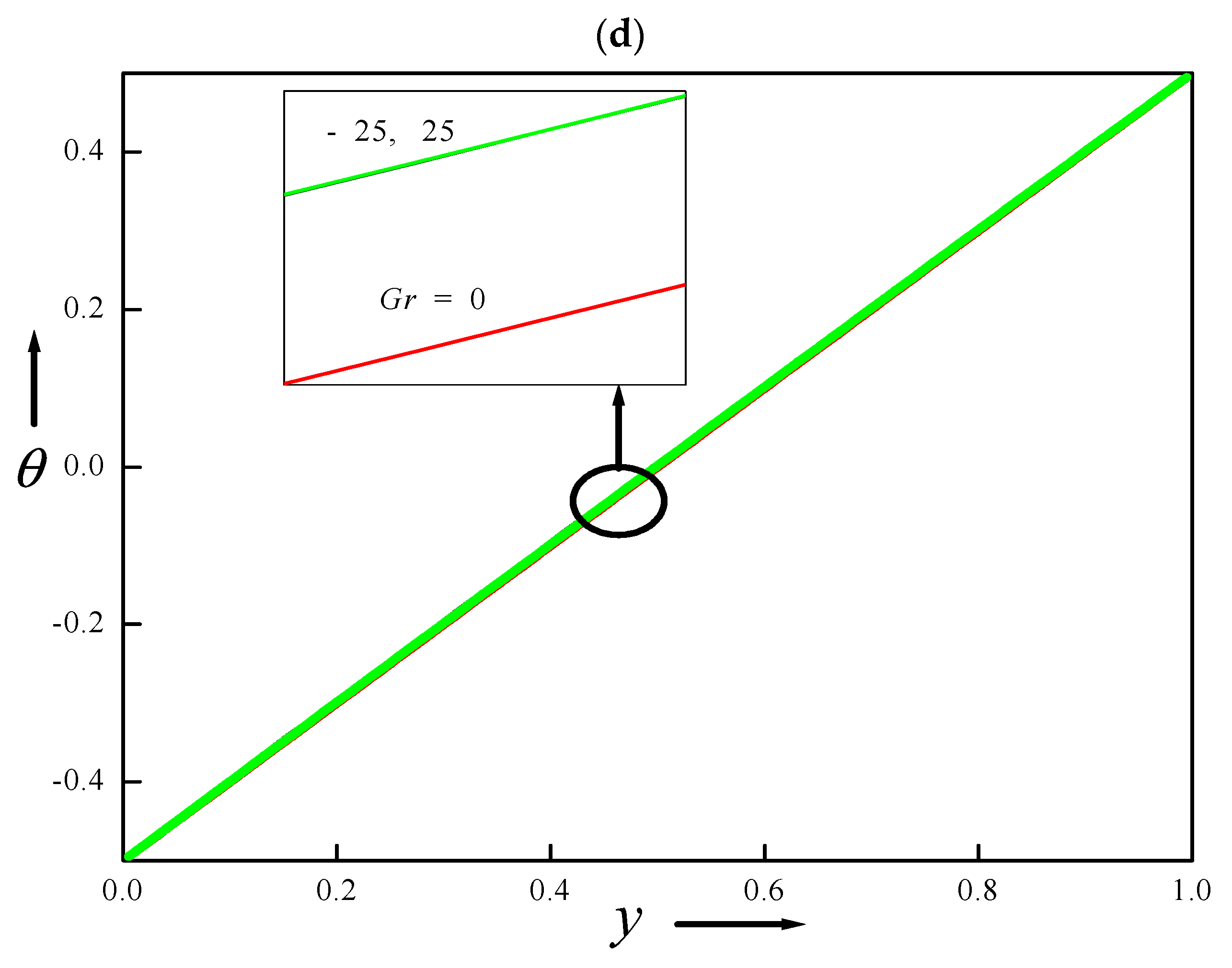
4.9. Velocity and Temperature Distributions for Different Values of Grashof Number
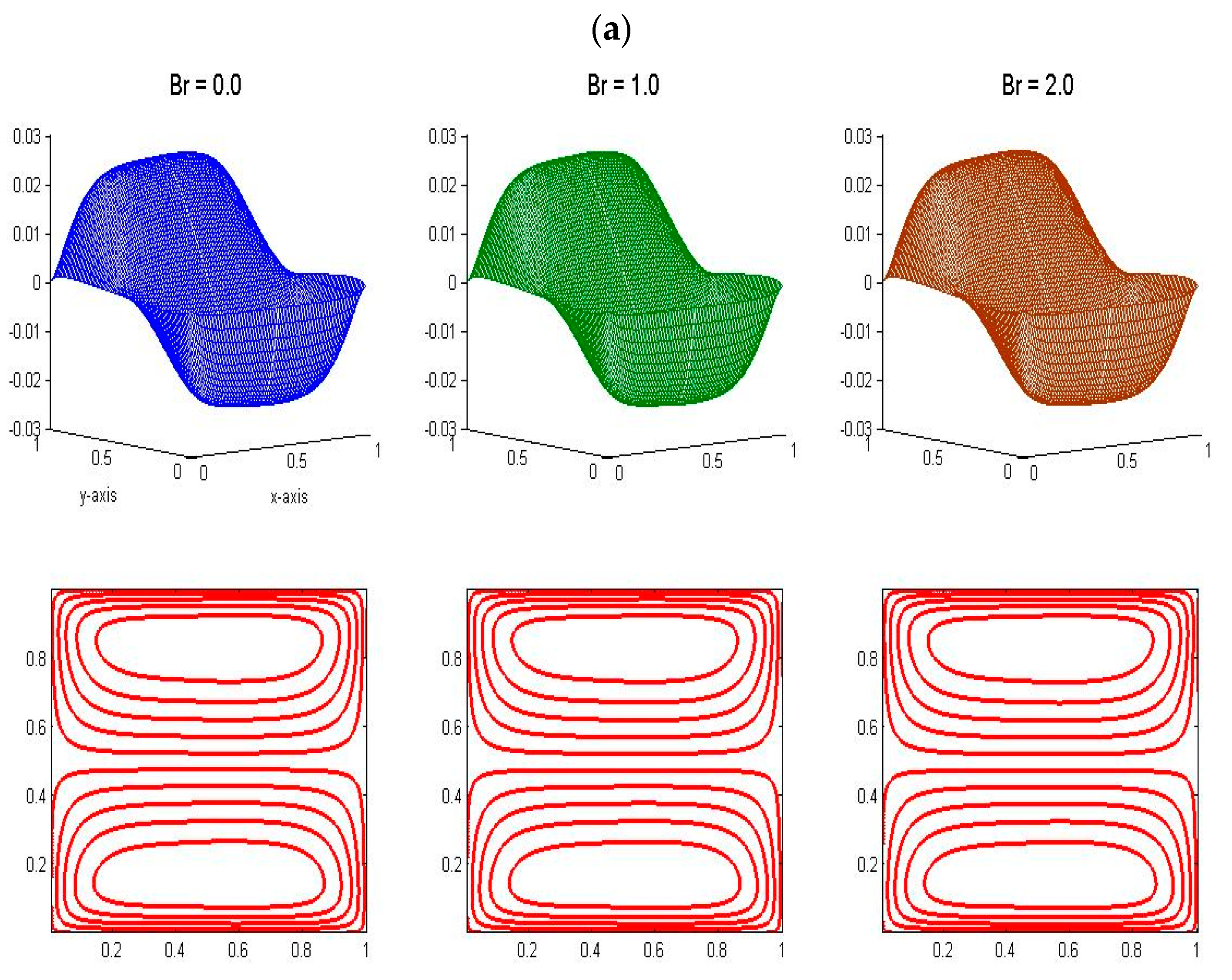
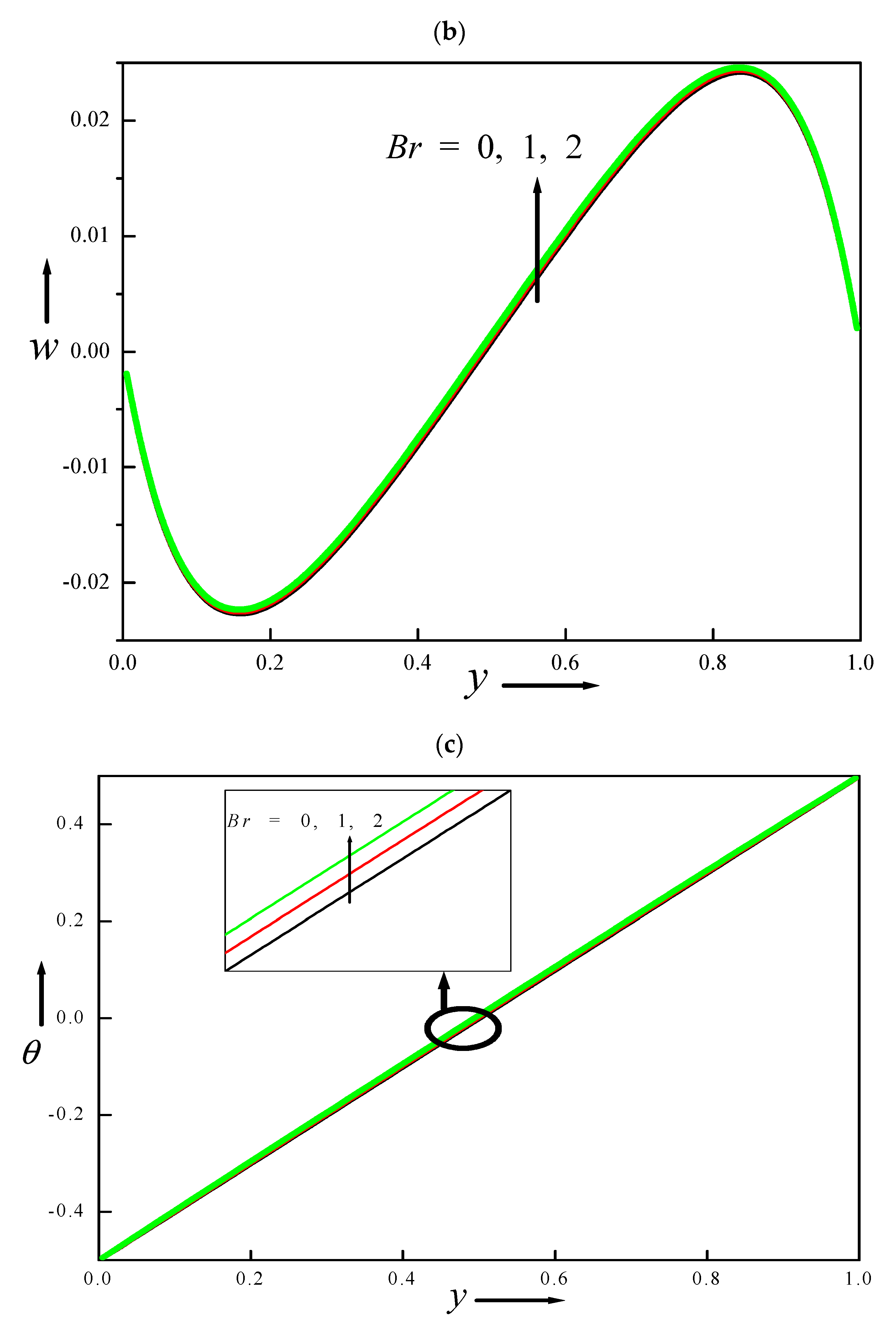
4.10. Velocity and Temperature Distributions for Different Values of Brikman Number
4.11. Values of Volumetric Flow Rate and Skin Friction
4.12. Values of Average Nusselt Number
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Yap, Y.; Lou, J.; Shang, Z. Numerical investigation of heat transfer in three-fluid stratified flows. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 89, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, A.R.A. Heat transfer enhancement in a vertical tube confining two immiscible falling co-flows. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 85, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Wong, T.N. Two immiscible layers of electro-osmotic driven flow with a layer of conducting non-Newtonian fluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 74, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redapangu, P.R.; Vanka, S.; Sahu, K.C. Multiphase lattice Boltzmann simulations of buoyancy-induced flow of two immiscible fluids with different viscosities. Eur. J. Mech.-B/Fluids 2012, 34, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umavathi, J.C.; Chamkha, A.J.; Sridhar, K.S.R. Generalised plain Couette flow heat transfer in a composite channel. Transp. Porous Media 2010, 85, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.-C.; Wang, H.-H.; Umavathi, J.C. Poiseuille-Couette flow and heat transfer in an inclined composite porous medium. J. Mech. 2012, 28, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umavathi, J.C.; Sheremet, M.A. Heat transfer of viscous fluid in a vertical channel sandwiched between nanofluid porous zones. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 144, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packham, B.A.; Shail, R. Stratified laminar flow of two immiscible fluids. