Improved Switchable Heat Pipe Based on Adsorption: Against-Gravity Operation and Enhanced Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Against-gravity operation—The adsorption-based heat pipe concept has been studied so far only in thermosiphons, which are a simple type of heat pipes that use gravity for the liquid return and hence only work if the condenser is located above the evaporator [12,13]. Therefore, this work aims to examine demonstrators based on heat pipes with a capillary structure (wick) to ensure against-gravity operation. This, for example, is necessary for thermal management in electrical vehicles, where the battery (heat source) is located above or on the same level as the heat sink [2];
- New demonstrator design—In the previous work given in reference [13], the heat pipe’s evaporator region served as a reservoir for adsorbent grains. In this work, a two-system design is introduced, separating the heat pipe and adsorbent reservoir. This improves the performance and enables a more extensive and systematic investigation of each system;
- Experimental characterization—The aim of previous works on adsorption-based heat pipes was developing a proof-of-concept of a passive regulator [12], as well as the determination and improvement of the switching ratio [13]. For this purpose, a simple experimental routine was designed. In this work, several advanced experimental characterization schemes were developed to examine the adsorption-based heat pipe both as a thermal switch and as regulator in terms of their characteristic properties, such as the maximum heat transfer rate, switching ratio, switching time, as well as the hysteresis behavior;
