Diagnostics of Interior PM Machine Rotor Faults Based on EMF Harmonics
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Short circuit faults, which occur when there is an electrical connection between two points in the winding that should not be connected (inter-turn—within the same winding, phase-to-phase—between two different windings, or winding-to-ground);
- Open circuit faults—the open circuit in the stator winding is essentially a break in the winding, and this could be due to a broken conductor or a poor soldering joint;
- Winding deformation—this is less of a fault and more a result of operational stress.
2. Mathematical Model for Diagnostic Purposes
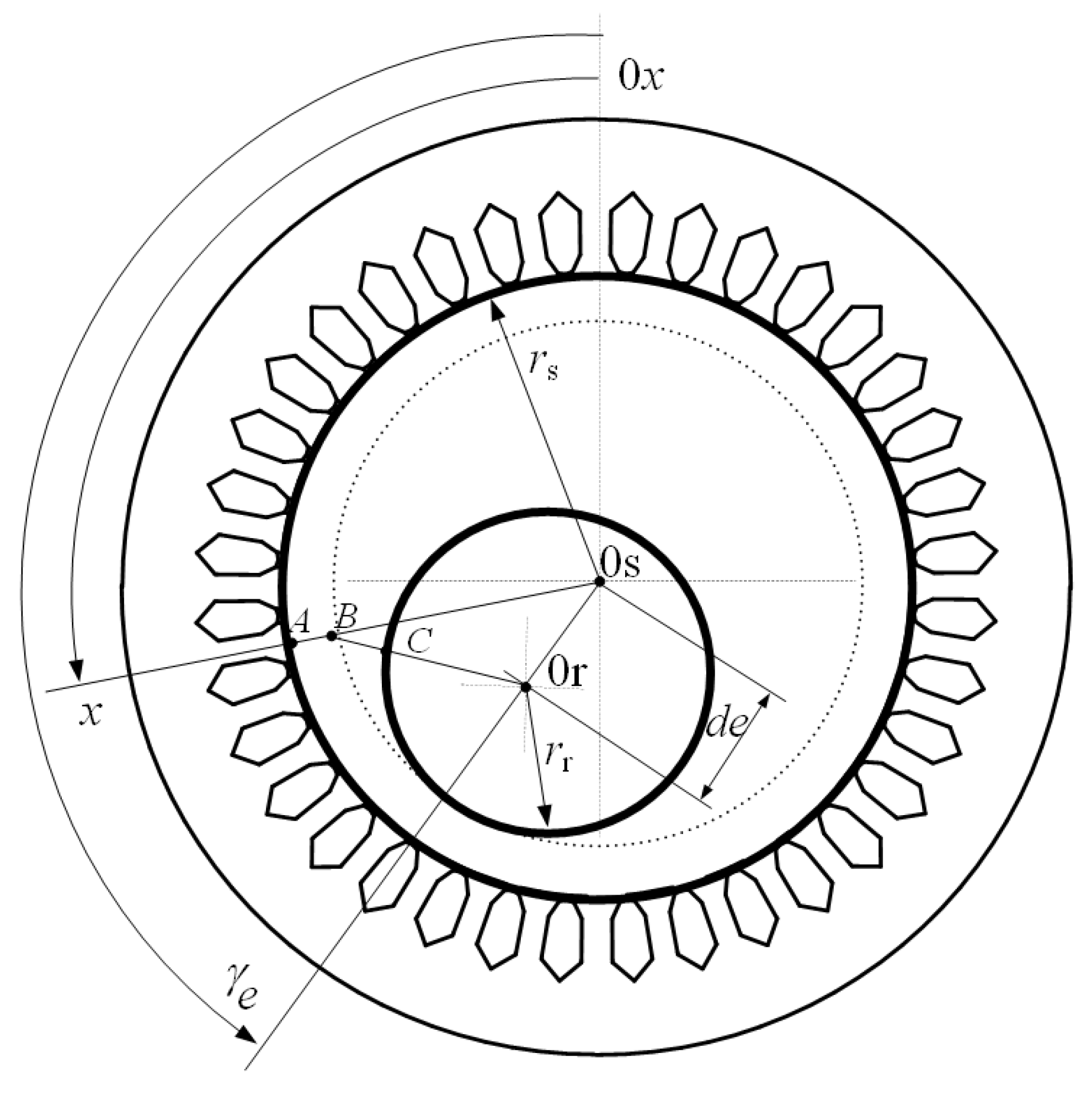
2.1. General Assumptions
2.2. EMF Induced by PM in Cases of Rotor Faults
2.2.1. Flux Density Distribution in the PM Machine Air Gap
2.2.2. PM Flux Linkages and EMF of Windings
- —winding with the integer number of slots per pole and phase;
- —winding with a fractional number of slots per pole and phase.
3. Discussion
- Symmetry of magnetic circuit ; ;
- Static eccentricity of rotor ; ;
- Dynamic eccentricity of rotor ; ;
- Mixed eccentricity of rotor; ; .
4. Case Study
4.1. Description of the Tested Machine
4.2. Results of Numerical Tests
4.2.1. Permeance Function
4.2.2. Air-Gap Flux Density
4.2.3. Electromotive Force
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- For static eccentricity:
- For dynamic eccentricity:
- For mixed eccentricity:
Appendix B
References
- Hsu, J.S.; Ayers, C.W.; Coomer, C.L. Report on Toyota/Prius Motor Design and Manufacturing Assessment; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2004; ORNL/TM-2004/137.
- Hsu, J.S.; Ayers, C.W.; Coomer, C.L.; Wiles, R.H.; Campbell, S.L.; Lowe, K.T.; Michelhaugh, R.T. Report on Toyota/Prius Motor Torque Capability, Torque Property, No-Load Back EMF and Mechanical Losses; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2004; ORNL/TM-2004/185.
