Unified Paradigm of Start-Up Strategy for Pumped Storage Hydropower Stations: Variable Universe Fuzzy PID Controller and Integrated Operation Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
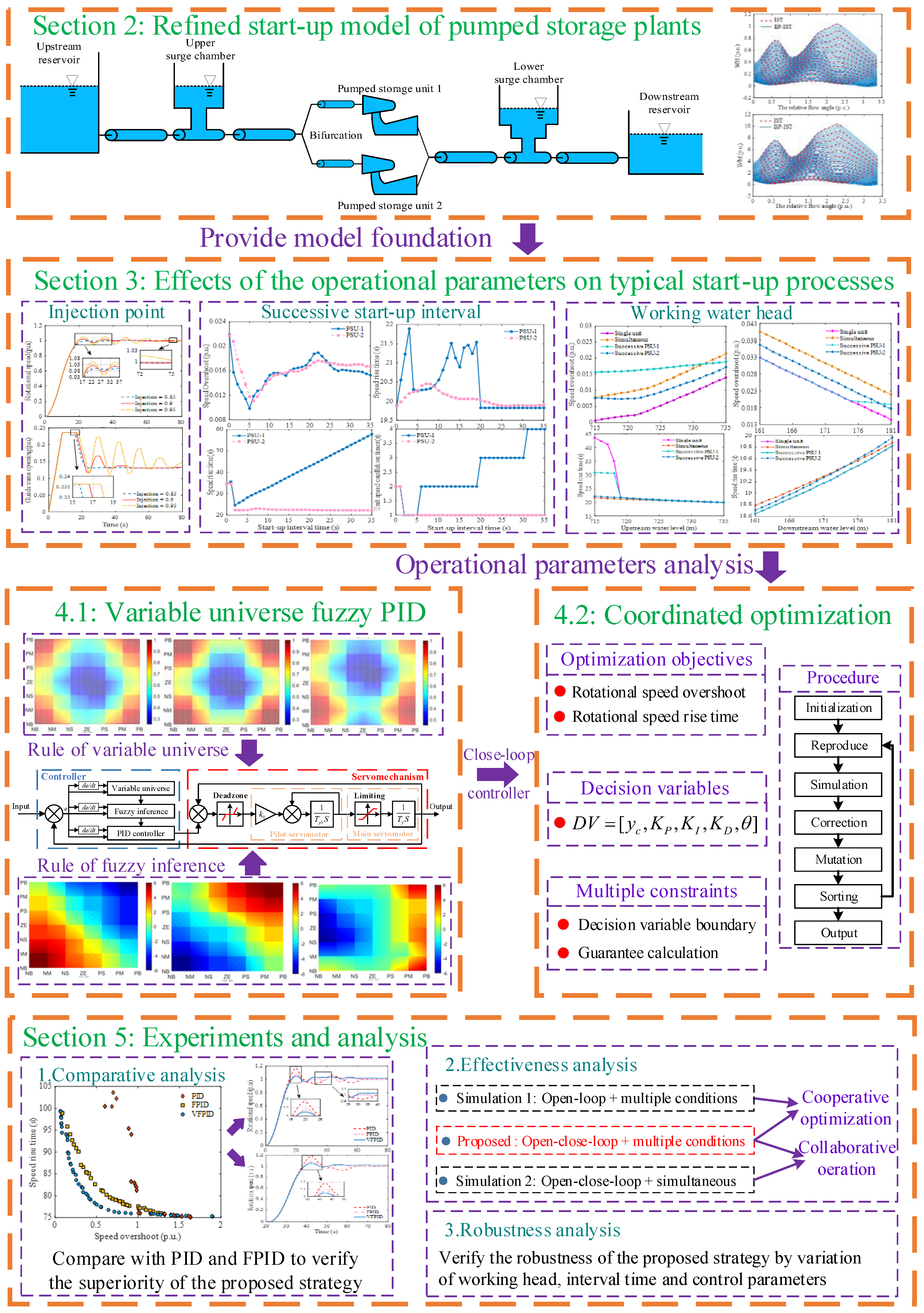
2. Refined Start-Up Model of Pumped Storage Plants
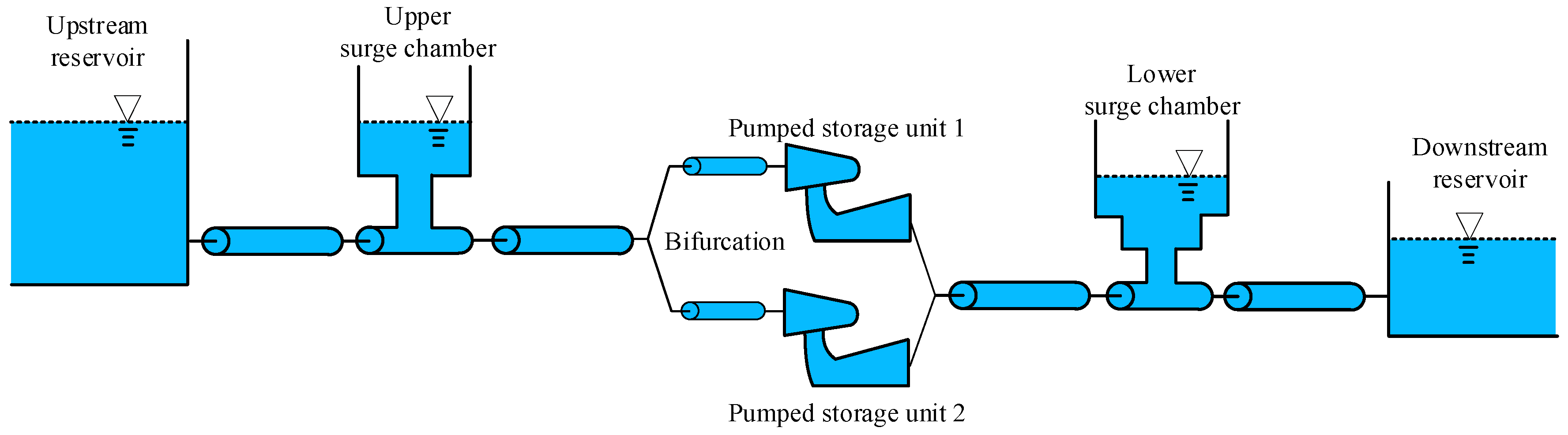
2.1. Model of Pipeline System
2.2. Model of Pumped Storage Unit
2.3. Model of Generator
2.4. Model of Governor System
3. Effects of the Operational Parameters on Typical Start-Up Processes
3.1. Effects of the Injection Point
3.2. Effects of the Start-Up Interval Time
3.3. Effects of the Water Head
4. Control Strategy and Coordinated Optimization
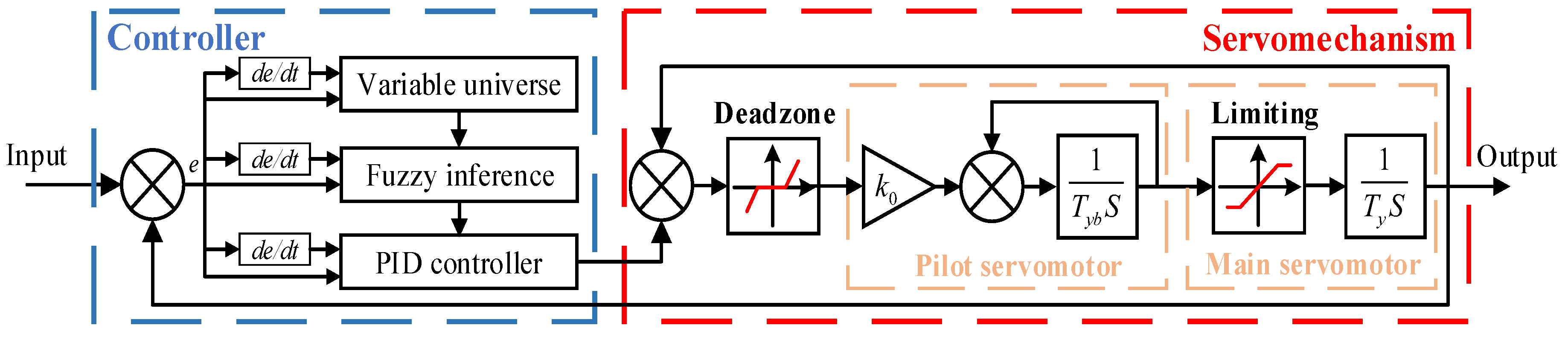
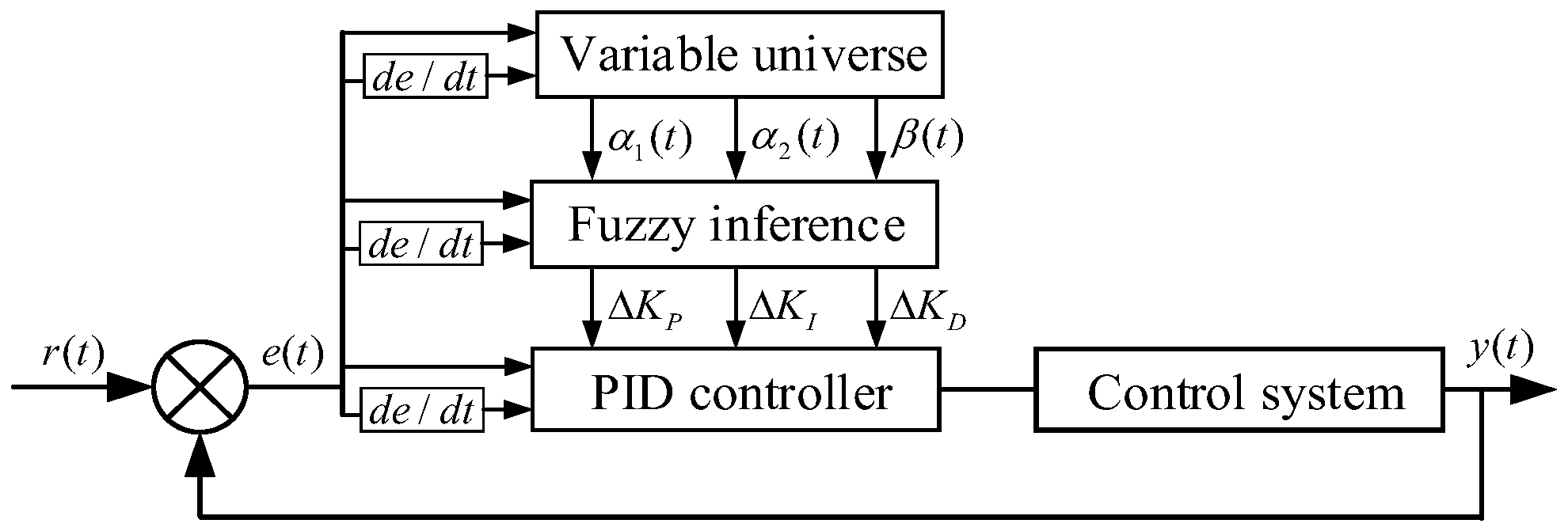
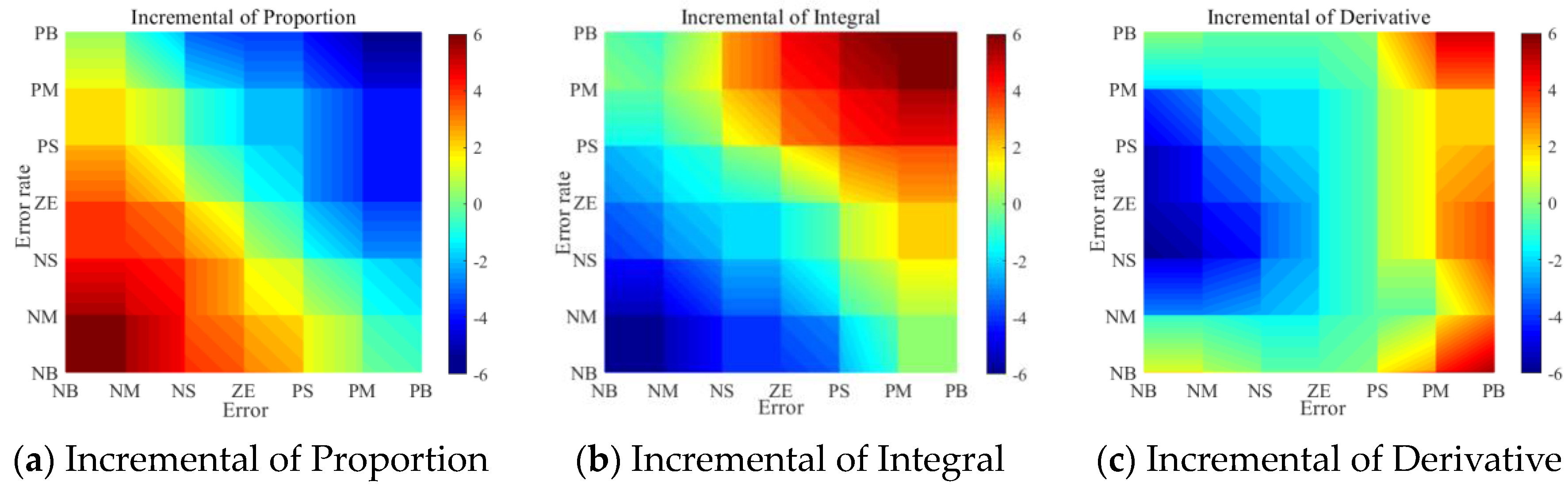
4.1. Variable Universe Fuzzy PID Controller
4.2. Coordinated Optimization of Start-Up Strategy
4.2.1. Optimization Objectives and Decision Variables
4.2.2. Optimization Constraints
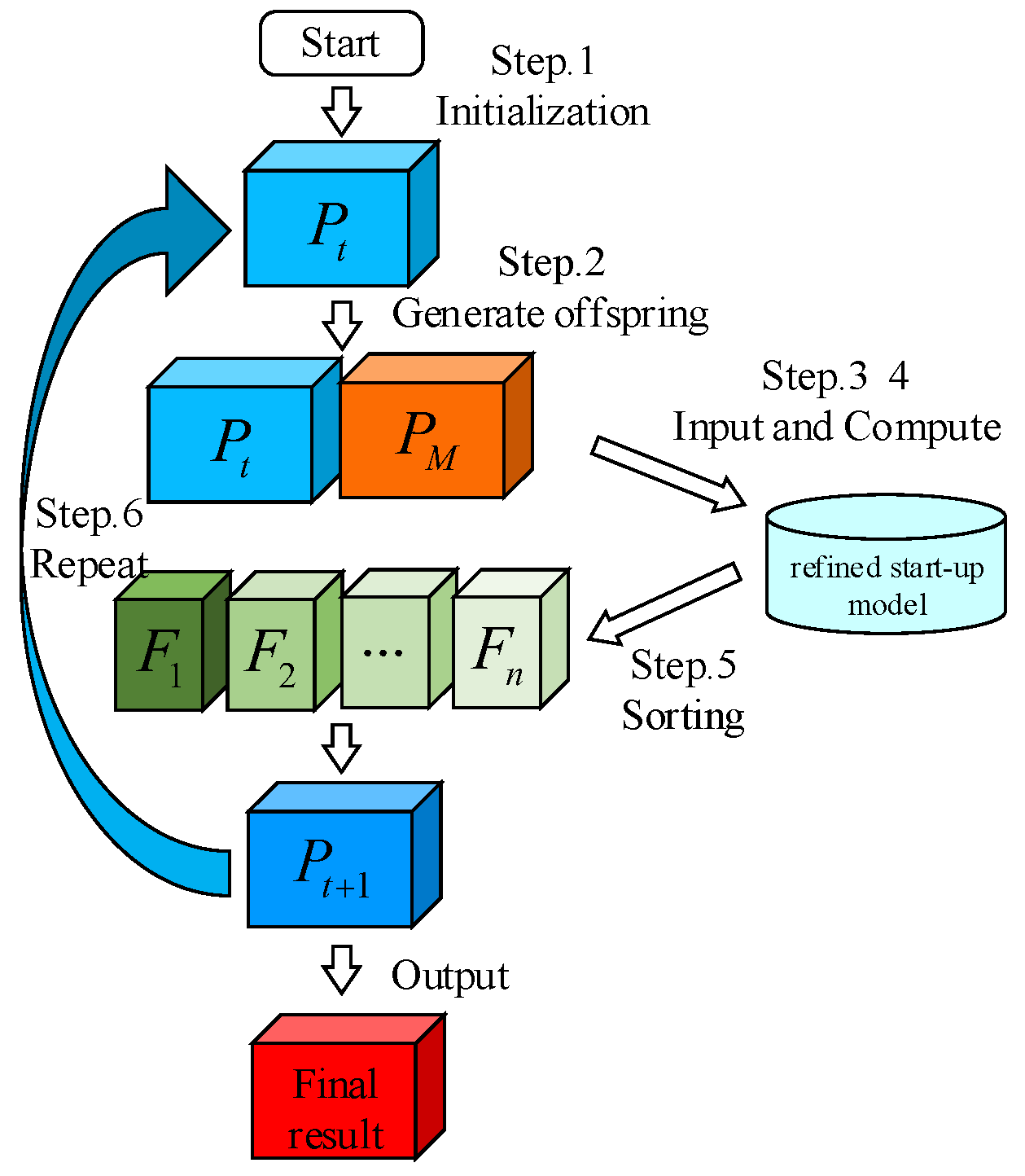
4.2.3. Optimization Procedure
5. Numerical Experiments and Analysis
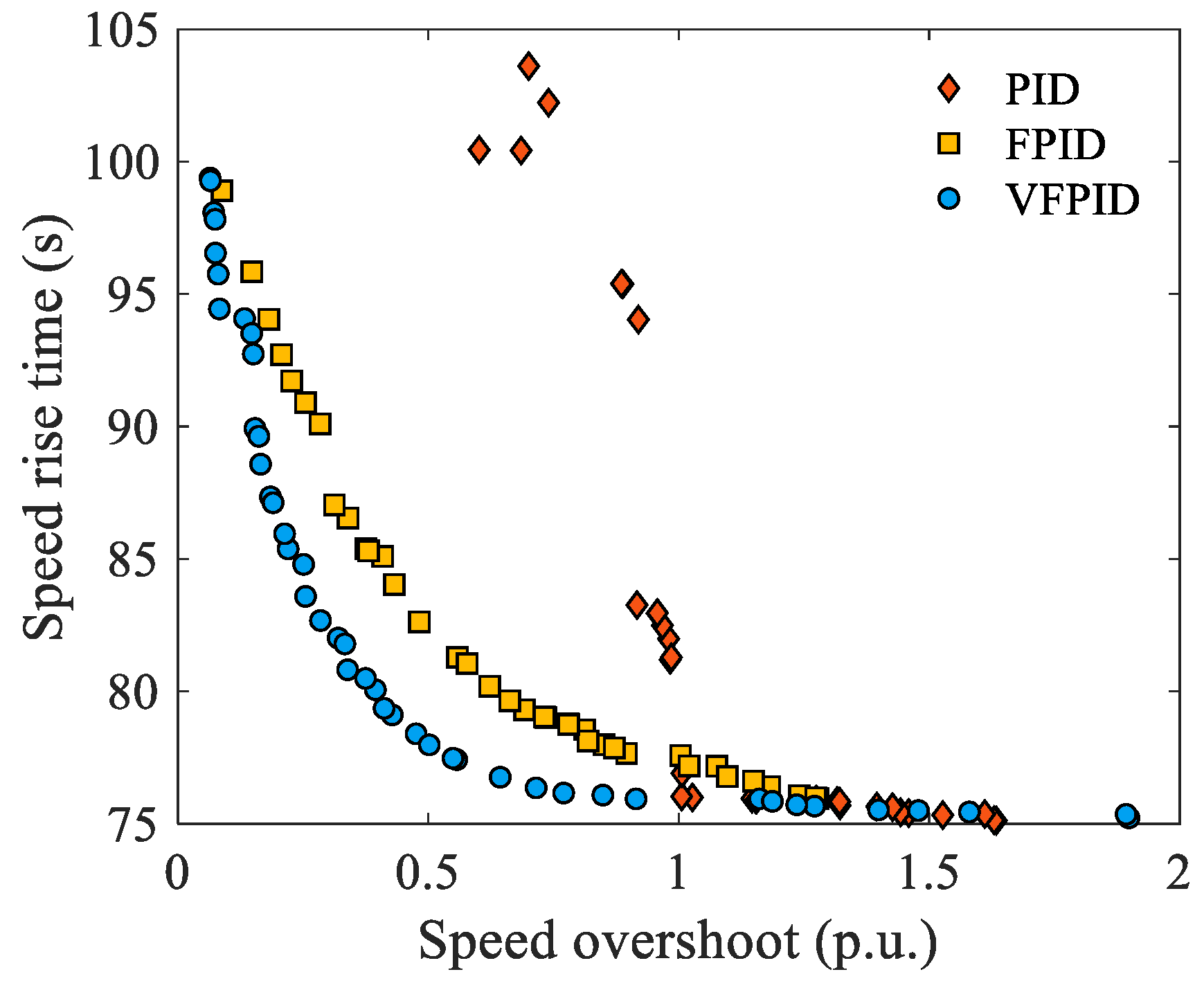
5.1. Comparative Analysis of Control Strategy Performance
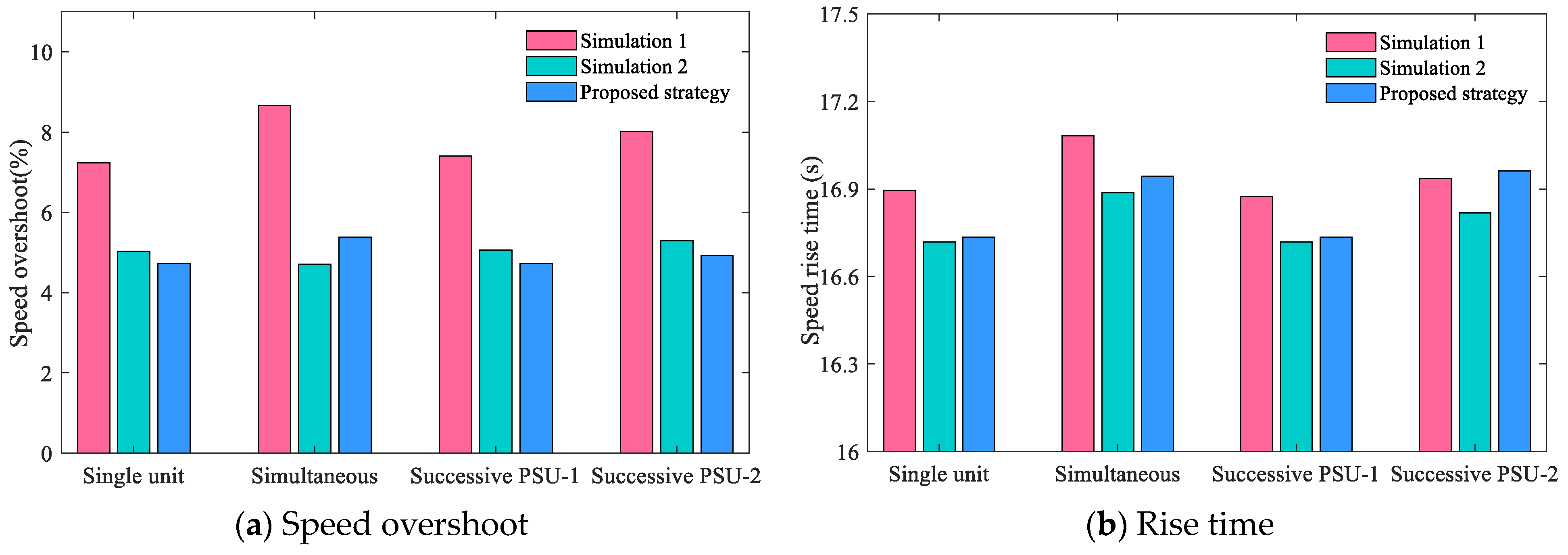
5.2. Effectiveness Analysis of Collaborative Operation and Collaborative Optimization
5.3. Robustness Analysis of the Unified Paradigm
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Unit flow, (m3/s) | Initial domain of input, p.u. | ||
| Time, (s) | Initial domain of output, p.u. | ||
| Gravitational acceleration, (m/s2) | Overshoot of rotational speed under | ||
| Equivalent pipe area, (m2) | single-unit start-up condition, p.u. | ||
| Hydrodynamic pressure, (m) | Overshoot of rotational speed under | ||
| Length of pipe, (m) | simultaneous start-up condition, p.u. | ||
| Darcy–Weisbach resistance coefficient, p.u. | Overshoot of rotational speed of prior | ||
| Diameter of pipe line, (m) | unit under successive start-up condition, p.u. | ||
| Celerity of water hammer wave, (m/s2) | Overshoot of rotational speed of rear unit | ||
| Relative value of water flow angle, p.u. | under successive start-up condition, p.u. | ||
| Relative value of guide vane opening, p.u. | Speed rise time under single-unit | ||
| Relative value of water head, p.u. | start-up condition, (s) | ||
| Relative value of rotational speed, p.u. | Speed rise time under simultaneous | ||
| Relative value of water flow, p.u. | start-up condition, (s) | ||
| Relative value of unit torque, p.u. | Speed rise time of prior unit under | ||
