Research on Magnetic–Thermal Coupling Calculation of Outer Rotor Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Magnetic Circuit Method and Thermal Network Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Magnetic Circuit Analysis
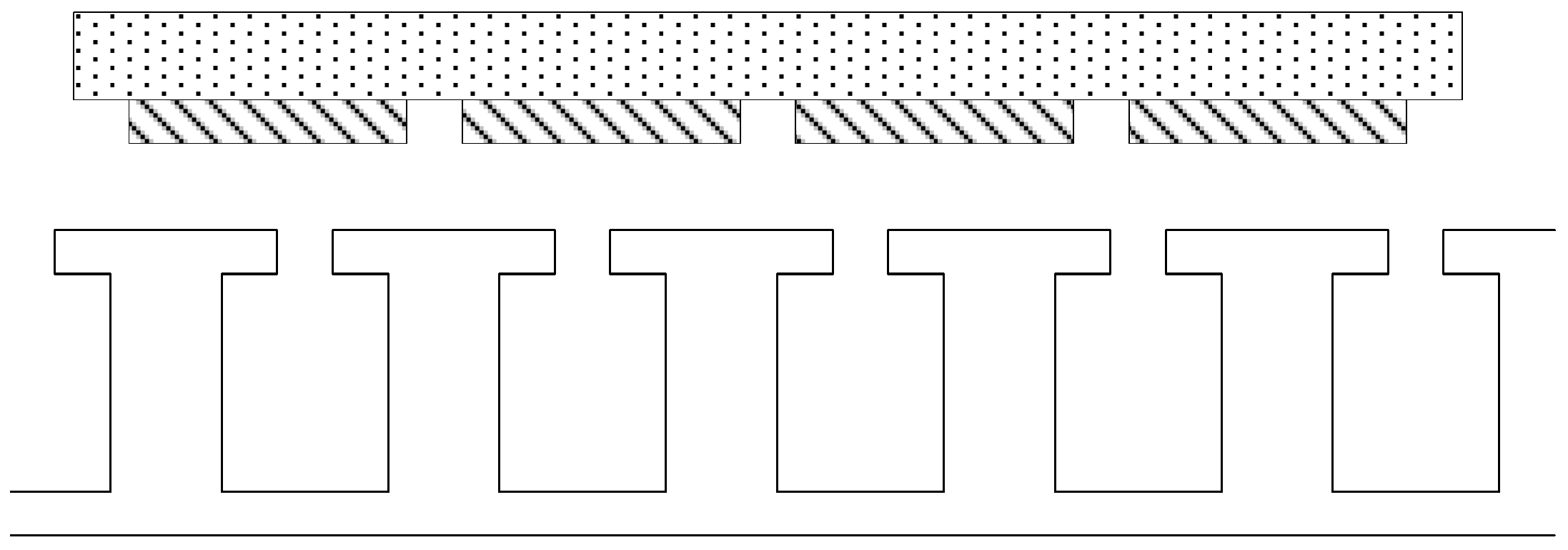
2.1. Motor Model
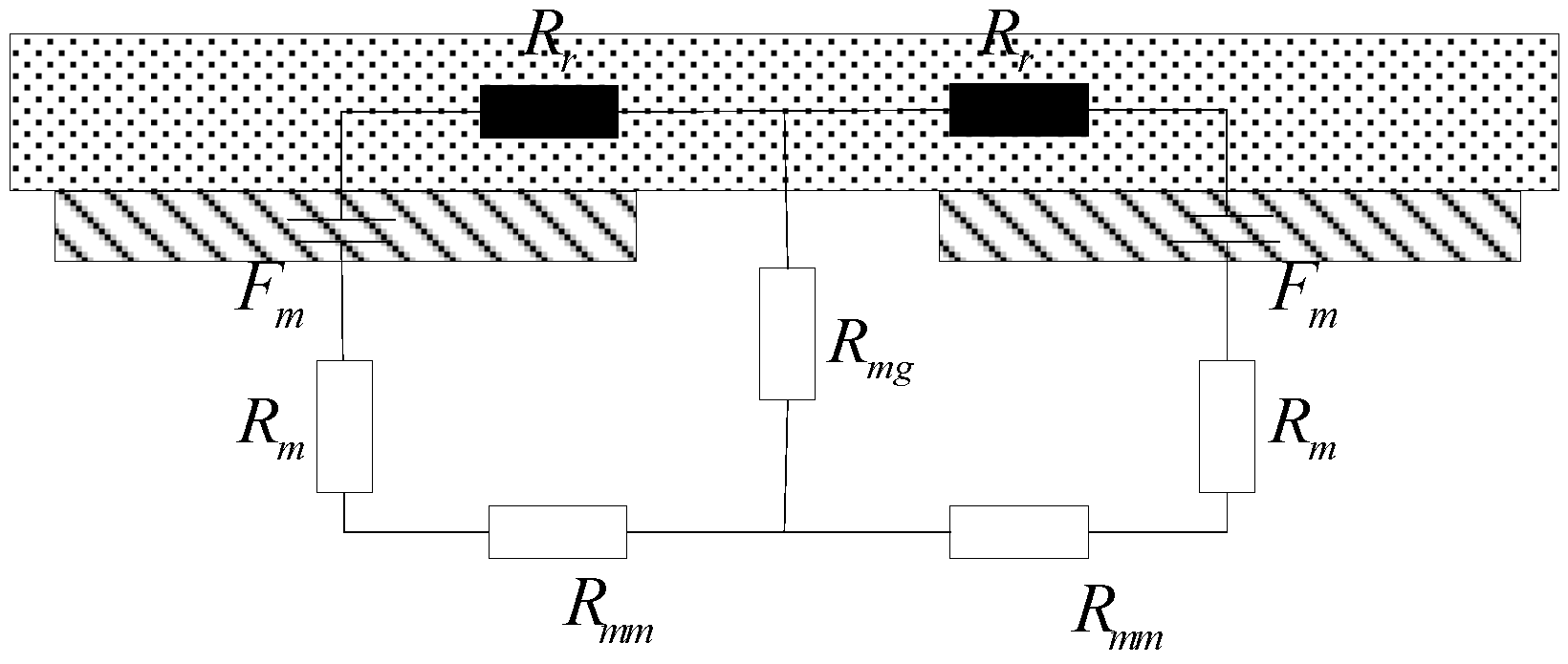
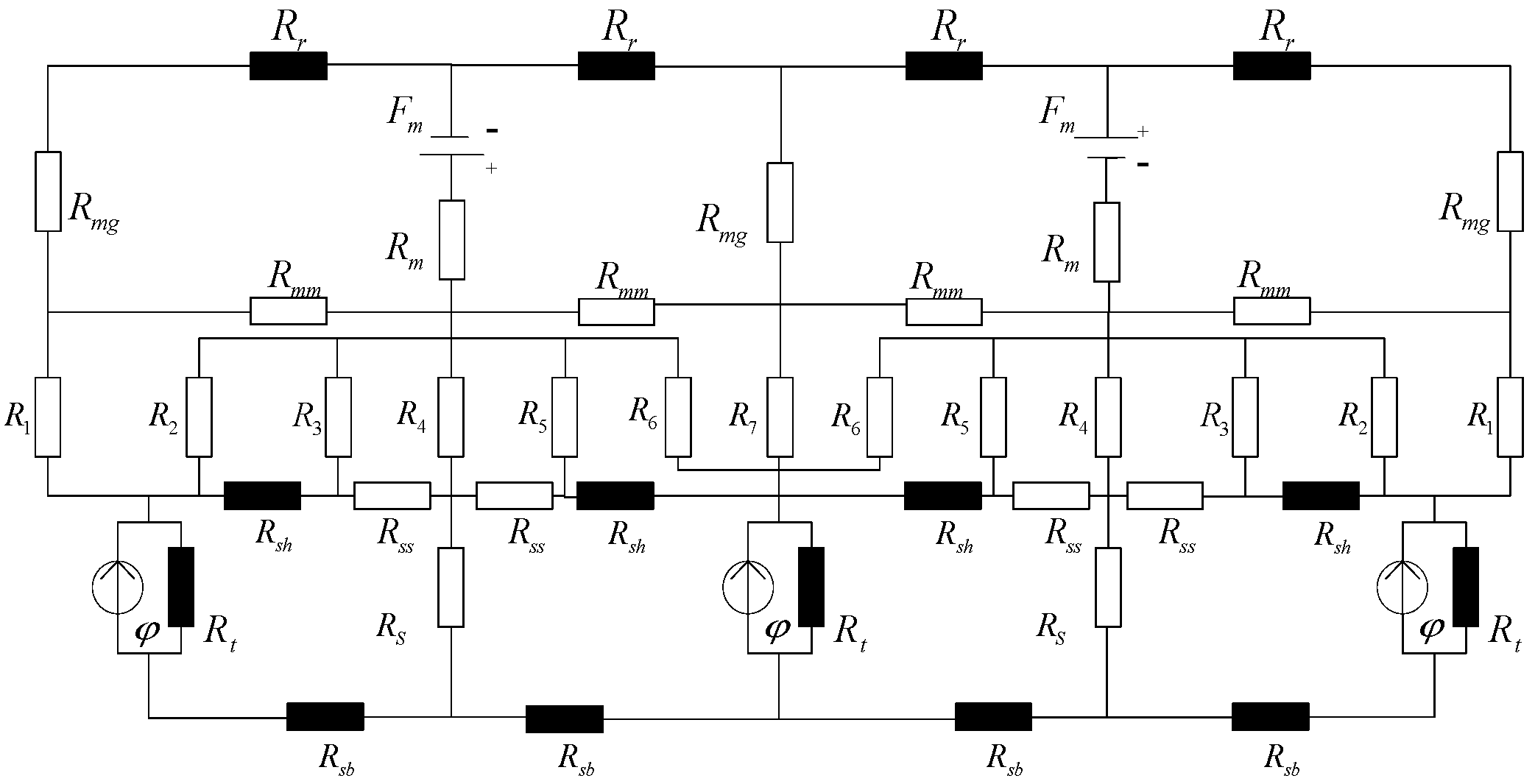
2.2. Magnetic Circuit Modelling
3. Loss Analysis
4. Thermal Network Analysis
4.1. Introduction to the Thermal Network Approach
- (1)
- Set the axis at the centre position of the motor rotor shaft with symmetrical temperature field distribution on both sides;
- (2)
- Neglect the thermal radiation process of the motor;
- (3)
- Neglect the skin effect;
- (4)
- The mutual conductance between two nodes is equal and independent of temperature.