- Dynamic performance improvement: Since previous works have only investigated the static properties of adsorption-based heat pipe demonstrators [12,13], this study aims to examine and improve the dynamic behavior, which involves the processes of switching between the on and off states. For this purpose, a demonstrator featuring an adsorbent reservoir with a finned tube adsorption heat exchanger is designed and tested. Significant improvements regarding the dynamic properties, i.e., switching time and hysteresis behavior, are achieved;
- Improved evaporator heater—With the aim of achieving higher switching ratios with a lower thermal resistance in the on state, an improved heater design is used to enhance the heat transfer coefficient between the heat source and the heat pipe’s evaporator section. In the previous work, as given in [13], the evaporator heater wire was identified as a bottleneck in terms of the heat transfer coefficient.
2. Materials and Methods
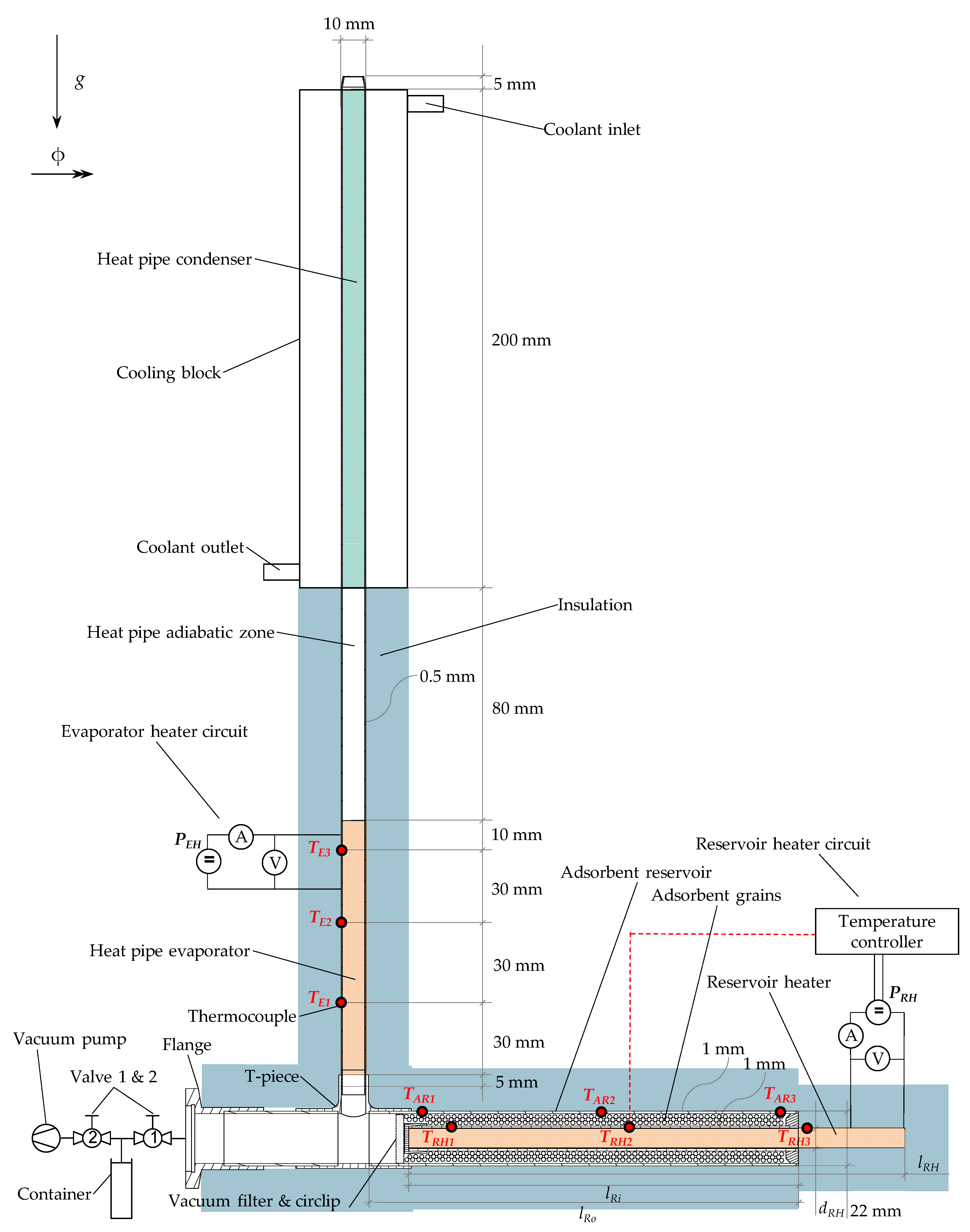
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.1.1. Heat Pipe
2.1.2. Adsorbent Material
2.1.3. Adsorbent Reservoir
2.1.4. Measurement Technology
2.2. Preparation Procedure
2.2.1. Water Loading Procedure
2.2.2. Demonstrator Start-Up
2.3. Experiments
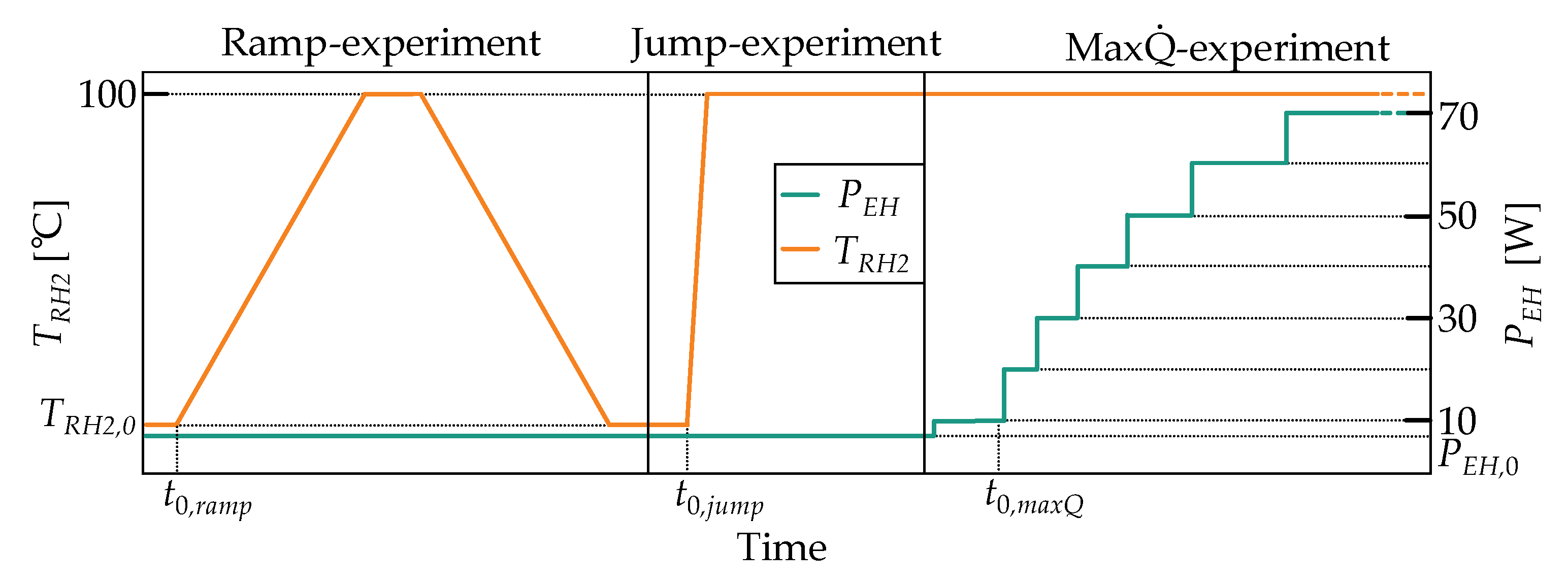
2.3.1. Characterization Schemes
