Abstract
This study addresses an identified literature gap regarding indoor environmental quality in residential buildings, where the primary focus has traditionally been on energy performance rather than comfort optimization. Leveraging the low-cost and easy-to-implement LoRaWAN protocol, this research collects and analyses real-time data on comfort parameters, including temperature, CO2 levels, humidity, lighting, atmospheric pressure, and total volatile organic compounds (TVOC) across various buildings within the INCUBE EU project. The results highlight the dynamic nature of the parameters and emphasize the importance of continuous monitoring to enhance comfort and energy efficiency in smart residential buildings. The findings advocate for integrating technologies like LoRaWAN to optimize indoor environmental quality, ultimately improving residential comfort and occupant well-being.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background: Building Comfort
Indoor environmental quality (IEQ) in buildings is increasingly recognized as a critical factor influencing occupant health, comfort, productivity, and overall well-being [1,2,3,4]. The concept of IEQ encompasses a range of environmental aspects, including air quality, thermal comfort, lighting, acoustics, ergonomics, and aesthetic comfort, which together define the quality of indoor spaces. As people spend a significant amount of their time indoors, the quality of these environments plays a crucial role in daily life, affecting physical and mental health. Improper management of indoor air quality, particularly inadequate air exchange and poor control over CO2 levels and humidity, can contribute to the development of sick building syndrome (SBS). This condition is characterized by a range of acute health effects, such as headaches, dizziness, and respiratory problems, which are linked to the time spent inside buildings with poor air quality [5,6]. The growing body of literature reflects the importance of optimizing IEQ to create healthy, comfortable, and efficient building environments [7,8,9].
However, the pursuit of enhanced energy performance in buildings has often overshadowed efforts to improve overall occupant comfort. Modern building practices have emphasized energy efficiency through advanced insulation [10], airtight designs, and energy-saving technologies, sometimes at the expense of indoor comfort factors [11,12]. Balancing energy efficiency with comprehensive IEQ measures requires a holistic approach that integrates robust heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems; effective ventilation; sound insulation; efficient lighting; ergonomic designs; and aesthetic elements [10]. The convergence of these factors is essential for achieving high levels of occupant satisfaction and well-being in residential and commercial buildings.
Advancements in smart control technologies, such as smart thermostats and HVAC systems utilizing machine-learning algorithms, have revolutionized the management of thermal comfort, enabling systems to predict user behavior and adjust indoor conditions dynamically [13,14]. These innovations enhance comfort and contribute to energy savings by optimizing the operation of building systems. Similarly, maintaining high indoor air quality (IAQ) is vital for preventing health issues and ensuring a comfortable indoor environment. Advanced ventilation technologies, including energy recovery ventilators (ERV) and heat recovery ventilators (HRVs), effectively provide fresh air while minimizing energy loss, demonstrating how modern solutions can address the dual goals of comfort and efficiency [15]. Such efforts align with the recent development of the Smart Readiness Indicator (SRI) within the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (2018/844/EU), which directs on taking action toward buildings’ capability assessment to enhance comfort and efficiency through smart technologies to support healthier and more adaptable indoor environments [16,17].
Acoustic comfort, lighting quality, and ergonomic design also play critical roles in the overall IEQ of buildings [18,19]. Sound insulation techniques are essential for mitigating noise pollution and enhancing the auditory comfort of indoor spaces, particularly in densely populated urban environments. Efficient lighting systems, such as LED technology and smart lighting controls, ensure optimal visual comfort while using energy effectively. Furthermore, ergonomic furniture and designs cater to the physical comfort needs of occupants, while aesthetic elements contribute to the emotional and psychological appeal of indoor environments, underscoring the multidimensional nature of building comfort [20,21].