- Ayers, C.W.; Hsu, J.S.; Marlino, L.D.; Miller, C.W.; Ott, G.W.; Oland, C.B. Evaluation of 2004 Toyota Prius Hybrid Electric Drive System Interim Report; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2004; ORNL/TM-2004/247.
- Loganayaki, A.; Kumar, R.B. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Electric Vehicle Applications. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 15–16 March 2019; pp. 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.K.; Jain, A. Advancements in electric motor technology: A review of emerging trends and future prospects. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2023, 8, 5–8. Available online: https://scientiamreearch.org/index.php/ijcsis/article/view/10 (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Ruoqiong, L.; Zonglin, W.; Li, X. Review on fault diagnosis and active fault tolerant control of permanent magnet synchronous motor drive system. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2021, 24, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, F.R.; Vavilov, V.Y.; Ayguzina, V.V. Method for diagnostic of permanent-magnet electrical machines. Chem. Technol. Control. Manag. 2018, 2018, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Yang, C.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, D.M.; Fernandez, D.; Reigosa, D.; Briz, F. Online Detection and Classification of Rotor and Load Defects in PMSMs Based on Hall Sensor Measurements. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 3803–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Hang, J.; Zhang, J. Overview of fault diagnosis theory and method for permanent magnet machine. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2015, 1, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Review of fault diagnosis of PMSM drive system in electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 7426–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Gonzalez, F.; Griffo, A.; Sen, B.; Wang, J. Real-Time Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Under Stator Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6960–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, W.; Liang, H.; Wang, C. Faults and Diagnosis Methods of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, C. Fault Detection of Stator Inter-Turn Short-Circuit in PMSM on Stator Current and Vibration Signal. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Kilic, A.; Thulfaut, C.; Reuss, H.-C. An Intelligent Diagnostic Method for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) in the Electric Drive of Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE ‘19 ECCE Europe), Genova, Italy, 3–5 September 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, P.; Wolkiewicz, M. Comparison of Selected Methods for the Stator Winding Condition Monitoring of a PMSM Using the Stator Phase Currents. Energies 2021, 14, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, P.; Wolkiewicz, M. Demagnetization Fault Diagnosis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on Stator Current Signal Processing and Machine Learning Algorithms. Sensors 2023, 23, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.S.; Djerdir, A.; Amirat, Y.A.; Khaburi, D.A. Demagnetization fault diagnosis in permanent magnet synchronous motors: A review of the state-of-the-art. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 391, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urresty, J.-C.; Riba, J.