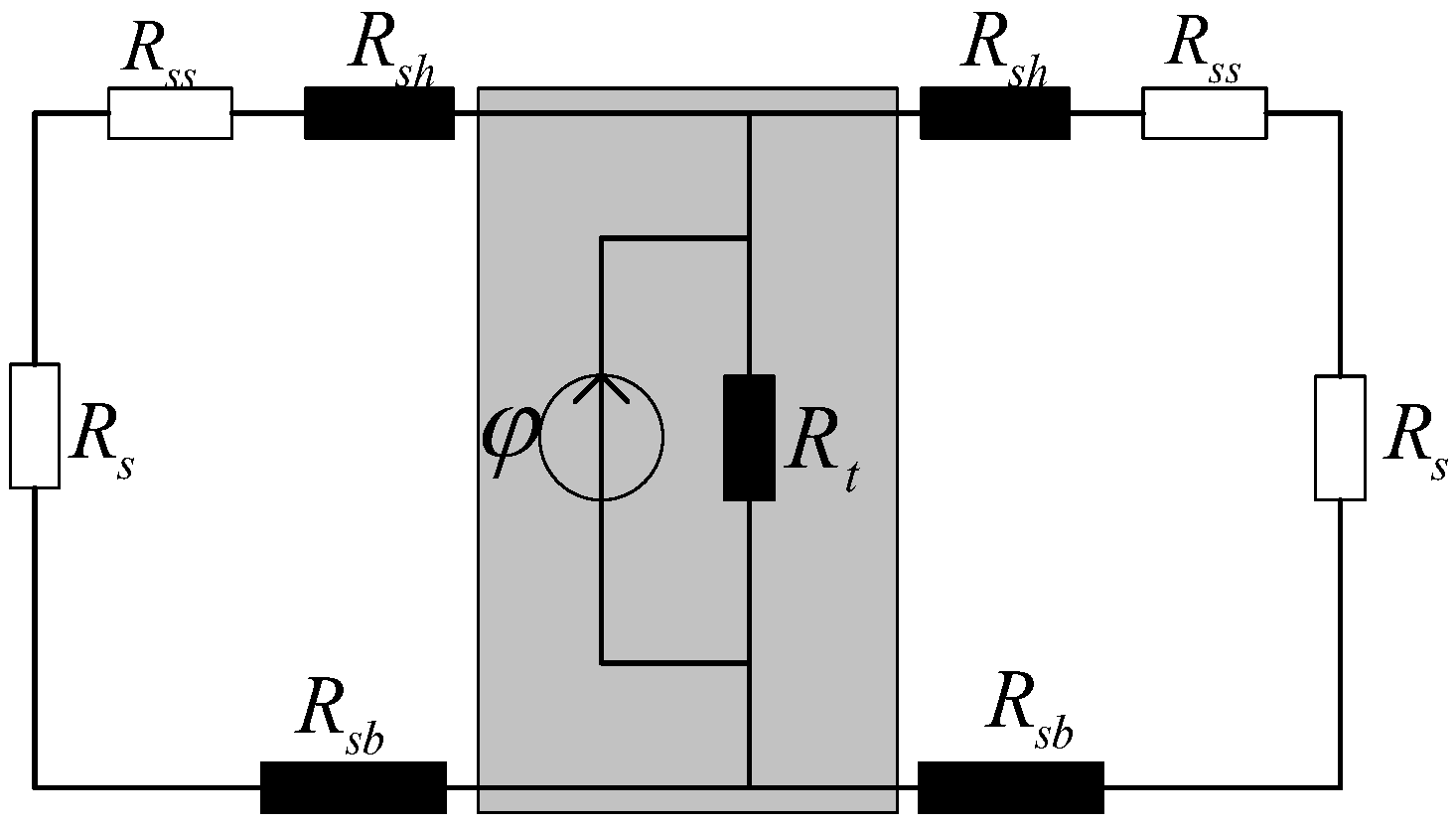
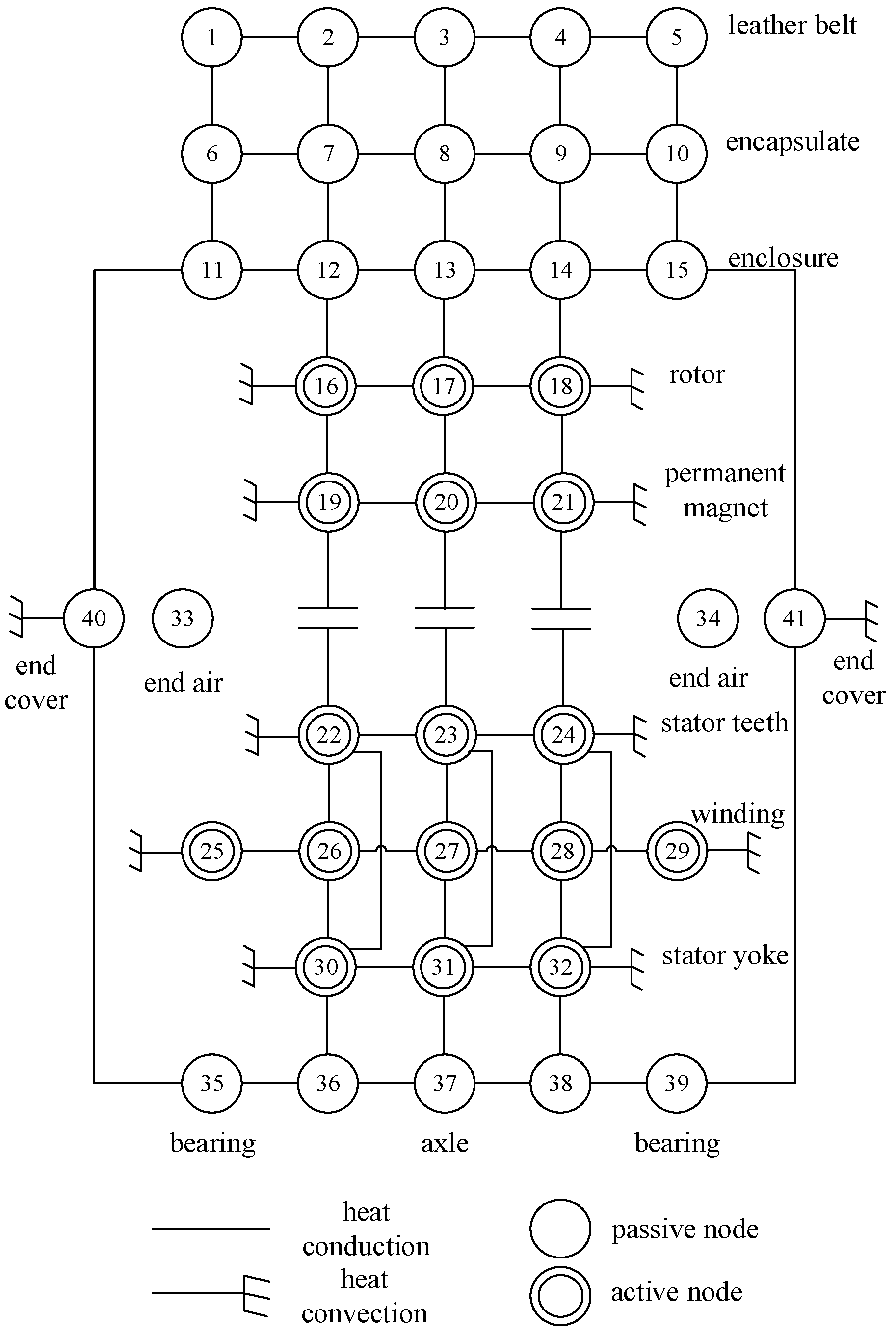
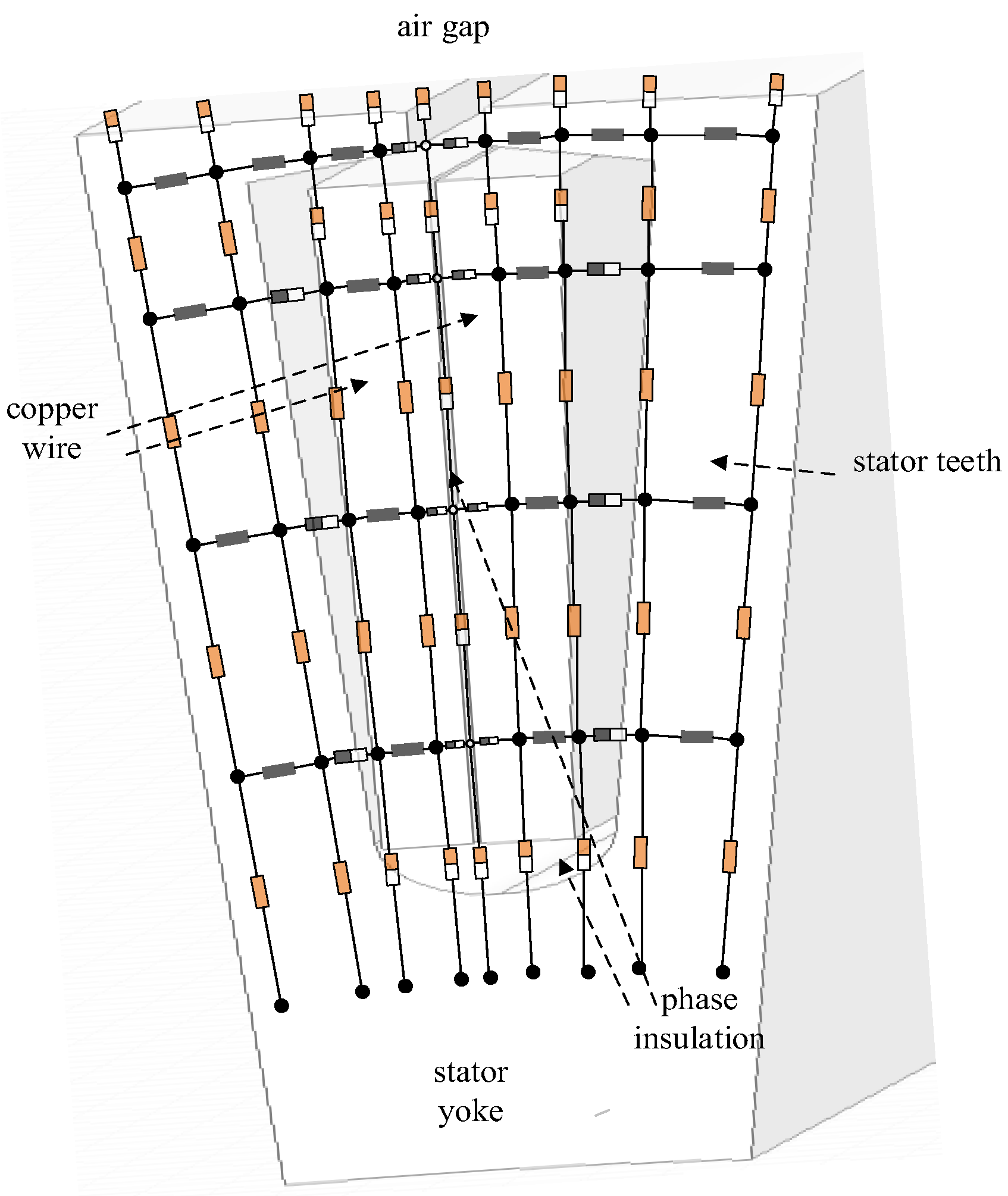
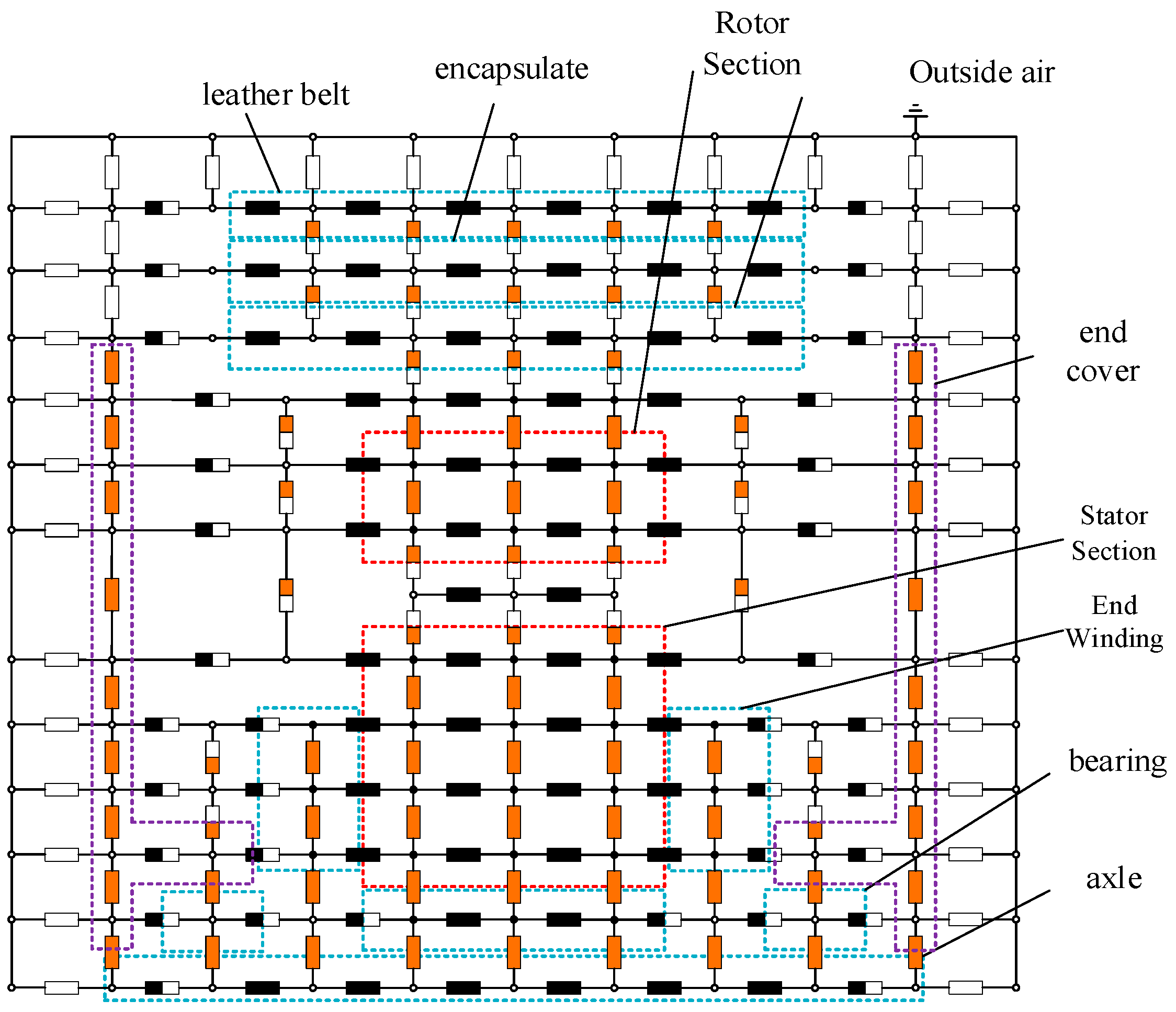
4.2. Thermal Network Modelling
- Calculation of thermal resistance between node 26 and stator tooth node 22where , , indicate the number of motor slots, the motor length and the thickness of the copper, guide wires, impregnating varnish and slot insulation in the y-direction, respectively.
- 2.
- Calculation of thermal resistance between node 26 and end winding node 25where , , represent winding end projection, winding radius, and number of conductors per slot, respectively.
- 3.
- Calculation of thermal resistance between node 26 and slot winding node 27
- 4.