These advancements and the efforts for energy efficiency in buildings have led to the increasing adoption of Building Automation Systems (BAS) [22,23,24]. BAS integrates various building functions to enhance comfort, operational efficiency, and energy management. However, implementing BAS, especially in existing structures, can be technically challenging, costly, and visually intrusive. Emerging technologies like LoRaWAN (Long-Range Wide-Area Network) provide a promising alternative for enhancing building automation [25,26]. LoRaWAN is a low-power, wide-area networking protocol that supports the wireless communication of IoT devices over long distances with minimal power consumption. Its application in smart-building management allows for the efficient monitoring and control of indoor environmental parameters, offering a cost-effective solution for retrofitting older buildings with modern comfort and energy management systems.
1.2. State of the Art: Building Comfort
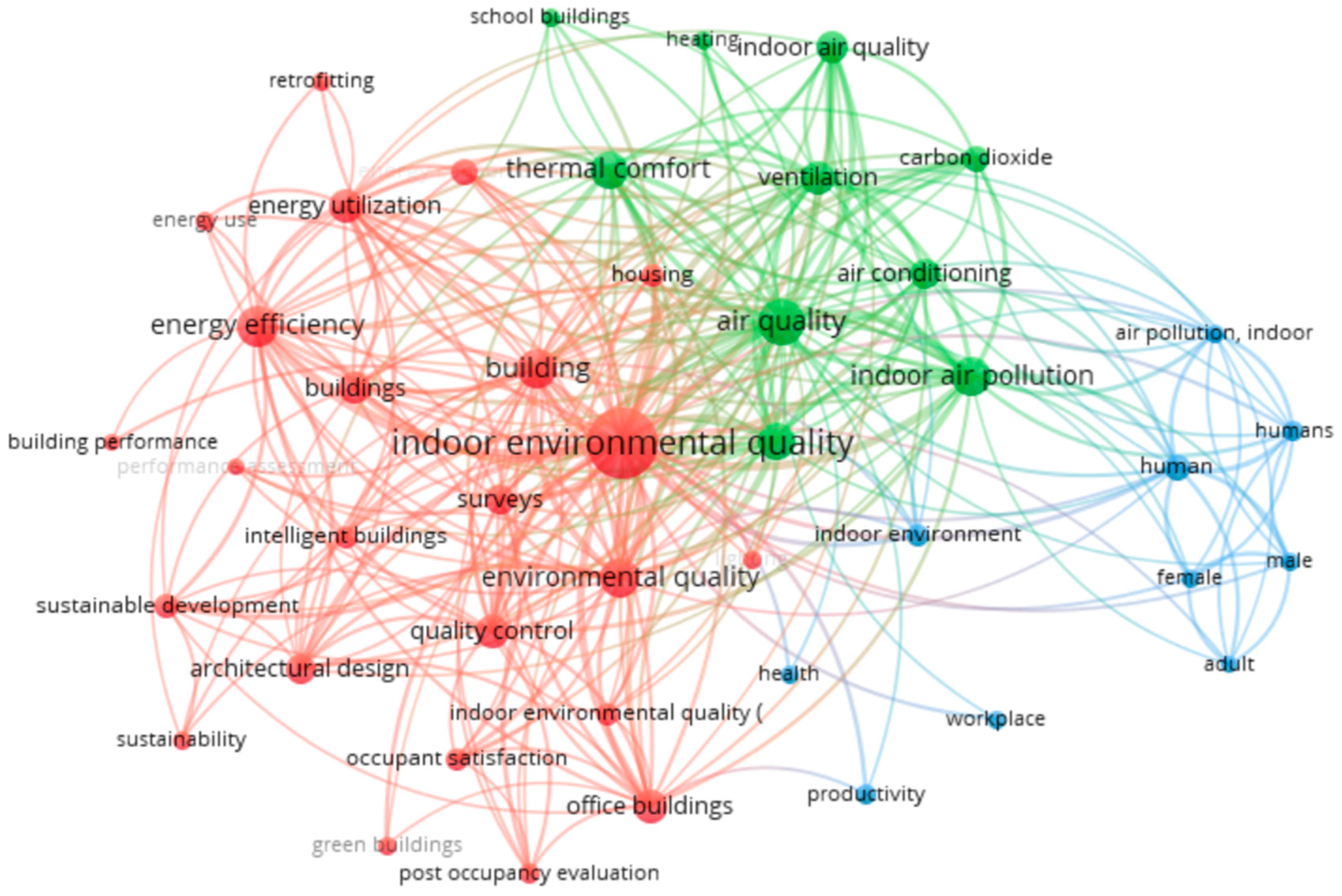
To assess the state of the art, a keyword analysis was conducted following the methodology applied by Mselle et al. [27] A dedicated query (Query: Title-abs-key (“indoor environmental quality” and “building*”) and (limit-to (doctype, “ar”))) and (exclude (pubyear, 2024)) was used to extract all relevant documents up to the end of 2023 from the Scopus database. The extracted data were then analyzed and visualized using VOSviewer (version 1.6.20) software, resulting in a literature map that clusters keywords occurring at least 50 times (see Figure 1). The keyword map highlights the interconnectedness of energy efficiency, IEQ, and human factors, reflecting the multidisciplinary nature of IEQ research. Key focus areas identified include air quality, thermal comfort, and energy utilization, which are essential for improving building performance and occupant well-being. Major themes such as ventilation, indoor air pollution, and energy efficiency are prominently featured. However, office buildings dominate the studies, while residential buildings are notably underrepresented, indicating a gap between research and application. This points to a need for integrated approaches that merge technical performance with occupant needs, especially in residential settings, to bridge the gap between research and practice.
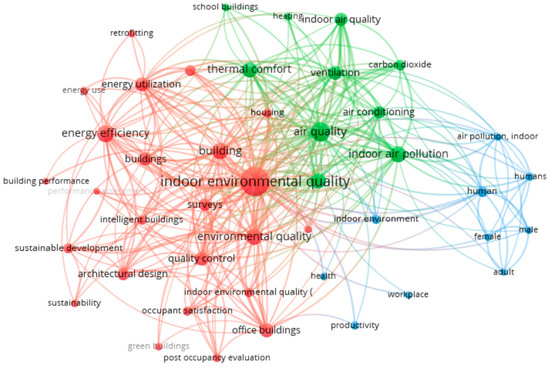
Figure 1.
Literature of the state of the art on buildings’ indoor environmental quality.
1.3. Scope and Objectives: Buildings’ Environmental Quality
This paper presents a pioneering experimental implementation of the LoRaWAN protocol to assess comfort parameters in multiple residential buildings. This study is key to feeding the literature gap identified about the low implementation of such technologies in residential buildings, which is often neglected compared to office buildings. The objectives and scope of the paper are covered using data from 13 apartments within the INCUBE EU project pilot/demo buildings. It includes the analysis of six key parameters for indoor environmental quality, i.e., temperature, CO2 levels, humidity, lighting, atmospheric pressure, and TVOC. This study offers real-time insights into residential environments, highlighting the potential of LoRaWAN technology for cost-effective and efficient data collection. By showcasing how LoRaWAN can be integrated into existing buildings without costly renovations, this approach not only enhances energy efficiency but also supports the advancement of smarter, sustainable building practices. The research is expected to improve occupants’ experiences and quality of life, emphasizing the importance of these technologies in optimizing comfort and energy efficiency in smart residential buildings. In interpreting the results, we followed recommendations from ASHRAE [28] and the US EPA [29] for optimal residential indoor air quality. Ideal indoor temperatures are 20–24 °C in winter and 23–26 °C in summer, with CO2 levels below 1000 ppm and relative humidity between 30% and 60%. Additionally, according to [30], TVOCs should remain within 300–500 µg/m3, and slight positive pressure is advised to prevent outdoor pollutants. Lighting should be 300–500 lux for general areas, with higher levels for tasks like cooking or studying.
2. Materials and Methods
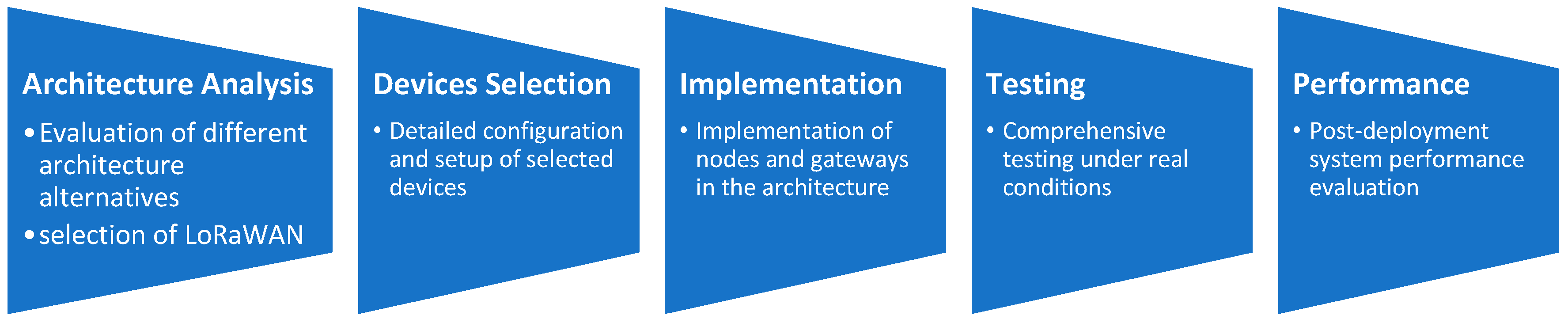
To meet the project’s objectives and address the application’s specific communication needs, we adopted a methodological process from the architecture’s conception to its deployment (see Figure 2). We began with a detailed analysis of various alternatives, including Sigfox, NB-IoT, and Zigbee, (comparison and detailed information available in Samad et al. [31] and Mekki et al. [32]), ultimately selecting LoRaWAN for its optimal combination of wide coverage, energy efficiency, and versatility. We conducted rigorous evaluations on key criteria such as range, energy consumption, costs, and scalability. The decision to use LoRaWAN laid a solid foundation for the project’s success.