-R.; Romeral, L. A Back-EMF Based Method to Detect Magnet Failures in PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameh, K.; Cité, N.; Hoblos, G.; Barakat, G. Vibration-based Fault Diagnosis Approach for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba Ruiz, J.-R.; Rosero, J.A.; Garcia Espinosa, A.; Romeral, L. Detection of Demagnetization Faults in Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors Under Nonstationary Conditions. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2961–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasid, S.A.; Gyftakis, K.N.; Mueller, M. Comparative Investigation of Three Diagnostic Methods Applied to Direct-Drive Permanent Magnet Machines Suffering from Demagnetization. Energies 2023, 16, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowron, M.; Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Kowalski, C.T. Detection of Permanent Magnet Damage of PMSM Drive Based on Direct Analysis of the Stator Phase Currents Using Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 13665–13675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, M.; Eker, M. Demagnetization Fault Diagnosis in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. Przegląd Elektrotech. 2013, 89, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yang, S.; Chen, X. Diagnosis of rotor demagnetization and eccentricity faults for IPMSM based on deep CNN and image recognition. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 5469–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyftakis, K.N.; Skarmoutsos, G.A.; Barajas-Solano, I.; Burchell, J.; Mueller, M. Critical Aspects of Demagnetization Faults in Multi-Stage Direct Drive Permanent Magnet Generators for Renewables. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 6655–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyftakis, K.N.; Rasid, S.A.; Skarmoutsos, G.A.; Mueller, M. The Demagnetization Harmonics Generation Mechanism in Permanent Magnet Machines with Concentrated Windings. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2934–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.M.; Javan Roshtkhari, M.; Faiz, J.; Khatami, S.V. Advanced Eccentricity Fault Recognition in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Stator Current Signature Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.M.; Faiz, J.; Araabi, B.N. Pattern identification for eccentricity fault diagnosis in permanent magnet synchronous motors using stator current monitoring. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2010, 4, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Gao, Y.; Degano, M.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Gerada, C.; Zhou, S.; Mu, Y. Eccentric position diagnosis of static eccentricity fault of external rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor as an in-wheel motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, W.; Harley, R.G.; Habetler, T.G. Detecting Rotor Faults in Low Power Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goktas, T.; Zafarani, M.; Akin, B. Separation of broken magnet and static eccentricity failures in PMSM. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Coeur d’Alene, ID, USA, 10–13 May 2015; pp. 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Exiri, S.A.H. Short-circuit fault diagnosis in permanent magnet synchronous motors—An overview. In Proceedings of the 2015 Intl Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines & Power Electronics (ACEMP), 2015 Intl Conference on Optimization of Electrical & Electronic Equipment (OPTIM) & 2015 Intl Symposium on Advanced Electromechanical Motion Systems (ELECTROMOTION), Side, Turkey, 2–4 September 2015; pp. 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan-Pragłowska, N.; Wegiel, T. Permanent Magnet Selections for AFPM Disc Generators. Energies 2022, 15, 7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D.; Ekkehard, B.; Ackermann, B. Instantaneous magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent magnet motors, part I: Open-circuit field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Instantaneous magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent magnet motors, part III: Effect of Stator Slotting. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, B.; Hamata, V. Harmonic Field Effect in Induction Machines; Elsevier Scientific: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Sobczyk, T.J.; Drozdowski, P. Inductances of electrical machine winding with a nonuniform air-gap. Arch. Elektrotech. 1993, 76, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczyk, T.J.; Weinreb, K.; Węgiel, T.; Sułowicz, M. Theoretical study of effects due to rotor eccentricities in induction motors. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (IEEE SDEMPED’99), Gijon, Spain, 1–9 September 1999; pp. 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Sobczyk, T.; Weinreb, K.; Węgiel, T.; Sułowicz, M. Influence of stator and rotor slotting on quantitative prediction of induction motor rotor eccentricity. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (IEEE SDEMPED’2001), Grado, Italy, 1–3 September 2001; pp. 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Węgiel, T.; Weinreb, K.; Sułowicz, M. Main inductances of induction motor for diagnostically specialized mathematical models. Arch. Electr. Eng. 2010, 59, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
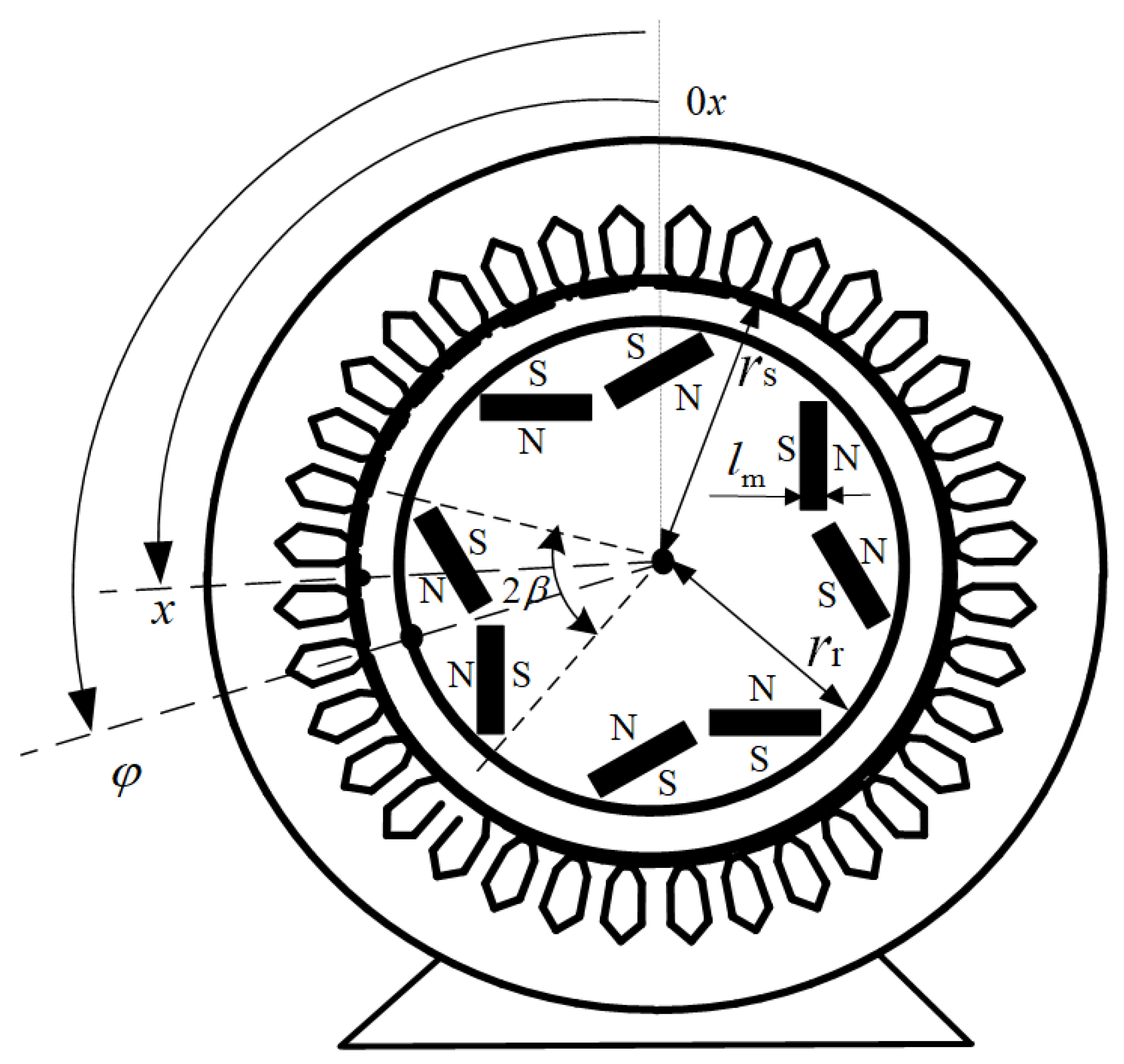
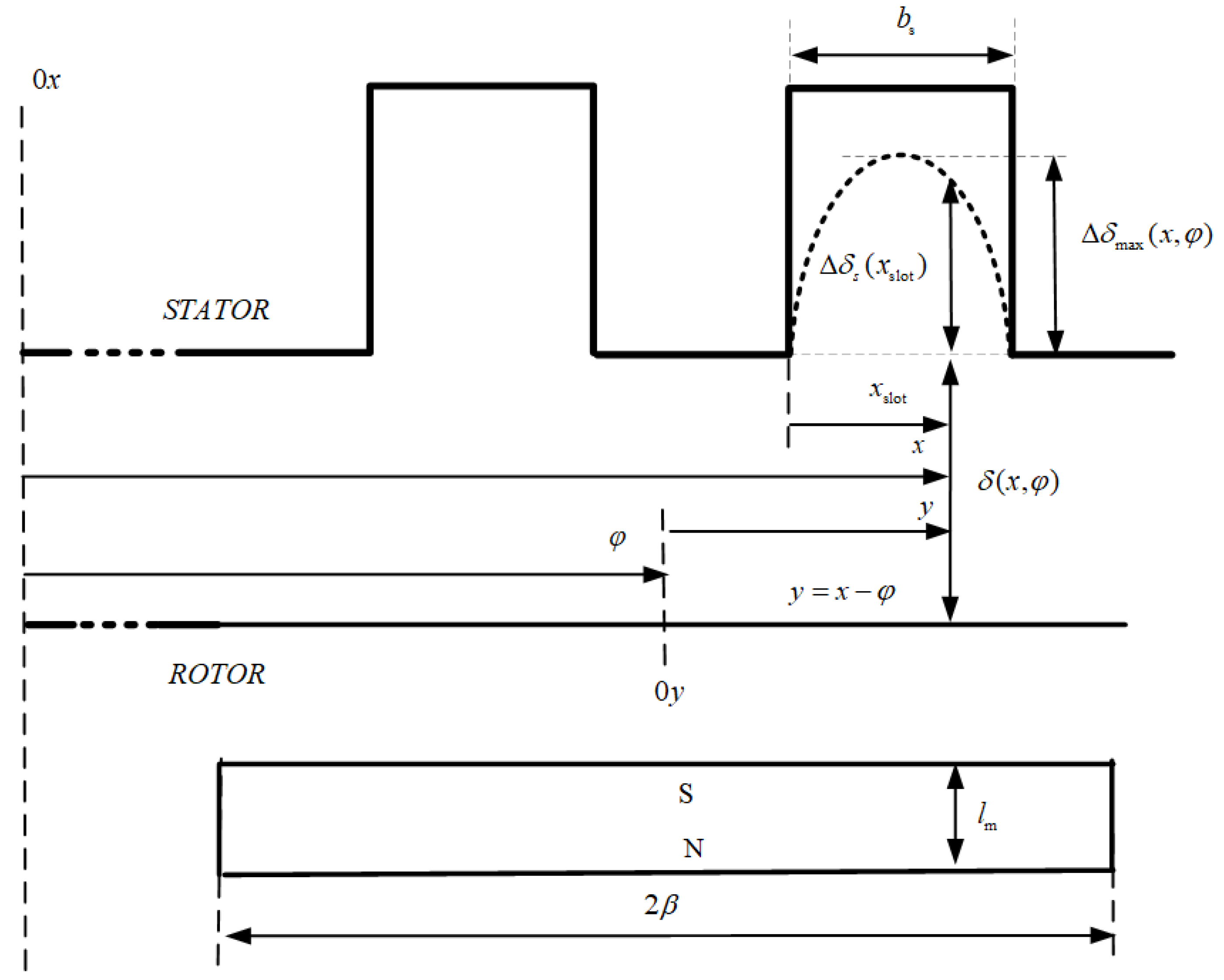
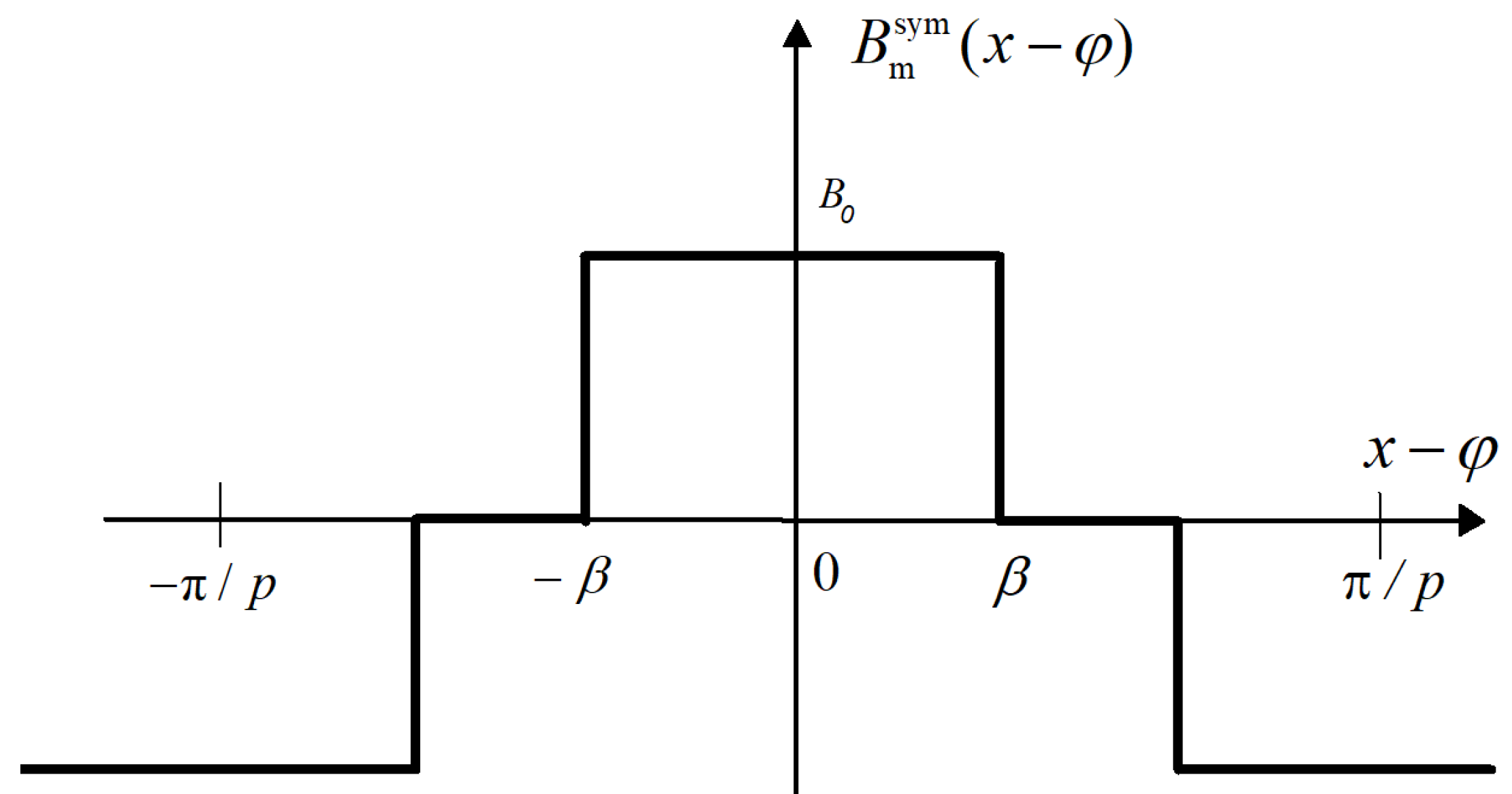