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1971, 69, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, A.; Pak, A. Numerical study of factors influencing relative permeabilities of two immiscible fluids flowing through porous media using lattice Boltzmann method. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2011, 77, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, J.C. A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1904. [Google Scholar]
- Sus, C.; Ja, E. Enhancing Thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 1995 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exhibition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–17 November 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bahiraei, M.; Heshmatian, S. Thermal performance and second law characteristics of two new microchannel heat sinks operated with hybrid nanofluid containing grapheme-silver nanoparticles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 168, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashi’Ie, N.S.; Waini, I.; Kasim, A.R.M.; Zainal, N.A.; Arifin, N.M.; Pop, I. Thermal progress of a non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid flow on a permeable Riga plate with temporal stability analysis. Chin. J. Phys. 2022, 77, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketchate, C.G.N.; Kapen, P.T.; Fokwa, D.; Tchuen, G. Stability analysis of mixed convection in a porous horizontal channel filled with a Newtonian Al2O3/Water nanofluid in presence of magnetic field and thermal radiation. Chin. J. Phys. 2022, 79, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, A.; Abbas, Z. Stability analysis of heat transfer in nanomaterial flow of boundary layer towards a shrinking surface: Hybrid nanofluid versus nanofluid. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 10757–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvan, K.M.; Mamourian, M.; Mirzakhanlari, S.; Ellahi, R. Numerical investigation of heat exchanger effectiveness in a double pipe heat exchanger filled with nanofluid: A sensitivity analysis by response surface methodology. Powder Technol. 2017, 313, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheremet, M.A.; Revnic, C.; Pop, I. Free convection in a porous wavy cavity filled with a nanofluid using Buongiorno’s mathematical model with thermal dispersion effect. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 299, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Ganji, D.D. Applications of Semi Analytical Methods for Nanofluid Flow and Heat Transfer; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Heris, S.Z.; Nassan, T.H.; Noie, S.H.; Sardarabadi, H.; Sardarabadi, M. Laminar convective heat transfer of Al2O3/water nanofluid through square cross-sectional duct. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2013, 44, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassan, T.H.; Heris, S.Z.; Noie, S.H. A comparison of experimental heat transfer characteristics for Al2O3/water and CuO/water nanofluids in square cross-section duct. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 37, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heris, S.Z.; Nassan, T.H.; Noie, S.H. CuO/water nanofluid convective heat transfer through square duct under uniform heat flux. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Chen, X. Two immiscible stratified fluids with one nanofluid layer in a horizontal annulus. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Mixed convection heat transfer of double immiscible fluids in functional gradient material preparation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 121, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Liao, S. Heat and mass transfer of two-layer flows of third-grade nano-fluids in a vertical channel. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 242, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam Khan, N.; Sultan, F.; Rubbab, Q. Optimal solution of nonlinear heat and mass transfer in a two-layer flow with nano-Eyring–Powell fluid. Results Phys. 2015, 5, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umavathi, J.C.; Anwar Bég, O. Effects of thermophysical properties on heat transfer at the interface of two immiscible fluids in a vertical duct: Numerical study. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 154, 119613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztop, H.F.; Yasin, V.; Ahmet, K. Natural convection in a vertically divided square enclosure by a solid partition into air and water regions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 5909–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshkin, N.P. Numerical model to study natural convection in a rectangular enclosure filled with two immiscible fluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2002, 23, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vahl Davis, G. Laminar natural convection in an enclosed rectangular cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1968, 1, 1167–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vahl Davis, G. Natural convection of air in a square cavity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 1983, 3, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Grid size | ||
|---|---|---|
| 11 × 11 | 1.031892 | 1.00173 |
| 51 × 51 | 1.031877 | 1.001716 |
| 101 × 101 | 1.031878 | 1.001717 |
| 151 × 151 | 1.031879 | 1.001717 |
| 201 × 201 | 1.031879 | 1.001717 |
| Present for ϕ= 0.01, Da = 0.01, I = 4.0, κ = 1.0 | Present for ϕ = 0.0, Da = 0.0, I = 0.0, κ = 0.0 | Umavathi and Bég [26] for ϕ = 0.0, Da = 0.0, I = 0.0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer-1 | Layer-2 | Layer-1 | Layer-2 | Layer-1 | Layer-2 |
| 1.0319 | 1.0017 | 1.0046 | 1.0046 | 1.0046 | 1.0046 |
| I | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | Velocity | Temperature | ||||
| 0.0 | 4.0 | 8.0 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 8.0 | |
| 0.005 | −0.00191 | −0.00191 | −0.00191 | −0.49499 | −0.49499 | −0.49499 |
| 0.205 | −0.02175 | −0.02174 | −0.02173 | −0.29476 | −0.29476 | −0.29476 |
| 0.405 | −0.00758 | −0.00758 | −0.00757 | −0.0947 | −0.0947 | −0.0947 |
| 0.605 | 0.01042 | 0.01042 | 0.01041 | 0.10531 | 0.10531 | 0.10531 |
| 0.805 | 0.0238 | 0.02379 | 0.02377 | 0.30525 | 0.30525 | 0.30525 |
| 0.995 | 0.00201 | 0.00201 | 0.00201 | 0.45508 | 0.45508 | 0.45508 |
| K | ||||||
| Velocity | Temperature | |||||
| 0.1 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |
| 0.005 | −0.00191 | −0.00191 | −0.00191 | −0.49498 | −0.49498 | −0.49498 |
| 0.205 | −0.02171 | −0.02173 | −0.02174 | −0.29458 | −0.29469 | −0.29476 |
| 0.405 | −0.00754 | −0.00757 | −0.00758 | −0.09446 | −0.0946 | −0.0947 |
| 0.605 | 0.01046 | 0.01043 | 0.01042 | 0.10556 | 0.10541 | 0.10531 |
| 0.805 | 0.02382 | 0.02379 | 0.02379 | 0.30544 | 0.30533 | 0.30525 |
| 0.995 | 0.00201 | 0.00201 | 0.00201 | 0.49502 | 0.49501 | 0.49501 |
| Different Nanoparticles | ||||||
| Velocity | Temperature | |||||
| Copper | Diamond | TiO2 | Copper | Diamond | TiO2 | |
| 0.005 | −0.00191 | −0.00191 | −0.00191 | −0.49499 | −0.49499 | −0.49499 |
| 0.205 | −0.02174 | −0.02167 | −0.02166 | −0.29476 | −0.29476 | −0.29476 |
| 0.405 | −0.00758 | −0.00755 | −0.00755 | −0.0947 | −0.0947 | −0.0947 |
| 0.605 | 0.01042 | 0.01039 | 0.01038 | 0.10531 | 0.10531 | 0.10531 |
| 0.805 | 0.02379 | 0.02372 | 0.0237 | 0.30525 | 0.30525 | 0.30525 |
| 0.995 | 0.00201 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.49501 | 0.49501 | 0.49501 |
| Layer-1 | Layer-2 | Layer-1 | Layer-2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | ||||||
| Gr | ||||||
| −25 | 0.000393 | 0.000395 | 0.849089 | 0.835412 | 0.894193 | 0.87991 |
| 0.0 | 0.000637 | 0.00065 | 0.008279 | −0.008279 | 0.0087 | −0.0087 |
| 25 | 0.00088 | 0.0009 | −0.832576 | −0.852003 | −0.876882 | −0.897309 |
| Br | ||||||
| 0.0 | 0.000637 | 0.000649 | −0.328675 | −0.345231 | −0.34635 | −0.363732 |
| 1.0 | 0.000794 | 0.000811 | −0.327791 | −0.346196 | −0.345403 | −0.364767 |
| 2.0 | −0.32692 | −0.347180 | −0.344466 | −0.365822 | 0.000951 | 0.000975 |
| Da | ||||||
| 0.001 | 0.000086 | 0.000088 | −0.130087 | −0.135780 | −0.137434 | −0.143431 |
| 1.0 | 0.003476 | 0.003481 | −0.575485 | −0.62336 | −0.603157 | −0.652663 |
| 2.0 | 0.003559 | 0.003563 | −0.578577 | −0.627279 | −0.606351 | −0.656694 |
| I | ||||||
| 0.0 | 0.000653 | 0.000666 | −0.328617 | −0.345361 | −0.34639 | −0.363988 |
| 4.0 | 0.000652 | 0.000665 | −0.328586 | −0.345326 | −0.346255 | −0.363834 |
| 8.0 | 0.000652 | 0.000664 | −0.328555 | −0.345292 | −0.346121 | −0.363681 |
| κ | ||||||
| 0.1 | 0.000806 | 0.001812 | −0.344783 | −0.363251 | −0.513519 | −0.545572 |
