New Sustainable Banana Value Chain: Waste Valuation toward a Circular Bioeconomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study, Scope of Problem, and Data Collection
2.2. Model Formulation
- The methane yield of each banana substrate is not affected by substrate mixtures [38].
- The exchange rate is THB/USD 35.
- The total cost of anaerobic digestion system is USD 230/m3, including capital cost of USD 87/m3, operational cost of USD 58/m3, and maintenance and other cost of USD 85/m3, according to Sritrakul and Hudakorn [53].
- The average cost of LPG in Thailand is USD 0.71/kg.
- Lifespan of an anaerobic digester is 15 years [53].
- The moisture content of banana residues affects transportation cost [32]. The moisture content of banana tree can be reduced by sun drying at banana farms [35], resulting in lower total transportation cost. For simplicity, the moisture content of banana tree biomass is reduced to 50% before transporting to the factory.
2.2.1. Profit Determination
2.2.2. Model Constraints
2.2.3. Waste Chain Valuation
2.3. Economic and Environmental Performance
2.4. New Sustainable Value Chain Modeling
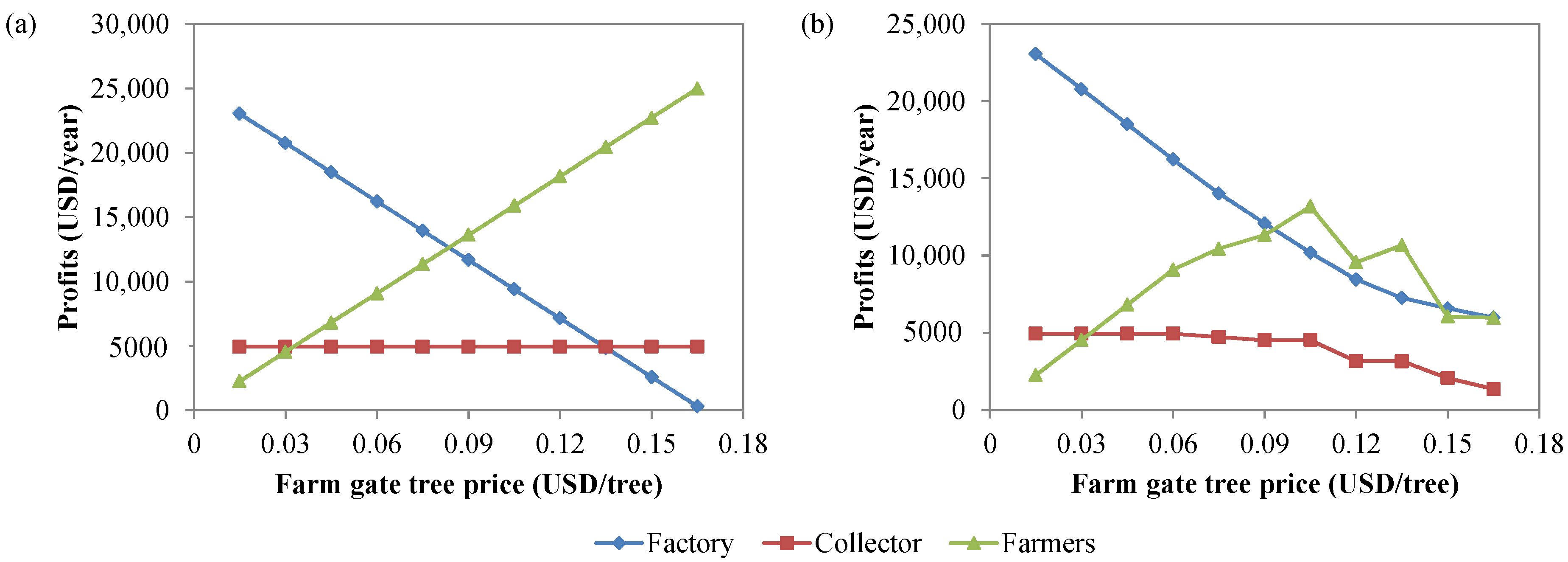
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Banana Chips Value Chain
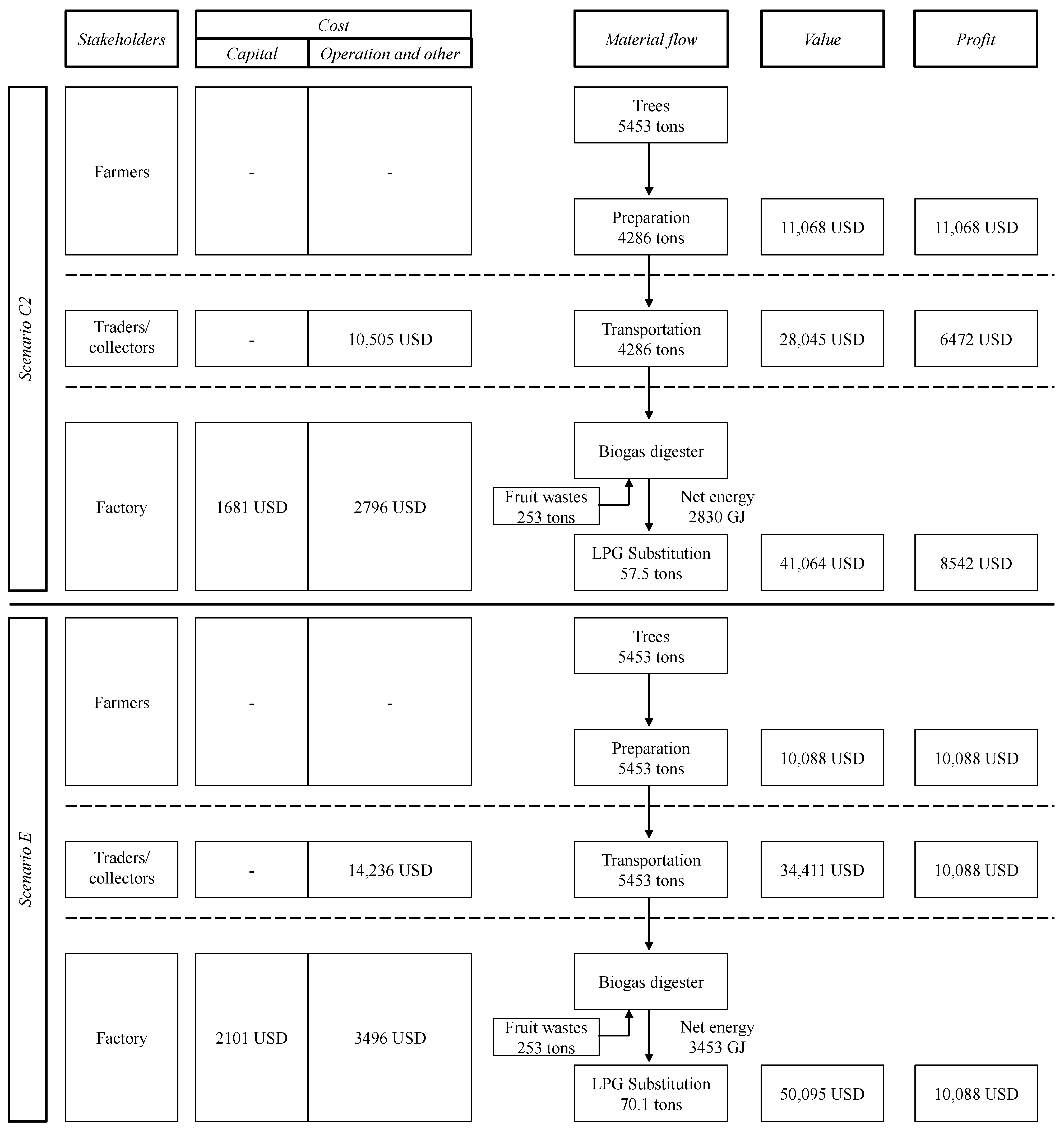
3.2. Waste Chain Valuation
3.2.1. Fruit Waste
3.2.2. Banana Tree
3.2.3. Transportation Cost
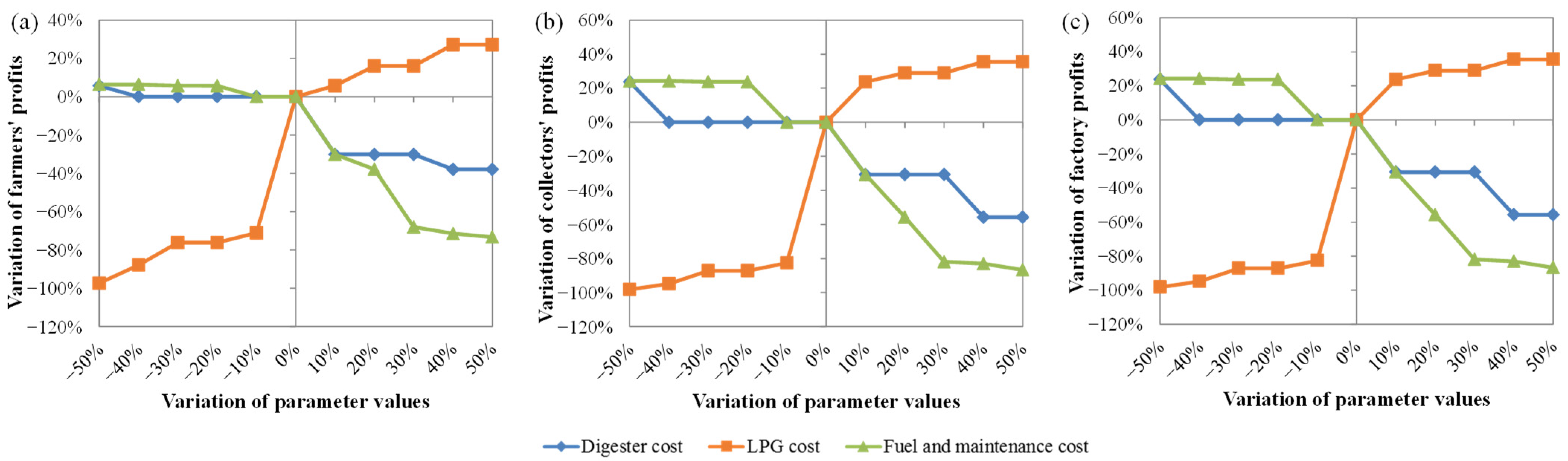
3.3. Sustainability Performance
3.3.1. Economic Performance
3.3.2. Environmental Performance
3.4. Sustainable Value Chain Modeling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, R.; Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A. A systematic literature review on machine learning applications for sustainable agriculture supply chain performance. Comput. Oper. Res. 2020, 119, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.; Agrawal, A.; Wollenberg, L. Enhancing the sustainability of commodity supply chains in tropical forest and agricultural landscapes. Global Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, F.O.; Thomas, C.L.P.; Afolabi, O.O.D. Integrated conversion technologies for sustainable agri-food waste valorization: A critical review. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 156, 106314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalde-Calonge, A.; Sáez-Martínez, F.J.; Ruiz-Palomino, P. Evolution of research on circular economy and related trends and topics. A thirteen-year review. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; López-Felices, B.; Román-Sánchez, I.M. Circular economy in agriculture. An analysis of the state of research based on the life cycle. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 34, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, G.G.; Rik, E.; Kijne, A. Analysis of banana value chain in Ethiopia: Approaches to sustainable value chain development. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1742516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utami, R.M.; Lantu, D.C. Development Competitiveness Model for Small-Medium Enterprises among the Creative Industry in Bandung. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 115, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Velásquez, C.; Leduc, S.; van der Meer, Y. Design of biobased supply chains on a life cycle basis: A bi-objective optimization model and a case study of biobased polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 30, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, G.G.; Fikadu, A.A.; Gebeyehu, T.K. Is banana value chain in East Africa sustainable? Evidence from Ethiopia. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 8, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.; Mishra, S.; Singh, C.B.; Jayas, D.S. Post-harvest Processing of Banana: Opportunities and Challenges. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2011, 4, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krungkaew, S.; Hülsemann, B.; Kingphadung, K.; Mahayothee, B.; Oechsner, H.; Müller, J. Methane production of banana plant: Yield, kinetics and prediction models influenced by morphological parts, cultivars and ripening stages. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, G.J. A review of root, tuber and banana crops in developing countries: Past, present and future. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 56, 1093–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbasiouny, H.; Elbanna, B.A.; Al-Najoli, E.; Alsherief, A.; Negm, S.; Abou El-Nour, E.; Nofal, A.; Sharabash, S. Agricultural Waste Management for Climate Change Mitigation: Some Implications to Egypt. In Waste Management in MENA Regions; Negm, A.M., Shareef, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 149–169. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Obadi, M.; Ayad, H.; Pokharel, S.; Ayari, M.A. Perspectives on food waste management: Prevention and social innovations. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 31, 190–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Jiménez, J.A.; Luna-Lama, F.; Caballero, Á.; Martín, M.d.l.Á.; Chica, A.F.; Siles, J.Á. Valorisation of banana peel waste as a precursor material for different renewable energy systems. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 155, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.H.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, J.; Rasool, T.; Naqvi, S.R. Thermo-kinetics and gaseous product analysis of banana peel pyrolysis for its bioenergy potential. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 122, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mylapilli, S.V.P.; Reddy, S.N. Thermogravimetric and kinetic studies of metal (Ru/Fe) impregnated banana pseudo-stem (Musa acuminate). Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawarkar, A.N.; Kirti, N.; Tagade, A.; Tekade, S.P. Bioethanol from various types of banana waste: A review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 18, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptak, M.; Skowrońska, A.; Pińkowska, H.; Krzywonos, M. Sugar Beet Pulp in the Context of Developing the Concept of Circular Bioeconomy. Energies 2022, 15, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufficiency, E.; Qamar, S.A.