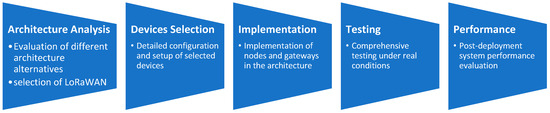
Figure 2.
Steps followed for implementation of the LoRaWAN protocol.
Once LoRaWAN was chosen, we focused on a meticulous system design, identifying nodes and gateways, and the necessary communication infrastructure. We carefully selected compatible hardware components to ensure coherence and stability. The development phase included implementing nodes, gateways, and data management systems and integrating the architecture across all system layers. Extensive testing was conducted to validate functionality under various conditions, ensuring robustness and reliability. After successful implementation and testing, we deployed the system in the field, installing nodes and gateways as per the design to ensure optimal operation in real environments. After deploying the protocol, we cross-checked the system performance, making necessary adjustments to ensure reliability.
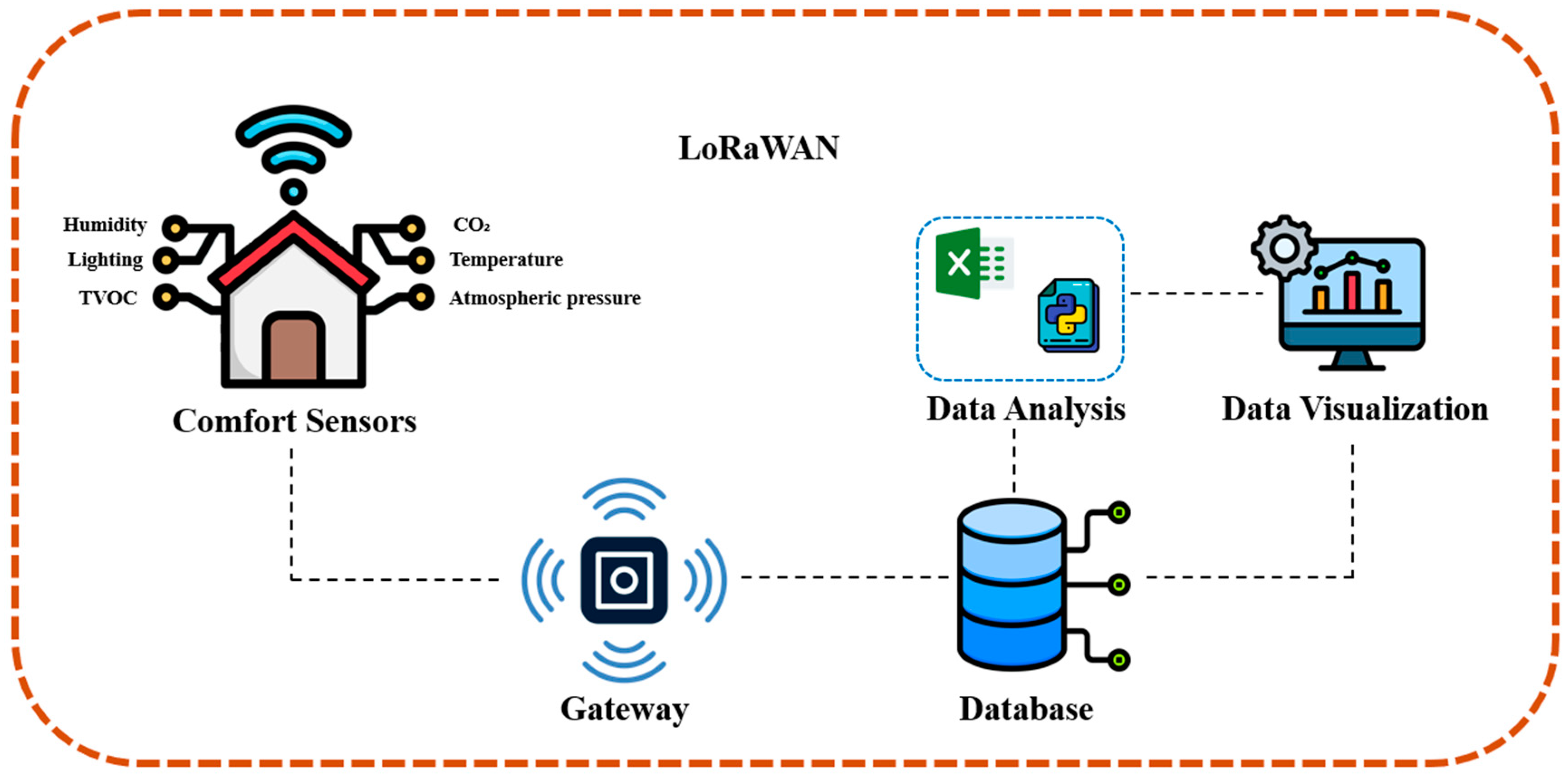
The LoRaWAN protocol was deployed across 13 residential buildings/apartments in Zaragoza participating in the INCUBE EU project, where comfort parameters were monitored and experimentally assessed (schematic in Figure 3). Zaragoza, located in the northeast of Spain within the Ebro River basin, experiences a continental Mediterranean climate. The climate is characterized by significant seasonal variability and extreme weather conditions regarding temperature, wind, and humidity. In summer, temperatures frequently reach between 35 °C and 40 °C, leading to intensive use of air-conditioning systems. Winters, though mild, can see temperatures drop close to 0 °C, with strong winds (known as ‘cierzo’) influencing the thermal sensation. The wind, common in autumn and winter, facilitates natural ventilation but can hinder the use of open windows due to the cold drafts it produces. Humidity levels remain relatively low throughout the year, especially in the warmer months, which can contribute to drier indoor conditions.
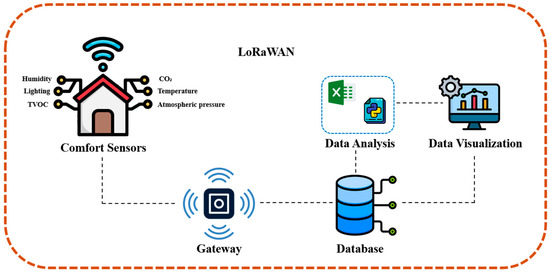
Figure 3.
Implementation of the LoRaWAN protocol.