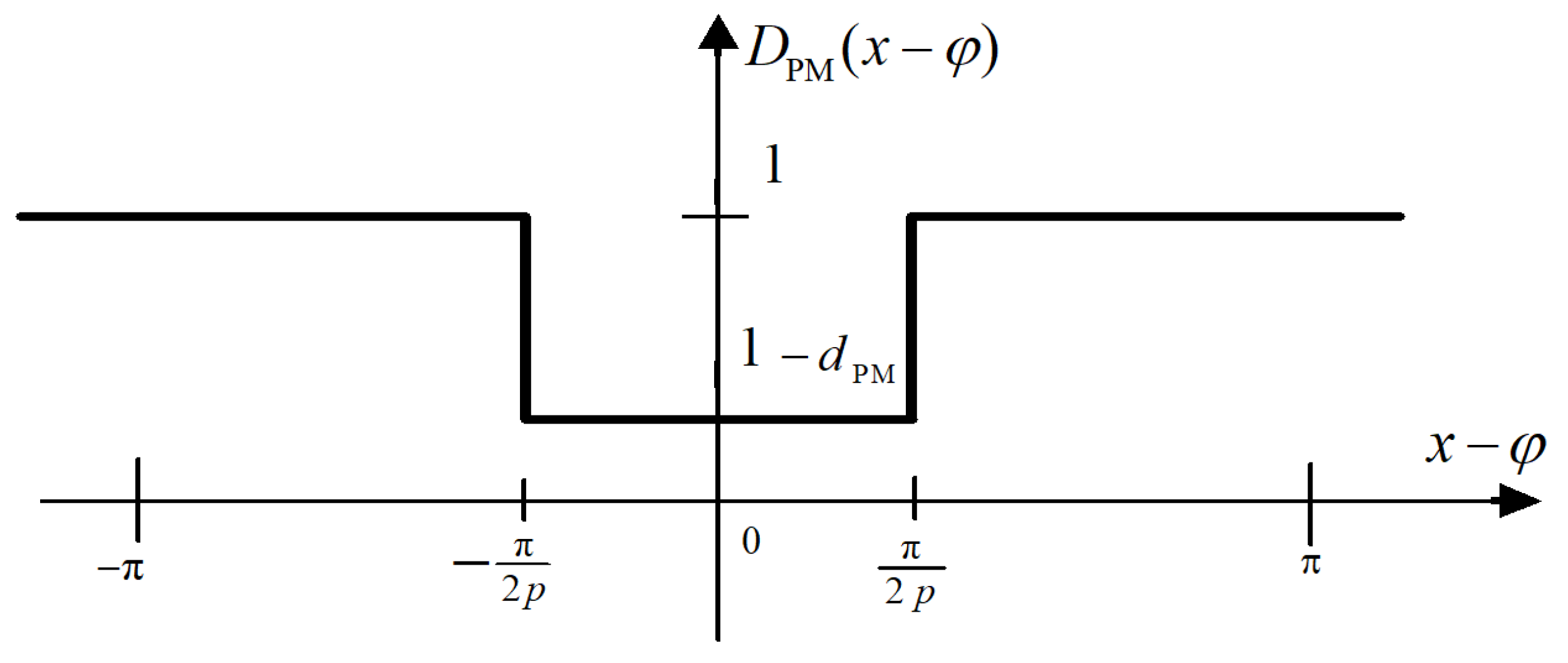
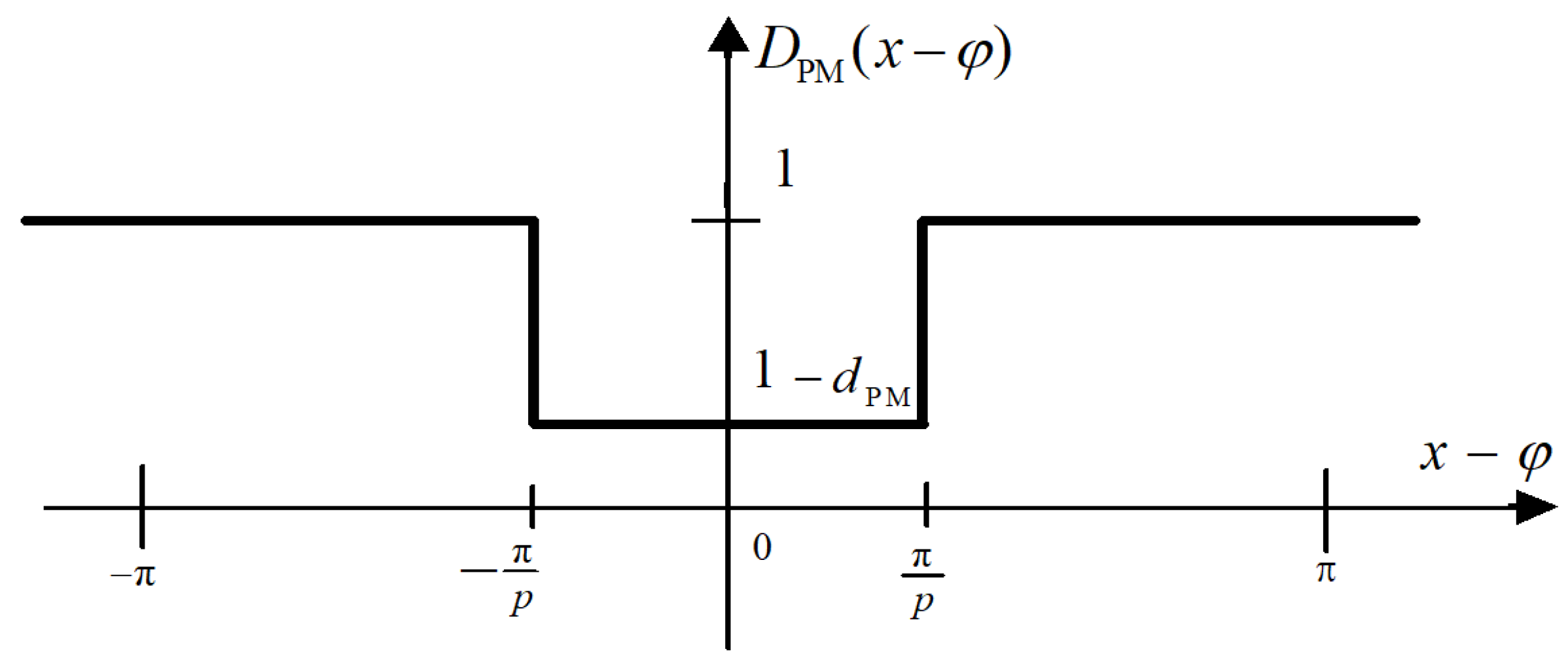
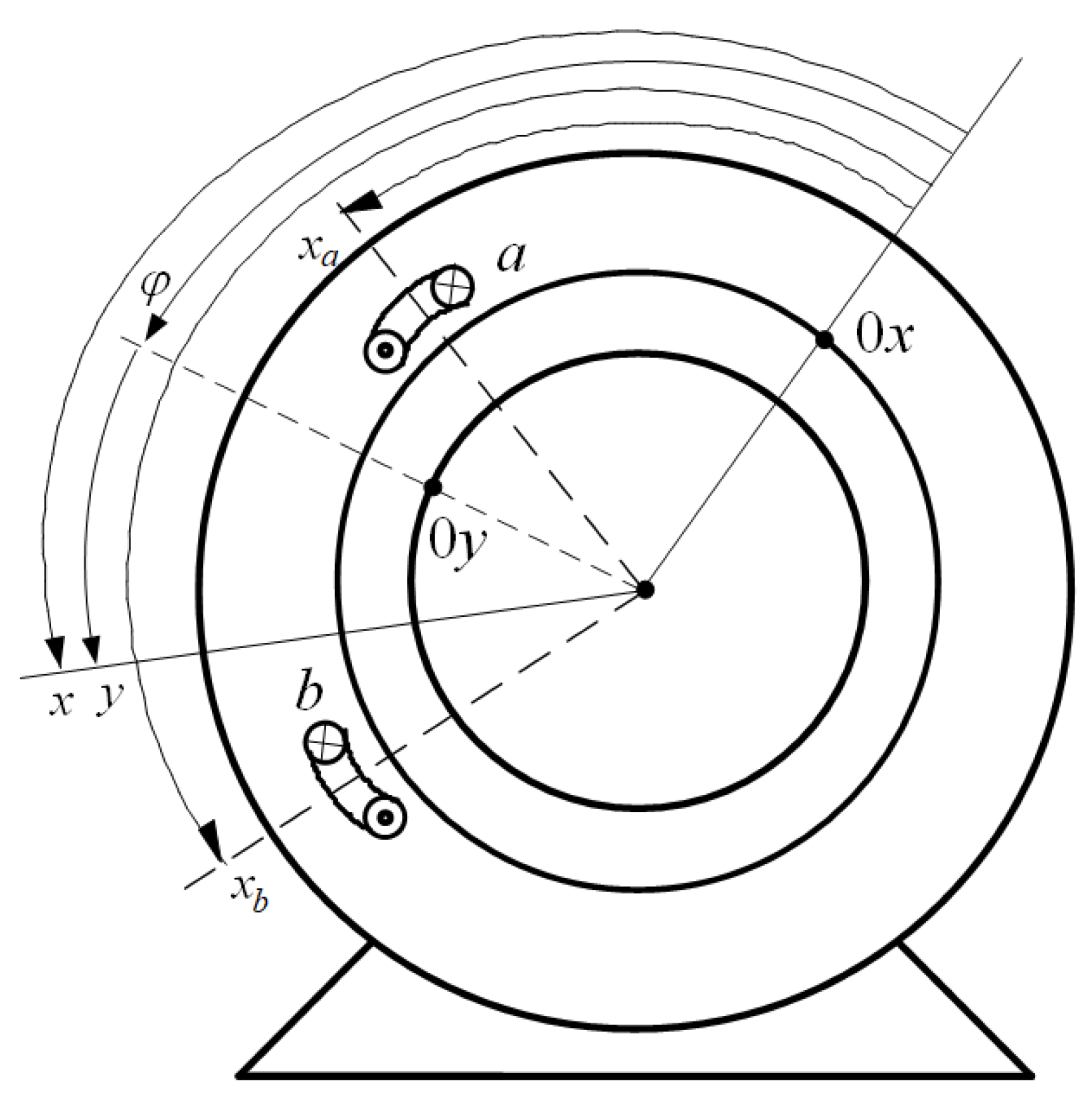
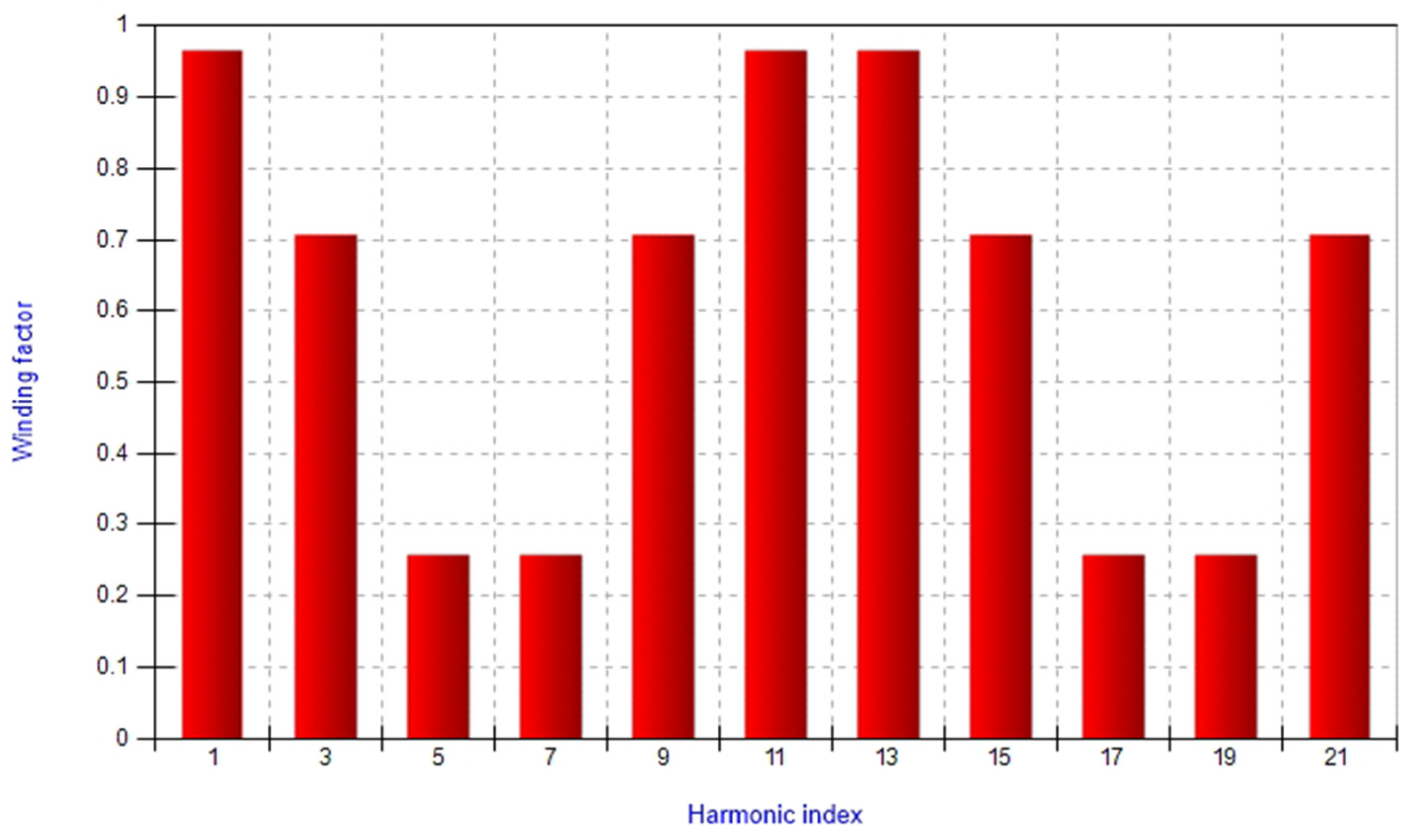
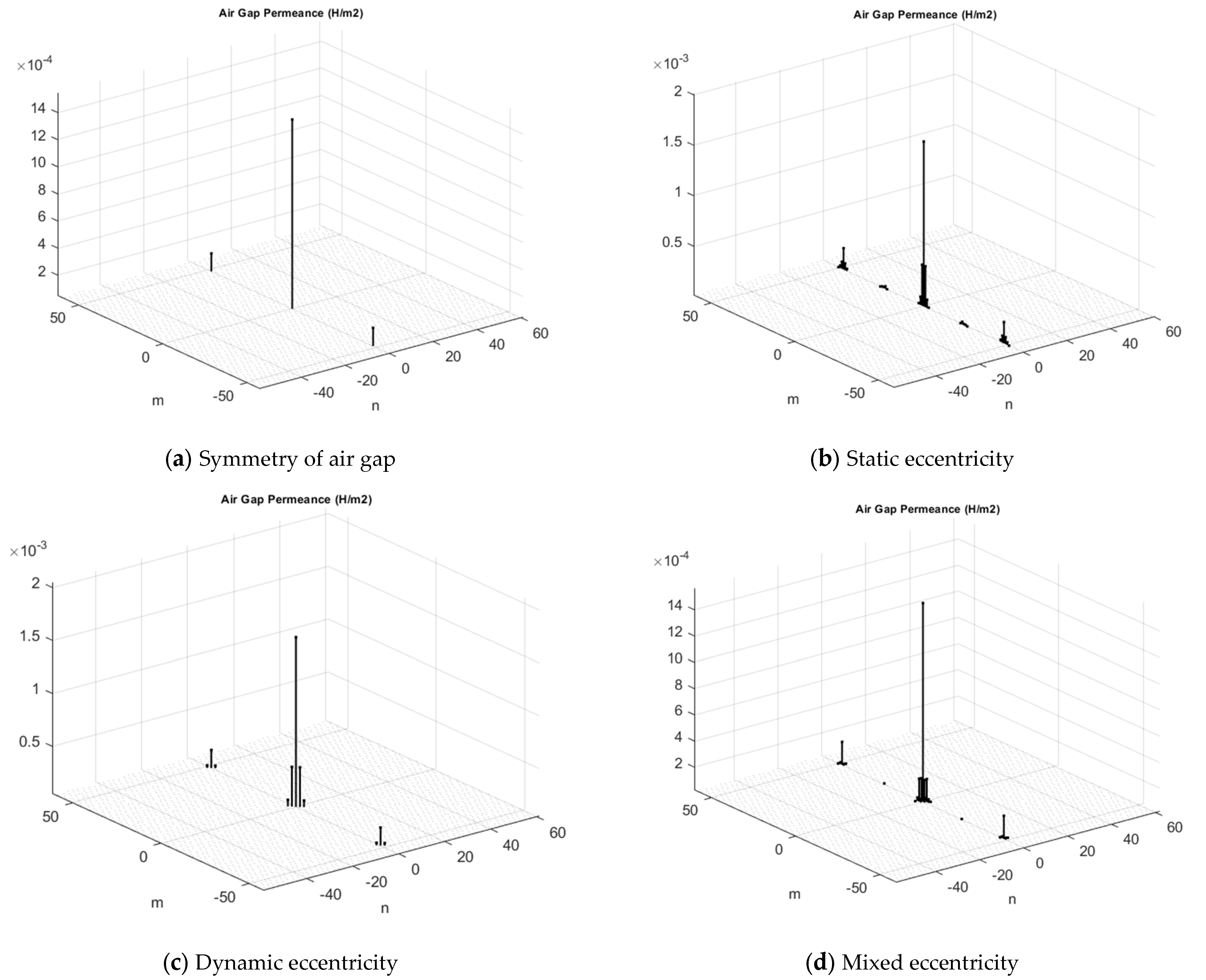
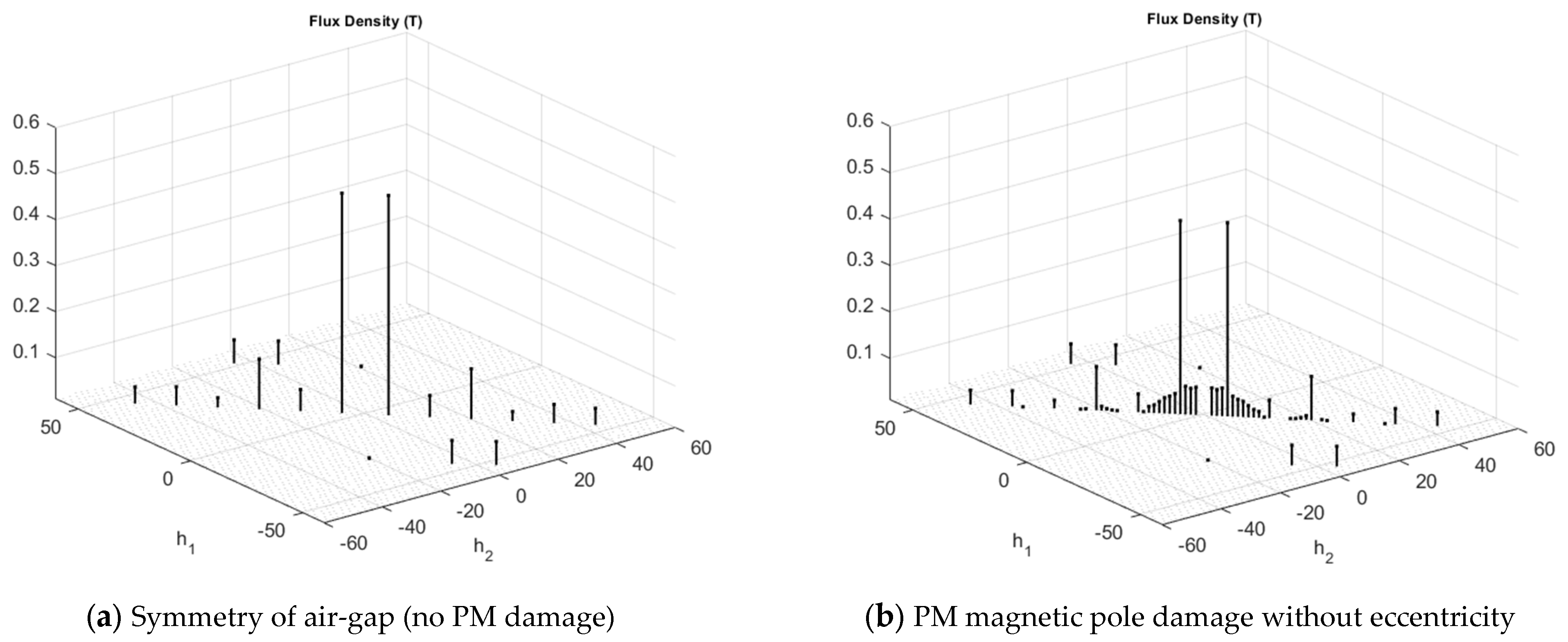
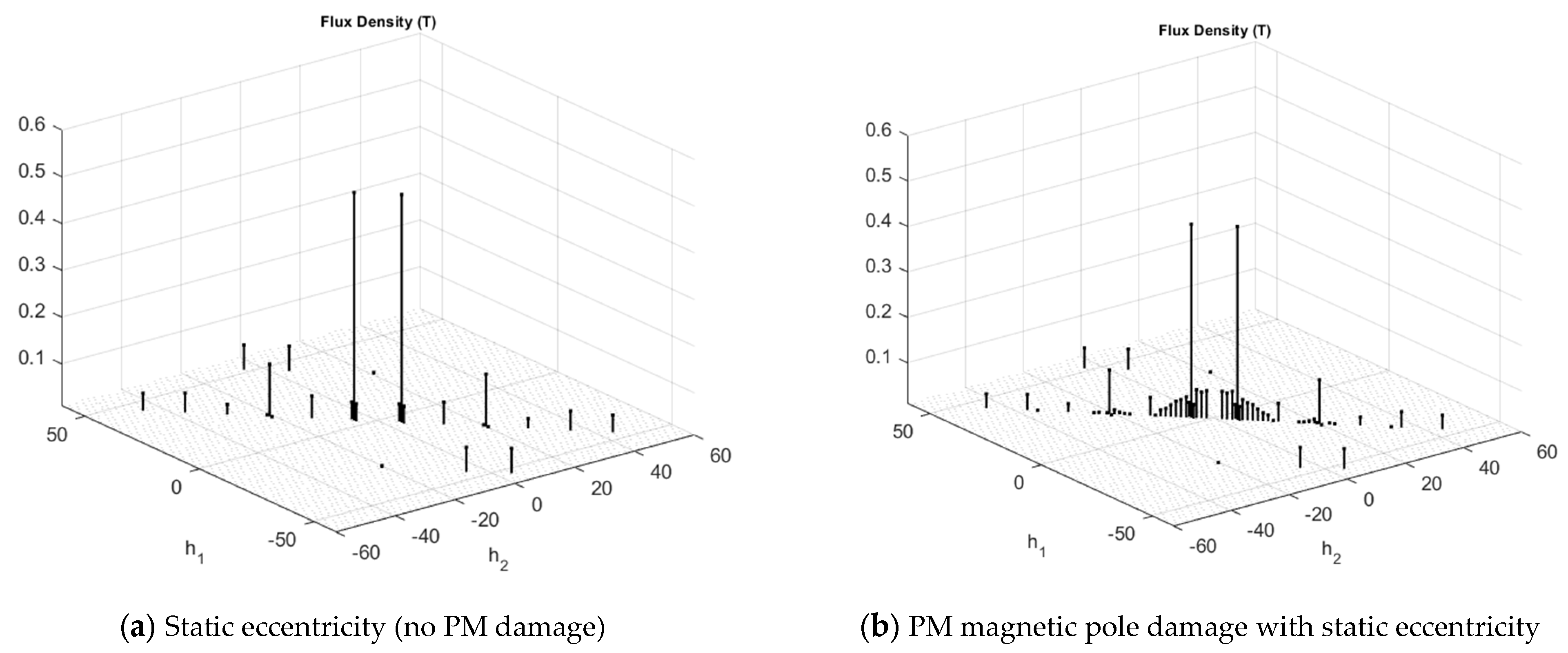
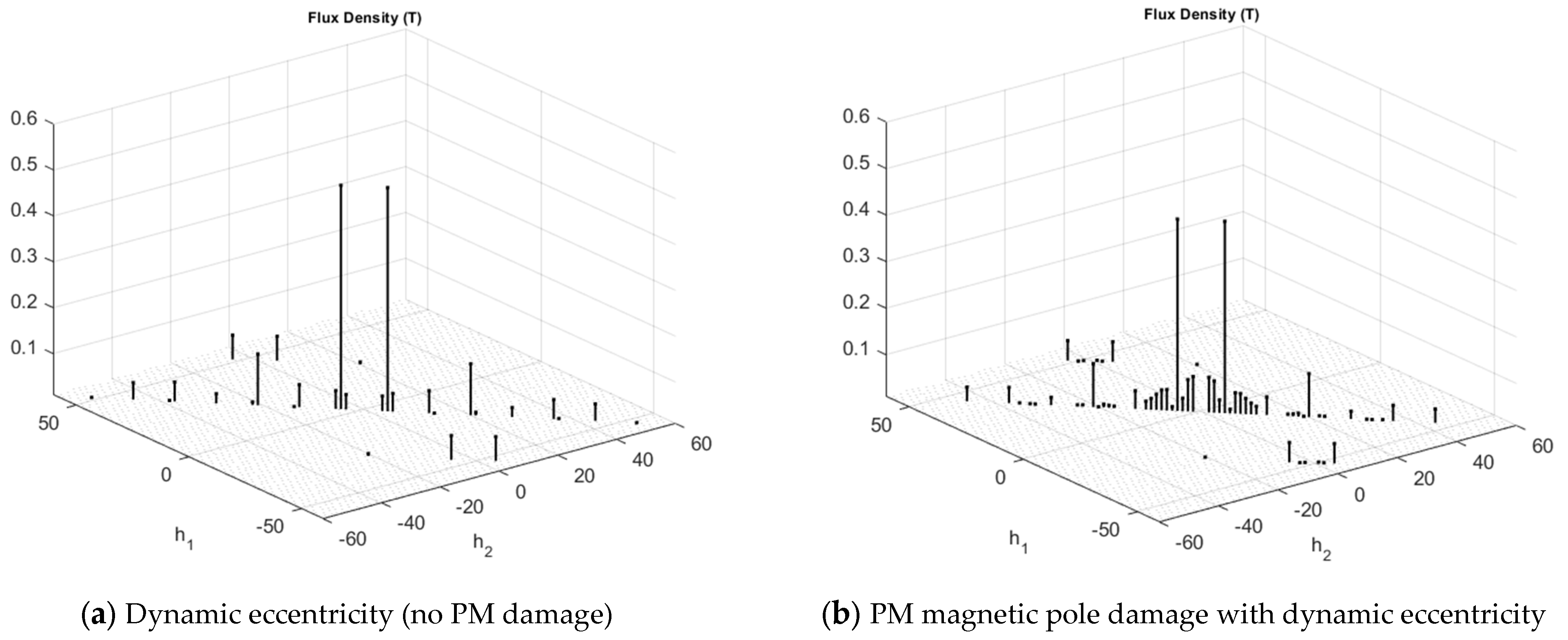
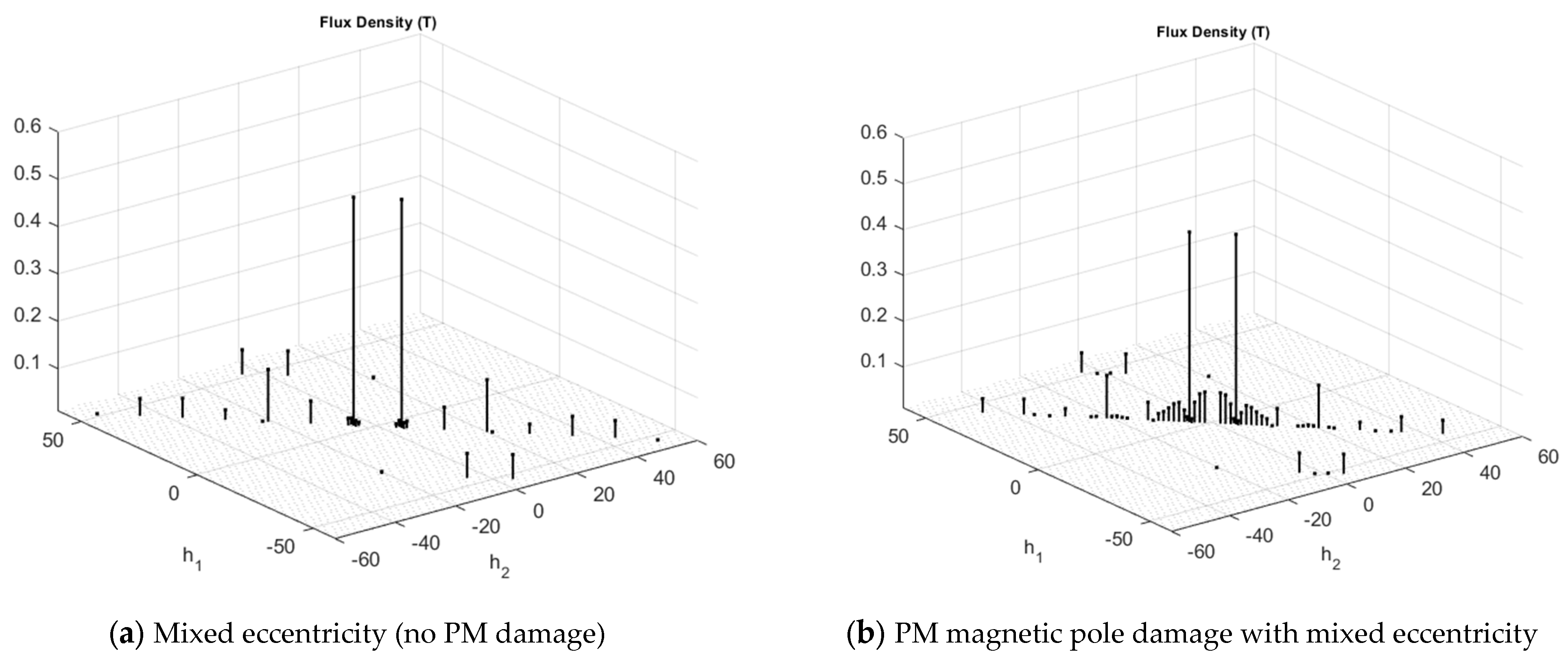
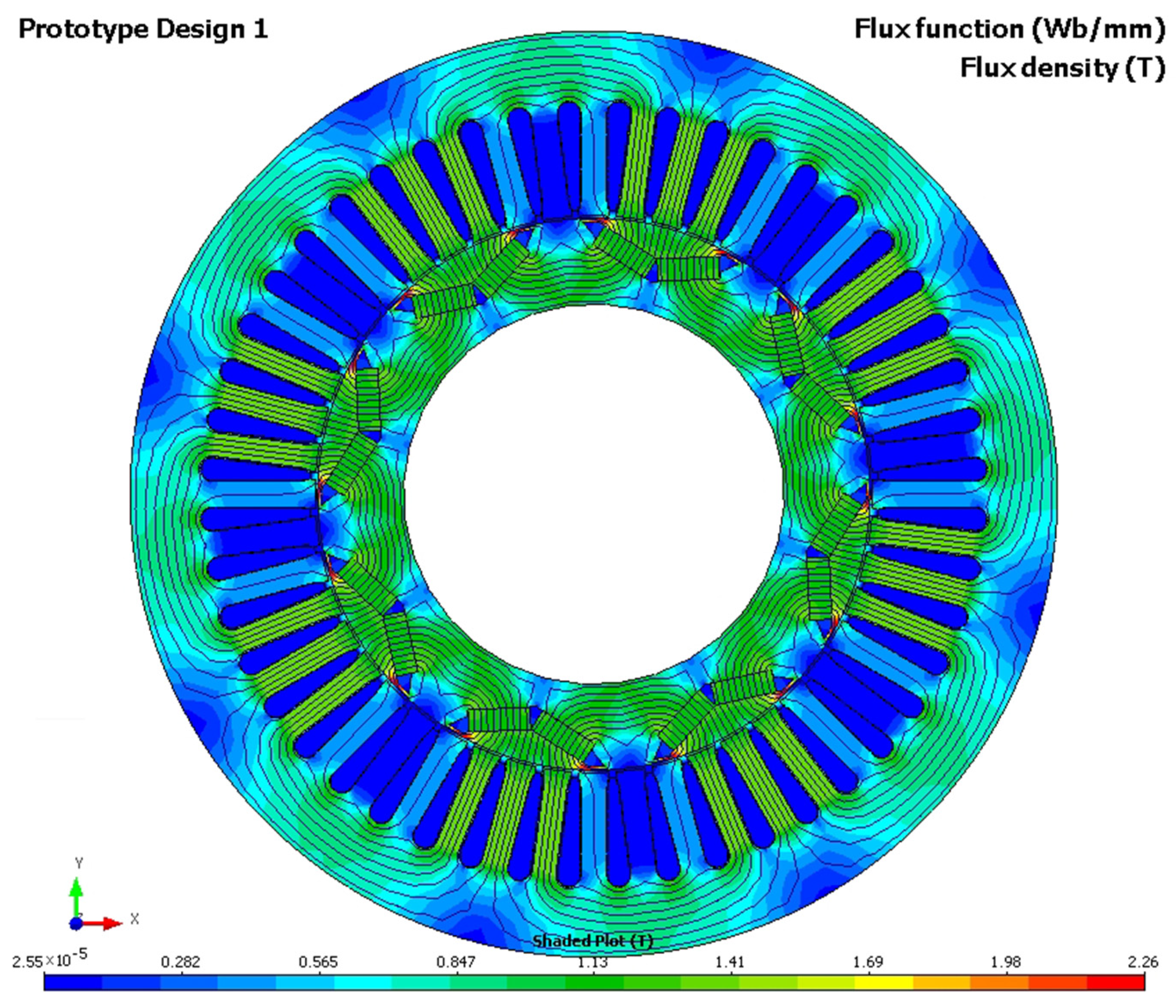
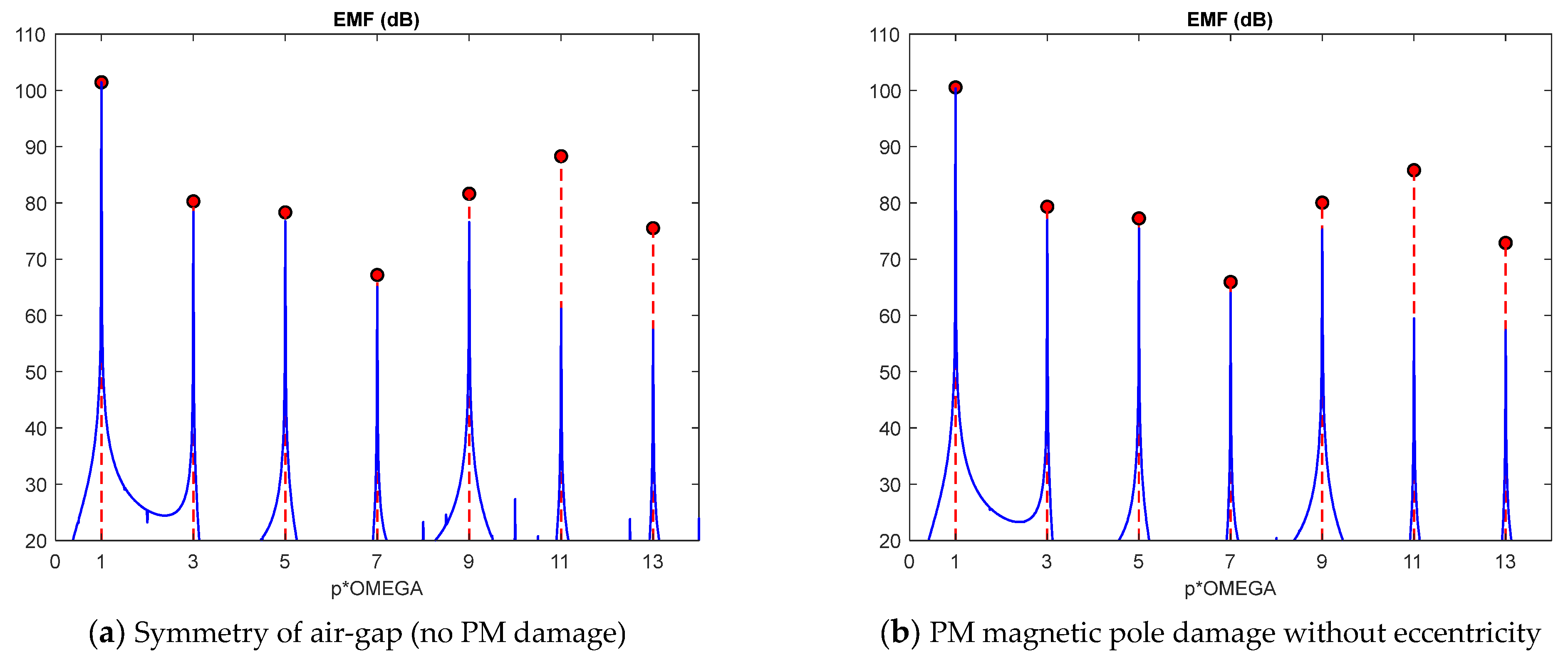
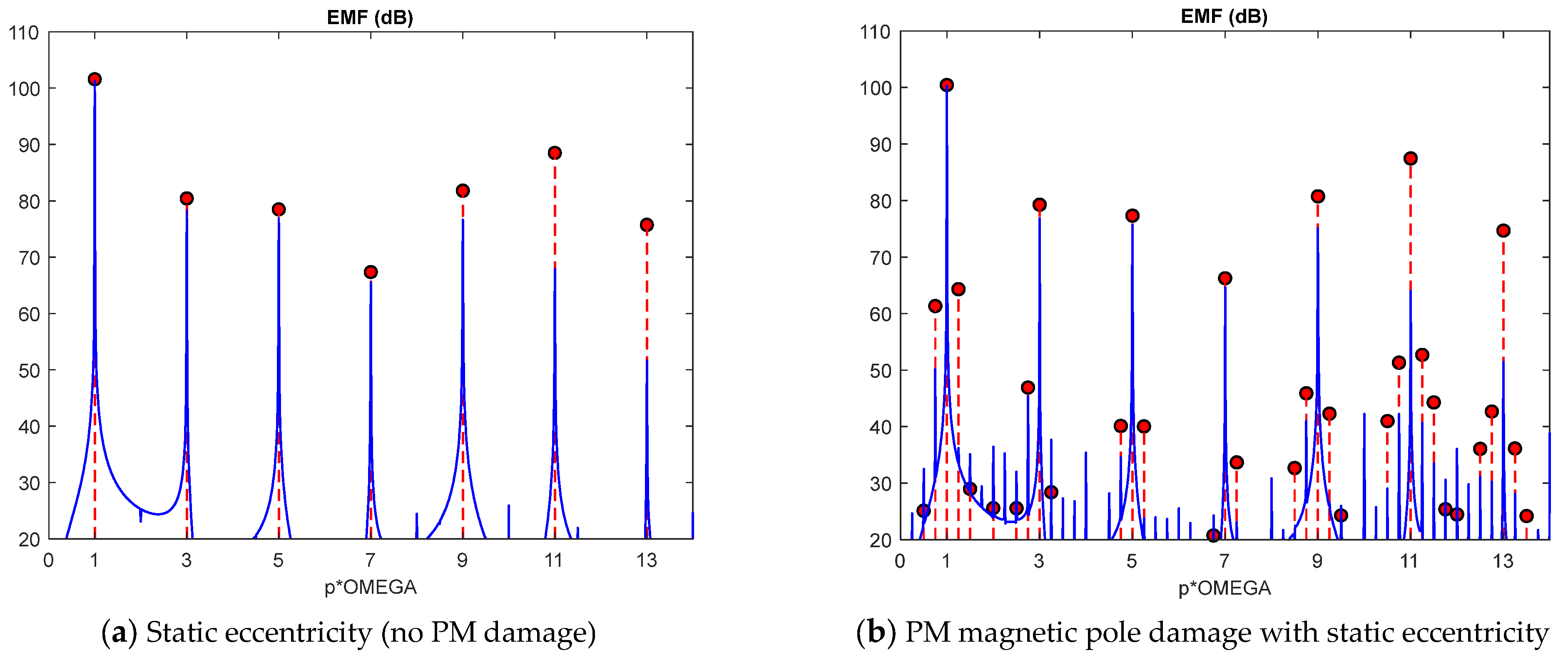
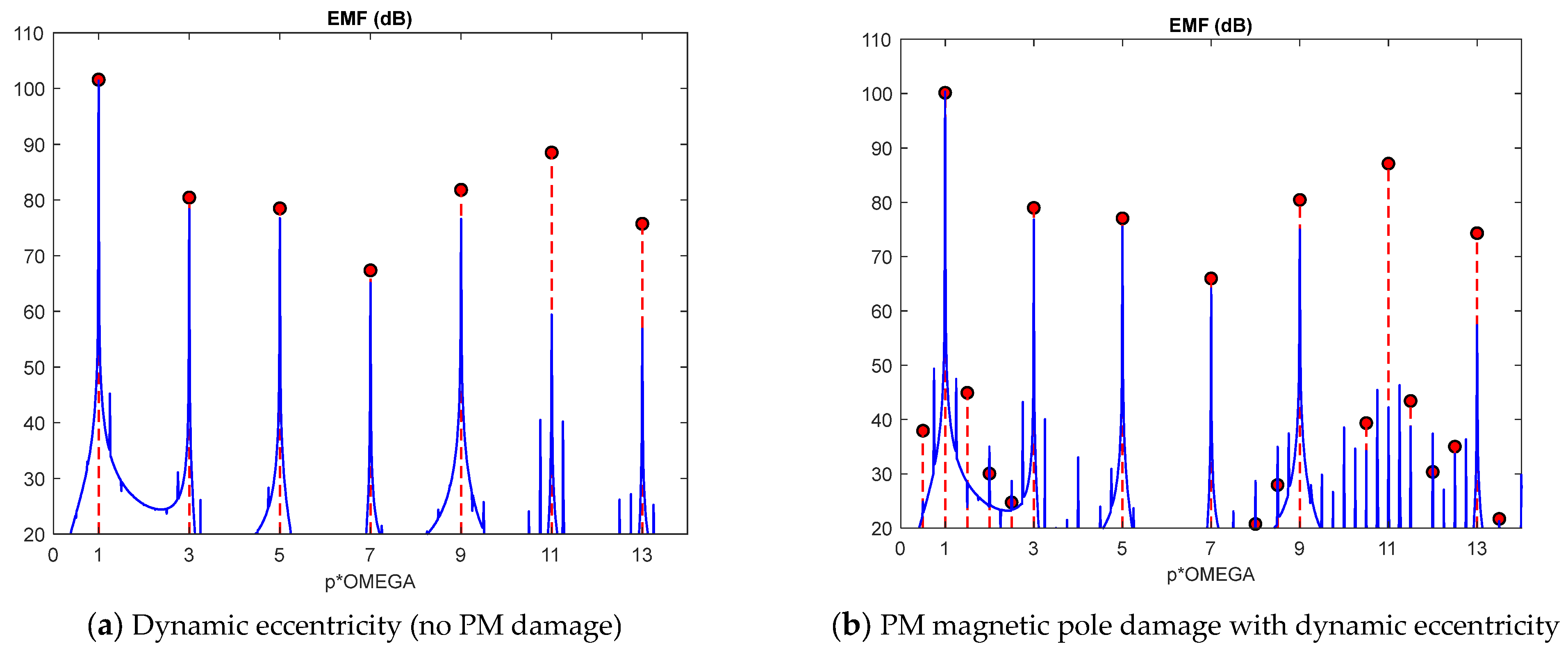

| Type of Rotor Fault | Stator Winding with the Integer Number Slots per Pole and Phase | Stator Winding with the Fractional Number Slots per Pole and Phase |
|---|---|---|
| PM without demagnetization (no PM damage) | ||
| Symmetry no PM demagnetization | ||
| Static eccentricity no PM demagnetization | ||
| Dynamic eccentricity no PM demagnetization | ||
| Mixed eccentricity no PM demagnetization | ||
| PM with demagnetization (PM damage) | ||
| Symmetry with PM demagnetization | ||
| Static eccentricity with PM demagnetization | ||
| Dynamic eccentricity with PM demagnetization | ||
| Mixed eccentricity with PM demagnetization | ||
| Parameters and Dimensions of the PM Machine |
|---|
| Machine rated data: peak power rating 50 kW (1200 rpm); peak torque rating 400 Nm; voltage constant 1.33 Vrms/Hz; number of pole pairs p = 4 |
| Axial length of stator and rotor core = 83.56 mm |
| Stator outer radius 134.62 mm; rotor outer radius = 80.20 mm |
| Stator internal radius = 80.95 mm; length of air gap = 0.75 mm |
| Single magnet dimensions: 18.00 × 6.48 mm ( = 6.48 mm); PM opening angle 145°; = 13.6° |
| PM residual flux density = 1.2 T; PM coercive force = 904 kA/m |
| Winding type—single layer; number of stator slots = 48; winding span—6 slots |
| Number of slots per pole and phase—2 |