- Calculation of thermal resistance between node 26 and stator yoke node 30where are the thicknesses of copper, conductor wire, impregnating varnish and slot insulation along the x-direction, respectively.
4.3. Heat Balance Equation
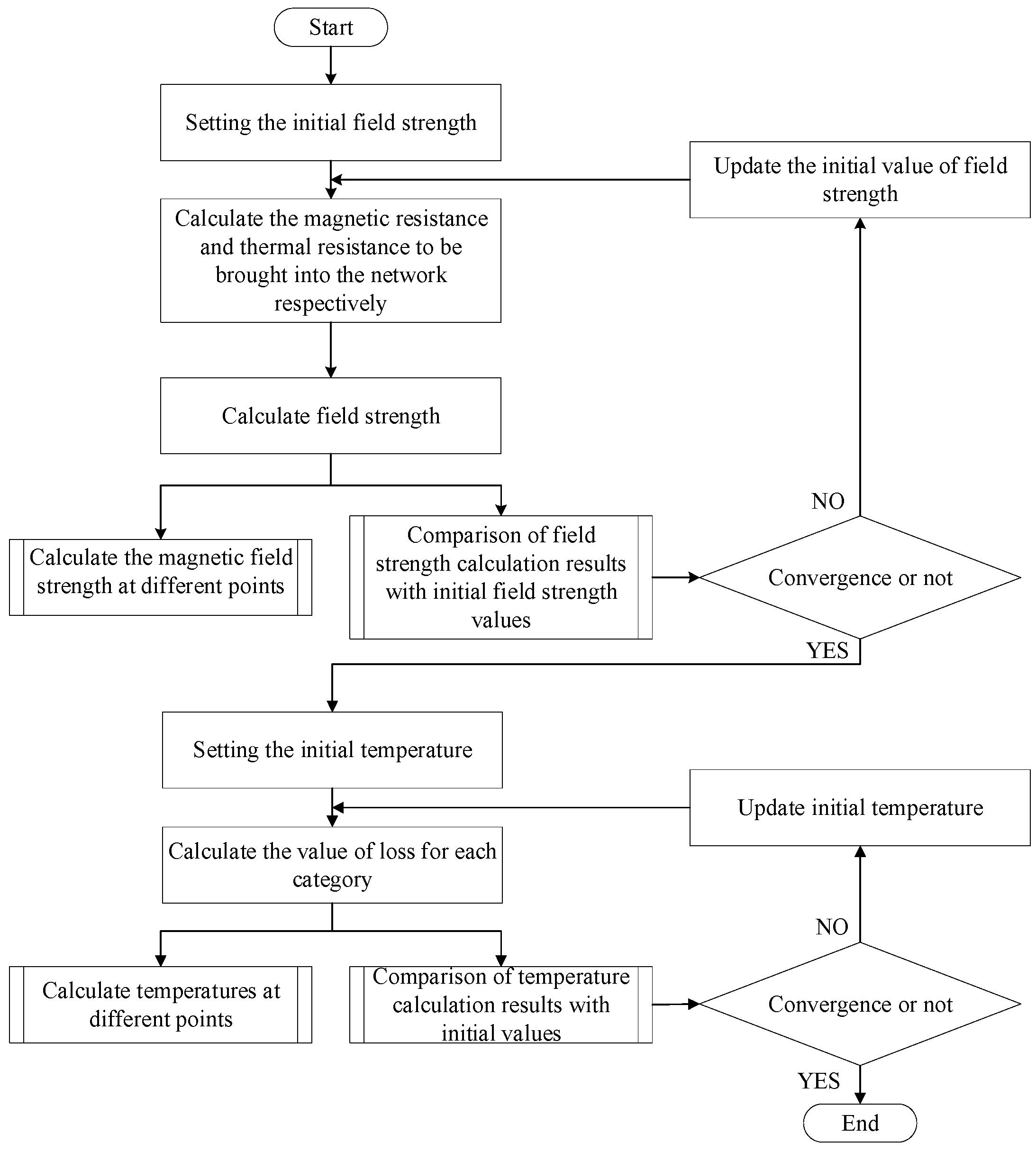
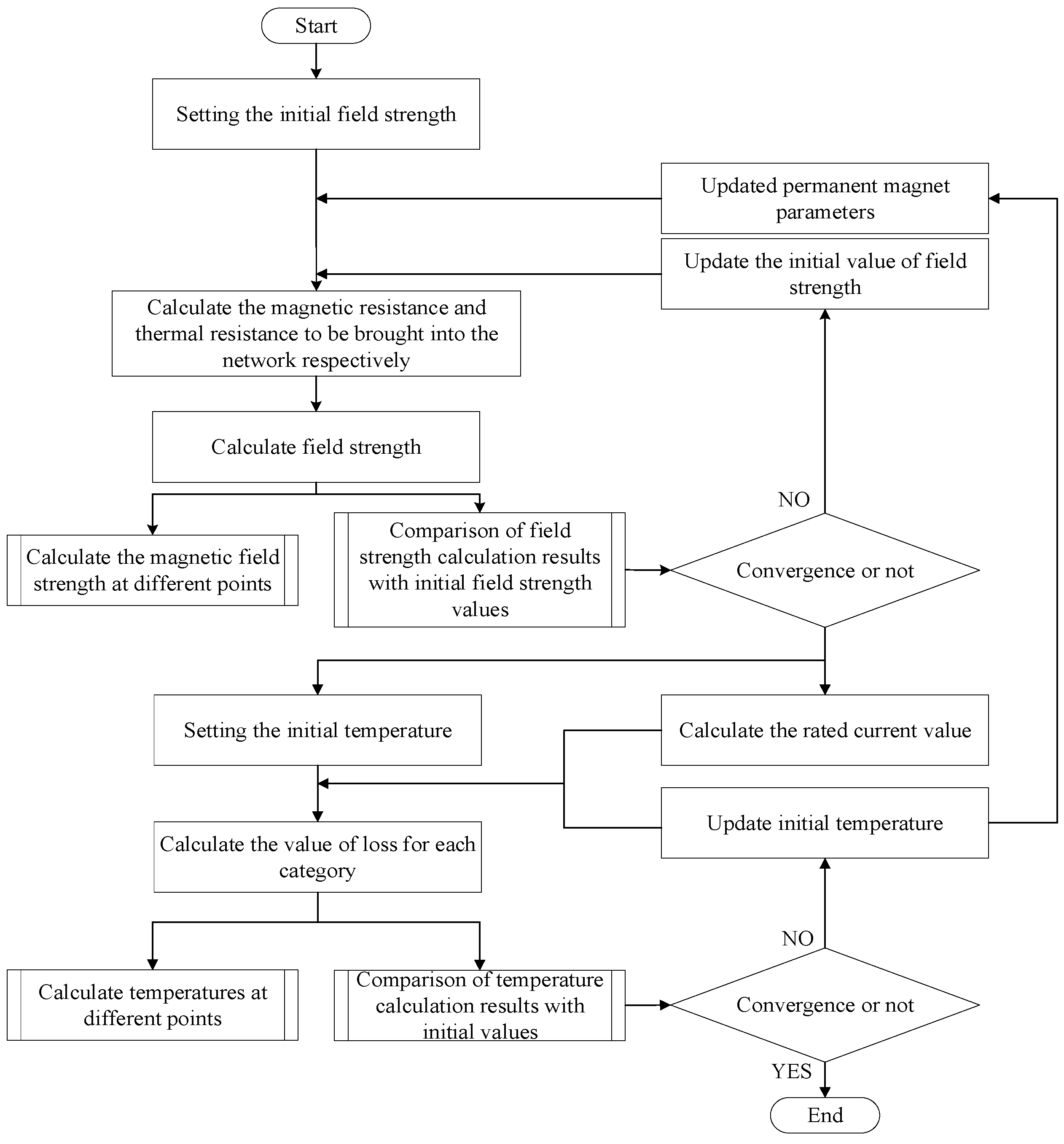
5. Calculation Method
5.1. Considering Only the Effect of Temperature on Copper Consumption
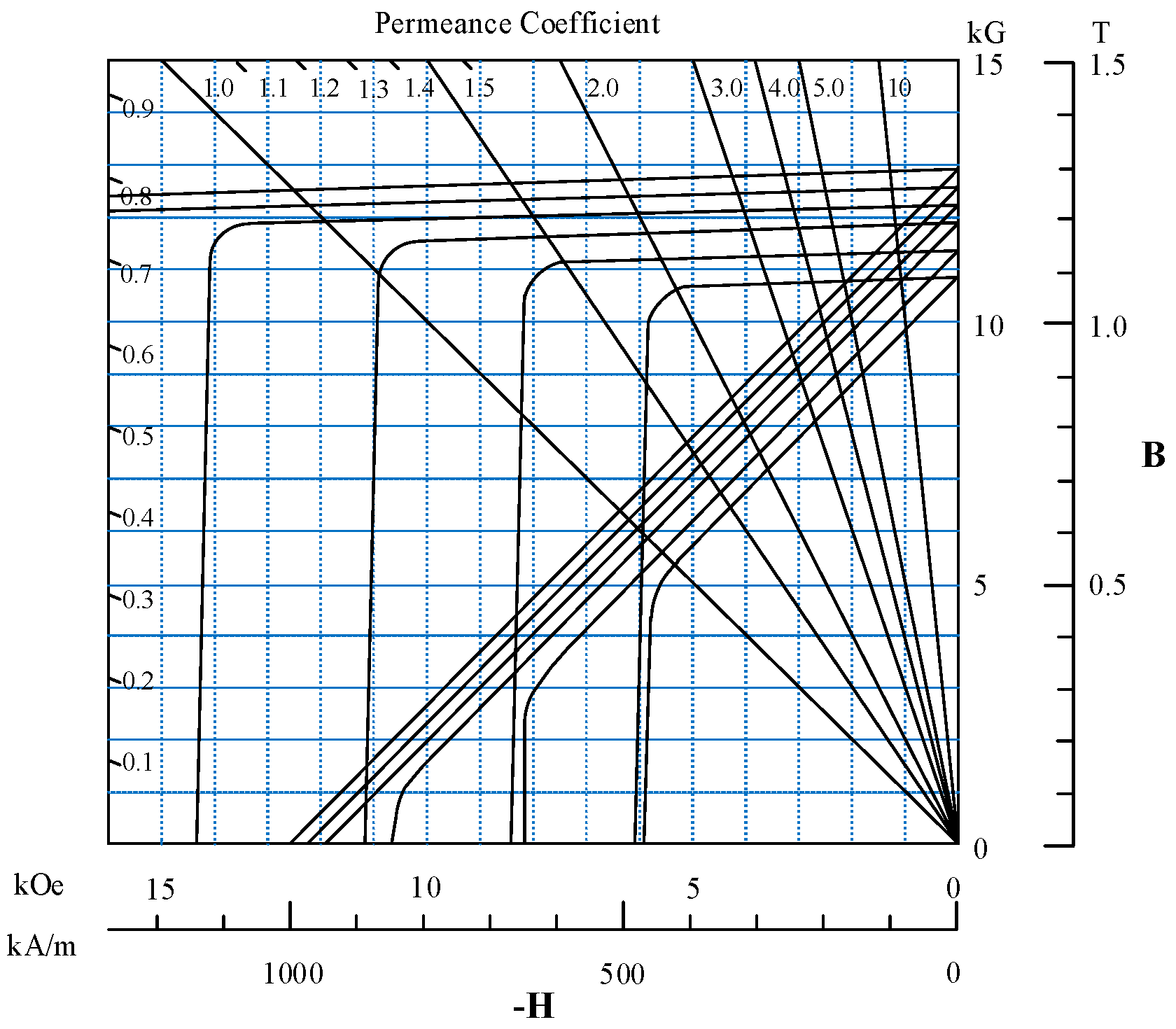
5.2. Consider the Effect of Temperature on the Performance of Permanent Magnets
6. Validation of Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, B. Analysis of torque characteristics of ultra-low speed and large torque permanent magnet motor for cement mill. Electr. Eng. 2021, 15, 188–191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Feng, B.; Feng, G. Design of Low-speed direct-drive external rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor. Micro Mot. 2022, 55, 24–29+51. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Pfister, P.; Tang, C.; Fang, Y. A hybrid model of permanent-magnet machines combining Fourier analytical model with finite element method, taking magnetic saturation into account. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 7400105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Shen, M.; Fang, Y.; Pfister, P. Comparison of subdomain, complex permeance and relative permeance models for a wide family of permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 57, 8101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Shi, Y. Study on the number of slot poles and rotor magnetic circuit structure based on 12-slot 10-pole permanent magnet motor. Small Spec. Electr. Mach. 2021, 49, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Huang, X.; Kou, B.; Pan, D. Numerical calculation of temperature field of cylindrical linear motor based on finite element method. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2013, 28, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.-W.; Lee, S.-G.; Chung, K.-S.; Cho, Y.-H. Investigation of auxiliary poles design criteria on reduction of end effect of detent force for PMLSM. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2863–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Xiang, Q. Mathematical model of magnetic levitation switched reluctance motor based on finite element method. Proc. CSEE 2007, 27, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Song, S.; Li, H. Characterization of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on equivalent magnetic circuit method. Small Spec. Electr. Mach. 2016, 44, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- An, L.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Jang, M.; Deng, Y. Aerospace permanent magnetic synchronous motor design and simulation based on magnetic circuit method and equivalent thermal network method. Astronaut. Syst. Eng. Technol. 2022, 6, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhen, W. Magnetic circuit model of internal magnet voice coil motors considering edge flux. Small Spec. Electr. Mach. 2021, 49, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Wen, X. Simulation calculation of three-dimensional temperature field of hydro generator stator. Power Syst. Eng. 2006, 2, 51–52, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Yao, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, H. A robust online junction temperature calibration method for power semiconductors in traction inverter application. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 11, 6602–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X. Temperature Field Analysis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor and Research on Cooling System. Ph.D. Thesis, Xiangtan University, Xiangtan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, B. Temperature field study of external rotor permanent magnet synchronous motors for belt conveyors. Explos.-Proof Electr. Mach. 2020, 22, 8–12, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W. Design of water-cooling system for mining explosion-proof permanent magnet synchronous motor. New Technol. New Prod. China 2020, 3, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y. Thermal circuit analysis and thermal resistance parameter testing of permanent magnet synchronous motors. Mechatron. Eng. 2014, 31, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y. Temperature Field Analysis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Electric Cars. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning University of Technology, Jinzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Deaconu, A.S. Permanent magnet synchronous motor thermal analysis. In Proceedings of the 6th IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives, Bristol, UK, 27–29 March 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, D. Electromagnetic Field and Thermal Linked Analysis of Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor for Agricultural Electric Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 7, 4242–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nategh, S.; Zhang, H.; Wallmark, O. Transient Thermal Modeling and Analysis of Railway Traction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, S.O.; Bocker, J. Global identification of a Low-Order Lumped-Parameter thermal network for permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 354–365. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.J.; Heyns, G.C. Thermal analysis of a water-cooled interior permanent magnet traction machine. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Cape Town, South Africa, 25–28 February 2013; pp. 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Tang, B.; Wang, R.; Zhan, G.; Yang, C.X.; Cui, G. Optimization and Calculation of Equivalent Thermal Network Method in the Temperature Field Research of Permanent Magnet Servo Motor. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2016, 9, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Q. Analysis of unidirectional and bidirectional magnetic-thermal coupling of permanent magnet synchronous motor. J. Vibroengineering 2022, 24, 1541–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cheng, M.; Qin, W.; Liu, Q. Fast Calculation Method of Bi-Direction Coupling Between Electromagnetic-Thermal Field for FSPM Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2023, 59, 8205909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, W. Magnetic-Thermal-Fluid Field Coupling Method Study on Temperature Rise Analysis of Permanent Magnet Motor. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum and Petrochemical Technology Conference, Shanghai, China, 25–27 August 2021; pp. 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, R.; Lipo, T.A. Analysis and modeling of air-gap and zigzag leakage fluxes in a surface-mounted permanent-magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Jin, L.; Zhang, H.; Hong, J. Magnetic Equivalent Circuit Modeling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with External Rotor. Front. Acad. Forum Electr. Eng. 2025, 1287, 659–668. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F. An improved iron loss estimation for permanent magnet brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1999, 14, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieras, J.; Wang, R.; Kamper, M. Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Brushless Machines; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Choi, D.; Cho, C.; Koo, D.H.; Cho, Y.H. Eddy-current calculation of solid components in fractional slot axial flux permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 4254–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
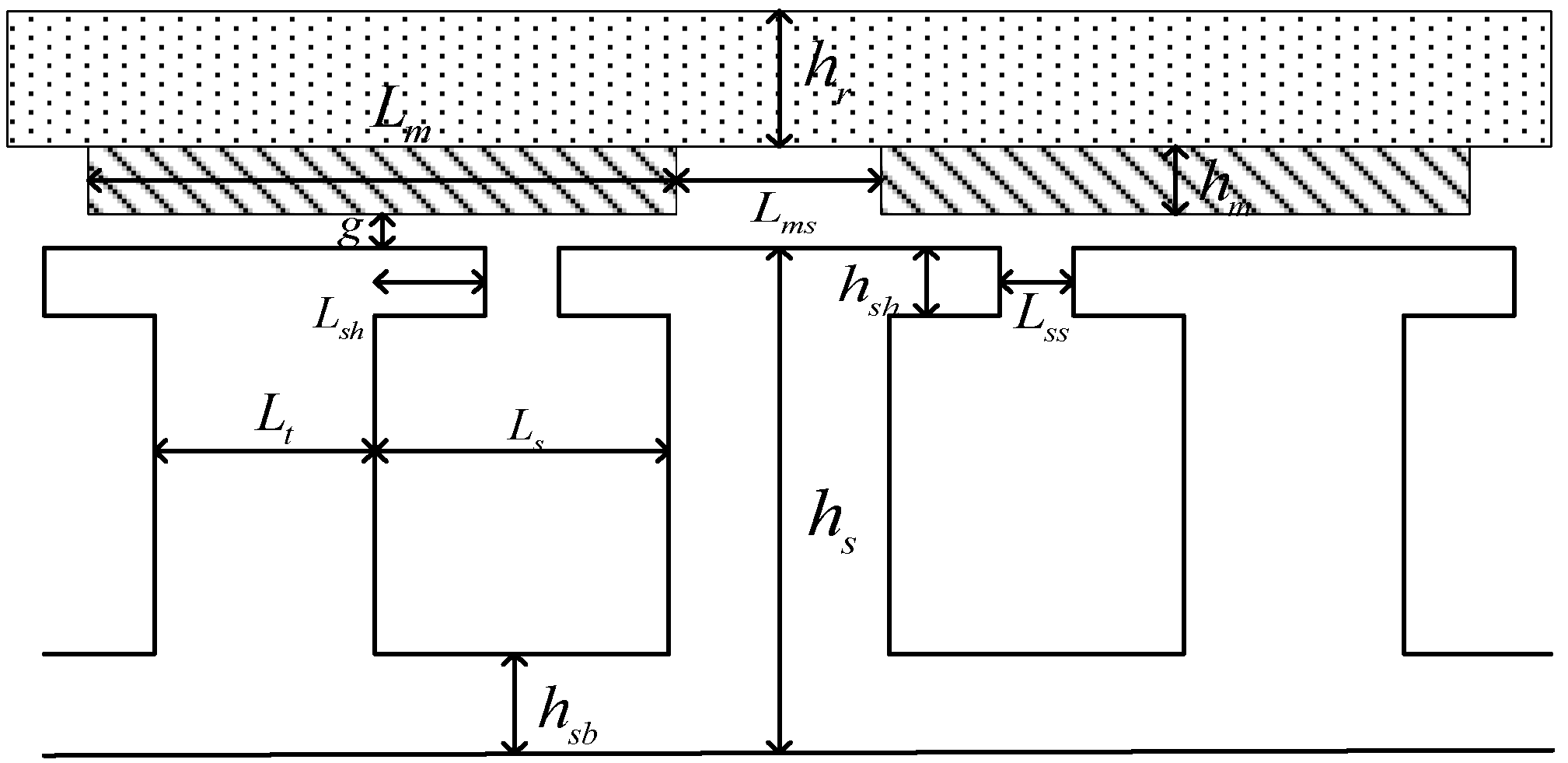


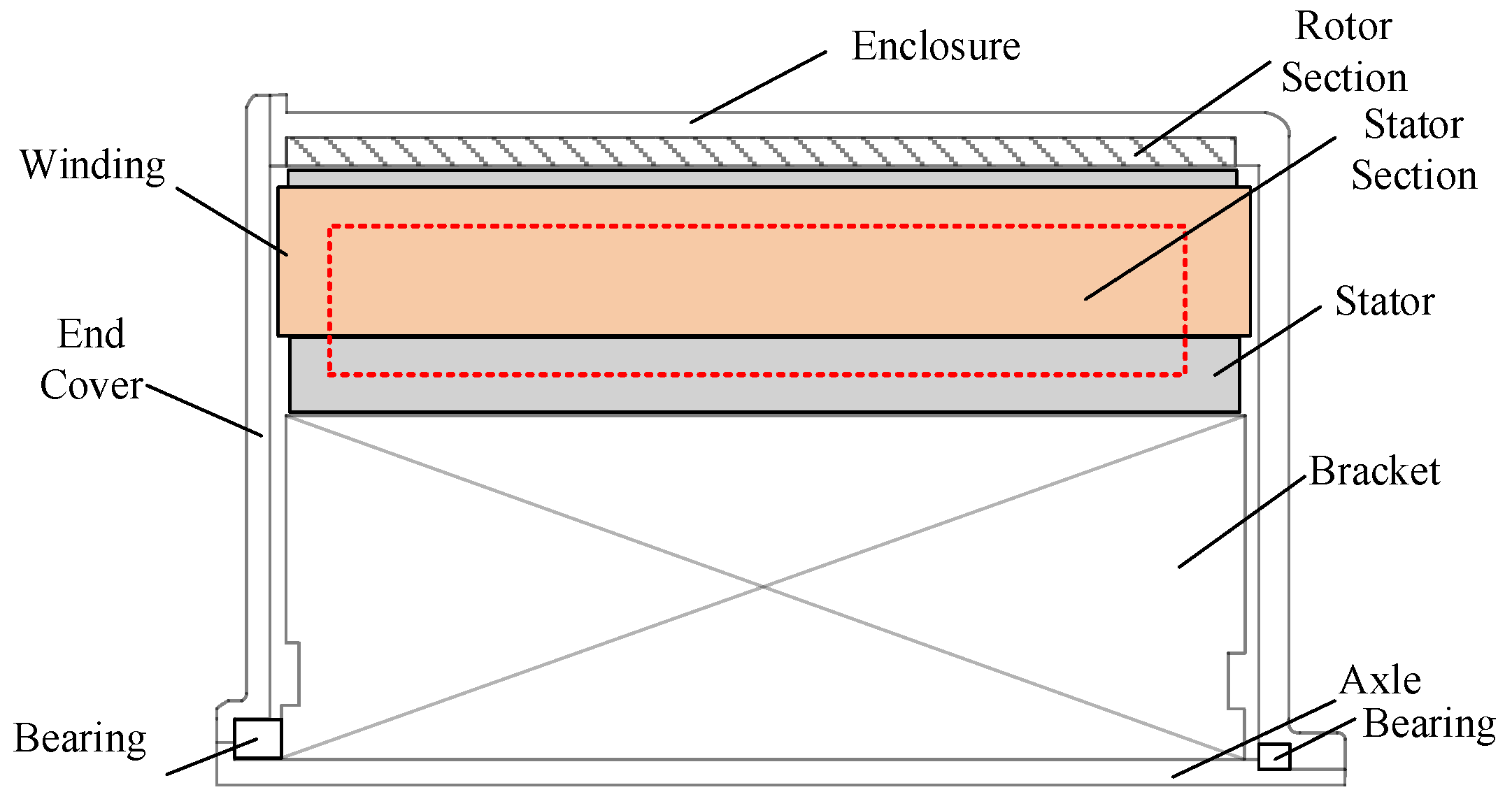

| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power | P | 131 | kW |
| Rated voltage | U | 806 | V |
| Stator outer diameter | Do | 734 | mm |
| Stator inner diameter | Di | 460 | mm |
| Air gap length | g | 1.5 | mm |
| Stator axial height | hs | 137 | mm |
| Rotor axial height | hr | 23 | mm |
| Magnet height | hm | 9 | mm |
| Magnet pole arc ratio | - | 0.8 | |
| Slot width | Ls | 28.8 | mm |
| Shoe width | Lss | 9.6 | mm |
| Stator shoulder height | hsh | 8 | mm |
| Stator shoulder width | Lsh | 9.6 | mm |
| Stator yoke height | hsb | 43 | mm |
| Stator tooth width | Lt | 19.2 | mm |
| Symbol | Value (μH−1) |
|---|---|
| Rm | 0.18 |
| Rmg | 0.97 |
| Rr | varied |
| Rmm | 8.14 |
| Rs | 2.80 |
| Rt | varied |
| Rsb | varied |
| Rsh | varied |
| Rss | 1.24 |
| R1 | 0.32 |
| R2 | 0.11 |
| R3 | 0.16 |
| R4 | 0.16 |
| R5 | 0.16 |
| R6 | 0.32 |
| R7 | 0.16 |
| Areas of Motor | MEC | FEA | Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator yoke/W | 1332.2 | 1273.6 | 4.6 |
| Stator teeth/W | 345.1 | 323.4 | 6.7 |
| Winding/W | 3149.2 | 3149.2 | 0 |
| Permanent magnet/W | 237.5 | 224.9 | 5.6 |
| Rotor/W | 845.1 | 813.4 | 3.9 |
| Section | X Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Y Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Z Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DW475 | 39 | 39 | 4.43 | 7800 |
| Winding | 385 | 385 | 385 | 8900 |