The buildings are relatively old, constructed in 1970, with a gross area from 75 m2 to 82 m2, with a usable area of 64.5 m2 each. They have apartments with a typical layout of two to three bedrooms, a living room, a kitchen, and a bathroom. They contain three to four medium-sized windows and a small balcony, allowing for natural ventilation but lacking modern automated systems. The windows are manually operated, with minimal insulation, making them a major source of heat loss during colder months. The apartments are equipped with basic heating systems, typically individual gas boilers, and some have air-conditioning units for cooling. The apartments’ energy use and daily routines follow typical residential patterns, including standard cooking schedules. Occupancy patterns assume primary activities, like cooking, occur around midday and evening, using common methods such as frying, baking, microwaving, and boiling. Within the scope of this paper, this general understanding of daily habits was assumed without needing specific data from individual tenants. Although these buildings share similar structural characteristics, they serve diverse functions, offering a comprehensive perspective on how different uses impact comfort dynamics. This study focused on six key metrics: temperature, CO2 levels, humidity, lighting, atmospheric pressure, and TVOC. Within the scope of this paper, data collected from 13 apartments are presented. Here, a comparative analysis was conducted on the buildings characterized by similar structures but different functions, highlighting the contrasts and key insights into comfort dynamics in residential buildings.
For this study, we installed various sensors to monitor indoor environmental conditions. Sensors were strategically placed in the main living areas, such as the living room, where occupants spend the most time. A single sensor type (Milesight AM307) with accuracy highlighted in Table 1 was used to monitor multiple parameters, including CO2, temperature, humidity, illuminance, and atmospheric pressure. The data collection intervals were set at 15 min for all parameters, ensuring frequent updates on indoor conditions. No internet speed tests were required during the gateway installation because the system operates independently of the apartment’s modem/router. The sensor-to-gateway communication uses the LoRaWAN protocol, and the gateway-to-server communication relies on 5G technology, ensuring stable and efficient data transmission without affecting the residents’ internet connection. There were no delays or interruptions, and the installation caused no inconvenience to residents.

Table 1.
Indoor ambience-monitoring sensor featuring LoRaWAN [33].
The analysis began with an evaluation of a short-term (one month) evolution of each parameter in five apartments, followed by a detailed long-term (seasonal) assessment across all 13 apartments. This approach enabled us to observe and compare variations in indoor environmental comfort over different timeframes. The results provide valuable insights into real-time residential comfort dynamics and underscore the importance of implementing efficient and cost-effective monitoring solutions like LoRaWAN for continuous data collection and analysis.
3. Results
This section presents key results from the monitored comfort parameters. It includes identified key trends, highlighting how building usage and seasonal changes impact indoor comfort and providing insights into optimizing residential environments.
3.1. Indoor Environmental Parameters Evolution in a Short Period
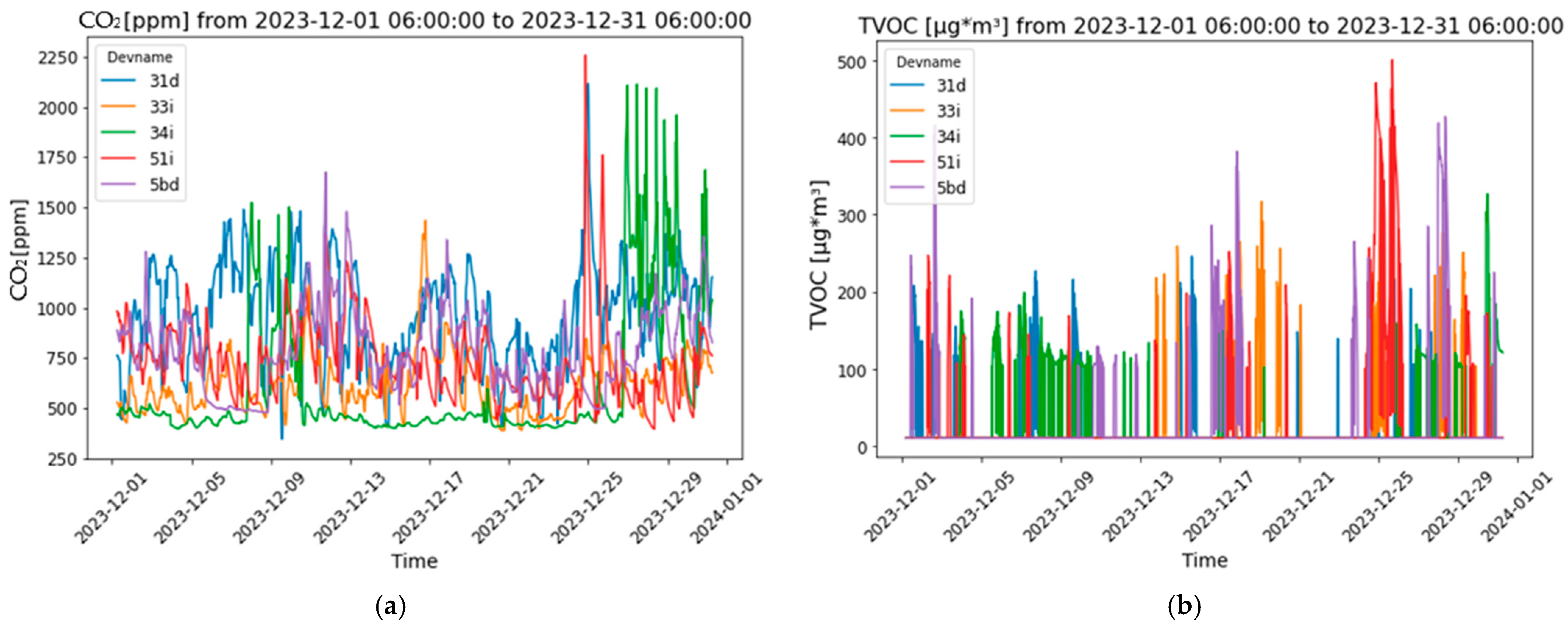
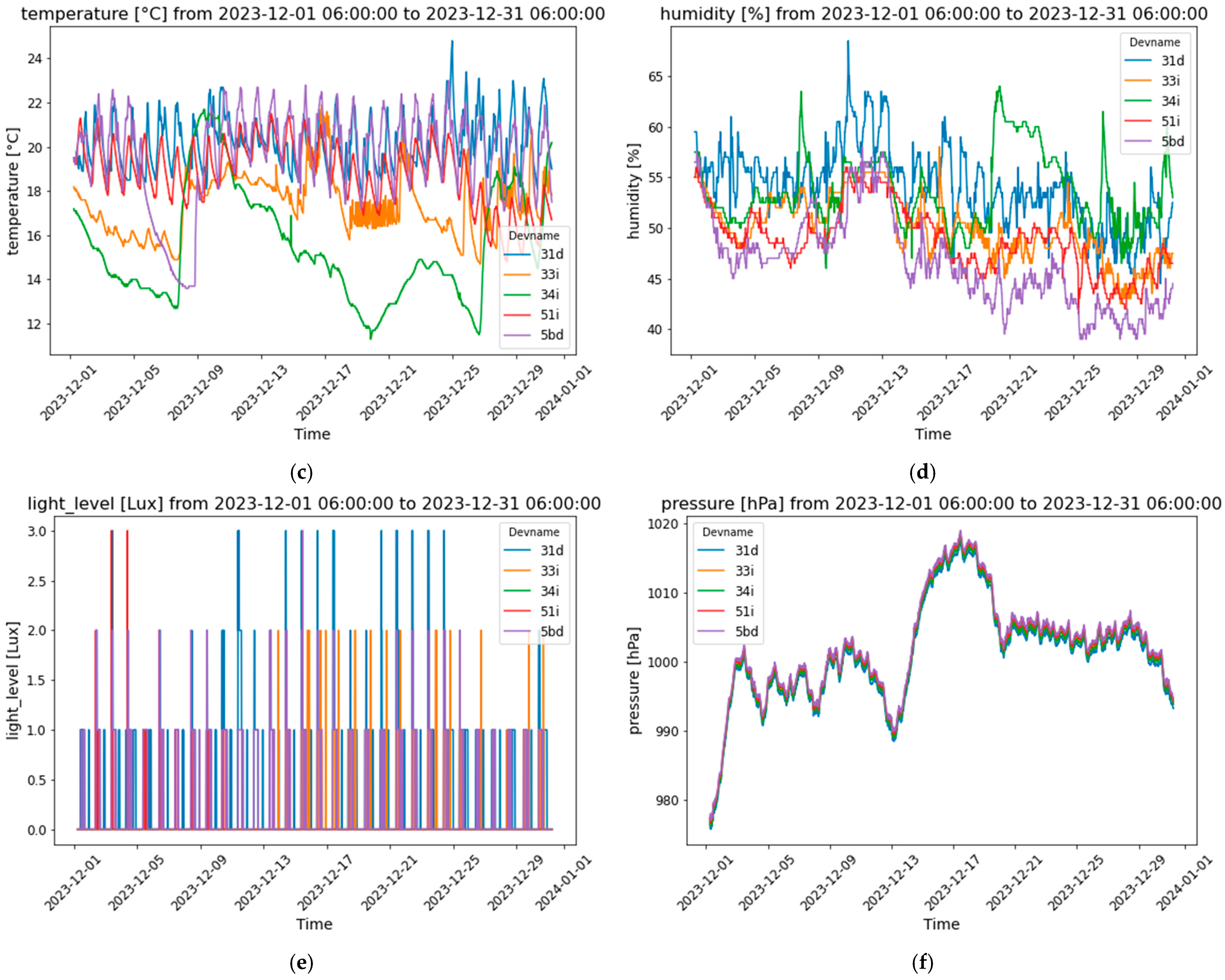
