Wind Power Prediction Method and Outlook in Microtopographic Microclimate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Traditional Wind Power Prediction Methods
2.1. Physical Modeling Approach
2.2. Statistical Forecasting Methods
2.2.1. Kalman Filter
2.2.2. Traditional Machine Learning
2.2.3. Time Course Prediction
2.2.4. Deep Learning
2.3. Combined Forecasting Methods
3. Wind Power Prediction Under Complex Meteorological Conditions
3.1. Numerical Simulation Analysis
3.2. Statistical Prediction Methods for Wind Turbine Blade Ice-Covered Conditions
4. Reflections on Accurate Prediction of Wind Power in Microtopographic Microclimates
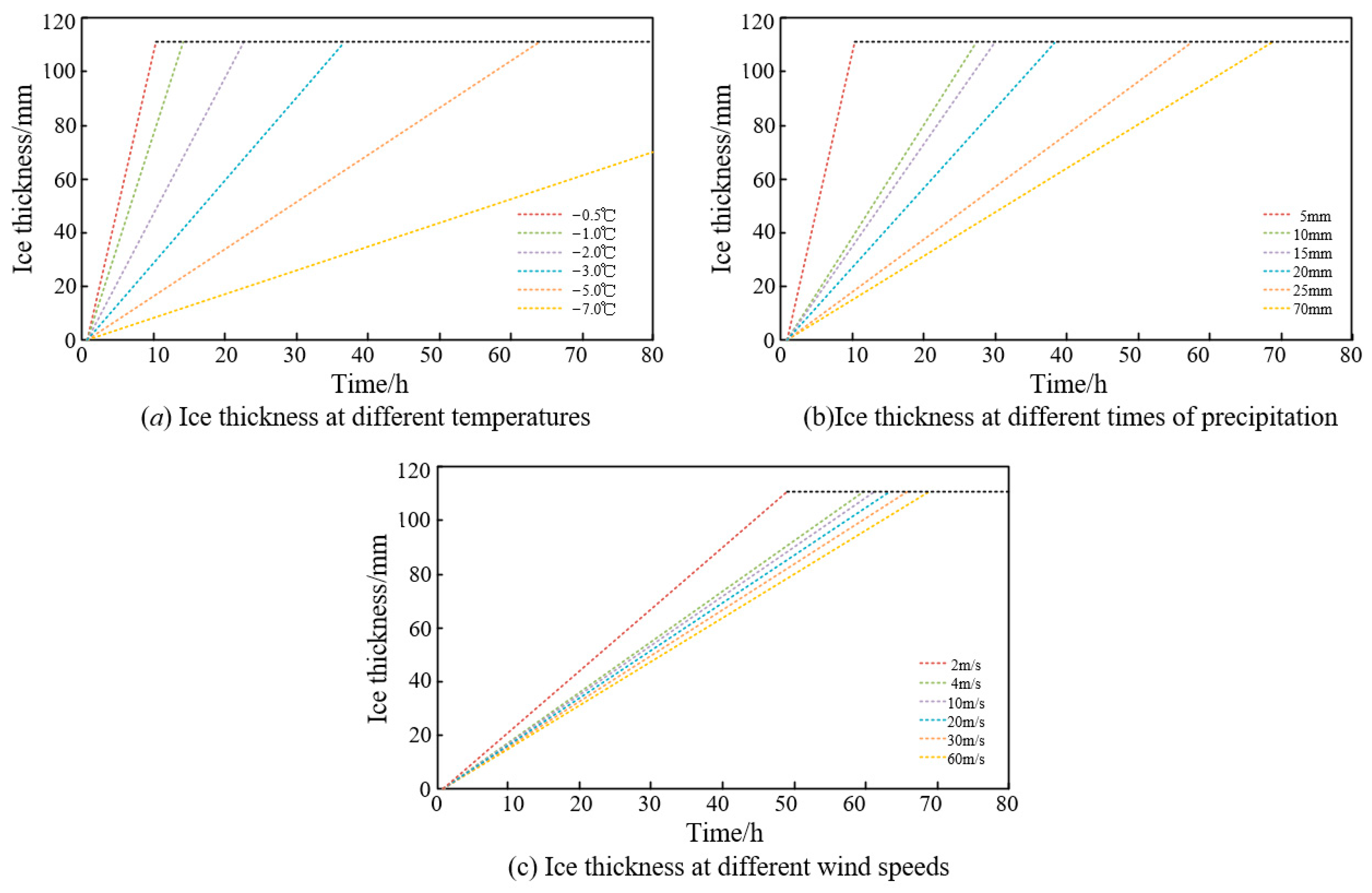
4.1. Analysis of Factors Affecting Ice Cover Thickness in Microtopographic and Microclimatic Areas
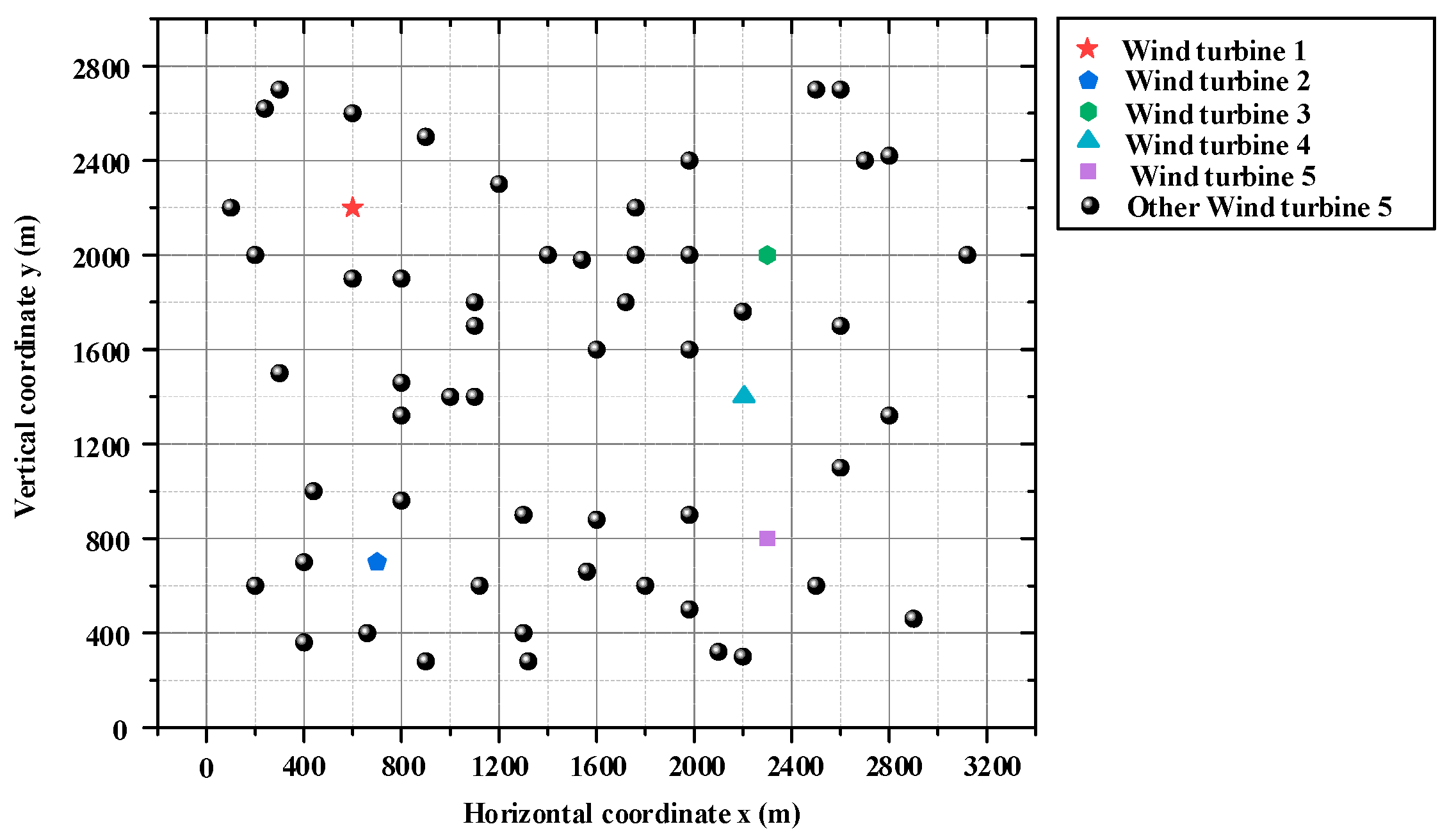
4.2. Power Prediction for Wind Farms in Microclimatic Domains of Microtopographic Areas
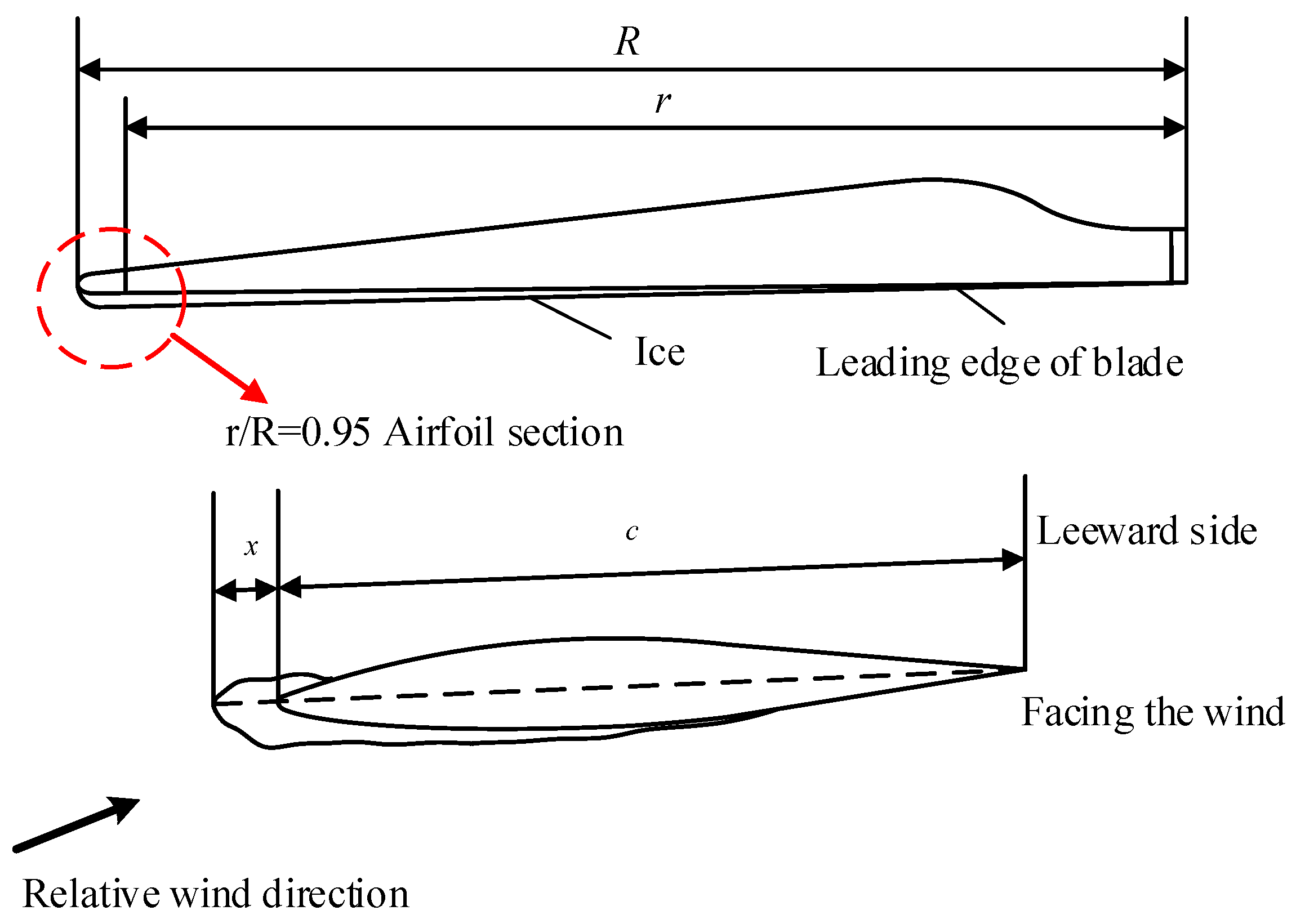
4.3. Conversion Modeling of Wind Turbine Output Power Under Ice-Covered Weather
5. Conclusions
6. Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, P.; Li, Z. Short-term strategy and long-term prospect of energy structure optimization under carbon neutrality target. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2022, 41, 5695–5708. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Tu, J.; Yang, X. Research of wind power prediction based on PSO-KELM. Electr. Meas. Instrum. 2020, 57, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, T.; He, Q.; Xu, H. Review on key technologies and applications in wind power forecasting. High Volt. Eng. 2021, 47, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Lu, Z.; Min, Y. Research & application of raising wind power prediction accuracy. Power Syst. Technol. 2017, 41, 3261–3268. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Han, L.; Wen, C. Day-ahead prediction of wind power based on NWP wind speed error correction. Power Syst. Technol. 2022, 46, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Kan, T.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H. DWT-DTCNA ultra-short-term wind power prediction considering wind power timing characteristics. Power Syst. Technol. 2023, 47, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Song, W. Short-term power prediction method of canyon wind power based on grid clustering. Power Supply Consum. 2023, 40, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Liu, H. Medium-term wind power forecasting based on multi-resolution multi-learner ensemble and adaptive model selection. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 206, 112492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, S.T.; Ageze, M.B.; Zeleke, M.A.; Miliket, T.A. Adama II wind farm long-term power generation forecasting based on machine learning models. Sci. Afr. 2023, 21, e01831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focken, U.; Lange, M.; Waldl, H.P. Previento-a wind power prediction system with an innovative upscaling algorithm. In Proceedings of the European Wind Energy Conference, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2–6 July 2001; p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Cassola, F.; Burlando, M. Wind speed and wind energy forecast through Kalman filtering of Numerical Weather Prediction model output. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yu, X.; Liu, S.; Dong, X.; Zang, H.; Xu, R. Wind power prediction based on PSO-Kalman. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Jin, Y. A multi-channel feature combination model for ultra-short-term wind power prediction under carbon neutral background. Power Gener. Technol. 2021, 42, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Lang, J.; Yanyan, Z. Study on Multi-Scenario wind power prediction based on LS-SVM algorithm. Smart Power 2017, 45, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- De Giorgi, M.G.; Ficarella, A.; Tarantino, M. Error analysis of short term wind power prediction models. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 1298–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Gao, K.; Song, Z.; Gao, Z. A wind farm power prediction method based on the combination of improved CFD and wavelet hybrid neural network. Grid Technol. 2017, 41, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Latimier, R.L.G.; Le Bouedec, E.; Monbet, V. Markov switching autoregressive modeling of wind power forecast errors. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 189, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kong, C.; Chen, B. A new prediction method based on VMD-PRBF-ARMA-E model considering wind speed characteristic. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 203, 112254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Tan, Q.; Lei, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, X. Wind power prediction using hybrid autoregressive fractionally integrated moving average and least square support vector machine. Energy 2017, 129, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Han, H.; Lü, X. Economic analysis of system spinning reserve based on improved CNN-LSTM short term wind power prediction. High Volt. Eng. 2022, 48, 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Olaofe, Z.; Folly, K. Wind power estimation using recurrent neural network technique. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society Conference and Exposition in Africa: Intelligent Grid Integration of Renewable Energy Resources (PowerAfrica), Johannesburg, South Africa, 9–13 July 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q. Ridgelet neural network model for short-term wind power forecasting based on the combination of chaos DNA genetic and particle swarm optimization algorithm. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2013, 41, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, B. Short-Term wind power forecasting based on LSTM. Power Syst. Technol. 2017, 41, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Tascikaraoglu, A.; Uzunoglu, M. A review of combined approaches for prediction of short-term wind speed and power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, E.; Laakso, T.; Ronsten, G.; Tallhaug, L.; Horbaty, R.; Baring-Gould, I.; Lacroix, A. State-of-the-art of wind energy in cold climates. IEA Annex XIX 2003, 24, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Fakorede, O.; Feger, Z.; Ibrahim, H.; Ilinca, A.; Perron, J.; Masson, C. Ice protection systems for wind turbines in cold climate: Characteristics, comparisons and analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariniotakis, G.N.; Stavrakakis, G.S.; Nogaret, E.F. Wind power forecasting using advanced neural networks models. IEEE Trans Energy Convers. 1996, 11, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormsbee, A.I.; Bragg, M.B. Trajectory Scaling Laws for a Particle Injected into the Wake of an Aircraft. Ph.D. Thesis, Aviation Research Laboratory, Institute of Aviation, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, F.; Hansen, M.H.; Thomsen, K.; Larsen, T.J.; Bertagnolio, F.; Johansen, J.; Madsen, H.A.; Bak, C.; Hansen, A.M. Present status of aeroelasticity of wind turbines. Wind Energy 2010, 6, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, M.B.; Broeren, A.P.; Blumenthal, L.A. Iced-airfoil aerodynamics. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2005, 41, 323–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochart, C.; Fortin, G.; Perron, J.; Ilinca, A. Wind turbine performance under icing conditions. Wind Energy Int. J. Prog. Appl. Wind Power Convers. Technol. 2008, 11, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, S.; Wang, Y.; Jafari, S.; Chokani, N.; Abhari, R.S. The impact of ice formation on wind turbine performance and aerodynamics. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2011, 133, 011007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamraoui, F.; Fortin, G.; Benoit, R.; Perron, J.; Masson, C. Atmospheric icing impact on wind turbine production. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2014, 100, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yirtici, O.; Cengiz, K.; Ozgen, S.; Tuncer, I.H. Aerodynamic validation studies on the performance analysis of iced wind turbine blades. Comput. Fluids 2019, 192, 104271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, G.M.; Pope, K.; Naterer, G.F. Extended scaling approach for droplet flow and glaze ice accretion on a rotating wind turbine blade. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2023, 233, 105296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, T.; Lu, X. Influence of icing pattern on aerodynamic performance of wind turbine airfoils. J. Chin. Soc. Power Eng. 2011, 31, 955–959. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, L. Study on ice numerical simulation and its power loss characteristics for the blades of wind turbine. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, 30, 292–300. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Shu, L.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, G. Numerical Simulation of Wind Turbine Blades Aerodynamic Performance Based on Ice Roughness Effect. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2018, 33, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Tao, T.; Liu, Y.; Hu, H. A field study of ice accretion and its effects on the power production of utility-scale wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2021, 167, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, X. Calculation method of wind turbine output power under clean and icing conditions verified by field tests. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2023, 38, 3041–3051. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B. A Hybrid Times-Scale Assessment Method for Wind Power Density in Complex Mountainous Areas Based on Improved Xgboost. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA), Phuket, Thailand, 28–29 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.; Wen, X.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y. Research on meteorological impact factors of wind farm output power in plateau mountainous areas. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy (ICPRE), Chengdu, China, 20–23 September 2017; pp. 372–376. [Google Scholar]
- Scher, S.; Molinder, J. Machine learning-based prediction of Icing-Related wind power production loss. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129421–129429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinder, J.; Scher, S.; Nilsson, E.; Körnich, H.; Bergström, H.; Sjöblom, A. Probabilistic forecasting of wind turbine icing related production losses using quantile regression forests. Energies 2021, 14, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, C. Short-term output modeling of wind farms accounting for the effects of snow and ice. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2016, 44, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Best, A.C. The size distribution of raindrops. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1950, 76, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minár, J.; Evans, I.S. Elementary forms for land surface segmentation: The theoretical basis of terrain analysis and geomorphological mapping. Geomorphology 2008, 95, 236–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, R. Factors Controlling the Surface Energy Budget over Snow and Ice; Finnish Meteorological Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nienhuys, S. Basics of Thermal Insulation in High Altitude Areas of the Himalayas; 2012. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sjoerd-Nienhuys/publication/231182890_BASICS_OF_THERMAL_INSULATION_IN_HIGH_ALTITUDE_AREAS_OF_THE_HIMALAYAS/links/09e41506562bba1f2b000000/BASICS-OF-THERMAL-INSULATION-IN-HIGH-ALTITUDE-AREAS-OF-THE-HIMALAYAS.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Oettli, P.; Camberlin, P. Influence of topography on monthly rainfall distribution over East Africa. Clim. Res. 2005, 28, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Li, H.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, G.; McClure, G.; Yang, H. Study of ice accretion feature and power characteristics of wind turbines at natural icing environment. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 147, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Li, H.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, G.; He, G.; Liu, Y. 3D numerical simulation of aerodynamic performance of iced contaminated wind turbine rotors. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 148, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Classification of Prediction Methods | Time Scale |
|---|---|
| Ultra-short-term forecasts | Within 30 min |
| Short-term projections | 30 min–6 h |
| Medium-term forecast | 6 h–24 h |
| Long-term projections | More than 24 h |
| Model Type | Applicable Scenarios | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kalman Filter |
|
|
|
| Traditional Machine Learning |
|
|
|
| Time Series Forecasting |
|
|
|
| Deep Learning |
|
|
|
| Weather Variables | Correlation Coefficient | Weather Variables | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air velocity | 0.472 | Direction of the wind | 0.025 |
| Pressure | −0.564 | Humidity | −0.433 |
| Temp | 0.491 | Rainfall | −0.448 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Tang, F.; Feng, J.; Liu, C.; Ni, M.; Chen, Y.; Mei, H.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, X. Wind Power Prediction Method and Outlook in Microtopographic Microclimate. Energies 2025, 18, 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071686
He J, Tang F, Feng J, Liu C, Ni M, Chen Y, Mei H, Hu Q, Jiang X. Wind Power Prediction Method and Outlook in Microtopographic Microclimate. Energies. 2025; 18(7):1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071686
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jia, Fangchun Tang, Junxin Feng, Chaoyang Liu, Mengyan Ni, Youguang Chen, Hongdeng Mei, Qin Hu, and Xingliang Jiang. 2025. "Wind Power Prediction Method and Outlook in Microtopographic Microclimate" Energies 18, no. 7: 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071686
APA StyleHe, J., Tang, F., Feng, J., Liu, C., Ni, M., Chen, Y., Mei, H., Hu, Q., & Jiang, X. (2025). Wind Power Prediction Method and Outlook in Microtopographic Microclimate. Energies, 18(7), 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071686