| Coefficients of transformation, p.u. | successive start-up condition, (s) | ||
| Stretch factor for error, p.u. | Speed rise time of rear unit under | ||
| Stretch factor for error rate, p.u. | successive start-up condition, (s) | ||
| Stretch factor for output, p.u. | Ascending turning point, p.u. | ||
| Moment of inertia, (ton/m2) | Rotational speed of descent moment, p.u. | ||
| Shaft mechanical moment, p.u. | Descending turning point, p.u. | ||
| Guide vane rising fixed point, p.u. | Initial proportional gain, p.u. | ||
| Incremental of proportion, p.u. | Initial integral gain, p.u. | ||
| Incremental of integral, p.u. | Initial derivative gain, p.u. | ||
| Incremental of derivative, p.u. | Injection point, p.u. | ||
| Start-up interval time, s |
References
- Hermans, M.; Bruninx, K.; Delarue, E. Impact of generator start-up lead times on short-term scheduling with high shares of renewables. Appl. Energy 2020, 268, 114935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Paramati, S.R.; Ozturk, I.; Bhattacharya, S. The effect of renewable energy consumption on economic growth: Evidence from top 38 countries. Appl. Energy Barking Then Oxf. 2016, 162, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, D. Stochastic multi-scenario optimization for a hybrid combined cooling, heating and power system considering multi-criteria. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 233, 113911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaun, K.; Cerda, E. Impacts of climate change on wind energy power—Four wind farms in Spain. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Felder, F.A. Generation expansion planning with renewable energy credit markets: A bilevel programming approach—ScienceDirect. Appl. Energy 2020, 276, 115472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Bergot, A.; Liang, C.; Xiang, W.; Huang, Z. Environmental issues associated with wind energy—A review. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Tian, L.; Fu, M.; Zhang, G. Green development growth momentum under carbon neutrality scenario. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Peng, K.; Wu, P.Z. Optimal trade-off planning for wind-solar power day-ahead scheduling under uncertainties. Energy 2017, 141 Pt 2, 1969–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.R.; Wan, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, D.; Soder, L. Analysis of wind power intermittency based on historical wind power data. Energy 2018, 150, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridnia, N.; Habibi, D.; Lachowicz, S.; Kavousifard, A. Optimal scheduling in a microgrid with a tidal generation. Energy 2019, 171, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousksou, T.; Bruel, P.; Jamil, A.; Rhafiki, T.E.; Zeraouli, Y. Energy storage: Applications and challenges. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 120, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Xu, T.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Tang, A.; Chen, Y. Optimal capacity configuration of the wind-photovoltaic-storage hybrid power system based on gravity energy storage system. Appl. Energy 2020, 271, 115052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Chow, J.H.; Desrochers, A.A. Pumped-storage hydro-turbine bidding strategies in a competitive electricity market. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2004, 19, 834–841. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, J.; Du, X. Experimental study on the vibrational performance and its physical origins of a prototype reversible pump turbine in the pumped hydro energy storage power station. Renew. Energy 2018, 130, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, C.; Malik, O.P. Operational characteristics and parameter sensitivity analysis of hydropower unit damping under ultra-low frequency oscillations. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 136, 107689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazarra, M.; Pérez-Díaz, J.I.; García-González, J. Deriving Optimal End of Day Storage for Pumped-Storage Power Plants in the Joint Energy and Reserve Day-Ahead Scheduling. Energies 2017, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, B.; Li, G.; Yang, B.; Hu, B.; Ma, M. Two-Part Tariff of Pumped Storage Power Plants for Wind Power Accommodation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Zhao, K.J.; Qian, Z.D.; Zhou, J.; Wu, X. Design of three-stage start-up optimal strategy based on fuzzy fractional-order proportion integration differentiation controller of pumped storage unit under low water head. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Lai, X.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Y.; Hou, J. An Integrated Start-Up Method for Pumped Storage Units Based on a Novel Artificial Sheep Algorithm. Energies 2018, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Mao, C.; Shen, C. Research on hydraulic–electric interference and optimisation of multi-turbine hydropower system based on the dual control mode. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yan, D.; Zhang, H. Equivalent circuit modelling of large hydropower plants with complex tailrace system for ultra-low frequency oscillation analysis. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 103, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Lai, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, M. An optimization decision-making framework for the optimal operation strategy of pumped storage hydropower system under extreme conditions. Renew. Energy 2021, 182, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Xu, B.; Patelli, E.; Tolo, S. Dynamic analysis of a pumped-storage hydropower plant with random power load. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 100, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Zeng, W.; Yang, J. Hydraulic interaction of two parallel pump-turbines in constant-speed oscillation: Measurement, simulation, and sensitivity analysis. Renew. Energy 2021, 176, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, P.; Sun, L. Transient analysis of a multi-unit pumped storage system during load rejection process. Renew. Energy 2020, 152, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Fan, H.; Liu, S.; Wu, L. S-shaped characteristics on the performance curves of pump-turbines in turbine mode—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, D.; Venkateshkumar, M.; Xiao, Y.; Yue, Y.; Xing, Y.; Li, P. Modeling a pumped storage hydropower integrated to a hybrid power system with solar-wind power and its stability analysis. Appl. Energy 2019, 248, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badur, J.; Bryk, M. Accelerated start-up of the steam turbine by means of controlled cooling steam injection. Energy 2019, 173, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, C.; Tian, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lai, X.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, T.; Wu, W. Multi-Objective Optimization of Start-up Strategy for Pumped Storage Units. Energies 2018, 11, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hou, J.; Gu, J.; Li, C.; Xu, Y. Dynamic Characteristics and Successive Start-Up Control Strategy Optimization of Pumped Storage Units under Low-Head Extreme Conditions. Energies 2022, 15, 5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, W.; Peng, X.; Li, C. Adaptive condition predictive-fuzzy PID optimal control of start-up process for pumped storage unit at low head area. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 177, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Li, F.; Kheav, K.; Jiang, W.; Luo, X.; Patelli, E.; Xu, B.; Chen, D. A start-up optimization strategy of a hydroelectric generating system: From a symmetrical structure to asymmetric structure on diversion pipes. Renew. Energy 2021, 180, 1148–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xu, X. Sliding mode control of regulating system of pumped storage power station considering nonlinear pump-turbine characteristics. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 105071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, J.; Chung, C.Y.; Yang, W.; He, X.; Chen, M. Performance enhancement of pumped storage units for system frequency support based on a novel small signal model. Energy 2021, 234, 121207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. A multi-objective optimization strategy for the optimal control scheme of pumped hydropower systems under successive load rejections. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; Wei, X.; Qin, D. Numerical simulation of hysteresis characteristic in the hump region of a pump-turbine model. Renew. Energy 2017, 115, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yang, K.; Guo, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Prediction Method for the Complete Characteristic Curves of a Francis Pump-Turbine. Water 2018, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezghi, A.; Riasi, A. Sensitivity analysis of transient flow of two parallel pump-turbines operating at runaway. Renew. Energy 2016, 86, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yan, D.; Liu, W. A two-stage numerical simulation framework for pumped-storage energy system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 210, 112676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, M.E.; Ardehali, M.M.; Jafari, S. Pumped-storage unit commitment with considerations for energy demand, economics, and environmental constraints. Energy 2010, 35, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xue, X.; Fu, W.; Zhu, W.; Li, C. An adaptively fast fuzzy fractional order PID control for pumped storage hydro unit using improved gravitational search algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 111, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Miao, Z.; Wang, J. Variable universe stable fuzzy control for nonlinear systems. Sci. China 2002, 32, 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulkhader, H.K.; Jacob, J.; Mathew, A.T. Robust type-2 fuzzy fractional order PID controller for dynamic stability enhancement of power system having RES based microgrid penetration. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 110, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Li, H. Relationship between similarity measure and entropy of interval valued fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2006, 157, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

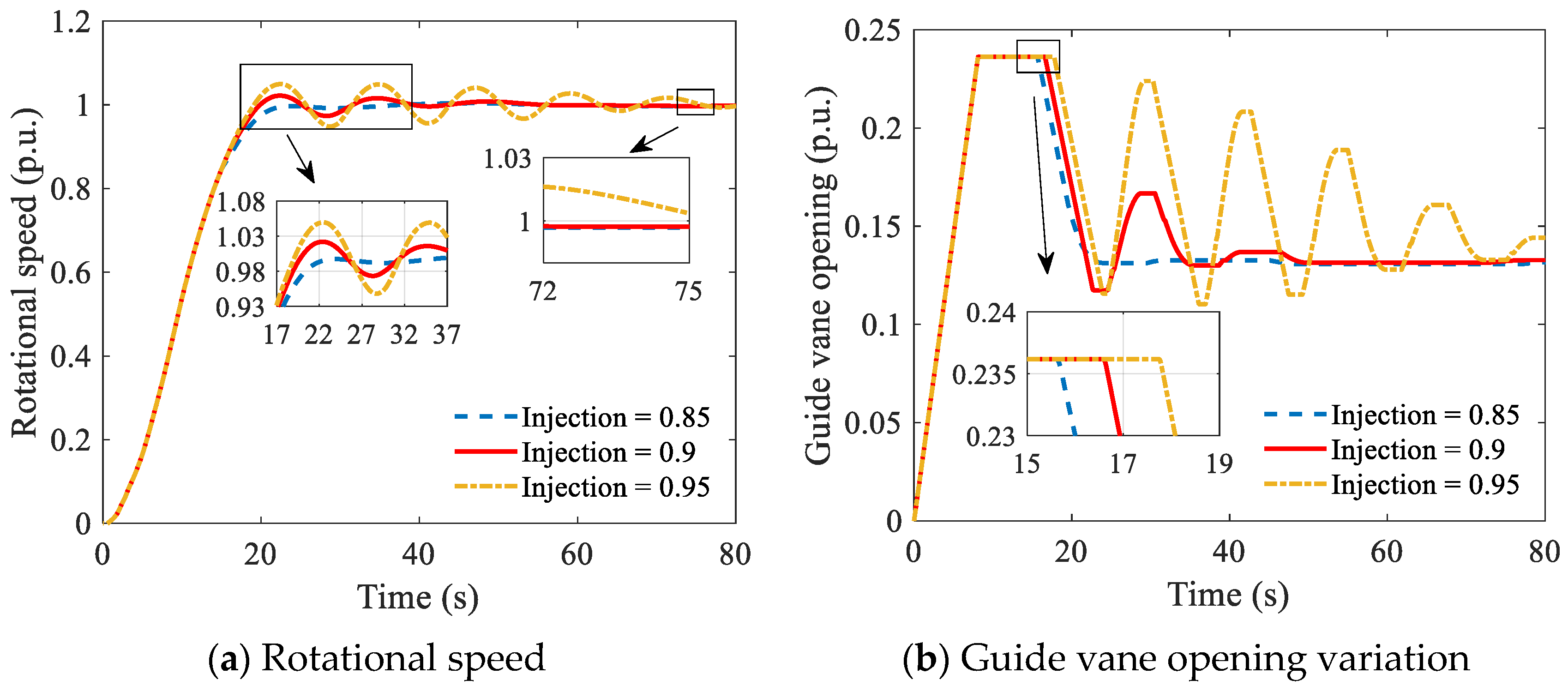
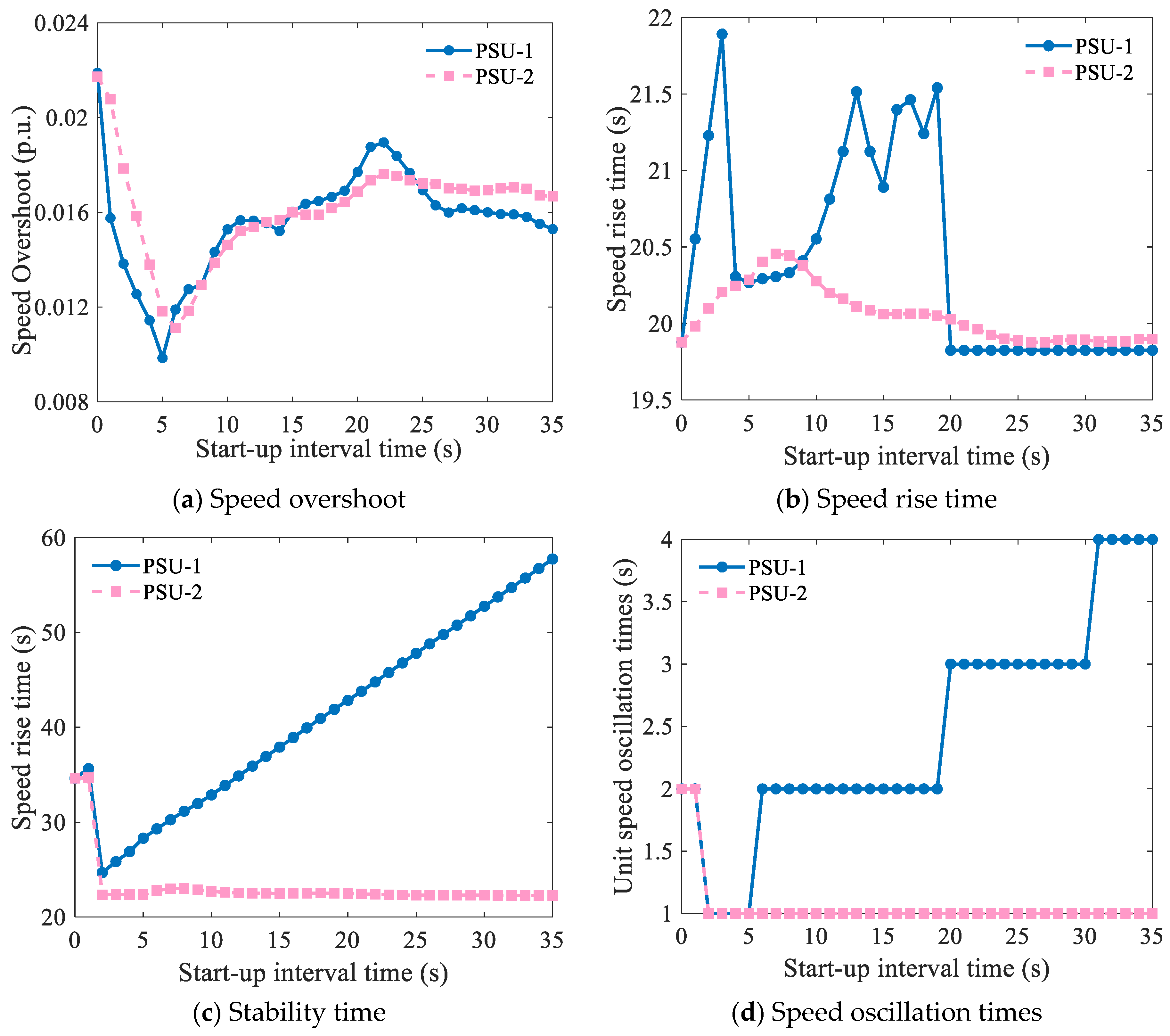
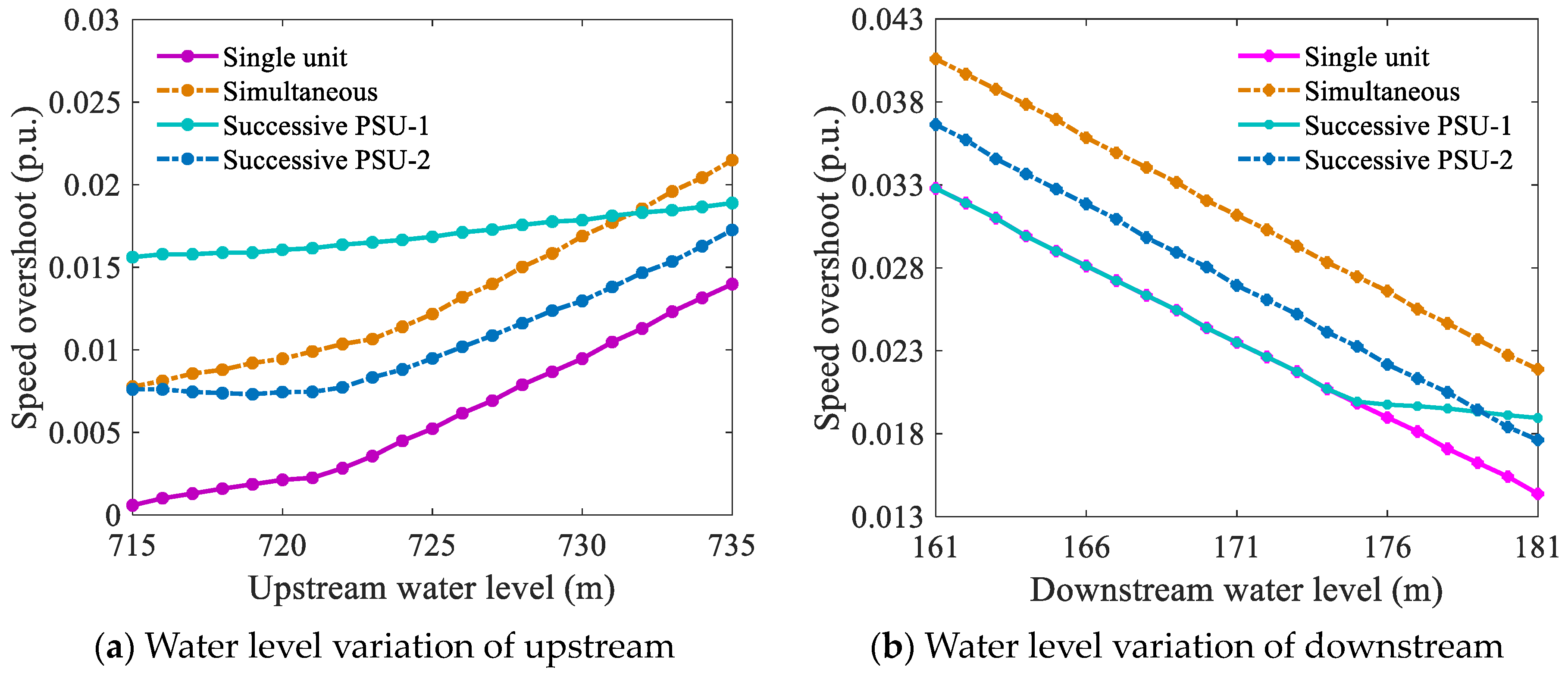
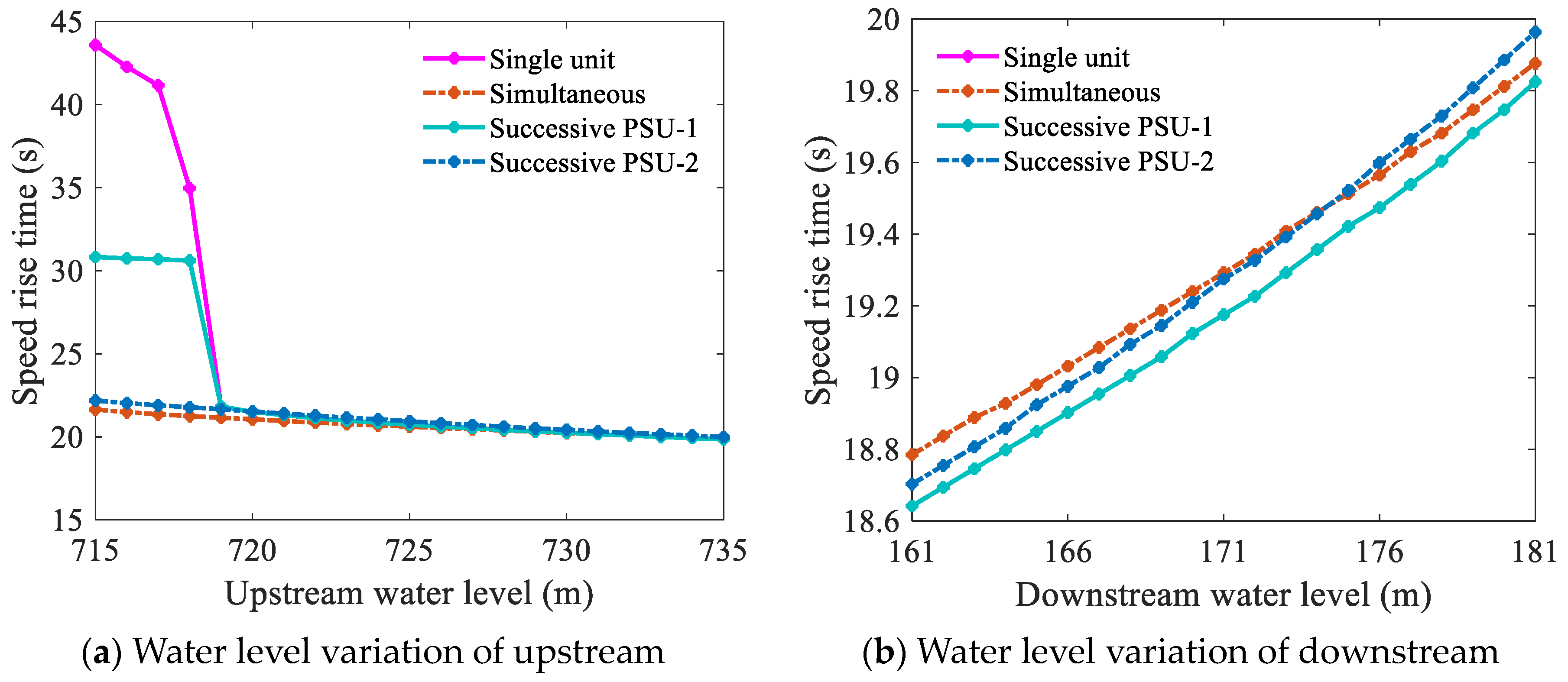



| Injection Point | Single Unit Start-Up | Simultaneous Start-Up | Successive Start-Up | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSU-1 | PSU-2 | |||||||
| Over-Shoot (%) | Entry Time (s) | Over-Shoot (%) | Entry Time (s) | Over-Shoot (%) | Entry Time (s) | Over-Shoot (%) | Entry Time (s) | |
| 85% rated | 0 | 14.89 | 0 | 15.09 | 0.51 | 15.22 | 0 | 15.48 |
| 90% rated | 1.44 | 16.01 | 2.19 | 16.24 | 0.98 | 16.34 | 1.18 | 16.26 |
| 95% rated | 3.98 | 17.24 | 4.94 | 17.49 | 3.64 | 17.60 | 3.31 | 17.11 |
| Parameters | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Parameters | Lower Limit | Upper Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volute water pressure (mH2O) | / | 850 | Draft tube water pressure (mH2O) | 0 | / |
| Surge in diversion chamber (mH2O) | 692 | 749 | Surge in tailwater chamber (mH2O) | 137 | 194 |
| Proportional gain | 0 | 10 | Integral gain | 0 | 10 |
| Differential gain | 0 | 10 | Rotational speed oscillation times | / | 2 |
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| (r/min) | 500 | (m3/s) | 62.09 |
| (m) | 735 | (m) | 161 |
| Worst start-up interval time (s) | 22 | Moment of inertia (ton/m2) | 3800 |
| (p.u.) | 1/27 | (p.u.) | 1/45 |
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of chromosomes | 40 | Maximum number of generations | 200 |
| Crossover probability | 0.9 | Mutation probability | 0.1 |
| Individuals | PID Controller | FPID Controller | VFPID Controller | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overshoot | Rise Time | Overshoot | Rise Time | Overshoot | Rise Time | |
| 1 | 0.6016 | 100.447 | 0.0880 | 98.903 | 0.0642 | 99.381 |
| 2 | 0.6853 | 100.421 | 0.0879 | 98.900 | 0.0652 | 99.277 |
| 3 | 0.7004 | 103.606 | 0.1477 | 95.845 | 0.0718 | 98.081 |
| 4 | 0.7402 | 102.228 | 0.1817 | 94.051 | 0.0746 | 97.821 |
| 5 | 0.8857 | 95.390 | 0.2075 | 92.712 | 0.0751 | 96.547 |
| 6 | 0.8885 | 95.377 | 0.2273 | 91.724 | 0.0806 | 95.754 |
