Comparative Studies of Three-Dimensional Complex Flow Field Designs in a Proton Exchange Membrane Hydrogen Fuel Cell
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Description
2.1. PEMFC Model Design
2.2. Mathematical Model Descriptions
2.3. Electrochemical Model Description
2.3.1. Exchange Current Density
2.3.2. Boundary Conditions and Water Management
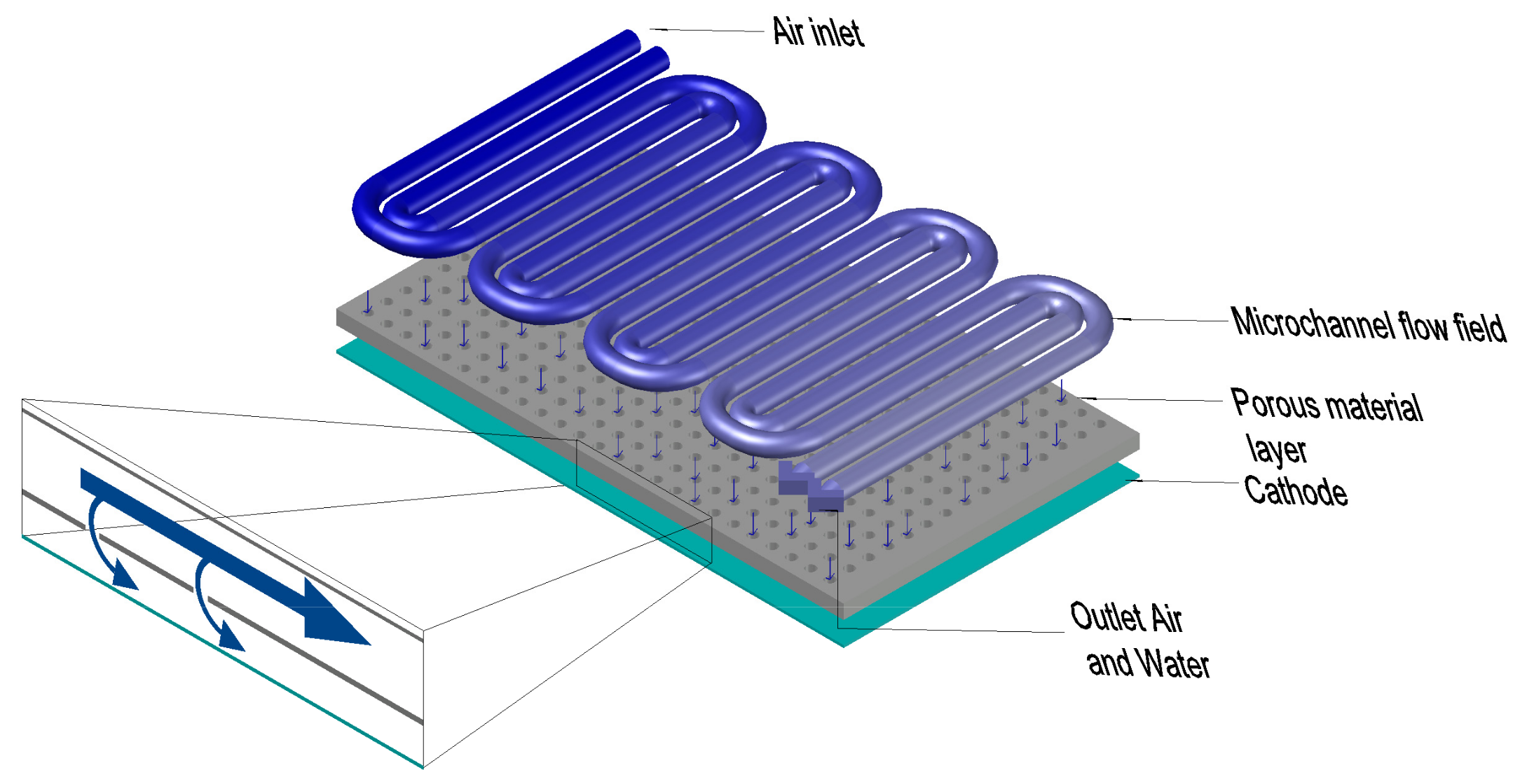
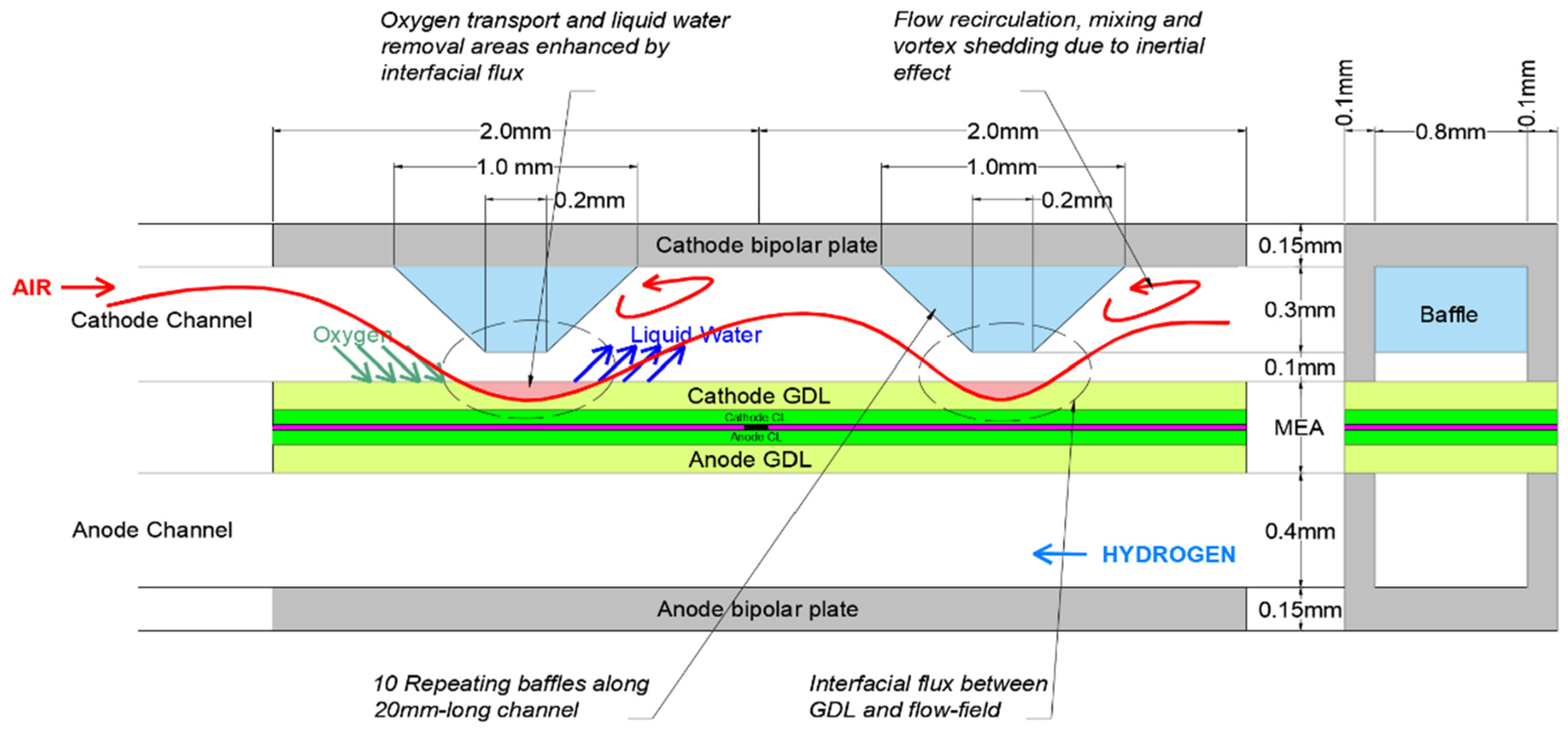
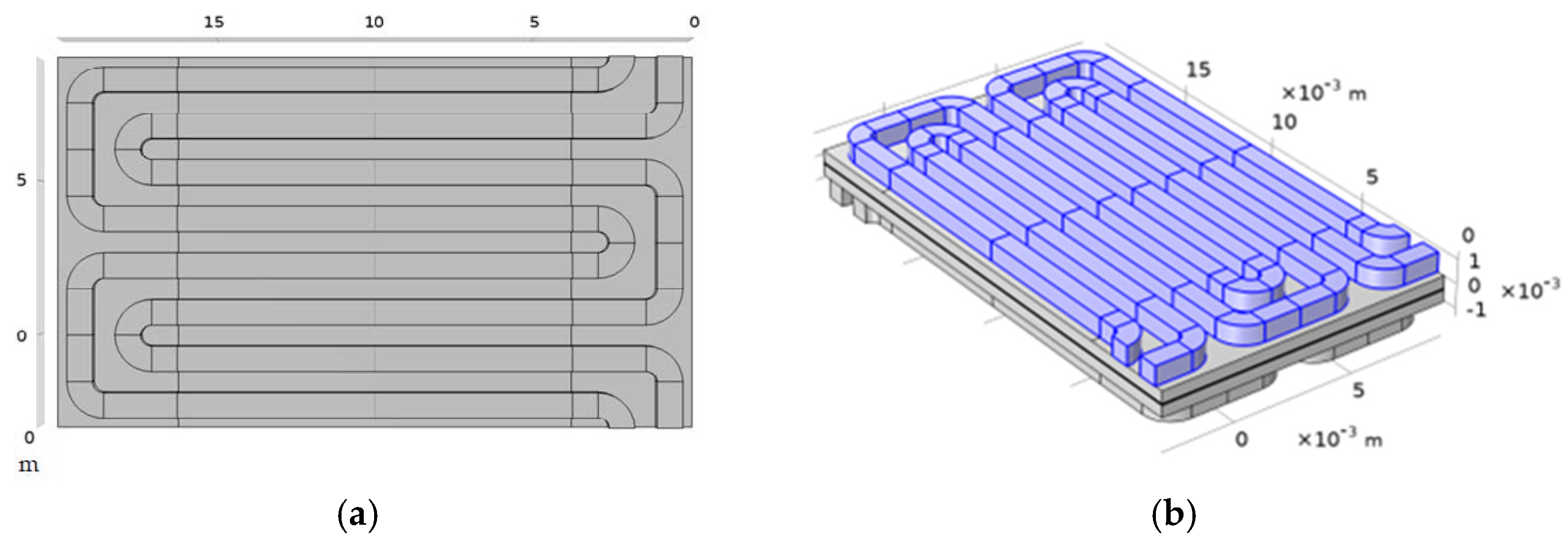
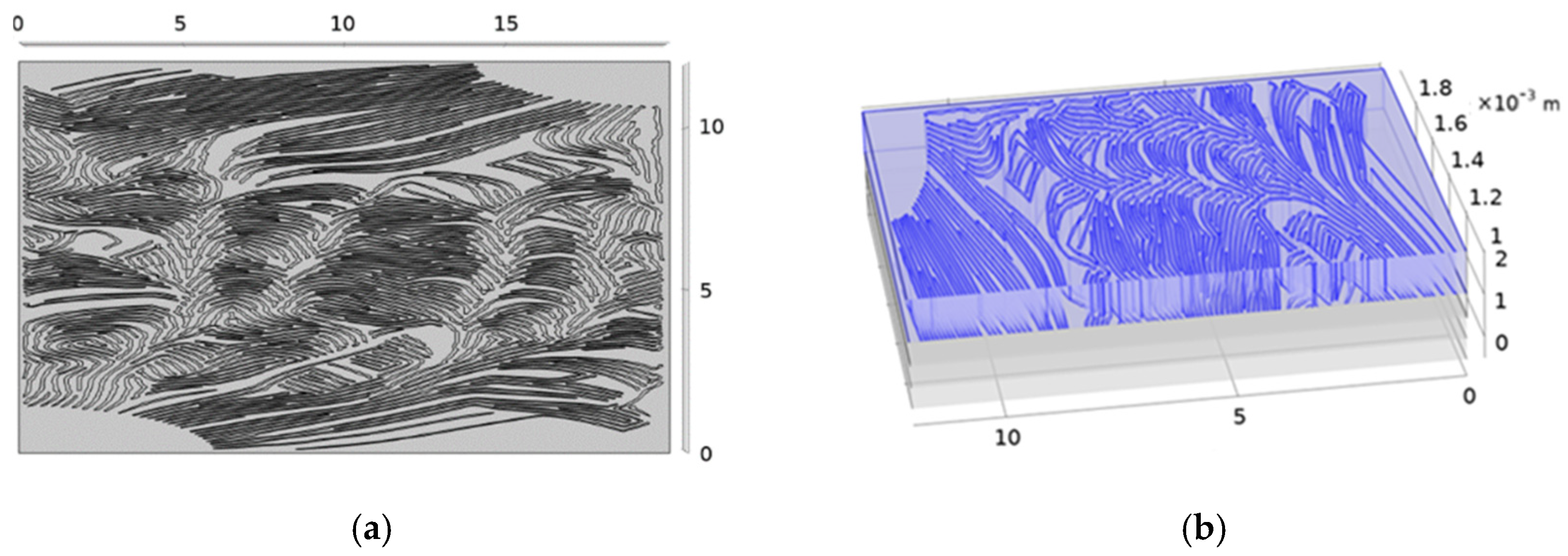
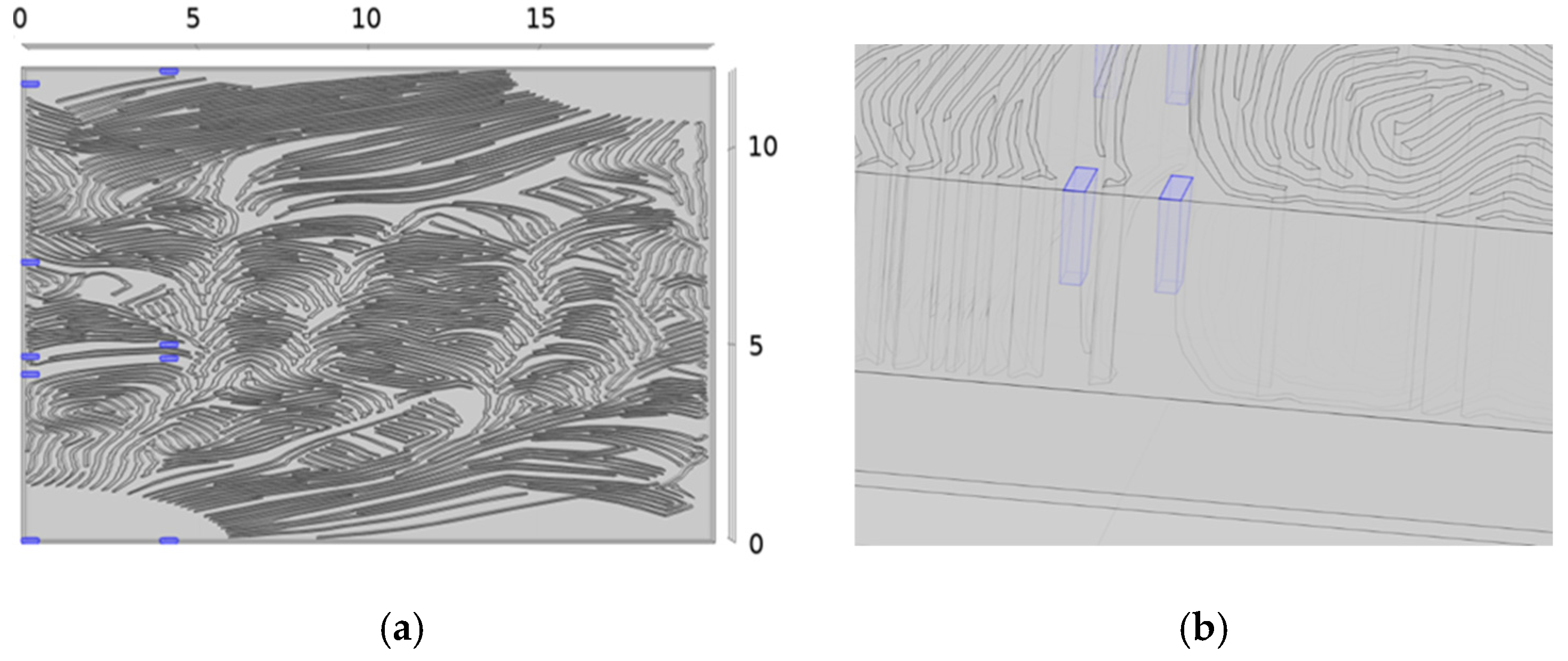
2.4. Flow Channel Configuration
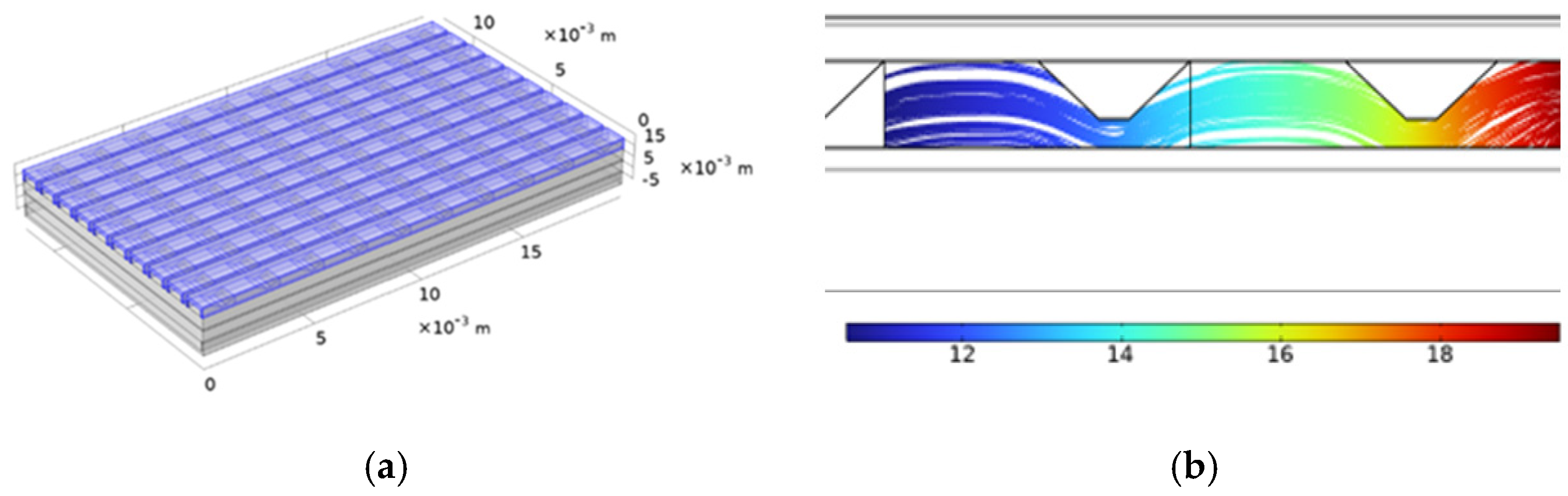
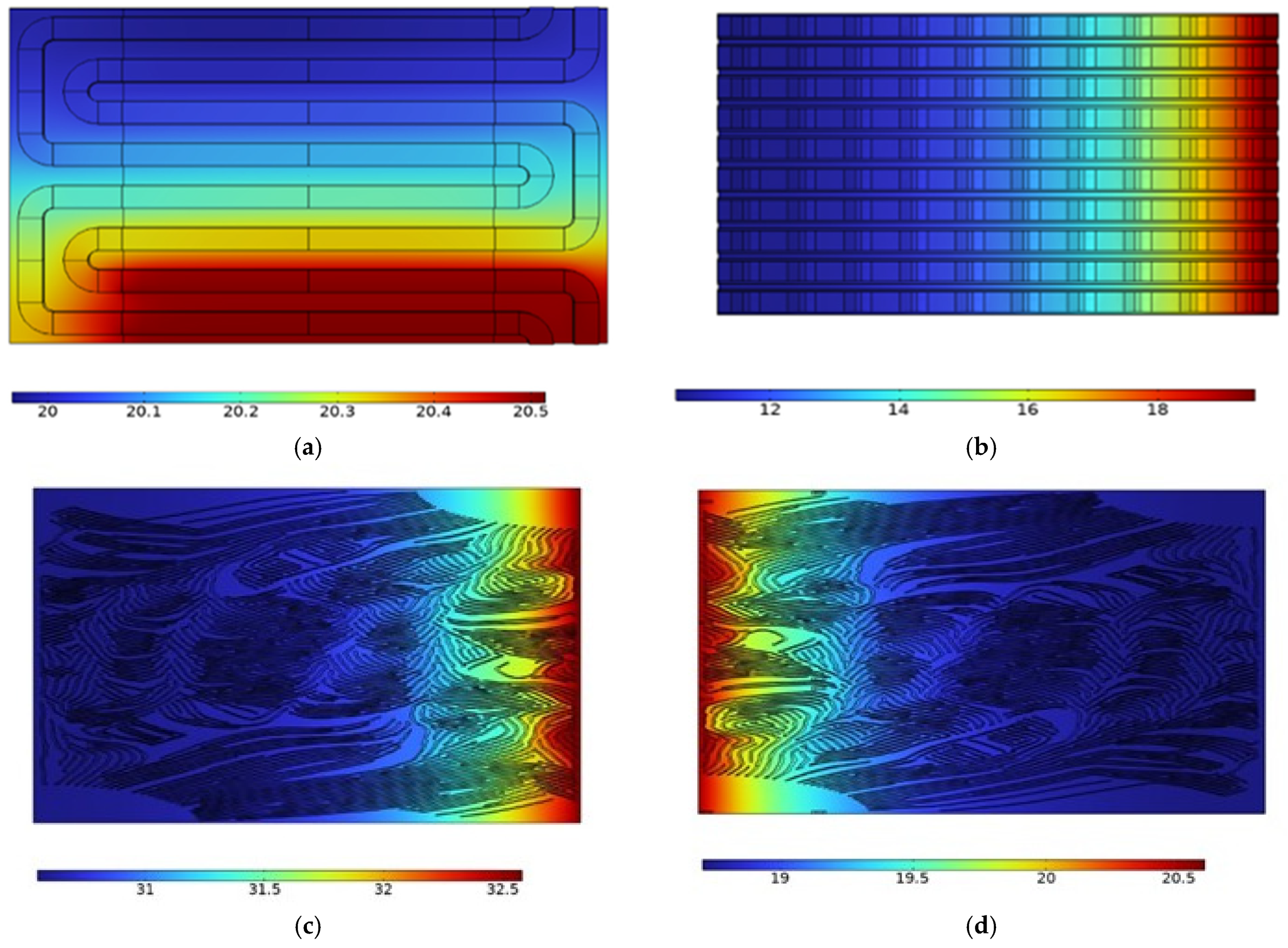
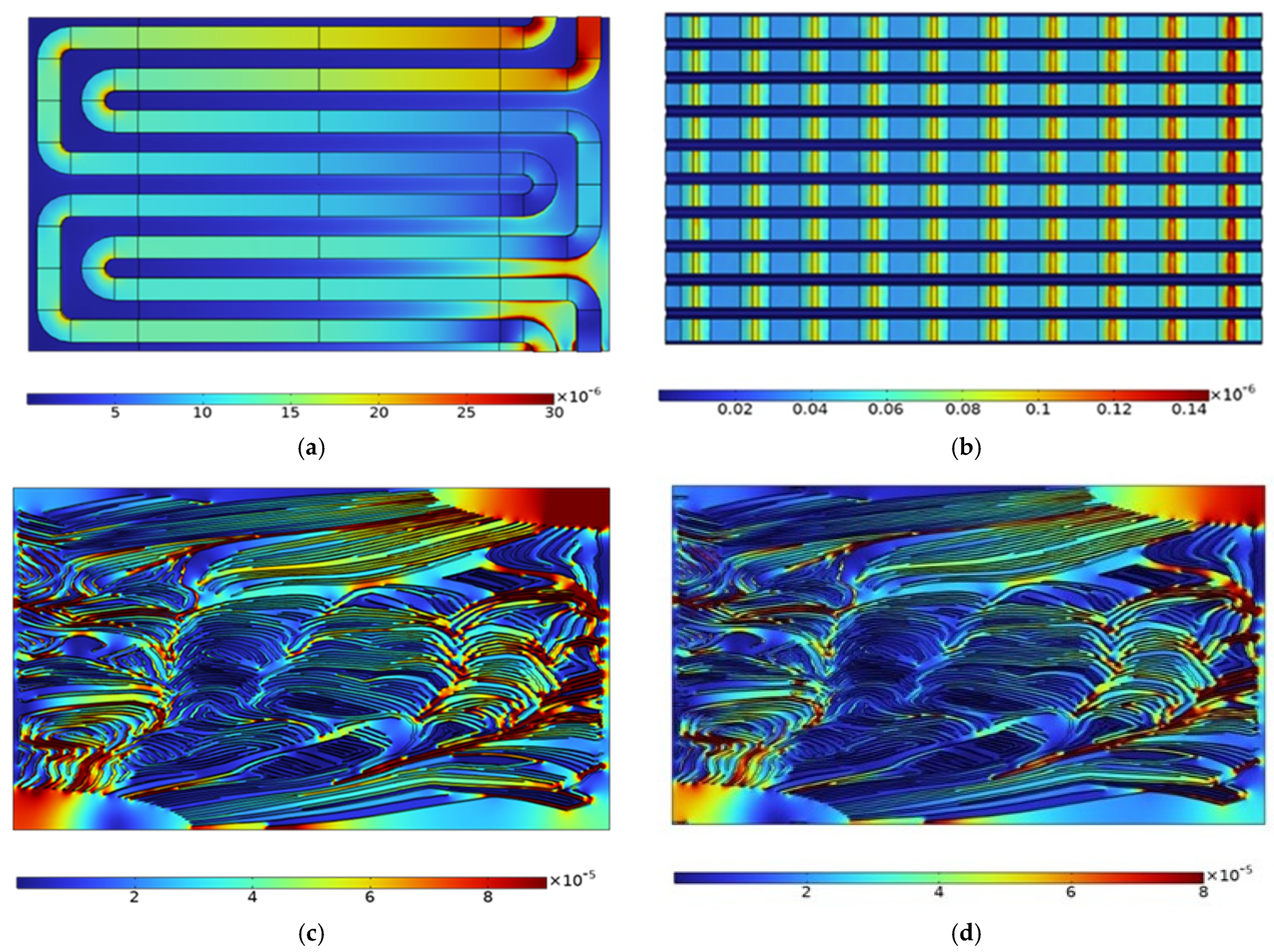
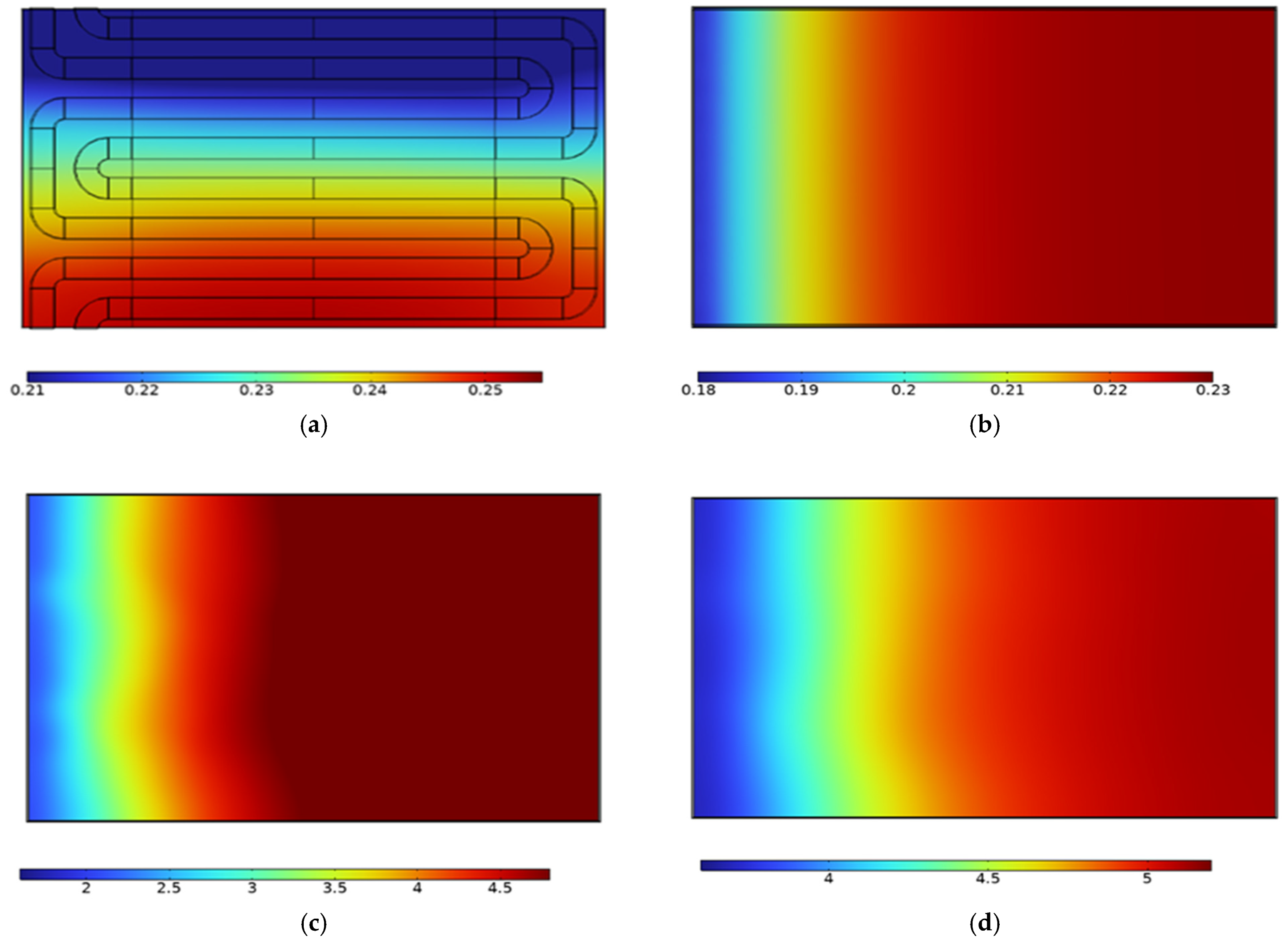
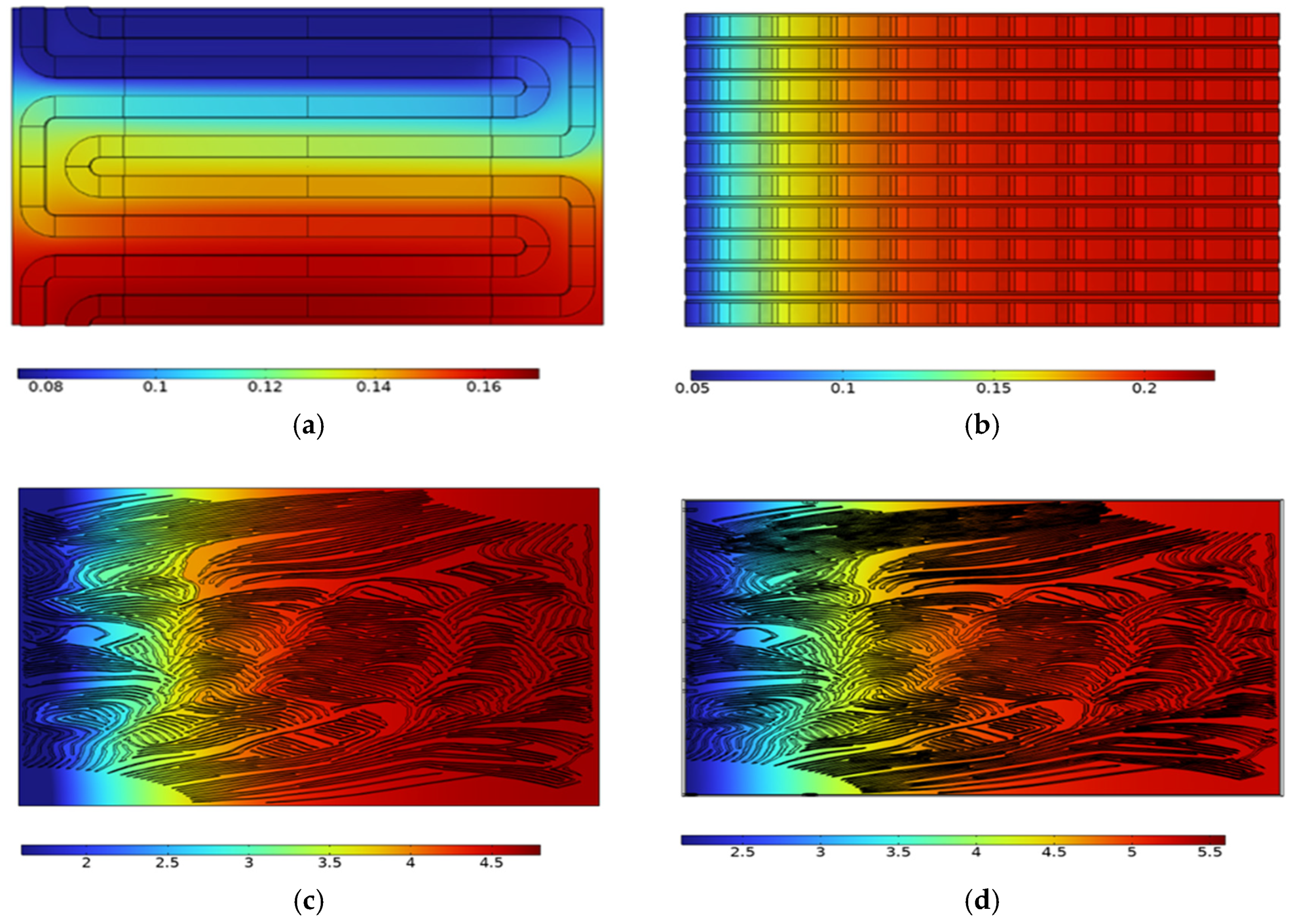
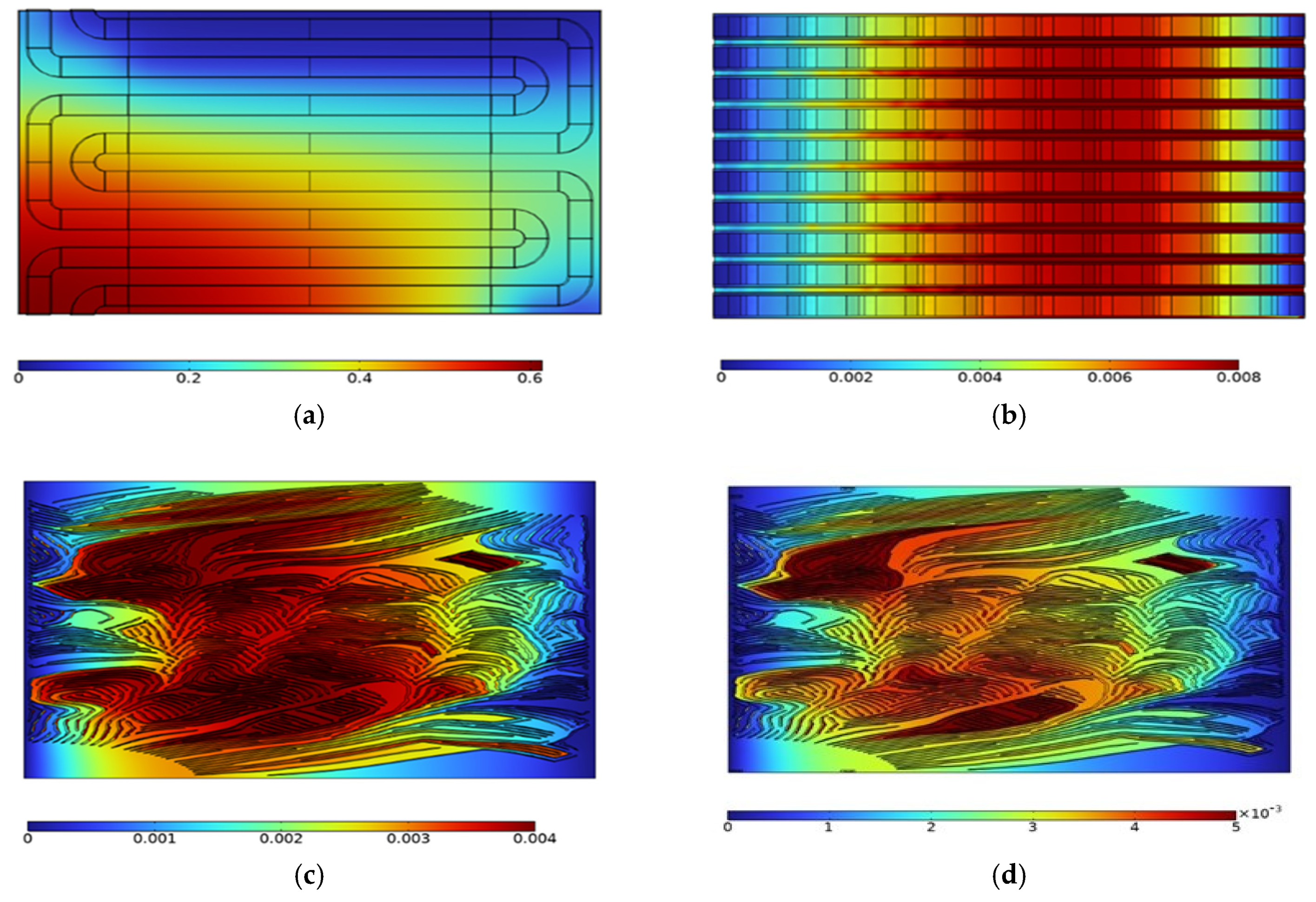
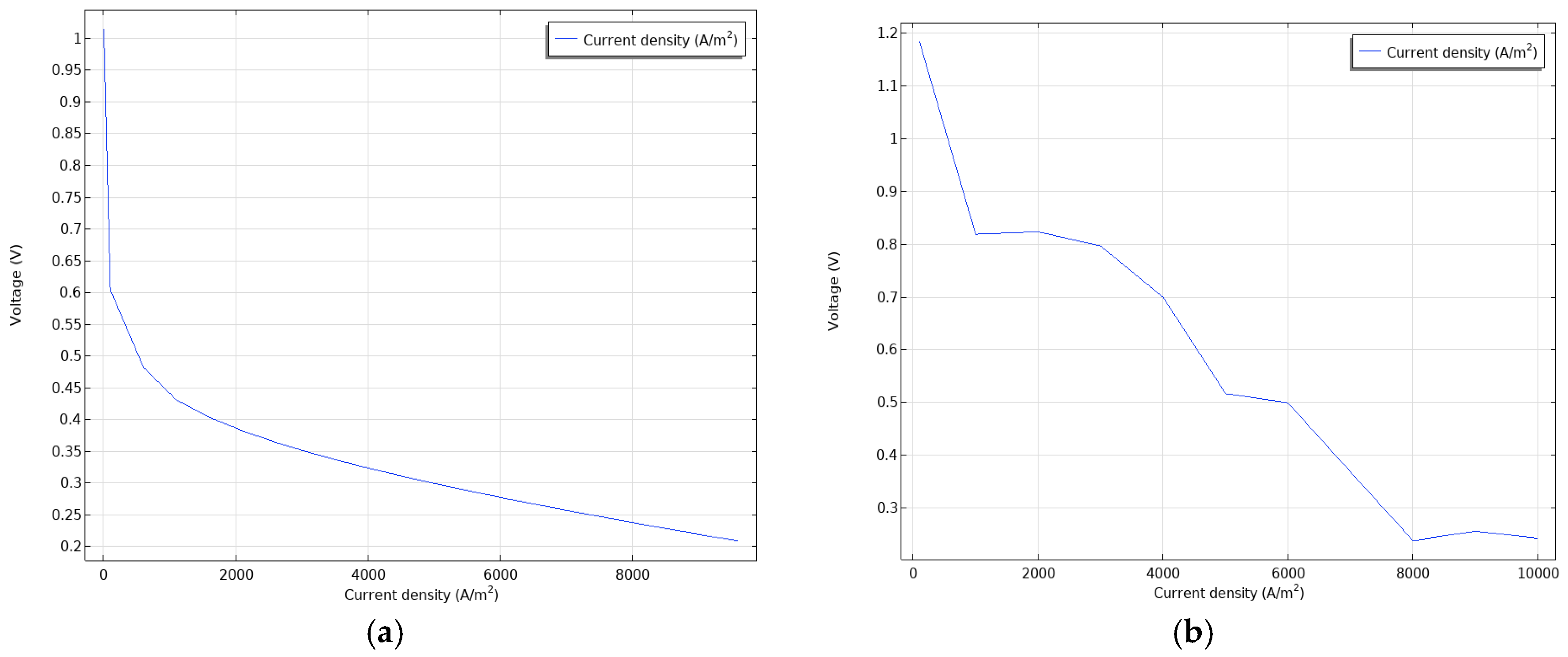
3. Results and Discussion
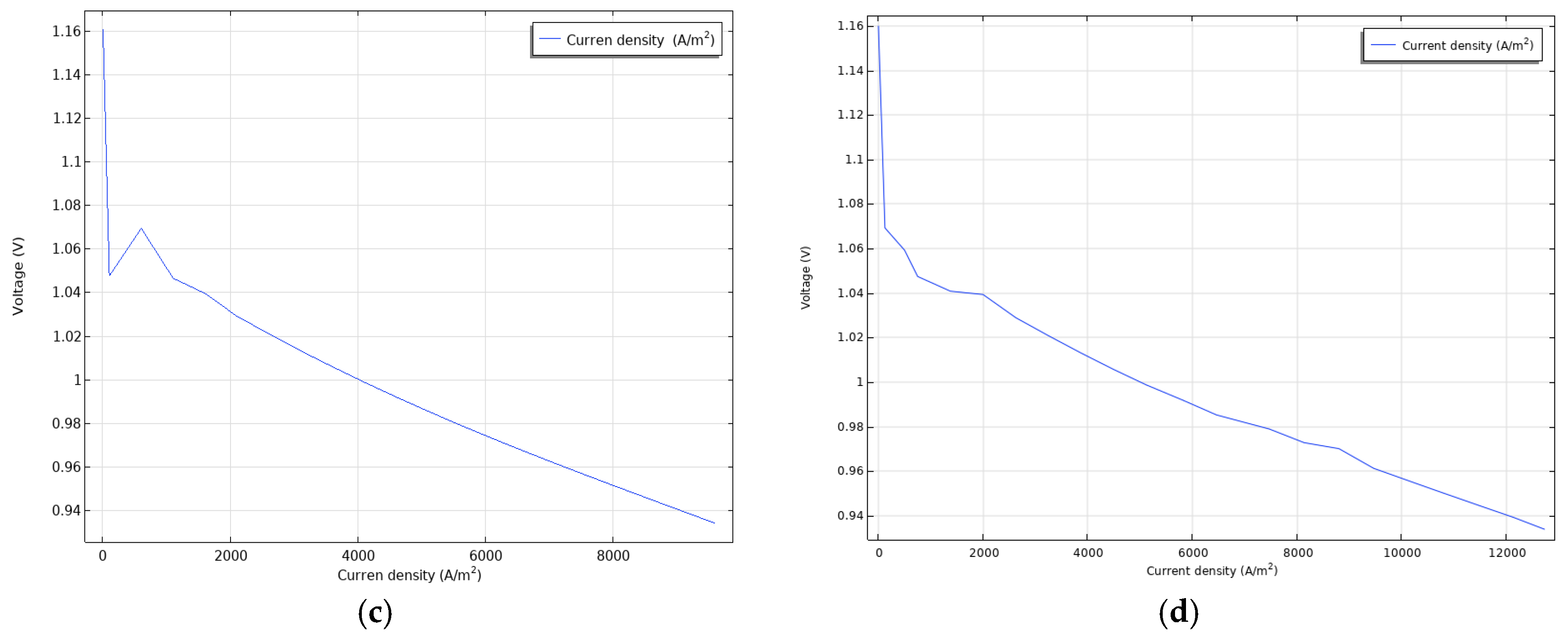
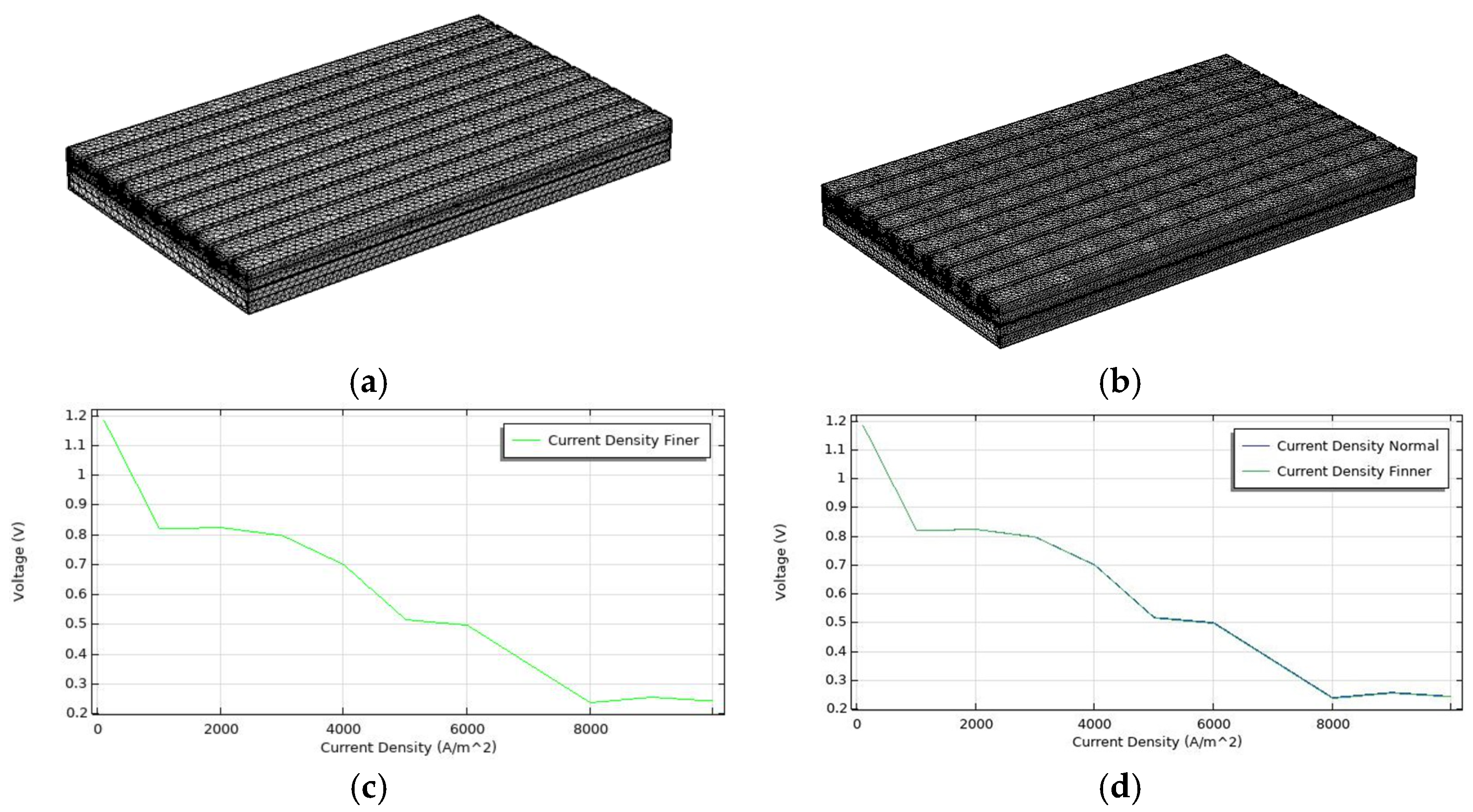
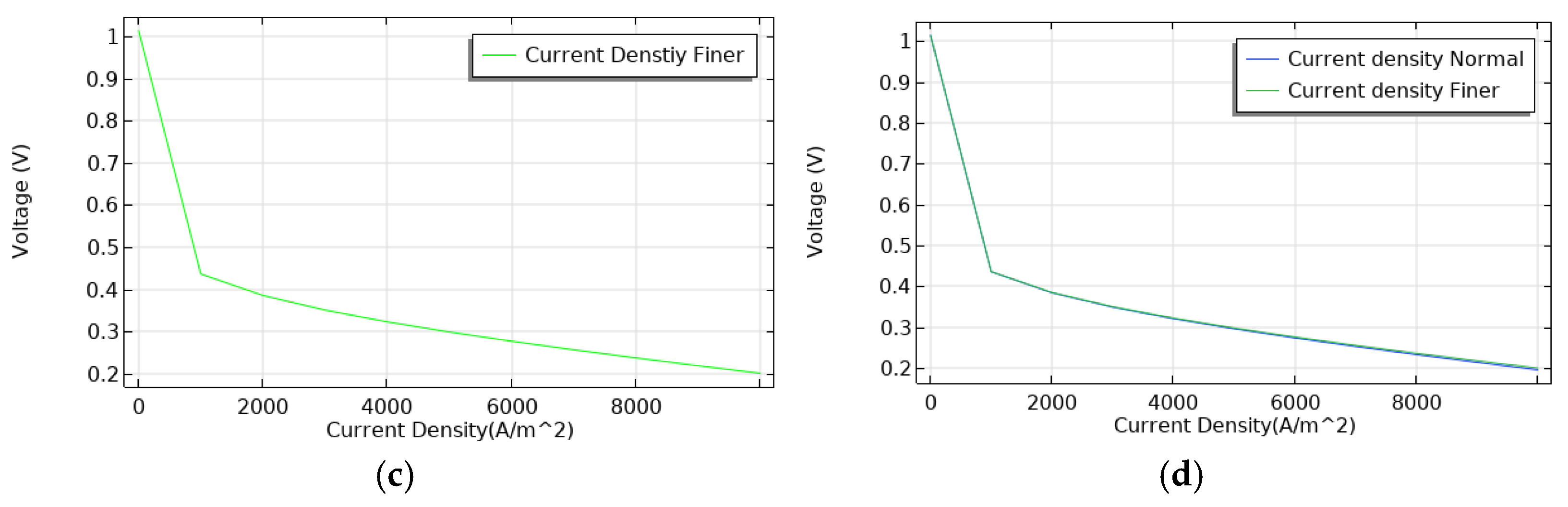
4. Mesh Independence Model Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamal, T.; Shafiullah, G.M.; Dawood, F.; Kaur, A.; Arif, M.T.; Pugazhendhi, R.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Ahmed, S.F. Fuelling the future: An in-depth review of recent trends, challenges and opportunities of hydrogen fuel cell for a sustainable hydrogen economy. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 2103–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Q.; Algburi, S.; Sameen, A.Z.; Salman, H.M.; Jaszczur, M. Green hydrogen: A pathway to a sustainable energy future. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 310–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.M.H.; Siddique, Z. Hydrogen as an alternative fuel: A comprehensive review of challenges and opportunities in production, storage, and transportation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 102, 1026–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, O.Z.; Orhan, M.F. An overview of fuel cell technology: Fundamentals and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 810–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C. Hydrogen and Fuel Cells. In Introduction to Materials for Advanced Energy Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 587–653. [Google Scholar]