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Franco, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Bilal, M. Emerging biotechnological strategies for food waste management: A green leap towards achieving high-value products and environmental abatement. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Brulé, M.; Maurer, C.; Argyropoulos, D.; Müller, J.; Oechsner, H. Batch anaerobic digestion of banana waste—Energy potential and modelling of methane production kinetics. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2016, 18, 110–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Fan, G.; Zhang, L. Alkaline pretreatment for enhancement of biogas production from banana stem and swine manure by anaerobic codigestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, V.B.; Rathore, V.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Anaerobic co-digestion of water hyacinth and banana peels with and without thermal pretreatment. Renew. Energy 2019, 134, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, V.C.; Sonakya, V.; Raizada, N. Anaerobic digestion of banana stem waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 73, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, W.P.; Radnidge, P.; Lai, T.E.; Jensen, P.D.; Hardin, M.T. Digestion of waste bananas to generate energy in Australia. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odedina, M.J.; Charnnok, B.; Saritpongteeraka, K.; Chaiprapat, S. Effects of size and thermophilic pre-hydrolysis of banana peel during anaerobic digestion, and biomethanation potential of key tropical fruit wastes. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achinas, S.; Krooneman, J.; Euverink, G.J.W. Enhanced Biogas Production from the Anaerobic Batch Treatment of Banana Peels. Engineering 2019, 5, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumutegyereize, P.; Muranga, F.I.; Kawongolo, J.; Nabugoomu, F. Optimization of biogas production from banana peels: Effect of particle size on methane yield. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 18243–18251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awedem Wobiwo, F.; Alleluya, V.K.; Emaga, T.H.; Boda, M.; Fokou, E.; Gillet, S.; Deleu, M.; Gerin, P.A. Recovery of fibers and biomethane from banana peduncles biomass through anaerobic digestion. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaseelan, V.N. Biochemical methane potential of fruits and vegetable solid waste feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 26, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adsal, K.A.; Üçtuğ, F.G.; Arikan, O.A. Environmental life cycle assessment of utilizing stem waste for banana production in greenhouses in Turkey. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2020, 22, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchôa, P.Z.; Porto, R.C.T.; Battisti, R.; Marangoni, C.; Sellin, N.; Souza, O. Ethanol from residual biomass of banana harvest and commercialization: A three-waste simultaneous fermentation approach and a logistic-economic assessment of the process scaling-up towards a sustainable biorefinery in Brazil. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 174, 114170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, N.; Razali, A.N.; Mahlia, T.M.; Chowdhury, T.; Chowdhury, H.; Ong, H.C.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Silitonga, A.S. Experimental Investigation, Techno-Economic Analysis and Environmental Impact of Bioethanol Production from Banana Stem. Energies 2019, 12, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Gómez, L.A.; Solarte-Toro, J.C.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Cardona-Alzate, C.A. Performance evaluation and economic analysis of the bioethanol and flour production using rejected unripe plantain fruits (Musa paradisiaca L.) as raw material. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 121, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, S.H.; Cardona, C.A.; Moncada, J. Techno-Economic and Environmental Analysis of Ethanol Production from 10 Agroindustrial Residues in Colombia. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ruano, J.A.; Caballero-Galván, A.S.; Restrepo-Serna, D.L.; Cardona, C.A. Techno-economic and environmental assessment of biogas production from banana peel (Musa paradisiaca) in a biorefinery concept. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 35971–35980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Alçada-Almeida, L.; Dias, L.C. Multiobjective programming for sizing and locating biogas plants: A model and an application in a region of Portugal. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 83, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsson, R.; Persson, U.M. Analyzing key constraints to biogas production from crop residues and manure in the EU-A spatially explicit model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasik, A.; Kanellopoulos, A.; Claassen, G.D.H.; Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J.M.; van der Vorst, J.G.A.J. Assessing alternative production options for eco-efficient food supply chains using multi-objective optimization. Ann. Oper. Res. 2017, 250, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasik, A.; Kanellopoulos, A.; Claassen, G.D.H.; Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J.M.; van der Vorst, J.G.A.J. Closing loops in agricultural supply chains using multi-objective optimization: A case study of an industrial mushroom supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaeenezhad, T.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Cheikhrouhou, N. Multi-objective mathematical modeling for sustainable supply chain management in the paper industry. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 135, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Fathollahi Fard, A.M. Sustainable closed-loop supply chain network design with discount supposition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 5343–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Mirjalili, S. Multi-objective stochastic closed-loop supply chain network design with social considerations. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 71, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarbossa, F.; Russo, I. A proactive model in sustainable food supply chain: Insight from a case study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He-Lambert, L.; Shylo, O.; English, B.C.; Eash, N.S.; Zahn, J.A.; Lambert, D.M. Supply chain and logistic optimization of industrial Spent Microbial Biomass distribution as a soil amendment for field crop production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Arshinder, K.; Agarwal, R. Robust optimization of sustainable food supply chain network considering food waste valorization and supply uncertainty. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 171, 108499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, S.; Heydari, J.; Sazvar, Z. Food waste recycling closed loop supply chain optimization through renting waste recycling facilities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 78, 103644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayılan, S.; Yılmaz, Ö.; Uysal, Ç.; Naneci, S. Prospective evaluation of circular economy practices within plastic packaging value chain through optimization of life cycle impacts and circularity. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 173, 105691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James Rubinsin, N.; Daud, W.R.W.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Masdar, M.S.; Rosli, M.I.; Samsatli, S.; Tapia, J.F.; Wan Ab Karim Ghani, W.A.; Lim, K.L. Optimization of oil palm empty fruit bunches value chain in Peninsular Malaysia. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 119, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiallos-Cárdenas, M.; Pérez-Martínez, S.; Ramirez, A.D. Prospectives for the development of a circular bioeconomy around the banana value chain. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 30, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.K.; Yang, G.-l.; Malesios, C.; De, D.; Evangelinos, K. Performance Management of Supply Chain Sustainability in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Using a Combined Structural Equation Modelling and Data Envelopment Analysis. Comput. Econ. 2021, 58, 573–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanadee, W.; Chanudomporn, C.; Tangkittipong, K.; Raweewan, M. Opportunity and Value Development for Thai Bananas. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Economics and Business Information, Bangkok, Thailand, 7–9 May 2011; pp. 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sritrakul, N.; Hudakorn, T. The economic value and satisfaction of substituting LPG in households by a biogas network: A case study of Bo Rae Subdistrict in Chai Nat Province Thailand. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zuo, J.; Gan, L.; Li, P.; Liu, F.; Wang, K.; Chen, L.; Gan, H. Effects of mixture ratio on anaerobic co-digestion with fruit and vegetable waste and food waste of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtane, R.D.; Suryawanshi, P.C.; Patil, M.R.; Chaudhari, A.B.; Kothari, R.M. Optimization of organic loading rate for different fruit wastes during biomethanization. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2009, 68, 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- Sritong, N.; Promjiraprawat, K.; Limmeechokchai, B. CO2 Mitigation in the Road Transport Sector in Thailand: Analysis of Energy Efficiency and Bio-energy. Energy Procedia 2014, 52, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongwiriya, P.; Nakamura, F.; Tanaka, S.; Ariyoshi, R.; Miura, S. The Role of Paratransit to Support Sustainable Transportation: Case Study of Khon Kaen City, Thailand. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 48, 2656–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balhasan, S.; Alnahhal, M.; Shawan, S.; Salah, B.; Saleem, W.; Tabash, M.I. Optimization of Exploration and Production Sharing Agreements Using the Maxi-Min and Nash Solutions. Energies 2022, 15, 8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.A.; Grabs, J. Rethinking the “Necessary” Trade-offs of Distributing Value to Suppliers: An Analysis of the Profit-Sharing Model; Harvard Kennedy School Working Paper Series; Harvard University: Camebridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traivivatana, S.; Wangjiraniran, W. Thailand Integrated Energy Blueprint (TIEB): One Step towards Sustainable Energy Sector. Energy Procedia 2019, 157, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, S. A spatial modeling approach for siting, sizing and economic assessment of centralized biogas plants in organic waste management. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Miller, R.; Sloan, W.; You, S. Economic and environmental assessment of organic waste to biomethane conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, I.; Garfí, M.; Cadena, E.; Ferrer, I. Technical, economic and environmental assessment of household biogas digesters for rural communities. Renew. Energy 2014, 62, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese, D.; Patrizio, P.; Nardin, G. Effects of changes in Italian bioenergy promotion schemes for agricultural biogas projects: Insights from a regional optimization model. Energy Policy 2014, 75, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stattman, S.L.; Mol, A.P.J. Social sustainability of Brazilian biodiesel: The role of agricultural cooperatives. Geoforum 2014, 54, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.H.; Ghazoul, J.; Obidzinski, K.; Koh, L.P. Oil palm smallholder yields and incomes constrained by harvesting practices and type of smallholder management in Indonesia. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Liu, C.; Xing, J.; Yang, W.; Ren, J. Linking bioenergy production by agricultural residues to sustainable development goals: Prospects by 2030 in China. Energy Conv. Manag. 2023, 276, 116568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, I.; Sassanelli, C. Biomethane Community: A Research Agenda towards Sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Sarangi, P.; Subudhi, S.; Bhatia, L.; Saha, K.; Mudgil, D.; Prasad Shadangi, K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Pattnaik, B.; Arya, R.K. Utilization of agricultural waste biomass and recycling toward circular bioeconomy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 8526–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