- The ramp experiment is conducted to determine the demonstrator’s deviation from its steady state switching temperature in the case of ramp profiles. In this experiment, the reservoir heater temperature is gradually increased (ramp-up) to 100 °C with a rate of 0.2 Kmin−1, held for 2 h, and then gradually decreased (ramp-down) with the same rate. Accordingly, the demonstrator’s switching on and off processes can be observed. The heat pipe evaporator heat input remains at = 7 W. The experiment is terminated once the demonstrator returns to its initial state.
- The jump experiment is conducted to determine how fast the demonstrator can switch between its on and off states. In this experiment, a temperature step profile with a set temperature of 100 °C is applied to the reservoir heater. The heat pipe evaporator heat input remains at = 7 W. The experiment is terminated once the demonstrator’s heat pipe reaches a steady (on) state.
- The max experiment is conducted to determine the maximum heat transfer rate of the heat pipe. In this experiment, the demonstrator is in the on state, hence the reservoir heater temperature remains at 100 °C. The maximum heat transfer rate is determined by increasing the heat pipe evaporator heat input in 10 W increments. Each power level is maintained until the temperature profile along the heat pipe is temporally constant. Once the heat pipe evaporator reaches temperatures of 150 °C, the experiment is terminated, and the corresponding heat transfer rate is considered as the performance limit.