This subsection presents the evolution of the six parameters, highlighting the values obtained across five apartments throughout December (Figure 4). The analysis highlights significant trends and underscores the importance of continuous monitoring and effective management of indoor environmental conditions. This is crucial for maintaining optimal air quality, thermal comfort, and occupant well-being, particularly in settings with fluctuating occupancy and ventilation efficiency.
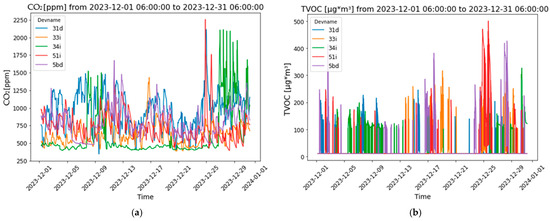
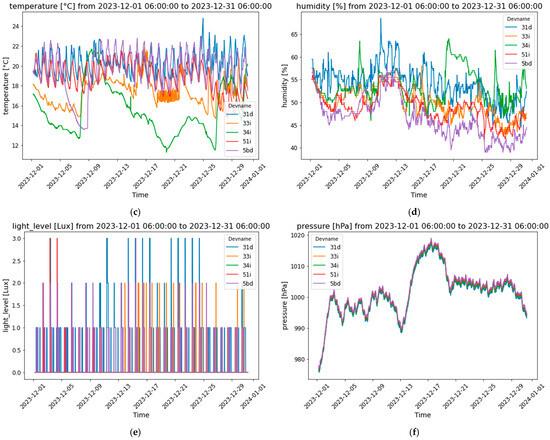
Figure 4.
Buildings’ interior comfort parameters evolution: (a) carbon dioxide levels; (b) TVOC levels; (c) indoor temperature; (d) relative humidity; (e) illuminance; and (f) pressure.
The monitoring of CO2 concentration levels demonstrated a significant variability, with marked fluctuations throughout the month (Figure 4a). Apartments “31d”, “33i”, and, particularly, “58d” exhibited frequent peaks in CO2 levels, with “58d” reaching concentrations near or above 2000 ppm on several occasions. These peaks suggest periods of inadequate ventilation, potentially compromising indoor air quality and occupant health if sustained over extended periods. Notably, the data showed a pattern of CO2 level increases across multiple apartments during the final week of December, possibly correlating with increased indoor activities related to the holiday season. In contrast, apartments “51i” and “34i” maintained relatively lower CO2 levels, indicating either more effective ventilation or lower occupancy.
The analysis of total volatile organic compounds (TVOCs) levels revealed notable variations in indoor air quality across the apartments (Figure 4b). TVOC concentrations, measured in µg/m3, showed frequent spikes, particularly in apartments “34i”, “33i”, and “51i”, where levels exceeded 400 µg/m3 towards the end of December. These spikes suggest potential indoor air quality issues during this period, likely due to increased indoor activities, reduced ventilation, or specific events like holiday gatherings. Interestingly, “58d” generally maintained lower TVOC levels, indicating better indoor air quality or different occupancy patterns. The temporal clustering of TVOC peaks around late December further supports the influence of occupant behavior, such as increased use of products or activities that release VOCs during the holiday season. However, differentiating between beneficial volatile phyto-organic compounds (VPOCs) and harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) is crucial when assessing total VOC levels in indoor environments. For instance, natural Christmas trees, such as pine and fir, release VPOCs like terpenes, which have antimicrobial properties that can enhance indoor air quality [34,35]. In contrast, artificial trees made from materials like PVC may emit harmful VOCs, contributing to indoor air pollution.
Temperature data for the apartments showed distinct patterns of thermal comfort. “31d” and “33i” consistently maintained temperatures between 20 °C and 24 °C, reflecting stable indoor conditions likely managed by effective heating systems (Figure 4c). Conversely, “58d” experienced a significant drop in temperature, particularly from mid-December onwards, with temperatures declining to around 12 °C, indicating possible issues with heating or temperature control. Apartment “51i” displayed moderate fluctuations between 16 °C and 22 °C, likely due to changes in external weather conditions or intermittent heating. The pronounced temperature drops in “58d” and the downward trend in “34i” mid-month suggest challenges in maintaining consistent thermal comfort, which could affect occupant comfort during colder periods.