| 1.0 | 0.000652 | 0.000665 | −0.328586 | −0.345326 | −0.346255 | −0.363834 |
| 2.0 | 0.000611 | 0.000399 | −0.321512 | −0.337719 | −0.275789 | −0.289002 |
| ϕ | ||||||
| 0.0 | −0.346946 | −0.364576 | −0.346842 | −0.364458 | 0.000668 | 0.000667 |
| 0.01 | 0.000652 | 0.000665 | −0.328586 | −0.345326 | −0.346255 | −0.363834 |
| 0.5 | 0.000134 | 0.000555 | −0.00873 | −0.009244 | −0.316545 | −0.332298 |
| λ | ||||||
| 0.1 | 0.000806 | 0.005461 | −0.359596 | −0.37863 | −3.032725 | −3.184318 |
| 0.5 | 0.000706 | 0.001244 | −0.341728 | −0.359329 | −0.663855 | −0.697464 |
| 1.0 | 0.000652 | 0.000665 | −0.328586 | −0.345326 | −0.346255 | −0.363834 |
| K | ||||||
| 0.1 | 0.000664 | 0.000725 | −0.328525 | −0.345392 | −0.345856 | −0.36428 |
| 0.5 | 0.000656 | 0.000674 | −0.328567 | −0.345346 | −0.346198 | −0.363897 |
| 1.0 | 0.000652 | 0.000665 | −0.328586 | −0.345326 | −0.346255 | −0.363834 |
| Nanoparticles | ||||||
| Copper | 0.000652 | 0.000665 | −0.328586 | −0.345326 | −0.346255 | −0.363834 |
| Diamond | 0.000652 | 0.000665 | −0.325075 | −0.341721 | −0.346139 | −0.363718 |
| Titanium oxide | 0.000652 | 0.000665 | −0.324219 | −0.340843 | −0.346111 | −0.363689 |
| Base fluids | ||||||
| Engine oil−Mineral oil | 0.000822 | 0.011935 | −0.354553 | −0.373580 | −8.154155 | −8.529412 |
| Ethylene Glycol−Mineral oil | 0.000661 | 0.000721 | −0.325498 | −0.342285 | −0.346757 | −0.36578 |
| Ethylene Glycol−Kerosene | 0.000763 | 0.005056 | −0.324544 | −0.343057 | −0.322369 | −0.468768 |
| Layer-1 | Layer-2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gr | ||||
| −25 | 1.041466 | 1.019122 | 1.011303 | 0.988959 |
| 0.0 | 1.030166 | 1.03016 | 1.000003 | 0.999997 |
| 25 | 1.041095 | 1.018737 | 1.010931 | 0.988572 |
| Br | ||||
| 0.0 | 1.030163 | 1.030163 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 1.0 | 1.047208 | 1.011305 | 1.017056 | 0.981116 |
| 2.0 | 1.064024 | 0.992075 | 1.033876 | 0.961852 |
| Da | ||||
| 0.001 | 1.030467 | 1.029834 | 1.000306 | 0.999668 |
| 1.0 | 1.034555 | 1.025214 | 1.004361 | 0.995088 |
| 2.0 | 1.034592 | 1.025167 | 1.004398 | 0.995042 |
| I | ||||