- Sebbani, I.; Ettouhami, M.K.; Boulakhbar, M. Fuel cells: A technical, environmental, and economic outlook. Clean. Energy Syst. 2025, 10, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez-Cruz, M.M.; Escorihuela, J.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Compañ, V. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs): Advances and Challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A. A recent overview of proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Fundamentals, applications, and advances. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 252, 123746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Tu, Z.; Chan, S.H. Recent development of hydrogen and fuel cell technologies: A review. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 8421–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrahmani, H.; Yavarinasab, A.; Siavashi, M.; Matian, M.; Van Herle, J. Progress in the proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) water/thermal management: From theory to the current challenges and real-time fault diagnosis methods. Energy Rev. 2022, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, S.; Tu, Z.; Chan, S.H. Recent development in degradation mechanisms of proton exchange membrane fuel cells for vehicle applications: Problems, progress, and perspectives. Energy Storage Sav. 2024, 3, 106–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreafico, C.; Thonemann, N. Prospective life cycle assessment of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Comparing data from patents and papers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 99, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-okbi, Y.; Jweeg, M.J.; Atiya, M.A.; Al-Dujele, R. Design, analysis and development of a proton exchange membrane in fuel cell. J. Eng. Res. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AhmadS, S.; Nawaz, T.; Ali, A.; Orhan, M.F.; Samreen, A.; Kannan, A.M. An overview of proton exchange membranes for fuel cells: Materials and manufacturing. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 19086–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, A. Powering Clean Energy Solutions. In Generative Design Puts Hydrogen Fuel Cell Development in High Gear COMSOL Multiphysics eBook; Toyota Research Institute of North America: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, K.; Li, X. Water transport in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2011, 37, 221–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sabir, I. Review of bipolar plates in PEM fuel cells: Flow-field designs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2005, 30, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitakamol, V.; Therdthianwong, A.; Therdthianwong, S. Mid-baffle interdigitated flow fields for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 3614–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Theory and practice of flow field designs for fuel cell scaling-up: A critical review. Appl. Energy 2015, 157, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jithesh, P.; Bansode, A.; Sundararajan, T.; Das, S.K. The effect of flow distributors on the liquid water distribution and performance of a PEM fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 17158–17171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.C.; Li, H.Y.; Kuo, J.K.; Yan, W.M. Transient response of proton exchange membrane fuel cell with serpentine flow field. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, Xi’an, China, 27–29 May 2011; pp. 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, N.; Leu, M.; Koylu, U. Optimization of Parallel and Serpentine Configurations for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2014, 14, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liao, X.; Liu, G.; Xu, H.; Guan, C.