Humidity levels across the apartments also varied, reflecting different degrees of indoor moisture control (Figure 4d). Apartments “31d” and “58d” exhibited the highest humidity levels, with “31d” consistently maintaining levels around 55% to 65%, and “58d” showing similar trends, although with a slight decrease towards the end of the month. This suggests higher moisture content, potentially due to limited ventilation or external weather influences. In contrast, “33i” and “34i” maintained more stable and lower humidity levels, fluctuating between 40% and 50%, indicating more effective humidity control. Apartment “51i” had moderate fluctuations between 45% and 55%, suggesting a balance between moisture control and environmental factors. The higher humidity levels in “31d” and “58d” could impact occupant comfort and increase the risk of condensation or mold growth if not managed properly.
The analysis of illuminance across the apartments revealed significant variability in indoor lighting conditions (Figure 4e). Most apartments consistently maintained low illuminance, primarily within Level 0 (0–5 lux) to Level 1 (6–50 lux), suggesting dim lighting conditions either due to low ambient light or limited exposure to natural light. However, “31d” and “33i” experienced occasional spikes in illuminance, reaching up to Level 3 (101–500 lux), indicating periods of moderate indoor lighting, possibly for activities requiring higher illumination or due to increased natural light during certain times of the day. In contrast, “34i”, “51i”, and “58d” maintained consistently low illuminance, implying a preference for or consistent conditions of subdued lighting. This variability in lighting could influence occupant comfort and functionality, especially if the lighting conditions do not align with the occupants’ activities or preferences.
Lastly, the atmospheric pressure data showed a consistent pattern of fluctuations across all apartments, with pressure levels generally ranging between 990 hPa and 1020 hPa (Figure 4f). A notable peak occurred around mid-December, where pressure values reached approximately 1020 hPa, followed by a gradual decline towards the end of the month, dropping below 1000 hPa. The synchronization of pressure trends across the apartments suggests that these changes were predominantly driven by external atmospheric conditions rather than specific indoor factors. This uniformity indicates that regional weather patterns likely influenced indoor environments, which could affect factors such as ventilation and air quality, depending on the building structure and location.
3.2. Indoor Environmental Parameters over Time
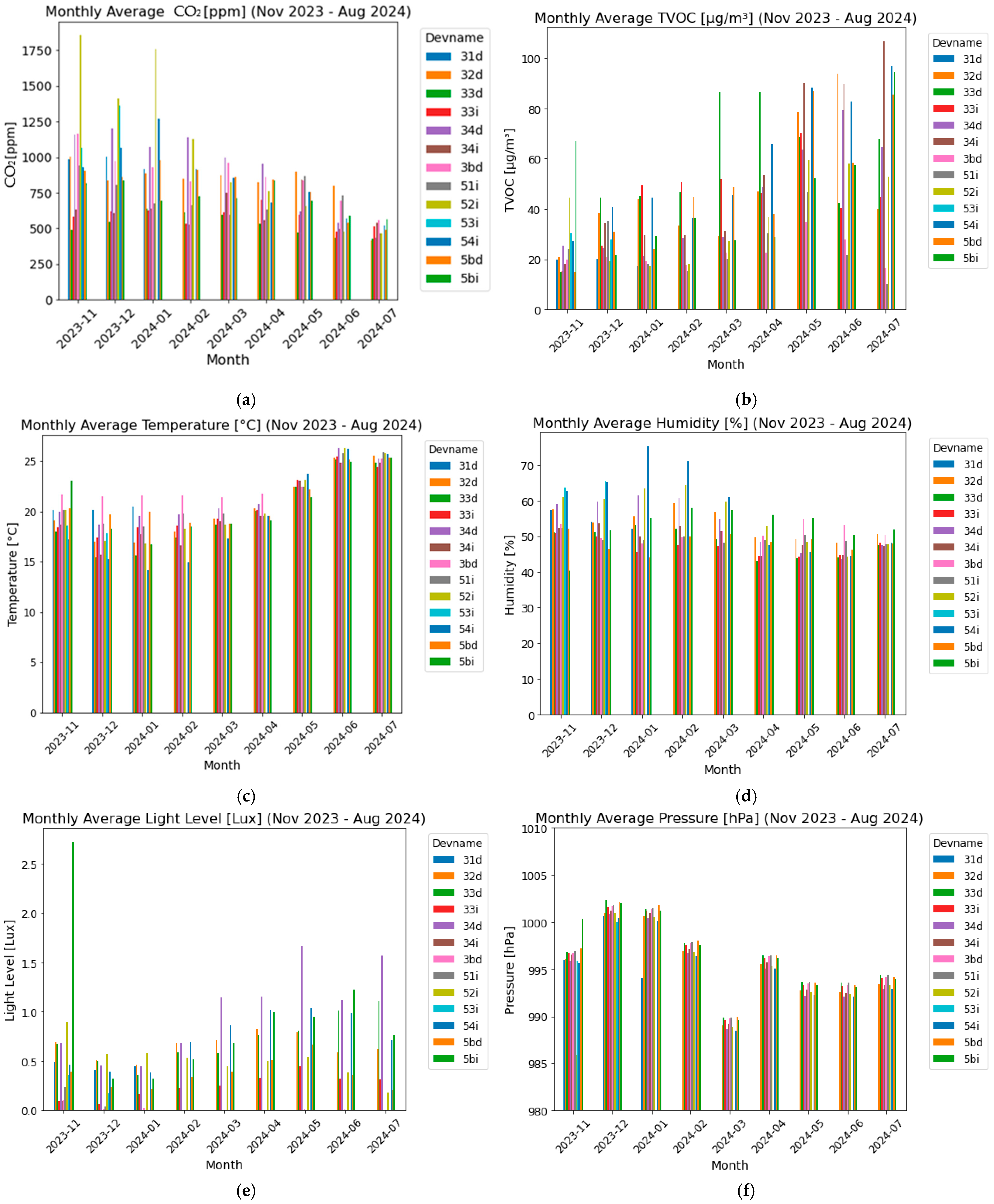
In this subsection, we delve deeper into the analysis of indoor environmental parameters, focusing on long-term observation across multiple apartments from November 2023 to August 2024. The data collected provide a comprehensive overview of how key comfort parameters fluctuate over time, revealing important insights into indoor environmental quality and comfort within residential settings.