| Total number of phase winding turns = 72; equivalent slot opening = 2 mm |
| Type of Rotor Fault | PM without Demagnetization (No PM Damage) EMF (RMS) | PM with Demagnetization (PM Damage) EMF (RMS) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Formulas | FEM Calculations | |ΔEMF (%)| | Analytical Formulas | FEM Calculations | |ΔEMF (%)| | |
| Symmetry of air gap | 81.9 V | 83.6 V | 2.4% | 71.6 V | 74.0 V | 3.2% |
| Static eccentricity | 83.5 V | 82.7 V | 1.0% | 73.0 V | 73.2 V | 0.3% |
| Dynamic eccentricity | 83.5 V | 83.7 V | 0.2% | 71.8 V | 74.2 V | 3.2% |
| Mixed eccentricity | 82.7 V | 83.6 V | 1.1% | 72.3 V | 74.0 V | 3.3% |
| Type of Rotor Fault | EMF Pulsations PM without Demagnetization (no PM Damage) | EMF Pulsations PM with Demagnetization (PM Damage) |
|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | ||
| Static eccentricity | ||
| Dynamic eccentricity | ||
| Mixed eccentricity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radwan-Pragłowska, N.; Wegiel, T. Diagnostics of Interior PM Machine Rotor Faults Based on EMF Harmonics. Energies 2024, 17, 2198. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092198
Radwan-Pragłowska N, Wegiel T. Diagnostics of Interior PM Machine Rotor Faults Based on EMF Harmonics. Energies. 2024; 17(9):2198. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092198
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadwan-Pragłowska, Natalia, and Tomasz Wegiel. 2024. "Diagnostics of Interior PM Machine Rotor Faults Based on EMF Harmonics" Energies 17, no. 9: 2198. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092198
APA StyleRadwan-Pragłowska, N., & Wegiel, T. (2024). Diagnostics of Interior PM Machine Rotor Faults Based on EMF Harmonics. Energies, 17(9), 2198. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092198