2.3.2. Data Evaluation
2.3.3. Uncertainty of Evaluated Data
3. Results
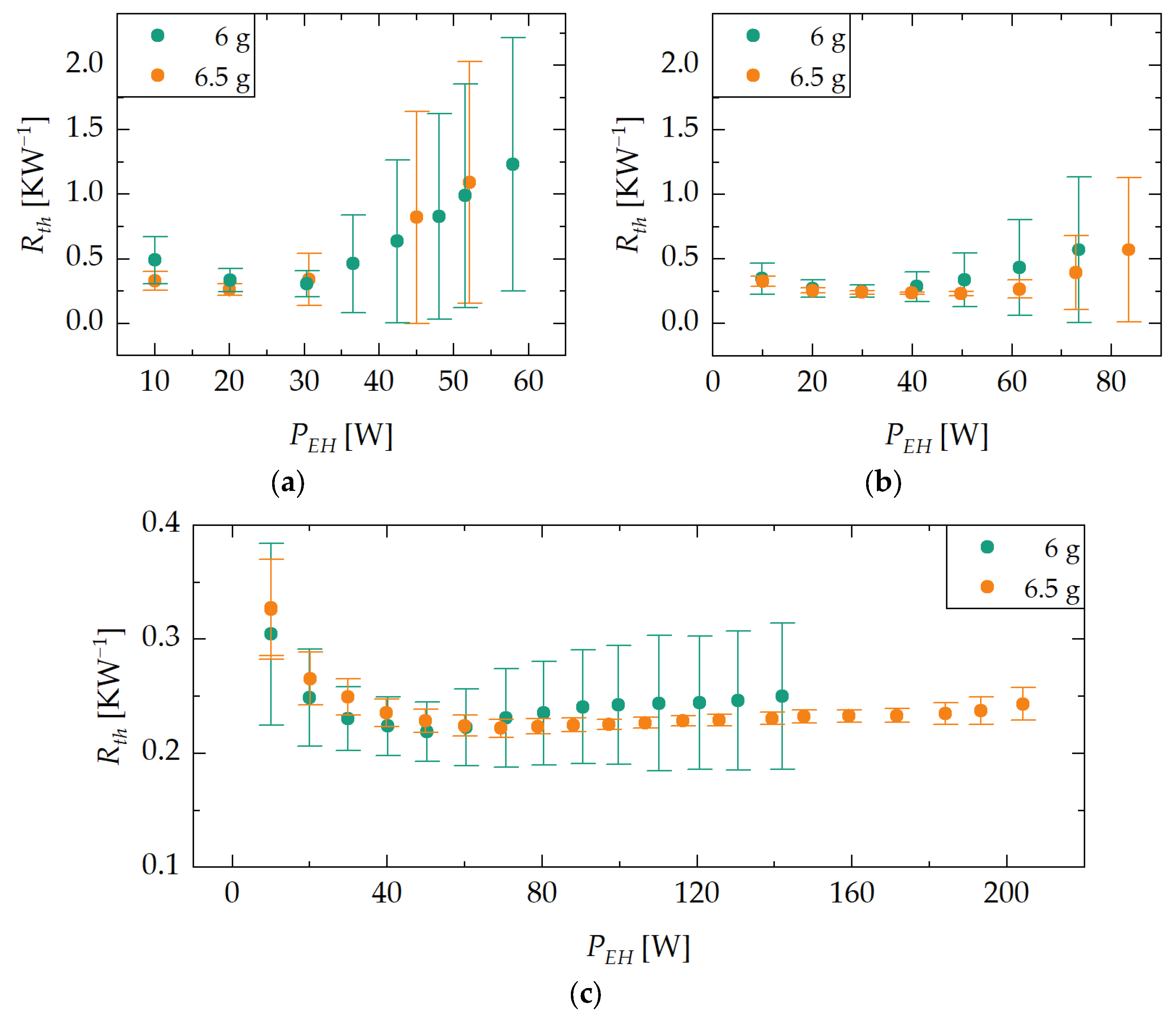
3.1. Maximum Heat Transfer Rate and Thermal Resistance
3.1.1. Maximum Heat Transfer Rate
3.1.2. Thermal Resistance
3.1.3. Interim Summary
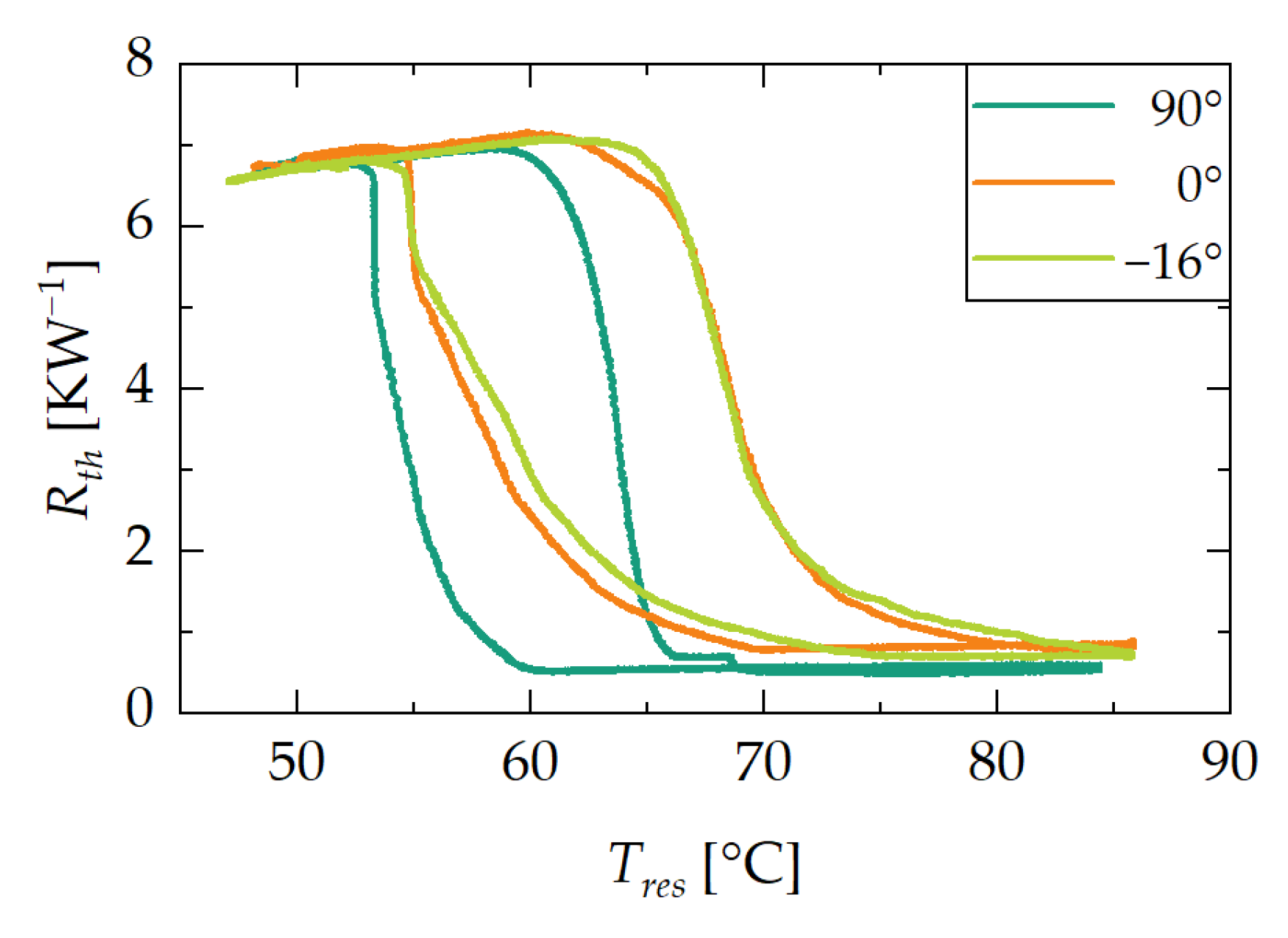
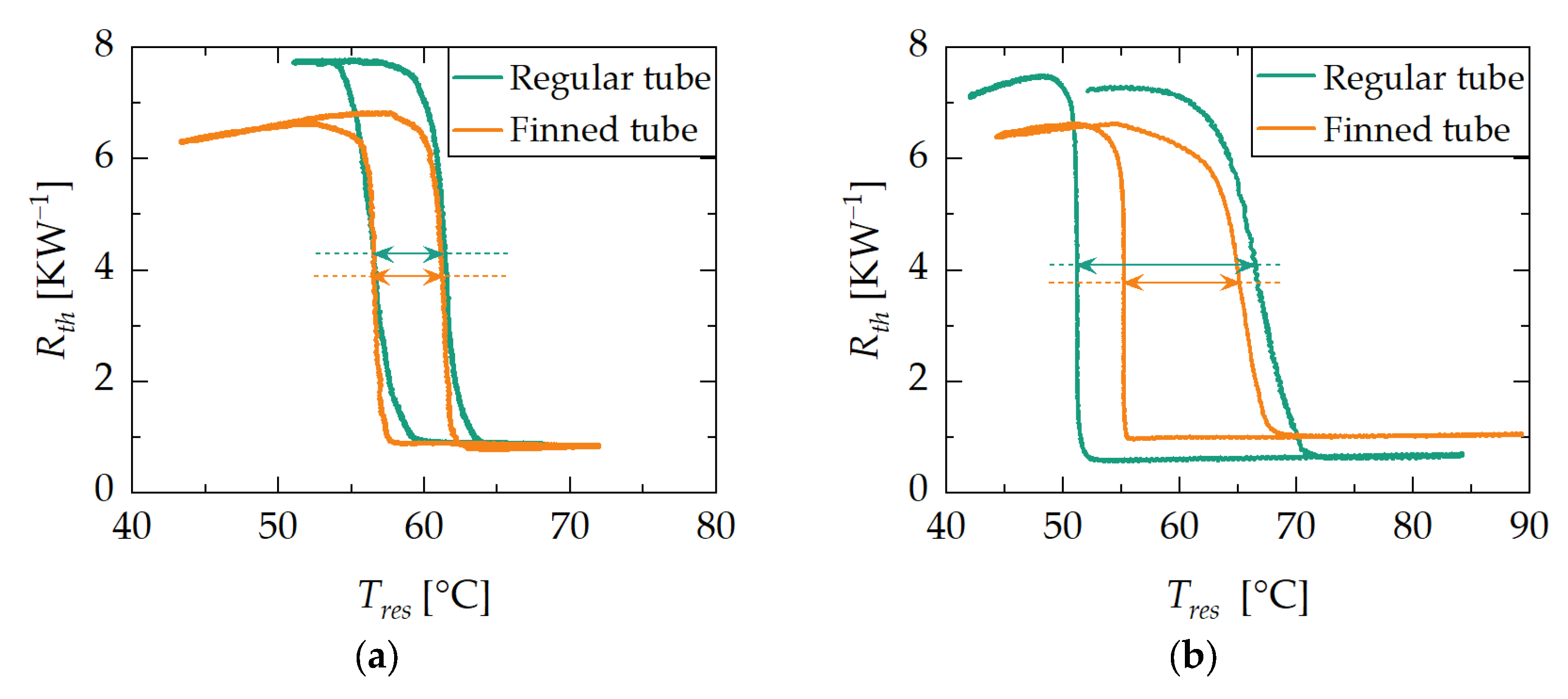
3.2. Switching Temperature and Hysteresis
3.2.1. Influence of Orientation
3.2.2. Influence of Ramp Rate and Adsorbent Reservoir Heat Exchanger Design
3.2.3. Interim Summary
3.3. Switching Time
3.3.1. Influence of Adsorbent Heat Exchanger Design
3.3.2. Power Supply and Limitations

3.3.3. Interim Summary
3.4. Switching Ratio
4. Conclusions
- Against-gravity operation—With the extension of a heat pipe with wick structure by an adsorbent reservoir, a system was built that can be used both as a thermal switch and a thermal regulator, which can be operated also in against-gravity orientation. The results of the experimental investigations suggest that the thermal resistance and the maximum heat transfer rate in the on state of the component correspond to those of a conventional heat pipe. Thereby, it has been demonstrated that the adsorption-based heat pipe has the potential to compensate for the drawbacks of the existing solutions, as presented in the introduction of this work;