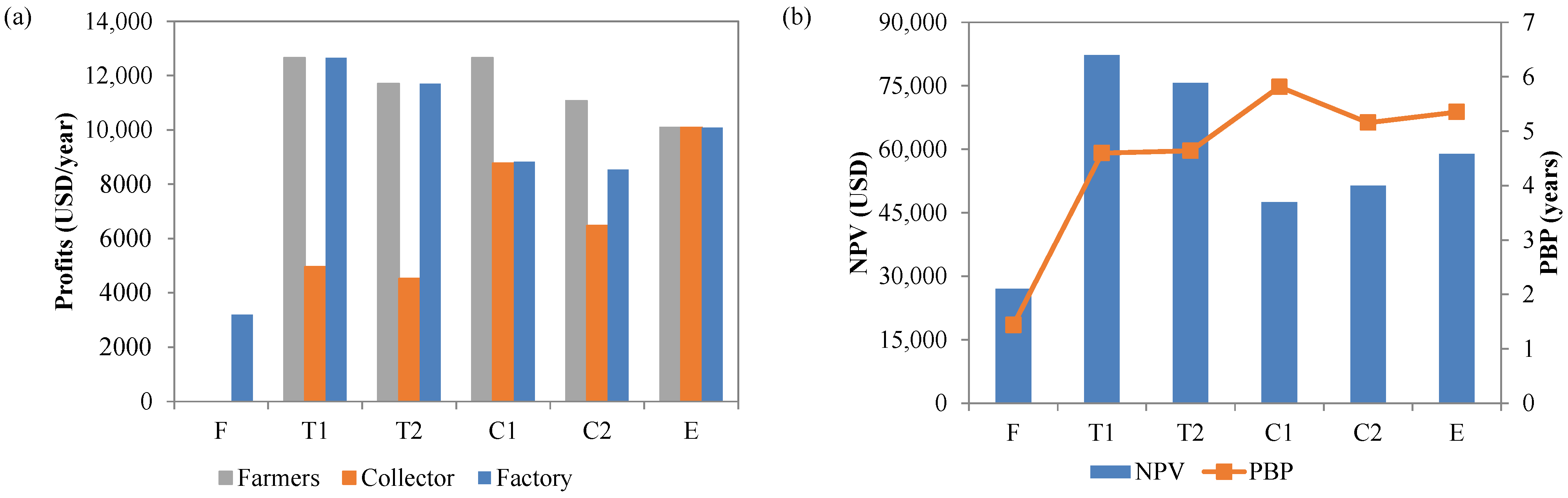




| Scenario | Utilized Wastes | Farm Gate Tree Price | Transportation Cost | Optimization Objective | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruit | Tree | ||||
| F | ✓ | - | - | - | Maximize factory profit |
| T1 | ✓ | ✓ | Varied | Fixed | Maximize chain profit |
| T2 | ✓ | ✓ | Varied | Fixed | Maximize factory profit |
| C1 | ✓ | ✓ | Fixed | Varied | Maximize chain profit |
| C2 | ✓ | ✓ | Fixed | Varied | Maximize factory profit |
| E | ✓ | ✓ | Solved | Solved | Maximize chain profit |
| Stakeholders | Added Value (USD) | Profit (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Farmers | 171,429 | 65,281 |
| Collectors | 120,000 | 113,028 |
| Factory | 737,143 | 243,429 |
| Scenario | Farm Gate Tree Price (USD/tree) | Transportation Cost (USD/km) |
|---|---|---|
| F | - | - |
| T1 | 0.084 | 0.31 |
| T2 | 0.093 | 0.31 |
| C1 | 0.084 | 0.37 |
| C2 | 0.093 | 0.37 |
| E | 0.067 | 0.39 |
| Stakeholders | Scenario C2 | Scenario E | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added Value (USD) | Profit (USD) | Added Value (USD) | Profit (USD) | |
| Farmers | 11,068 | 11,068 | 10,088 | 10,088 |
| Collectors | 16,977 | 6472 | 24,323 | 10,088 |
| Factory | 13,019 | 8542 | 15,684 | 10,088 |
| Stakeholders | Scenario C2 | Scenario E | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added Value (USD) | Profit (USD) | Added Value (USD) | Profit (USD) | |
| Farmers | 182,497 | 76,349 | 181,516 | 75,368 |
| Collectors | 136,977 | 119,500 | 144,323 | 123,116 |
| Factory | 750,162 | 251,970 | 752,827 | 253,516 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krungkaew, S.; Hülsemann, B.; Kingphadung, K.; Mahayothee, B.; Oechsner, H.; Müller, J. New Sustainable Banana Value Chain: Waste Valuation toward a Circular Bioeconomy. Energies 2023, 16, 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16083453
Krungkaew S, Hülsemann B, Kingphadung K, Mahayothee B, Oechsner H, Müller J. New Sustainable Banana Value Chain: Waste Valuation toward a Circular Bioeconomy. Energies. 2023; 16(8):3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16083453
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrungkaew, Samatcha, Benedikt Hülsemann, Kanokwan Kingphadung, Busarakorn Mahayothee, Hans Oechsner, and Joachim Müller. 2023. "New Sustainable Banana Value Chain: Waste Valuation toward a Circular Bioeconomy" Energies 16, no. 8: 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16083453
APA StyleKrungkaew, S., Hülsemann, B., Kingphadung, K., Mahayothee, B., Oechsner, H., & Müller, J. (2023). New Sustainable Banana Value Chain: Waste Valuation toward a Circular Bioeconomy. Energies, 16(8), 3453. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16083453