| 7 | 0.9167 | 83.261 | 0.2273 | 91.724 | 0.0831 | 94.441 |
| 8 | 0.9195 | 94.038 | 0.2546 | 90.905 | 0.1475 | 93.518 |
| 9 | 0.9195 | 94.038 | 0.2836 | 90.099 | 0.1507 | 92.738 |
| 10 | 0.9569 | 82.949 | 0.3126 | 87.044 | 0.1539 | 89.930 |
| 11 | 0.9573 | 82.962 | 0.3396 | 86.550 | 0.1653 | 88.578 |
| 12 | 0.9674 | 82.494 | 0.3758 | 85.393 | 0.1849 | 87.343 |
| 13 | 0.9797 | 81.987 | 0.3804 | 85.302 | 0.1901 | 87.122 |
| 14 | 0.9797 | 81.987 | 0.4093 | 85.094 | 0.2202 | 85.380 |
| 15 | 0.9831 | 81.194 | 0.4321 | 84.041 | 0.2551 | 83.586 |
| 16 | 0.9853 | 81.285 | 0.4825 | 82.624 | 0.2848 | 82.676 |
| 17 | 1.0059 | 76.033 | 0.5581 | 81.285 | 0.3201 | 82.013 |
| 18 | 1.0065 | 76.904 | 0.5775 | 81.051 | 0.3390 | 80.817 |
| 19 | 1.0273 | 75.994 | 0.5775 | 81.051 | 0.3748 | 80.492 |
| 20 | 1.1462 | 75.955 | 0.6223 | 80.193 | 0.3944 | 80.063 |
| 21 | 1.1538 | 75.929 | 0.6628 | 79.647 | 0.4118 | 79.361 |
| 22 | 1.1557 | 75.929 | 0.6920 | 79.309 | 0.4280 | 79.114 |
| 23 | 1.2744 | 75.916 | 0.7317 | 79.036 | 0.4757 | 78.399 |
| 24 | 1.2751 | 75.903 | 0.7354 | 79.023 | 0.5019 | 77.983 |
| 25 | 1.2751 | 75.903 | 0.7798 | 78.789 | 0.5493 | 77.476 |
| 26 | 1.3165 | 75.864 | 0.7800 | 78.750 | 0.5567 | 77.424 |
| 27 | 1.3189 | 75.838 | 0.8123 | 78.555 | 0.6436 | 76.761 |
| 28 | 1.3192 | 75.773 | 0.8190 | 78.126 | 0.7153 | 76.358 |
| 29 | 1.3213 | 75.838 | 0.8512 | 77.983 | 0.7703 | 76.163 |
| 30 | 1.3219 | 75.695 | 0.8714 | 77.866 | 0.8486 | 76.085 |
| 31 | 1.3219 | 75.695 | 0.8958 | 77.658 | 0.9148 | 75.942 |
| 32 | 1.3955 | 75.656 | 1.0036 | 77.580 | 1.1609 | 75.942 |
| 33 | 1.4268 | 75.630 | 1.0203 | 77.190 | 1.1869 | 75.851 |
| 34 | 1.4429 | 75.435 | 1.0760 | 77.177 | 1.2356 | 75.721 |
| 35 | 1.4592 | 75.409 | 1.0969 | 76.787 | 1.2713 | 75.669 |
| 36 | 1.5271 | 75.331 | 1.1490 | 76.618 | 1.3989 | 75.526 |
| 37 | 1.6109 | 75.370 | 1.1818 | 76.410 | 1.4785 | 75.500 |
| 38 | 1.6295 | 75.136 | 1.2412 | 76.072 | 1.5803 | 75.448 |
| 39 | 1.6296 | 75.136 | 1.2735 | 75.994 | 1.8932 | 75.357 |
| 40 | 1.6339 | 75.123 | 1.2779 | 75.955 | 1.8987 | 75.227 |
| Description | Operational Parameters of Control Strategy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation 1 | Open-loop optimization under multiple conditions | 0.275 | 1.73 | 9.92 | 7.62 | 0.90 |
| Simulation 2 | Open–close loop optimization under simultaneous start-up | 0.252 | 6.87 | 4.63 | 1.37 | 0.89 |
| Proposed strategy | Open–close loop optimization under multiple conditions | 0.268 | 3.96 | 7.05 | 1.57 | 0.85 |