- Dynamic performance—Investigations of dynamic properties have revealed that the heat exchanger design of the adsorbent reservoir is crucial for achieving short switching times and minimal deviations of the steady state switching temperature. The results of the experimental investigations have shown that a finned tube heat exchanger with loose adsorbent grains provides significant improvements in terms of dynamic properties compared to a regular tube heat exchanger. Thus, the adsorption-based heat pipe is suitable for applications that impose high demands on the time response of thermal components;
- Size and weight—In this work, the adsorbent reservoir and the heat pipe are approximately the same size. The use of heat exchanger structures such as finned tubes further increases the weight and volume of the system. Hereby, a conservative design specification is proposed, which assists in the design of thermal management systems using adsorption-based heat pipes.
- Constant condenser temperature—Unlike in this study, the temperature of the heat sink and therefore the temperature of the condenser is not necessarily constant in real-life applications;
- Power supply limitation—The power supply of the reservoir heater ran into its current limitation during the jump experiments with the finned tube adsorbent reservoir demonstrator D2;
- Adsorbent and Adsorptive—As mentioned in Section 2.1.2, the characteristics of the adsorbent–adsorptive pairing have a significant influence on the switching temperature of the adsorption-based heat pipe thermal regulator. With the materials used in this work, TAPSO-34 and water, switching temperatures of 60 °C can be achieved within an operating range of 0–100 °C, which therefore may only serve a limited range of applications.
- Varying condenser temperature—Since the condenser temperature affects the pressure within the adsorption-based heat pipe and thus the adsorption characteristics, the influence of a varying condenser temperature will be investigated in future studies;
- Upgrade experimental setup—Implementation of a power supply for the reservoir heater with current limitation larger than 5 A to achieve lower switching times. Implementation of pressure measurement to gain deeper understanding of the adsorption and desorption processes within the adsorbent reservoir;
- Dynamic performance—To achieve further significant improvements regarding dynamic performance, coated adsorbent heat exchangers could make an important contribution. While Guilleminot et al. [24] measured comparably low heat transfer coefficients of 20 Wm−2K−1 between the wall and loose adsorbent grains, coating the heated surface with the adsorbent material yields heat transfer coefficients up to 700 Wm−2K−1 [25];
- Considering potential applications to better align research effort. Possible applications could include the cooling of the batteries of electric vehicles [2] or the thermal management of spacecraft [1]. Depending on the application, we can explore alternative adsorbent–adsorptive pairings for specifically altering the characteristics of the thermal component, such as the switching temperature, as well as the operating range.