The monitoring of CO2 levels reveals notable fluctuations, particularly during the winter months when higher values are observed in several apartments (Figure 5a). This seasonal trend suggests that reduced natural ventilation, likely due to closed windows and doors during colder periods, leads to an accumulation of CO2 indoors. The data indicate that certain apartments may experience suboptimal ventilation, potentially leading to poor air quality and discomfort among occupants. Continuous monitoring and the implementation of adequate ventilation strategies are essential to mitigate these peaks and maintain healthy indoor air quality.
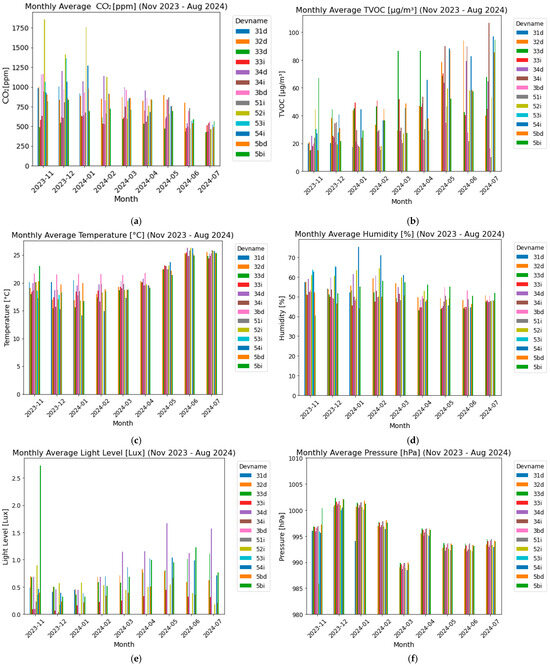
Figure 5.
Long-term average buildings´ interior comfort parameters evolution: (a) carbon dioxide levels; (b) TVOC levels; (c) indoor temperature; (d) relative humidity; (e) illuminance; and (f) pressure.
TVOC levels show a pattern of variation, with some apartments experiencing higher concentrations, particularly during the warmer months (Figure 5b). Elevated TVOC levels can indicate the presence of indoor air pollutants from various sources, such as cleaning products, furnishings, and building materials. The data suggest a need for improved air purification and ventilation, especially in the summer, to reduce these levels and enhance indoor air quality.
The recorded temperature data reflect effective climate control within the apartments, with indoor temperatures consistently (more than 80%) maintained within the comfort range of 19–26 °C (Figure 5c). Seasonal variations are observed, with slight decreases in winter and increases in summer, as expected. The stability of these readings indicates that the heating and cooling systems are functioning efficiently, ensuring thermal comfort for the occupants year-round.
Relative humidity levels across the monitored apartments generally (more than 70%) fall within the acceptable range for indoor comfort (30–60%) (Figure 5d). However, some apartments exhibit periods of elevated humidity, especially during the winter months. These increases may be attributed to reduced ventilation and increased indoor moisture production, which are common during colder weather. High humidity levels can contribute to mold growth and other moisture-related issues, emphasizing the need for effective humidity control measures, particularly during winter.
The analysis of illuminance indicates a significant reduction in natural light during the winter months, consistent with shorter daylight hours and overcast conditions (Figure 5e). This reduction may negatively impact occupant well-being, particularly in terms of mood and circadian rhythm regulation. The data underscore the importance of optimizing artificial lighting during these periods to compensate for the lack of natural light, thereby ensuring adequate indoor illumination and supporting occupant health.
Pressure readings across the apartments are remarkably consistent throughout the monitoring period, indicating stable indoor conditions (Figure 5f). This stability is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the buildings and ensuring the effective operation of HVAC systems. The absence of significant pressure fluctuations suggests that the indoor environments are well managed in this regard, with no immediate concerns identified. We acknowledge that the influence of wind and ventilation on indoor pressure is minimal compared to atmospheric pressure, which is approximately 101 kPa. The slight variations observed in pressure are negligible and do not significantly impact overall indoor pressure levels. This has been clarified in the analysis to emphasize that external atmospheric conditions primarily drive any fluctuations.
4. Conclusions
This study underscores the critical role of continuous monitoring and management of indoor environmental comfort parameters (temperature, CO2 levels, humidity, lighting, total volatile organic compounds (TVOCs), and atmospheric pressure) in residential buildings. The analysis revealed significant fluctuations in CO2 and TVOC levels, particularly during periods of increased indoor activity, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced ventilation strategies to maintain acceptable air quality. Specifically, CO2 levels were observed to peak at over 2000 ppm in certain apartments, exceeding the recommended thresholds for indoor comfort. Similarly, TVOC concentrations surpassed 400 µg/m3 in several instances, suggesting potential air quality concerns. Temperature and humidity inconsistencies pointed to challenges in achieving thermal comfort in specific apartments, indicating a need for improved climate control systems. For example, some apartments recorded temperatures as low as 12 °C during winter, falling below comfort standards. Lighting levels were frequently below optimal thresholds, especially during winter, suggesting potential impacts on occupant comfort and overall well-being. Specifically, indoor illuminance remained below 50 lux in most cases, requiring improved artificial lighting solutions.
Long-term data highlighted seasonally consistent patterns in CO2 and humidity with reduced natural ventilation in colder months. Although temperature and atmospheric pressure were generally well regulated, the study identified CO2, humidity, lighting, and TVOC as key areas needing targeted improvements. These findings emphasize the importance of real-time monitoring using efficient, cost-effective technologies like LoRaWAN to enhance indoor environmental quality.