| Conditions | Start-Up Interval (s) | Water Level | Control Strategy Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper (m) | Lower (m) | |||||||
| N0 | 22 | 735 | 161 | 0.267 | 3.96 | 7.05 | 1.57 | 0.85 |
| N1 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N2 | 12 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| N3 | - | 735 | 180 | - | - | - | - | - |
| N4 | - | 716 | 161 | - | - | - | - | - |
| N5 | 8 | 722 | 165 | 0.260 | 4.16 | 7.15 | 1.67 | 0.88 |
| N6 | 18 | 728 | 163 | 0.276 | 3.75 | 6.95 | 1.45 | 0.82 |
| Conditions | Single Unit | Simultaneous Start-Up | Successive Start-Up | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSU-1 | PSU-2 | |||||||
| Overshoot | Rise Time | Overshoot | Rise Time | Overshoot | Rise Time | Overshoot | Rise Time | |
| N0 | 4.73 | 16.874 | 5.38 | 17.043 | 4.73 | 16.874 | 4.92 | 16.961 |
| N1 | / | / | / | / | 0.16 ↓ | 0.403 ↑ | 0.01 ↑ | 0.16 ↓ |
| N2 | / | / | / | / | 1.16 ↓ | 0.376 ↑ | 0.05 ↓ | 0.049 ↑ |
| N3 | 1.43 ↓ | 0.715 ↑ | 0.15 ↑ | 0.702 ↑ | 0.52 ↑ | 0.715 ↑ | 0.93 ↓ | 0.689 ↑ |
| N4 | 1.38 ↓ | 0.728 ↑ | 0.15 ↑ | 0.728 ↑ | 0.56 ↑ | 0.272 ↓ | 0.34 ↓ | 0.715 ↑ |
| N5 | 1.17 ↓ | 0.780 ↑ | 0.20 ↑ | 0.793 ↑ | 1.47 ↓ | 1.365 ↑ | 1.89 ↓ | 0.87 ↑ |
| N6 | 0.64 ↓ | 0.195 ↑ | 0.02 ↑ | 0.182 ↑ | 0.74 ↓ | 0.195 ↑ | 0.87 ↓ | 0.23 ↑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Li, M.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, J. Unified Paradigm of Start-Up Strategy for Pumped Storage Hydropower Stations: Variable Universe Fuzzy PID Controller and Integrated Operation Optimization. Energies 2024, 17, 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133293
Liu B, Li M, Yuan Y, Liu J. Unified Paradigm of Start-Up Strategy for Pumped Storage Hydropower Stations: Variable Universe Fuzzy PID Controller and Integrated Operation Optimization. Energies. 2024; 17(13):3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133293
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Baonan, Mengyao Li, Yuan Yuan, and Jie Liu. 2024. "Unified Paradigm of Start-Up Strategy for Pumped Storage Hydropower Stations: Variable Universe Fuzzy PID Controller and Integrated Operation Optimization" Energies 17, no. 13: 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133293
APA StyleLiu, B., Li, M., Yuan, Y., & Liu, J. (2024). Unified Paradigm of Start-Up Strategy for Pumped Storage Hydropower Stations: Variable Universe Fuzzy PID Controller and Integrated Operation Optimization. Energies, 17(13), 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133293