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Celotti, L.; Solyga, M.; Nadalini, R.; Kravets, V.; Khairnasov, S.; Baturkin, V.; Lange, C.; Findlay, R.; Ziach, C.; Ho, T. MASCOT thermal subsystem design challenges and solution for contrasting requirements. In Proceedings of the 45th International Conference on Environmental Systems, Bellevue, WA, USA, 12–16 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Illner, M.; Thüsing, K.; Salles, A.; Trettenhann, A.; Albrecht, S.; Winkler, M. Switchable Heat Pipes for Eco-Friendly Battery Cooling in Electric Vehicles: A Life Cycle Assessment. Energies 2024, 17, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehmeyer, G.; Yabuki, T.; Monachon, C.; Wu, J.; Dames, C. Thermal diodes, regulators, and switches: Physical mechanisms and potential applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2017, 4, 41304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, H.; Tian, X.; He, T. Size-dependent thermo-electromechanical responses analysis of multi-layered piezoelectric nanoplates for vibration control. Compos. Struct. 2019, 225, 111112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tian, X.; He, T. An investigation into size-dependent dynamic thermo-electromechanical response of piezoelectric-laminated sandwich smart nanocomposites. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 7235–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselman, G.A.A.; Green, B.B. Heat pipes. Philips Tech. Rev. 1973, 1973, 104–113. [Google Scholar]
- Benafan, O.; Notardonato, W.U.; Meneghelli, B.J.; Vaidyanathan, R. Design and development of a shape memory alloy activated heat pipe-based thermal switch. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Montes, P.; Campo, S.; García, A.; Torres, A.; Munì, M.; Negri, F. ExoMars 2020 LHPs: From the concept to the flight models. In Proceedings of the 47th International Conference on Environmental Systems, Charleston, SC, USA, 16–20 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mock, P.R.; Marcus, D.B.; Edelman, E.A. Communications Technology Satellite: A Variable Conductance Heat Pipe Application. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 1975, 12, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarau, C.; Ababneh, M.; Anderson, W.; Alvarez-Hernandez, A.; Ortega, S.; Farmer, J.; Hawkins, R. Advanced Passive Thermal eXperiment (APTx) for Warm Reservior Hybrid Wick Variable Conductance Heat Pipes on the International Space Station. In Proceedings of the 48th International Conference on Enviornmental Systems (ICES), Albuquerque, NM, USA, 8–12 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Leriche, M.; Harmand, S.; Lippert, M.; Desmet, B. An experimental and analytical study of a variable conductance heat pipe: Application to vehicle thermal management. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 38, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.; Teicht, C.; Corhan, P.; Polyzoidis, A.; Bartholomé, K.; Schäfer-Welsen, O.; Pappert, S. Thermal Switch Based on an Adsorption Material in a Heat Pipe. Energies 2021, 14, 5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.; Schipper, J.; Teicht, C.; Corhan, P.; Polyzoidis, A.; Bartholomé, K.; Schäfer-Welsen, O.; Pappert, S. Improved Thermal Switch Based on an Adsorption Material in a Heat Pipe. Energies 2022, 15, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, M.M. Theory of the physical adsorption of gases and vapors and adsorption properties of adsorbents of various natures and porous structures. translated version. Russ. Chem. B 1960, 9, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerbeck, S.; Manoylova, O.; Tissler, A.; Dienersberger, M. Titano-Silico-Alumino-Phosphate. U.S. Patent 2013/0334460 A1, 19 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Teicht, C. An easy-to-use modification of the potential theory of adsorption and creation of an adsorbent data base. Energy 2023, 263, 125968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, D.A.; Kew, P.A.; McGlen, R.J. Heat Pipes: Theory, Design and Applications, 6th ed.; Butterworth-Heineman: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi, M.; Tiari, S.; de Schampheleire, S.; Qiu, S. Experimental study of the thermal characteristics of a heat pipe. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018, 93, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghri, A. Heat Pipes: Review, Opportunities and Challenges. Front. Heat Pipes 2014, 5, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, P.; Čaja, A.; Malcho, M. Mathematical model for heat transfer limitations of heat pipe. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 57, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, B.D.; Davis, T.W.; Garimella, S.V.; North, M.T.; Kang, S.S. Heat and Mass Transport in Heat Pipe Wick Structures. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2007, 21, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.S.; Liao, Q.; Cheng, P. Variations of Buoyancy-Induced Mass Flux From Single-Phase to Two-Phase Flow in a Vertical Porous Tube with Constant Heat Flux. J. Heat Transf. 1999, 121, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminot, J.J.; Choisier, A.; Chalfen, J.B.; Nicolas, S.; Reymoney, J.L. Heat transfer intensification in fixed bed adsorbers. Heat Recovery Syst. CHP 1993, 13, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzica, A.; Füldner, G.; Sapienza, A.; Freni, A.; Schnabel, L. Experimental and theoretical analysis of the kinetic performance of an adsorbent coating composition for use in adsorption chillers and heat pumps. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 73, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Property | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Original state length | mm | 400 |
| Total length 1 | mm | 390 |
| Evaporator length | mm | 100 |
| Adiabatic zone length | mm | 80 |
| Condenser length | mm | 200 |
| Outer diameter | mm | 10 |
| Wall thickness | mm | 0.5 |
| Average wick thickness | mm | 0.87 |
| Property | Unit | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D2 | ||
| Adsorbent grain size | mm | 1.5 to 3 | 0.5 to 1 |
| Outer tube length | mm | 172 | 249 |
| Inner tube length | mm | 152 | 230 |
| Outer tube outer diameter | mm | 22 | |
| Inner tube outer diameter | mm | 10 | 12 |
| Outer tube wall thickness | mm | 1 | |
| Inner tube wall thickness | mm | 1 | |
| Inner tube outside area per length | m2m−1 | 0.03 | 0.18 |
| Reservoir heater length | mm | 200 | 300 |
| Reservoir heater diameter | mm | 8 | 10 |
| Property | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | K | ±0.33 1 |
| Voltage | µV | ±(0.05% of m.v. 2 + 10) |
| Electrical resistance | mΩ | ±0.0375 |
| Property | Unit | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|
| Average adsorbent reservoir temperature | K | 0.16 |
| Off state thermal resistance | KW−1 | 0.07 |
| On state thermal resistance | KW−1 | 0.05 |
| Property | Unit | Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orientation | ° | 90 | 0 | −16 | |||
| Loading | g | 6 | 6.5 | 6 | 6.5 | 6 | 6.5 |
| W | 142 | 204 | 72 | 83 | 57 | 52 | |
| @ | W | 50 | 69 | 30 | 49 | 30 | 20 |
| KW−1 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.25 | |
| @ | KW−1 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 1.23 | 1.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boda, S.; Winkler, M.; Schießl, R.; Teicht, C.; Schwarz, D.; Schipper, J.; Bartholomé, K.; Schäfer-Welsen, O.; Pappert, S. Improved Switchable Heat Pipe Based on Adsorption: Against-Gravity Operation and Enhanced Dynamics. Energies 2024, 17, 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092088
Boda S, Winkler M, Schießl R, Teicht C, Schwarz D, Schipper J, Bartholomé K, Schäfer-Welsen O, Pappert S. Improved Switchable Heat Pipe Based on Adsorption: Against-Gravity Operation and Enhanced Dynamics. Energies. 2024; 17(9):2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092088
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoda, Simon, Markus Winkler, Robert Schießl, Christian Teicht, Daniel Schwarz, Jan Schipper, Kilian Bartholomé, Olaf Schäfer-Welsen, and Sandra Pappert. 2024. "Improved Switchable Heat Pipe Based on Adsorption: Against-Gravity Operation and Enhanced Dynamics" Energies 17, no. 9: 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092088
APA StyleBoda, S., Winkler, M., Schießl, R., Teicht, C., Schwarz, D., Schipper, J., Bartholomé, K., Schäfer-Welsen, O., & Pappert, S. (2024). Improved Switchable Heat Pipe Based on Adsorption: Against-Gravity Operation and Enhanced Dynamics. Energies, 17(9), 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092088