Based on the conclusions derived from this study, we recommend improving ventilation strategies to address CO2 and TVOC fluctuations, especially during winter months when windows are less likely to be opened. Further interventions should include upgrading insulation and window systems in these old buildings to improve overall thermal comfort. Future research should focus on implementing proactive and adaptive strategies to address the evolving nature of residential indoor environmental quality and its impact on occupant health, aiming for more sustainable management practices. These strategies should leverage the combined strengths of various technologies, such as smart thermostats and HVAC systems, and advanced ventilation systems like smart energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) and heat recovery ventilators (HRVs). Additionally, more efforts are encouraged to adopt the Smart Readiness Indicator (SRI), which can enhance building capabilities by assessing how effectively smart technologies improve energy efficiency, comfort, and overall performance. Finally, when implementing the LoRaWAN protocol, it is recommended to consider integration with artificial intelligence (AI) for monitoring and automated responses, which can further minimize human error, particularly in detecting hard-to-notice factors like CO2 and TVOC levels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.D.M. and J.M.L.; methodology, B.D.M., J.M.L. and J.I.G.G.; validation, B.D.M., J.M.L. and J.I.G.G.; formal analysis, B.D.M. and J.M.L.; investigation, B.D.M. and J.M.L.; data curation, B.D.M.; writing—original draft preparation, B.D.M. and J.M.L.; writing—review and editing, V.B. and J.I.G.G.; supervision, V.B.; project administration, V.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper is based on the experience and results gained from InCUBE; a project co-funded by the Horizon Europe (HORIZON) of the European Commission under grant agreement No. 101069610. (InCUBE—An Inclusive Toolbox for Accelerating and Smartening Deep Renovation).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to the restrictions: e.g., privacy, legal, ethical reasons, etc.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wyon, D.P. The effects of indoor air quality on performance and productivity. Indoor Air Suppl. 2004, 14 (Suppl. 7), 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisk, W.J.; Black, D.; Brunner, G. Benefits and costs of improved IEQ in U.S. offices. Indoor Air 2011, 21, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorizas, P.V.; Assimakopoulos, M.-N.; Santamouris, M. A holistic approach for the assessment of the indoor environmental quality, student productivity, and energy consumption in primary schools. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakellaris, I.A.; Saraga, D.E.; Mandin, C.; Roda, C.; Fossati, S.; De Kluizenaar, Y.; Carrer, P.; Dimitroulopoulou, S.; Mihucz, V.G.; Szigeti, T.; et al. Perceived indoor environment and occupants’ comfort in European ‘Modern’ office buildings: The OFFICAIR Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subri, M.S.M.; Arifin, K.; Sohaimin, M.F.A.M.; Abas, A. The parameter of the Sick Building Syndrome: A systematic literature review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felgueiras, F.; Mourão, Z.; Moreira, A.; Gabriel, M.F. Indoor environmental quality in offices and risk of health and productivity complaints at work: A literature review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, F.; Coruzzolo, A.M.; Balugani, E. The Indoor Environmental Quality: A TOPSIS-based approach with indirect elicitation of criteria weights. Saf. Sci. 2022, 148, 105652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Comesaña, M.; Eguía-Oller, P.; Martínez-Torres, J.; Febrero-Garrido, L.; Granada-Álvarez, E. Optimisation of thermal comfort and indoor air quality estimations applied to in-use buildings combining NSGA-III and XGBoost. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chang-Richards, A.; Wang, K.I.-K.; Dirks, K.N. Critical indoor environmental factors affecting productivity: Perspectives from university staff and postgraduate students. Build. Res. Inf. 2023, 51, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, L.; Serra, V.; Fantucci, S.; Dutto, M.; Massolino, M. Thermal insulating plaster as a solution for refurbishing historic building envelopes: First experimental results. Energy Build. 2015, 95, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.J.; Levin, H. Indoor environmental quality research needs for low-energy homes. Sci. Technol. Built Environ. 2015, 21, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Jiménez, A.; Lizana, J.; Molina-Huelva, M.; Barrios-Padura, Á. Indoor environmental quality in social housing with elderly occupants in Spain: Measurement results and retrofit opportunities. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broday, E.E.; da Silva, M.C.G. The role of internet of things (IoT) in the assessment and communication of indoor environmental quality (IEQ) in buildings: A review. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2023, 12, 584–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Razek, S.A.; Marie, H.S.; Alshehri, A.; Elzeki, O.M. Energy Efficiency through the Implementation of an AI Model to Predict Room Occupancy Based on Thermal Comfort Parameters. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ito, K. Optimization of indoor environmental quality and ventilation load in office space by multilevel coupling of building energy simulation and computational fluid dynamics. Build. Simul. 2014, 7, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. DIRECTIVE (EU) 2018/844 of the European Parliament and of the Council. May 2018. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/publications/levels-and-european-climate-pact_en (accessed on 17 September 2024).
- REHVA. European Framework for Sustainable Buildings. Available online: www.rehva.eu (accessed on 17 September 2024).
- Salamone, F.; Belussi, L.; Danza, L.; Galanos, T.; Ghellere, M.; Meroni, I. Design and development of a nearablewireless system to control indoor air quality and indoor lighting quality. Sensors 2017, 17, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, M.; Kostyrko, K.; Pykacz, S. Indoor environmental quality assessment: Part 1: Choice of the indoor environmental quality sub-component models. J. Build. Phys. 2017, 41, 264–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, J.; Hedge, A. Re-evaluation of a LEED Platinum Building: Occupant experiences of health and comfort. Work 2017, 57, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, C.; Marzban, S.; Haddad, S.; Mackey, M.; Loder, A. Designing healthy workspaces: Results from Australian certified open-plan offices. Facilities 2021, 39, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himeur, Y.; Elnour, M.; Fadli, F.; Meskin, N.; Petri, I.; Rezgui, Y.; Bensaali, F.; Amira, A. AI-big data analytics for building automation and management systems: A survey, actual challenges and future perspectives. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 4929–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnour, M.; Himeur, Y.; Fadli, F.; Mohammedsherif, H.; Meskin, N.; Ahmad, A.M.; Petri, I.; Rezgui, Y.; Hodorog, A. Neural network-based model predictive control system for optimizing building automation and management systems of sports facilities. Appl. Energy 2022, 318, 119153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, S.M.A.; Pavlak, G.S.; Bahnfleth, W.P. Performance of advanced control sequences in handling uncertainty in energy use and indoor environmental quality using uncertainty and sensitivity analysis for control components. Energy Build. 2020, 225, 110308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetti, M.; Ferrari, P.; Silva, D.R.C.; Silva, I.; Sisinni, E. On the use of LoRaWAN for the monitoring and control of distributed energy resources in a smart campus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechowiak, M.; Zwierzykowski, P.; Musznicki, B. LoRaWAN Metering Infrastructure Planning in Smart Cities. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mselle, B.D.; Zsembinszki, G.; Borri, E.; Vérez, D.; Cabeza, L.F. Trends and future perspectives on the integration of phase change materials in heat exchangers. J. Energy Storage 2021, 38, 102544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE Committee. ASHRAE Position Document on Indoor Carbon Dioxide; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. The Inside Story: A Guide to Indoor Air Quality; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Attune. Comprehensive Guide to Indoor Air Quality Parameters. Available online: https://www.attuneiot.com/resources/iaq-parameters-guide (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Samad, A. A Comparative Study on Emerging Radio Technologies for IoT. 2020. Available online: www.preprints.org (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- Mekki, K.; Bajic, E.; Chaxel, F.; Meyer, F. A comparative study of LPWAN technologies for large-scale IoT deployment. ICT Express 2017, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesight. User Guide: Indoor Ambience Monitoring Sensor. Featuring LoRaWAN. AM300 (L) Series. 2024. Available online: https://resource.milesight.com/milesight/iot/document/am300-series-user-guide-en.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Skulberg, K.R.; Nyrud, A.Q.; Goffeng, L.O.; Wisthaler, A. Health and Exposure to VOCs From Pinewood in Indoor Environments. Front. Built Environ. 2019, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.; Donelli, D.; Barbieri, G.; Valussi, M.; Maggini, V.; Firenzuoli, F. Forest volatile organic compounds and their effects on human health: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).