| Winding insulation | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 200 |
| Permanent magnet | 9 | 9 | 9 | 7400 |
| End Cavity Air | 0.0305 | 0.0305 | 0.0305 | 1.005 |
| Enclosure | 210 | 210 | 210 | 7800 |
| Encapsulate | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 1.15 |
| Leather belt | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 1400 |
| End cover | 39 | 39 | 39 | 7800 |
| Axle | 43 | 43 | 43 | 7800 |
| Bearing | 18 | 18 | 18 | 7800 |
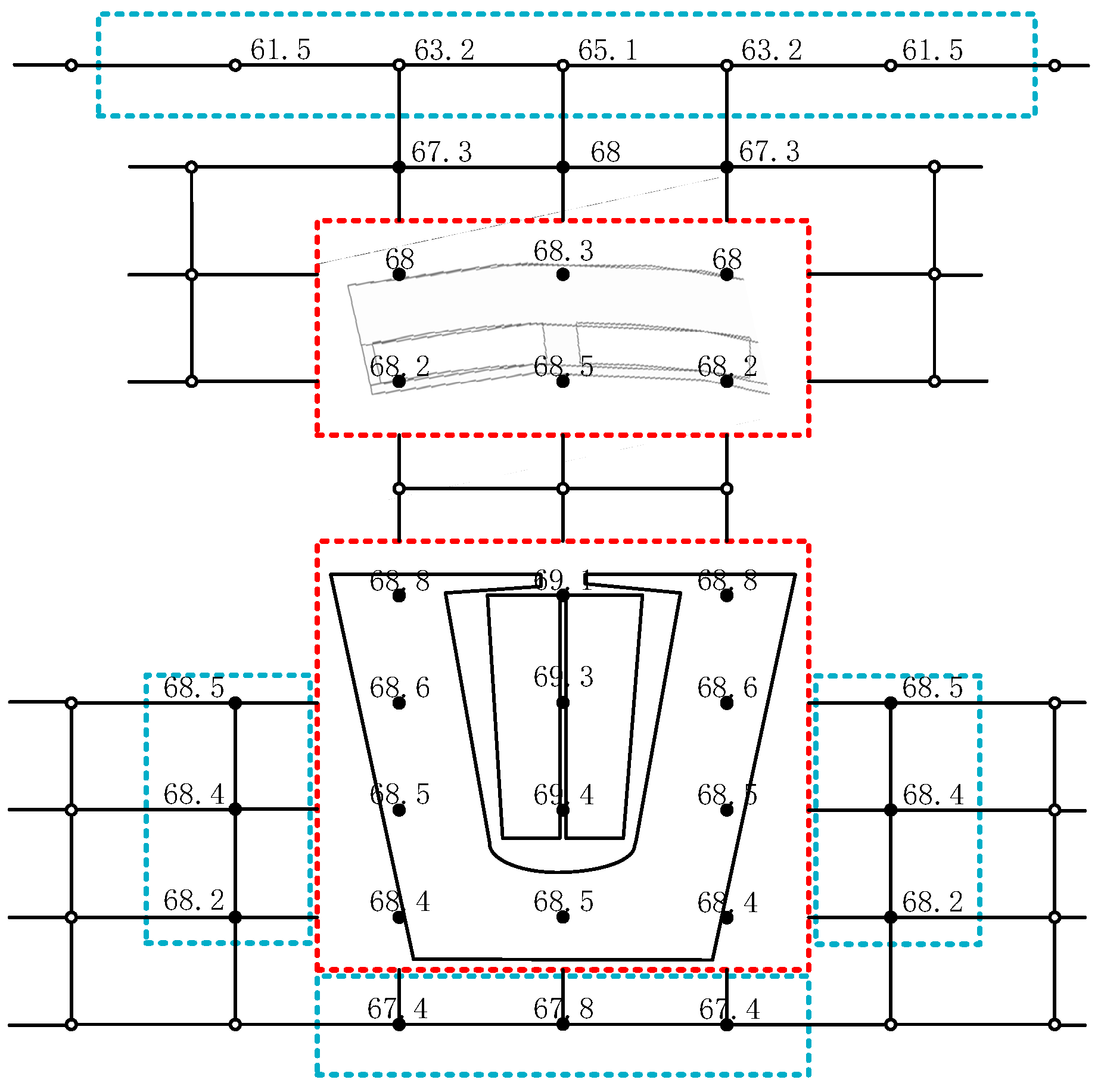
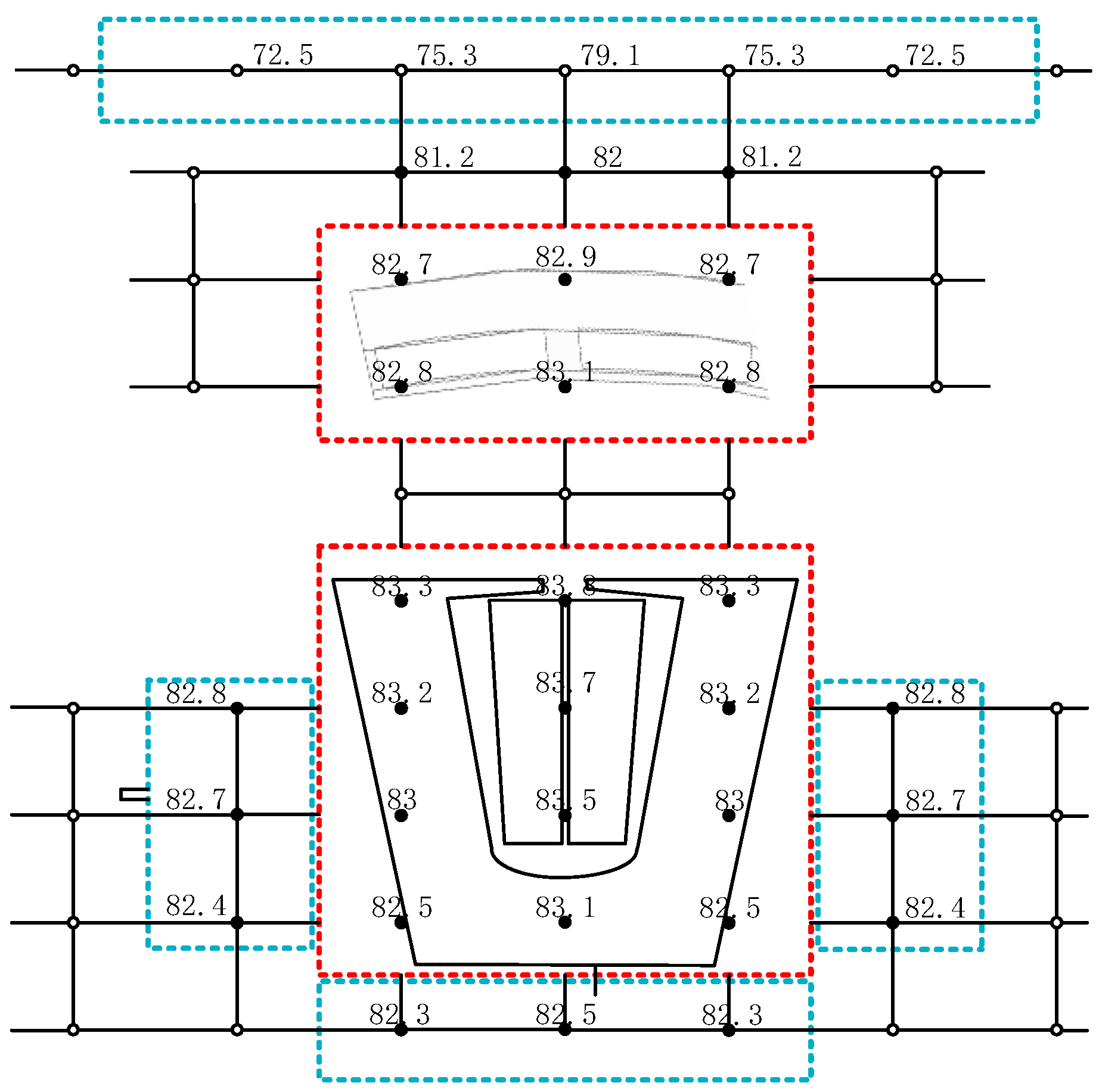
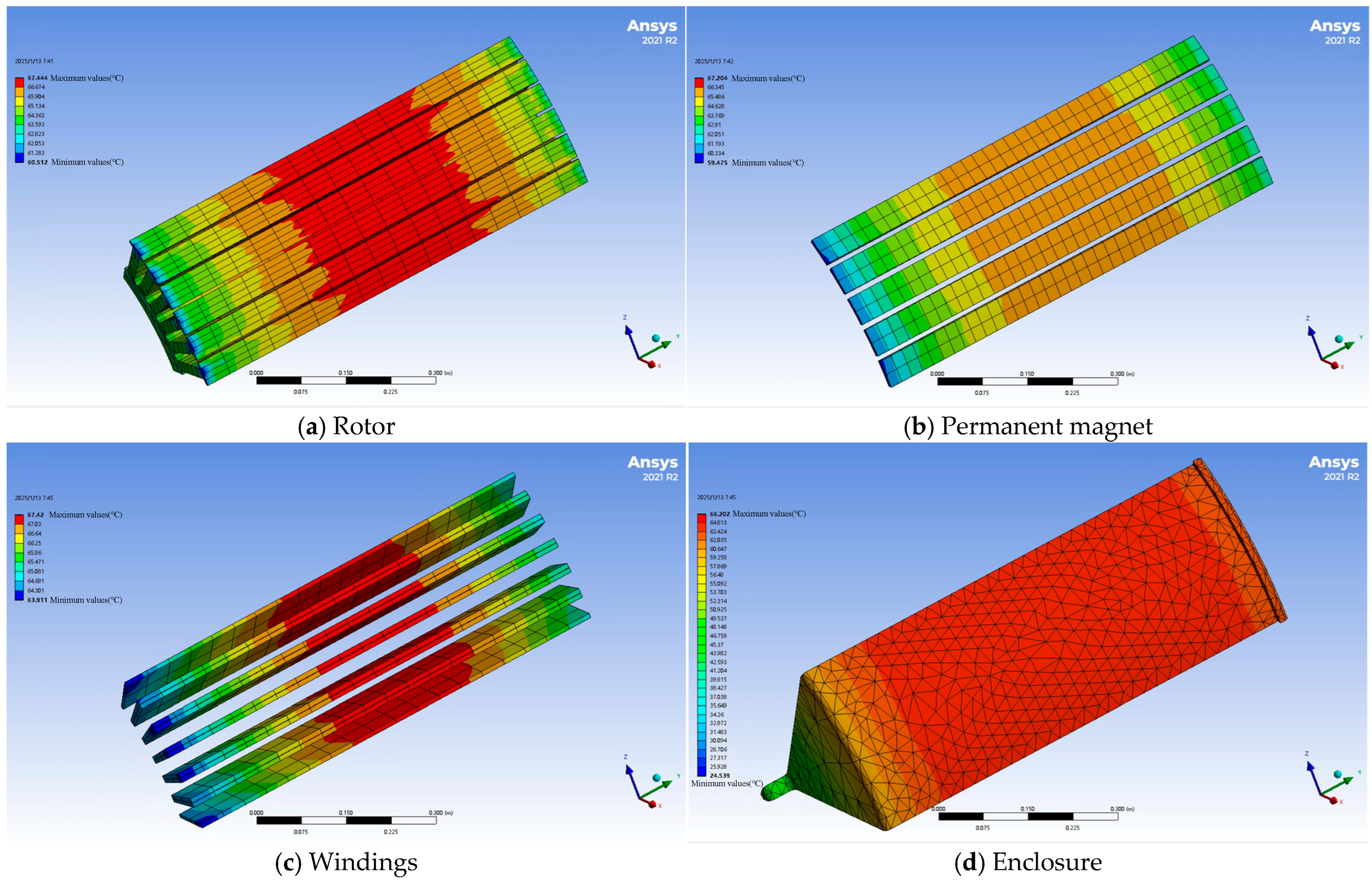
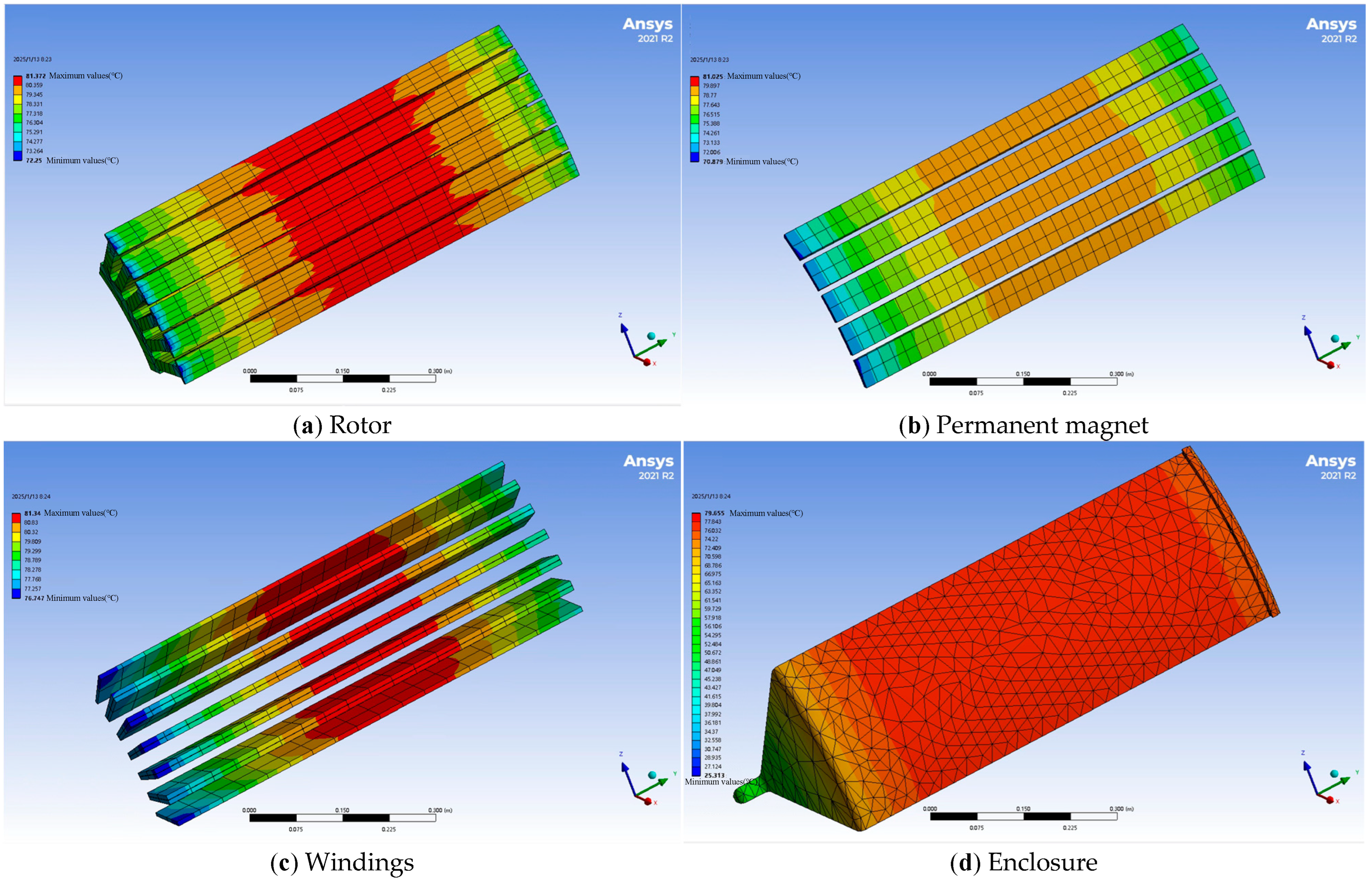
| Average Temperature | LPTN 1 | FEA 1 | Error/% | LPTN 2 | FEA 2 | Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stator yoke/°C | 68.4 | 66 | 3.6 | 82.7 | 79.5 | 4 |
| Stator teeth/°C | 68.8 | 66.2 | 4 | 83.1 | 79.7 | 4.3 |
| Winding/°C | 68.6 | 66.4 | 3.3 | 83 | 80 | 3.8 |
| Permanent magnet/°C | 68.3 | 65.3 | 4.4 | 82.9 | 78.5 | 5.6 |
| Enclosure/°C | 62.9 | 58.4 | 7.7 | 74.9 | 69.4 | 7.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhang, H.; Hong, J. Research on Magnetic–Thermal Coupling Calculation of Outer Rotor Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Magnetic Circuit Method and Thermal Network Method. Energies 2025, 18, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081891
Xu Z, Wang Y, Jin L, Zhang H, Hong J. Research on Magnetic–Thermal Coupling Calculation of Outer Rotor Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Magnetic Circuit Method and Thermal Network Method. Energies. 2025; 18(8):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081891
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhike, Yewei Wang, Long Jin, Hongbin Zhang, and Jun Hong. 2025. "Research on Magnetic–Thermal Coupling Calculation of Outer Rotor Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Magnetic Circuit Method and Thermal Network Method" Energies 18, no. 8: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081891
APA StyleXu, Z., Wang, Y., Jin, L., Zhang, H., & Hong, J. (2025). Research on Magnetic–Thermal Coupling Calculation of Outer Rotor Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Magnetic Circuit Method and Thermal Network Method. Energies, 18(8), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081891






