Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control for Linear Motor Traction Systems with Prescribed Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- PPC is used to restrict the tracking errors, leading to enhancements in the dynamic response, mitigation of overshoot, and a reduction in tracking errors.
- FTSMC contributes to an increased system robustness and accelerates the convergence time of speed errors.
- The fixed-time stability of both the sliding mode surface and the system states under the composite control scheme proposed is substantiated through Lyapunov stability theory.
2. Problem Description
2.1. Mathematical Modelling of PMLSMs
2.2. Some Lemmas and Assumptions
3. PPC-FTSMC Schemes for the Velocity Control Loop
3.1. Prescribed Performance Control
3.2. Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Controller Design
4. Simulations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, X.; She, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M.; Kaynak, O. Chaos suppression in speed control for permanent-magnet-synchronous-motor drive system. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 13283–13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Yu, J.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Y. Adaptive fuzzy control for permanent magnet synchronous motors considering input saturation in electric vehicle stochastic drive systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 8473–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kou, B.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, H. Investigation of auxiliary poles optimal design on reduction of end effect detent force for PMLSM with typical slot–pole combinations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yang, R.; Zhang, C.; Cao, J.; Li, L. Inner loop design for PMLSM drives with thrust ripple compensation and high-performance current control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9905–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Z. Bias compensation based partially coupled recursive least squares identification algorithm with forgetting factors for MIMO systems: Application to PMSMs. J. Frankl. Inst. 2016, 353, 3057–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.J.; Hwang, J.C.; Chou, P.H.; Hung, Y.C. FPGA-based intelligent-complementary sliding-mode control for PMLSM servo-drive system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2573–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.B.; Oh, S. A High-Precision Motion Control Based on a Periodic Adaptive Disturbance Observer in a PMLSM. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 2158–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommuri, S.K.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.B. Online Compensation of Mechanical Load Defects With Composite Control in PMSM Drives. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, L.; Pan, D.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Q. High-Bandwidth and Strong Robust Current Regulation for PMLSM Drives Considering Thrust Ripple. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 6646–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D. Application of fuzzy PID control in PMLSM servo drive system. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Beijing, China, 2–5 August 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liu, T.S. Intelligent tracking control of a PMLSM using self-evolving probabilistic fuzzy neural network. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.S.; Tsai, T.M. Sliding mode and neural network control of sensorless PMSM controlled system for power consumption and performance improvement. Energies 2017, 10, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jon, R.; Wang, Z.; Luo, C.; Jong, M. Adaptive robust speed control based on recurrent elman neural network for sensorless PMSM servo drives. Neurocomputing 2017, 227, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Anti-disturbance speed control of low-speed high-torque PMSM based on second-order non-singular terminal sliding mode load observer. ISA Trans. 2019, 88, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, X.; Man, Z. Non-singular terminal sliding mode control of rigid manipulators. Automatica 2002, 38, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcugil, H. Non-singular terminal sliding-mode control of DC–DC buck converters. Control Eng. Pract. 2013, 21, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulay, E.; Léchappé, V.; Bernuau, E.; Defoort, M.; Plestan, F. Fixed-time sliding mode control with mismatched disturbances. Automatica 2022, 136, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Zeng, L. Robust adaptive fixed-time sliding-mode control for uncertain robotic systems with input saturation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; He, G.