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; He, W.; Qin, Y. Review of Flow Field Designs for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Energies 2023, 16, 4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboto, J.; Canizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Pinar, J.; Mena, E.; Ubeda, D. Three-dimensional model of a 50 cm2 high temperature PEM fuel cell. Study of the flow channel geometry influence. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 5510–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, S.; Wang, C. Three-dimensional analysis of transport and electrochemical reactions in polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2004, 125, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, A.; Salva, A.; Rosa, F. Fluid Flow in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. In Fluid Dynamics, Computational Modeling and Applications; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Liu, H. A two-phase flow and transport model for the cathode of PEM fuel cells. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Tan, J. Numerical Investigation of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells with Symmetrical Serpentine Channels Equipped with Baffles. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, K.S. Two-phase flow and transport in the air cathode of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2001, 94, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Gu, A.; Wang, M.; Zhu, X.; Yu, L. Three dimensional, two phase flow mathematical model for PEM fuel cell: Parts I and II. Analysis and discussion of the internal transport mechanism. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 1861–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauermoser, M.; Kizilova, N.; Pollet, B.; Kjelstrup, S. Flow Field Patterns for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Martin, J.J.; Yang, D.; Qiao, J.; Ma, J. A review on water balance in the membrane electrode assembly of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 461–9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liso, L.; Pagh, M.N.; Knudsen, S.K.; Mortensen, H.H. Thermal modeling and temperature control of a PEM fuel cell system for forklift applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 8410–8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y. Fundamental models for fuel cell engineering. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4727–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidary, H.; Kermani, M.; Prasad, A.A. Experimental investigation of in-line and staggered blockages in parallel flowfield channels of PEM fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 6885–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Mu, D. The impact of baffle and taper channel tilt angle on the output performance of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Fuel Cells 2024, 24, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizaki, M.; Asai, H.; Yumiya, H. Toyota Fuel Cell System (TFCS). World Electr. Veh. J. 2015, 7, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankins, S.N.; Zhou, Y.; Lohan, D.J.; Dede, E.M. Generative design of large-scale fluid flow structures via steady-state diffusion-based dehomogenization. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turing, A.M. The chemical basis of morphogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 1952, 237, 37–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Kermani, M.J. Generalization of the method of flow channel blocking in PEM fuel cells; extensions from straight-parallel to parallel-serpentine flow fields. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Liu, S.; Talkhoncheh, F.K. Bio-inspired flow channel designs for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A review. J. Power Source 2022, 522, 231003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.C.; Jum, K.M.; Sohn, Y.J. Performance of unit PEM fuel cells with a leaf-vein-simulating flow field-patterned bipolar plate. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 24036–24042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Design and optimization of bio-inspired wave-like channel for a PEM fuel cell applying genetic algorithm. Energy 2020, 192, 116670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagiz, M.; Çelik, S. Experimental investigation of bio-inspired flow field designs for direct methanol fuel cell. Fuel 2025, 381, 133624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Liu, C.; Ge, J.; Xing, W. Non-noble metals as activity sites for ORR catalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). Indust. Chem. Mat. 2023, 1, 388–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Luo, G.; Wang, C.-Y. Modeling two-phase flow in three-dimensional complex flow-fields of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 365, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchheimer Flow. COMSOL Multiphysics 5.6, Library COMSOL Fluid Flow 5.6. Available online: https://doc.comsol.com/5.6/doc/com.comsol.help.models.ssf.forchheimer_flow/models.ssf.forchheimer_flow.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Amiri, A.; Vafai, K. Transient Analysis of Incompressible Flow Through a Packed Bed. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 1998, 41, 4259–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbir, F. Fuel Cell Operating Conditions. In PEM Fuel Cells, 2nd ed.; Barbir, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 119–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kadyk, T.; Kadow, M.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R. Experimental assessment and analysis of mass transport limiting current densities in PEM fuel cells. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12345. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, W.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Shao-Horn, Y. Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reaction Kinetics on Platinum: Acid vs. Alkaline Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, B1529–B1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, B.A.; Krishnan, Y.; Buchauer, F.L.; Hansen, H.A.; Hjelm, J. Unifying the ORR and OER with surface oxygen and extracting their intrinsic activities on platinum. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, A.P.; Marzo, F.F.; Barranco, J.; Garikano, X.; Mujika, M.G. Influence of geometric parameters of the flow fields on the performance of a PEM fuel cell. A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 15256–15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.; Knöri, T.; Ribeirinha, P.; Gazdzicki, P. A review on flow field design for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Challenges to increase the active area for MW applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 192, 114198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, A.L.R.; Robalinho, E.; Cunha, E.F.; Passos, R.R.; Santiago, E.I. Current Distribution on PEM Fuel Cells with Different Flow Channel Patterns. In Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference in Boston, Newton, MA, USA, 9–11 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kandlikar, S.; Lu, Z.; Domigan, W.; White, A.; Benedict, M. Measurement of flow maldistribution in parallel channels and its application to ex-situ and in-situ experiments in PEMFC water management studies. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2009, 52, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guo, H.; Ye, F.; Ma, C.F. A numerical study of orientated-type flow channels with porous-blocked baffles of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 29443–29458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, N.; Ueda, M. 3D-print infill generation using the biological phase field of an optimized discrete material orientation vector field. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 232, 109626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.K.; Mukherjee, P.P.; Wang, C.-Y. Impact of GDL structure and wettability on water management in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Mat. Chem. Issue 2007, 17, 3089–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, F.; Dam, V.; Janssen, G. Review: Durability and Degradation Issues of PEM Fuel Cell Components. Fuel Cells 2008, 8, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, D.G.; Ruiu, T.; Biswas, I.; Friedrich, A.; Sanchez-Monreal, J.; Vera, M. Effect of the Inlet Gas Humidification on PEMFC Behavior and Current Density Distribution. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 64, 603–617. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.-W.; Ou, K.; Jung, S.; Kim, Y.-B. Analyzing and Modeling of Water Transport Phenomena in Open-Cathode Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Reddy, R.G. Effect of gas flow-field design in the bipolar/end plates on the steady and transient state performance of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2006, 155, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunyan, S.T.; Dhahad, H.A.; Khudhur, D.S.; Yusaf, T. The Effect of Flow Field Design Parameters on the Performance of PEMFC: A Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Unit | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| μ | 10−3 kg/(m·s) | Dynamic viscosity |
| k | 10−12 m2 | Permeability |
| ρ | 1000 kg/m3 | Density |
| εp | 0.5 | Porosity |
| - | 2.53 × 10−5 kg/s | Inlet flow rate |
| - | 0.55 | Forchheimer coefficient |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavrailov, D.; Boycheva, S. Comparative Studies of Three-Dimensional Complex Flow Field Designs in a Proton Exchange Membrane Hydrogen Fuel Cell. Energies 2025, 18, 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092165
Gavrailov D, Boycheva S. Comparative Studies of Three-Dimensional Complex Flow Field Designs in a Proton Exchange Membrane Hydrogen Fuel Cell. Energies. 2025; 18(9):2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092165
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavrailov, Dilyan, and Silviya Boycheva. 2025. "Comparative Studies of Three-Dimensional Complex Flow Field Designs in a Proton Exchange Membrane Hydrogen Fuel Cell" Energies 18, no. 9: 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092165
APA StyleGavrailov, D., & Boycheva, S. (2025). Comparative Studies of Three-Dimensional Complex Flow Field Designs in a Proton Exchange Membrane Hydrogen Fuel Cell. Energies, 18(9), 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092165