| 0.0 | 1.03188 | 1.028292 | 1.001719 | 0.998125 |
| 4.0 | 1.031878 | 1.028293 | 1.001717 | 0.998128 |
| 8.0 | 1.031877 | 1.028294 | 1.001715 | 0.99813 |
| Κ | ||||
| 0.1 | 1.032403 | 1.02772 | 1.003029 | 0.996647 |
| 1 | 1.031878 | 1.028293 | 1.001717 | 0.998128 |
| 2 | 1.031692 | 1.028494 | 1.00125 | 0.998643 |
| ϕ | ||||
| 0.0 | 1.001743 | 0.998099 | 1.001742 | 0.998101 |
| 0.01 | 1.031878 | 1.028293 | 1.001717 | 0.998128 |
| 0.5 | 3.973438 | 3.971892 | 1.001020 | 0.998873 |
| λ | ||||
| 0.1 | 1.03447 | 1.025534 | 1.010732 | 0.988207 |
| 0.5 | 1.032297 | 1.027845 | 1.002908 | 0.996818 |
| 1.0 | 1.031878 | 1.028293 | 1.001717 | 0.998128 |
| K | ||||
| 0.1 | 1.032476 | 1.027657 | 1.011136 | 0.987557 |
| 0.5 | 1.032124 | 1.028033 | 1.002941 | 0.996774 |
| 1.0 | 1.031878 | 1.028293 | 1.001717 | 0.998128 |
| Nanoparticles | ||||
| Copper | 1.031878 | 1.028293 | 1.001717 | 0.998128 |
| Diamond | 1.031948 | 1.028392 | 1.001712 | 0.998133 |
| Titanium oxide | 1.026479 | 1.022934 | 1.001713 | 0.998132 |
| Base fluids | ||||
| Engine oil–Mineral oil | 1.036451 | 1.023681 | 1.020135 | 0.978092 |
| Ethylene Glycol–Mineral oil | 1.032169 | 1.028151 | 1.002844 | 0.996861 |
| Ethylene Glycol–Kerosene | 1.031712 | 1.028603 | 1.000655 | 0.999104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umavathi, J.C.; Sheremet, M.A. Linear Model for Two-Layer Porous Bed Suspended with Nano Sized Particles. Energies 2023, 16, 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16042044
Umavathi JC, Sheremet MA. Linear Model for Two-Layer Porous Bed Suspended with Nano Sized Particles. Energies. 2023; 16(4):2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16042044
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmavathi, Jawali C., and Mikhail A. Sheremet. 2023. "Linear Model for Two-Layer Porous Bed Suspended with Nano Sized Particles" Energies 16, no. 4: 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16042044
APA StyleUmavathi, J. C., & Sheremet, M. A. (2023). Linear Model for Two-Layer Porous Bed Suspended with Nano Sized Particles. Energies, 16(4), 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16042044