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S. Robust fixed-time sliding mode attitude control of tilt trirotor UAV in helicopter mode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 10322–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, H.; Khandani, K.; Majd, V.J. Fixed-time sliding-mode distributed consensus and formation control of disturbed fractional-order multi-agent systems. ISA Trans. 2023, 138, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, G.; Ouyang, H.; Mei, L. Novel fixed-time nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for second-order uncertain systems based on adaptive disturbance observer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 126615–126627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, D.; Zhu, W. Implementation of integral fixed-time sliding mode controller for speed regulation of PMSM servo system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 102, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Ni, S.; Xu, D.; Zhang, L.; Yan, X.G. Disturbance-observer based prescribed-performance fuzzy sliding mode control for PMSM in electric vehicles. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 104, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Han, Y.; Xiao, K. Barrier Lyapunov function-based adaptive prescribed performance control of the PMSM used in robots with full-state and input constraints. J. Vib. Control 2023, 29, 1400–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Wu, X.; Huang, J.; Wei, D. Robust estimation-free prescribed performance back-stepping control of air-breathing hypersonic vehicles without affine models. Int. J. Control 2016, 89, 2185–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H. Disturbance-observer-based prescribed performance fault-tolerant trajectory tracking control for ocean bottom flying node. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 49004–49013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Li, S. Composite finite-time control for PMSM with prescribed performance using disturbance compensation technique. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 141, 105677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Xu, D.; Jiang, B.; Shi, P.; Yang, W. Disturbance-observer-based terminal sliding mode control for linear traction system with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 7, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechlioulis, C.P.; Rovithakis, G.A. Robust adaptive control of feedback linearizable MIMO nonlinear systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 53, 2090–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

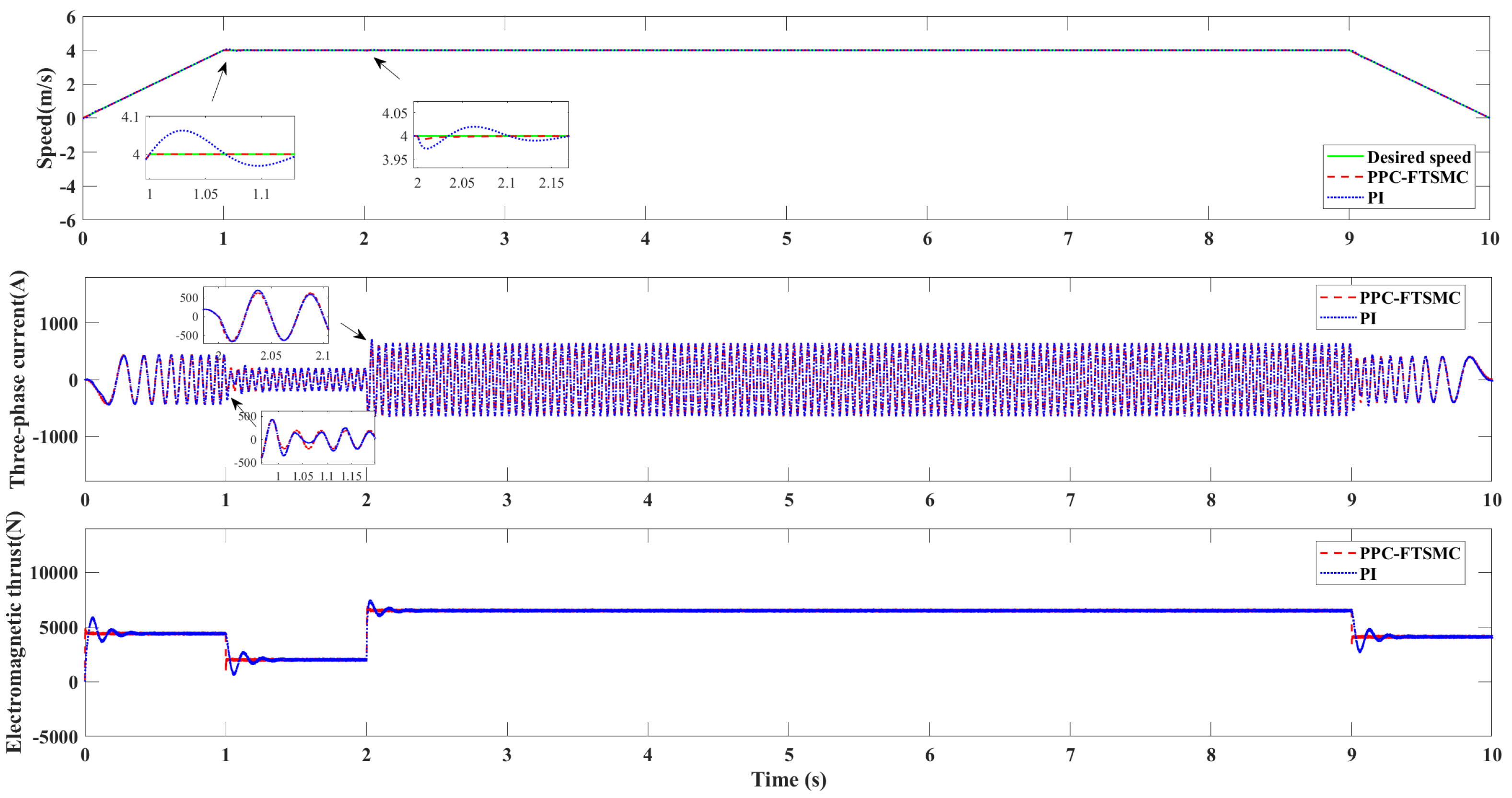
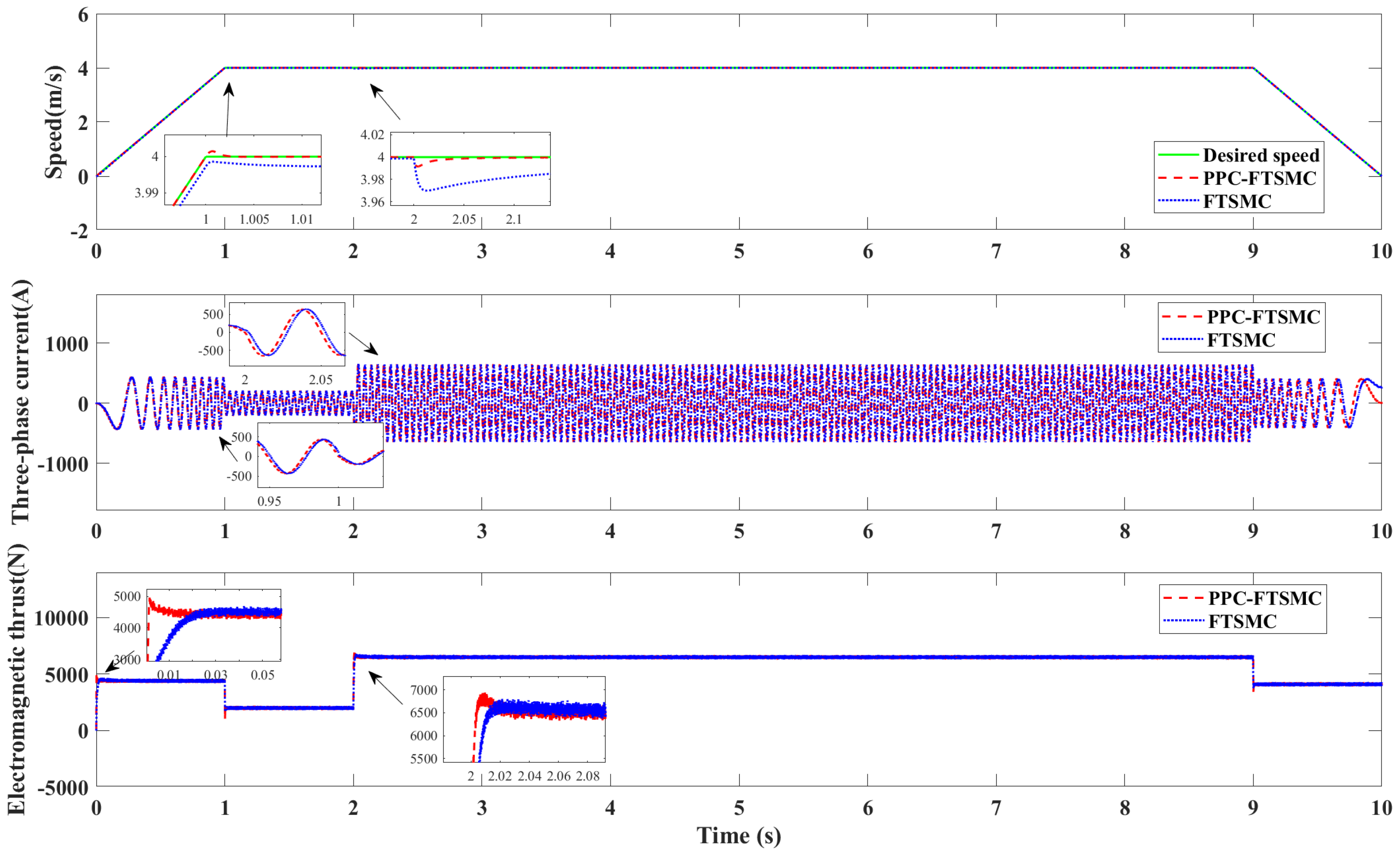


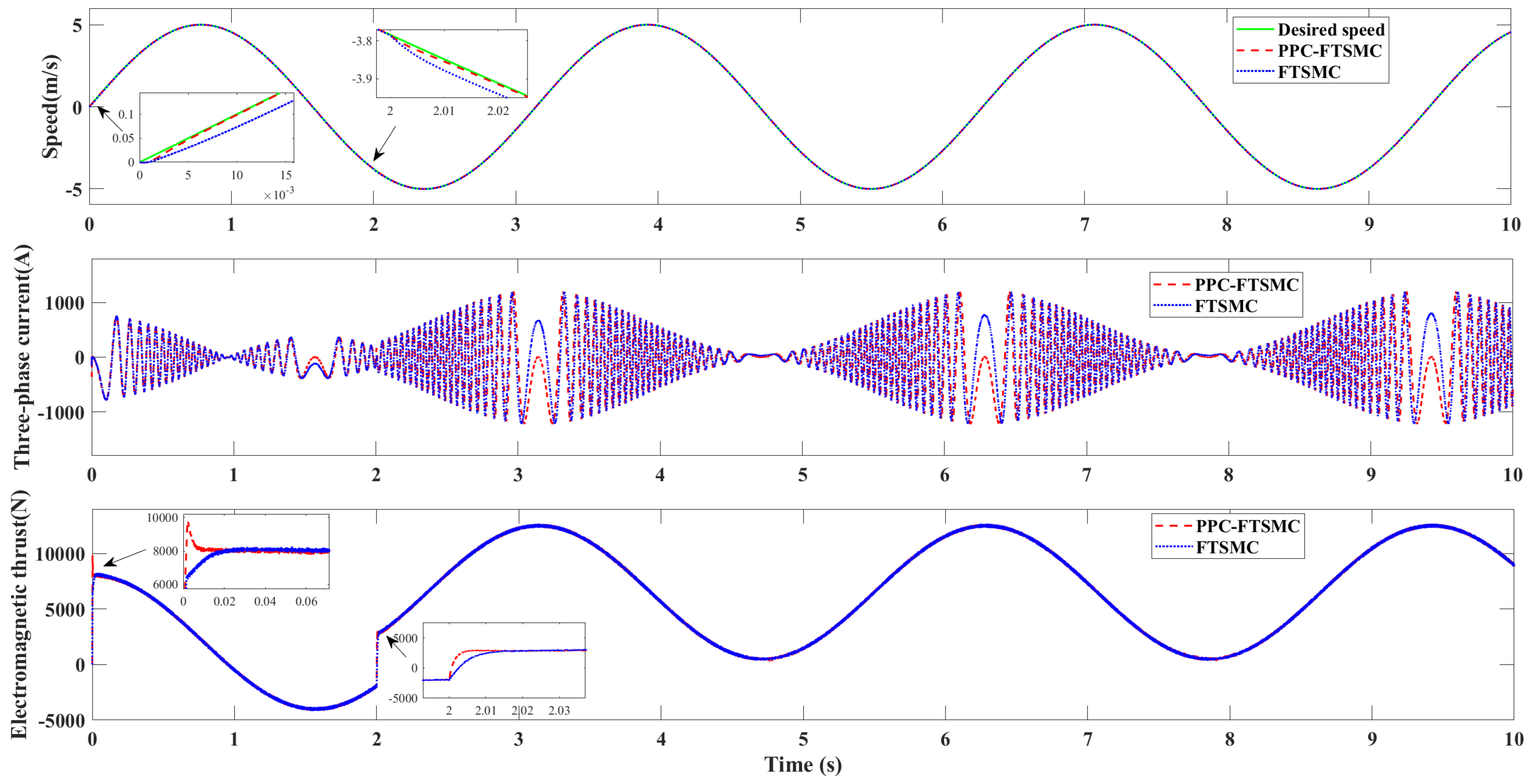

| Parameters | Variable Name | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Stator resistance [] | 0.045 | |
| Stator Inductance [mH] | 1.15 | |
| Mover mass [kg] | M | 600 |
| Friction coefficient [N·s/m] | 0.5 | |
| pole-pitch [mm] | 200 | |
| permanent magnet flux linkage [Wb] | 0.145 | |
| number of pole pairs | n | 2 |
| Error | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPC-FTSMC | FTSMC | PI | PPC-FTSMC | FTSMC | PI | |
| Maximum Error (m/s) | ||||||
| Average Absolute Error (m/s) | ||||||
| Root Mean Squared Error (m/s) | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Hu, G.; Song, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W. Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control for Linear Motor Traction Systems with Prescribed Performance. Energies 2024, 17, 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040952
Yang C, Hu G, Song Q, Wang Y, Yang W. Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control for Linear Motor Traction Systems with Prescribed Performance. Energies. 2024; 17(4):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040952
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chunguang, Guanyang Hu, Qichao Song, Yachao Wang, and Weilin Yang. 2024. "Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control for Linear Motor Traction Systems with Prescribed Performance" Energies 17, no. 4: 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040952
APA StyleYang, C., Hu, G., Song, Q., Wang, Y., & Yang, W. (2024). Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control for Linear Motor Traction Systems with Prescribed Performance. Energies, 17(4), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040952






